信号量主要API及综合应用
1.信号量概述
信号量是一个底层核心模块【int】类型变量,记录当前信号量数据。
信号量 P 操作 (sem_wait)
线程检测对应信号量底层 int 数据数值,如果大于 0,当前线程获得 CPU 执行权,同时将信号量底层 int 数据-1 操作。
如果底层数据为 0,当前线程无法获取 CPU 执行权,进入阻塞状态。同时等待信号量 > 0
信号量 V 操作 (sem_post)
线程任务执行完毕,执行 V 操作,对当信号量底层 int 数据 +1,相当于释放 CPU 执行权。
信号量可以控制线程互斥和线程同步。
2.信号量相关API
2.1sem_init初始化
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value)函数功能:
用于初始化一个信号量变量,提供必要的参数,限制当前信号量是针对于【线程操作】还是【进程操作】
函数参数:
sen_t *sem: 信号量变量地址
int pshared: 控制值当前信号量,限制内容为线程还是进程,线程参数要求为 0, 不等于 0 为进程间操作。建议 0 线程, 1 进程。
unsigned int value: 信号量初始化数据,通常情况下为 1
返回值:
成功返回 0
失败返回 -1
2.2sem_wait P操作/等待操作
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem)函数功能:
信号量 P 操作,当前信号量-1。
如果为 0 当前线程/进程进入阻塞状态。
如果不为 0,信号量 -= 1,同时可以执行目标线程/进程代码。
函数参数:
sem_t *sem: 信号量变量地址
返回值类型:
成功返回 0
失败返回 -1
2.3sem_post V操作/释放操作
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_post(sem_t *sem)函数功能:
信号量 V 操作,当前信号量 +1
信号量不为 0,相当于解除与当前信号量相关的其他线程/进程阻塞状态
函数参数:
sem_t *sem : 信号量变量地址
返回值类型
成功返回 0
失败返回 -1
2.4sem_destroy 销毁操作
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem)函数功能:
销毁当前信号量变量
函数参数:
sem_t *sem: 信号量变量地址
返回值类型
成功返回 0
失败返回 -1
2.5信号量的操作案例
将上面的信号量函数进行综合应用
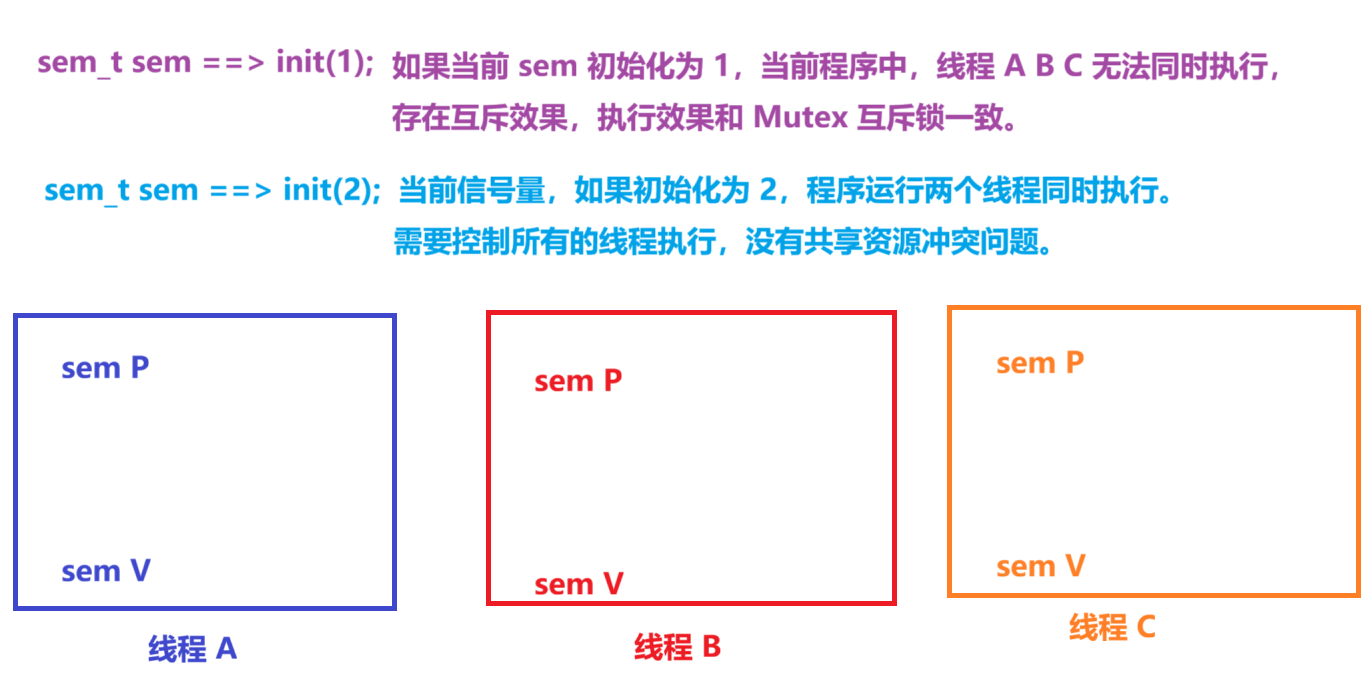
2.5.1信号量互斥控制
相当于互斥锁的作用
#define _POSIX_C_SOURCE 200112L
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
sem_t sem;
void *threadA_task(void *arg);
void *threadB_task(void *arg);
void *threadC_task(void *arg);
void print_string(const char *str);
// 线程 A 对应的线程【句柄】类型
pthread_t tid1;
// 线程 B 对应的线程【句柄】类型
pthread_t tid2;
// 线程 C 对应的线程【句柄】类型
pthread_t tid3;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{int status = 0;/*1. 初始化信号量初始化当前信号量,对应的控制目标为线程,初始化数据为 1int sem_init (sem_t *__sem, int __pshared, unsigned int __value)*/status = sem_init(&sem, 0, 3);//int pshared: 控制值当前信号量,限// 制内容为线程还是进程,线程参数要求为 0, //不等于 0 为进程间操作。建议 0 线程, 1 进程。if (status){printf("semaphore init failed!\n");_exit(1);}status = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, threadA_task, "Hello World!");if (status){printf("pthread_create threadA failed!\n");_exit(1);}status = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, threadB_task, "Hello HH!");if (status){printf("pthread_create threadB failed!\n");_exit(1);}status = pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, threadC_task, "Hello GL!");if (status){printf("pthread_create threadC failed!\n");_exit(1);}pthread_join(tid1, NULL);pthread_join(tid2, NULL);pthread_join(tid3, NULL);return 0;
}
void *threadA_task(void *arg)
{// 信号量 P 操作sem_wait(&sem);print_string((const char *)arg);// 信号量 V 操作sem_post(&sem);
}
void *threadB_task(void *arg)
{// 信号量 P 操作sem_wait(&sem);print_string((const char *)arg);// 信号量 V 操作sem_post(&sem);
}
void *threadC_task(void *arg)
{// 信号量 P 操作sem_wait(&sem);print_string((const char *)arg);// 信号量 V 操作sem_post(&sem);
}
void print_string(const char *str)
{while (*str){printf("%c\n", *str);sleep(1);str += 1;}
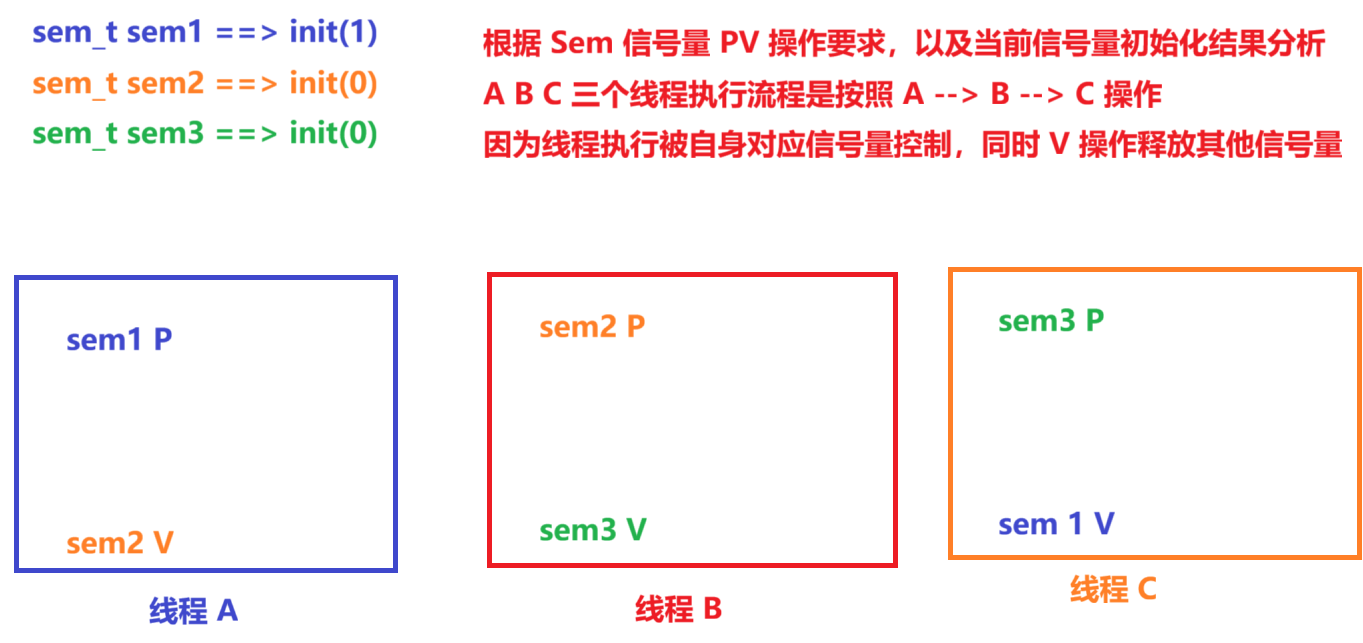
}2.5.1信号量执行流程控制
#define _POSIX_C_SOURCE 200112L
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
sem_t sem1;
sem_t sem2;
sem_t sem3;
void *threadA_task(void *arg);
void *threadB_task(void *arg);
void *threadC_task(void *arg);
void print_string(const char *str);
// 线程 A 对应的线程【句柄】类型
pthread_t tid1;
// 线程 B 对应的线程【句柄】类型
pthread_t tid2;
// 线程 C 对应的线程【句柄】类型
pthread_t tid3;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{int status = 0;/*1. 初始化信号量初始化当前信号量,对应的控制目标为线程,初始化数据为 1int sem_init (sem_t *__sem, int __pshared, unsigned int __value)*/status = sem_init(&sem1, 0, 1);if (status){printf("semaphore init failed!\n");_exit(1);}status = sem_init(&sem2, 0, 0);if (status){printf("semaphore init failed!\n");_exit(1);}status = sem_init(&sem3, 0, 0);if (status){printf("semaphore init failed!\n");_exit(1);}status = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, threadA_task, "Hello World!");if (status){printf("pthread_create threadA failed!\n");_exit(1);}status = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, threadB_task, "Hello HH!");if (status){printf("pthread_create threadB failed!\n");_exit(1);}status = pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, threadC_task, "Hello GL!");if (status){printf("pthread_create threadC failed!\n");_exit(1);}pthread_join(tid1, NULL);pthread_join(tid2, NULL);pthread_join(tid3, NULL);// 线程销毁pthread_cancel(tid1);pthread_cancel(tid2);pthread_cancel(tid3);// 信号量销毁sem_destroy(&sem1);sem_destroy(&sem2);sem_destroy(&sem3);return 0;
}
void *threadA_task(void *arg)
{// sem1 信号量 P 操作sem_wait(&sem1);print_string((const char *)arg);// sem2 信号量 V 操作sem_post(&sem2);
}
void *threadB_task(void *arg)
{// sem2 信号量 P 操作sem_wait(&sem2);print_string((const char *)arg);// sem3 信号量 V 操作sem_post(&sem3);
}
void *threadC_task(void *arg)
{// sem3 信号量 P 操作sem_wait(&sem3);print_string((const char *)arg);// sem1 信号量 V 操作sem_post(&sem1);
}
void print_string(const char *str)
{printf("%s\n", str);sleep(5);
}