嵌入式学习 day58 驱动字符设备驱动
一、字符设备驱动框架
1、字符设备流程
字符设备驱动可以通过2种方式加载到Linux内核中,分别为:静态加载和动态加载。静态加载是在内核编译阶段,编译到内核中,Linux内核启动后直接拥有了该内核模块,动态加载是Linux内核启动完毕后通过insmod加载、rmmod卸载。我们这里更多采用动态加载。
动态加载需要创建一个cdev结构体,结构体需要关联两个结构,一个是dev_t类型的设备号,还有一个对设备具体操作的file_operations结构体。
dev_t类型的设备号由主次设备号构成,主设备号表示设备类型,次设备号表示该类型的第几个设备。file_operations中都是操作设备对应的函数指针,来实现具体对设备的open、read、write、ioctl等一系列对设备的操作。
用户空间通过open打开对应的设备文件,设备文件通过VFS文件系统找到对应的设备号,通过设备号可以找到字符设备cdev结构体,通过结构体可以找到对设备操作的file_operations结构体,最终通过这个结构体中的函数指针实现对设备具体的操作。
2、框架
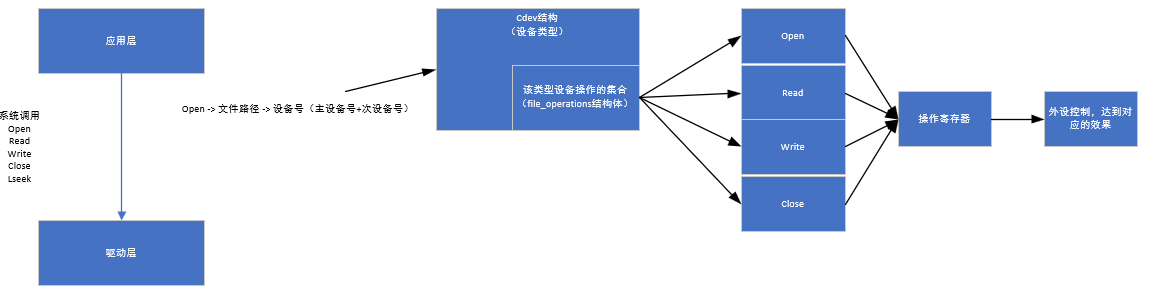
注:源代码追踪:
(1)、
(2)
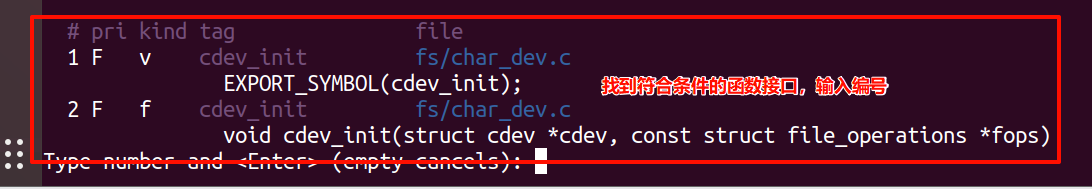
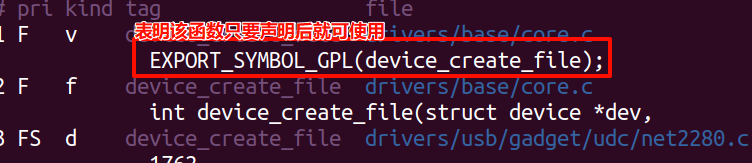
(3)
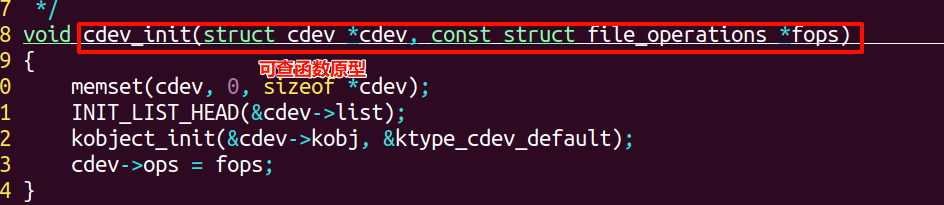
(4)
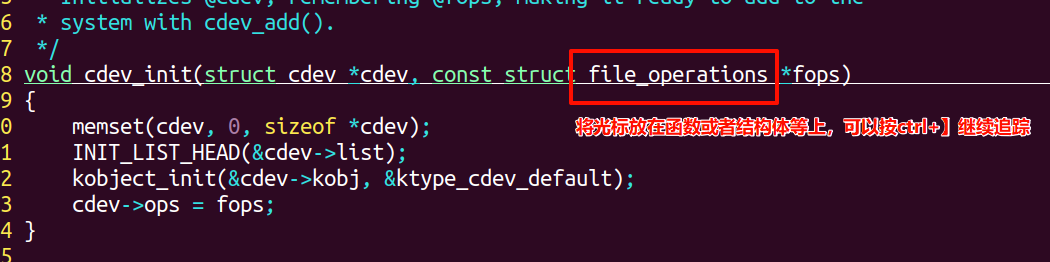
(5)
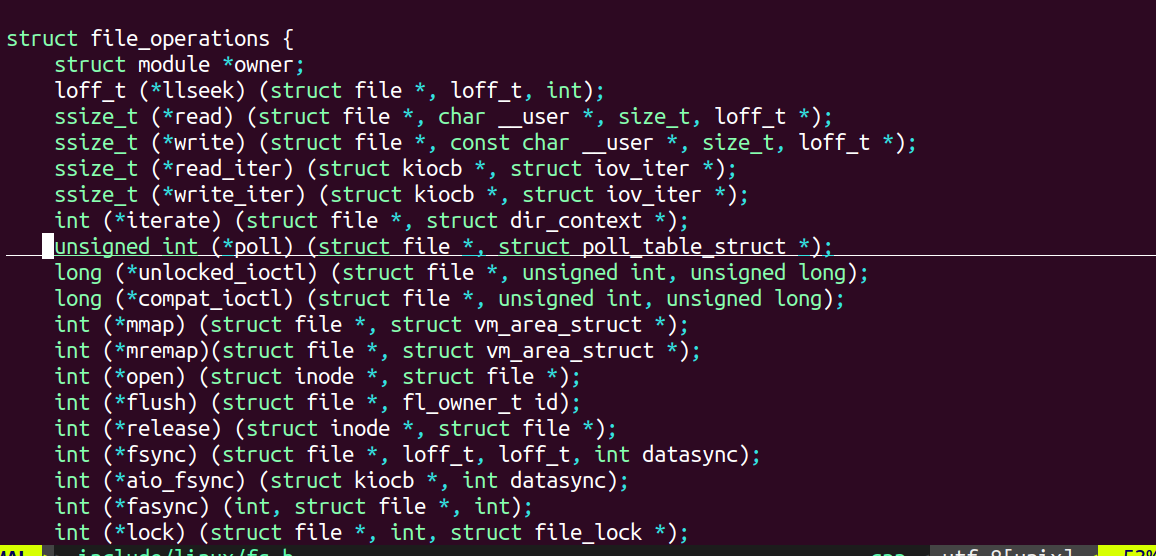
3、.字符设备操作接口

可用源代码追踪查看各函数的原型
4、.设备类创建
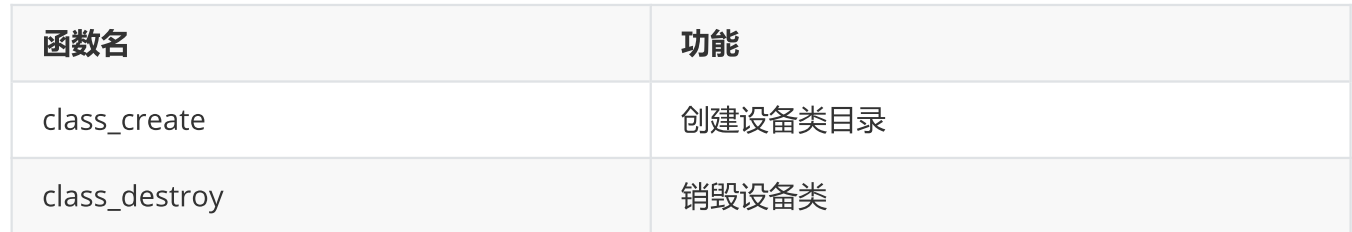
5、设备创建
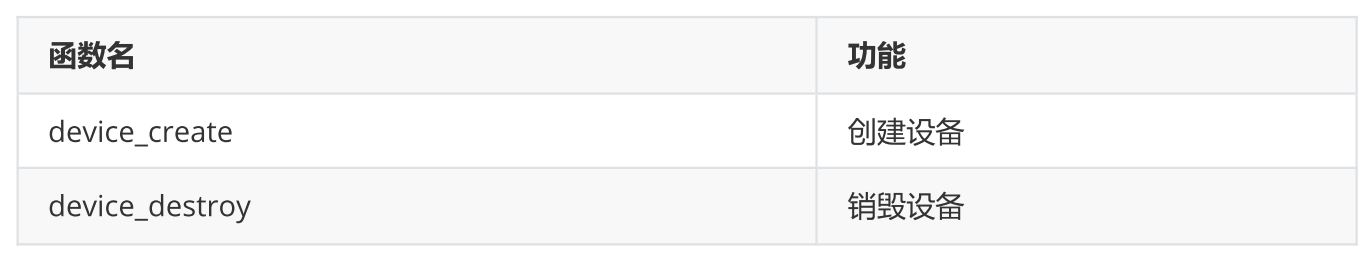
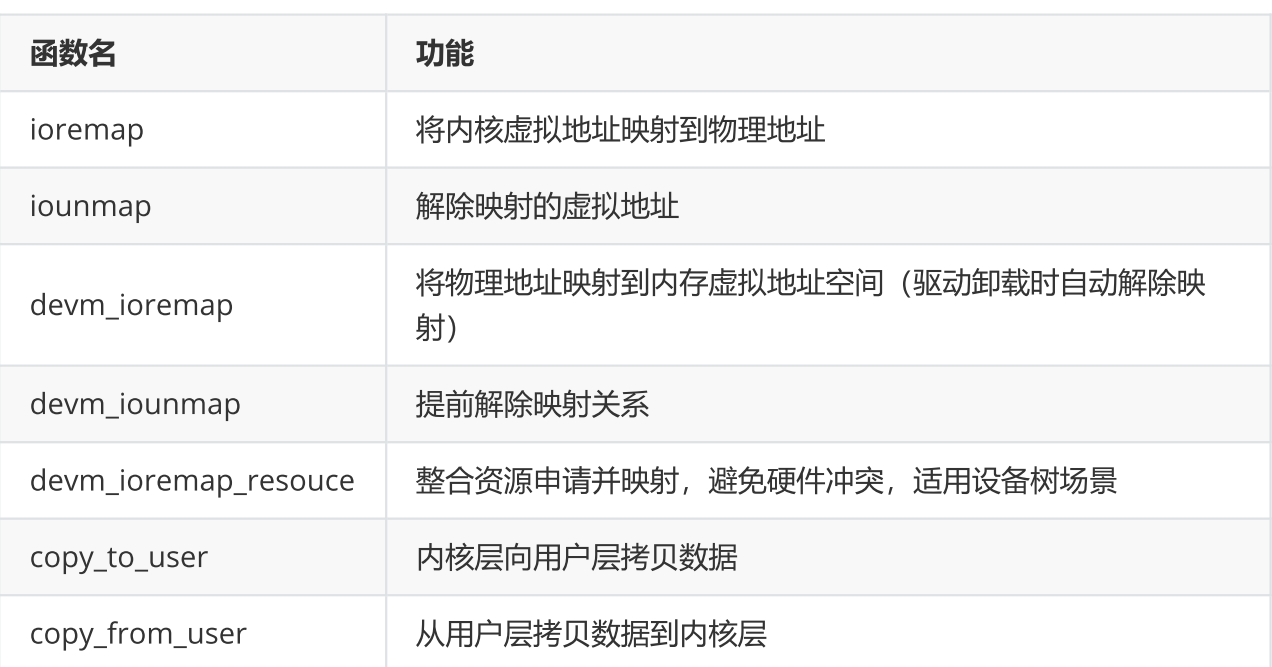
6、LED灯驱动
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
static struct cdev *pcdev = NULL;
static dev_t devno = 0;
static ssize_t led_read(struct file *fp, char __user *puser, size_t n, loff_t *off);
static ssize_t led_write(struct file *fp, const char __user *puser, size_t n, loff_t *off);
static int led_open(struct inode *node, struct file *fp);
static int led_release(struct inode *node, struct file *fp);
static struct file_operations fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = led_open,
.release = led_release,
.read = led_read,
.write = led_write,
};
static ssize_t led_read(struct file *fp, char __user *puser, size_t n, loff_t *off)
{
pr_info("led read success!\n");
return 0;
}
static ssize_t led_write(struct file *fp, const char __user *puser, size_t n, loff_t *off)
{
pr_info("led write success!\n");
return 0;
}
static int led_open(struct inode *node, struct file *fp)
{
pr_info("led open success!\n");
return 0;
}
static int led_release(struct inode *node, struct file *fp)
{
pr_info("led close success!\n");
return 0;
}
//驱动程序入口
static int __init init_demo(void)
{
int ret = 0;
//申请一个新的cdev设备类型
pcdev = cdev_alloc();
if (NULL == pcdev) {
pr_info("cdev_alloc failed\n");
return -1;
}
pcdev->ops = &fops;
//申请并注册cdev对应的设备号范围
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, 0, 10, "myled");
if (ret) {
pr_info("alloc_chrdev_region failed\n");
return -1;
}
pr_info("alloc cdev major:%d, minor:%d\n", MAJOR(devno), MINOR(devno));
//在内核中加入新cdev设备类型
ret = cdev_add(pcdev, devno, 10);
if (ret) {
pr_info("cdev_add failed\n");
return -1;
}
pr_info("init demo success\n");
return 0;
}
//驱动程序出口
static void __exit exit_demo(void)
{
cdev_del(pcdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, 10);
pr_info("exit demo success\n");
return;
}
//设置驱动程序的入口
module_init(init_demo);
//设置驱动程序的出口
module_exit(exit_demo);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("pute");
二、misc设备驱动(优化led代码)

1、概念:
我们可以在Linux系统中通过 cat /proc/devices查看系统中所有加载的驱动。
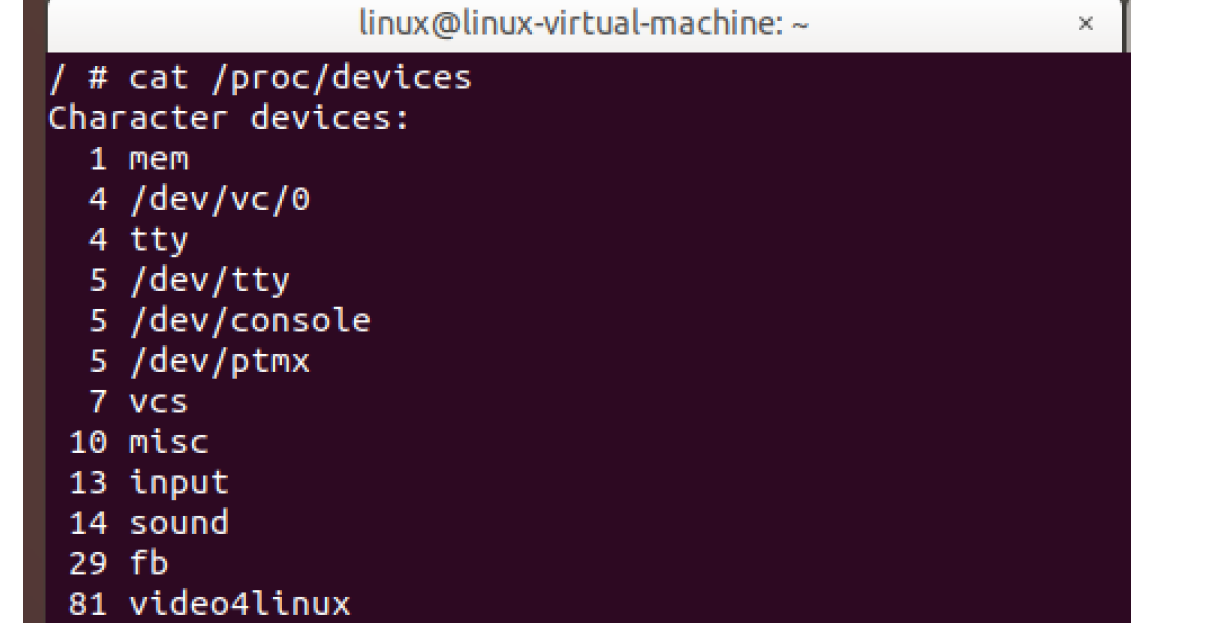
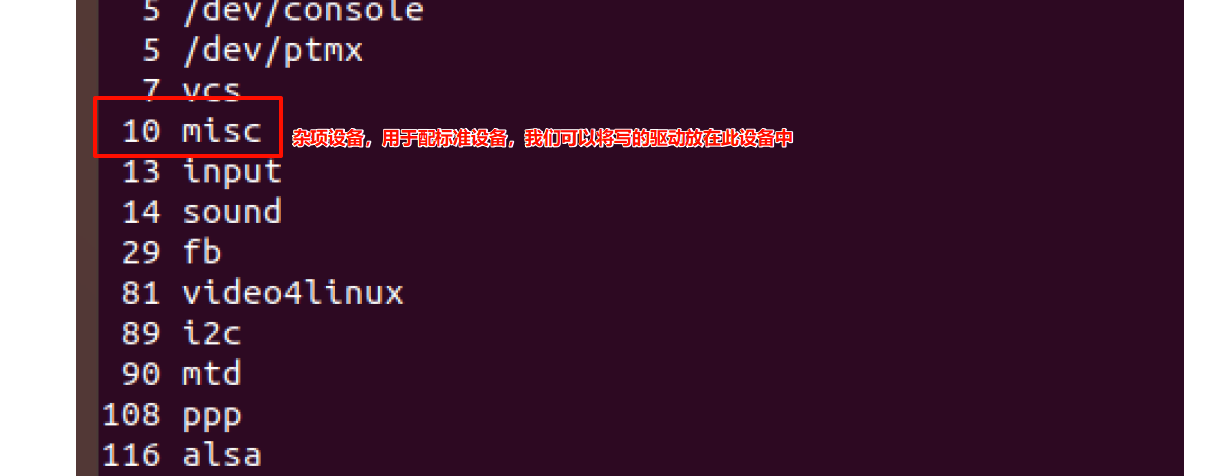
2、混杂设备操作接口:
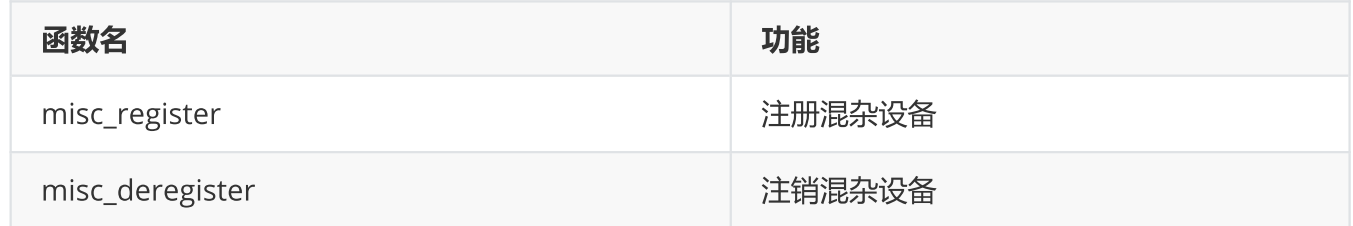
可自动创建设备节点
三、sys文件系统(优化led代码)

1、概念:
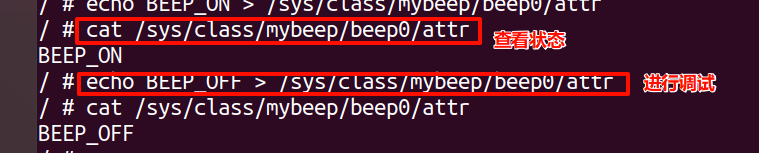
sysfs是Linux内核中一种特殊虚拟文件系统,用来向用户空间提供内核设备和驱动程序的信息。它提供了一种统一的接口,用于查看和操作设备、驱动程序、文件系统等内核对象。sysfs存放在内存中,挂载在/sys目录下,文件系统中的文件不对应硬盘上任何文件。
2、sys的目录结构
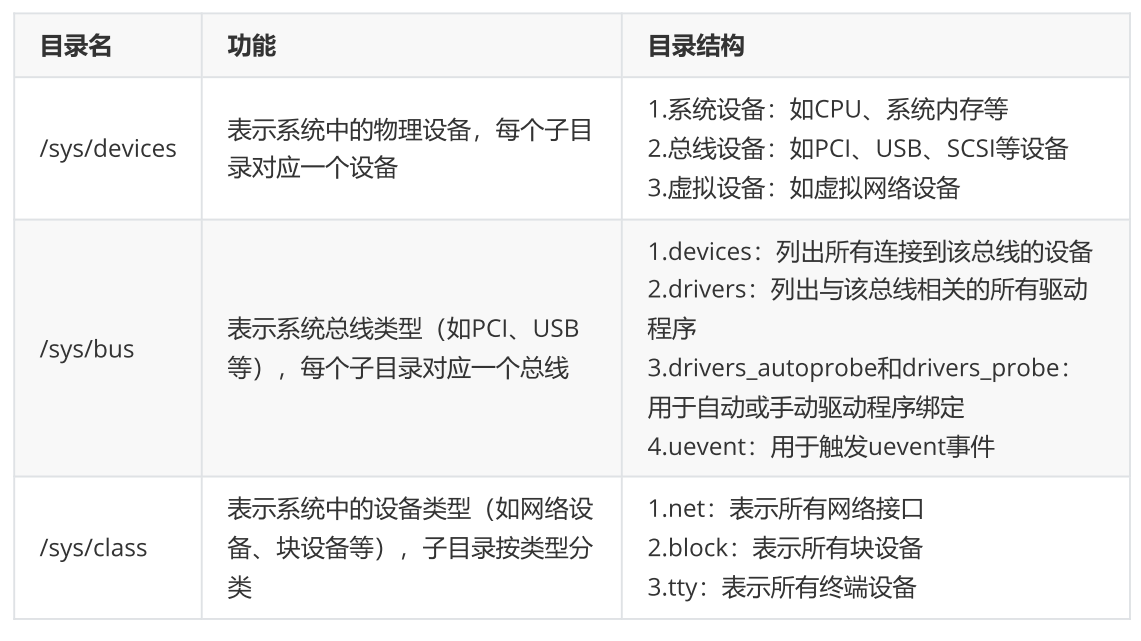
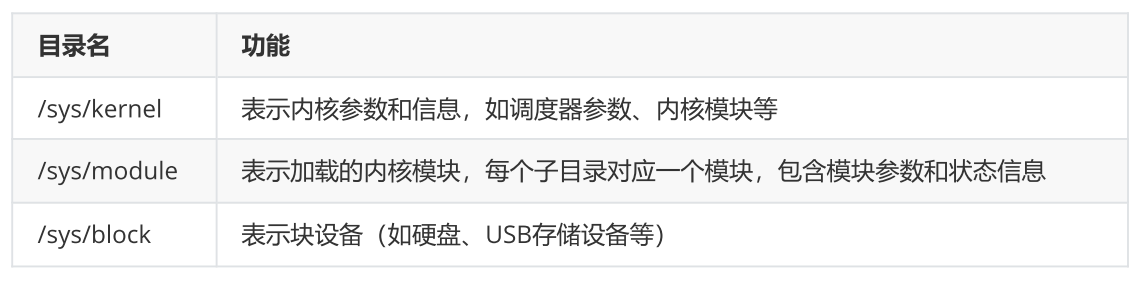
3、sys文件系统使用
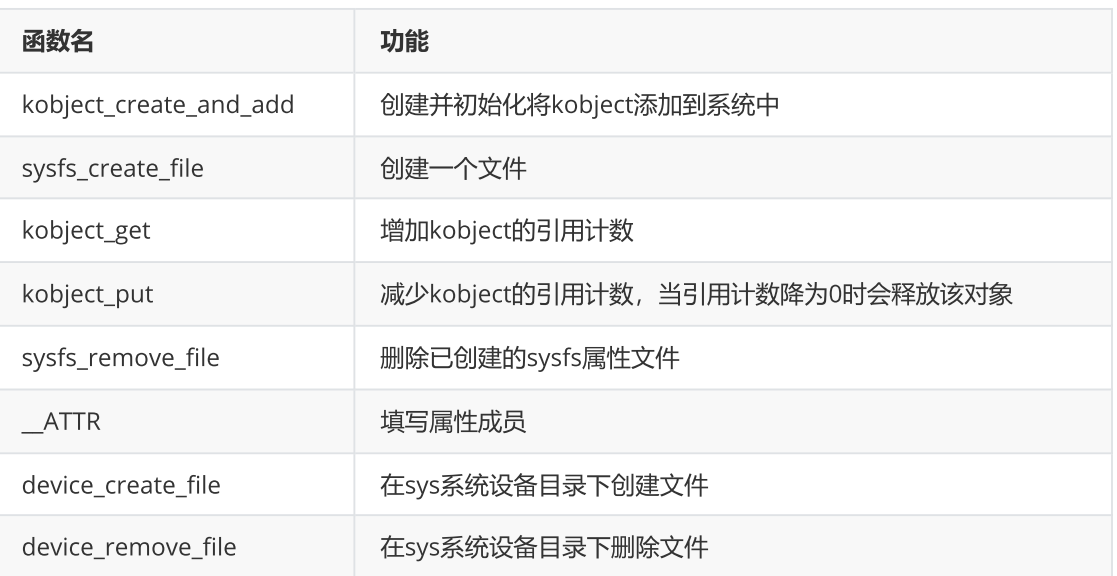

(1)函数使用
①查看函数原型
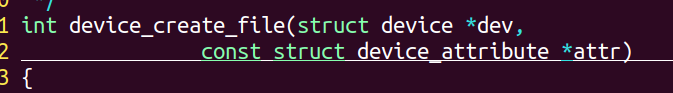
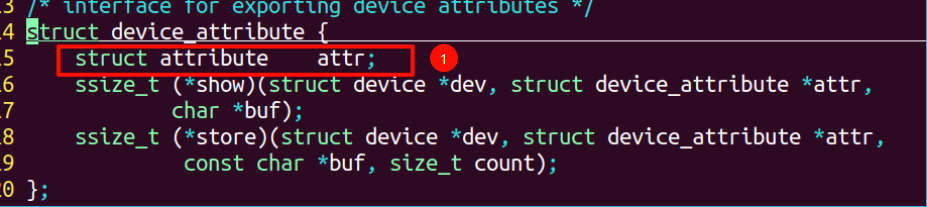
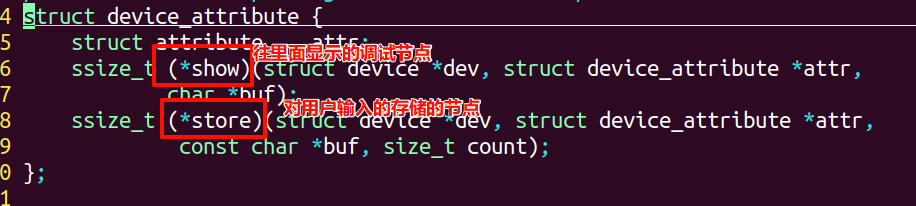
②查看各参数

#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/of.h>
static struct mutex lock;
static int beepstat;
static void __iomem *piomux = NULL;
static void __iomem *piopad = NULL;
static void __iomem *piodir = NULL;
static void __iomem *piodat = NULL;
static ssize_t beep_read(struct file *fp, char __user *puser, size_t n, loff_t *off);
static ssize_t beep_write(struct file *fp, const char __user *puser, size_t n, loff_t *off);
static int beep_open(struct inode *node, struct file *fp);
static int beep_release(struct inode *node, struct file *fp);
static ssize_t beep_show(struct device *dev,struct device_attribute *attr,char *buf);
static ssize_t beep_store(struct device *dev,struct device_attribute *attr,const char *buf,size_t count);
extern void __iomem *of_iomap(struct device_node *np, int index);
struct device_attribute attr = __ATTR(attr,0664,beep_show,beep_store);
static struct file_operations fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = beep_open,
.release = beep_release,
.read = beep_read,
.write = beep_write,
};
static struct miscdevice misc = {
.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,
.name = "misc_beep",
.fops = &fops,
};
static ssize_t beep_read(struct file *fp, char __user *puser, size_t n, loff_t *off)
{
unsigned long nret = 0;
mutex_lock(&lock);
nret = copy_to_user(puser,&beepstat,sizeof(beepstat));
if(nret){
pr_info("copt_to_user failed\n");
return -1;
}
mutex_unlock(&lock);
pr_info("beep read success!\n");
return 0;
}
static ssize_t beep_write(struct file *fp, const char __user *puser, size_t n, loff_t *off)
{
int val = 0;
long ret = 0;
ret = copy_from_user(&val, puser, 4);
if(ret){
pr_info("cpoy_from_user failed\n");
return -1;
}
mutex_lock(&lock);
if (1 == val)
{
writel(readl(piodat) & (~(0x1 << 1)), piodat);
}
else if (0 == val)
{
writel(readl(piodat) | (0x1 << 1), piodat);
}
mutex_unlock(&lock);
pr_info("beep write success!\n");
return 0;
}
static int beep_open(struct inode *node, struct file *fp)
{
pr_info("beep open success!\n");
return 0;
}
static int beep_release(struct inode *node, struct file *fp)
{
pr_info("beep close success!\n");
return 0;
}
static ssize_t beep_show(struct device *dev,struct device_attribute *attr,char *buf)
{
int cnt = 0;
char status[32] = {0};
mutex_lock(&lock);
if(1 == beepstat){
strcpy(status,"BEEP_ON");
}else if(0 == beepstat){
strcpy(status,"BEEP_OFF");
}
mutex_unlock(&lock);
cnt = sprintf(buf,"%s\n",status);
return cnt;
}
static ssize_t beep_store(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t count)
{
mutex_lock(&lock);
if(0 == strcmp(buf,"BEEP_ON\n")){
writel(readl(piodat) & (~(0x1 << 1)),piodat);
beepstat = 1;
}else if(0 == strcmp(buf,"BEEP_OFF\n")){
writel(readl(piodat) | (0x1 << 1),piodat);
beepstat = 0;
}
mutex_unlock(&lock);
return count;
}
//驱动程序入口
static int __init init_demo(void)
{
int ret = 0;
unsigned long val = 0;
struct device_node *plednode = NULL;
u32 regarray[8] = {0};
ret = misc_register(&misc);
if(ret){
pr_info("misc_register failed\n");
return -1;
}
plednode = of_find_node_by_path("/putebeep");
if(NULL == plednode){
pr_info("of_find_node_by_path failed\n");
return -1;
}
ret = of_property_read_u32_array(plednode,"reg",regarray,8);
if(ret){
pr_info("of_property_read_u32_array failed\n");
return -1;
}
piomux = of_iomap(plednode, 0);
if (NULL == piomux)
{
pr_info("fail to ioremap\n");
return -1;
}
piopad = of_iomap(plednode, 1);
if (NULL == piopad)
{
pr_info("fail to ioremap\n");
return -1;
}
piodir = of_iomap(plednode, 2);
if (NULL == piodir)
{
pr_info("fail to ioremap\n");
return -1;
}
piodat = of_iomap(plednode, 3);
if (NULL == piodat)
{
pr_info("fail to ioremap\n");
return -1;
}
//设置引脚复用为GPIO功能
writel(0x5, piomux);
//设置引脚的电器属性
writel(0x10b0, piopad);
//设置GPIO为输出
val = readl(piodir);
val |= (0x1 << 1);
writel(val, piodir);
//设置GPIO为高电平(关灯)
val = readl(piodat);
val |= (0x1 << 1);
writel(val, piodat);
mutex_init(&lock);
device_create_file(misc.this_device,&attr);
pr_info("init demo success\n");
return 0;
}
//驱动程序出口
static void __exit exit_demo(void)
{
int ret = 0;
device_remove_file(misc.this_device,&attr);
mutex_destroy(&lock);
if (piomux != NULL)
{
iounmap(piomux);
}
if (piopad != NULL)
{
iounmap(piopad);
}
if (piodir != NULL)
{
iounmap(piodir);
}
if (piodat != NULL)
{
iounmap(piodat);
}
ret = misc_deregister(&misc);
if(ret){
pr_info("misc_deregister failed\n");
return ;
}
pr_info("exit demo success\n");
return;
}
//设置驱动程序的入口
module_init(init_demo);
//设置驱动程序的出口
module_exit(exit_demo);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("pute");
(2)调试