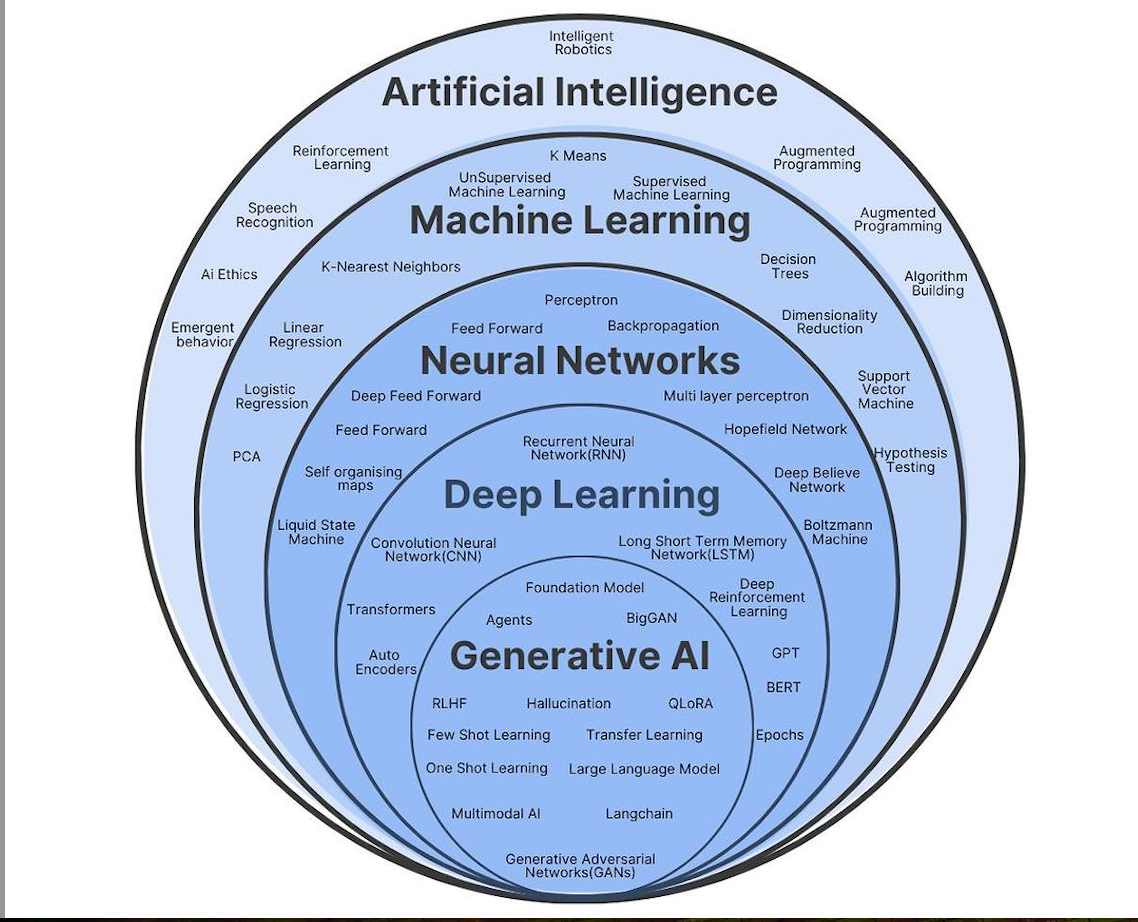
AI vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning vs. Neural Networks
注:本文为 “AI ML DL NN” 相关英文合辑。
英文引文,机翻未校。
如有内容异常,请看原文。
AI vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning vs. Neural Networks
人工智能、机器学习、深度学习、神经网络
Last Updated: 06 Aug, 2025
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Neural Networks (NN) are terms often used interchangeably. However, they represent different layers of complexity and specialization in the field of intelligent systems.
人工智能(AI)、机器学习(ML)、深度学习(DL)和神经网络(NN)是经常互换使用的术语。然而,它们代表了智能系统领域不同层次的复杂性和专业化。
This article will clarify the difference between AI vs. machine learning vs. deep learning vs. neural networks.
本文将阐明人工智能、机器学习、深度学习与神经网络之间的区别。
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? 什么是人工智能(AI)?
Artificial Intelligence is the broadest concept, referring to machines designed to simulate human intelligence. AI involves systems that can perform tasks such as problem-solving, decision-making, and learning, tasks typically requiring human cognition. AI spans across a spectrum of functionalities, from simple rule-based systems to complex deep learning models.
人工智能是最广泛的概念,指的是旨在模拟人类智能的机器。人工智能涉及可以执行解决问题、决策和学习等任务的系统,这些任务通常需要人类认知。人工智能涵盖一系列功能,从简单的基于规则的系统到复杂的深度学习模型。
Types of AI: 人工智能的类型:
- Narrow AI: Focuses on specific tasks, such as voice assistants (e.g., Siri) or recommendation systems.
- 狭义人工智能:专注于特定任务,例如语音助手(例如 Siri)或推荐系统。
- General AI: A theoretical form that can perform any cognitive task a human can do, not yet achieved.
- 通用人工智能:一种理论形式,可以执行人类可以完成但尚未实现的任何认知任务。
Common Applications: 常见应用:
- Autonomous vehicles
- 自动驾驶汽车
- Voice recognition (e.g., Alexa, Google Assistant)
- 语音识别(例如 Alexa、Google Assistant)
- Chatbots and virtual assistants
- 聊天机器人和虚拟助手
What is Machine Learning (ML)? 什么是机器学习(ML)?
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that allows systems to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. ML systems identify patterns in data and make predictions or decisions based on those patterns.
机器学习是人工智能的一个子集,它允许系统自动学习和改进经验,而无需明确编程。机器学习系统识别数据中的模式,并根据这些模式做出预测或决策。
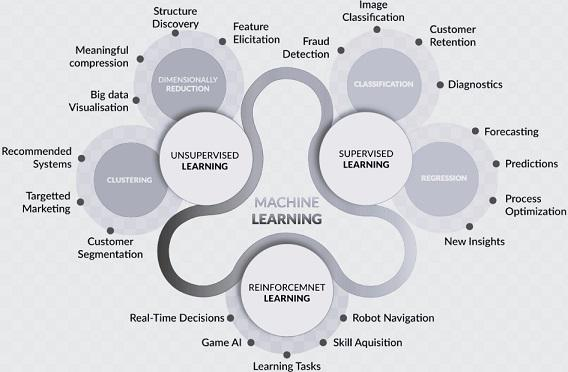
Types of Machine Learning: 机器学习的类型:
- Supervised Learning: Involves training a model on labeled data, where the output is known.
- 监督学习:涉及在标记数据上训练模型,其中输出是已知的。
- Unsupervised Learning: The system learns patterns from unlabeled data.
- 无监督学习:系统从未标记的数据中学习模式。
- Reinforcement Learning: The model learns through trial and error, receiving feedback for its actions.
- 强化学习:模型通过反复试验学习,接收其行为的反馈。
Key Applications: 主要应用:
- Spam filtering
- 垃圾邮件过滤
- Product recommendations (e.g., Netflix, Amazon)
- 产品推荐(例如 Netflix、Amazon)
- Fraud detection
- 欺诈检测
What is Deep Learning (DL)? 什么是深度学习(DL)?
Deep Learning is a specialized subset of ML, focused on using artificial neural networks with multiple layers (hence “deep”). DL models are capable of handling vast amounts of data and automatically learning high-level representations, making them well-suited for complex tasks like image and speech recognition.
深度学习是 ML 的一个专门子集,专注于使用具有多层(因此称为“深度”)的人工神经网络。DL 模型能够处理大量数据并自动学习高级表示,使其非常适合图像和语音识别等复杂任务。
Core Components of Deep Learning: 深度学习的核心组件:
- Neural Networks: Layers of nodes (artificial neurons) that work together to analyze and learn from data.
- 神经网络:协同工作以分析和学习数据的节点层(人工神经元)。
- Backpropagation: A process for fine-tuning the weights of neural networks, improving prediction accuracy over time.
- 反向传播:微调神经网络权重的过程,随着时间的推移提高预测准确性。
Popular Applications: 热门应用:
- Image classification
- 图像分类
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- 自然语言处理(NLP)
- Facial recognition
- 人脸识别
What are Neural Networks? 什么是神经网络?
Neural Networks are the foundation of Deep Learning. Inspired by the human brain, they consist of interconnected nodes (neurons) organized into layers. Each node receives input, processes it through weighted connections, and passes the output to the next layer. Neural networks can “learn” by adjusting these weights during training.
神经网络是深度学习的基础。受人脑的启发,它们由组织成层的相互连接的节点(神经元)组成。每个节点接收输入,通过加权连接进行处理,并将输出传递到下一层。神经网络可以通过在训练过程中调整这些权重来“学习”。
Structure of Neural Networks: 神经网络的结构:
- Input Layer: Receives data and passes it to the hidden layers.
- 输入层:接收数据并将其传递给隐藏层。
- Hidden Layers: Perform computations, extracting relevant features from the data.
- 隐藏层:执行计算,从数据中提取相关特征。
- Output Layer: Produces the final prediction or classification.
- 输出层:生成最终预测或分类。
Types of Neural Networks: 神经网络的类型:
- Feedforward Neural Networks (FNN): The simplest type, where data moves in one direction from input to output.
- 前馈神经网络(FNN):最简单的类型,其中数据从输入到输出沿一个方向移动。
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN): Specialized for image recognition, analyzing spatial hierarchies in data.
- 卷积神经网络(CNN):专门用于图像识别,分析数据中的空间层次结构。
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN): Used for sequential data, like time series or language modeling, with the ability to maintain information from previous inputs.
- 循环神经网络(RNN):用于顺序数据,例如时间序列或语言建模,能够维护来自先前输入的信息。
AI vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning vs. Neural Networks: Key Differences
人工智能、机器学习、深度学习、神经网络:主要区别
| Aspect 方面 | Artificial Intelligence (AI) 人工智能(AI) | Machine Learning (ML) 机器学习(ML) | Deep Learning (DL) 深度学习(DL) | Neural Networks (NN) 神经网络(NN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition 定义 | Broad field focused on creating intelligent systems that can mimic human behavior or perform tasks autonomously. 广泛领域,专注于创建可以模仿人类行为或自主执行任务的智能系统。 | Subset of AI that enables systems to learn and improve from data without being explicitly programmed. 人工智能的子集,使系统能够从数据中学习和改进,而无需明确编程。 | Subset of ML that uses complex neural networks with many layers to learn from vast amounts of data. ML 的子集,它使用具有多层的复杂神经网络从大量数据中学习。 | A computational model inspired by the human brain, forming the backbone of Deep Learning. 受人脑启发的计算模型,构成深度学习的支柱。 |
| Core Goal 核心目标 | Simulate human intelligence to solve complex tasks or make decisions. 模拟人类智能以解决复杂的任务或做出决策。 | Enable machines to learn from data to make predictions or decisions. 使机器能够从数据中学习以做出预测或决策。 | Use large datasets and deep neural networks to learn hierarchical data representations. 使用大型数据集和深度神经网络来学习分层数据表示。 | Mimic the structure and function of the brain to recognize patterns and solve tasks. 模仿大脑的结构和功能来识别模式并解决任务。 |
| Types of Learning 学习类型 | Can include rule-based systems, search algorithms, and logic. 可以包括基于规则的系统、搜索算法和逻辑。 | Primarily uses supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. 主要使用监督学习、无监督学习和强化学习。 | Mainly relies on supervised and unsupervised learning but operates with deep layers. 主要依赖于监督学习和无监督学习,但具有深层结构。 | Can be used for supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, but is most often applied in deep learning models. 可用于监督学习、无监督学习和强化学习,但最常应用于深度学习模型。 |
| Complexity 复杂性 | Most general and broadest category. 最一般和最广泛的类别。 | More specialized within AI, focused on algorithms that learn from data. 更专业于人工智能,专注于从数据中学习的算法。 | More complex than ML due to its multi-layered neural networks. 由于其多层神经网络,比 ML 更复杂。 | Forms the core of Deep Learning but can also be used in simpler ML models. 构成深度学习的核心,但也可用于更简单的 ML 模型。 |
| Data Dependency 数据依赖关系 | Can work with both structured and unstructured data. 可以处理结构化和非结构化数据。 | Requires data to improve and learn patterns. 需要数据来改进和学习模式。 | Requires massive amounts of labeled data for training to perform effectively. 需要大量标记数据才能进行训练才能有效执行。 | Requires large datasets and sufficient computational power to train effectively. 需要大型数据集和足够的计算能力才能有效训练。 |
| Application Examples 应用示例 | Robotics, virtual assistants, autonomous systems, expert systems. 机器人、虚拟助手、自主系统、专家系统。 | Recommendation engines, fraud detection, predictive maintenance. 推荐引擎、欺诈检测、预测性维护。 | Image recognition, natural language processing, autonomous driving. 图像识别、自然语言处理、自动驾驶。 | Facial recognition, speech-to-text systems, translation tasks. 面部识别、语音转文本系统、翻译任务。 |
| Hardware Requirements 硬件要求 | Generally runs on standard hardware but may need specialized chips for advanced tasks. 通常在标准硬件上运行,但可能需要专门的芯片来执行高级任务。 | Can run on standard hardware but benefits from GPUs for large datasets. 可以在标准硬件上运行,但受益于大型数据集的 GPU。 | Requires powerful hardware like GPUs/TPUs due to large computational needs. 由于计算需求大,需要强大的硬件,如 GPU/TPU。 | Typically requires GPUs/TPUs for deep architectures and large-scale models. 通常需要 GPU/TPU 来进行深度架构和大规模模型。 |
| Processing Layers 处理层 | May not use layers (rule-based or logical approaches). 不得使用层(基于规则或逻辑方法)。 | Often shallow models with 1-2 layers. 通常是 1-2 层的浅模型。 | Involves many layers (hence “deep”) in neural networks. 涉及神经网络中的许多层(因此是“深层”)。 | Neural networks consist of input, hidden, and output layers. 神经网络由输入层、隐藏层和输出层组成。 |
How AI vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning vs. Neural Networks Work Together?
人工智能、机器学习、深度学习、神经网络如何协同工作?
- AI: The overall goal is to build an AI system that can recognize objects in images like humans do.
- AI:总体目标是构建一个能够像人类一样识别图像中物体的 AI 系统。
- ML: Machine learning is used to train the system by feeding it labeled images (e.g., “cat,” “dog”). The ML algorithms learn to associate image features with specific labels through training.
- ML:机器学习用于通过向系统提供标记的图像(例如“猫”、“狗”)来训练系统。机器学习算法通过训练学习将图像特征与特定标签相关联。
- DL and NNs: Deep learning, using neural networks, processes these images with multiple layers, automatically detecting complex patterns like edges, shapes, and textures without manual feature engineering. The neural networks then classify the images based on what they’ve learned.
- DL 和 NN:深度学习使用神经网络处理这些多层图像,自动检测边缘、形状和纹理等复杂图案,无需手动特征工程。然后,神经网络根据所学到的内容对图像进行分类。
Conclusion
结论
Understanding the distinctions between AI, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Neural Networks is crucial for navigating the evolving world of intelligent systems. Each plays a significant role, from broad AI applications like robotics to specialized DL models that power modern advancements like self-driving cars and voice assistants.
了解人工智能、机器学习、深度学习和神经网络之间的区别对于驾驭不断发展的智能系统世界至关重要。从机器人技术等广泛的人工智能应用到为自动驾驶汽车和语音助手等现代进步提供动力的专用 DL 模型,每个都发挥着重要作用。
History and Evolution of LLMs
大型语言模型的历史和演变
Last Updated: 23 Jul, 2025
AI has completely transformed the interaction pattern between humans and computers. Evolved from basic rule-based chatbots up to gigantic systems called Large Language Models (LLMs) that can generate human-like text, AI communication has indeed emerged. It has changed the industries linked with customer service, content generation, code writing, and research.
人工智能彻底改变了人与计算机之间的交互模式。从基本的基于规则的聊天机器人发展到可以生成类似人类文本的大型语言模型(LLMs)的巨大系统,人工智能通信确实已经出现。它改变了与客户服务、内容生成、代码编写和研究相关的行业。
—
What is a Large Language Model (LLM)?
什么是大型语言模型(LLM)?
A Large Language Model (LLM), as the name suggests, is an AI which has been trained with tremendous amounts of textual data to understand and generate responses that sound like human beings. Most of these models employ deep learning techniques with transformers to analyze context and anticipate what makes a good next word following some tokens in a sentence. This simple mechanism, however, allows it to do complex tasks such as question-answering, summarizing information, translating languages, and even writing code.
顾名思义,大型语言模型(LLM)是一种经过大量文本数据训练的人工智能,可以理解并生成听起来像人类的响应。这些模型中的大多数都采用深度学习技术和转换器来分析上下文并预测句子中某些标记后面的下一个好词是什么。然而,这种简单的机制允许它执行复杂的任务,例如问答、总结信息、翻译语言,甚至编写代码。
While LLMs might seem like advanced autocomplete systems, they go beyond simple text prediction. They can:
虽然大型语言模型(LLMs)看起来像是先进的自动完成系统,但它们超越了简单的文本预测。它们可以:
- Reason and infer insights from text
从文本中推理和推断见解 - Generate creative content
生成创意内容 - Recall factual information
回忆事实信息
—
History and Evolution of LLMs
大型语言模型的历史和演变
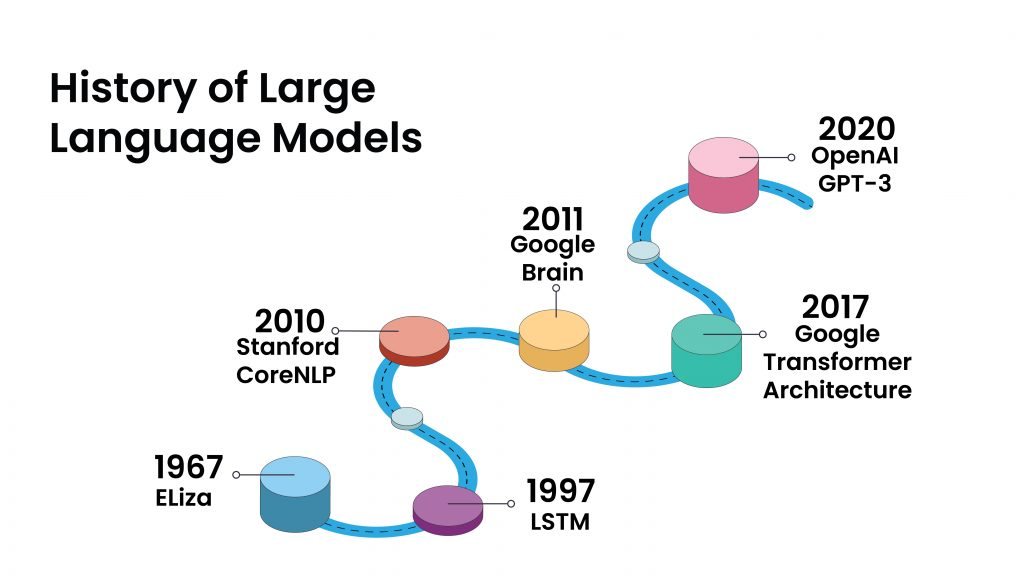
The journey of Large Language Models (LLMs) started decades ago with simple rule-based systems and evolved into today’s powerful AI-driven models. Let’s explore how we got here!
大型语言模型(LLMs)的旅程始于几十年前简单的基于规则的系统,并演变成当今强大的人工智能驱动模型。让我们来探讨一下我们是如何走到这一步的!
1. The First Steps in NLP (1960s - 1990s)
1. NLP 的第一步(1960 年代 - 1990 年代)
The journey of Large Language Models (LLMs) began in 1966 with ELIZA, a simple chatbot that mimicked conversation using predefined rules but lacked true understanding. By the 1980s, AI transitioned from manual rules to statistical models, improving text analysis. In the 1990s, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) introduced the ability to process sequential data, laying the foundation for modern NLP.
大型语言模型(LLMs)的旅程始于 1966 年的 ELIZA,这是一个简单的聊天机器人,使用预定义的规则模仿对话,但缺乏真正的理解。到 1980 年代,人工智能从手动规则过渡到统计模型,改进了文本分析。在 1990 年代,递归神经网络(RNNs)引入了处理顺序数据的能力,为现代自然语言处理(NLP)奠定了基础。
2. The Rise of Neural Networks and Machine Learning (1997 - 2010)
2. 神经网络和机器学习的兴起(1997 - 2010)
A breakthrough came in 1997 with Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), which solved RNNs’ memory limitations, making AI better at understanding long sentences. By 2010, tools like Stanford’s CoreNLP helped researchers process text more efficiently.
1997 年,长短期记忆(LSTM)取得了突破,它解决了 RNN 的记忆限制,使人工智能能够更好地理解长句子。到 2010 年,斯坦福大学的 CoreNLP 等工具帮助研究人员更有效地处理文本。
3. The AI Revolution and the Birth of Modern LLMs (2011 - 2017)
3. 人工智能革命和现代大型语言模型的诞生(2011 - 2017)
The AI revolution gained momentum in 2011 with Google Brain, which leveraged big data and deep learning for advanced language processing. In 2013, Word2Vec improved AI’s ability to understand word relationships through numerical representations. Then in 2017, Google introduced Transformers in “Attention is All You Need,” revolutionizing LLMs by making them faster, smarter, and more powerful.
人工智能革命在 2011 年随着 Google Brain 的出现而势头强劲,它利用大数据和深度学习进行高级语言处理。2013 年,Word2Vec 提高了人工智能通过数字表示理解单词关系的能力。然后在 2017 年,谷歌在 “Attention is All You Need” 中引入了 Transformers,通过让大型语言模型更快、更智能、更强大,彻底改变了它们。
4. The Deep Learning Era: Large-Scale LLMs Take Over (2018 - Present)
4. 深度学习时代:大规模大型语言模型接管(2018 年至今)
The deep learning era took off in 2018 with BERT, which enhanced context understanding in sentences. OpenAI’s GPT series (2018-2024) transformed AI-powered text generation, while platforms like Hugging Face and Meta’s LLaMA made open-source LLMs widely accessible, shaping the future of AI-driven applications.
深度学习时代于 2018 年随着 BERT 而起飞,它增强了句子中的上下文理解。OpenAI 的 GPT 系列(2018-2024 年)改变了人工智能驱动的文本生成,而 Hugging Face 和 Meta 的 LLaMA 等平台使开源大型语言模型变得广泛可用,塑造了人工智能驱动应用程序的未来。
—
Comparison of Major Large Language Models (LLMs)
主要大型语言模型(LLMs)的比较
| Model | Year | Developer | Architecture | Key Features | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELIZA | 1966 | MIT | Rule-Based 基于规则 | First chatbot, keyword matching 第一个聊天机器人,关键字匹配 | No real understanding, limited responses 没有真正的理解,有限的回应 |
| LSTM | 1997 | Sepp Hochreiter and Jürgen Schmidhuber 塞普·霍赫赖特和尤尔根·施米德胡贝尔 | Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) 递归神经网络(RNN) | Overcomes vanishing gradient problem, better memory retention 克服渐变消失问题,记忆力更好 | Struggles with long-term dependencies 与长期依赖关系作斗争 |
| Word2Vec | 2013 | Google 谷歌 | Neural Embeddings 神经嵌入 | Captures word relationships, semantic similarity 捕获单词关系、语义相似性 | Context-independent representations 与上下文无关的表示 |
| BERT | 2018 | Google 谷歌 | Transformer (Bidirectional) 变压器(双向) | Context-aware understanding, fine-tuned for NLP tasks 上下文感知理解,针对 NLP 任务进行微调 | Cannot generate text, requires large datasets 无法生成文本,需要大型数据集 |
| GPT-2 | 2019 | OpenAI 开放人工智能 | Transformer (Unidirectional) 变压器(单向) | Large-scale text generation, creative writing 大规模文本生成,创意写作 | Prone to biases, generates misinformation 容易产生偏见,产生错误信息 |
| GPT-3 | 2020 | OpenAI 开放人工智能 | Transformer (Unidirectional) 变压器(单向) | 175B parameters, human-like text generation, few-shot learning 175B参数,类人文本生成,少样本学习 | High computational cost, occasional factual errors 计算成本高,偶尔出现事实错误 |
| GPT-4 | 2023 | OpenAI 开放人工智能 | Transformer (Multimodal) 变压器(多模态) | Handles text, images, and code, more accurate responses 处理文本、图像和代码,响应更准确 | Still expensive, not fully autonomous 仍然昂贵,不是完全自主的 |
| Gemma 3 | 2025 | Google 谷歌 | Transformer (Self-Learning) Transformer(自学习) | Enhanced factual accuracy, real-time learning 提高事实准确性,实时学习 | Emerging, yet to be widely tested 新兴,尚未得到广泛测试 |
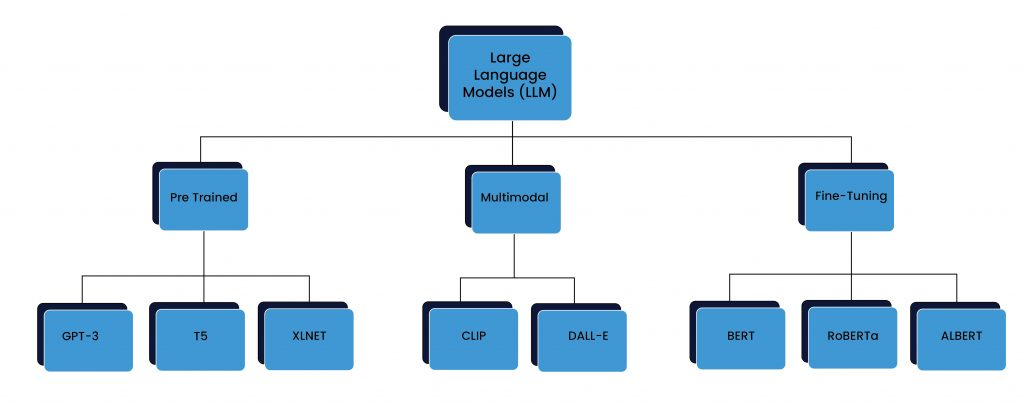
Different Types of LLMs
不同类型的大型语言模型
1. Pre-Trained Models
1. 预训练模型
Models like GPT-4, XLNet, and T5 are trained on vast amounts of text data, allowing them to generate human-like responses, translate languages, summarize text, and more. They serve as general-purpose AI tools that can handle a variety of tasks without additional training.
GPT-4、XLNet 和 T5 等模型经过大量文本数据的训练,使它们能够生成类似人类的响应、翻译语言、总结文本等。它们作为通用人工智能工具,无需额外培训即可处理各种任务。
2. Fine-Tuned Models
2. 微调模型
Models like BERT, ROBERTa, and ALBERT start as pre-trained models but are further refined on specific datasets for specialized tasks. For example, BERT can be fine-tuned for sentiment analysis, legal text processing, or medical diagnostics, making it more accurate for those particular use cases.
BERT、ROBERTa 和 ALBERT 等模型最初是预训练模型,但在特定数据集上进一步完善以执行专门任务。例如,BERT 可以针对情感分析、法律文本处理或医疗诊断进行微调,使其更准确地适应这些特定用例。
3. Multimodal LLMs
3. 多模态大型语言模型
AI is no longer limited to just text. Models like CLIP and DALL·E can understand and generate images based on text prompts, bringing AI closer to human-like perception. Meanwhile, speech-enabled models like Whisper are revolutionizing voice recognition, making AI more accessible through spoken language.
人工智能不再局限于文本。CLIP 和 DALL·E 可以根据文本提示理解和生成图像,使 AI 更接近人类感知。与此同时,像 Whisper 这样的语音模型正在彻底改变语音识别,使人工智能更容易通过口语访问。
4. Domain-Specific LLMs
4. 特定领域的大型语言模型
These are designed for specialized industries like healthcare, finance, and law. Instead of general knowledge, these models are trained on industry-specific data to provide more accurate insights. For example, Med-PaLM helps doctors by understanding medical texts and answering health-related queries, while BloombergGPT is tailored for financial markets, analyzing stock trends and news. These models ensure AI delivers expert-level accuracy in specialized fields.
这些专为医疗保健、金融和法律等专业行业而设计。这些模型不是一般知识,而是根据行业特定数据进行训练,以提供更准确的见解。例如,Med-PaLM 通过理解医学文本和回答与健康相关的查询来帮助医生,而 BloombergGPT 则专为金融市场量身定制,分析股票趋势和新闻。这些模型确保人工智能在专业领域提供专家级的准确性。
—
Limitations and Concerns
限制和担忧
Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized how we interact with technology, but their rise brings several challenges and ethical dilemmas that require careful consideration.
大型语言模型(LLMs)彻底改变了我们与技术交互的方式,但它们的兴起带来了一些需要仔细考虑的挑战和道德困境。
1. The Bias Problem: When AI Learns the Wrong Things
1. 偏见问题:当人工智能学习错误的东西时
LLMs learn from vast datasets that may contain biases present in society. When biases are present in the data used to train AI systems, they can be incorporated and even enhanced into the AI systems, resulting in unfair outcomes. Research reveals that AI models that are used in mortgage lending are likely to discriminate against Black applicants, as it reflects the prevailing social bias. However, in the case of AI tools in hiring, they tend to prefer some groups of candidates over others, which is a significant issue for fairness and equality.
大型语言模型从大量数据集中学习,这些数据集可能包含社会中存在的偏见。当用于训练人工智能系统的数据中存在偏见时,它们可能会被纳入甚至增强到人工智能系统中,从而导致不公平的结果。研究表明,抵押贷款中使用的人工智能模型可能会歧视黑人申请人,因为它反映了普遍存在的社会偏见。然而,就招聘中的人工智能工具而言,他们往往更喜欢某些候选人群体而不是其他候选人群体,这对于公平和平等来说是一个重大问题。
2. Privacy Risks: Who Owns the Data LLMs Learn From?
2. 隐私风险:谁拥有大型语言模型从中学习的数据?
LLMs are trained across huge datasets, which may include copyright and private materials, though such practice raises ethics on ownership and consent in data. It’s still taking shape in the legal ecosystem concerning AI-generated content, thus leaving gray areas around intellectual property rights and proprietary data use without express permission. The lack of clarity is threatening to individuals and organizations regarding their privacy and data security.
大型语言模型在庞大的数据集中进行训练,其中可能包括版权和私人材料,尽管这种做法提高了数据所有权和同意的道德规范。它仍在有关人工智能生成内容的法律生态系统中形成,从而在未经明确许可的情况下在知识产权和专有数据使用方面留下了灰色地带。缺乏明确性对个人和组织的隐私和数据安全构成威胁。
3. Computational Costs and Environmental Impact
3. 计算成本和环境影响
The use of huge computations during training LLMs will end in significant energy consumption and wide-ranging carbon emissions. GPT-3’s training alone is reported to have had a pretty high carbon footprint as environmental concerns arise with large-scale AI models. Because of these, researchers are studying other energy-efficient architectures, such as sparse expert models, to make reiteration efforts less environmentally impactful while still being high-performance.
在训练大型语言模型期间使用大量计算将导致大量的能源消耗和广泛的碳排放。据报道,仅 GPT-3 的训练就产生了相当高的碳足迹,随着大型人工智能模型出现了环境问题。正因为如此,研究人员正在研究其他节能架构,例如稀疏专家模型,以减少重复工作对环境的影响,同时仍然保持高性能。
As LLMs become more integrated into various applications, addressing these ethical and environmental challenges is crucial to ensure that AI technologies benefit society responsibly and sustainably.
随着大型语言模型越来越多地融入各种应用,解决这些道德和环境挑战对于确保人工智能技术负责任和可持续地造福社会至关重要。
—
Future of LLMs
大型语言模型的未来
The next wave of Large Language Models (LLMs) will push the boundaries of AI intelligence, making them more adaptive, interactive, and efficient. Here’s what lies ahead:
下一波大型语言模型(LLMs)将突破人工智能智能的界限,使其更具适应性、交互性和高效性。以下是未来:
Adaptive AI: Models That Evolve in Real Time
自适应人工智能:实时进化的模型
AI systems are fed with an open-world model and look out to observe changes like a regular human. Companies like Anthropic and OpenAI are looking to implement a system whereby AIs will be made aware of context and will evolve in real-time to improve their performance, negating the need for data collection of feedback loops running on existing databases.
人工智能系统被灌输了一个开放世界的模型,并像普通人一样观察变化。Anthropic 和 OpenAI 等公司正在寻求实施一个系统,通过该系统,人工智能将了解上下文并实时发展以提高其性能,从而消除对现有数据库上运行的反馈循环进行数据收集的需要。
Personalized AI Assistants: Smarter and More Context-Aware
个性化人工智能助手:更智能、更上下文感知
The new waves of the future will be AI assistants, which sometimes understand users better than friends or relatives, truly recalling past interactions and changing the response accordingly. Wouldn’t it be great to have AI customize its tone and recommendations and also change the methods of problem-solving just because a user does it in a particular style? Personalized AI into the operating system would redefine all digital interaction in daily life, with pioneering companies like Apple and Microsoft in the business of deeply embedding an AI system.
未来的新浪潮将是人工智能助手,它有时比朋友或亲戚更能理解用户,真正回忆起过去的互动并相应地改变反应。让人工智能定制其语气和建议,并仅仅因为用户以特定风格解决问题而改变解决问题的方法,这不是很好吗?将个性化人工智能融入操作系统将重新定义日常生活中的所有数字交互,苹果和 Microsoft 等先驱公司致力于深度嵌入人工智能系统。
Beyond Text: LLMs in Robotics, VR, and the Metaverse
超越文本:机器人、VR 和元宇宙中的大型语言模型
LLMs are moving beyond text processing and into real-world applications. The design of multi-modal AI models, such as Gemini and GPT-4 Turbo, is to create understanding and interactivity across text, images, and speech. AI is also transforming fields such as VR and robotics to facilitate life-like digital humans engaged in real-time metaverse conversations. Firms securing this transition into digital experiences with AI-assisted avatars include Meta and Nvidia.
大型语言模型正在超越文本处理并进入实际应用。Gemini 和 GPT-4 Turbo 等多模态 AI 模型的设计旨在跨文本、图像和语音创建理解和交互性。人工智能还在改变 VR 和机器人技术等领域,以促进栩栩如生的数字人参与实时元宇宙对话。通过人工智能辅助化身确保向数字体验过渡的公司包括 Meta 和 Nvidia。
—
Conclusion
结论
Large Language Models (LLMs) have evolved from simple rule-based systems to powerful AI assistants that generate human-like text, code, and even images. Their impact is undeniable, transforming industries, automating tasks, and enhancing creativity. However, challenges remain. Bias, misinformation, data privacy, and the environmental impact of training massive models need urgent solutions. AI must become more ethical, transparent, and efficient to ensure responsible usage.
大型语言模型(LLMs)已经从简单的基于规则的系统发展成为强大的人工智能助手,可以生成类似人类的文本、代码甚至图像。它们的影响是不可否认的,改变了行业、自动化了任务并增强了创造力。然而,挑战依然存在。偏见、错误信息、数据隐私以及训练海量模型对环境的影响需要紧急解决方案。人工智能必须变得更加道德、透明和高效,以确保负责任的使用。
Looking ahead, LLMs will continue to shape the way we work, learn, and communicate. The real question is: How do we harness AI’s potential while ensuring it aligns with human values? The future of AI is not just about smarter models—it’s about how we choose to use them.
展望未来,大型语言模型将继续塑造我们的工作、学习和交流方式。真正的问题是:我们如何利用人工智能的潜力,同时确保其符合人类价值观?人工智能的未来不仅关乎更智能的模型,还关乎我们选择如何使用它们。
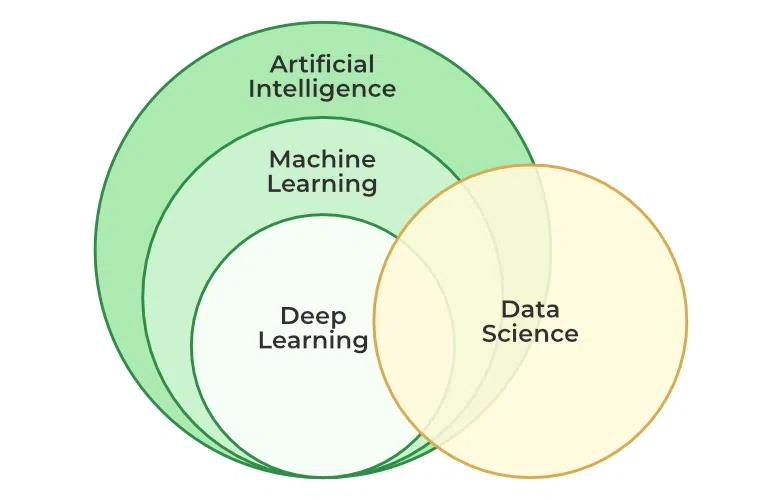
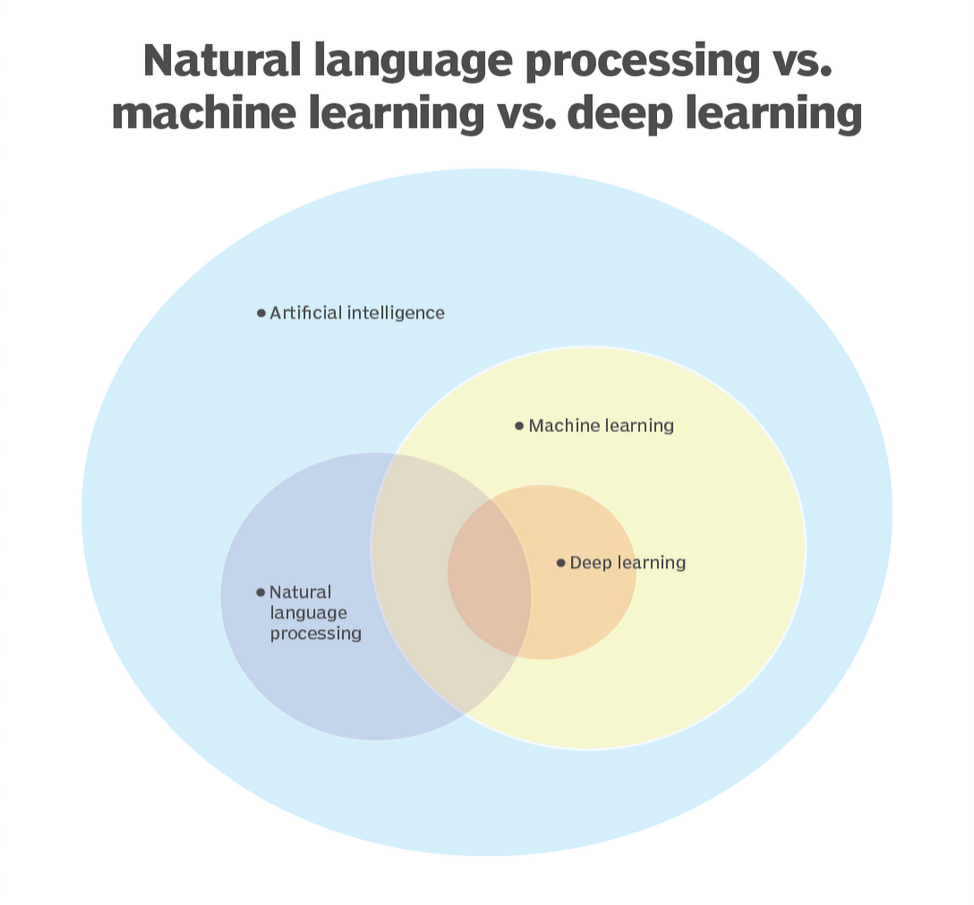
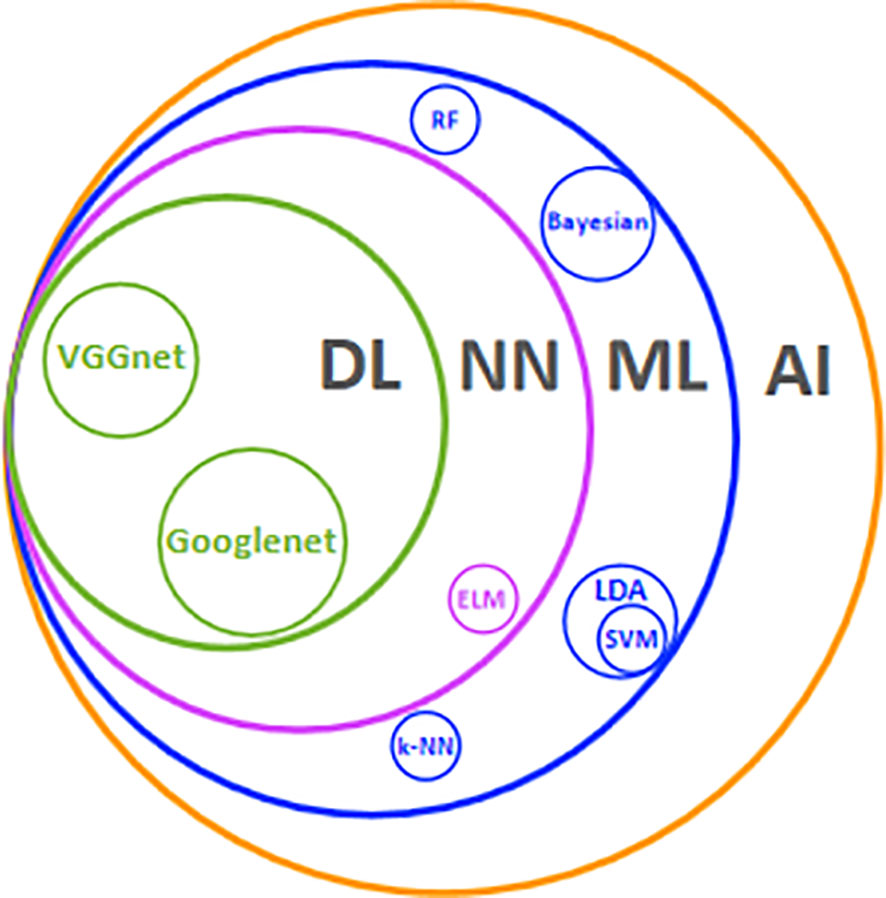
人工智能、机器学习、深度学习和神经网络之间的关系及特点
引言
-
人工智能是一种广泛的目标,旨在使计算机系统能够执行通常需要人类智能的任务。
-
机器学习是实现人工智能的一个重要途径,通过让计算机从数据中学习规律和模式,从而实现特定的任务。
-
深度学习是机器学习的一个重要分支,它使用多层神经网络来学习数据的复杂表示,这些网络能够自动提取数据的特征。
-
神经网络是深度学习的核心工具之一,通过模拟人脑神经元结构,能够处理复杂的非线性关系。深度学习需要大量的数据和强大的计算能力来训练模型,以发挥其优势。
人工智能
- 定义:人工智能(AI)是一种广泛的目标,旨在使计算机系统能够执行通常需要人类智能的任务,如视觉识别、语言理解、决策制定等。
- 目标:人工智能的目标不仅仅是模拟人类的思维方式,还包括实现超越人类水平的智能行为,以解决复杂的现实问题。
- 范围:人工智能是一个涵盖多个子领域的广泛概念,包括机器学习、深度学习、自然语言处理、计算机视觉、机器人技术等。
机器学习
- 定义:机器学习(ML)是实现人工智能的一个重要途径,也是人工智能的核心领域之一。它通过让计算机从数据中学习规律和模式,从而实现特定的任务。
- 模型:机器学习有多种模型可供选择,包括监督学习、无监督学习、强化学习等,每种学习方式下又有不同的算法,如线性回归、决策树、支持向量机等。
- 应用:机器学习在许多领域都有广泛应用,如金融风险预测、医疗诊断、推荐系统等。
深度学习
- 定义:深度学习(DL)是机器学习的一个重要分支,它使用多层神经网络来学习数据的复杂表示。这些网络通常具有多个隐藏层,能够自动提取数据的特征。
- 优势:深度学习模型在图像识别、语音识别、自然语言处理等领域表现出色,因为它们能够自动学习数据的层次化特征。
- 数据和算力需求:深度学习需要大量的数据来训练模型,以确保模型能够学习到足够的特征。同时,深度学习模型通常计算复杂度较高,需要强大的计算能力来支持训练和推理过程。
神经网络
- 定义:神经网络是深度学习的核心工具之一,它是一种模拟人脑神经元结构的计算模型。神经网络由输入层、隐藏层和输出层组成,每个神经元通过权重连接到其他神经元,通过激活函数进行非线性变换。
- 类型:常见的神经网络类型包括前馈神经网络(FNN)、卷积神经网络(CNN)、循环神经网络(RNN)及其变体长短期记忆网络(LSTM)和门控循环单元(GRU)。
- 应用:神经网络在图像识别、语音识别、自然语言处理等领域有广泛的应用,是深度学习的基础。
图示
via:
-
AI vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning vs. Neural Networks - GeeksforGeeks
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/machine-learning/ai-vs-machine-learning-vs-deep-learning-vs-neural-networks/ -
History and Evolution of LLMs - GeeksforGeeks
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/blogs/history-and-evolution-of-llms/ -
Large Language Models 101: History, Evolution and Future
https://www.scribbledata.io/blog/large-language-models-history-evolutions-and-future/ -
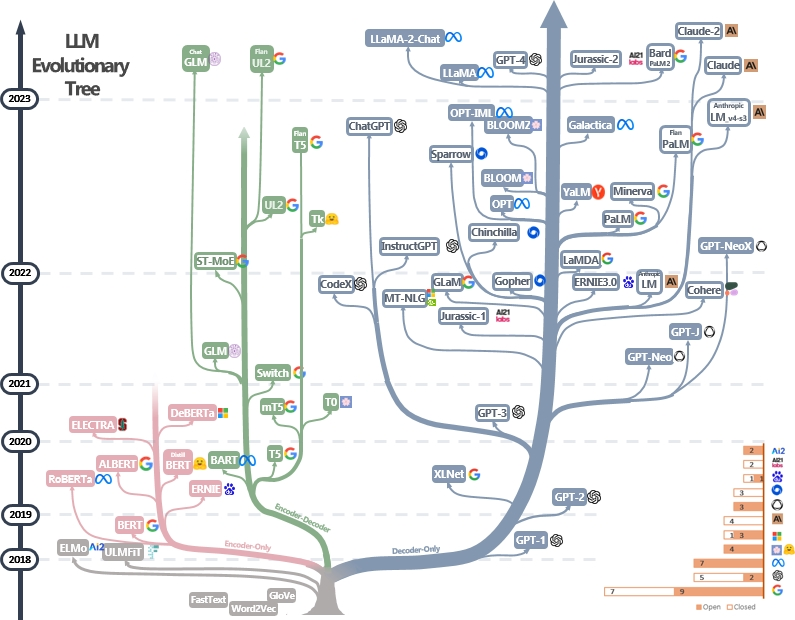
LLMsPracticalGuide/imgs/tree.jpg at main · Mooler0410/LLMsPracticalGuide · GitHub
https://github.com/Mooler0410/LLMsPracticalGuide -
一文读懂!人工智能、机器学习、深度学习的区别与联系!_机器学习或者深度学习 与 ai 区别-CSDN博客
https://blog.csdn.net/python122_/article/details/138791308
