Qwen3Next注意力机制详解与实现
Qwen3Next注意力机制详解与实现
本文将深入探讨Qwen3Next模型中注意力机制的实现细节,包括其特殊的注意力层设计、旋转位置编码以及实际的测试示例。
核心组件介绍
1. 注意力层配置
Qwen3Next的注意力机制采用了分组注意力(Grouped-Query Attention, GQA)的设计思路,主要配置参数包括:
- 查询头数(num_attention_heads):16个
- 键值头数(num_key_value_heads):2个
- 头维度(head_dim):256
- 隐藏层大小(hidden_size):2048
- 注意力偏置(attention_bias):启用
- 注意力dropout率:0.1
2. 注意力层结构
-
投影层:
- Q投影:
hidden_size -> num_attention_heads * head_dim * 2 - K投影:
hidden_size -> num_key_value_heads * head_dim - V投影:
hidden_size -> num_key_value_heads * head_dim - O投影:
num_attention_heads * head_dim -> hidden_size
- Q投影:
-
归一化层:
- 查询归一化:
q_norm - 键归一化:
k_norm
使用RMSNorm进行归一化处理
- 查询归一化:
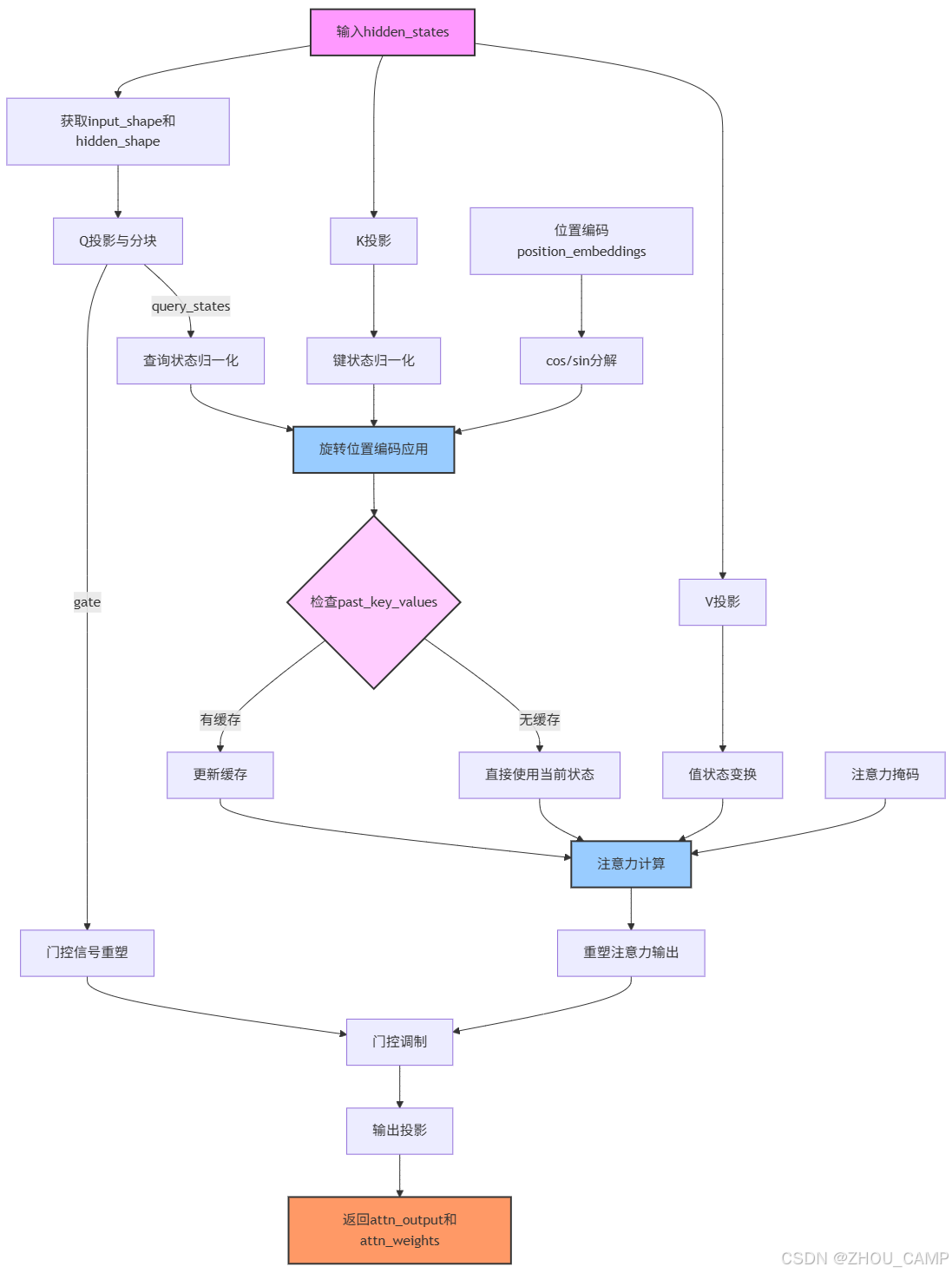
3. 前向传播流程
-
输入处理:
- 接收hidden_states、位置编码和注意力掩码
- 计算输入形状和隐藏形状
-
查询处理:
- 通过Q投影生成查询状态和门控信号
- 对查询状态进行RMSNorm归一化
-
键值处理:
- 生成并归一化键状态
- 生成值状态
-
位置编码:
- 应用旋转位置编码(RoPE)到查询和键状态
-
注意力计算:
- 使用eager_attention_forward计算注意力输出和权重
- 支持缓存机制优化推理性能
-
输出处理:
- 重塑注意力输出
- 应用门控机制
- 通过O投影生成最终输出
前向过程图示
测试实现
from transformers.models.qwen3_next.modeling_qwen3_next import (eager_attention_forward,apply_rotary_pos_emb,Qwen3NextRMSNorm,Qwen3NextRotaryEmbedding)from transformers.cache_utils import Cache
from transformers.modeling_flash_attention_utils import FlashAttentionKwargs
from transformers.models.qwen3_next.configuration_qwen3_next import Qwen3NextConfig
ALL_ATTENTION_FUNCTIONS = {"eager": eager_attention_forward}import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Optional, Tuple, Callable, Dict, Any
from typing_extensions import Unpack
class Qwen3NextAttention(nn.Module):def __init__(self, config: Qwen3NextConfig, layer_idx: int):super().__init__()self.config = configself.layer_idx = layer_idx self.head_dim = getattr(config, "head_dim", config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads) # 256self.num_key_value_groups = config.num_attention_heads // config.num_key_value_heads # 16 /2 8self.scaling = self.head_dim**-0.5self.attention_dropout = config.attention_dropoutself.is_causal = Trueself.q_proj = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_attention_heads * self.head_dim * 2, bias=config.attention_bias) # 2048 -> 16 * 256 * 2self.k_proj = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias) # 2048 -> 2 * 256self.v_proj = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias) # 2048 -> 2 * 256self.o_proj = nn.Linear(config.num_attention_heads * self.head_dim, config.hidden_size, bias=config.attention_bias) # 16 * 256 -> 2048self.q_norm = Qwen3NextRMSNorm(self.head_dim, eps=config.rms_norm_eps) # self.k_norm = Qwen3NextRMSNorm(self.head_dim, eps=config.rms_norm_eps) # def forward(self,hidden_states: torch.Tensor,position_embeddings: tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor],attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor],past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,**kwargs: Unpack[FlashAttentionKwargs],) -> tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor]]:input_shape = hidden_states.shape[:-1] # 2 4 hidden_shape = (*input_shape, -1, self.head_dim) # 2 4 -1 256query_states, gate = torch.chunk(self.q_proj(hidden_states).view(*input_shape, -1, self.head_dim * 2), 2, dim=-1) # 2048 > 8192 > 2 4 16 512 > 2 4 16 256,2 4 16 256gate = gate.reshape(*input_shape, -1) # 2 4 4096query_states = self.q_norm(query_states.view(hidden_shape)).transpose(1, 2) # 2 4 16 256 > 2 16 4 256key_states = self.k_norm(self.k_proj(hidden_states).view(hidden_shape)).transpose(1, 2)# 2 4 2048 > 2 4 512 > 2 4 2 256 > 2 2 4 256value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states).view(hidden_shape).transpose(1, 2)# 2 4 2048 > 2 4 512 > 2 4 2 256 > 2 2 4 256cos, sin = position_embeddings query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)if past_key_values is not None:cache_kwargs = {"sin": sin, "cos": cos, "cache_position": cache_position}key_states, value_states = past_key_values.update(key_states, value_states, self.layer_idx, cache_kwargs)attention_interface: Callable = eager_attention_forwardif self.config._attn_implementation != "eager":attention_interface = ALL_ATTENTION_FUNCTIONS[self.config._attn_implementation]attn_output, attn_weights = attention_interface(self,query_states,key_states,value_states,attention_mask,dropout=0.0 if not self.training else self.attention_dropout,scaling=self.scaling,**kwargs,) # 输出形状: ([2, 4, 16, 256]) ([2, 16, 4, 4])attn_output = attn_output.reshape(*input_shape, -1).contiguous() # 2 4 4096attn_output = attn_output * torch.sigmoid(gate)attn_output = self.o_proj(attn_output) # 2 4 4096 》 2 4 2048return attn_output, attn_weights
# 测试代码
def test_qwen3next_attention():# 设置随机种子以保证结果可复现torch.manual_seed(42)config = Qwen3NextConfig(num_attention_heads=16, # Q的注意力头数num_key_value_heads=2, # KV的注意力头数head_dim=256, # 每个注意力头的维度hidden_size=2048, # 隐藏层大小 = 注意力头数 * 头维度attention_bias=True, # 使用注意力偏置attention_dropout=0.1, # 注意力dropout率rms_norm_eps=1e-6, # RMSNorm的epsilon值_attn_implementation="eager", # 使用eager模式的注意力实现max_position_embeddings= 64)attention = Qwen3NextAttention(config, layer_idx=0)# 创建输入数据batch_size = 2seq_len = 4hidden_size = config.hidden_size # 2048hidden_states = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size) # 2 4 2048rotary_emb = Qwen3NextRotaryEmbedding(config)position_ids = torch.arange(seq_len).unsqueeze(0).expand(batch_size, -1) # 4 -> 1,4 -> 2,4position_embeddings = rotary_emb(hidden_states, position_ids) # # 创建注意力掩码attention_mask = torch.zeros(batch_size, 1, seq_len, seq_len) # 2 1 4 4attention_mask[:, :, :, 0] = float('-inf') # 屏蔽第一个token的注意力# 测试前向传播output, attn_weights = attention(hidden_states=hidden_states,position_embeddings=position_embeddings,attention_mask=attention_mask,past_key_values=None,cache_position=None)# 验证输出形状assert output.shape == hidden_states.shape, f"输出形状 {output.shape} 与输入形状 {hidden_states.shape} 不匹配"# 验证注意力权重形状expected_attn_shape = (batch_size, config.num_attention_heads, seq_len, seq_len)assert attn_weights.shape == expected_attn_shape, f"注意力权重形状 {attn_weights.shape} 与预期形状 {expected_attn_shape} 不匹配"# 打印结果print("输入形状:", hidden_states.shape)print("输出形状:", output.shape)print("注意力权重形状:", attn_weights.shape)print("\n第一个批次,第一个头的注意力权重:")print(attn_weights[0, 0])print("\n所有测试通过!")# 运行测试
test_qwen3next_attention()
torch.Size([2, 4, 16, 256]) torch.Size([2, 16, 4, 4])
输入形状: torch.Size([2, 4, 2048])
输出形状: torch.Size([2, 4, 2048])
注意力权重形状: torch.Size([2, 16, 4, 4])第一个批次,第一个头的注意力权重:
tensor([[0.0000, 0.3215, 0.4939, 0.2957],[0.0000, 0.5109, 0.0814, 0.5188],[0.0000, 0.1700, 0.6891, 0.2519],[0.0000, 0.1437, 0.8513, 0.1161]], grad_fn=<SelectBackward0>)所有测试通过!
技术特点
-
分组查询注意力:通过较少的KV头数(2个)和较多的Q头数(16个)实现计算效率和表达能力的平衡。
-
门控机制:在查询投影中额外生成门控信号,用于调节注意力输出的影响程度。
-
RMSNorm归一化:对查询和键状态使用RMSNorm进行归一化,有助于稳定训练。
-
旋转位置编码:采用RoPE(Rotary Position Embedding)实现相对位置编码,增强模型对位置信息的感知。
通过这些技术特点的组合,Qwen3Next的注意力机制在保持强大表达能力的同时,实现了较高的计算效率。
