数据结构:树及二叉树--堆(下)
上篇文章回顾:https://blog.csdn.net/2401_86123468/article/details/151366890?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
本章代码见:https://gitee.com/jxxx404/c-language-learning/commit/d14d68230c1e529bf90230d6129bbf8686871d64
https://gitee.com/jxxx404/c-language-learning/commit/1fbbad517be3138aa5fbf249fc6a48a4976efa78
https://gitee.com/jxxx404/c-language-learning/commit/3ad4a24284a8fc91f65cec496b28e4a1712f5dd0
1.向上调整算法建堆时间复杂度
考虑到堆是完全二叉树,满二叉树也是完全二叉树,因此简化使用满二叉树来证明。
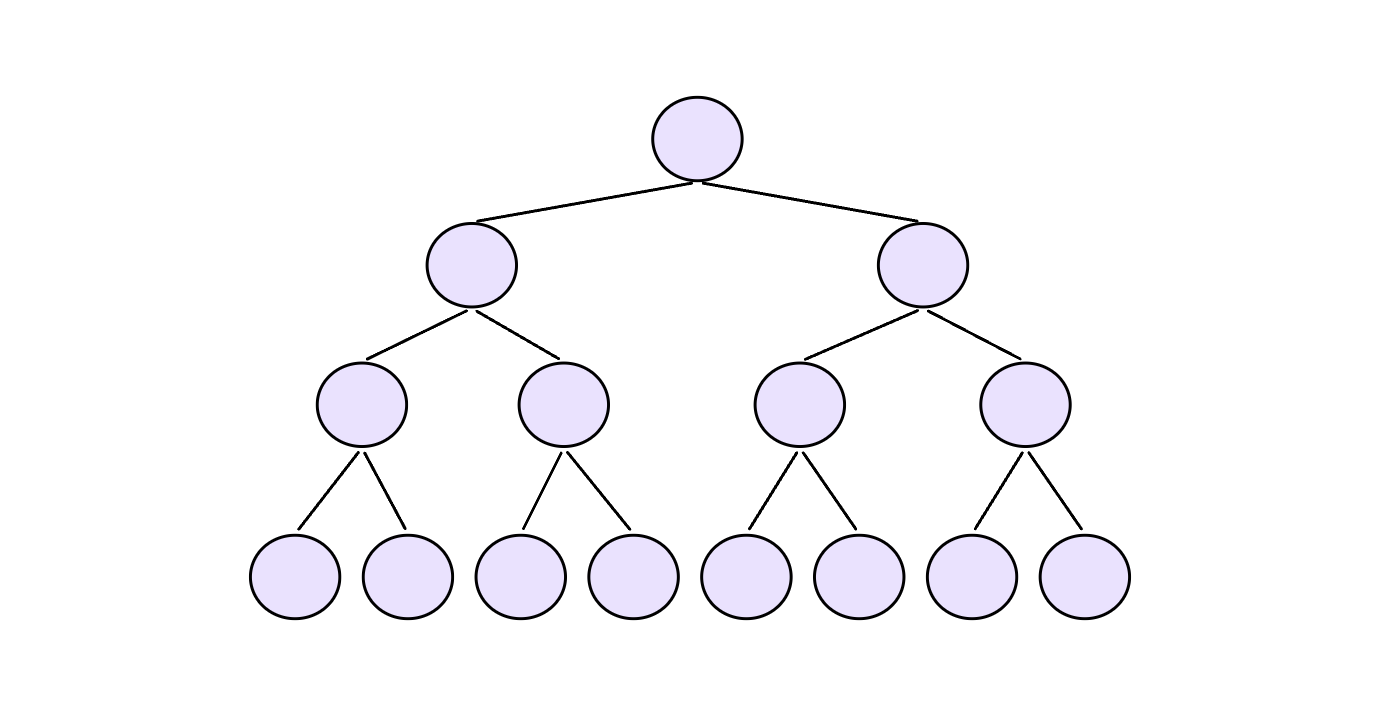
分析:
第1层,2^0个结点,需要向上移动0层
第2层,2^1个结点,需要向上移动1层
第3层,2^2个结点,需要向上移动2层
第4层,2^3个结点,需要向上移动3层
……
第h层,2^(h-1)个结点,需要向上移动h-1层

因此:向上调整算法建堆的时间复杂度为:O(n * logn),log以2为底。
2.向下调整算法建堆时间复杂度
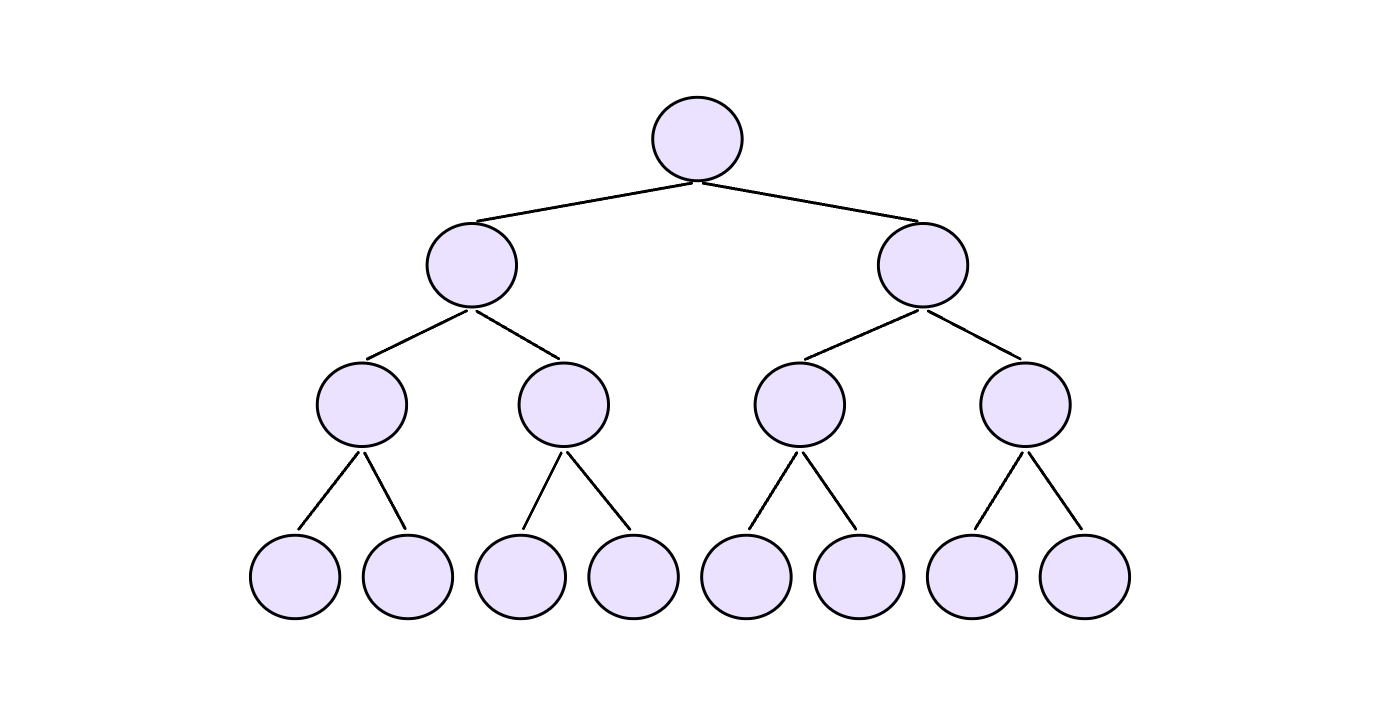
分析:
第1层,2^0个结点,需要向下移动h-1层
第2层,2^1个结点,需要向下移动h-2层
第3层,2^2个结点,需要向下移动h-3层
第4层,2^3个结点,需要向下移动h-4层
……
第h-1层,2^(h-2)个结点,需要向下移动1层

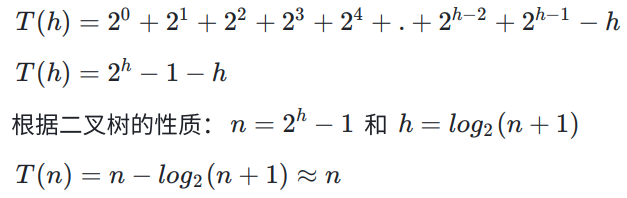
因此:向下调整算法建堆的时间复杂度为:O(n)
3.TOP-K问题
TOP-K问题:即求数据结合中前K个最大的元素或者最小的元素,一般情况下数据量都比较大。
比如:专业前10名、世界500强、富豪榜、游戏中前100的活跃玩家等。
对于Top-K问题,能想到的最简单直接的方式就是排序,但是:如果数据量非常大,排序就不太可
取了(可能数据都不能一下子全部加载到内存中)。最佳的方式就是用堆来解决,基本思路如下:
前k个最大的元素,则建小堆,遍历剩下的数据和堆顶比,比堆顶大就和堆顶交换。
前k个最小的元素,则建大堆,遍历剩下的数据和堆顶比,比堆顶小就和堆顶交换。
具体代码实现如下:
void CreateNData()
{//造数据int n = 100000;srand(time(0));const char* file = "data.txt";FILE* fin = fopen(file, "w");if (fin == NULL){perror("fopen fail!");return;}for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){int x = (rand() + i) % 100000;fprintf(fin, "%d\n", x);}fclose(fin);
}void TopK()
{int k = 0;printf("输入k: ");scanf("%d", &k);const char* file = "data.txt";FILE* fout = fopen(file, "r");if (fout == NULL){perror("fopen fail!");exit(1);}//申请空间大小为k的整型数组int* minHeap = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * k);if (minHeap == NULL){perror("malloc fail!");exit(2);}//读取文件中k个数据放到数组中for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){fscanf(fout, "%d", &minHeap[i]);}//数组调整建堆--向下调整建堆//找最大的前k个数,建小堆for (int i = (k - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--){AdjustDown(minHeap, i, k);}//遍历剩下的n - k个数,跟堆顶比较,谁小谁入堆int data = 0;while (fscanf(fout, "%d", &data) != EOF){if (data > minHeap[0]){minHeap[0] = data;AdjustDown(minHeap, 0, k);}}//打印for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){printf("%d ", minHeap[i]);}printf("\n");fclose(fout);
}int main()
{//CreateNData();TopK();return 0;
}时间复杂度为:O(n) = k + (n - k) * logk(logk以2为底)。
4.实现链式结构二叉树
用链表来表示一棵二叉树(用链来表示元素的逻辑关系)。通常方法为链表中每个结点由三个域组成,数据域和左右指针域,左右指针分别用来给出该结点左孩子和右孩子所在的链结点的存储地址。
结构如下:
//定义二叉树结点结构
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode {BTDataType data;struct BinaryTreeNode* left;struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;手动创建一棵链式二叉树:
BTNode* buyNode(char x)
{BTNode* newnode = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));newnode->data = x;newnode->left = newnode->right = NULL;return newnode;
}void test01()
{BTNode* nodeA = buyNode('A');BTNode* nodeB = buyNode('B');BTNode* nodeC = buyNode('C');BTNode* nodeD = buyNode('D');BTNode* nodeE = buyNode('E');BTNode* nodeF = buyNode('F');nodeA->left = nodeB;nodeA->right = nodeC;nodeB->left = nodeD;nodeC->left = nodeE;nodeC->right = nodeF;return nodeA;
}int main()
{test01();return 0;
}4.1前中后序遍历
以上述代码构造的二叉树为例:
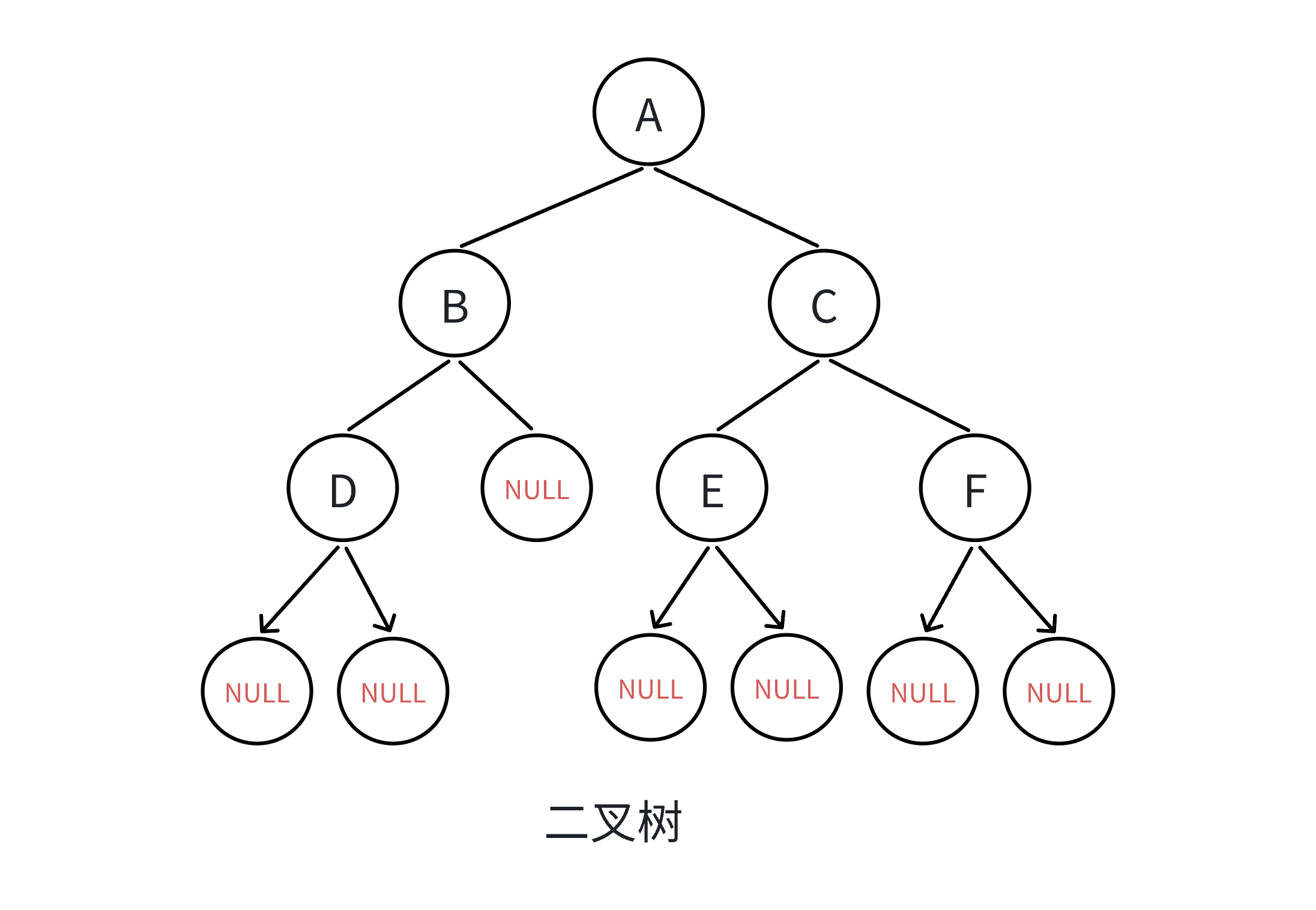
4.1.1遍历规则
二叉树的遍历有:前序/中序/后序的递归结构遍历:
(1)前序遍历(PreorderTraversal亦称先序遍历):访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前,访问顺序为:根结点、左子树、右子树
(2)中序遍历(InorderTraversal):访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之中(间),访问顺序为:左子树、根结点、右子树
(3)后序遍历(PostorderTraversal):访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后,访问顺序为:左子树、右子树、根结点
4.1.2代码实现
1.前序遍历
//前序遍历--根左右
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}printf("%c ", root->data);PreOrder(root->left);PreOrder(root->right);
}结果正确:
![]()
递归分析:
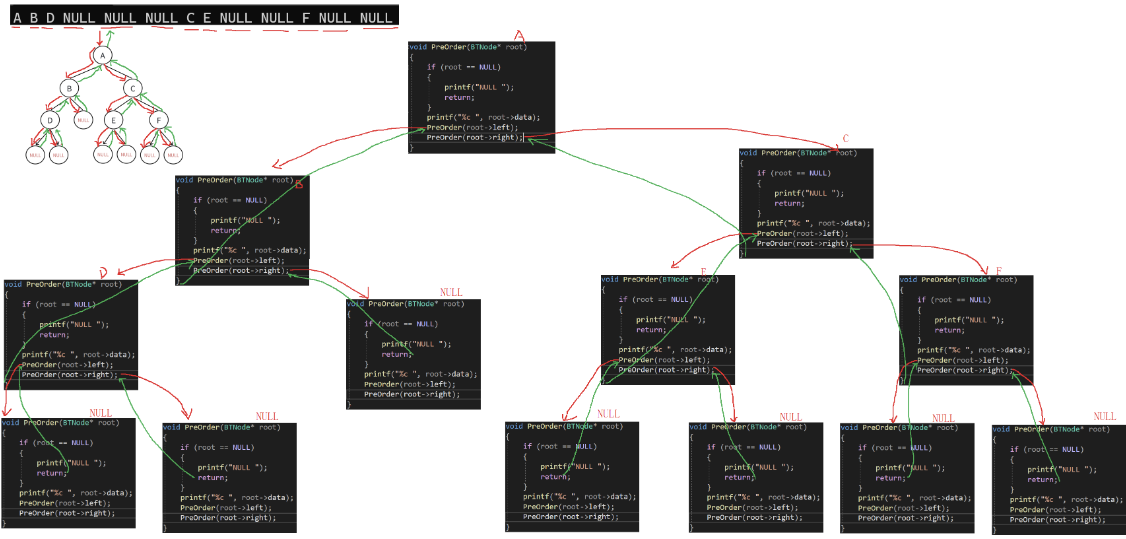
2.中序遍历
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}InOrder(root->left);printf("%c ", root->data);InOrder(root->right);
}结果正确:
![]()
3.后序遍历
//后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}PostOrder(root->left);PostOrder(root->right);printf("%c ", root->data);
}结果正确:
![]()
相关的函数递归栈帧图:
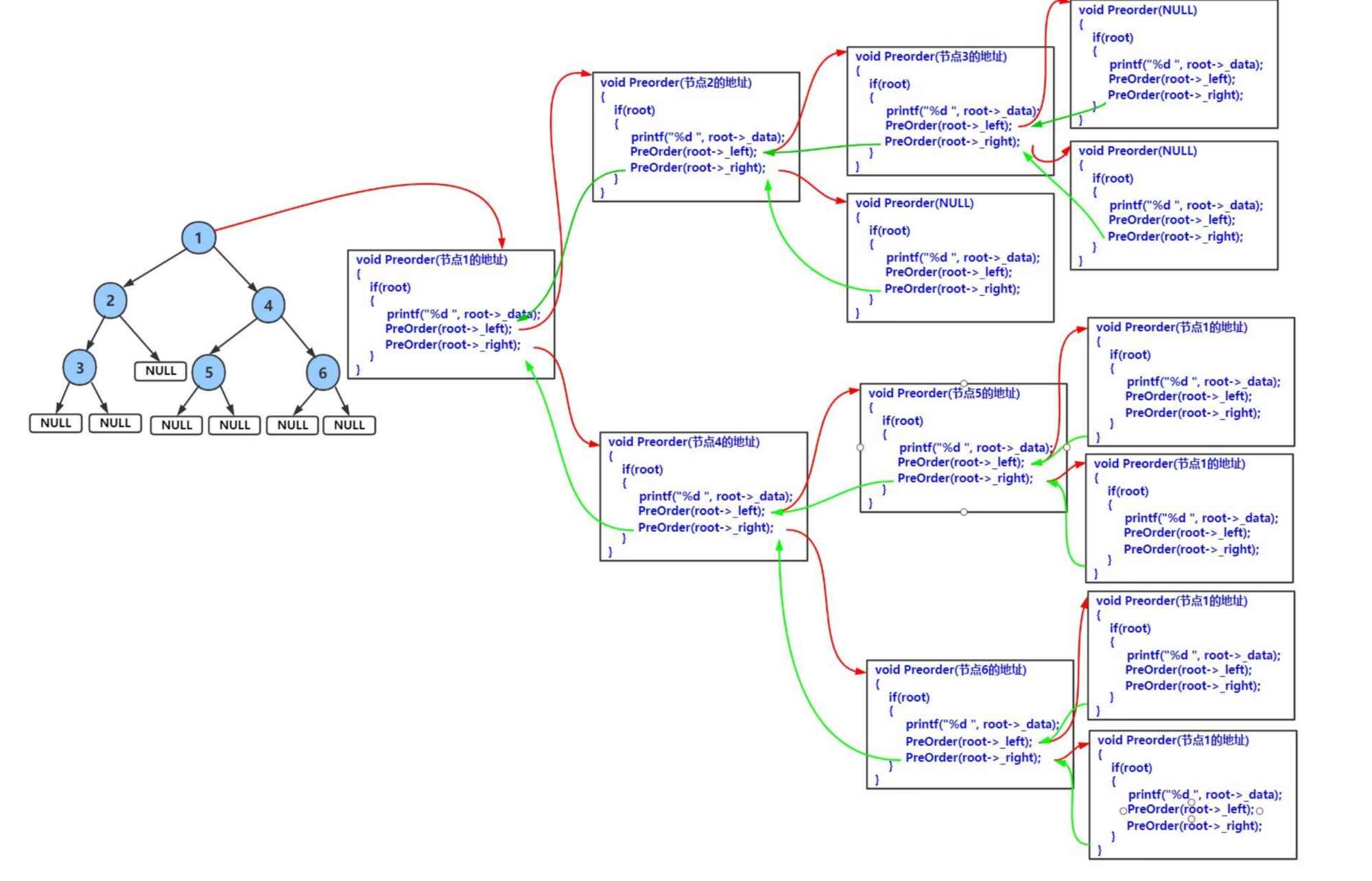
前序遍历结果:123456
中序遍历结果:321546
后序遍历结果:315641
4.2结点个数及高度计算等
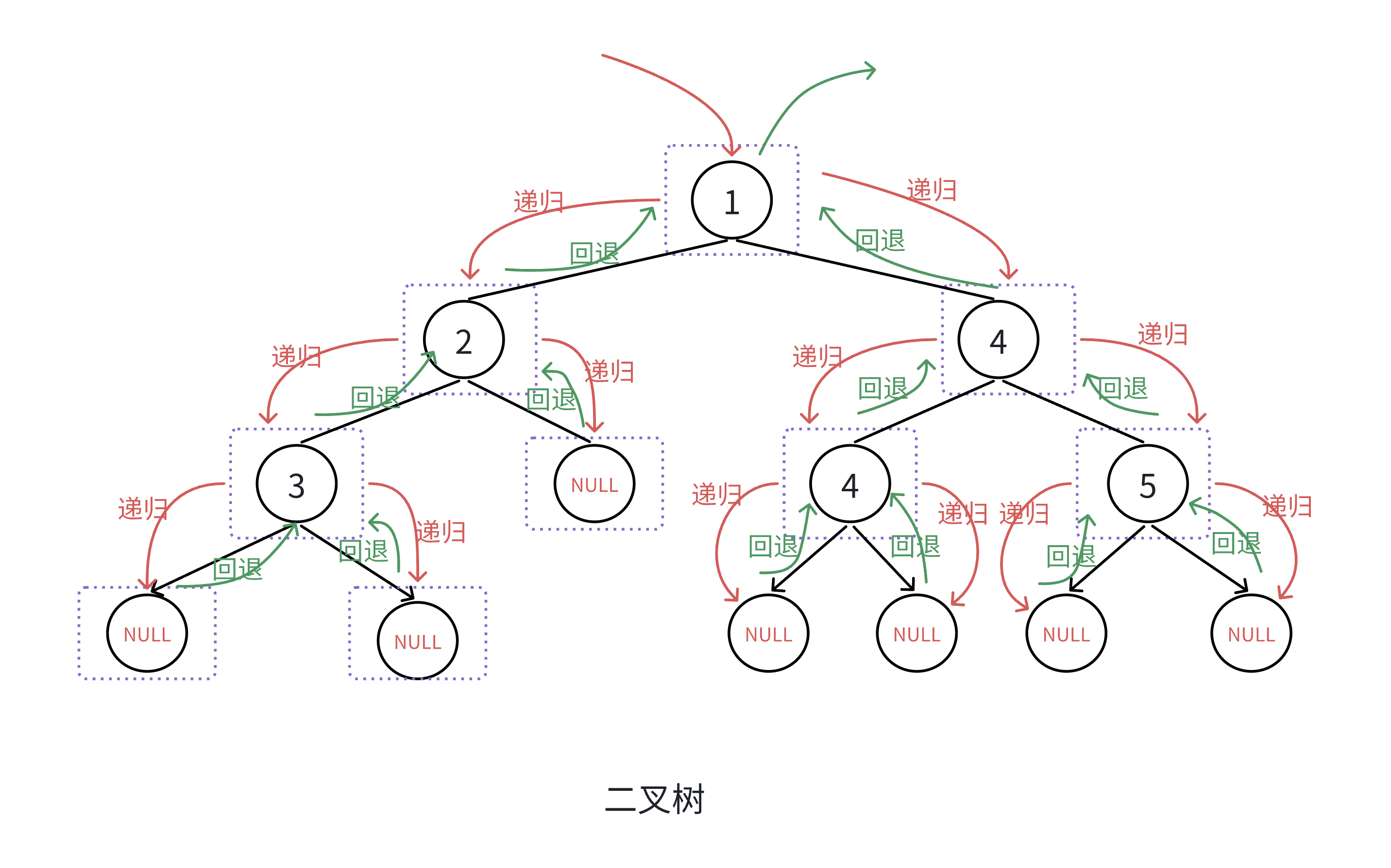
4.2.1二叉树结点个数
代码一:
//代码一
int size = 0;
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}size++;BinaryTreeSize(root->left);BinaryTreeSize(root->right);return size;
}但是测试结果并不满足我们的要求:
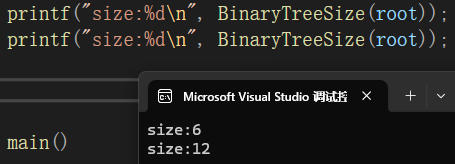
可见代码有创建全局变量,多次调用方法会出现累加情况的错误。
代码二:
//代码二:改造函数定义
void BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root,int* psize)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}(*psize)++;BinaryTreeSize(root->left, psize);BinaryTreeSize(root->right, psize);
}
结果正确:
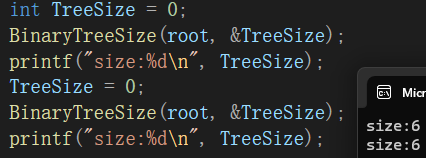
代码三:
//代码三
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}return 1 + BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right);
}符合要求,结果正确:
![]()
4.2.2求二叉树叶子结点个数
叶子结点个数 = 左子树叶子结点个数 + 右子树叶子结点个数
代码见下:
// ⼆叉树叶⼦结点个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}//判断是否为叶子结点if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL){return 1;}return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}![]()
4.2.3求二叉树第K层结点个数
// ⼆叉树第k层结点个数
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}if (k == 1){return 1;}return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k-1)+ BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k-1);
}4.2.4二叉树的深度
//⼆叉树的深度/⾼度
int BinaryTreeDepth(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}int leftDep = BinaryTreeDepth(root->left);int rightDep = BinaryTreeDepth(root->right);return 1 + (leftDep > rightDep ? leftDep : rightDep);
}4.2.5二叉树查找值为x的结点
// ⼆叉树查找值为x的结点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{if (root == NULL){return NULL;}if (root->data == x){return root;}BTNode* leftfind = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);if (leftfind){return leftfind;}BTNode* rightfind = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);if (rightfind){return rightfind;}return NULL;
}
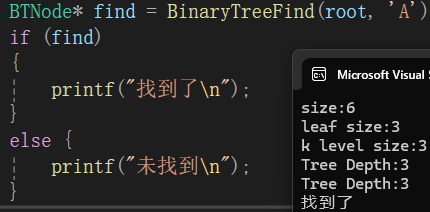
4.2.6二叉树的销毁
// ⼆叉树销毁
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode** root)
{if (*root == NULL){return;}BinaryTreeDestory(&((*root)->left));BinaryTreeDestory(&((*root)->right));free(*root);*root = NULL;
}4.3层序遍历
前中后序遍历属于深度优先遍历,层序遍历属于广度优先遍历。
利用数据结构--队列,将Queue.h和Queue.c引入,来实现层序遍历。
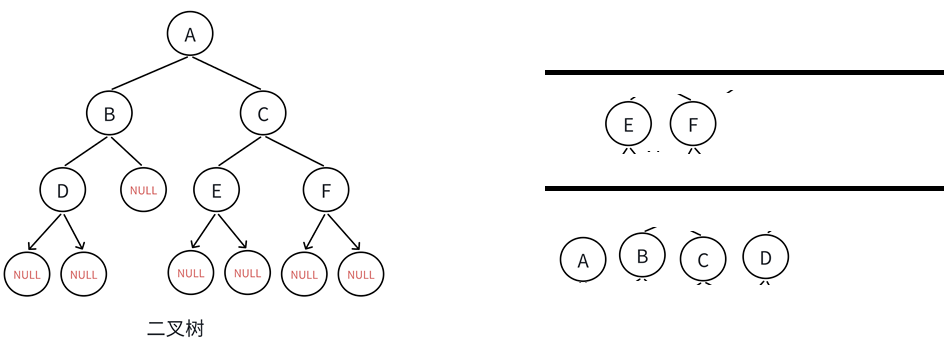
将根节点保存在队列中,使队列不为空,循环判断队列是否为空,不为空取对头,将对头结点不为空的孩子结点入队列。
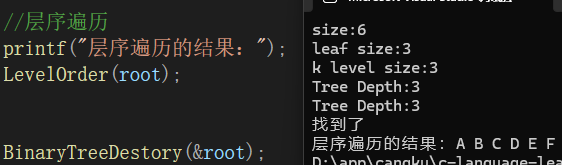
// 层序遍历
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);QueuePush(&q, root);while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){//取对头,打印对头BTNode* top = QueueFront(&q);printf("%c ", top->data);QueuePop(&q);//队头结点不为空的孩子结点入队列if (top->left)QueuePush(&q, top->left);if (top->right)QueuePush(&q, top->right);}QueueDestroy(&q);
}
4.2.8判断二叉树是否为完全二叉树
判断基础:最后一层结点个数不一定达到最大 ,其他每次结点个数都达到最大,结点从左到右依次排序。
思路:判断每层结点个数,叶子结点是否从左到右依次排列。
根结点先入队列,保证队列不为空,循环判断队列是否为空,不为空取对头,出对头,将对头结点的左右孩子都入队列。
非完全二叉树:
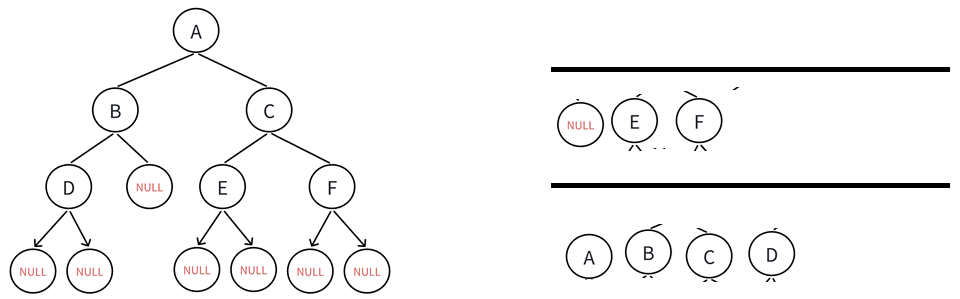
取到空的队头,跳出循环,此时队列中剩下了空结点和非空结点。
完全二叉树:
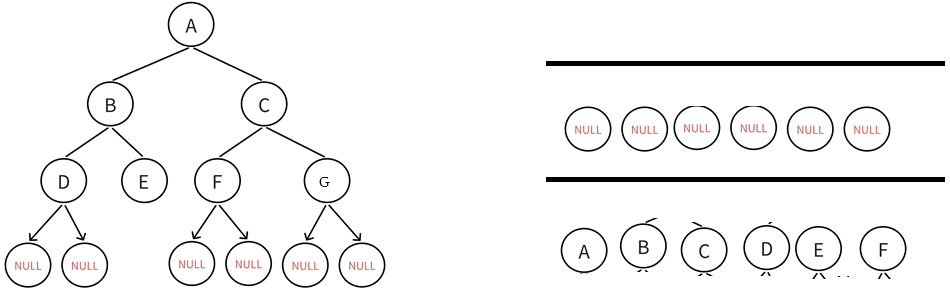
取到空的队头,此时队列中剩下了NULL,跳出循环。
代码:
// 判断⼆叉树是否是完全⼆叉树
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
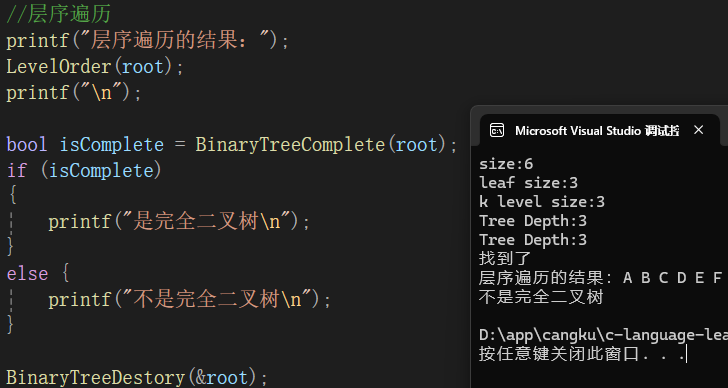
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);//头结点入队列QueuePush(&q, root);while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){//取队头,出队头BTNode* top = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);if (top == NULL){break;}//左右孩子入列QueuePush(&q, top->left);QueuePush(&q, top->right);}//队列不为空,继续取队列中的队头while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* top = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);if (top != NULL){//不是完全二叉树QueueDestroy(&q);return false;}}QueueDestroy(&q);return true;}测试结果:
本章完。
