初步认识 Spring Boot 自动装配
一、自动装配定义与核心目标
在传统的 Spring 应用开发中,配置往往繁琐且容易出错。开发者需要手动配置数据源、事务管理器、Web 容器等组件,导致大量重复性工作。而 Spring Boot 通过 自动装配 机制,将这些配置自动化,让开发者专注于业务逻辑,而非框架细节。
自动装配的本质:根据项目依赖、类路径和配置属性,动态决定是否加载特定的 Spring Bean 配置。这不仅大幅提升了开发效率,还确保了应用的可维护性和可扩展性。
1.1 什么是自动装配?
自动装配是Spring Boot框架的核心特性之一,它通过条件化配置和约定优于配置的原则,根据项目依赖、类路径、配置属性等动态决定是否启用某个组件或配置。开发者无需手动编写大量XML或Java配置,只需引入对应的Starter依赖,Spring Boot便会自动完成必要的配置。
1.2 自动装配的核心目标
| 目标 | 说明 | 实现方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 简化配置 | 减少重复性配置工作 | 默认配置、Starter依赖 |
| 条件化加载 | 仅在满足条件时启用配置 | @Conditional系列注解 |
| 模块化设计 | 功能集成与依赖管理 | Starter POMs |
| 可扩展性 | 允许自定义配置 | 自定义AutoConfiguration类 |
二、自动装配全景图:
📌 重点提示:下文将结合源码位置、关键类、核心方法,带你一步步走通自动装配的完整链路。建议配合 IDE 打开源码同步阅读。
🎯 流程图:Spring Boot 自动装配完整生命周期
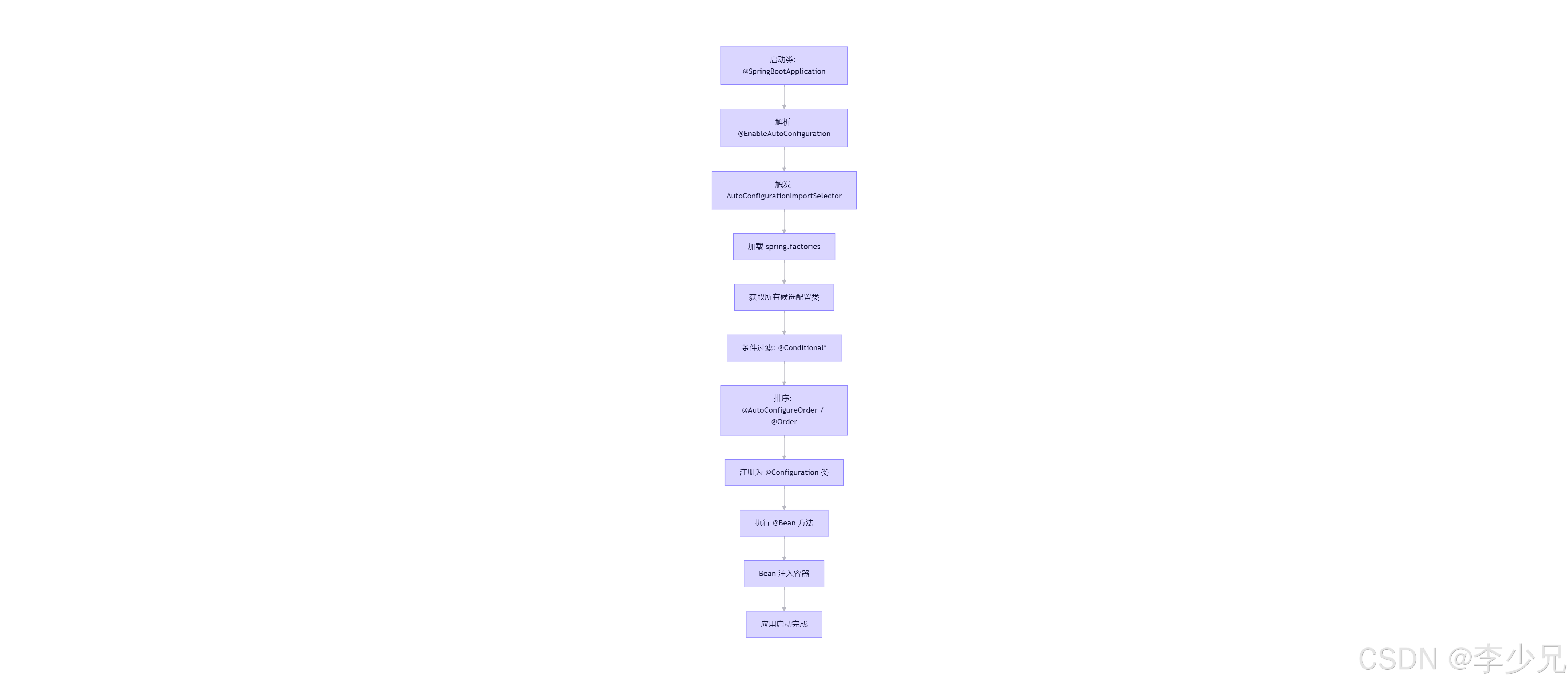
💡 建议保存此图:它是你阅读源码的导航地图。每一步我们都将在下文详细展开。
三、源码逐层剖析:手把手教你定位关键代码
▶ 第一步:入口 —— @SpringBootApplication 注解
源码位置:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration // ← 核心!
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class)
})
public @interface SpringBootApplication { ... }
- 关键点:
@EnableAutoConfiguration是自动装配的总开关。 - 下一步看哪里:进入
@EnableAutoConfiguration源码。
▶ 第二步:引擎启动 —— @EnableAutoConfiguration
源码位置:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage // ← 扫描主类所在包
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) // ← 自动装配核心处理器
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
}
- 关键点:
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)是自动装配的“发动机”。 - 下一步看哪里:深入
AutoConfigurationImportSelector类。
▶ 第三步:核心处理器 —— AutoConfigurationImportSelector
源码位置:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector
1. 核心方法:selectImports()
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {return NO_IMPORTS;}AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
2. 关键方法:getAutoConfigurationEntry()
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {return EMPTY_ENTRY;}AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); // ← 加载候选配置configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations); // 去重Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes); // 获取排除项checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);configurations.removeAll(exclusions); // 移除排除项configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations); // ← 条件过滤(核心!)fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
3. 加载候选配置:getCandidateConfigurations()
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), // ← EnableAutoConfiguration.classgetBeanClassLoader());Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found...");return configurations;
}
- 关键点:
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()从所有META-INF/spring.factories文件中加载配置类。 - 下一步看哪里:查看
spring-boot-autoconfigure模块中的spring.factories文件。
▶ 第四步:配置源 —— spring.factories 文件
文件位置:spring-boot-autoconfigure-{version}.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
...(上百个自动配置类)
- 关键点:这是所有自动配置类的“注册表”,Spring Boot 启动时会读取并加载这些类。
- 调试技巧:在 IDE 中按
Ctrl+Shift+N(IntelliJ)搜索spring.factories,可查看所有模块的配置。
▶ 第五步:条件过滤 —— ConfigurationClassFilter
回到 getAutoConfigurationEntry() 中的这行:
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
源码位置:AutoConfigurationImportSelector#getConfigurationClassFilter()
private ConfigurationClassFilter getConfigurationClassFilter() {if (this.configurationClassFilter == null) {this.configurationClassFilter = new ConfigurationClassFilter(this.beanClassLoader);}return this.configurationClassFilter;
}
过滤器内部:filter() 方法
List<String> filter(List<String> classNames) {if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(classNames)) {return classNames;}List<String> allowed = new ArrayList<>(classNames.size());for (String className : classNames) {if (isAllowed(className)) { // ← 判断是否满足条件allowed.add(className);}}return allowed;
}
核心判断:isAllowed()
private boolean isAllowed(String className) {if (this.autoConfigurationMetadata == null) {return true;}String candidates = this.autoConfigurationMetadata.get(className, "ConditionalOnClass");if (candidates != null) {return matches(candidates); // ← 实际调用 Spring 的 Condition 接口}return true;
}
- 关键点:最终调用的是 Spring Framework 的
Condition接口实现,如OnClassCondition、OnBeanCondition等。 - 源码位置:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition包下。
▶ 第六步:条件判断 —— @ConditionalOnClass 等注解
以 DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration 为例:
源码位置:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass(DispatcherServlet.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@AutoConfigureAfter(ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.class)
public class DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration {// ...
}
条件注解处理器:OnClassCondition
源码位置:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition
@Override
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader();ConditionMessage matchMessage = ConditionMessage.empty();List<String> onClasses = getCandidates(metadata, ConditionalOnClass.class);if (onClasses != null) {List<String> missing = filter(onClasses, ClassNameFilter.MISSING, classLoader);if (!missing.isEmpty()) {return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnClass.class).didNotFind("required class", "required classes").items(Style.QUOTE, missing));}matchMessage = matchMessage.andCondition(ConditionalOnClass.class).found("required class", "required classes").items(Style.QUOTE, filter(onClasses, ClassNameFilter.PRESENT, classLoader));}return ConditionOutcome.match(matchMessage);
}
- 关键逻辑:检查类路径中是否存在指定类,不存在则跳过该配置。
- 调试技巧:在
getMatchOutcome方法中打断点,可观察具体哪些类导致配置被过滤。
▶ 第七步:注册与执行 —— ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
经过过滤的配置类会被注册为 @Configuration 类,由 Spring 的 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 处理。
源码位置:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
- 它会解析
@Bean、@Import、@ComponentScan等注解。 - 最终将 Bean 定义注册到
BeanDefinitionRegistry中。
▶ 第八步:Bean 初始化 —— AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()
在 refresh() 方法中:
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
此时,自动配置类中定义的 @Bean 方法会被调用,Bean 实例被创建并注入容器。
四、条件注解大全:自动装配的“智能开关”
Spring Boot 提供了丰富的条件注解,让配置只在特定环境下生效:
| 注解 | 作用 | 源码位置 |
|---|---|---|
@ConditionalOnClass | 类路径存在指定类时生效 | OnClassCondition |
@ConditionalOnMissingClass | 类路径不存在指定类时生效 | OnClassCondition |
@ConditionalOnBean | 容器中存在指定 Bean 时生效 | OnBeanCondition |
@ConditionalOnMissingBean | 容器中不存在指定 Bean 时生效 | OnBeanCondition |
@ConditionalOnProperty | 配置文件中属性满足条件时生效 | OnPropertyCondition |
@ConditionalOnWebApplication | Web 应用环境下生效 | OnWebApplicationCondition |
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication | 非 Web 应用环境下生效 | OnWebApplicationCondition |
@ConditionalOnExpression | SpEL 表达式为 true 时生效 | SpringBootCondition |
@ConditionalOnResource | 指定资源存在时生效 | OnResourceCondition |
@ConditionalOnJndi | JNDI 存在时生效 | OnJndiCondition |
💡 最佳实践:自定义自动配置时,务必使用条件注解,避免冲突。
五、高级调试技巧:如何“看见”自动装配?
1. 启用调试日志
在 application.properties 中添加:
debug=true
启动时将输出:
============================
CONDITIONS EVALUATION REPORT
============================Positive matches:
-----------------DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration matched:- @ConditionalOnClass found required class 'org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet' (OnClassCondition)- @ConditionalOnWebApplication (required) found 'session' scope (OnWebApplicationCondition)Negative matches:
-----------------DataSourceAutoConfiguration:Did not match:- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required class 'javax.sql.DataSource' (OnClassCondition)
2. 查看自动配置报告
访问 Actuator 端点(需添加 spring-boot-starter-actuator):
GET /actuator/conditions
返回 JSON 格式的详细条件评估报告。
3. 在 IDE 中调试源码
- 在
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.selectImports()打断点,观察加载了哪些配置类。 - 在
OnClassCondition.getMatchOutcome()打断点,观察条件判断过程。 - 在
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.processConfigBeanDefinitions()打断点,观察配置类解析过程。
六、自定义 Starter 实战:从零构建一个企业级组件
场景:构建一个“企业消息推送” Starter
步骤 1:创建自动配置类
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(MessageService.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MessageProperties.class)
public class MessageAutoConfiguration {@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic MessageService messageService(MessageProperties properties) {return new DefaultMessageService(properties.getEndpoint(), properties.getApiKey());}@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic MessageTemplate messageTemplate(MessageService messageService) {return new MessageTemplate(messageService);}
}
步骤 2:创建配置属性类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "company.message")
public class MessageProperties {private String endpoint = "https://api.company.com/messages";private String apiKey;// getters & setters
}
步骤 3:创建 spring.factories
在 src/main/resources/META-INF/spring.factories:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.company.message.autoconfigure.MessageAutoConfiguration
步骤 4:创建 Starter POM
<project><groupId>com.company</groupId><artifactId>company-message-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId><optional>true</optional></dependency></dependencies>
</project>
步骤 5:用户使用
<dependency><groupId>com.company</groupId><artifactId>company-message-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
company.message.api-key=YOUR_API_KEY
@RestController
public class DemoController {@Autowiredprivate MessageTemplate messageTemplate;@PostMapping("/send")public void send(@RequestBody Message message) {messageTemplate.send(message);}
}
七、性能优化:如何加速自动装配?
1. 排除不必要的自动配置
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class,SecurityAutoConfiguration.class
})
或在 application.properties 中:
spring.autoconfigure.exclude=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityAutoConfiguration
2. 使用 @AutoConfigureBefore / @AutoConfigureAfter 控制顺序
避免循环依赖和重复初始化。
3. 启用懒加载
spring.main.lazy-initialization=true
4. 使用 Spring Boot 2.4+ 的自动配置索引(提升启动速度)
在 spring.factories 同级目录创建 spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties:
# 提前声明条件,避免运行时反射
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.ConditionalOnClass=org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
八、常见问题与解决方案
❓ 问题1:自动配置没有生效?
排查步骤:
- 检查
spring.factories是否包含该配置类。 - 检查条件注解是否满足(如类路径、Bean、属性)。
- 启用
debug=true查看条件评估报告。 - 检查是否被
exclude排除。
❓ 问题2:Bean 冲突?
解决方案:
- 使用
@ConditionalOnMissingBean确保用户自定义优先。 - 使用
@Primary或@Qualifier指定首选 Bean。
❓ 问题3:启动慢?
优化方案:
- 排除不需要的自动配置。
- 启用懒加载。
- 使用自动配置索引。
九、总结:
Spring Boot 自动装配的成功,源于三大设计哲学:
- 约定优于配置:提供合理的默认值,减少开发者决策负担。
- 条件化智能装配:仅在必要时加载组件,避免资源浪费。
- 模块化与可扩展:通过 Starter 机制,实现功能的即插即用。
“好的框架,应该像空气一样——你感觉不到它的存在,但它无处不在。”
掌握自动装配,你不仅是在学习一个技术特性,更是在理解现代框架设计的精髓。
附录:源码阅读路线图
| 步骤 | 关键类/方法 | 源码位置 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | @SpringBootApplication | spring-boot-autoconfigure |
| 2 | @EnableAutoConfiguration | spring-boot-autoconfigure |
| 3 | AutoConfigurationImportSelector.selectImports() | spring-boot-autoconfigure |
| 4 | SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames() | spring-core |
| 5 | ConfigurationClassFilter.filter() | spring-boot-autoconfigure |
| 6 | OnClassCondition.getMatchOutcome() | spring-boot-autoconfigure |
| 7 | ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.processConfigBeanDefinitions() | spring-context |
| 8 | AbstractApplicationContext.refresh() | spring-context |
