【Nginx开荒攻略】Nginx配置文件结构:从全局配置到虚拟主机的完整指南
目录
引言
1 Nginx配置文件结构概述
1.1 配置文件层次结构
1.2 配置文件基本语法规则
1.3 配置文件作用域
2 主配置文件nginx.conf详解
2.1 nginx.conf完整结构
2.2 Main全局块详解
2.2.1 用户和进程配置
2.2.2 日志和PID配置
2.2.3 性能优化配置
2.3 Events事件块详解
2.4 HTTP块详解
2.4.1 HTTP全局块配置
2.4.2 Server块配置
2.4.3 Location块配置
3 include指令与配置文件组织
3.1 include指令详解
3.1.1 include语法规则
3.1.2 include指令使用场景
3.2 配置文件组织实践建议
3.2.1 按功能模块组织
3.2.2 按环境组织
3.2.3 按应用组织
3.3 配置文件管理实践建议
3.3.1 配置文件命名规范
3.3.2 配置文件管理流程
3.3.3 配置文件安全建议
4 配置文件语法规则
4.1 基本语法规则
4.1.1 指令语法
4.1.2 变量使用
4.1.3 正则表达式
4.2 配置指令详解
4.2.1 全局指令
4.2.2 事件指令
4.2.3 HTTP指令
4.2.4 Server指令
4.2.5 Location指令
4.3 高级配置技巧
4.3.1 条件判断
4.3.2 URL重写
4.3.3 负载均衡配置
5 配置文件测试与优化
5.1 配置文件测试
5.1.1 语法检查
5.1.2 功能测试
5.2 配置优化技巧
5.2.1 性能优化
5.2.2 安全优化
6 总结
引言
Nginx作为当今最流行的Web服务器和反向代理服务器之一,其强大的功能和卓越的性能离不开其灵活而强大的配置系统。Nginx的配置文件结构清晰、层次分明,通过合理的配置文件组织和管理,可以实现复杂的服务器功能需求。
1 Nginx配置文件结构概述
Nginx的配置文件采用层次化的结构设计,通过不同的配置块来组织和管理各种配置指令。这种结构设计使得配置文件既简洁又功能强大,能够满足各种复杂的服务器配置需求。
1.1 配置文件层次结构
- Nginx的配置文件结构从上到下可以分为以下几个主要层次:
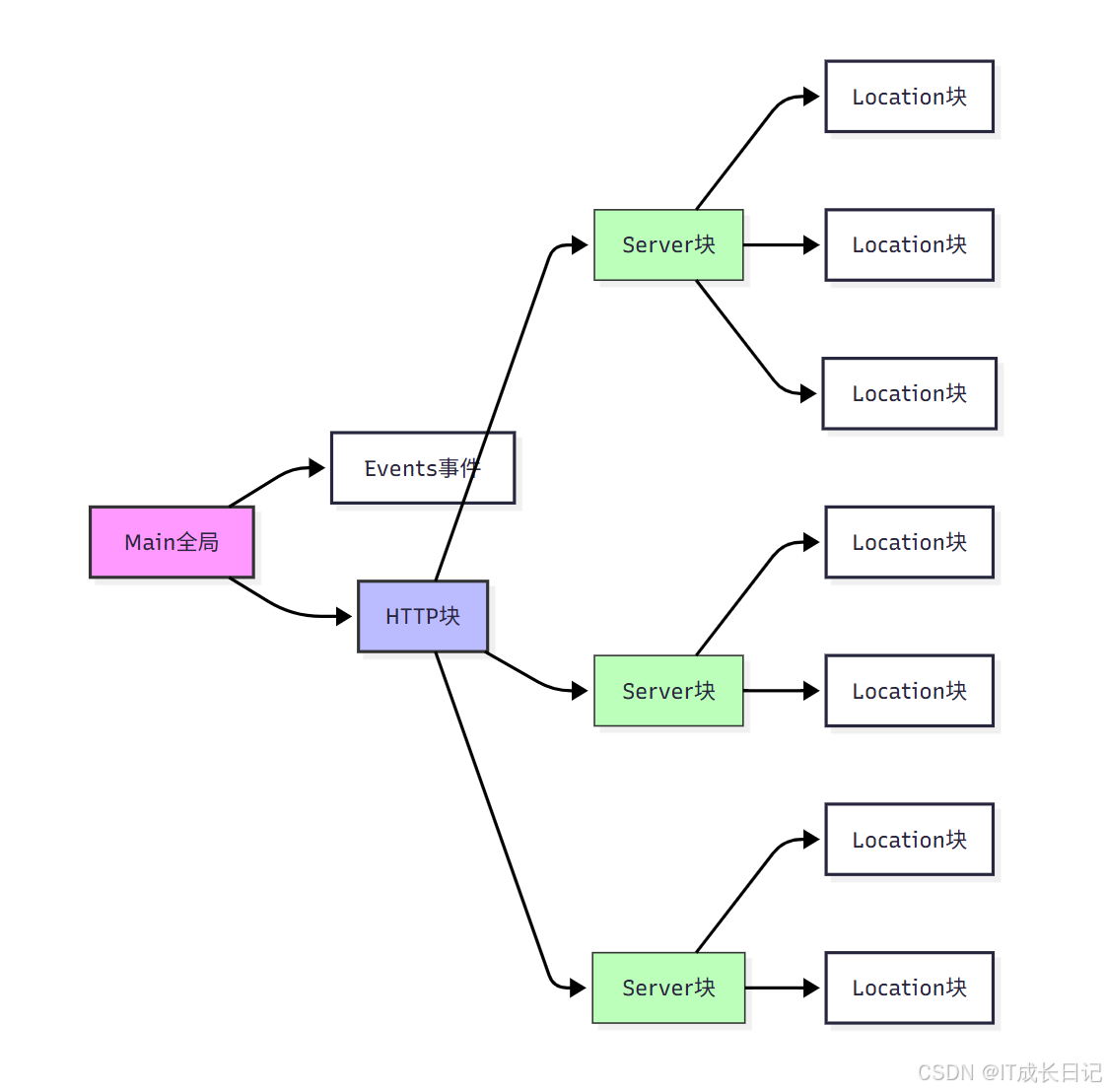
- Main全局块:位于配置文件的最顶部,包含影响Nginx全局运行的配置指令
- Events事件块:配置Nginx服务器与用户的网络连接相关参数
- HTTP块:包含HTTP服务器的主要配置,可以包含多个Server块
- Server块:定义虚拟主机的配置,一个HTTP块中可以有多个Server块
- Location块:配置请求的路由规则和处理方式,每个Server块中可以有多个Location块
1.2 配置文件基本语法规则
Nginx配置文件遵循以下语法规则:
- 指令分类:配置指令分为简单指令和指令块两种类型
- 指令格式:指令名称和参数之间用空格分隔,每条指令以分号(;)结尾
- 指令块:指令块使用大括号({})将多条指令组织在一起
- 注释:使用#符号添加注释,提高配置文件的可读性
- 变量:使用$符号引用变量
- 文件包含:使用include指令引入其他配置文件
1.3 配置文件作用域
Nginx配置指令的作用域遵循"就近原则",具体表现为:
- 继承关系:子配置块继承父配置块的设置
- 覆盖原则:在子配置块中重新定义相同指令会覆盖父配置块的设置
- 优先级:当同一指令在多个层级中出现时,以最低层级的配置为准
2 主配置文件nginx.conf详解
2.1 nginx.conf完整结构
# Main全局块
user nginx nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;# Events事件块
events {worker_connections 1024;use epoll;multi_accept on;
}# HTTP块
http {# HTTP全局块include /etc/nginx/mime.types;default_type application/octet-stream;log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;sendfile on;tcp_nopush on;tcp_nodelay on;keepalive_timeout 65;types_hash_max_size 2048;gzip on;gzip_disable "msie6";include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;# Server块server {listen 80;server_name example.com;root /var/www/html;index index.html index.htm;# Location块location / {try_files $uri $uri/ =404;}location /images/ {alias /var/www/images/;}error_page 404 /404.html;error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;location = /50x.html {root /usr/share/nginx/html;}}# 更多Server块...
}2.2 Main全局块详解
Main全局块是nginx.conf的最顶层配置,包含影响Nginx全局运行的指令。这些指令通常在整个配置文件中只出现一次。
2.2.1 用户和进程配置
# 指定运行Nginx worker进程的用户和用户组
user nginx nginx;# 指定worker进程数量,auto表示自动检测CPU核心数
worker_processes auto;# 设置worker进程的CPU亲和性,将进程绑定到特定CPU核心
worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000;# 设置worker进程的优先级,值越小优先级越高
worker_priority -10;# 设置worker进程可以打开的最大文件句柄数
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
- user指令:指定运行Nginx worker进程的用户和用户组,出于安全考虑,建议使用非root用户
- worker_processes指令:指定worker进程数量,通常设置为CPU核心数或auto
- worker_cpu_affinity指令:将worker进程绑定到特定的CPU核心,提高缓存命中率
- worker_priority指令:调整进程优先级,负值表示高优先级
- worker_rlimit_nofile指令:设置进程可以打开的最大文件数,防止文件描述符耗尽
2.2.2 日志和PID配置
# 设置错误日志路径和日志级别
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;# 设置主进程PID文件路径
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;# 设置worker进程异常终止后的core文件路径和大小
worker_rlimit_core 50M;
working_directory /tmp;
- error_log指令:指定错误日志文件路径和日志级别(debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg)
- pid指令:指定主进程PID文件路径,用于进程管理
- worker_rlimit_core指令:设置core文件大小,用于故障排查
- working_directory指令:设置worker进程的工作目录
2.2.3 性能优化配置
# 设置计时器精度,减少系统调用
timer_resolution 100ms;# 设置worker进程优雅退出超时时间
worker_shutdown_timeout 5s;# 设置daemon运行模式,off用于调试,on用于生产
daemon on;
- timer_resolution指令:调整计时器精度,较大的值减少系统调用
- worker_shutdown_timeout指令:设置优雅退出超时时间
- daemon指令:控制运行模式,调试时设为off,生产环境设为on
2.3 Events事件块详解
events {# 设置每个worker进程的最大连接数worker_connections 1024;# 使用epoll事件驱动模型(Linux)use epoll;# 允许一个worker进程同时接受多个连接multi_accept on;# 开启负载均衡互斥锁,防止多个worker进程争抢连接accept_mutex on;# 设置监听队列大小accept_mutex_delay 500ms;
}
- worker_connections指令:设置每个worker进程的最大连接数
- use指令:指定事件驱动模型(epoll|select|poll|kqueue等)
- multi_accept指令:允许同时接受多个新连接
- accept_mutex指令:控制连接分配的互斥锁
- accept_mutex_delay指令:设置互斥锁延迟时间
2.4 HTTP块详解
HTTP块是nginx.conf中最重要的部分,包含HTTP服务器的主要配置,可以包含多个Server块。
2.4.1 HTTP全局块配置
http {# 包含MIME类型定义文件include /etc/nginx/mime.types;default_type application/octet-stream;# 定义日志格式log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';# 设置访问日志access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;# 开启sendfile零拷贝传输sendfile on;tcp_nopush on;tcp_nodelay on;# 设置连接超时参数keepalive_timeout 65;keepalive_requests 100;# 设置MIME类型哈希表大小types_hash_max_size 2048;# 开启gzip压缩gzip on;gzip_vary on;gzip_min_length 1024;gzip_comp_level 6;gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;# 包含其他配置文件include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
}
- include指令:引入MIME类型定义文件
- default_type指令:设置默认MIME类型
- log_format指令:定义自定义日志格式
- access_log指令:设置访问日志路径和格式
- sendfile指令:开启零拷贝文件传输
- tcp_nopush指令:优化网络包发送
- tcp_nodelay指令:禁用Nagle算法
- keepalive_timeout指令:设置连接保持超时时间
- keepalive_requests指令:设置单连接最大请求数
- gzip指令:配置HTTP压缩
2.4.2 Server块配置
Server块定义虚拟主机的配置,每个Server块对应一个网站或服务。
server {# 监听端口和地址listen 80;listen [::]:80;# 服务器名称server_name example.com www.example.com;# 设置字符集charset utf-8;# 设置根目录root /var/www/html;# 设置默认首页index index.html index.htm;# 设置访问日志access_log /var/log/nginx/example.com.access.log main;# 设置错误页面error_page 404 /404.html;error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;# 配置location块location / {try_files $uri $uri/ =404;}location /images/ {alias /var/www/images/;expires 30d;add_header Cache-Control "public, no-transform";}location /api/ {proxy_pass http://backend_servers;proxy_set_header Host $host;proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;}# 配置SSLlisten 443 ssl http2;ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/example.com.crt;ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/example.com.key;ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;# 命名location@error_handler {return 503;}
}
- listen指令:配置监听端口和地址
- server_name指令:配置虚拟主机域名
- charset指令:设置字符集
- root指令:设置网站根目录
- index指令:设置默认首页文件
- access_log指令:设置访问日志
- error_page指令:配置错误页面
- location指令:配置URL路由规则
2.4.3 Location块配置
Location块定义具体的URL处理规则,是Nginx配置中最灵活的部分。
# 普通前缀匹配
location / {try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}# 精确匹配
location = /login {proxy_pass http://auth_server;
}# 正则匹配(区分大小写)
location ~ \.php$ {fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;fastcgi_index index.php;fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;include fastcgi_params;
}# 正则匹配(不区分大小写)
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|css|js)$ {expires 30d;add_header Cache-Control "public, no-transform";
}# 抢占式前缀匹配
location ^~ /static/ {alias /var/www/static/;
}# 命名location
location @error_handler {return 503;
}# 条件判断
location /admin {if ($http_user_agent ~* MSIE) {return 403;}proxy_pass http://admin_server;
}
- 普通前缀匹配:匹配以指定前缀开头的URL
- 精确匹配:完全匹配指定URL
- 正则匹配:使用正则表达式匹配URL
- 抢占式前缀匹配:匹配到后立即处理,不再检查正则
- 命名location:用于内部重定向
- 条件判断:使用if指令进行条件判断
3 include指令与配置文件组织
3.1 include指令详解
include指令是Nginx配置文件管理的重要工具,它允许将复杂的配置拆分成多个文件,提高配置的可维护性和可读性。
3.1.1 include语法规则
# 基本语法
include path;# 支持的路径类型
include /etc/nginx/mime.types; # 绝对路径
include conf.d/*.conf; # 相对路径,支持通配符
include sites-enabled/*; # 包含目录下所有文件语法说明:
- path参数:可以是绝对路径或相对路径,支持通配符
- 相对路径:以nginx.conf所在目录为基准
- 通配符:支持*匹配多个文件,?匹配单个字符
3.1.2 include指令使用场景
- MIME类型定义
# 主配置文件
http {include /etc/nginx/mime.types;default_type application/octet-stream;
}- 虚拟主机配置
# 主配置文件
http {include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
}# 虚拟主机配置文件(/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/example.com)
server {listen 80;server_name example.com;root /var/www/html;index index.html;location / {try_files $uri $uri/ =404;}
}- 负载均衡配置
# 主配置文件
http {include /etc/nginx/upstreams/*.conf;
}# 负载均衡配置文件(/etc/nginx/upstreams/backend.conf)
upstream backend_servers {server 192.168.1.101:8080 weight=3;server 192.168.1.102:8080 weight=1;server 192.168.1.103:8080 weight=2;
}- 日志格式定义
# 主配置文件
http {include /etc/nginx/log_formats/*.conf;
}# 日志格式配置文件(/etc/nginx/log_formats/main.conf)
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';3.2 配置文件组织实践建议
3.2.1 按功能模块组织
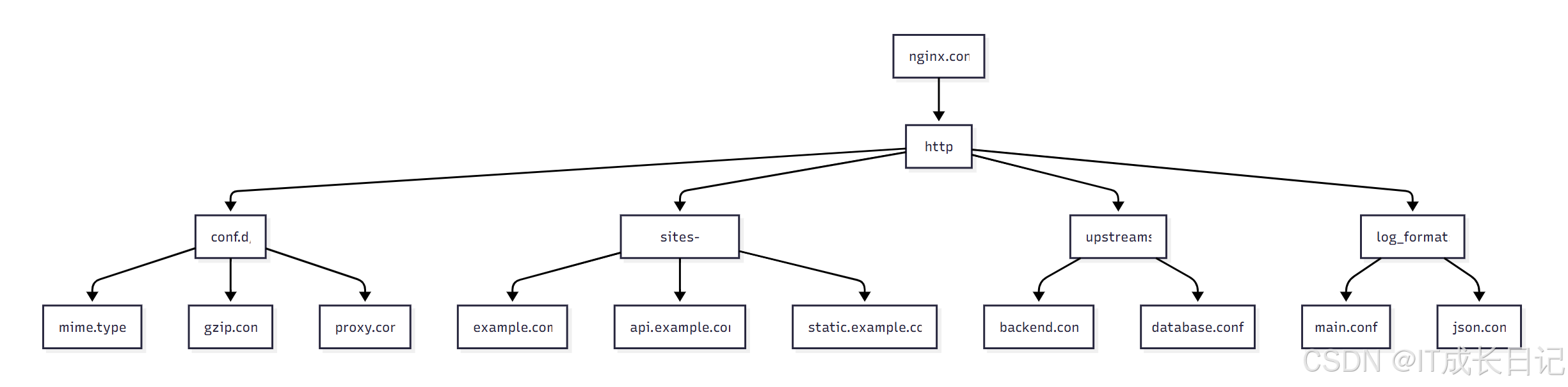
- 目录结构说明:
/etc/nginx/
├── nginx.conf # 主配置文件
├── conf.d/ # 通用配置模块
│ ├── mime.types # MIME类型定义
│ ├── gzip.conf # 压缩配置
│ └── proxy.conf # 代理配置
├── sites-available/ # 可用站点配置
│ ├── example.com # 主站配置
│ ├── api.example.com # API站点配置
│ └── static.example.com # 静态资源站点配置
├── sites-enabled/ # 启用站点配置(软链接)
├── upstreams/ # 负载均衡配置
│ ├── backend.conf # 后端服务器配置
│ └── database.conf # 数据库服务器配置
├── log_formats/ # 日志格式定义
│ ├── main.conf # 主日志格式
│ └── json.conf # JSON格式日志
└── ssl/ # SSL证书目录├── example.com.crt└── example.com.key3.2.2 按环境组织
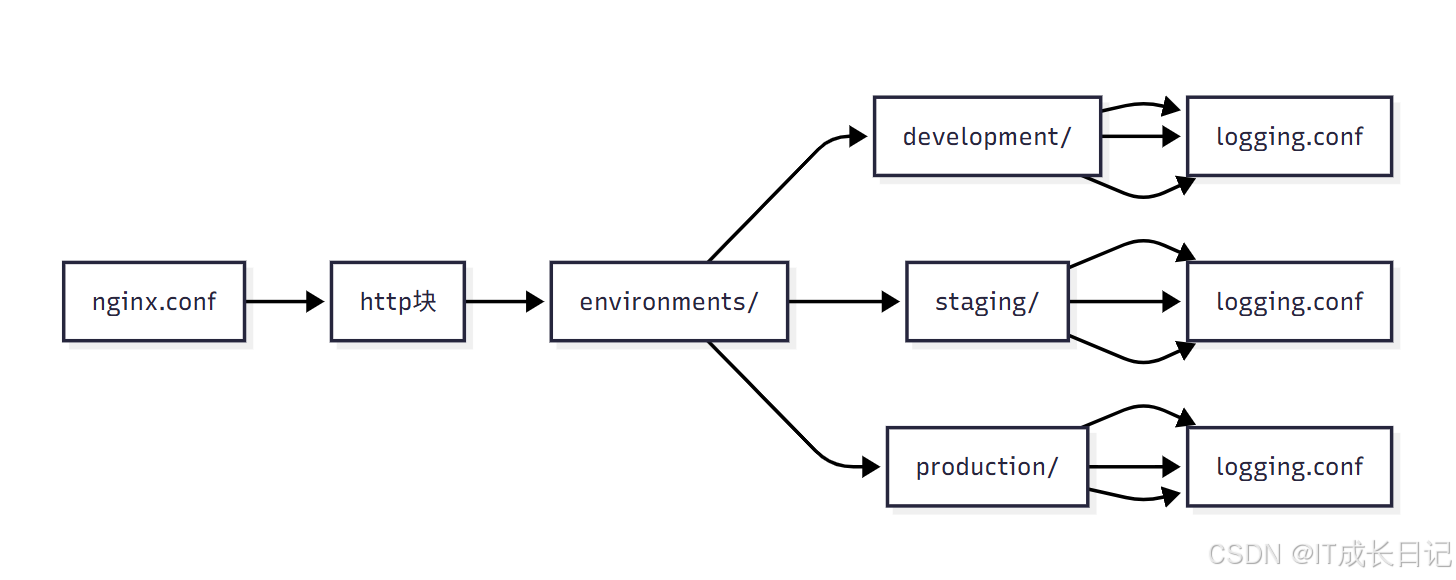
- 环境配置说明:
/etc/nginx/
├── nginx.conf # 主配置文件
└── environments/ # 环境配置目录├── development/ # 开发环境│ ├── servers.conf # 开发环境服务器配置│ ├── upstreams.conf # 开发环境负载均衡配置│ └── logging.conf # 开发环境日志配置├── staging/ # 预发布环境│ ├── servers.conf│ ├── upstreams.conf│ └── logging.conf└── production/ # 生产环境├── servers.conf├── upstreams.conf└── logging.conf3.2.3 按应用组织
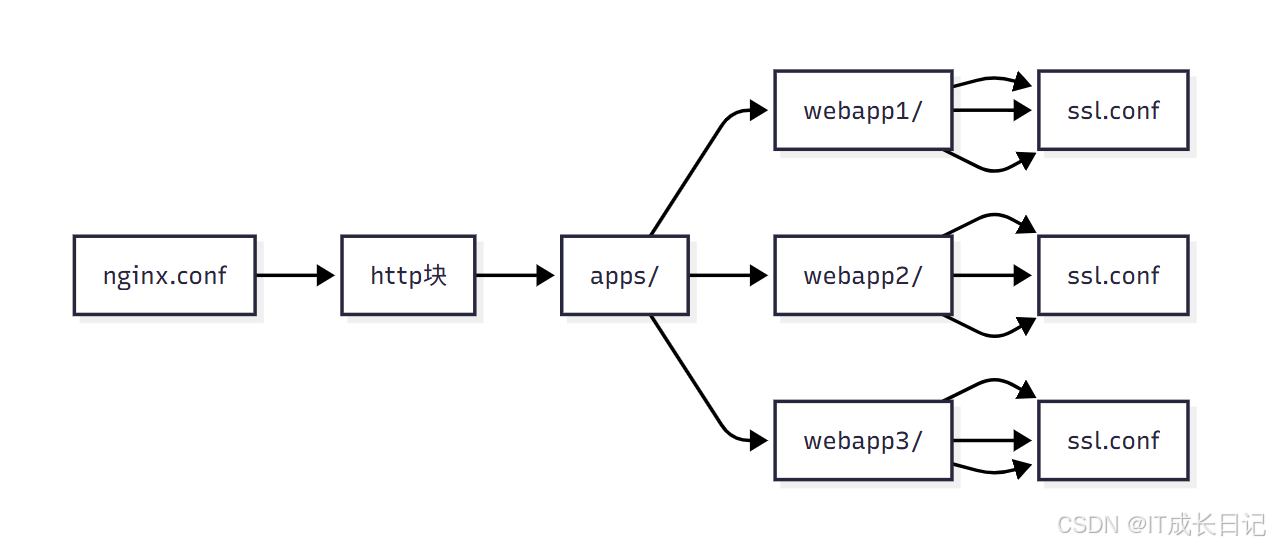
- 应用配置说明:
/etc/nginx/
├── nginx.conf # 主配置文件
└── apps/ # 应用配置目录├── webapp1/ # 应用1配置│ ├── nginx.conf # 应用1 Nginx配置│ ├── upstream.conf # 应用1负载均衡配置│ └── ssl.conf # 应用1 SSL配置├── webapp2/ # 应用2配置│ ├── nginx.conf│ ├── upstream.conf│ └── ssl.conf└── webapp3/ # 应用3配置├── nginx.conf├── upstream.conf└── ssl.conf3.3 配置文件管理实践建议
3.3.1 配置文件命名规范
# 主配置文件
nginx.conf# 通用配置模块
mime.types # MIME类型定义
gzip.conf # 压缩配置
proxy.conf # 代理配置
ssl.conf # SSL配置
security.conf # 安全配置# 虚拟主机配置
example.com.conf # 主站配置
api.example.com.conf # API站点配置
static.example.com.conf # 静态资源站点配置# 负载均衡配置
backend.conf # 后端服务器配置
database.conf # 数据库服务器配置# 日志配置
access.conf # 访问日志配置
error.conf # 错误日志配置# 环境配置
development.conf # 开发环境配置
staging.conf # 预发布环境配置
production.conf # 生产环境配置3.3.2 配置文件管理流程
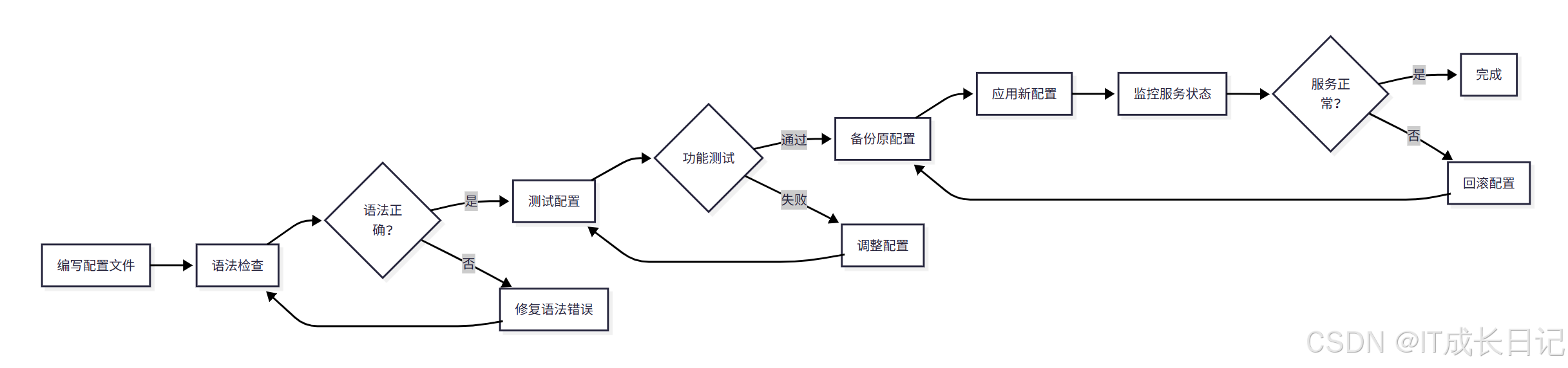
- 编写配置文件:按照规范编写新的配置文件
- 语法检查:使用nginx -t检查配置文件语法
- 功能测试:在测试环境中验证配置功能
- 备份原配置:备份当前生效的配置文件
- 应用新配置:使用nginx -s reload重新加载配置
- 监控服务状态:监控服务是否正常运行
- 回滚配置:如果出现问题,回滚到之前的配置
3.3.3 配置文件安全建议
- 文件权限:配置文件应该限制访问权限,通常设置为640
- 敏感信息:避免在配置文件中存储敏感信息,如密码、密钥等
- 配置备份:定期备份配置文件,防止意外丢失
- 版本控制:使用Git等版本控制工具管理配置文件变更
- 配置审查:定期审查配置文件,确保安全性和最佳实践
4 配置文件语法规则
4.1 基本语法规则
4.1.1 指令语法
# 简单指令格式
指令名 参数1 参数2 ... 参数N;# 指令块格式
指令名 {指令1;指令2;...指令N;
}语法规则说明:
- 指令分隔:每条指令必须以分号(;)结尾
- 指令块:使用大括号({})将多条指令组织在一起
- 指令嵌套:指令块可以嵌套,形成层次结构
- 注释:使用#符号添加注释,提高可读性
4.1.2 变量使用
# 内置变量
$remote_addr # 客户端IP地址
$remote_user # 客户端用户名
$time_local # 本地时间
$request # 完整请求行
$status # 响应状态码
$body_bytes_sent # 发送给客户端的字节数
$http_referer # HTTP Referer
$http_user_agent # HTTP User-Agent
$http_x_forwarded_for # X-Forwarded-For头# 自定义变量
set $my_var "hello world";
if ($http_user_agent ~* Chrome) {set $browser "chrome";
}变量使用规则:
- 变量引用:使用$符号引用变量
- 变量赋值:使用set指令赋值给变量
- 变量条件:在if条件中使用变量进行判断
- 变量作用域:变量只在当前配置块中有效
4.1.3 正则表达式
# 基本正则表达式
location ~ \.php$ { # 匹配.php结尾fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
}# 不区分大小写的正则表达式
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$ {expires 30d;
}# 复杂正则表达式
location ~ ^/user/(\d+)/profile$ {rewrite ^/user/(\d+)/profile$ /user.php?id=$1 last;
}正则表达式规则:
- 区分大小写:~表示区分大小写
- 不区分大小写:~*表示不区分大小写
- 正则语法:支持标准Perl正则表达式语法
- 捕获组:使用()捕获匹配的内容,可以在rewrite中使用
4.2 配置指令详解
4.2.1 全局指令
# 用户配置
user nginx nginx; # 指定运行用户和组# 进程配置
worker_processes 4; # worker进程数量
worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000; # CPU亲和性
worker_priority -10; # 进程优先级# 日志配置
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn; # 错误日志
pid /var/run/nginx.pid; # PID文件路径# 性能配置
timer_resolution 100ms; # 计时器精度
worker_shutdown_timeout 5s; # 优雅退出超时4.2.2 事件指令
events {worker_connections 1024; # 每个worker最大连接数use epoll; # 事件驱动模型multi_accept on; # 多连接接受accept_mutex on; # 连接互斥锁
}4.2.3 HTTP指令
http {# 基础配置include /etc/nginx/mime.types; # MIME类型default_type application/octet-stream; # 默认类型# 日志配置log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;# 性能配置sendfile on; # 零拷贝传输tcp_nopush on; # 优化网络包tcp_nodelay on; # 禁用Nagle算法keepalive_timeout 65; # 连接超时keepalive_requests 100; # 单连接最大请求数# 压缩配置gzip on; # 开启压缩gzip_vary on; # 添加Vary头gzip_min_length 1024; # 最小压缩大小gzip_comp_level 6; # 压缩级别gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json; # 压缩类型# 包含其他配置include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}4.2.4 Server指令
server {# 监听配置listen 80; # 监听80端口listen [::]:80; # 监听IPv6的80端口listen 443 ssl; # 监听443端口,启用SSLlisten [::]:443 ssl; # 监听IPv6的443端口,启用SSL# 服务器名称配置server_name example.com www.example.com; # 精确匹配server_name *.example.com; # 左侧通配server_name example.com.*; # 右侧通配server_name ~^www\.example\.com$; # 正则匹配# 基础配置charset utf-8; # 字符集root /var/www/html; # 根目录index index.html index.htm; # 默认首页# 日志配置access_log /var/log/nginx/example.com.access.log main;error_log /var/log/nginx/example.com.error.log warn;# SSL配置ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/example.com.crt;ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/example.com.key;ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;# 错误页面error_page 404 /404.html;error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;# 配置location块location / {try_files $uri $uri/ =404;}
}4.2.5 Location指令
# 普通前缀匹配
location / {try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}# 精确匹配
location = /login {proxy_pass http://auth_server;
}# 正则匹配(区分大小写)
location ~ \.php$ {fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;fastcgi_index index.php;fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;include fastcgi_params;
}# 正则匹配(不区分大小写)
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|css|js)$ {expires 30d;add_header Cache-Control "public, no-transform";
}# 抢占式前缀匹配
location ^~ /static/ {alias /var/www/static/;
}# 命名location
location @error_handler {return 503;
}4.3 高级配置技巧
4.3.1 条件判断
# 基于变量判断
if ($http_user_agent ~* MSIE) {return 403;
}# 基于文件存在判断
if (-f $request_filename) {break;
}# 基于目录存在判断
if (-d $request_filename) {rewrite ^/(.*?)/$ /$1 permanent;
}# 嵌套条件
if ($http_host ~* ^www\.(.+)$) {set $host_without_www $1;if ($scheme = http) {rewrite ^(.*)$ https://$host_without_www$1 permanent;}
}条件判断规则:
- 变量判断:直接使用变量名,非空即为真
- 文件判断:使用-f判断文件是否存在
- 目录判断:使用-d判断目录是否存在
- 权限判断:使用-r判断文件是否可读,-w判断文件是否可写
- 执行判断:使用-x判断文件是否可执行
4.3.2 URL重写
# 基本重写
rewrite ^/old-path/(.*)$ /new-path/$1 permanent;# 条件重写
if ($http_host ~* ^example\.com$) {rewrite ^(.*)$ https://www.example.com$1 permanent;
}# 带参数重写
rewrite ^/search/(.*)$ /search.php?q=$1 last;# 复杂重写规则
location / {rewrite ^/user/(\d+)$ /user.php?id=$1 last;rewrite ^/category/(\w+)$ /category.php?name=$1 last;
}# 重写标记
rewrite ^/product/(\d+)$ /product.php?id=$1 last; # 发起新请求
rewrite ^/product/(\d+)$ /product.php?id=$1 break; # 在当前location中处理
rewrite ^/product/(\d+)$ /new-product/$1 redirect; # 临时重定向
rewrite ^/product/(\d+)$ /new-product/$1 permanent; # 永久重定向重写规则说明:
- last标记:停止当前请求处理,发起新请求
- break标记:在当前location中处理,不再检查其他location
- redirect标记:返回302临时重定向
- permanent标记:返回301永久重定向
4.3.3 负载均衡配置
# 定义后端服务器池
upstream backend_servers {# 轮询策略(默认)server 192.168.1.101:8080;server 192.168.1.102:8080;server 192.168.1.103:8080;# 权重策略server 192.168.1.101:8080 weight=3;server 192.168.1.102:8080 weight=1;server 192.168.1.103:8080 weight=2;# IP哈希策略ip_hash;server 192.168.1.101:8080;server 192.168.1.102:8080;# 最少连接策略(第三方模块)least_conn;server 192.168.1.101:8080;server 192.168.1.102:8080;# 健康检查server 192.168.1.101:8080 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;server 192.168.1.102:8080 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;server 192.168.1.103:8080 backup; # 备份服务器# 保持长连接keepalive 32;
}# 使用负载均衡
server {listen 80;server_name example.com;location / {proxy_pass http://backend_servers;proxy_set_header Host $host;proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;# 超时设置proxy_connect_timeout 5s;proxy_read_timeout 30s;proxy_send_timeout 30s;# 失败重试proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;proxy_next_upstream_tries 2;proxy_next_upstream_timeout 10s;}
}负载均衡策略说明:
- 轮询策略:默认策略,按顺序分配请求
- 权重策略:根据服务器权重分配请求
- IP哈希策略:根据客户端IP分配固定服务器
- 最少连接策略:将请求分配到连接数最少的服务器
- 响应时间策略:将请求分配到响应时间最短的服务器
5 配置文件测试与优化
5.1 配置文件测试
5.1.1 语法检查
# 检查配置文件语法
nginx -t# 检查特定配置文件
nginx -t -c /path/to/nginx.conf# 详细输出
nginx -t -v5.1.2 功能测试
# 测试配置文件加载
nginx -T# 测试特定模块
nginx -V 2>&1 | grep -o -- '--with-\w*'# 测试配置文件包含
nginx -t -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf 2>&1 | grep -o 'included.*conf'5.2 配置优化技巧
5.2.1 性能优化
# 优化worker进程数量
worker_processes auto;# 优化连接数
events {worker_connections 65535;use epoll;multi_accept on;
}# 优化文件传输
http {sendfile on;tcp_nopush on;tcp_nodelay on;# 优化缓存open_file_cache max=65535 inactive=60s;open_file_cache_valid 80s;open_file_cache_min_uses 1;open_file_cache_errors on;# 优化压缩gzip on;gzip_comp_level 6;gzip_min_length 1000;gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/javascript;
}5.2.2 安全优化
# 限制请求方法
if ($request_method !~ ^(GET|POST|HEAD)$) {return 405;
}# 限制文件类型
location ~* \.(php|pl|py|jsp|asp|sh)$ {deny all;
}# 限制上传大小
client_max_body_size 1M;# 隐藏版本信息
server_tokens off;# 安全头配置
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
add_header Referrer-Policy "strict-origin-when-cross-origin" always;6 总结
Nginx配置文件是Web服务架构的重要组成部分,掌握Nginx配置的精髓对于构建高性能、高可用的Web服务至关重要。无论是初学者还是经验丰富的开发者,深入理解Nginx配置文件的工作原理和最佳实践,都将对提升Web服务性能和可靠性带来巨大的帮助,在实际工作中更好地应用和优化Nginx。
