Active Directory Basics

目录如下

Task1 Introduction 引言
图片版
Task2 Windows Domains Windows 域
图片版

文字版
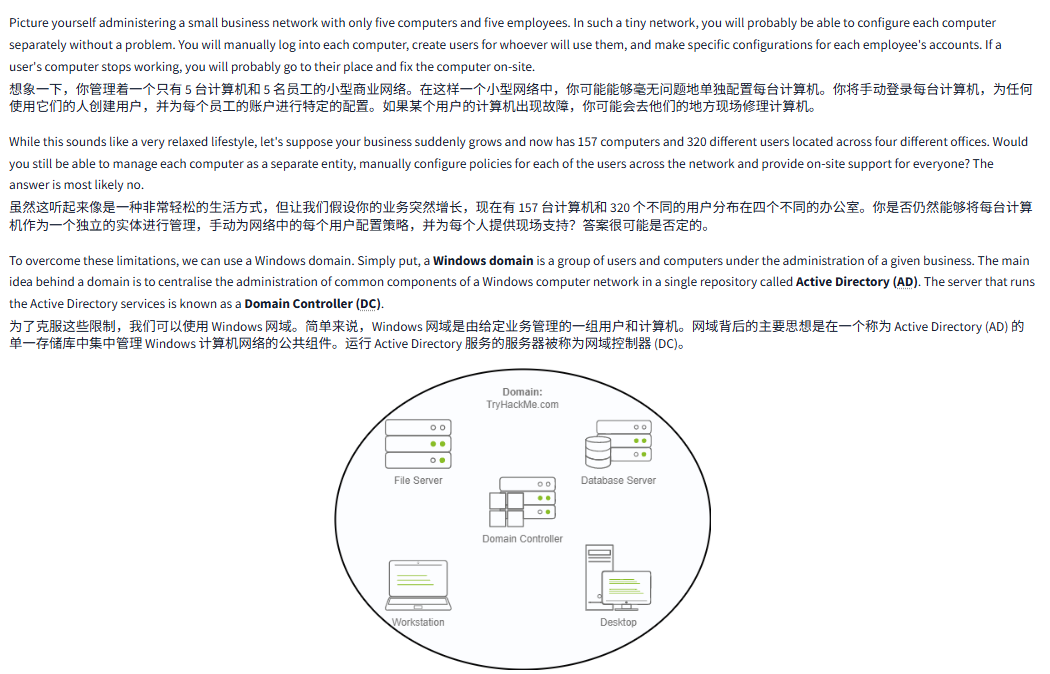
Picture yourself administering a small business network with only five computers and five employees. In such a tiny network, you will probably be able to configure each computer separately without a problem. You will manually log into each computer, create users for whoever will use them, and make specific configurations for each employee's accounts. If a user's computer stops working, you will probably go to their place and fix the computer on-site.
想象一下,你管理着一个只有 5 台计算机和 5 名员工的小型商业网络。在这样一个小型网络中,你可能能够毫无问题地单独配置每台计算机。你将手动登录每台计算机,为任何使用它们的人创建用户,并为每个员工的账户进行特定的配置。如果某个用户的计算机出现故障,你可能会去他们的地方现场修理计算机。
While this sounds like a very relaxed lifestyle, let's suppose your business suddenly grows and now has 157 computers and 320 different users located across four different offices. Would you still be able to manage each computer as a separate entity, manually configure policies for each of the users across the network and provide on-site support for everyone? The answer is most likely no.
虽然这听起来像是一种非常轻松的生活方式,但让我们假设你的业务突然增长,现在有 157 台计算机和 320 个不同的用户分布在四个不同的办公室。你是否仍然能够将每台计算机作为一个独立的实体进行管理,手动为网络中的每个用户配置策略,并为每个人提供现场支持?答案很可能是否定的。
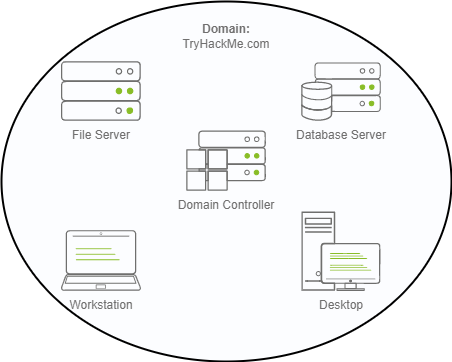
To overcome these limitations, we can use a Windows domain. Simply put, a Windows domain is a group of users and computers under the administration of a given business. The main idea behind a domain is to centralise the administration of common components of a Windows computer network in a single repository called Active Directory (AD). The server that runs the Active Directory services is known as a Domain Controller (DC).
为了克服这些限制,我们可以使用 Windows 网域。简单来说,Windows 网域是由给定业务管理的一组用户和计算机。网域背后的主要思想是在一个称为 Active Directory (AD) 的单一存储库中集中管理 Windows 计算机网络的公共组件。运行 Active Directory 服务的服务器被称为网域控制器 (DC)。
The main advantages of having a configured Windows domain are:
配置 Windows 域的主要优势包括:
- Centralised identity management: All users across the network can be configured from Active Directory with minimum effort.
集中式身份管理:网络中的所有用户都可以通过 Active Directory 进行配置,而且只需要最少的努力。 - Managing security policies: You can configure security policies directly from Active Directory and apply them to users and computers across the network as needed.
管理安全策略:您可以直接从 Active Directory 配置安全策略,并根据需要将其应用于网络中的用户和计算机。
A Real-World Example真实世界示例
If this sounds a bit confusing, chances are that you have already interacted with a Windows domain at some point in your school, university or work.
如果这听起来有点令人困惑,很可能你在学校、大学或工作中的某个时候已经与 Windows 域进行过交互。
In school/university networks, you will often be provided with a username and password that you can use on any of the computers available on campus. Your credentials are valid for all machines because whenever you input them on a machine, it will forward the authentication process back to the Active Directory, where your credentials will be checked. Thanks to Active Directory, your credentials don't need to exist in each machine and are available throughout the network.
在学校 / 大学网络中,你通常会获得一个用户名和密码,可以在校园中任何可用的计算机上使用。你的凭据对所有计算机都有效,因为每当你在计算机上输入凭据时,它都会将身份验证过程转发回 Active Directory, 在那里将检查你的凭据。多亏了 Active Directory, 你的凭据不需要存在于每台计算机上,而是可以在整个网络中使用。
Active Directory is also the component that allows your school/university to restrict you from accessing the control panel on your school/university machines. Policies will usually be deployed throughout the network so that you don't have administrative privileges over those computers.
Active Directory 也是一个组件,允许您的学校 / 大学限制您访问学校 / 大学机器上的控制面板。策略通常会部署在整个网络中,以确保您对这些计算机没有管理权限。
Welcome to THM Inc.欢迎来到 THM Inc.
During this task, we'll assume the role of the new IT admin at THM Inc. As our first task, we have been asked to review the current domain "THM.local" and do some additional configurations. You will have administrative credentials over a pre-configured Domain Controller (DC) to do the tasks.
在本任务中,我们将担任 THM 公司新 IT 管理员的角色。作为我们的第一个任务,我们被要求查看当前的域 “THM.local” 并进行一些额外的配置。您将通过预配置的网域控制器 (DC) 获得执行这些任务的管理凭证。
Be sure to click the Start Machine button below now, as you'll use the same machine for all tasks. This should open a machine in your browser.
请确保现在点击下面的 “开始机器” 按钮,因为你将使用同一台机器执行所有任务。这应该会在浏览器中打开一台机器。
Start Machine启动机
Should you prefer to connect to it via RDP, you can use the following credentials:
如果您更喜欢通过 RDP 连接,可以使用以下凭证:

| Username用户名 | Administrator管理员 |
| Password密码 | Password321密码 321 |
| IP (RDP)IP(RDP) | MACHINE_IP |
Note: When connecting via RDP, use THM\Administrator as the username to specify you want to log in using the user Administrator on the THM domain.
注意:通过 RDP 连接时,使用 THMAdministrator 作为用户名,指定您想要使用 THM 域中的用户 Administrator 登录。
Since we will be connecting to the target machine via RDP, this is also a good time to start the AttackBox (unless you are using your own machine).
由于我们将通过 RDP 连接到目标机器,这也是启动 AttackBox 的好时机 (除非你使用的是自己的机器)。
问题
答案
Task3 Active Directory
图片版




文字版
The core of any Windows Domain is the Active Directory Domain Service (AD DS). This service acts as a catalogue that holds the information of all of the "objects" that exist on your network. Amongst the many objects supported by AD, we have users, groups, machines, printers, shares and many others. Let's look at some of them:
任何 Windows 域的核心都是活动目录域服务 (AD DS)。该服务充当一个目录,存储网络上所有 “对象” 的信息。在 AD 支持的众多对象中,我们有用户、组、机器、打印机、共享和许多其他对象。让我们看看其中的一些:
Users用户
Users are one of the most common object types in Active Directory. Users are one of the objects known as security principals, meaning that they can be authenticated by the domain and can be assigned privileges over resources like files or printers. You could say that a security principal is an object that can act upon resources in the network.
用户是 Active Directory 中最常见的对象类型之一。用户是被称为安全主体的对象之一,这意味着他们可以通过域进行身份验证,并且可以被授予对文件或打印机等资源的权限。可以说,安全主体是一个可以对网络中的资源进行操作的对象。
Users can be used to represent two types of entities:
用户可以用来表示两种类型的实体:
- People: users will generally represent persons in your organisation that need to access the network, like employees.
人员:用户通常代表组织中需要访问网络的人员,例如员工。 - Services: you can also define users to be used by services like IIS or MSSQL. Every single service requires a user to run, but service users are different from regular users as they will only have the privileges needed to run their specific service.
服务:您还可以定义用户以供 IIS 或 MSSQL 等服务使用。每个单独的服务都需要一个用户来运行,但服务用户与普通用户不同,因为他们只拥有运行特定服务所需的权限。
Machines机器
Machines are another type of object within Active Directory; for every computer that joins the Active Directory domain, a machine object will be created. Machines are also considered "security principals" and are assigned an account just as any regular user. This account has somewhat limited rights within the domain itself.
计算机是 Active Directory 中的另一种对象类型;每台加入 Active Directory 域的计算机都将创建一个计算机对象。计算机也被视为 “安全主体”, 并像任何普通用户一样被分配一个帐户。这个帐户在域内的权限相当有限。
The machine accounts themselves are local administrators on the assigned computer, they are generally not supposed to be accessed by anyone except the computer itself, but as with any other account, if you have the password, you can use it to log in.
计算机账户本身是分配的计算机上的本地管理员,通常除了计算机本身外,其他人不应该访问它们,但与任何其他账户一样,如果你有密码,你可以使用它来登录。
Note: Machine Account passwords are automatically rotated out and are generally comprised of 120 random characters.
注意:机器帐户密码会自动轮换输出,通常由 120 个随机字符组成。
Identifying machine accounts is relatively easy. They follow a specific naming scheme. The machine account name is the computer's name followed by a dollar sign. For example, a machine named DC01 will have a machine account called DC01$.
识别机器账户相对容易。它们遵循特定的命名方案。机器账户名称是计算机的名称,后面跟着美元符号。例如,名为 DC01 的机器将有一个名为 DC01$ 的机器账户。
Security Groups安全组
If you are familiar with Windows, you probably know that you can define user groups to assign access rights to files or other resources to entire groups instead of single users. This allows for better manageability as you can add users to an existing group, and they will automatically inherit all of the group's privileges. Security groups are also considered security principals and, therefore, can have privileges over resources on the network.
如果你熟悉 Windows, 你可能知道可以定义用户组,将文件或其他资源的访问权限分配给整个组,而不是单个用户。这样可以提高可管理性,因为你可以向现有组添加用户,他们将自动继承该组的所有权限。安全组也被视为安全主体,因此可以对网络上的资源拥有权限。
Groups can have both users and machines as members. If needed, groups can include other groups as well.
组可以包含用户和机器作为成员。如果需要,组还可以包含其他组。
Several groups are created by default in a domain that can be used to grant specific privileges to users. As an example, here are some of the most important groups in a domain:
默认情况下,在一个可用于向用户授予特定权限的域中创建了几个组。例如,以下是一个域中一些最重要的组:
| Security Group安全组 | Description描述 |
| Domain Admins域名管理 | Users of this group have administrative privileges over the entire domain. By default, they can administer any computer on the domain, including the DCs. |
| Server Operators服务器操作员 | Users in this group can administer Domain Controllers. They cannot change any administrative group memberships. |
| Backup Operators备份操作员 | Users in this group are allowed to access any file, ignoring their permissions. They are used to perform backups of data on computers. |
| Account Operators账户操作员 | Users in this group can create or modify other accounts in the domain. |
| Domain Users域用户 | Includes all existing user accounts in the domain. |
| Domain Computers域计算机 | Includes all existing computers in the domain. |
| Domain Controllers域控制器 | Includes all existing DCs on the domain. |
You can obtain the complete list of default security groups from the Microsoft documentation.
可以从 Microsoft 文档中获取默认安全组的完整列表。
Active Directory Users and ComputersActive Directory 用户和计算机
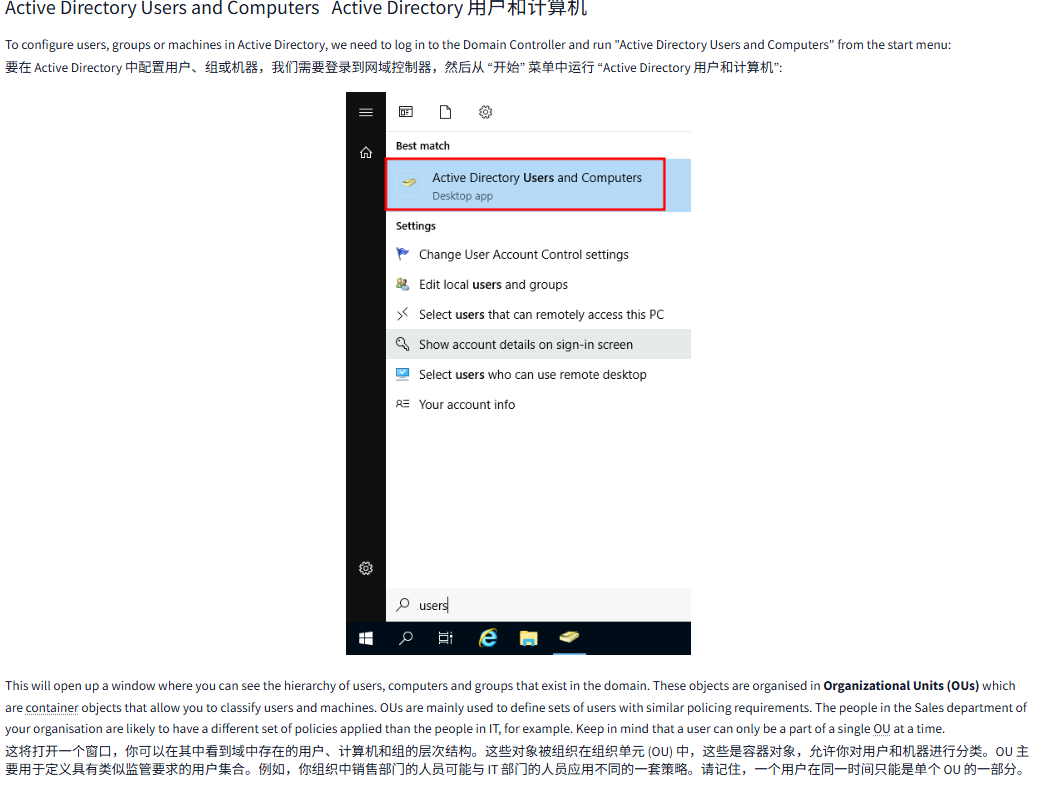
To configure users, groups or machines in Active Directory, we need to log in to the Domain Controller and run "Active Directory Users and Computers" from the start menu:
要在 Active Directory 中配置用户、组或机器,我们需要登录到网域控制器,然后从 “开始” 菜单中运行 “Active Directory 用户和计算机”:
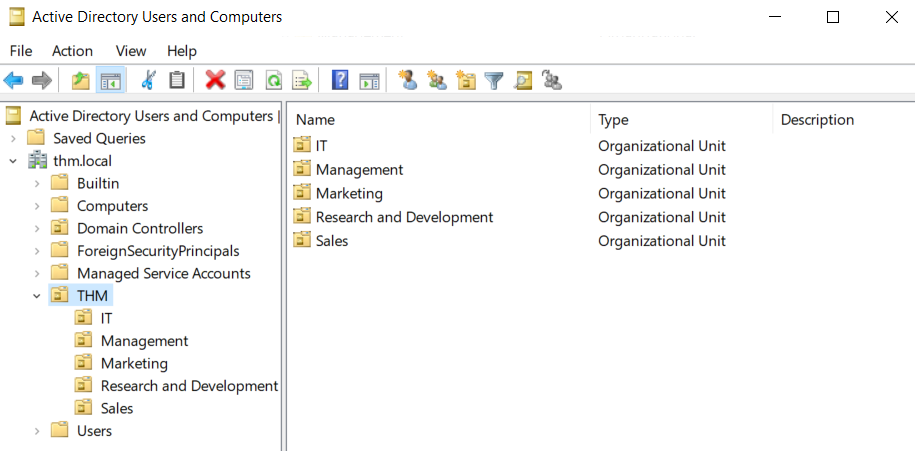
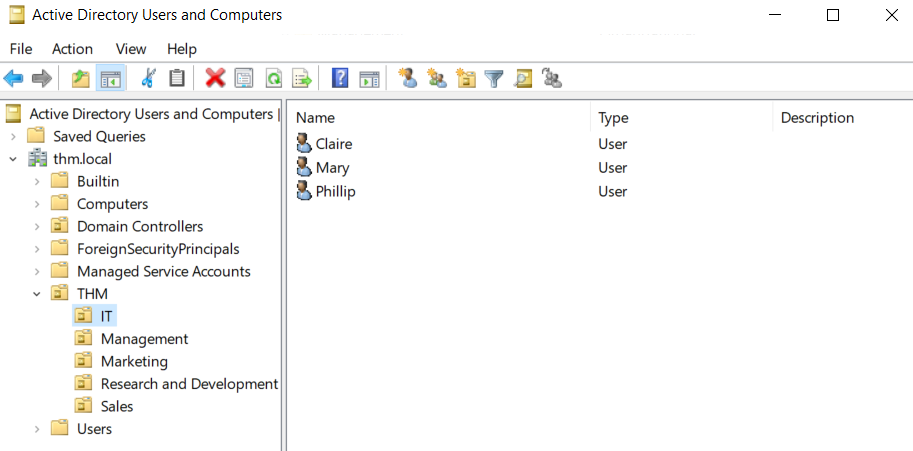
This will open up a window where you can see the hierarchy of users, computers and groups that exist in the domain. These objects are organised in Organizational Units (OUs) which are container objects that allow you to classify users and machines. OUs are mainly used to define sets of users with similar policing requirements. The people in the Sales department of your organisation are likely to have a different set of policies applied than the people in IT, for example. Keep in mind that a user can only be a part of a single OU at a time.
这将打开一个窗口,你可以在其中看到域中存在的用户、计算机和组的层次结构。这些对象被组织在组织单元 (OU) 中,这些是容器对象,允许你对用户和机器进行分类。OU 主要用于定义具有类似监管要求的用户集合。例如,你组织中销售部门的人员可能与 IT 部门的人员应用不同的一套策略。请记住,一个用户在同一时间只能是单个 OU 的一部分。
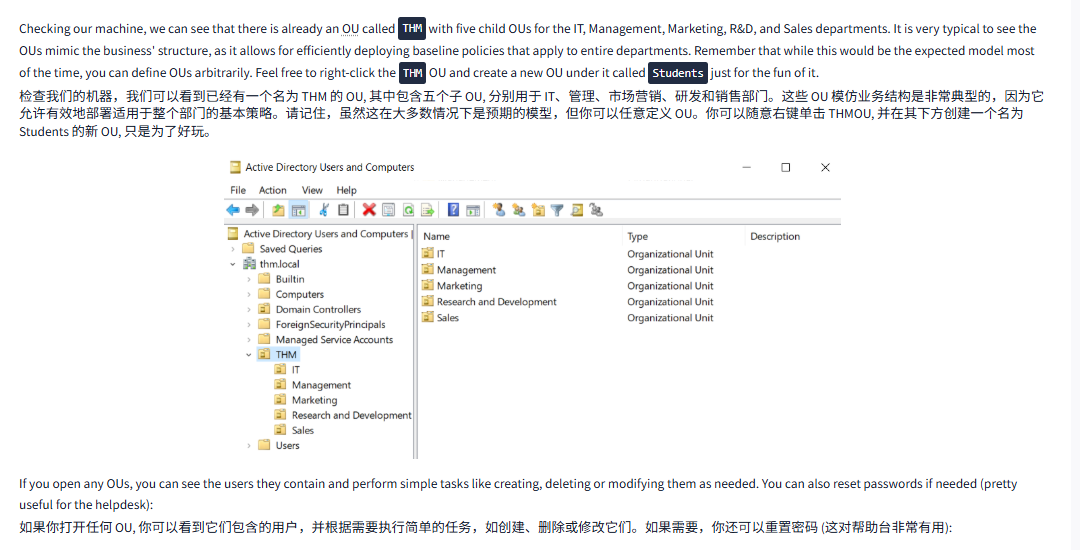
Checking our machine, we can see that there is already an OU called THM with five child OUs for the IT, Management, Marketing, R&D, and Sales departments. It is very typical to see the OUs mimic the business' structure, as it allows for efficiently deploying baseline policies that apply to entire departments. Remember that while this would be the expected model most of the time, you can define OUs arbitrarily. Feel free to right-click the THM OU and create a new OU under it called Students just for the fun of it.
检查我们的机器,我们可以看到已经有一个名为 THM 的 OU, 其中包含五个子 OU, 分别用于 IT、管理、市场营销、研发和销售部门。这些 OU 模仿业务结构是非常典型的,因为它允许有效地部署适用于整个部门的基本策略。请记住,虽然这在大多数情况下是预期的模型,但你可以任意定义 OU。你可以随意右键单击 THMOU, 并在其下方创建一个名为 Students 的新 OU, 只是为了好玩。
If you open any OUs, you can see the users they contain and perform simple tasks like creating, deleting or modifying them as needed. You can also reset passwords if needed (pretty useful for the helpdesk):
如果你打开任何 OU, 你可以看到它们包含的用户,并根据需要执行简单的任务,如创建、删除或修改它们。如果需要,你还可以重置密码 (这对帮助台非常有用):
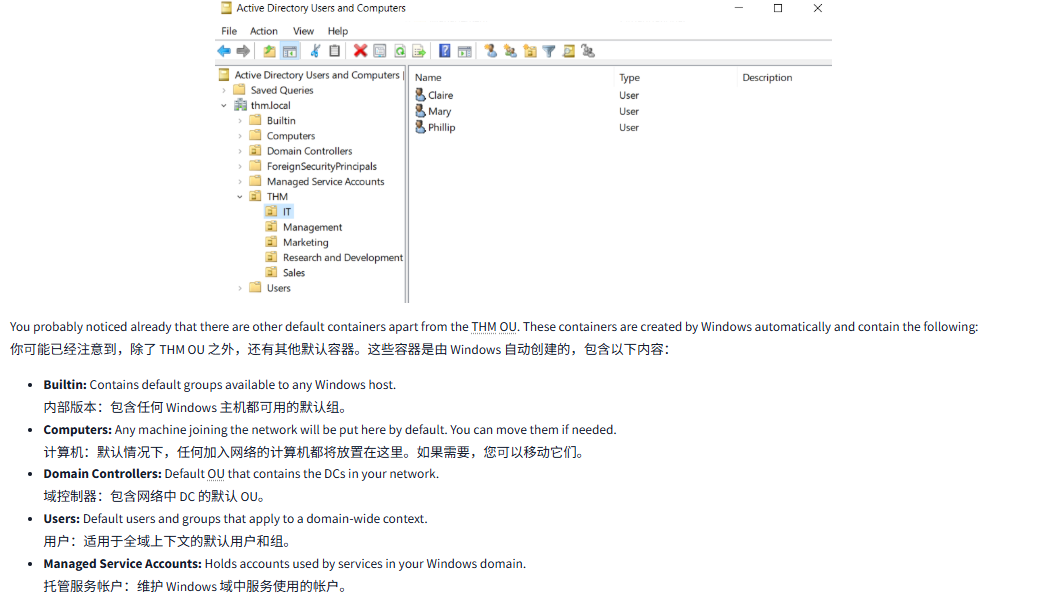
You probably noticed already that there are other default containers apart from the THM OU. These containers are created by Windows automatically and contain the following:
你可能已经注意到,除了 THM OU 之外,还有其他默认容器。这些容器是由 Windows 自动创建的,包含以下内容:
- Builtin: Contains default groups available to any Windows host.
内部版本:包含任何 Windows 主机都可用的默认组。 - Computers: Any machine joining the network will be put here by default. You can move them if needed.
计算机:默认情况下,任何加入网络的计算机都将放置在这里。如果需要,您可以移动它们。 - Domain Controllers: Default OU that contains the DCs in your network.
域控制器:包含网络中 DC 的默认 OU。 - Users: Default users and groups that apply to a domain-wide context.
用户:适用于全域上下文的默认用户和组。 - Managed Service Accounts: Holds accounts used by services in your Windows domain.
托管服务帐户:维护 Windows 域中服务使用的帐户。
Security Groups vs OUs安全组与 OU
You are probably wondering why we have both groups and OUs. While both are used to classify users and computers, their purposes are entirely different:
你可能想知道为什么我们同时使用组和 OU。虽然这两者都用于对用户和计算机进行分类,但它们的目的完全不同:
- OUs are handy for applying policies to users and computers, which include specific configurations that pertain to sets of users depending on their particular role in the enterprise. Remember, a user can only be a member of a single OU at a time, as it wouldn't make sense to try to apply two different sets of policies to a single user.
OU 便于将策略应用于用户和计算机,其中包括根据用户在企业中的特定角色,针对不同用户组的特定配置。请记住,一个用户在同一时间只能是一个 OU 的成员,因为试图将两组不同的策略应用于同一个用户是没有意义的。 - Security Groups, on the other hand, are used to grant permissions over resources. For example, you will use groups if you want to allow some users to access a shared folder or network printer. A user can be a part of many groups, which is needed to grant access to multiple resources.
另一方面,安全组用于授予对资源的权限。例如,如果你想允许一些用户访问共享文件夹或网络打印机,你将使用组。一个用户可以是许多组的一部分,这些组是授予对多个资源的访问权限所需的。
问题
答案
Task4 Managing Users in AD AD 域中的用户管理
图片版

文字版
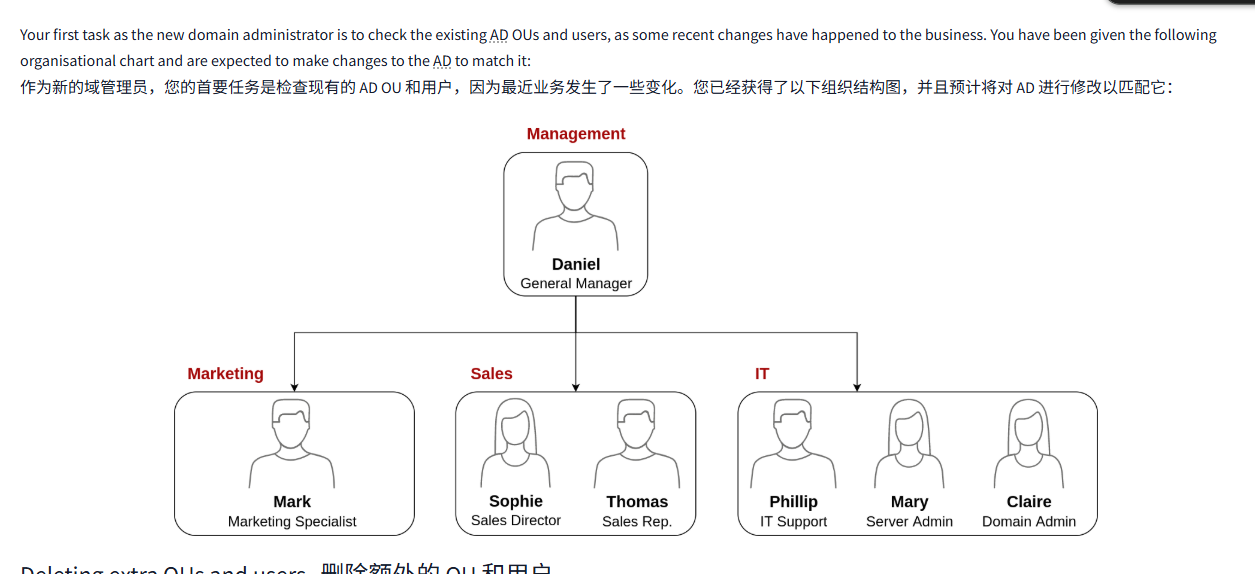
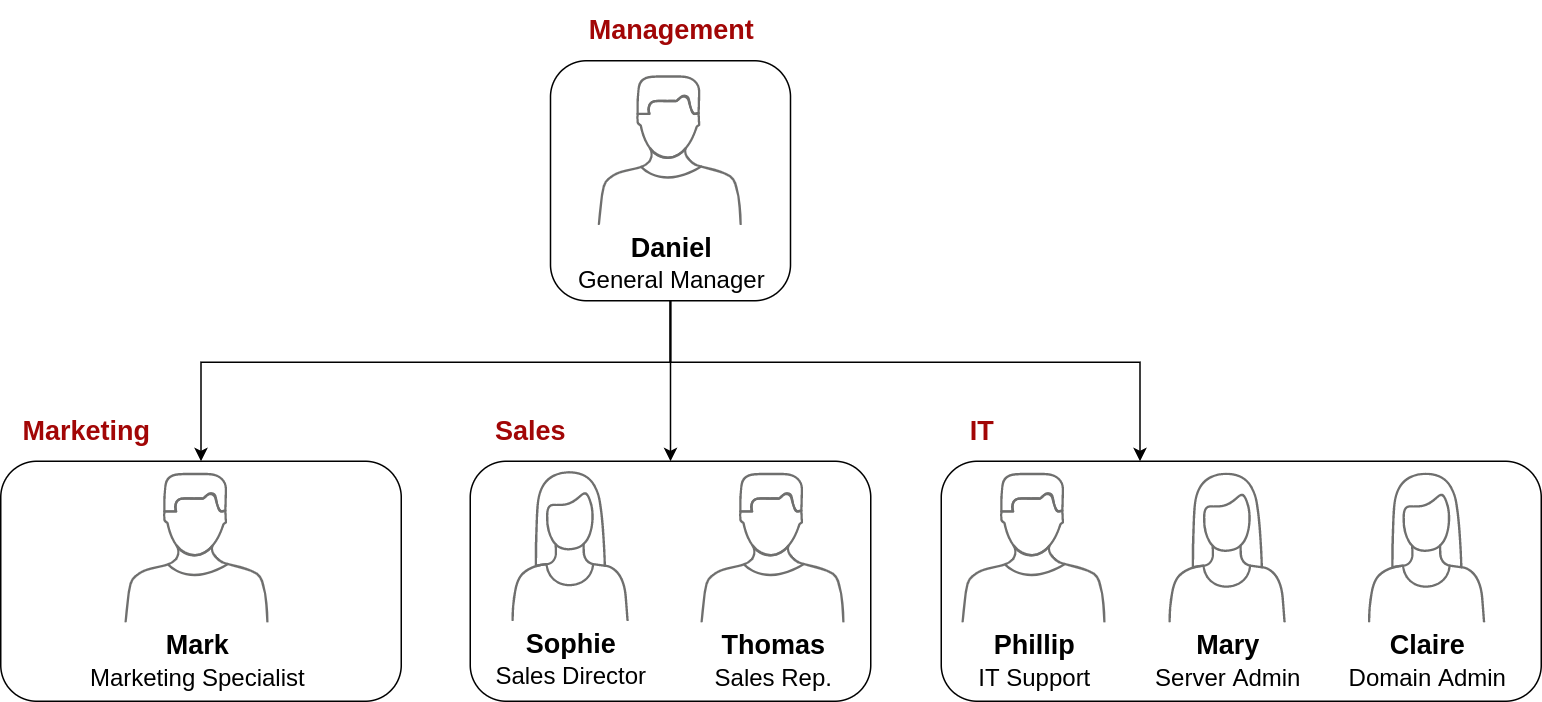
Your first task as the new domain administrator is to check the existing AD OUs and users, as some recent changes have happened to the business. You have been given the following organisational chart and are expected to make changes to the AD to match it:
作为新的域管理员,您的首要任务是检查现有的 AD OU 和用户,因为最近业务发生了一些变化。您已经获得了以下组织结构图,并且预计将对 AD 进行修改以匹配它:
Deleting extra OUs and users删除额外的 OU 和用户
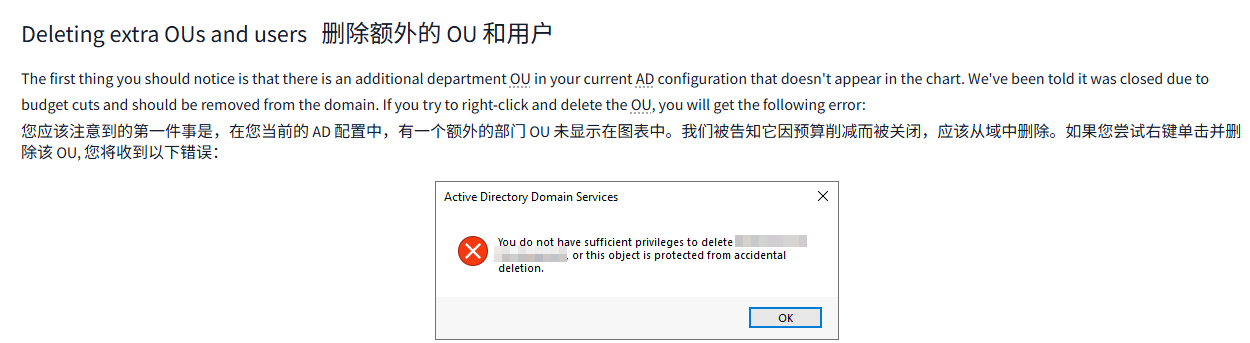
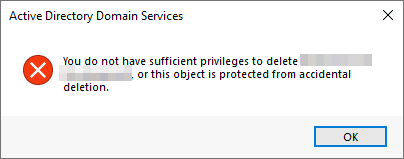
The first thing you should notice is that there is an additional department OU in your current AD configuration that doesn't appear in the chart. We've been told it was closed due to budget cuts and should be removed from the domain. If you try to right-click and delete the OU, you will get the following error:
首先需要注意的是,在您当前的 AD 配置中,有一个额外的部门 OU 未显示在图表中。我们被告知它因预算削减而被关闭,应该从域中删除。如果您尝试右键单击并删除该 OU, 您将收到以下错误:
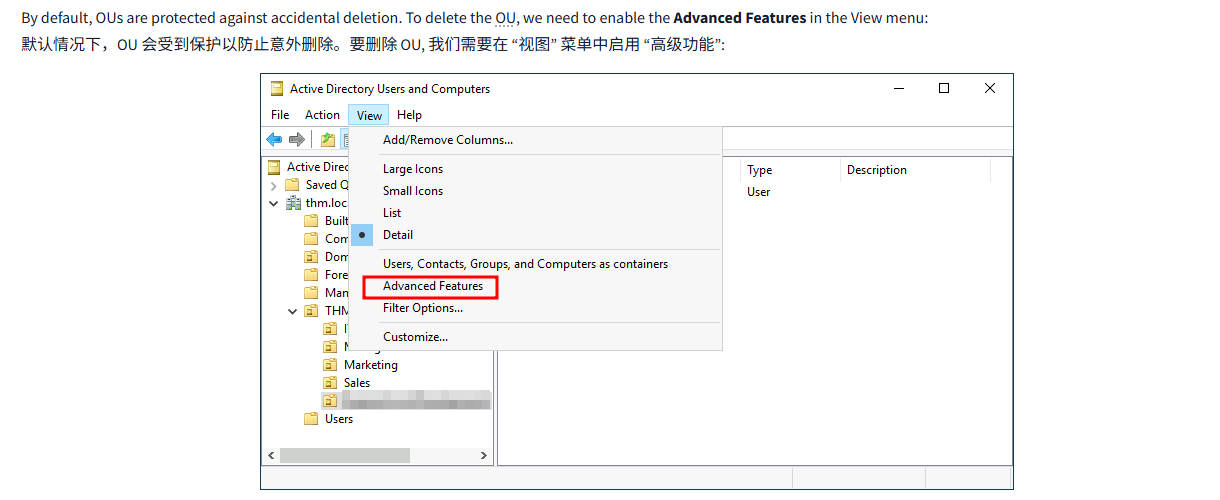
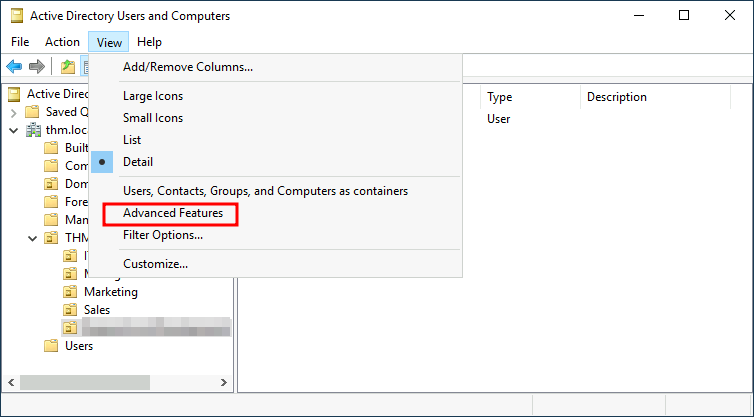
By default, OUs are protected against accidental deletion. To delete the OU, we need to enable the Advanced Features in the View menu:
默认情况下,OU 会受到保护以防止意外删除。要删除 OU, 我们需要在 “视图” 菜单中启用 “高级功能”:
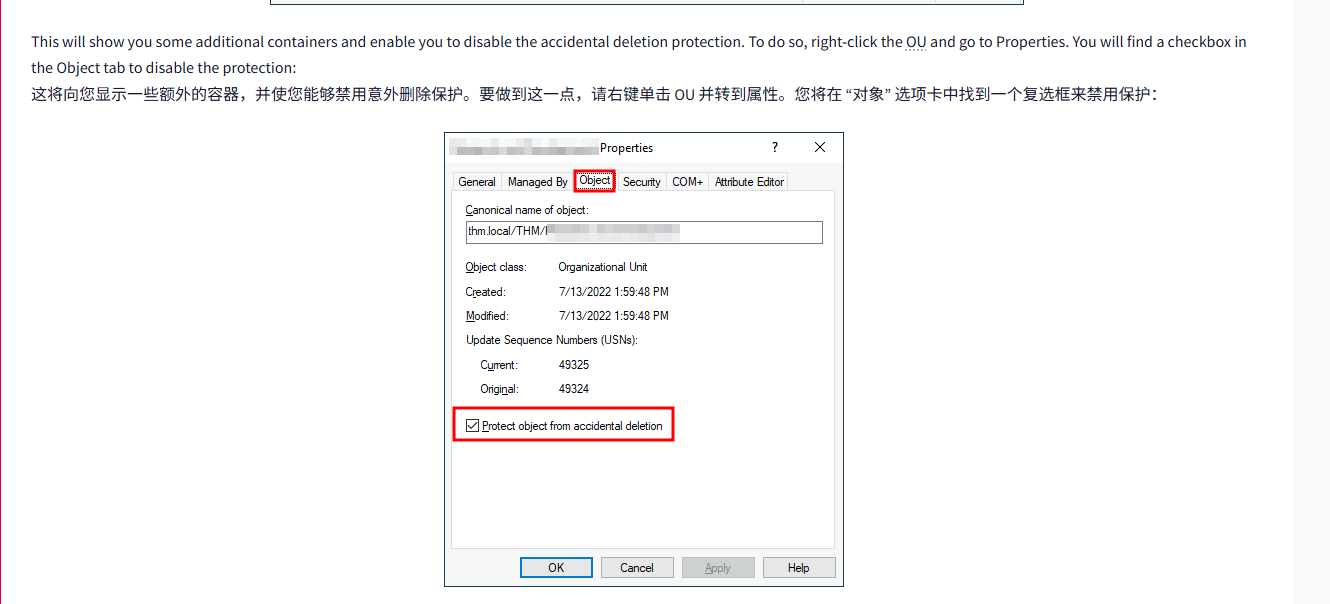
This will show you some additional containers and enable you to disable the accidental deletion protection. To do so, right-click the OU and go to Properties. You will find a checkbox in the Object tab to disable the protection:
这将向您显示一些额外的容器,并使您能够禁用意外删除保护。要做到这一点,请右键单击 OU 并转到属性。您将在 “对象” 选项卡中找到一个复选框来禁用保护:
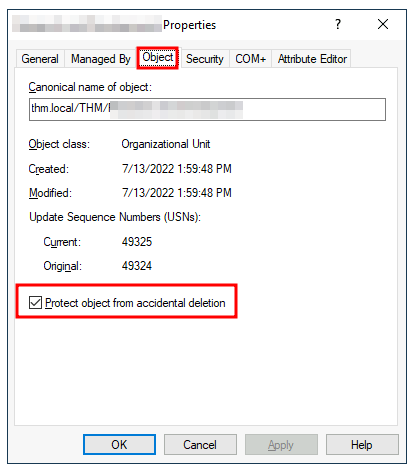
Be sure to uncheck the box and try deleting the OU again. You will be prompted to confirm that you want to delete the OU, and as a result, any users, groups or OUs under it will also be deleted.
请务必取消选中该复选框并再次尝试删除 OU。系统将提示您确认是否要删除 OU, 因此,该 OU 下的任何用户、组或 OU 也将被删除。
After deleting the extra OU, you should notice that for some of the departments, the users in the AD don't match the ones in our organisational chart. Create and delete users as needed to match them.
删除额外的 OU 后,您应该注意到,对于某些部门,AD 中的用户与我们组织结构图中的用户不匹配。根据需要创建和删除用户以匹配它们。
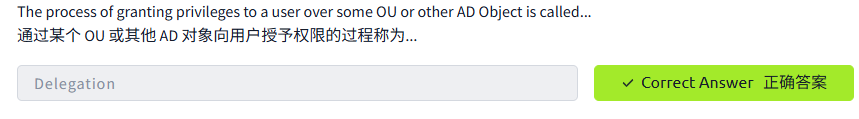
Delegation委托
One of the nice things you can do in AD is to give specific users some control over some OUs. This process is known as delegation and allows you to grant users specific privileges to perform advanced tasks on OUs without needing a Domain Administrator to step in.
AD 中可以做的一件好事是赋予特定用户对某些 OU 的一些控制权。这个过程称为授权,允许你授予用户特定权限,以便在 OU 上执行高级任务,而无需域管理员介入。
One of the most common use cases for this is granting IT support the privileges to reset other low-privilege users' passwords. According to our organisational chart, Phillip is in charge of IT support, so we'd probably want to delegate the control of resetting passwords over the Sales, Marketing and Management OUs to him.
最常见的用例之一是授予 IT 支持人员重置其他低权限用户密码的权限。根据我们的组织结构图,Phillip 负责 IT 支持,因此我们可能希望将重置密码的控制权委托给他。
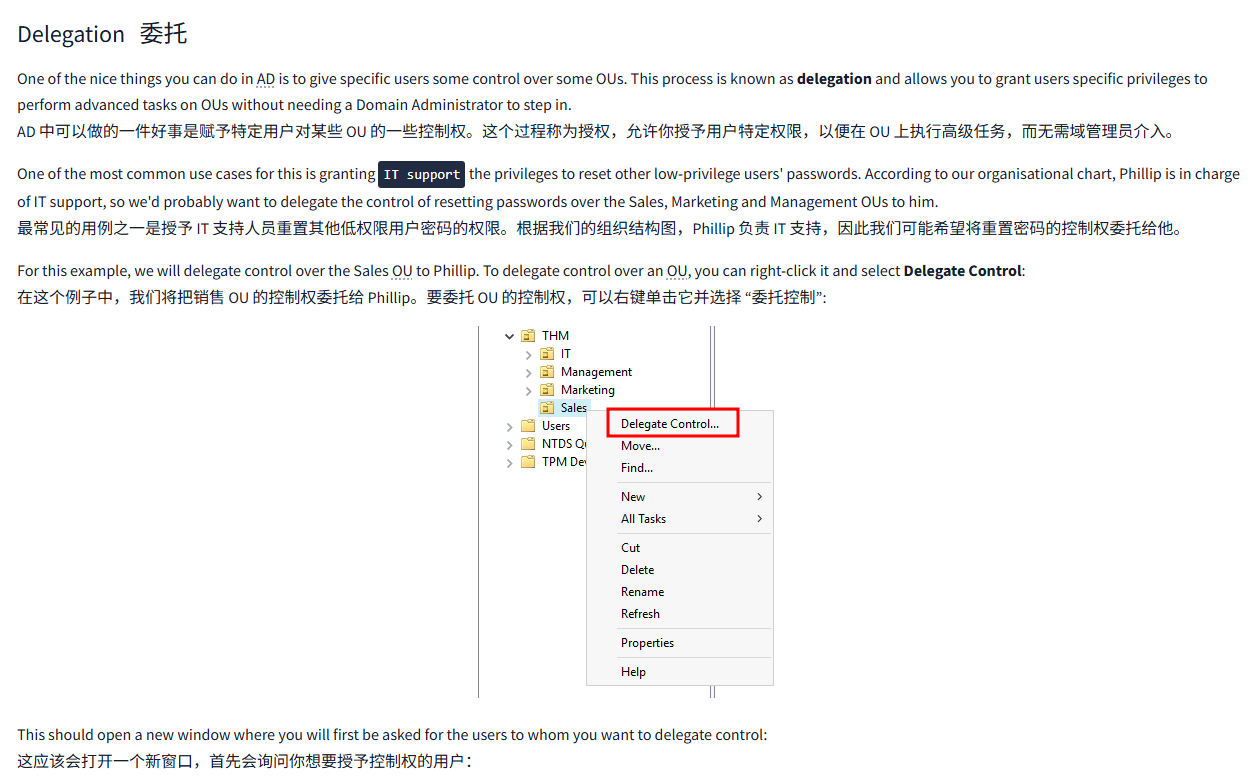
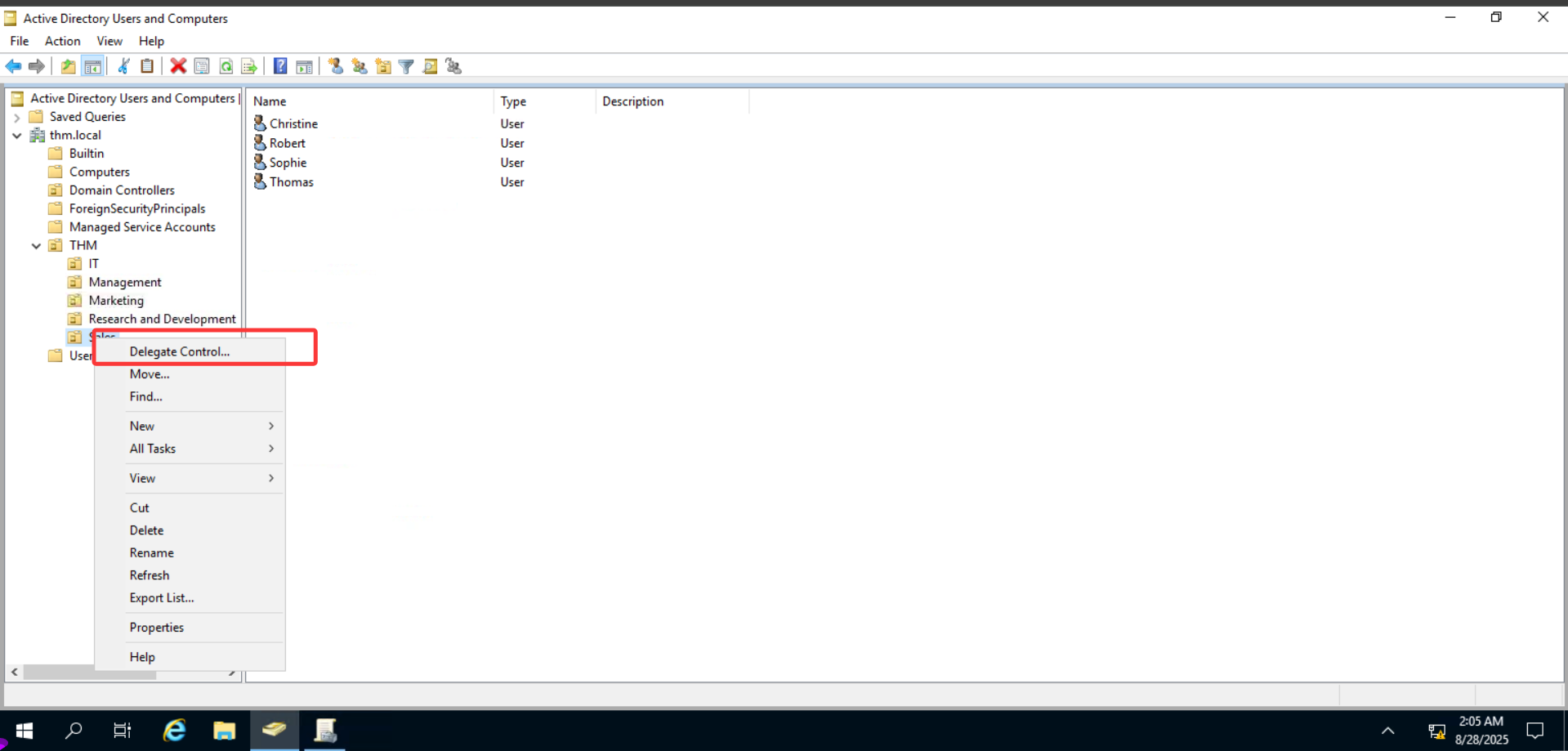
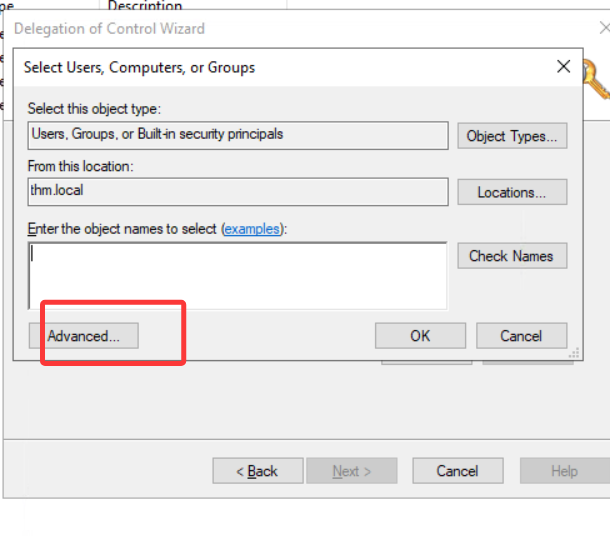
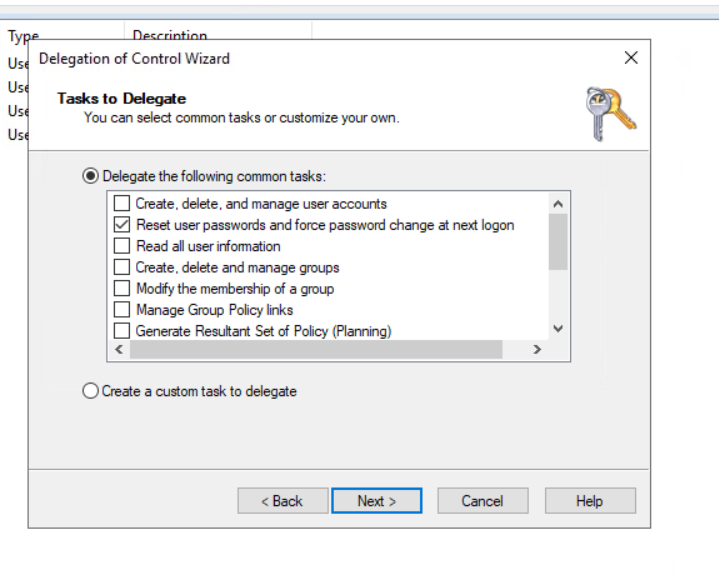
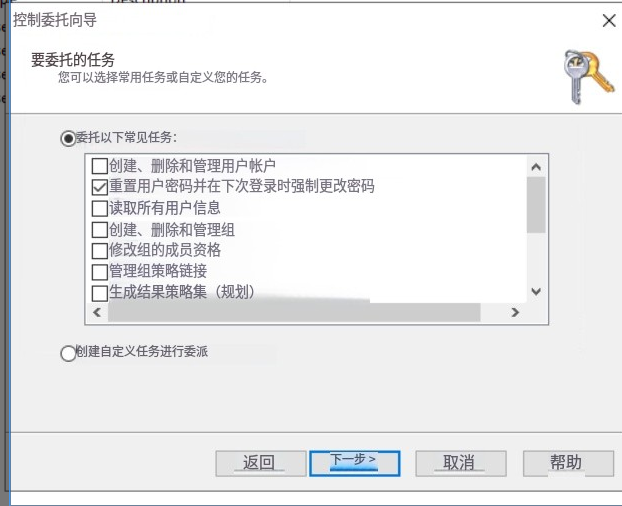
For this example, we will delegate control over the Sales OU to Phillip. To delegate control over an OU, you can right-click it and select Delegate Control:
在这个例子中,我们将把销售 OU 的控制权委托给 Phillip。要委托 OU 的控制权,可以右键单击它并选择 “委托控制”:
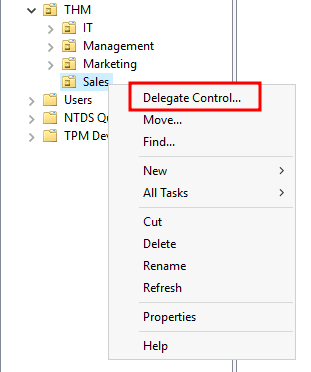
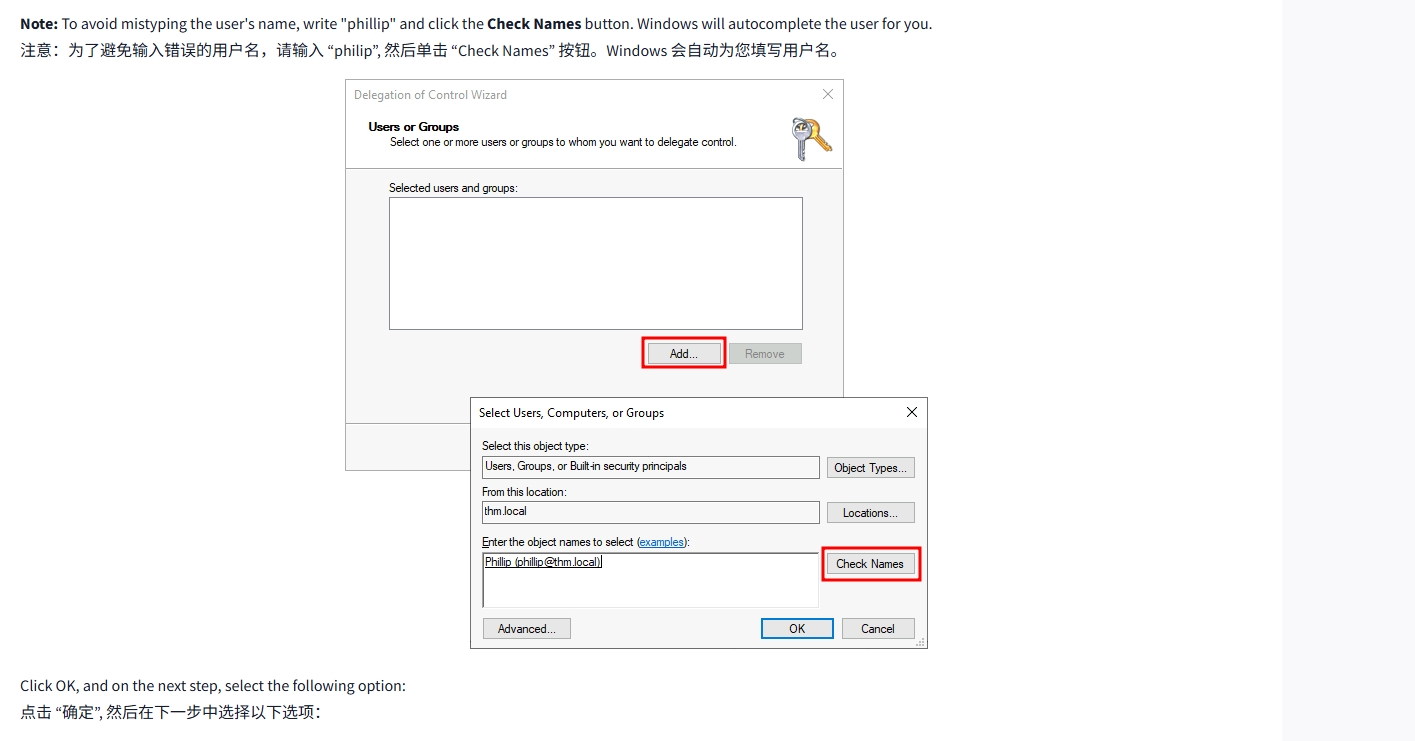
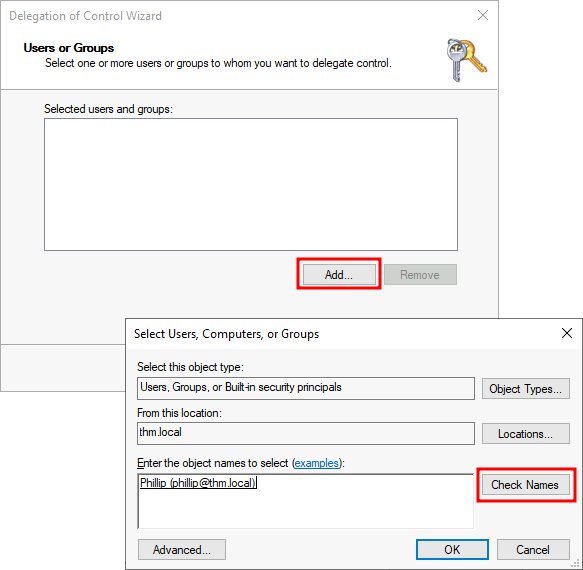
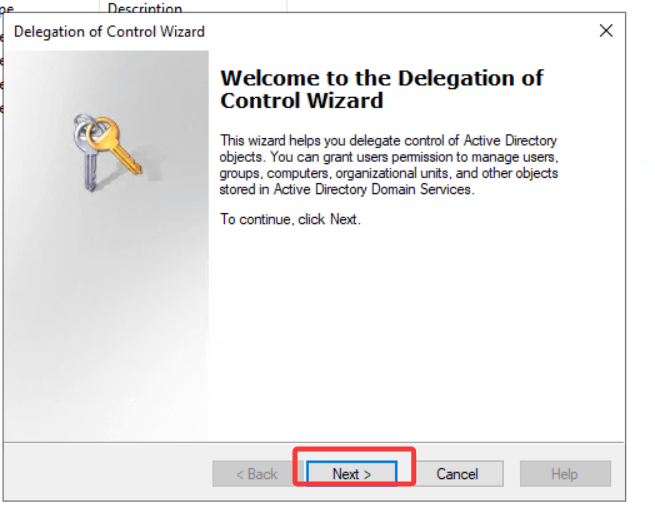
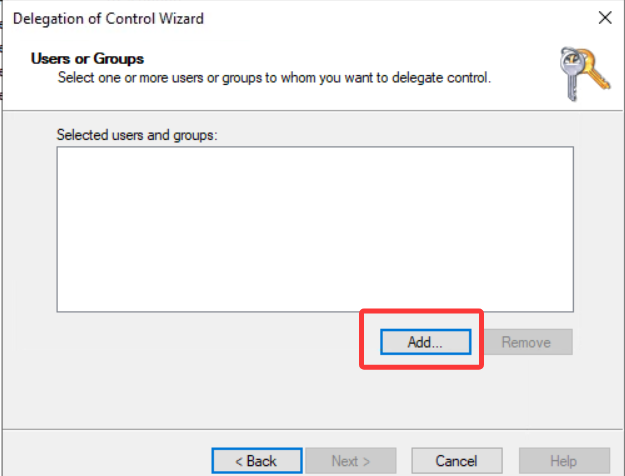
This should open a new window where you will first be asked for the users to whom you want to delegate control:
这应该会打开一个新窗口,首先会询问您想要委托控制的用户:
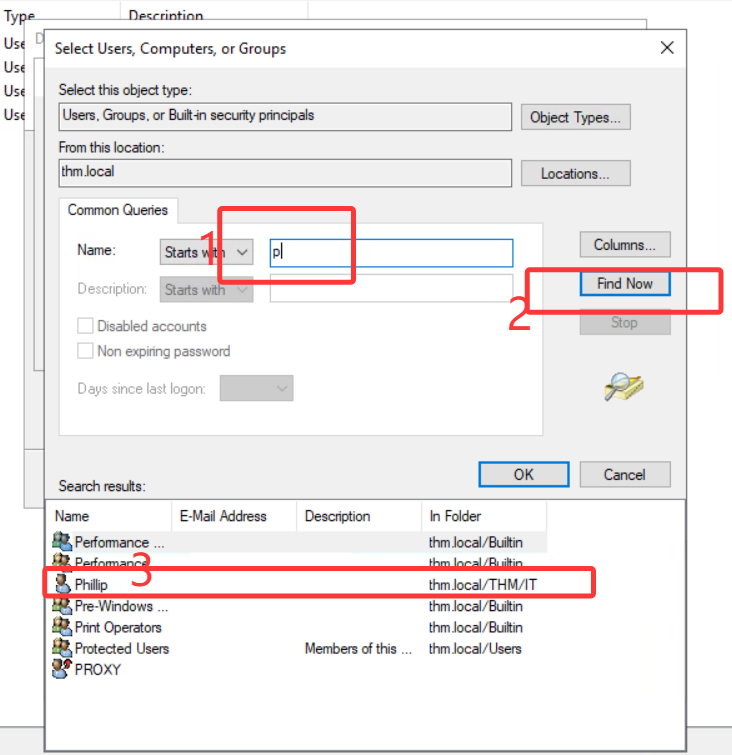
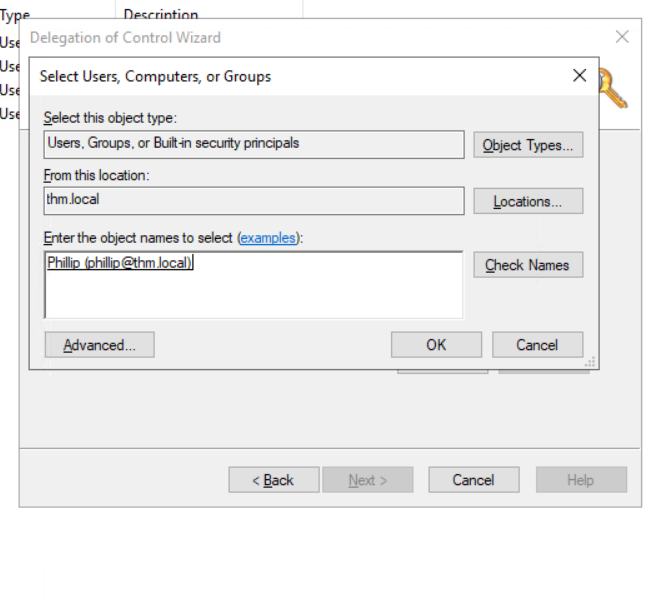
Note: To avoid mistyping the user's name, write "phillip" and click the Check Names button. Windows will autocomplete the user for you.
注意:为了避免输入错误的用户名,请输入 “philip”, 然后单击 “检查名称” 按钮。Windows 会自动为您填写用户名。
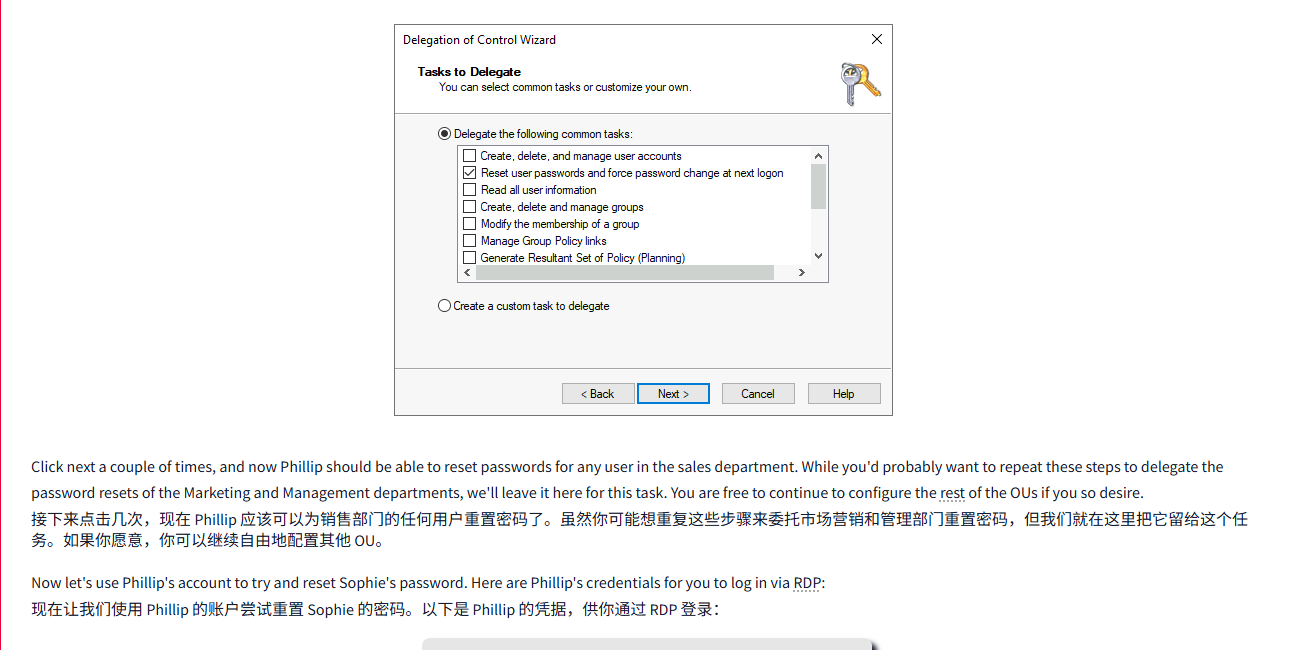
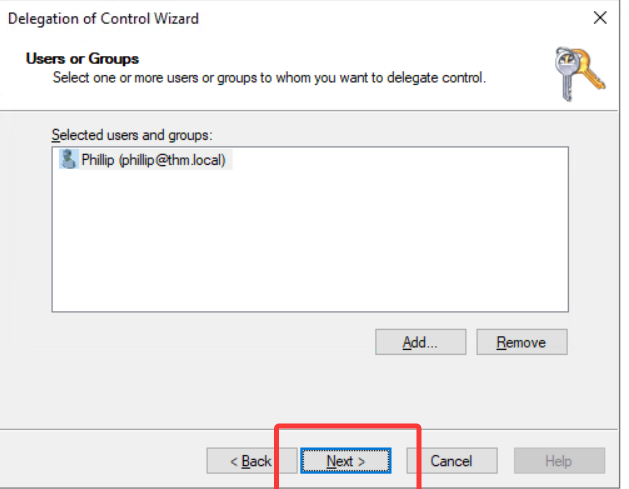
Click OK, and on the next step, select the following option:
点击 “确定”, 然后在下一步中选择以下选项:
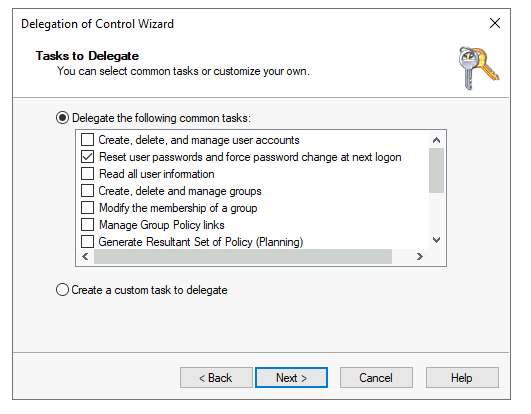
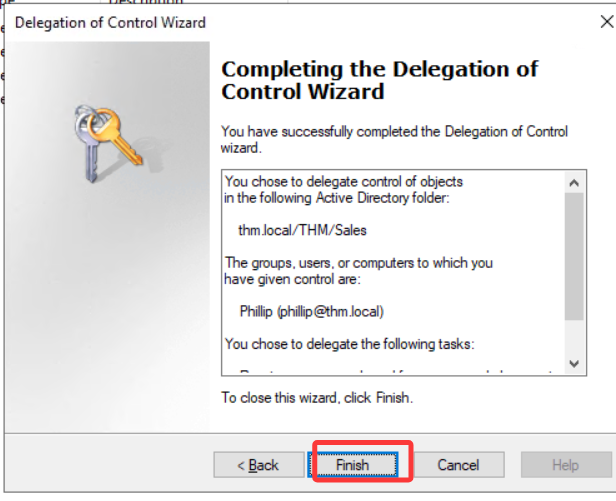
Click next a couple of times, and now Phillip should be able to reset passwords for any user in the sales department. While you'd probably want to repeat these steps to delegate the password resets of the Marketing and Management departments, we'll leave it here for this task. You are free to continue to configure the rest of the OUs if you so desire.
接下来点击几次,现在 Phillip 应该可以为销售部门的任何用户重置密码了。虽然你可能想重复这些步骤来委托市场营销和管理部门重置密码,但我们就在这里把它留给这个任务。如果你愿意,你可以继续自由地配置其他 OU。
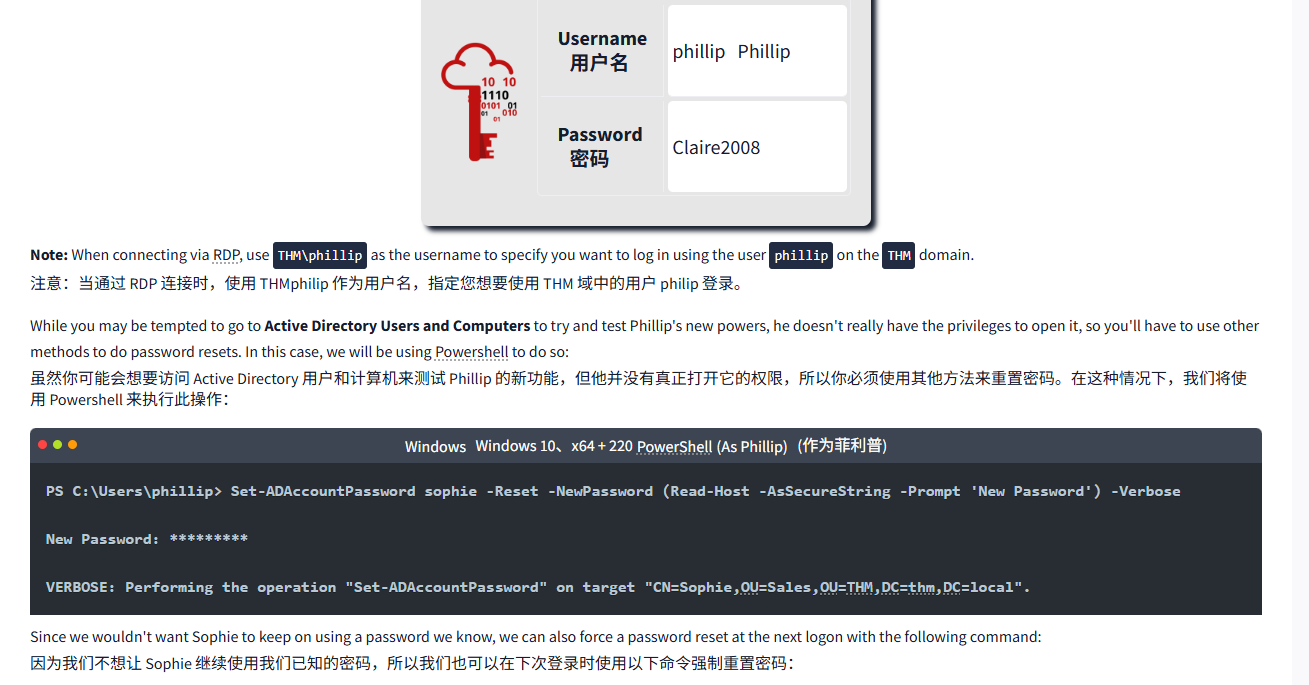
Now let's use Phillip's account to try and reset Sophie's password. Here are Phillip's credentials for you to log in via RDP:
现在让我们使用 Phillip 的账户尝试重置 Sophie 的密码。以下是 Phillip 的凭据,供你通过 RDP 登录:

| Username 用户名 | phillipPhillip |
| Password 密码 | Claire2008 |
Note: When connecting via RDP, use THM\phillip as the username to specify you want to log in using the user phillip on the THM domain.
注意:当通过 RDP 连接时,使用 THMphilip 作为用户名,指定您想要使用 THM 域中的用户 philip 登录。
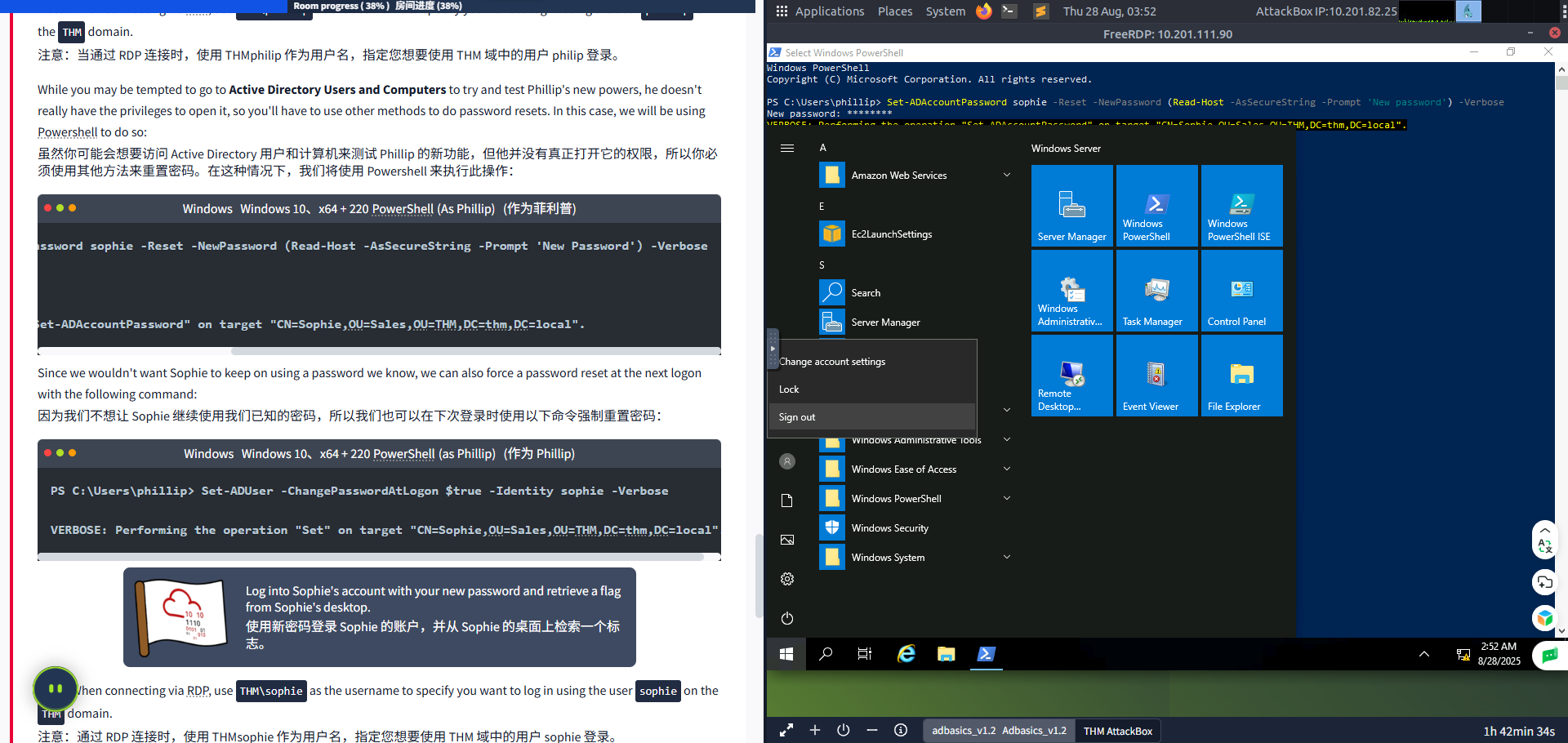
While you may be tempted to go to Active Directory Users and Computers to try and test Phillip's new powers, he doesn't really have the privileges to open it, so you'll have to use other methods to do password resets. In this case, we will be using Powershell to do so:
虽然你可能会想要访问 Active Directory 用户和计算机来测试 Phillip 的新功能,但他并没有真正打开它的权限,所以你必须使用其他方法来重置密码。在这种情况下,我们将使用 Powershell 来执行此操作:
WindowsWindowsPowerShell(As Phillip)(作为 Phillip)
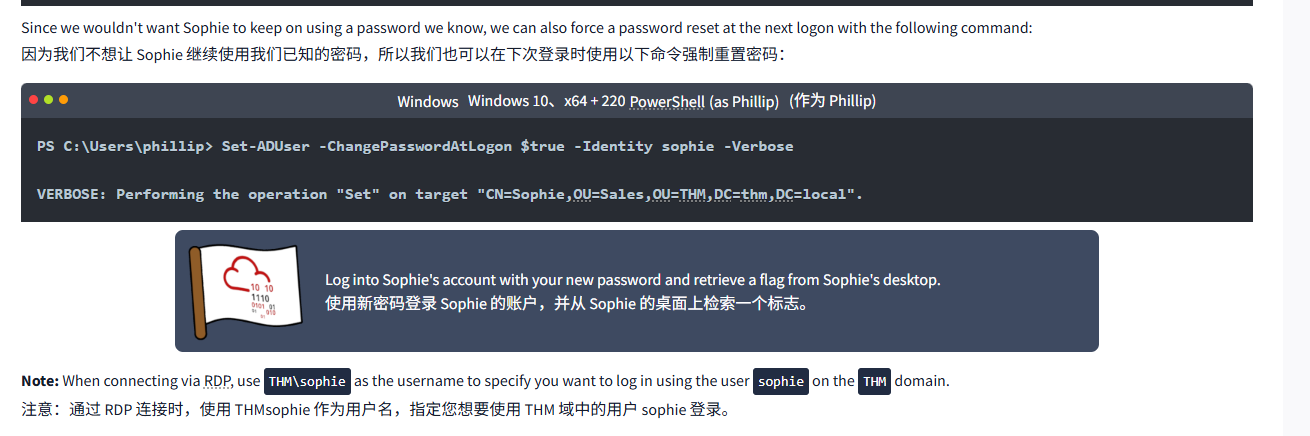
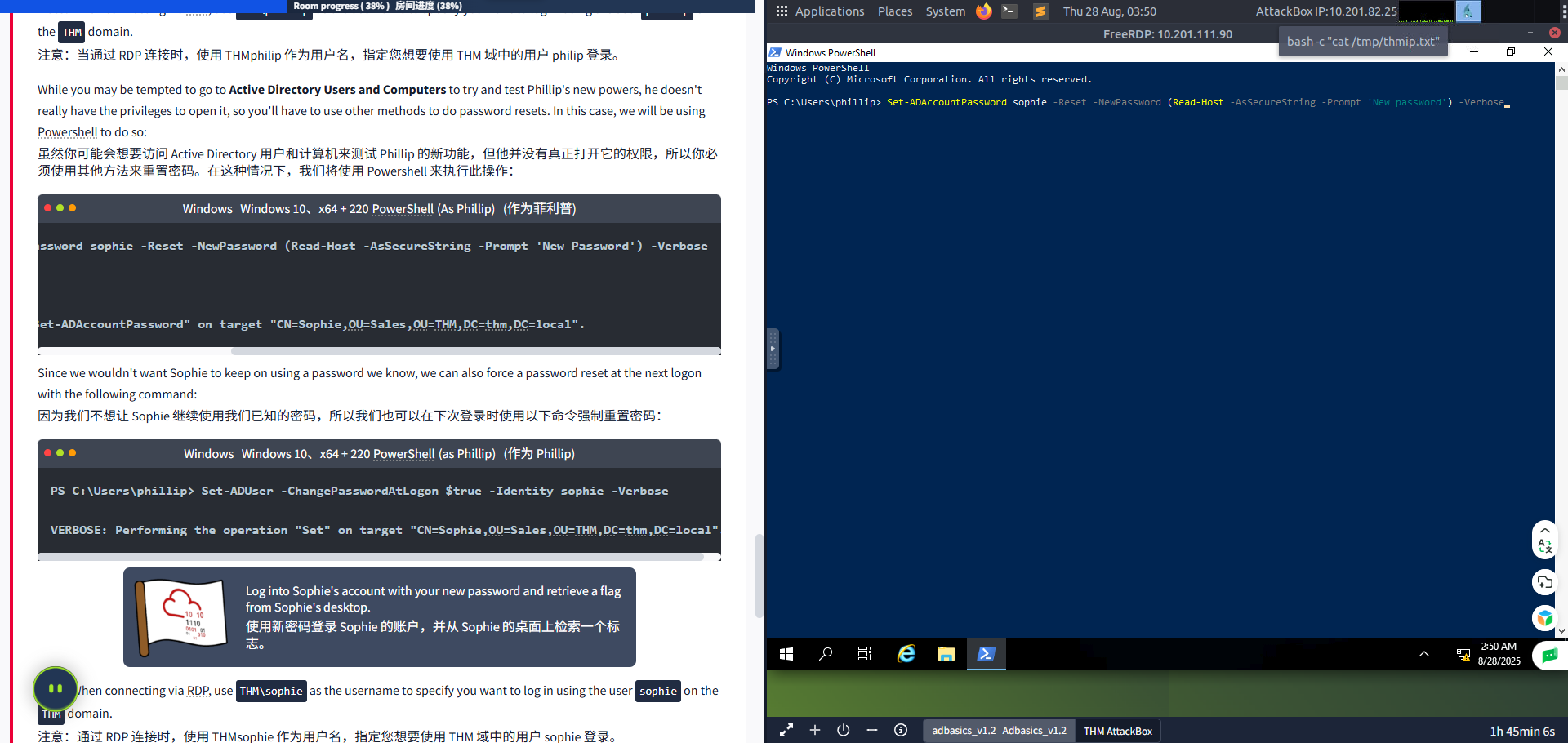
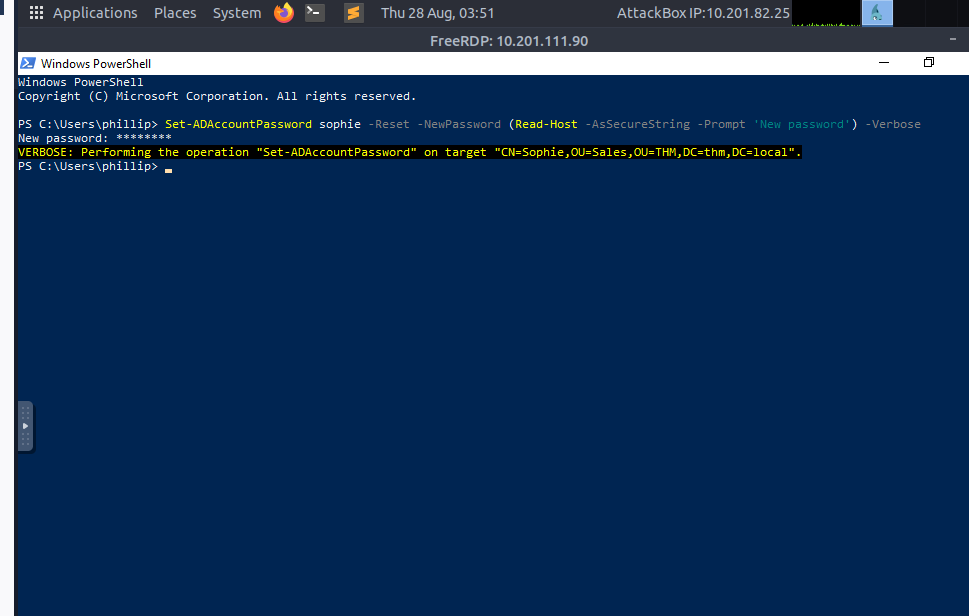
PS C:\Users\phillip> Set-ADAccountPassword sophie -Reset -NewPassword (Read-Host -AsSecureString -Prompt 'New Password') -VerboseNew Password: *********VERBOSE: Performing the operation "Set-ADAccountPassword" on target "CN=Sophie,OU=Sales,OU=THM,DC=thm,DC=local".Since we wouldn't want Sophie to keep on using a password we know, we can also force a password reset at the next logon with the following command:
由于我们不希望 Sophie 继续使用我们已知的密码,我们也可以在下次登录时使用以下命令强制重置密码:
WindowsWindowsPowerShell(as Phillip)(作为 Phillip)
PS C:\Users\phillip> Set-ADUser -ChangePasswordAtLogon $true -Identity sophie -VerboseVERBOSE: Performing the operation "Set" on target "CN=Sophie,OU=Sales,OU=THM,DC=thm,DC=local".
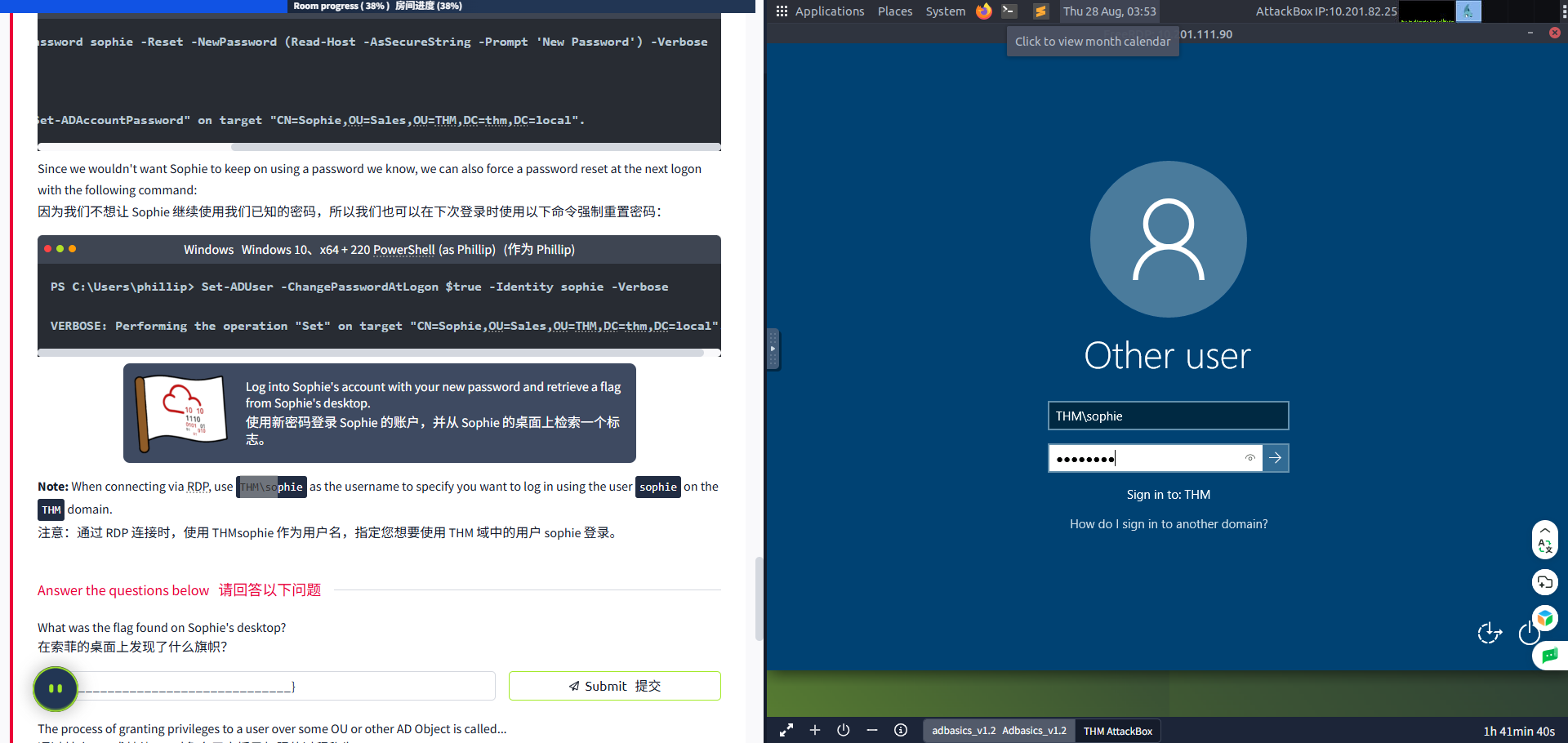
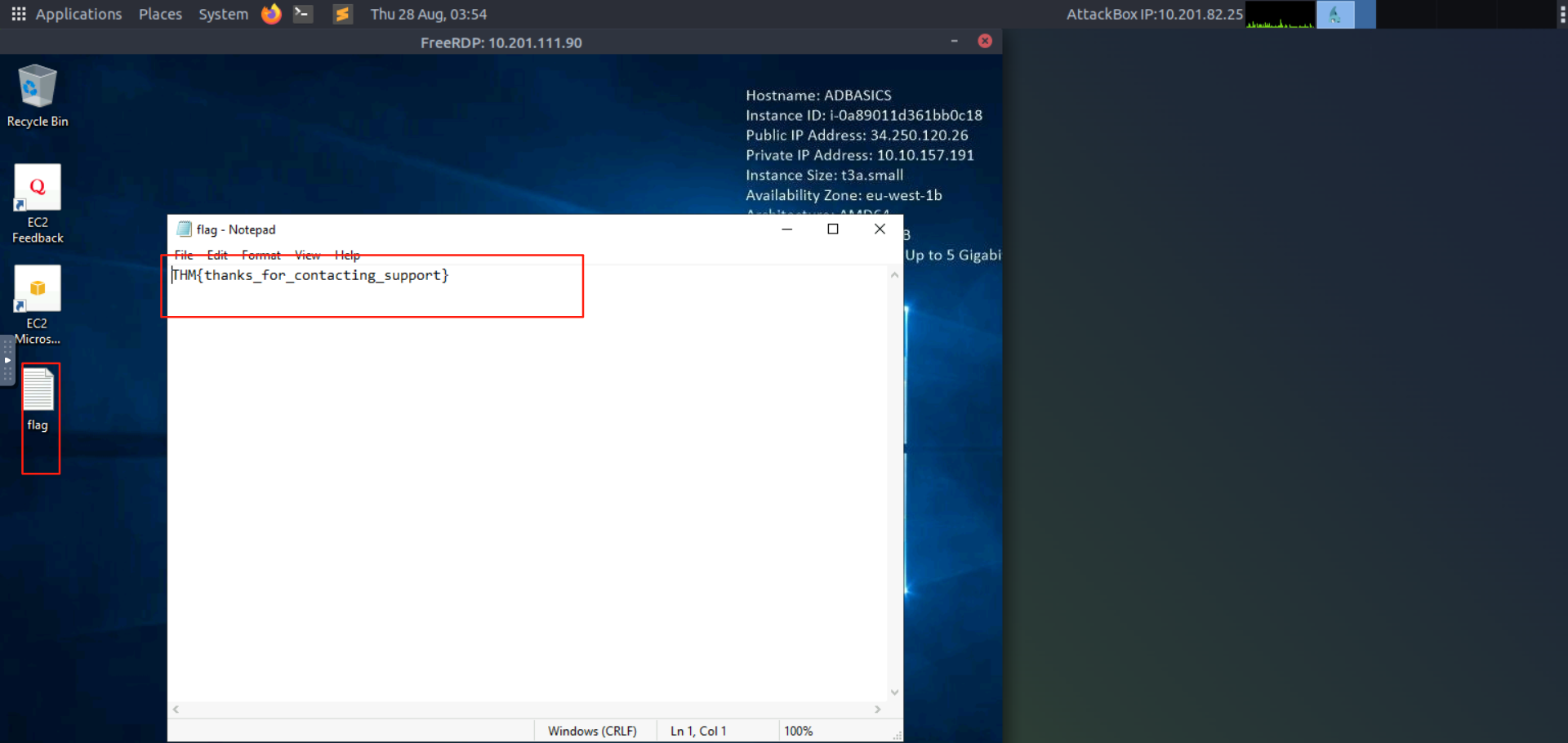
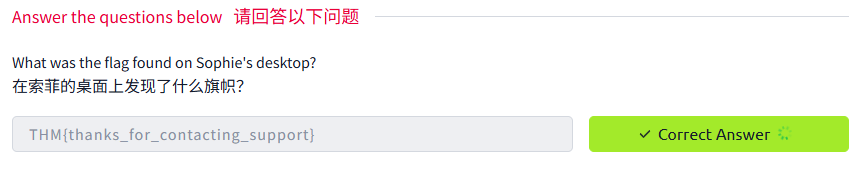
Log into Sophie's account with your new password and retrieve a flag from Sophie's desktop.
使用您的新密码登录 Sophie 的账户,并从 Sophie 的桌面上检索一个标志。
Note: When connecting via RDP, use THM\sophie as the username to specify you want to log in using the user sophie on the THM domain.
注意:当通过 RDP 连接时,使用 THMsophie 作为用户名,指定您想要使用 THM 域中的用户 sophie 登录。
问题
答案
点 OK就行了
登录成功
输入这串修改目标用户的密码
修改成功
、
注销
登录账号
Task5 Managing Users in ADAD 中的用户管理
图片版

文字版
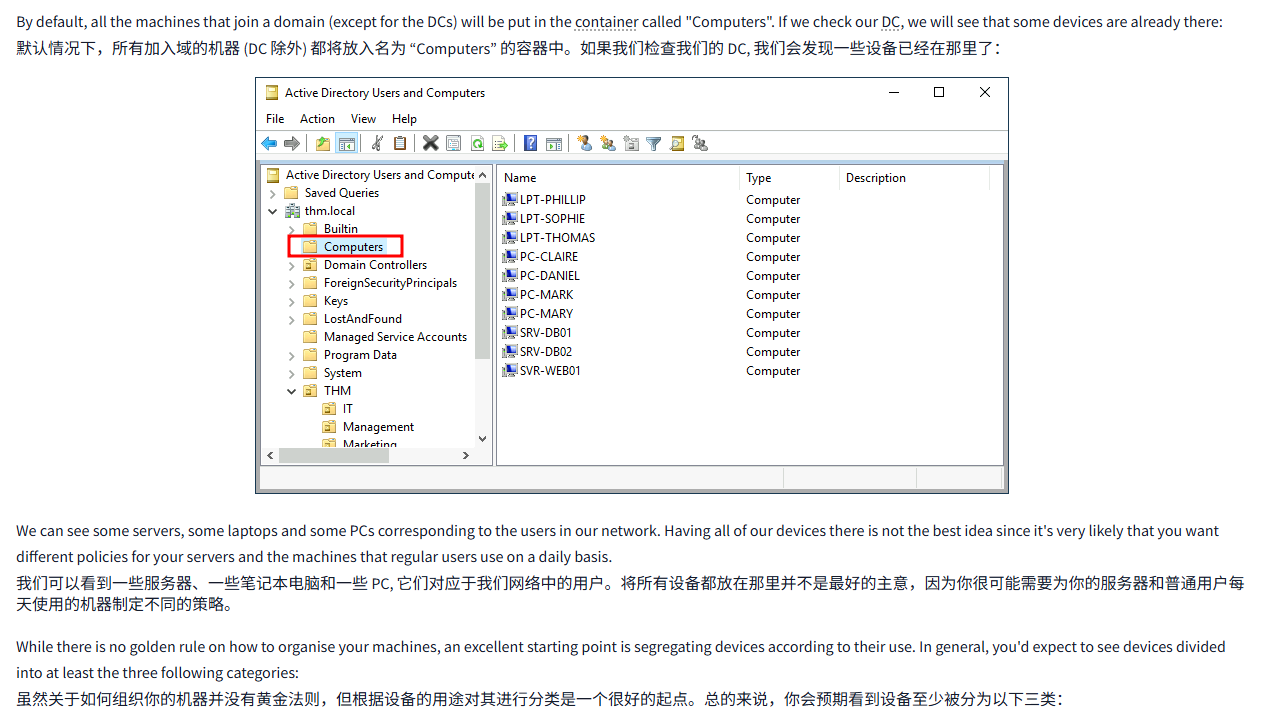
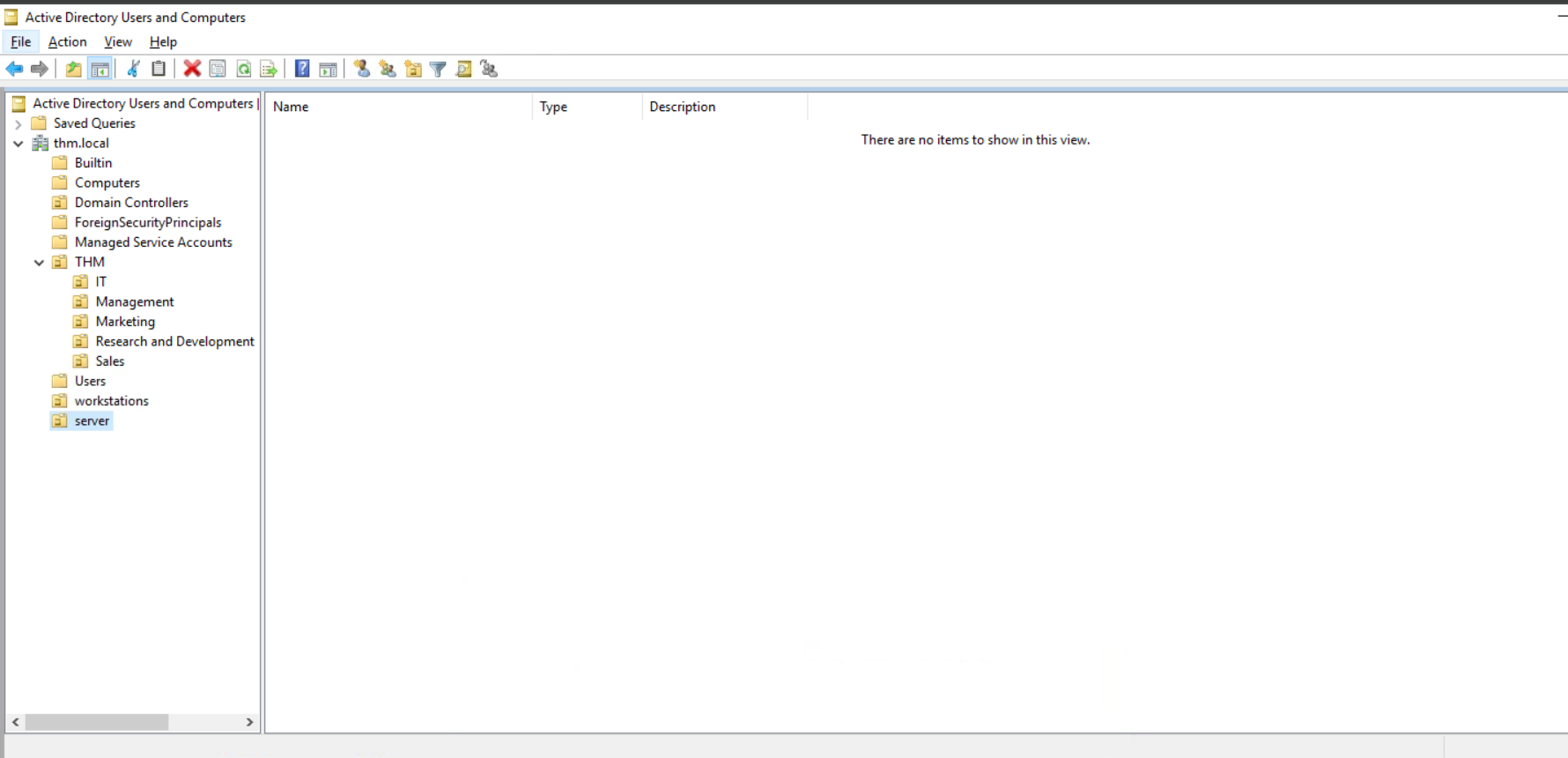
By default, all the machines that join a domain (except for the DCs) will be put in the container called "Computers". If we check our DC, we will see that some devices are already there:
默认情况下,所有加入域的机器 (DC 除外) 都将放入名为 “Computers” 的容器中。如果我们检查我们的 DC, 我们会发现一些设备已经在那里了:
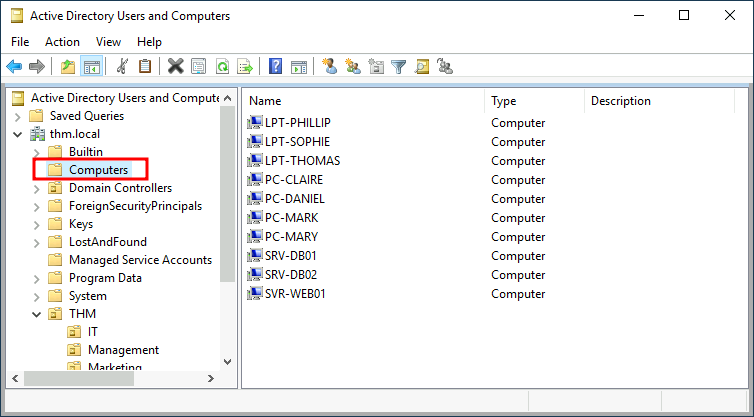
We can see some servers, some laptops and some PCs corresponding to the users in our network. Having all of our devices there is not the best idea since it's very likely that you want different policies for your servers and the machines that regular users use on a daily basis.
我们可以看到一些服务器、一些笔记本电脑和一些 PC, 它们对应于我们网络中的用户。将所有设备都放在那里并不是最好的主意,因为你很可能需要为你的服务器和普通用户每天使用的机器制定不同的策略。
While there is no golden rule on how to organise your machines, an excellent starting point is segregating devices according to their use. In general, you'd expect to see devices divided into at least the three following categories:
虽然关于如何组织你的机器并没有黄金法则,但根据设备的用途对其进行分类是一个很好的起点。总的来说,你会预期看到设备至少被分为以下三类:
1. Workstations1. 工作站
Workstations are one of the most common devices within an Active Directory domain. Each user in the domain will likely be logging into a workstation. This is the device they will use to do their work or normal browsing activities. These devices should never have a privileged user signed into them.
工作站是 Active Directory 域中最常见的设备之一。域中的每个用户都可能会登录到工作站。这是他们用来完成工作或进行正常浏览活动的设备。这些设备永远不应该由特权用户登录。
2. Servers2. 服务器
Servers are the second most common device within an Active Directory domain. Servers are generally used to provide services to users or other servers.
服务器是 Active Directory 域中第二常见的设备。服务器通常用于向用户或其他服务器提供服务。
3. Domain Controllers3. 域控制器
Domain Controllers are the third most common device within an Active Directory domain. Domain Controllers allow you to manage the Active Directory Domain. These devices are often deemed the most sensitive devices within the network as they contain hashed passwords for all user accounts within the environment.
域控制器是 Active Directory 域中第三常见的设备。域控制器允许您管理 Active Directory 域。这些设备通常被认为是网络中最敏感的设备,因为它们包含环境中所有用户帐户的哈希密码。
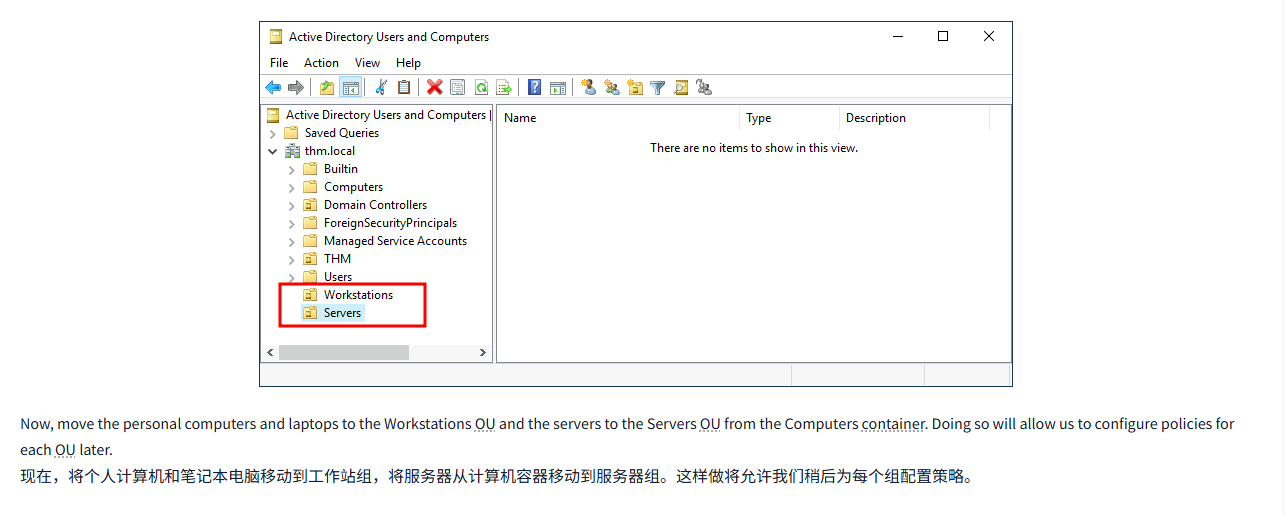
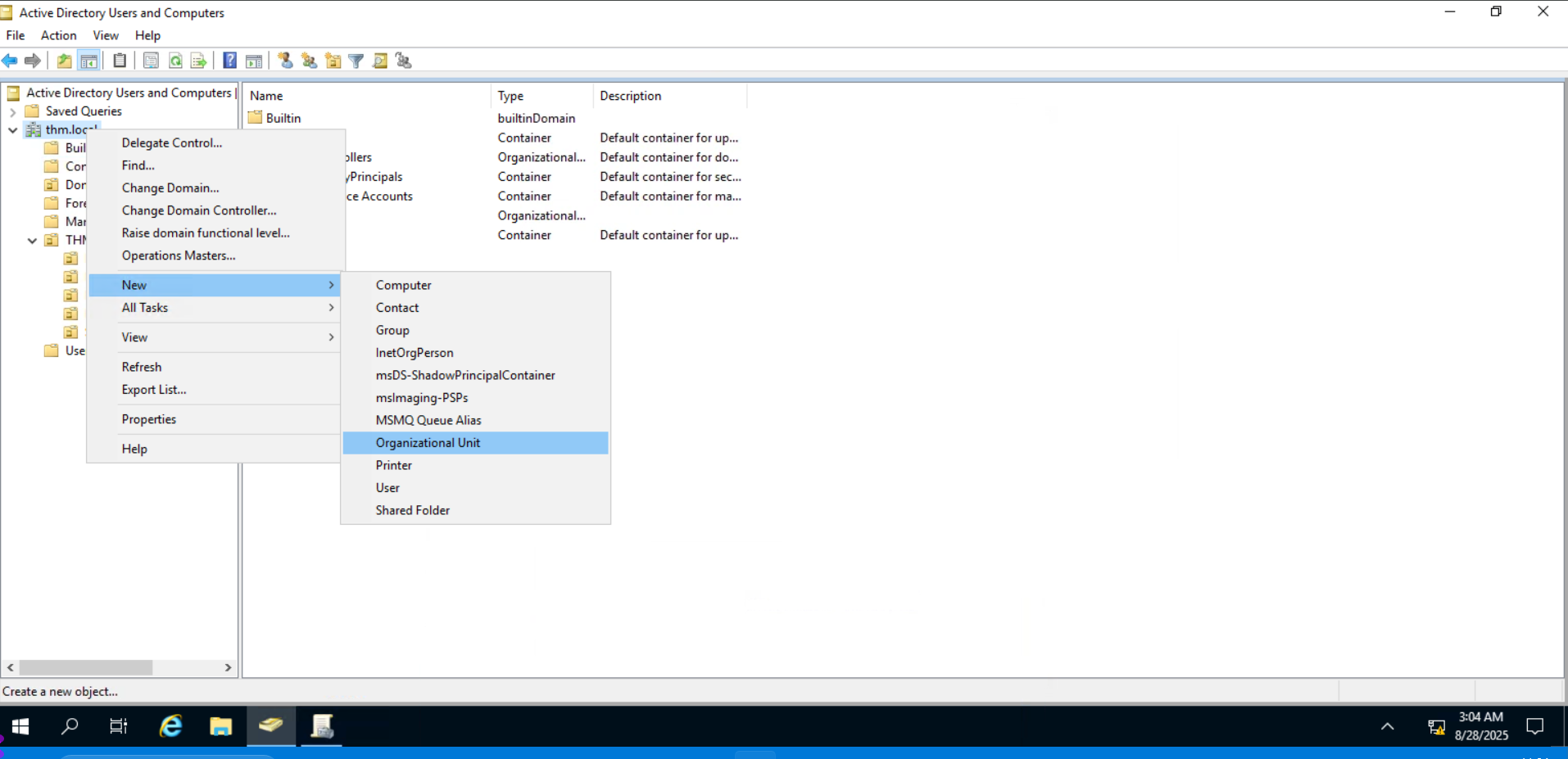
Since we are tidying up our AD, let's create two separate OUs for Workstations and Servers (Domain Controllers are already in an OU created by Windows). We will be creating them directly under the thm.local domain container. In the end, you should have the following OU structure:
由于我们正在整理 AD, 让我们为工作站和服务器创建两个独立的 OU (域控制器已经在 Windows 创建的 OU 中)。我们将直接在 thm.local 域容器下创建它们。最后,你应该有以下 OU 结构:
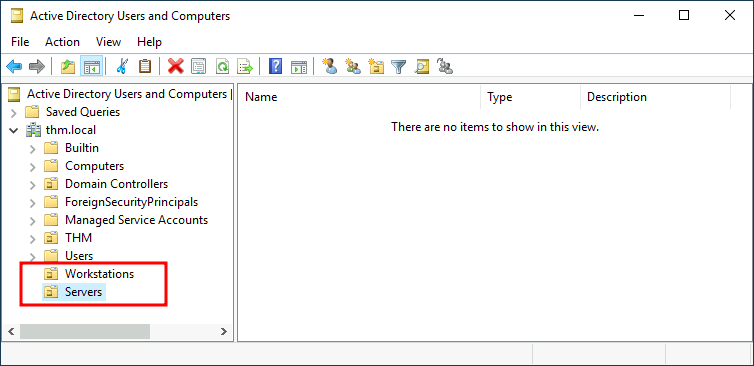
Now, move the personal computers and laptops to the Workstations OU and the servers to the Servers OU from the Computers container. Doing so will allow us to configure policies for each OU later.
现在,将个人计算机和笔记本电脑移动到工作站组,将服务器从计算机容器移动到服务器组。这样做将允许我们稍后为每个组配置策略。
问题
答案
创建工作区和服务器区
将相应电脑移动进去
通过这样创建组织单元
打开 computers
将电脑移动到工作区
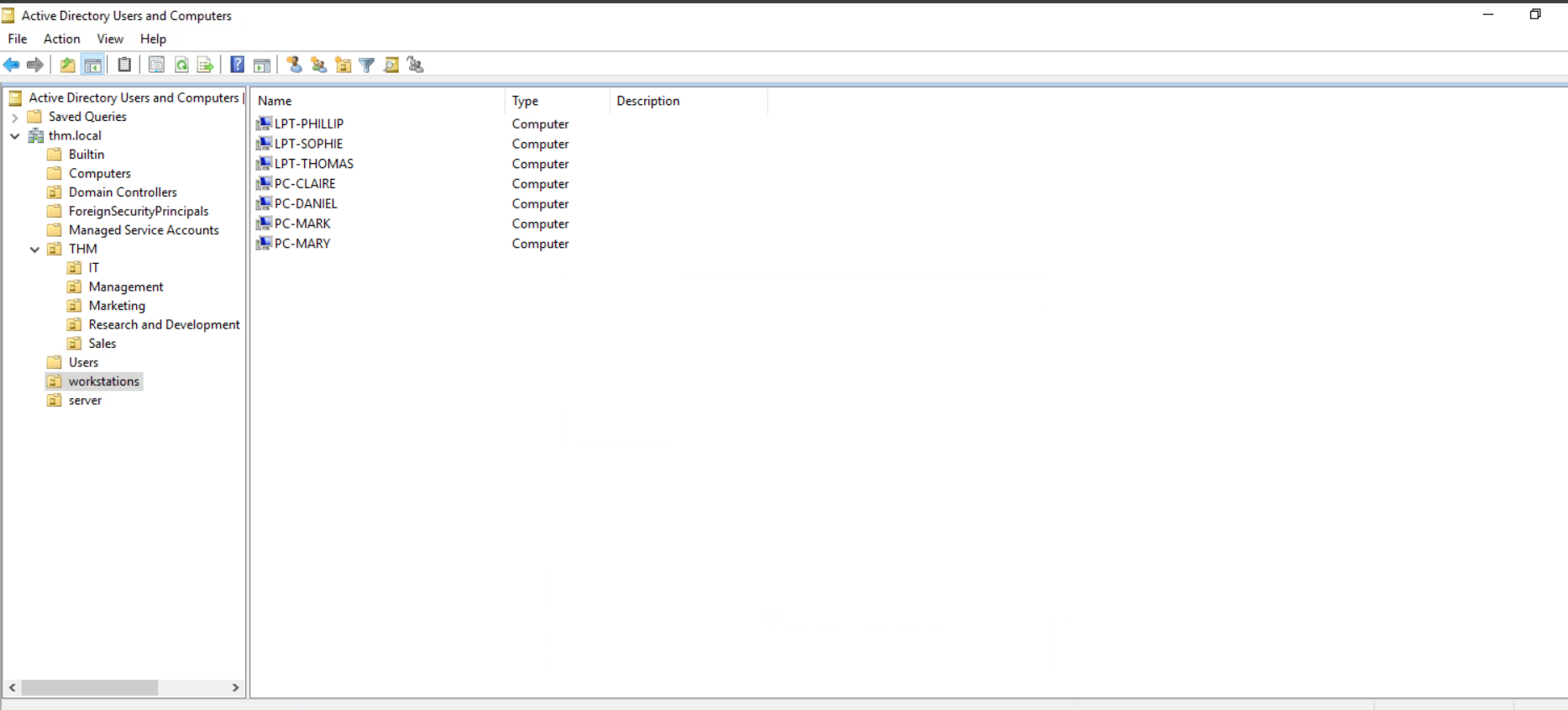
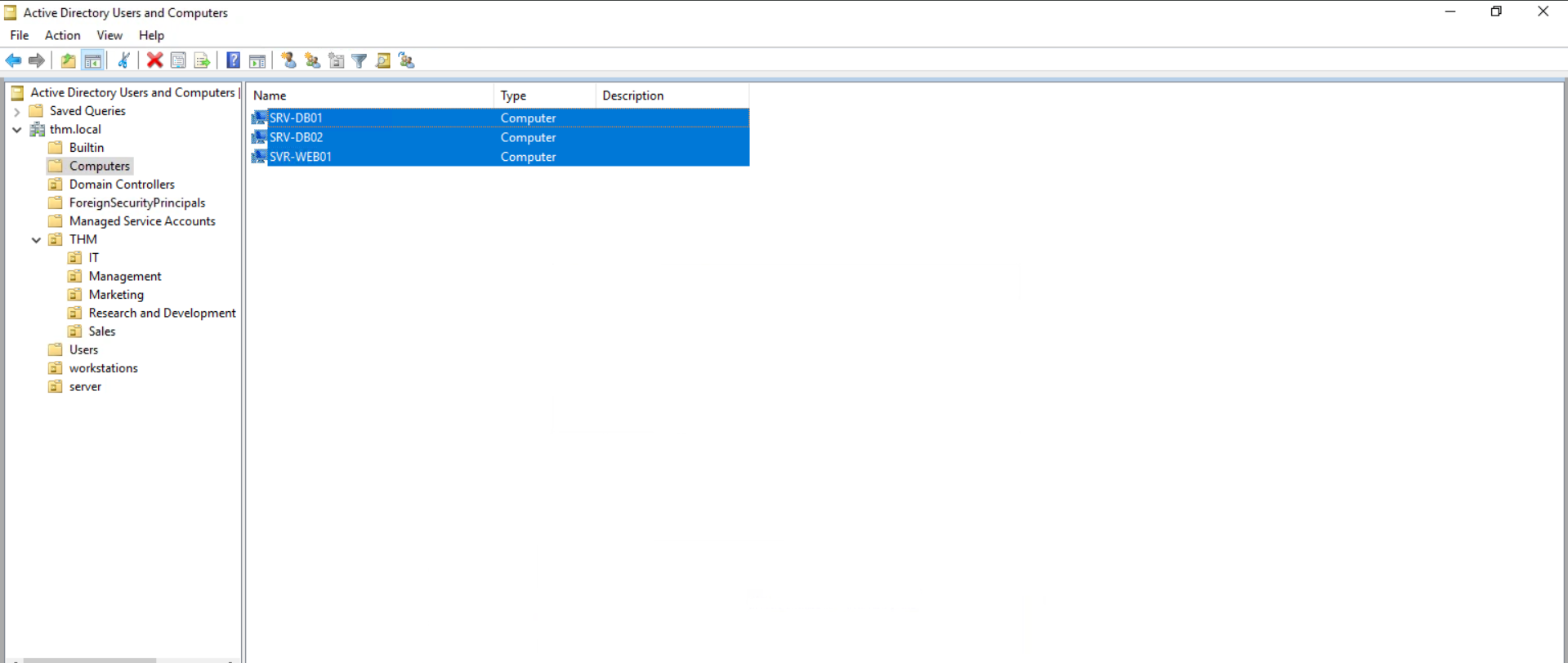
将这些移动到 server
Task6 Group Policies 组策略
图片版




文字版
So far, we have organised users and computers in OUs just for the sake of it, but the main idea behind this is to be able to deploy different policies for each OU individually. That way, we can push different configurations and security baselines to users depending on their department.
到目前为止,我们仅仅是为了这个目的而组织用户和计算机进入 OU, 但这背后的主要想法是能够为每个 OU 单独部署不同的策略。这样,我们就可以根据用户所在的部门,向他们推送不同的配置和安全基线。
Windows manages such policies through Group Policy Objects (GPO). GPOs are simply a collection of settings that can be applied to OUs. GPOs can contain policies aimed at either users or computers, allowing you to set a baseline on specific machines and identities.
Windows 通过组策略对象 (GPO) 管理这些策略。GPO 仅仅是可以应用于 OU 的设置集合。GPO 可以包含针对用户或计算机的策略,允许您为特定的机器和身份设定基线。
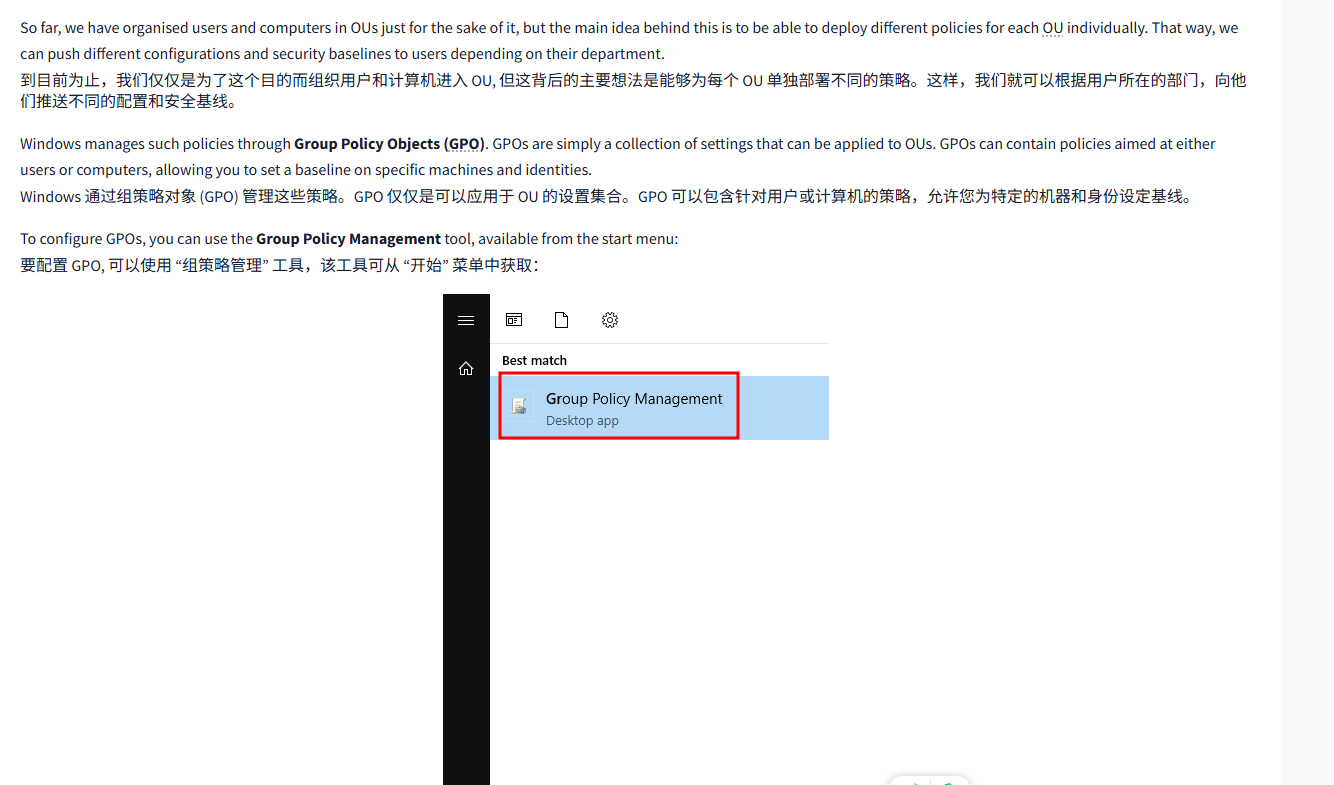
To configure GPOs, you can use the Group Policy Management tool, available from the start menu:
要配置 GPO, 可以使用 “组策略管理” 工具,该工具可从 “开始” 菜单中获取:

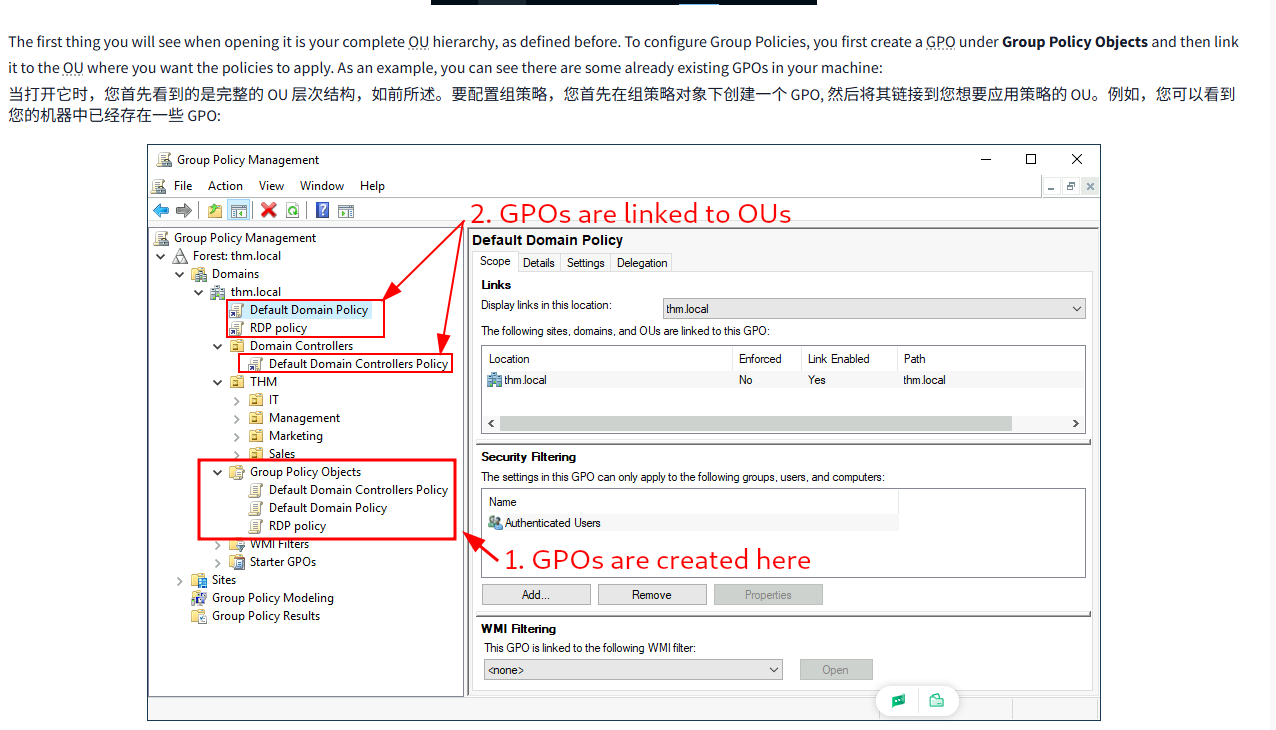
The first thing you will see when opening it is your complete OU hierarchy, as defined before. To configure Group Policies, you first create a GPO under Group Policy Objects and then link it to the OU where you want the policies to apply. As an example, you can see there are some already existing GPOs in your machine:
当打开它时,您首先看到的是完整的 OU 层次结构,如前所述。要配置组策略,您首先在组策略对象下创建一个 GPO, 然后将其链接到您想要应用策略的 OU。例如,您可以看到您的机器中已经存在一些 GPO:
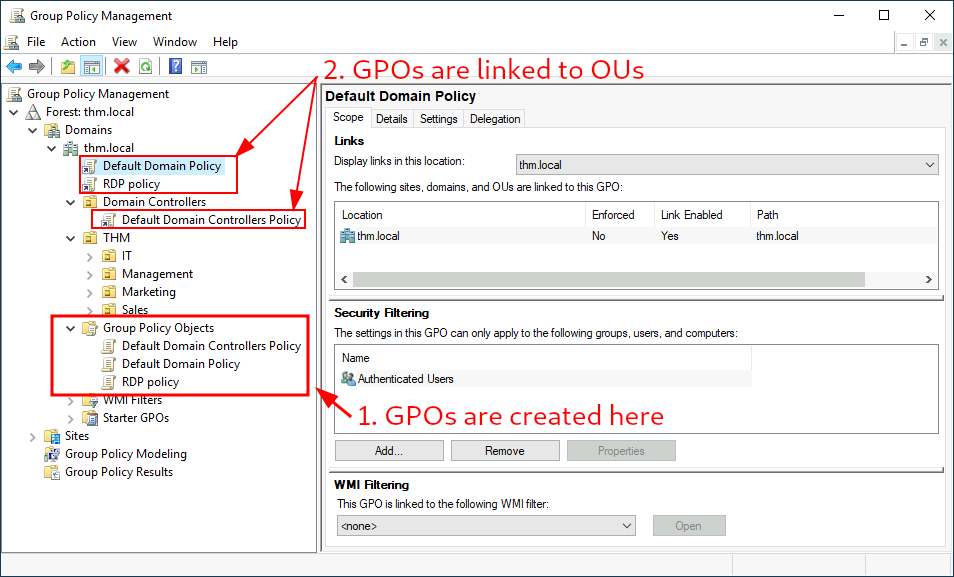
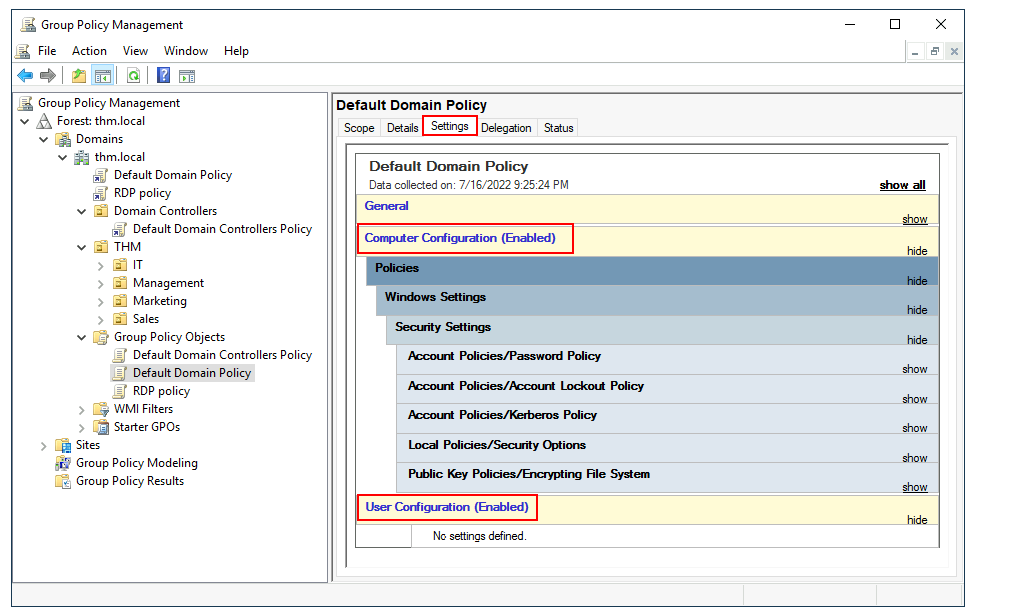
We can see in the image above that 3 GPOs have been created. From those, the Default Domain Policy and RDP Policy are linked to the thm.local domain as a whole, and the Default Domain Controllers Policy is linked to the Domain Controllers OU only. Something important to have in mind is that any GPO will apply to the linked OU and any sub-OUs under it. For example, the Sales OU will still be affected by the Default Domain Policy.
我们可以在上图中看到已经创建了 3 个 GPO。从这些 GPO 中,默认域策略和 RDP 策略链接到整个 thm.local 域,而默认域控制器策略仅链接到域控制器 OU。需要注意的是,任何 GPO 都将适用于链接的 OU 及其下的任何子 OU。例如,销售 OU 仍将受到默认域策略的影响。
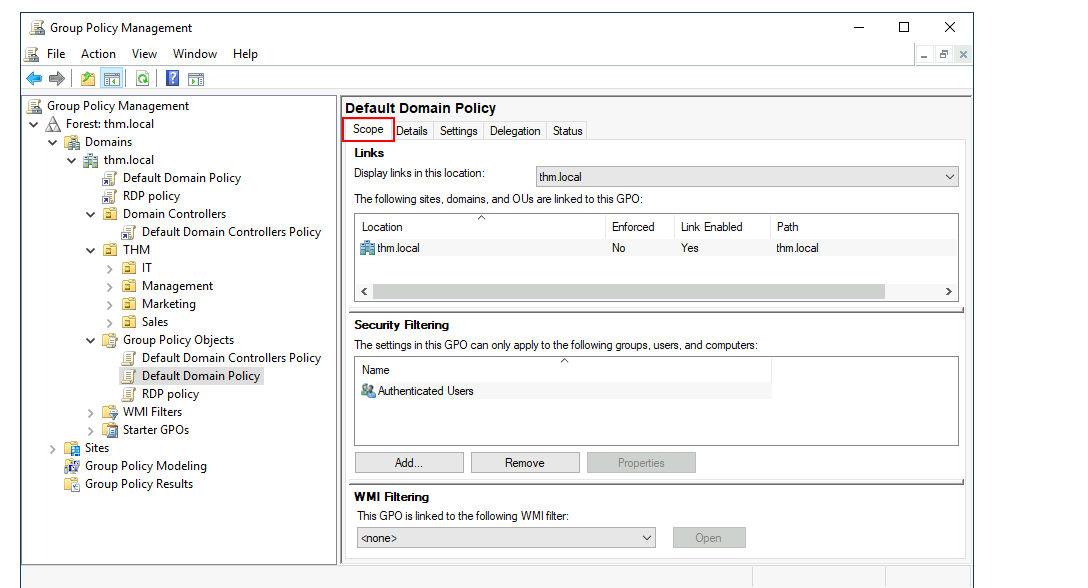
Let's examine the Default Domain Policy to see what's inside a GPO. The first tab you'll see when selecting a GPO shows its scope, which is where the GPO is linked in the AD. For the current policy, we can see that it has only been linked to the thm.local domain:
让我们查看默认域策略,以了解 GPO 内部的情况。选择 GPO 时,你看到的第一个选项卡显示了其范围,即 GPO 在 AD 中链接的位置。对于当前策略,我们可以看到它只链接到了 thm.local 域:
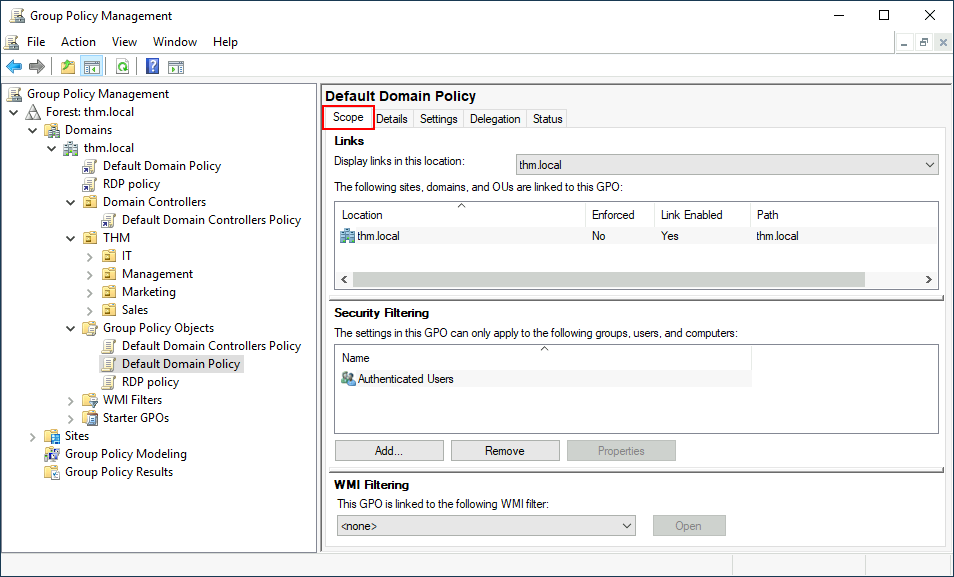
As you can see, you can also apply Security Filtering to GPOs so that they are only applied to specific users/computers under an OU. By default, they will apply to the Authenticated Users group, which includes all users/PCs.
如您所见,您还可以将安全过滤应用于 GPO, 使其仅应用于 OU 下的特定用户 / 计算机。默认情况下,它们将应用于 Authenticated Users 组,该组包括所有用户 / PC。
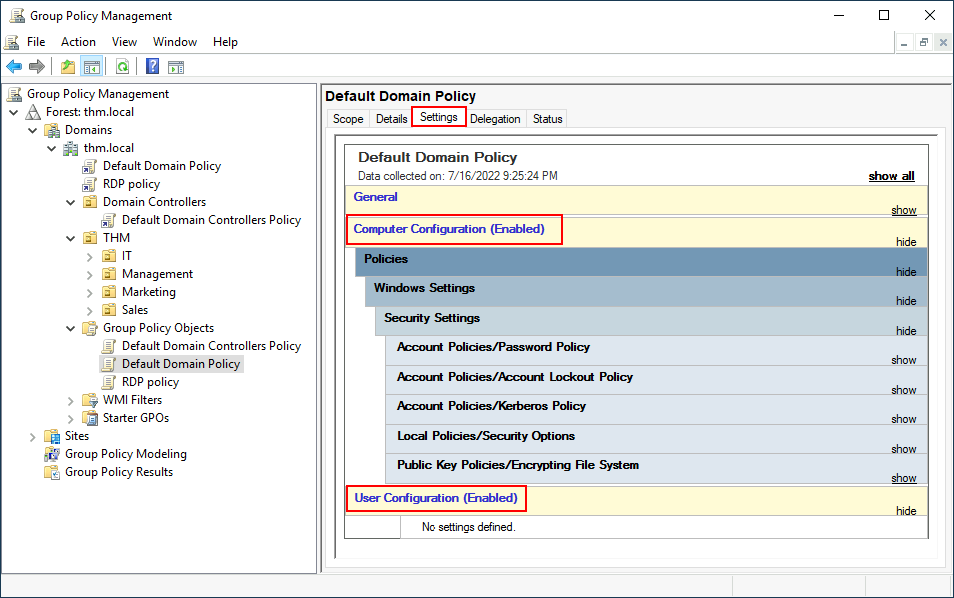
The Settings tab includes the actual contents of the GPO and lets us know what specific configurations it applies. As stated before, each GPO has configurations that apply to computers only and configurations that apply to users only. In this case, the Default Domain Policy only contains Computer Configurations:
“设置” 选项卡包含 GPO 的实际内容,并让我们了解它应用的具体配置。如前所述,每个 GPO 都有仅适用于计算机的配置和仅适用于用户的配置。在这种情况下,默认域策略仅包含计算机配置:
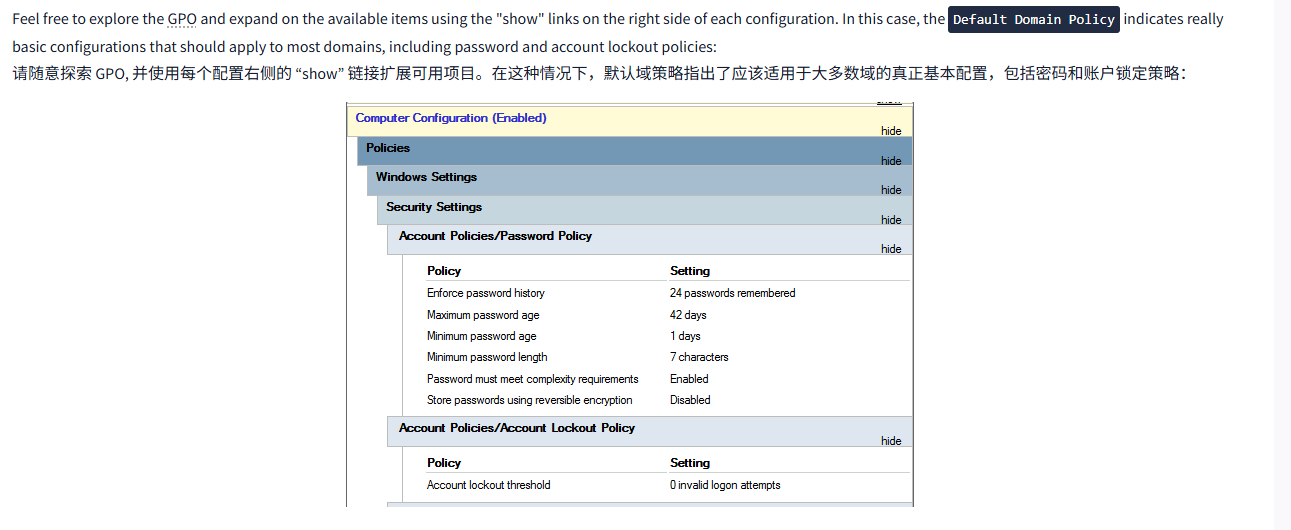
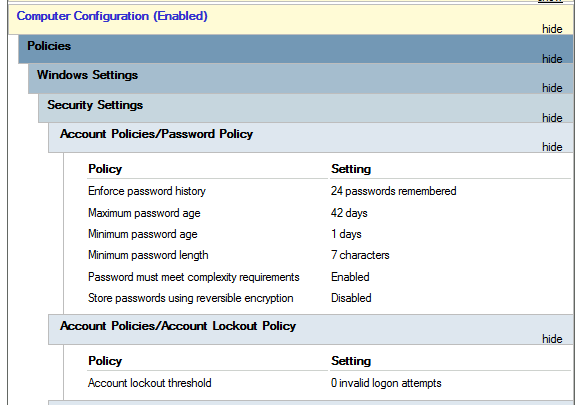
Feel free to explore the GPO and expand on the available items using the "show" links on the right side of each configuration. In this case, the Default Domain Policy indicates really basic configurations that should apply to most domains, including password and account lockout policies:
请随意探索 GPO, 并使用每个配置右侧的 “show” 链接扩展可用项目。在这种情况下,默认域策略指出了应该适用于大多数域的真正基本配置,包括密码和账户锁定策略:
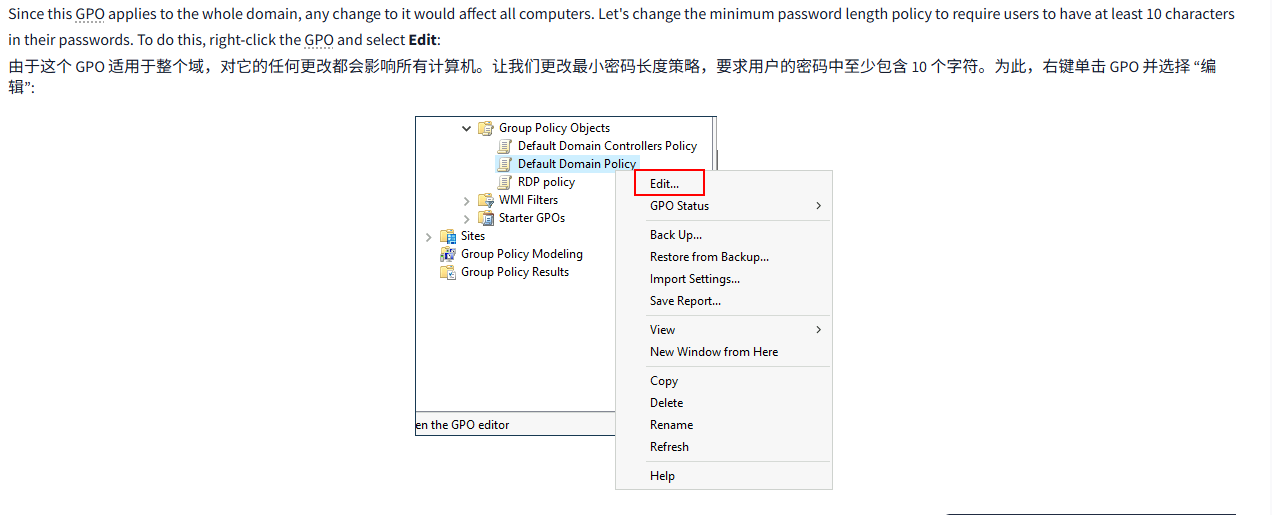
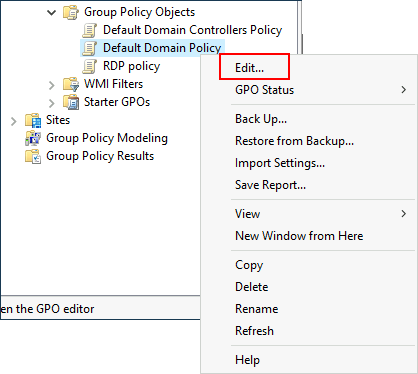
Since this GPO applies to the whole domain, any change to it would affect all computers. Let's change the minimum password length policy to require users to have at least 10 characters in their passwords. To do this, right-click the GPO and select Edit:
由于这个 GPO 适用于整个域,对它的任何更改都会影响所有计算机。让我们更改最小密码长度策略,要求用户的密码中至少包含 10 个字符。为此,右键单击 GPO 并选择 “编辑”:
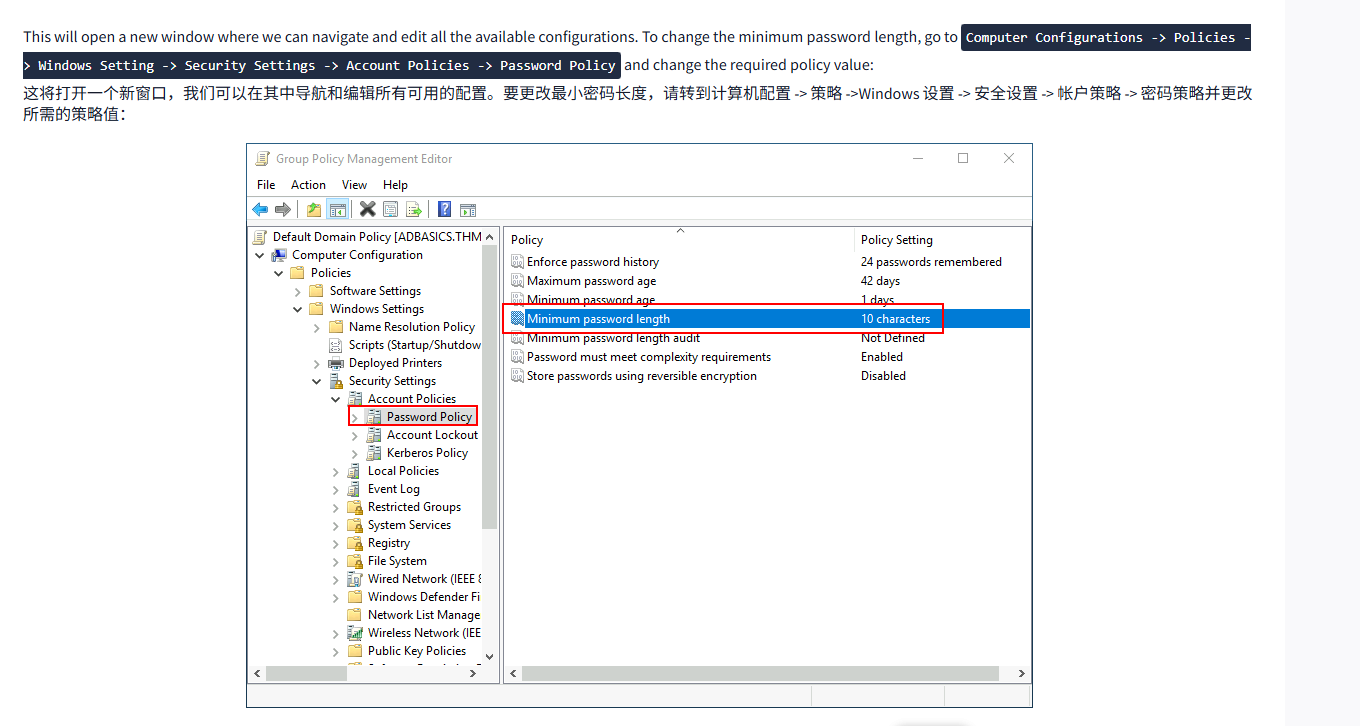
This will open a new window where we can navigate and edit all the available configurations. To change the minimum password length, go to Computer Configurations -> Policies -> Windows Setting -> Security Settings -> Account Policies -> Password Policy and change the required policy value:
这将打开一个新窗口,我们可以在其中导航和编辑所有可用的配置。要更改最小密码长度,请转到计算机配置 -> 策略 ->Windows 设置 -> 安全设置 -> 帐户策略 -> 密码策略并更改所需的策略值:
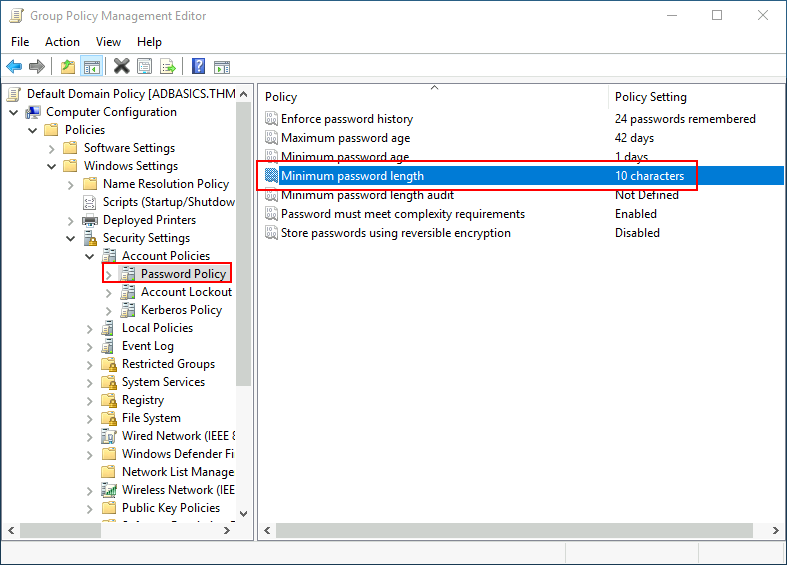
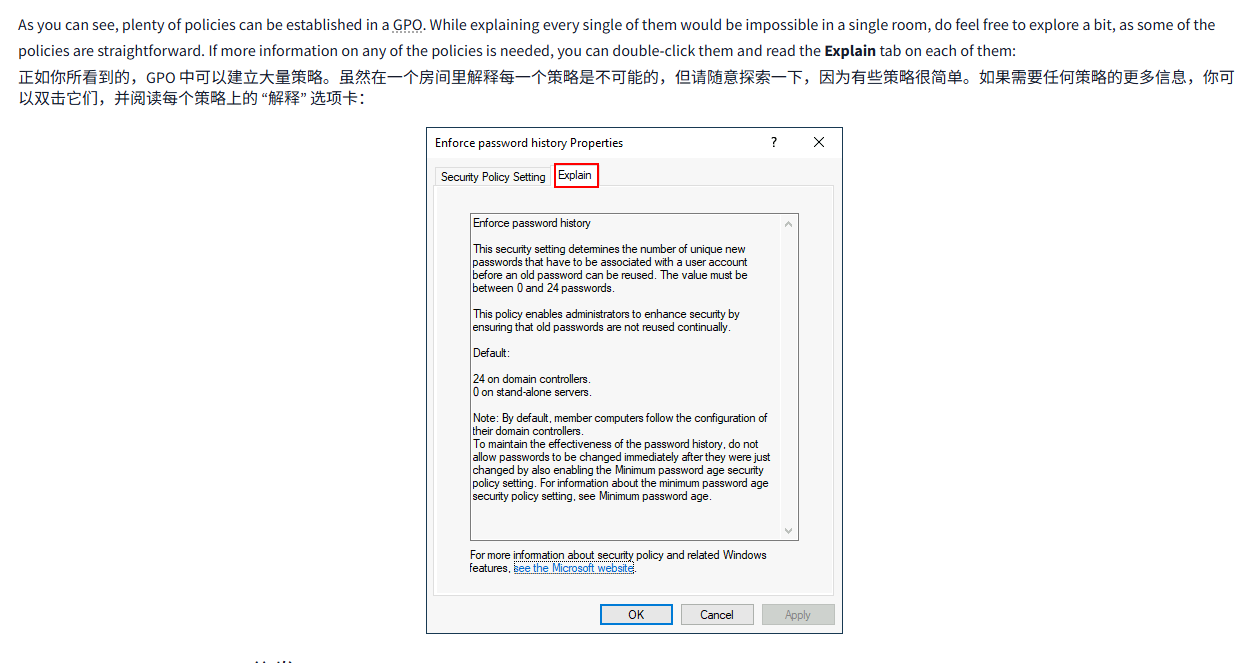
As you can see, plenty of policies can be established in a GPO. While explaining every single of them would be impossible in a single room, do feel free to explore a bit, as some of the policies are straightforward. If more information on any of the policies is needed, you can double-click them and read the Explain tab on each of them:
正如你所看到的,GPO 中可以建立大量策略。虽然在一个房间里解释每一个策略是不可能的,但请随意探索一下,因为有些策略很简单。如果需要任何策略的更多信息,你可以双击它们,并阅读每个策略上的 “解释” 选项卡:
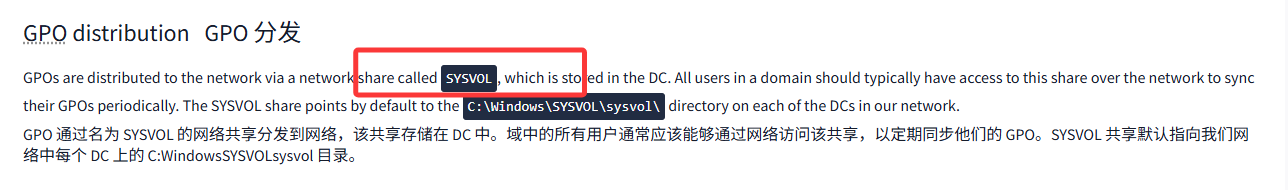
GPO distributionGPO 分发
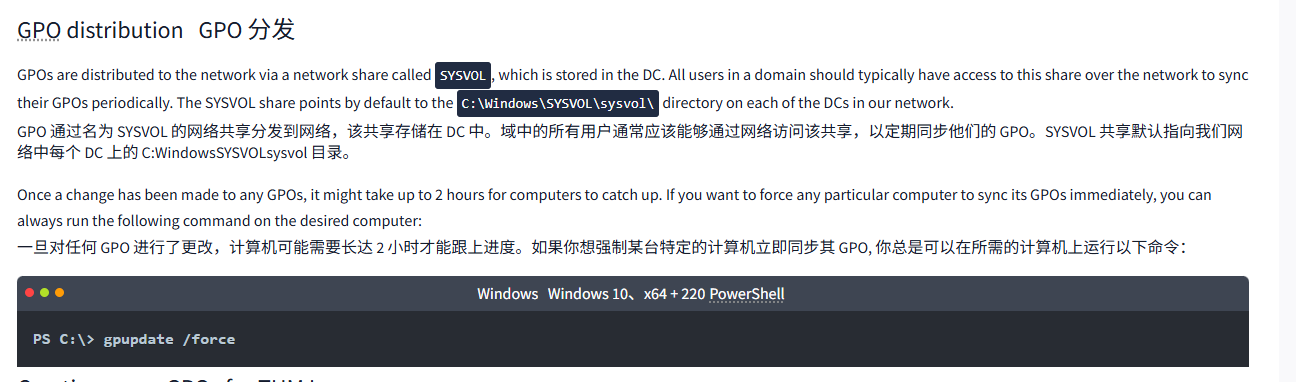
GPOs are distributed to the network via a network share called SYSVOL, which is stored in the DC. All users in a domain should typically have access to this share over the network to sync their GPOs periodically. The SYSVOL share points by default to the C:\Windows\SYSVOL\sysvol\ directory on each of the DCs in our network.
GPO 通过名为 SYSVOL 的网络共享分发到网络,该共享存储在 DC 中。域中的所有用户通常应该能够通过网络访问该共享,以定期同步他们的 GPO。SYSVOL 共享默认指向我们网络中每个 DC 上的 C:WindowsSYSVOLsysvol 目录。
Once a change has been made to any GPOs, it might take up to 2 hours for computers to catch up. If you want to force any particular computer to sync its GPOs immediately, you can always run the following command on the desired computer:
一旦对任何 GPO 进行了更改,计算机可能需要长达 2 小时才能跟上进度。如果你想强制某台特定的计算机立即同步其 GPO, 你总是可以在所需的计算机上运行以下命令:
WindowsWindows 10、x64 + 220PowerShell
PS C:\> gpupdate /forceCreating some GPOs for THM Inc.
为 THM 公司创建一些 GPO。
As part of our new job, we have been tasked with implementing some GPOs to allow us to:
作为我们新工作的一部分,我们被要求实现一些 GPO, 以便我们能够:
- Block non-IT users from accessing the Control Panel.
阻止非 IT 用户访问控制面板。 - Make workstations and servers lock their screen automatically after 5 minutes of user inactivity to avoid people leaving their sessions exposed.
让工作站和服务器在用户不活跃 5 分钟后自动锁定其屏幕,以避免人们暴露他们的会话。
Let's focus on each of those and define what policies we should enable in each GPO and where they should be linked.
让我们专注于这些策略中的每一个,并定义我们应该在每个 GPO 中启用哪些策略以及它们应该在哪里关联。
Restrict Access to Control Panel限制对控制面板的访问
We want to restrict access to the Control Panel across all machines to only the users that are part of the IT department. Users of other departments shouldn't be able to change the system's preferences.
我们希望限制只有 IT 部门的用户才能访问所有机器上的控制面板。其他部门的用户应该无法更改系统偏好设置。
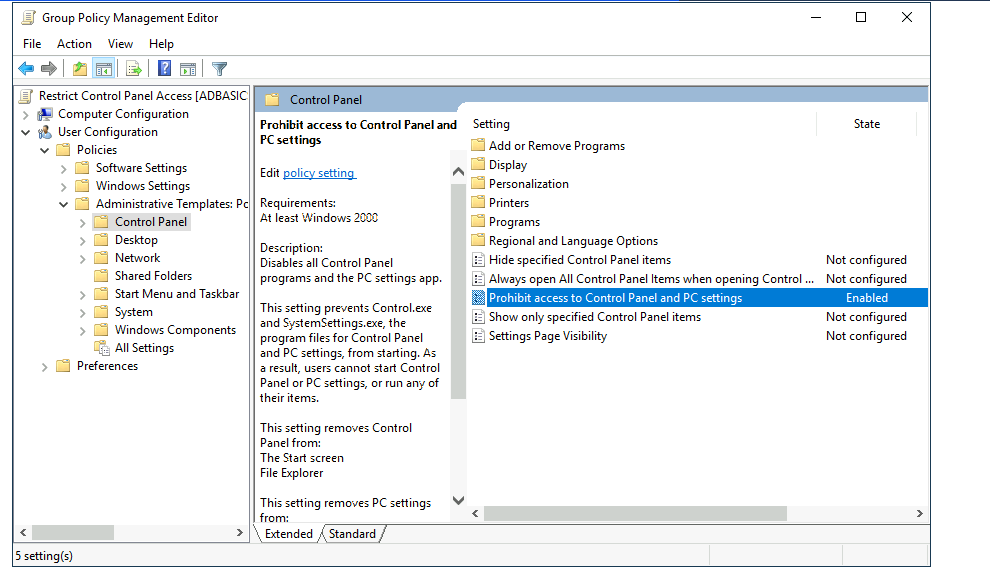
Let's create a new GPO called Restrict Control Panel Access and open it for editing. Since we want this GPO to apply to specific users, we will look under User Configuration for the following policy:
让我们创建一个名为 Restrict Control Panel Access 的新 GPO, 并打开它进行编辑。由于我们希望这个 GPO 适用于特定用户,我们将在 “用户配置” 下查看以下策略:
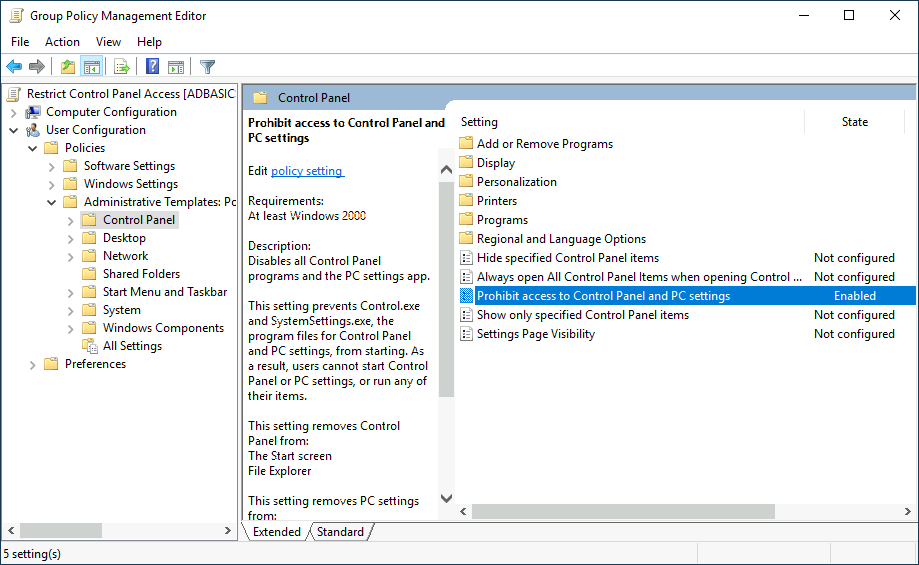
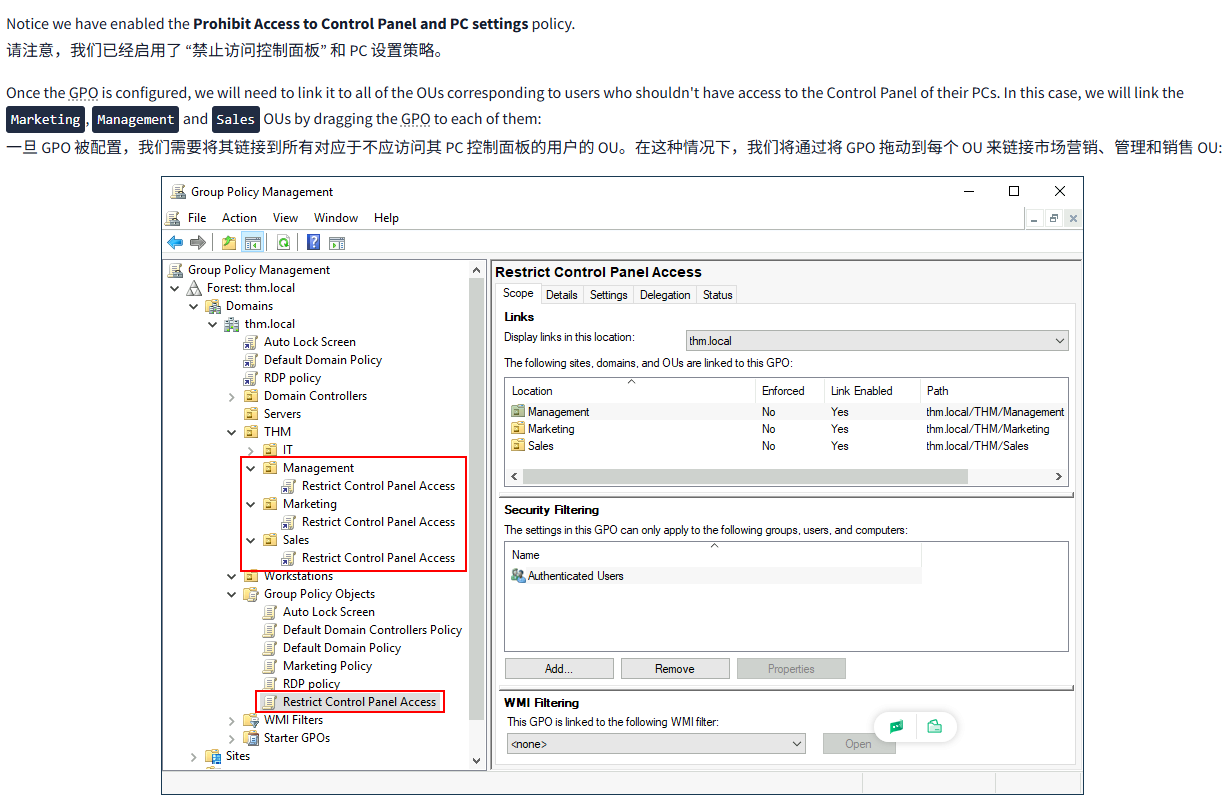
Notice we have enabled the Prohibit Access to Control Panel and PC settings policy.
请注意,我们已经启用了 “禁止访问控制面板” 和 PC 设置策略。
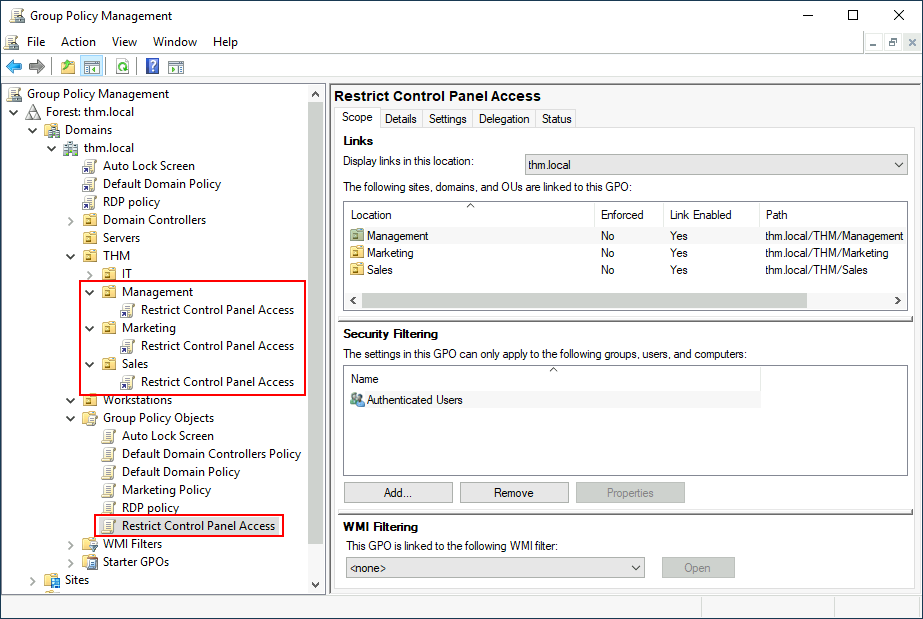
Once the GPO is configured, we will need to link it to all of the OUs corresponding to users who shouldn't have access to the Control Panel of their PCs. In this case, we will link the Marketing, Management and Sales OUs by dragging the GPO to each of them:
一旦 GPO 被配置,我们需要将其链接到所有对应于不应访问其 PC 控制面板的用户的 OU。在这种情况下,我们将通过将 GPO 拖动到每个 OU 来链接市场营销、管理和销售 OU:
Auto Lock Screen GPO自动锁定屏幕 GPO
For the first GPO, regarding screen locking for workstations and servers, we could directly apply it over the Workstations, Servers and Domain Controllers OUs we created previously.
对于第一个 GPO, 关于工作站和服务器的屏幕锁定,我们可以直接在之前创建的工作站、服务器和域控制器 OU 上应用它。
While this solution should work, an alternative consists of simply applying the GPO to the root domain, as we want the GPO to affect all of our computers. Since the Workstations, Servers and Domain Controllers OUs are all child OUs of the root domain, they will inherit its policies.
虽然这个解决方案应该可行,但另一种选择是简单地将 GPO 应用于根域,因为我们希望 GPO 影响我们所有的计算机。由于工作站、服务器和域控制器 OU 都是根域的子 OU, 它们将继承其策略。
Note: You might notice that if our GPO is applied to the root domain, it will also be inherited by other OUs like Sales or Marketing. Since these OUs contain users only, any Computer Configuration in our GPO will be ignored by them.
注意:您可能会注意到,如果我们的 GPO 应用于根域,它也会被其他 OU (如销售或营销) 继承。由于这些 OU 只包含用户,因此我们 GPO 中的任何计算机配置都将被它们忽略。
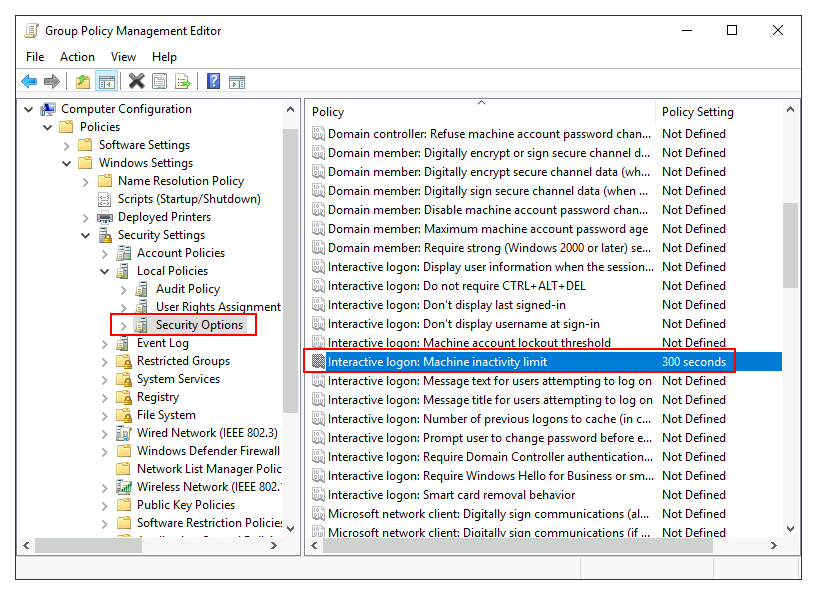
Let's create a new GPO, call it Auto Lock Screen, and edit it. The policy to achieve what we want is located in the following route:
让我们创建一个新的 GPO, 将其命名为 “自动锁定屏幕”, 并对其进行编辑。实现我们所需要的策略位于以下路径中:
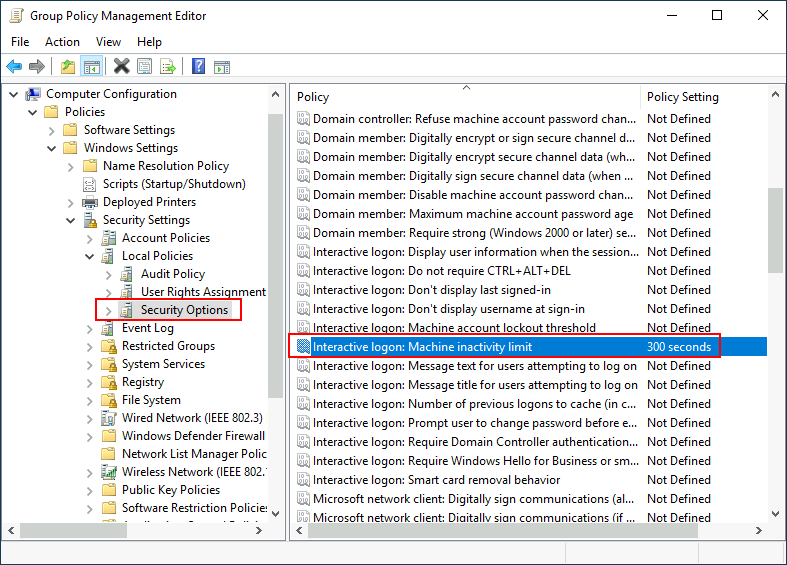
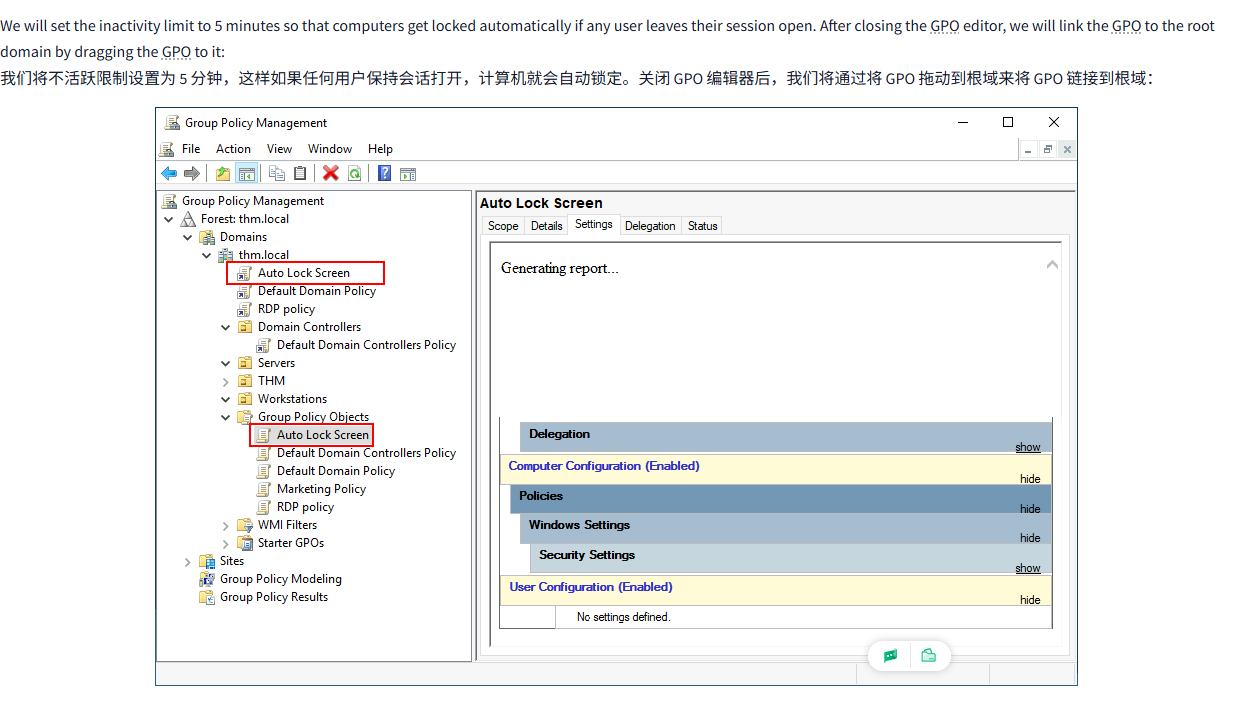
We will set the inactivity limit to 5 minutes so that computers get locked automatically if any user leaves their session open. After closing the GPO editor, we will link the GPO to the root domain by dragging the GPO to it:
我们将不活跃限制设置为 5 分钟,这样如果任何用户保持会话打开,计算机就会自动锁定。关闭 GPO 编辑器后,我们将通过将 GPO 拖动到根域来将 GPO 链接到根域:
Once the GPOs have been applied to the correct OUs, we can log in as any users in either Marketing, Sales or Management for verification. For this task, let's connect via RDP using Mark's credentials:
一旦 GPO 应用于正确的 OU, 我们就可以作为任何用户登录到市场营销、销售或管理系统进行验证。对于这项任务,让我们使用 Mark 的凭证通过 RDP 连接:

| Username 用户名 | Mark马克 |
| Password 密码 | M4rk3t1ng.21 |
Note: When connecting via RDP, use THM\Mark as the username to specify you want to log in using the user Mark on the THM domain.
注意:当通过 RDP 连接时,使用 THMMark 作为用户名,指定您想要使用 THM 域中的用户 Mark 登录。
If we try opening the Control Panel, we should get a message indicating this operation is denied by the administrator. You can also wait 5 minutes to check if the screen is automatically locked if you want.
如果我们尝试打开控制面板,我们应该会收到一条消息,指出此操作被管理员拒绝。如果您愿意,您也可以等待 5 分钟来检查屏幕是否自动锁定。
Since we didn't apply the control panel GPO on IT, you should still be able to log into the machine as any of those users and access the control panel.
由于我们没有在 IT 上应用控制面板 GPO, 您应该仍然能够以这些用户的身份登录机器并访问控制面板。
Note: If you created and linked the GPOs, but for some reason, they still don't work, remember you can run gpupdate /force to force GPOs to be updated.
注意:如果您创建并链接了 GPO, 但由于某种原因,它们仍然无法工作,请记住可以运行 gpupdate /force 来强制更新 GPO。
问题
答案
Task7 Authentication Methods 认证方法
图片版


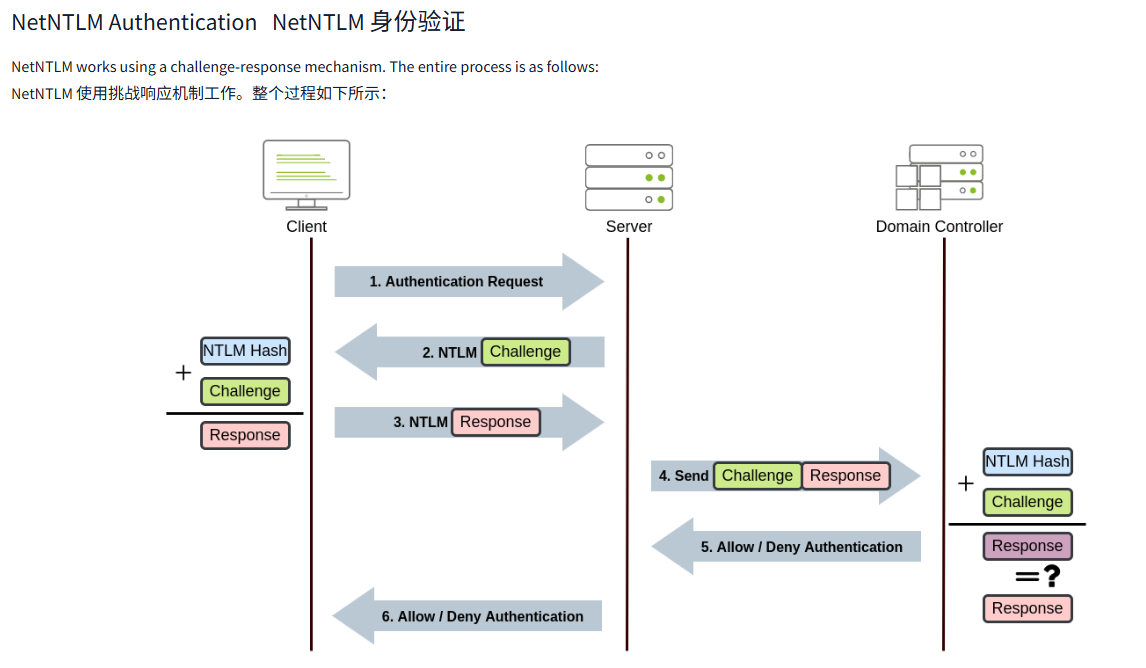

文字版
When using Windows domains, all credentials are stored in the Domain Controllers. Whenever a user tries to authenticate to a service using domain credentials, the service will need to ask the Domain Controller to verify if they are correct. Two protocols can be used for network authentication in windows domains:
使用 Windows 域时,所有凭据都存储在网域控制器中。每当用户尝试使用域凭据对服务进行身份验证时,服务都需要请求网域控制器验证凭据是否正确。可以使用两种协议在 Windows 域中进行网络身份验证:
- Kerberos: Used by any recent version of Windows. This is the default protocol in any recent domain.
Kerberos: 由任何最新版本的 Windows 使用。这是任何最新域的默认协议。 - NetNTLM: Legacy authentication protocol kept for compatibility purposes.
NetNTLM: 出于兼容性考虑,保留了传统认证协议。
While NetNTLM should be considered obsolete, most networks will have both protocols enabled. Let's take a deeper look at how each of these protocols works.
虽然 NetNTLM 应该被认为是过时的,但大多数网络都会启用这两种协议。让我们深入了解一下这两种协议的工作原理。
Kerberos AuthenticationKerberos 认证
Kerberos authentication is the default authentication protocol for any recent version of Windows. Users who log into a service using Kerberos will be assigned tickets. Think of tickets as proof of a previous authentication. Users with tickets can present them to a service to demonstrate they have already authenticated into the network before and are therefore enabled to use it.
Kerberos 身份验证是任何最新版本 Windows 的默认身份验证协议。使用 Kerberos 登录服务的用户将被分配票证。将票证视为之前身份验证的证明。持有票证的用户可以将其提交给服务,以证明他们之前已经对网络进行过身份验证,因此可以使用该网络。
When Kerberos is used for authentication, the following process happens:
当 Kerberos 用于身份验证时,会发生以下过程:
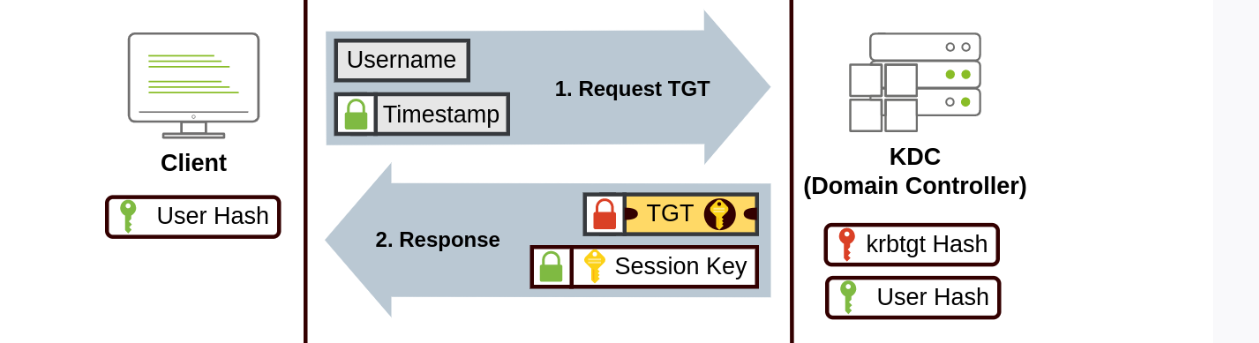
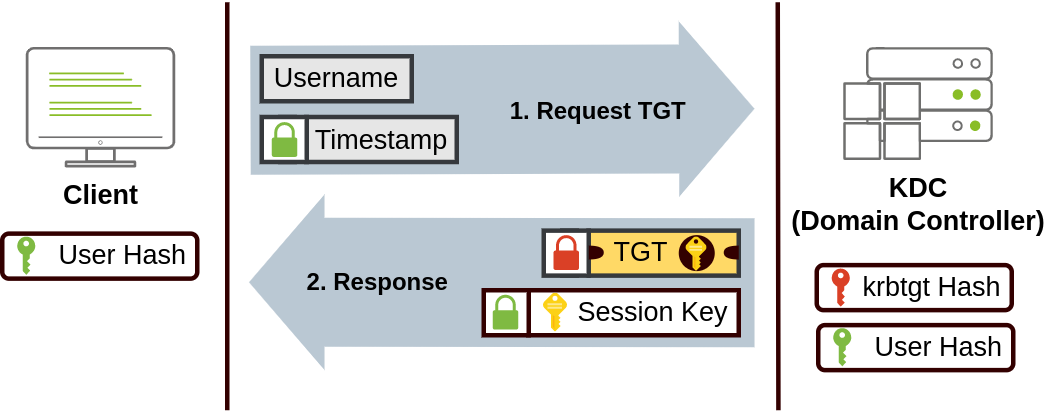
- The user sends their username and a timestamp encrypted using a key derived from their password to the Key Distribution Center (KDC), a service usually installed on the Domain Controller in charge of creating Kerberos tickets on the network.
用户将其用户名和时间戳发送到密钥分发中心 (KDC),该服务通常安装在网域控制器上,负责在网络上创建 Kerberos 票证。
The KDC will create and send back a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT), which will allow the user to request additional tickets to access specific services. The need for a ticket to get more tickets may sound a bit weird, but it allows users to request service tickets without passing their credentials every time they want to connect to a service. Along with the TGT, a Session Key is given to the user, which they will need to generate the following requests.
KDC 将创建并返回一个票证授予票证 (TGT), 该票证将允许用户请求额外的票证以访问特定服务。用一张票证获取更多票证的需求可能听起来有点奇怪,但它允许用户在每次想要连接到服务时请求服务票证,而无需传递他们的凭证。除了 TGT 外,还会向用户提供一个会话密钥,他们将需要该密钥来生成以下请求。
Notice the TGT is encrypted using the krbtgt account's password hash, and therefore the user can't access its contents. It is essential to know that the encrypted TGT includes a copy of the Session Key as part of its contents, and the KDC has no need to store the Session Key as it can recover a copy by decrypting the TGT if needed.
请注意,TGT 是使用 krbtgt 账户的密码哈希进行加密的,因此用户无法访问其内容。重要的是要知道,加密的 TGT 包含会话密钥的副本作为其内容的一部分,KDC 不需要存储会话密钥,因为如果需要,它可以通过解密 TGT 来恢复副本。
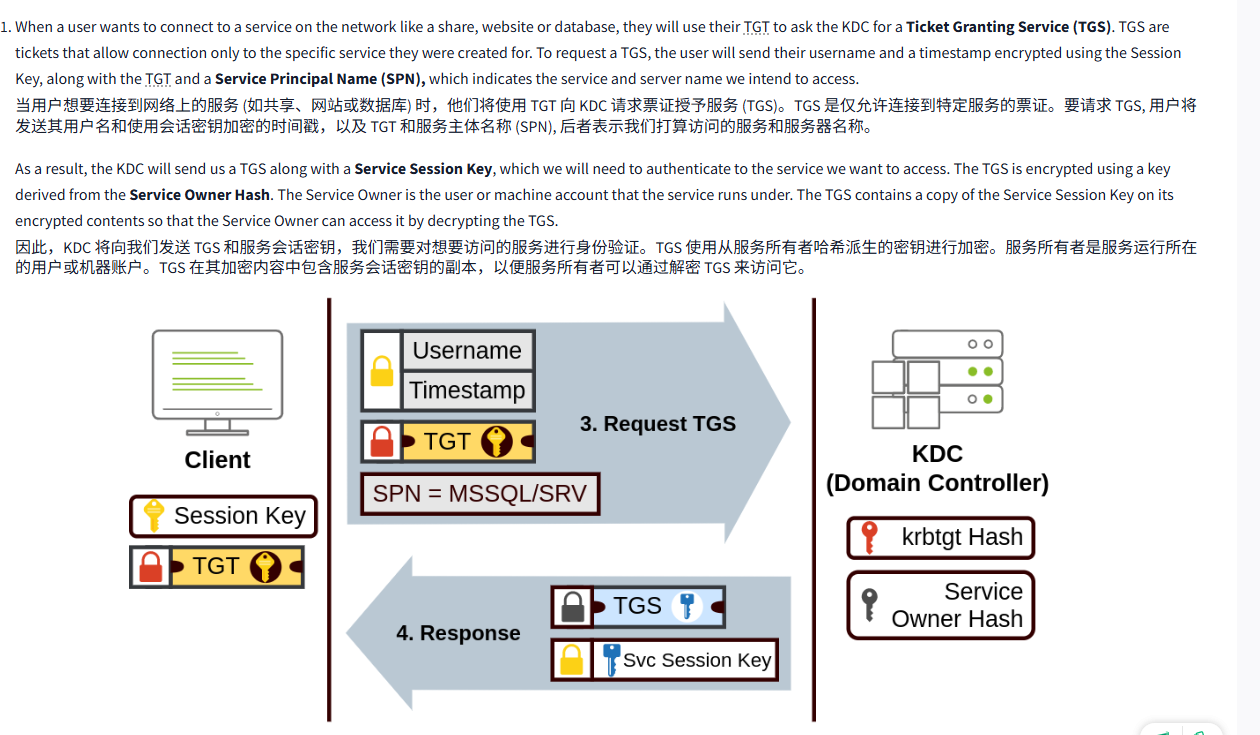
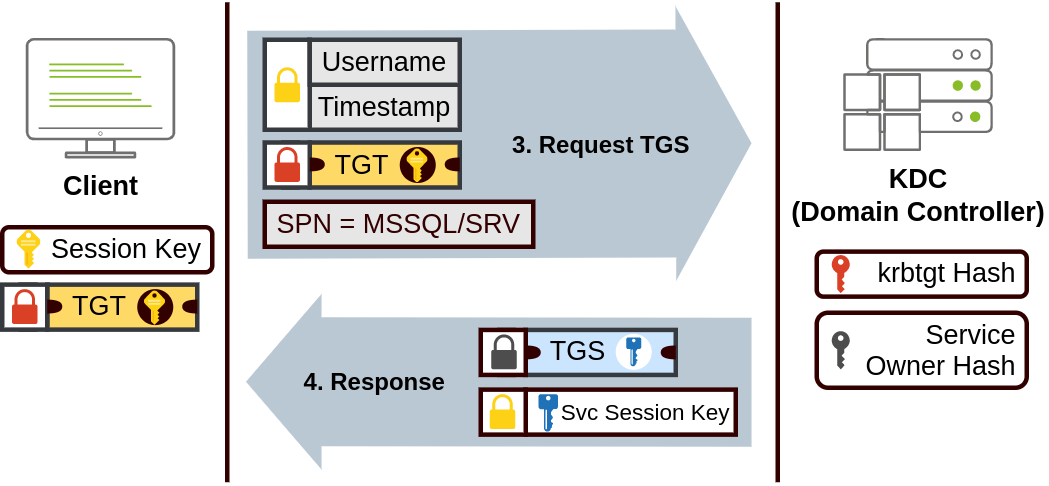
- When a user wants to connect to a service on the network like a share, website or database, they will use their TGT to ask the KDC for a Ticket Granting Service (TGS). TGS are tickets that allow connection only to the specific service they were created for. To request a TGS, the user will send their username and a timestamp encrypted using the Session Key, along with the TGT and a Service Principal Name (SPN), which indicates the service and server name we intend to access.
当用户想要连接到网络上的服务 (如共享、网站或数据库) 时,他们将使用 TGT 向 KDC 请求票证授予服务 (TGS)。TGS 是仅允许连接到特定服务的票证。要请求 TGS, 用户将发送其用户名和使用会话密钥加密的时间戳,以及 TGT 和服务主体名称 (SPN), 后者表示我们打算访问的服务和服务器名称。
As a result, the KDC will send us a TGS along with a Service Session Key, which we will need to authenticate to the service we want to access. The TGS is encrypted using a key derived from the Service Owner Hash. The Service Owner is the user or machine account that the service runs under. The TGS contains a copy of the Service Session Key on its encrypted contents so that the Service Owner can access it by decrypting the TGS.
因此,KDC 将向我们发送 TGS 和服务会话密钥,我们需要对想要访问的服务进行身份验证。TGS 使用从服务所有者哈希派生的密钥进行加密。服务所有者是服务运行所在的用户或机器账户。TGS 在其加密内容中包含服务会话密钥的副本,以便服务所有者可以通过解密 TGS 来访问它。
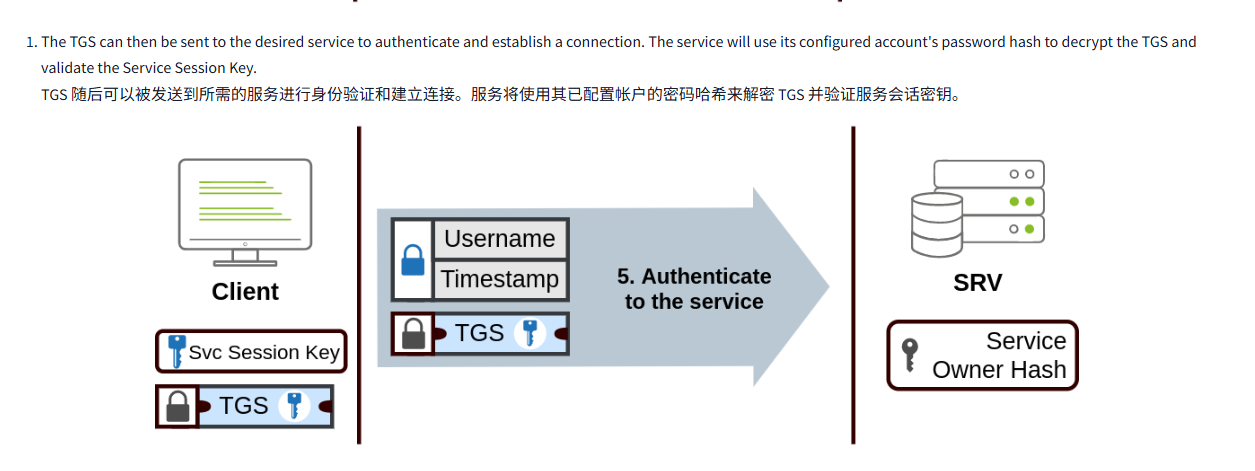
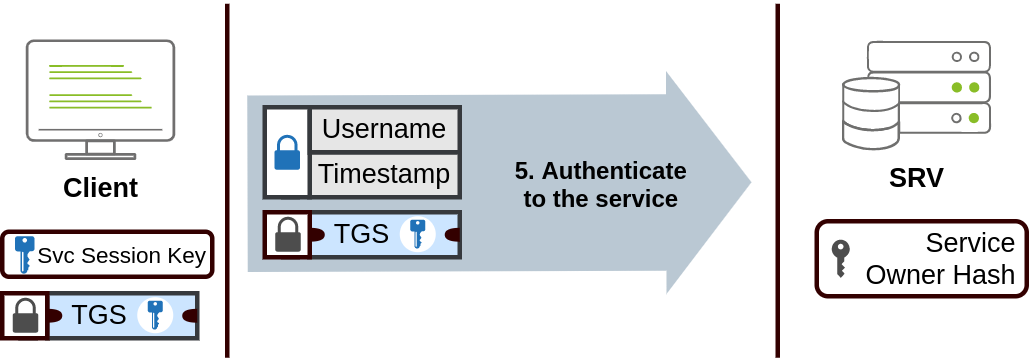
- The TGS can then be sent to the desired service to authenticate and establish a connection. The service will use its configured account's password hash to decrypt the TGS and validate the Service Session Key.
TGS 随后可以被发送到所需的服务进行身份验证和建立连接。服务将使用其已配置帐户的密码哈希来解密 TGS 并验证服务会话密钥。
NetNTLM AuthenticationNetNTLM 身份验证
NetNTLM works using a challenge-response mechanism. The entire process is as follows:
NetNTLM 使用挑战响应机制工作。整个过程如下所示:
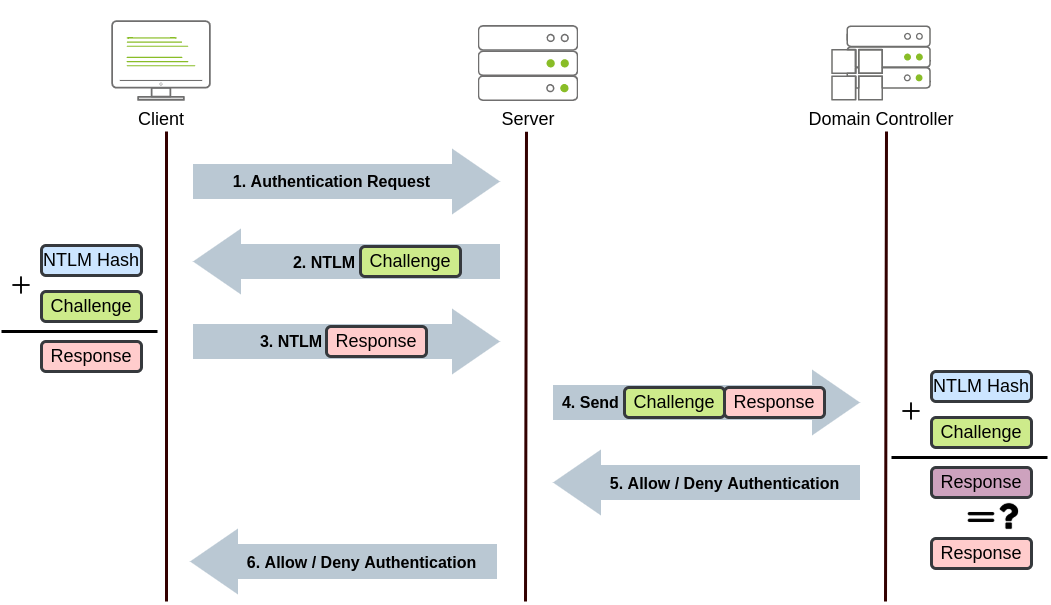
- The client sends an authentication request to the server they want to access.
客户端向它们想要访问的服务器发送身份验证请求。 - The server generates a random number and sends it as a challenge to the client.
服务器生成一个随机数,并将其作为挑战发送给客户端。 - The client combines their NTLM password hash with the challenge (and other known data) to generate a response to the challenge and sends it back to the server for verification.
客户端将其 NTLM 密码哈希值与挑战 (以及其他已知数据) 相结合,生成对挑战的响应,并将其发送回服务器进行验证。 - The server forwards the challenge and the response to the Domain Controller for verification.
服务器将挑战和响应转发给网域控制器进行验证。 - The domain controller uses the challenge to recalculate the response and compares it to the original response sent by the client. If they both match, the client is authenticated; otherwise, access is denied. The authentication result is sent back to the server.
网域控制器使用挑战重新计算响应,并将其与客户端发送的原始响应进行比较。如果两者匹配,则对客户端进行身份验证;否则,拒绝访问。身份验证结果会发送回服务器。 - The server forwards the authentication result to the client.
服务器将认证结果转发给客户端。
Note that the user's password (or hash) is never transmitted through the network for security.
请注意,出于安全考虑,用户的密码 (或哈希值) 绝不会通过网络传输。
Note: The described process applies when using a domain account. If a local account is used, the server can verify the response to the challenge itself without requiring interaction with the domain controller since it has the password hash stored locally on its SAM.
注意:使用域帐户时,描述的过程适用。如果使用本地帐户,服务器可以自行验证对挑战的响应,而无需与域控制器交互,因为它在其 SAM 上本地存储了密码哈希。
问题
答案
Task8 Trees, Forests and Trusts 树木、森林和信任
图片版




文字版
So far, we have discussed how to manage a single domain, the role of a Domain Controller and how it joins computers, servers and users.
到目前为止,我们已经讨论了如何管理单一域、域控制器的作用,以及它如何连接计算机、服务器和用户。
As companies grow, so do their networks. Having a single domain for a company is good enough to start, but in time some additional needs might push you into having more than one.
随着公司的发展,它们的网络也会随之增长。一家公司拥有一个域名已经足够好了,但随着时间的推移,一些额外的需求可能会促使你拥有多个域名。
Trees树
Imagine, for example, that suddenly your company expands to a new country. The new country has different laws and regulations that require you to update your GPOs to comply. In addition, you now have IT people in both countries, and each IT team needs to manage the resources that correspond to each country without interfering with the other team. While you could create a complex OU structure and use delegations to achieve this, having a huge AD structure might be hard to manage and prone to human errors.
例如,想象一下,你的公司突然扩展到一个新的国家。这个新国家有不同的法律法规,要求你更新你的 GPO 以符合规定。此外,你现在在两个国家都有 IT 人员,每个 IT 团队都需要管理与每个国家相应的资源,而不干扰其他团队。虽然你可以创建一个复杂的 OU 结构并使用委托来实现这一目标,但拥有庞大的 AD 结构可能很难管理,并容易出现人为错误。
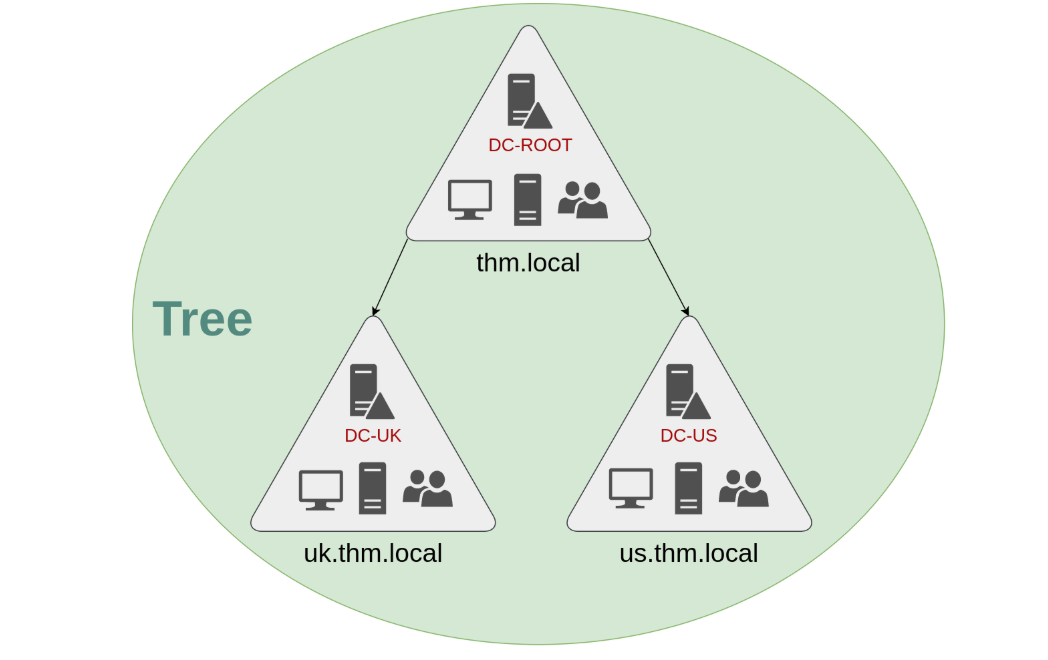
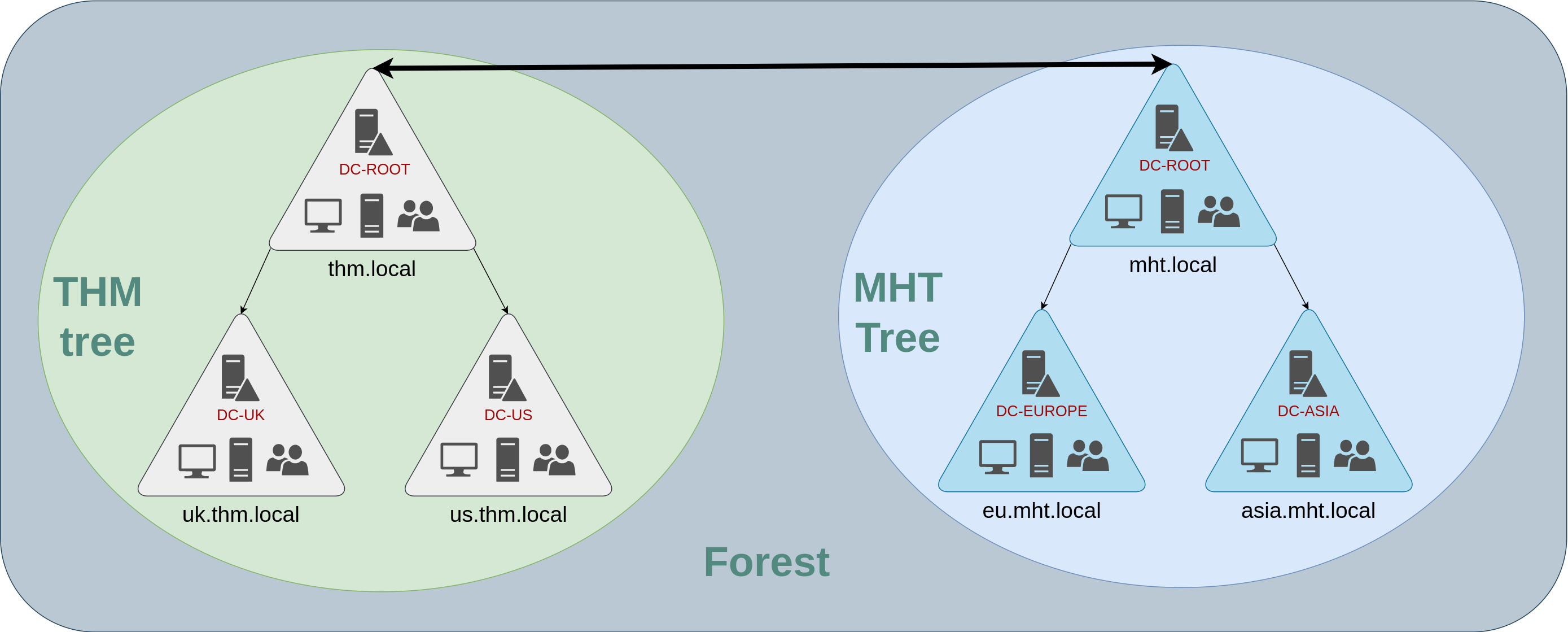
Luckily for us, Active Directory supports integrating multiple domains so that you can partition your network into units that can be managed independently. If you have two domains that share the same namespace (thm.local in our example), those domains can be joined into a Tree.
对我们来说幸运的是,Active Directory 支持整合多个域,这样你就可以将网络划分为可以独立管理的单元。如果有两个域共享同一个命名空间 (在我们的示例中是 thm.local), 那么这些域可以被合并到一个 Tree 中。
If our thm.local domain was split into two subdomains for UK and US branches, you could build a tree with a root domain of thm.local and two subdomains called uk.thm.local and us.thm.local, each with its AD, computers and users:
如果我们的 thm.local 域被划分为两个子域,分别用于英国和美国的分支,你可以构建一棵树,其中包含一个 thm.local 的根域和两个名为 uk.thm.local 和 us.thm.local 的子域,每个子域都有自己的 AD、计算机和用户:
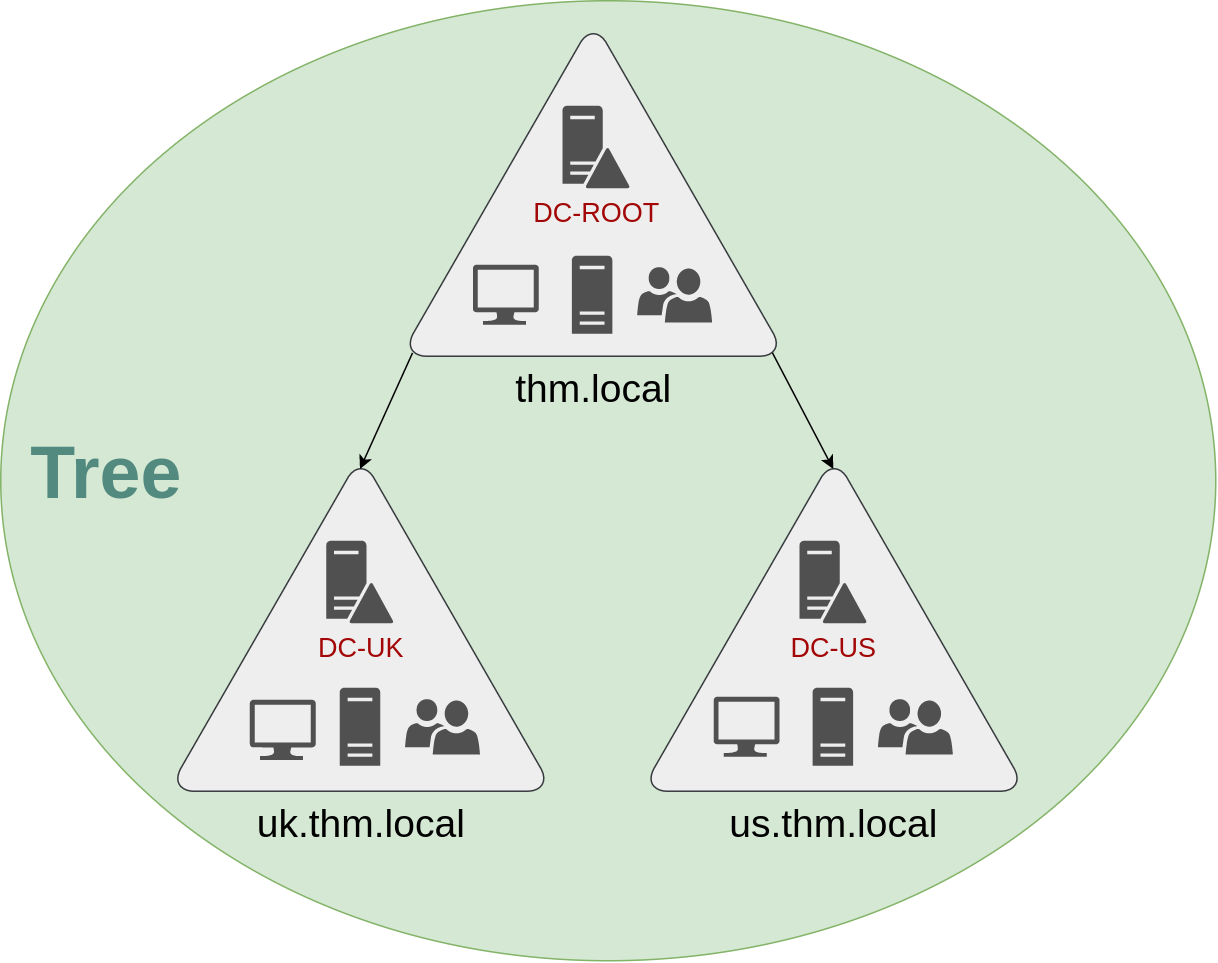
This partitioned structure gives us better control over who can access what in the domain. The IT people from the UK will have their own DC that manages the UK resources only. For example, a UK user would not be able to manage US users. In that way, the Domain Administrators of each branch will have complete control over their respective DCs, but not other branches' DCs. Policies can also be configured independently for each domain in the tree.
这种分区结构使我们能够更好地控制谁可以访问域中的内容。来自英国的 IT 人员将拥有自己的 DC, 只管理英国资源。例如,一个英国用户将无法管理美国用户。这样,每个分支的域管理员将完全控制他们各自的 DC, 但不能控制其他分支的 DC。策略也可以为树中的每个域独立配置。
A new security group needs to be introduced when talking about trees and forests. The Enterprise Admins group will grant a user administrative privileges over all of an enterprise's domains. Each domain would still have its Domain Admins with administrator privileges over their single domains and the Enterprise Admins who can control everything in the enterprise.
在讨论树木和森林时,需要引入一个新的安全组。企业管理员组将授予用户对企业所有域的管理权限。每个域仍将拥有其具有对其单个域的管理员权限的域管理员,以及可以控制企业中一切的企业管理员。
Forests森林
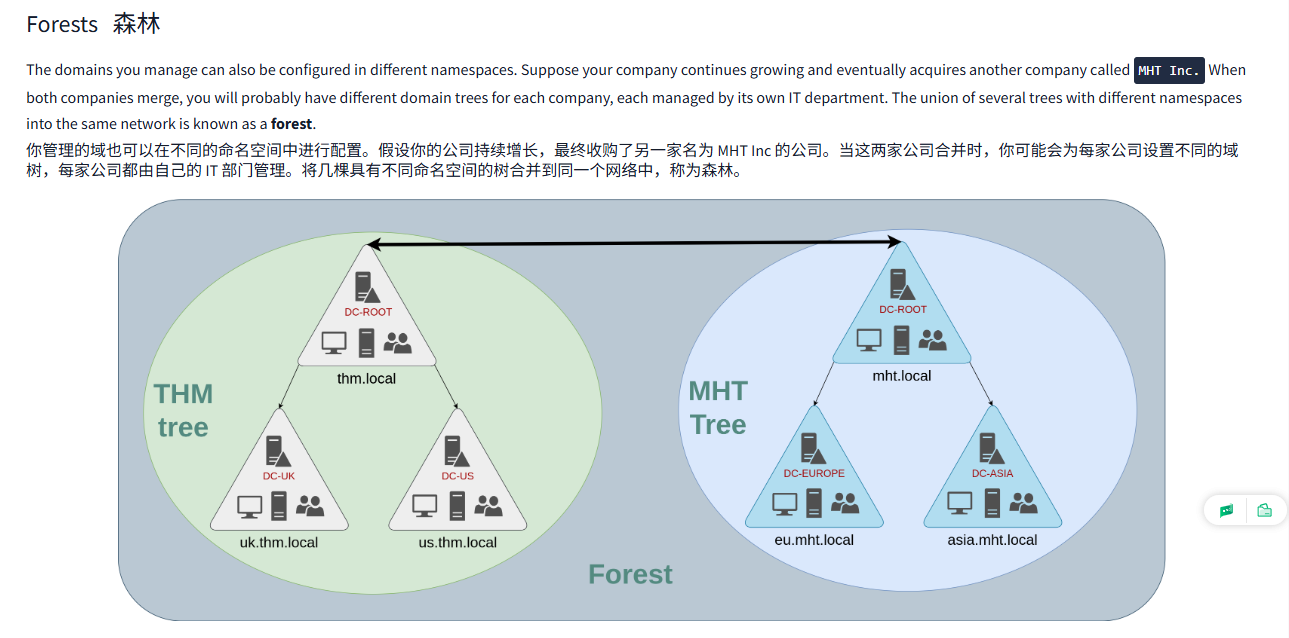
The domains you manage can also be configured in different namespaces. Suppose your company continues growing and eventually acquires another company called MHT Inc. When both companies merge, you will probably have different domain trees for each company, each managed by its own IT department. The union of several trees with different namespaces into the same network is known as a forest.
你管理的域也可以在不同的命名空间中进行配置。假设你的公司持续增长,最终收购了另一家名为 MHT Inc 的公司。当这两家公司合并时,你可能会为每家公司设置不同的域树,每家公司都由自己的 IT 部门管理。将几棵具有不同命名空间的树合并到同一个网络中,称为森林。
Trust Relationships信任关系
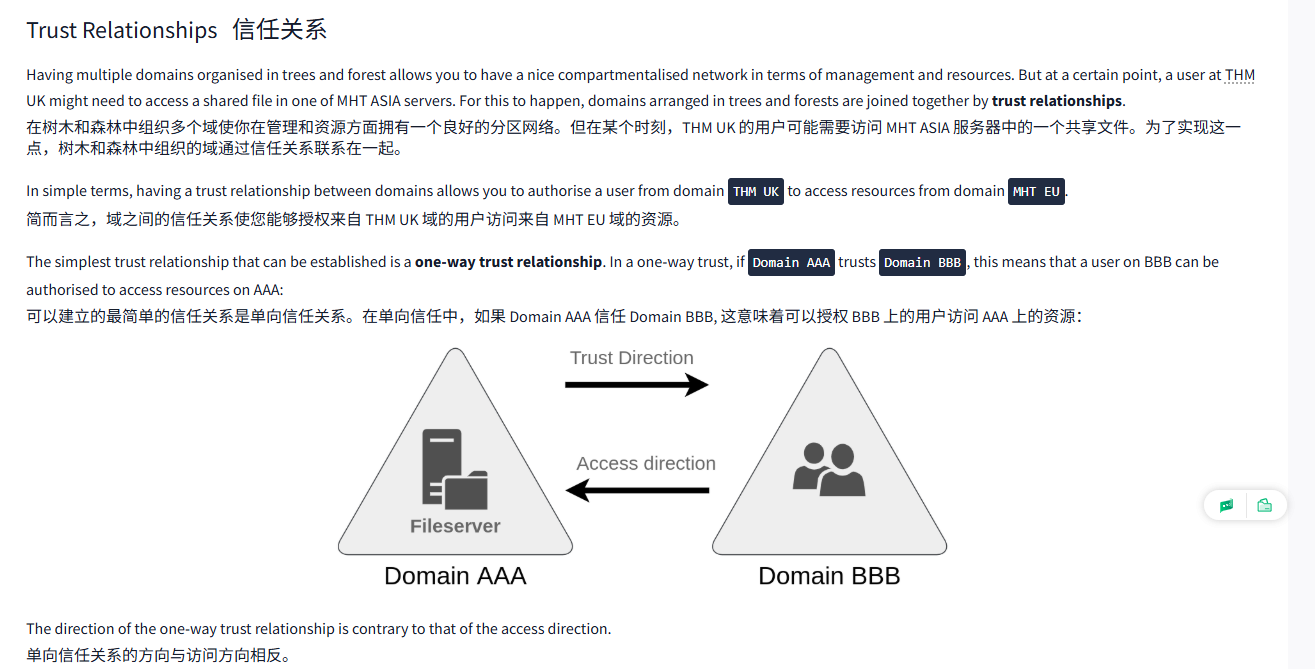
Having multiple domains organised in trees and forest allows you to have a nice compartmentalised network in terms of management and resources. But at a certain point, a user at THM UK might need to access a shared file in one of MHT ASIA servers. For this to happen, domains arranged in trees and forests are joined together by trust relationships.
在树木和森林中组织多个域使你在管理和资源方面拥有一个良好的分区网络。但在某个时刻,THM UK 的用户可能需要访问 MHT ASIA 服务器中的一个共享文件。为了实现这一点,树木和森林中组织的域通过信任关系联系在一起。
In simple terms, having a trust relationship between domains allows you to authorise a user from domain THM UK to access resources from domain MHT EU.
简而言之,域之间的信任关系使您能够授权来自 THM UK 域的用户访问来自 MHT EU 域的资源。
The simplest trust relationship that can be established is a one-way trust relationship. In a one-way trust, if Domain AAA trusts Domain BBB, this means that a user on BBB can be authorised to access resources on AAA:
可以建立的最简单的信任关系是单向信任关系。在单向信任中,如果 Domain AAA 信任 Domain BBB, 这意味着可以授权 BBB 上的用户访问 AAA 上的资源:
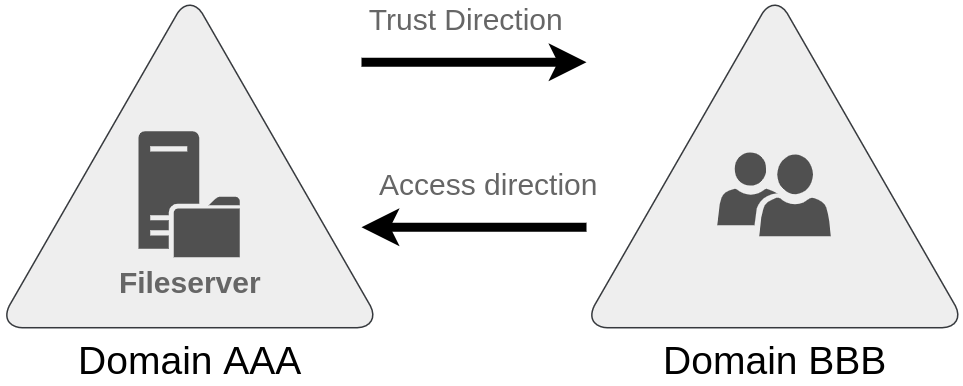
The direction of the one-way trust relationship is contrary to that of the access direction.
单向信任关系的方向与访问方向相反。
Two-way trust relationships can also be made to allow both domains to mutually authorise users from the other. By default, joining several domains under a tree or a forest will form a two-way trust relationship.
双向信任关系也可以建立,以允许两个域相互授权对方的用户。默认情况下,在一棵树或一片森林下加入多个域将形成双向信任关系。
It is important to note that having a trust relationship between domains doesn't automatically grant access to all resources on other domains. Once a trust relationship is established, you have the chance to authorise users across different domains, but it's up to you what is actually authorised or not.
需要注意的是,在域之间建立信任关系并不会自动授予对其他域中所有资源的访问权限。一旦建立了信任关系,你就有机会跨域授权用户,但实际授权与否取决于你。
问题
答案
Task9 Conclusion 结论
In this room, we have shown the basic components and concepts related to Active Directories and Windows Domains. Keep in mind that this room should only serve as an introduction to the basic concepts, as there's quite a bit more to explore to implement a production-ready Active Directory environment.
在这个房间里,我们展示了与 Active Directory 和 Windows 域相关的基本组件和概念。请记住,这个房间只应该作为基本概念的介绍,因为实现生产就绪的 Active Directory 环境还有很多需要探索的内容。
If you are interested in learning how to secure an Active Directory installation, be sure to check out the Active Directory Hardening Room. If, on the other hand, you'd like to know how attackers can take advantage of common AD misconfigurations and other AD hacking techniques, the Compromising Active Directory module is the way to go.
如果您对学习如何保护 Active Directory 安装感兴趣,请务必查看 Active Directory 强化室。另一方面,如果您想了解攻击者如何利用常见的 AD 错误配置和其他 AD 黑客技术,Commising Active Directory 模块是不错的选择。