2025-简单点-ultralytics之LetterBox
LetterBox源码
class LetterBox:"""Resize image and padding for detection, instance segmentation, pose.This class resizes and pads images to a specified shape while preserving aspect ratio. It also updatescorresponding labels and bounding boxes.Attributes:new_shape (tuple): Target shape (height, width) for resizing.auto (bool): Whether to use minimum rectangle.scaleFill (bool): Whether to stretch the image to new_shape.scaleup (bool): Whether to allow scaling up. If False, only scale down.stride (int): Stride for rounding padding.center (bool): Whether to center the image or align to top-left.Methods:__call__: Resize and pad image, update labels and bounding boxes.Examples:>>> transform = LetterBox(new_shape=(640, 640))>>> result = transform(labels)>>> resized_img = result["img"]>>> updated_instances = result["instances"]"""def __init__(self, new_shape=(640, 640), auto=False, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True, center=True, stride=32):"""Initialize LetterBox object for resizing and padding images.This class is designed to resize and pad images for object detection, instance segmentation, and pose estimationtasks. It supports various resizing modes including auto-sizing, scale-fill, and letterboxing.Args:new_shape (Tuple[int, int]): Target size (height, width) for the resized image.auto (bool): If True, use minimum rectangle to resize. If False, use new_shape directly.scaleFill (bool): If True, stretch the image to new_shape without padding.scaleup (bool): If True, allow scaling up. If False, only scale down.center (bool): If True, center the placed image. If False, place image in top-left corner.stride (int): Stride of the model (e.g., 32 for YOLOv5).Attributes:new_shape (Tuple[int, int]): Target size for the resized image.auto (bool): Flag for using minimum rectangle resizing.scaleFill (bool): Flag for stretching image without padding.scaleup (bool): Flag for allowing upscaling.stride (int): Stride value for ensuring image size is divisible by stride.Examples:>>> letterbox = LetterBox(new_shape=(640, 640), auto=False, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True, stride=32)>>> resized_img = letterbox(original_img)"""self.new_shape = new_shapeself.auto = autoself.scaleFill = scaleFillself.scaleup = scaleupself.stride = strideself.center = center # Put the image in the middle or top-leftdef __call__(self, labels=None, image=None):"""Resizes and pads an image for object detection, instance segmentation, or pose estimation tasks.This method applies letterboxing to the input image, which involves resizing the image while maintaining itsaspect ratio and adding padding to fit the new shape. It also updates any associated labels accordingly.Args:labels (Dict | None): A dictionary containing image data and associated labels, or empty dict if None.image (np.ndarray | None): The input image as a numpy array. If None, the image is taken from 'labels'.Returns:(Dict | Tuple): If 'labels' is provided, returns an updated dictionary with the resized and padded image,updated labels, and additional metadata. If 'labels' is empty, returns a tuple containing the resizedand padded image, and a tuple of (ratio, (left_pad, top_pad)).Examples:>>> letterbox = LetterBox(new_shape=(640, 640))>>> result = letterbox(labels={"img": np.zeros((480, 640, 3)), "instances": Instances(...)})>>> resized_img = result["img"]>>> updated_instances = result["instances"]"""if labels is None:labels = {}img = labels.get("img") if image is None else imageshape = img.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]new_shape = labels.pop("rect_shape", self.new_shape)if isinstance(new_shape, int):new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)# Scale ratio (new / old)r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])if not self.scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better val mAP)r = min(r, 1.0)# Compute paddingratio = r, r # width, height ratiosnew_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh paddingif self.auto: # minimum rectangledw, dh = np.mod(dw, self.stride), np.mod(dh, self.stride) # wh paddingelif self.scaleFill: # stretchdw, dh = 0.0, 0.0new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratiosif self.center:dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sidesdh /= 2if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resizeimg = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)) if self.center else 0, int(round(dh + 0.1))left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)) if self.center else 0, int(round(dw + 0.1))img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=(114, 114, 114)) # add borderif labels.get("ratio_pad"):labels["ratio_pad"] = (labels["ratio_pad"], (left, top)) # for evaluationif len(labels):labels = self._update_labels(labels, ratio, left, top)labels["img"] = imglabels["resized_shape"] = new_shapereturn labelselse:return img@staticmethoddef _update_labels(labels, ratio, padw, padh):"""Updates labels after applying letterboxing to an image.This method modifies the bounding box coordinates of instances in the labelsto account for resizing and padding applied during letterboxing.Args:labels (Dict): A dictionary containing image labels and instances.ratio (Tuple[float, float]): Scaling ratios (width, height) applied to the image.padw (float): Padding width added to the image.padh (float): Padding height added to the image.Returns:(Dict): Updated labels dictionary with modified instance coordinates.Examples:>>> letterbox = LetterBox(new_shape=(640, 640))>>> labels = {"instances": Instances(...)}>>> ratio = (0.5, 0.5)>>> padw, padh = 10, 20>>> updated_labels = letterbox._update_labels(labels, ratio, padw, padh)"""labels["instances"].convert_bbox(format="xyxy")labels["instances"].denormalize(*labels["img"].shape[:2][::-1])labels["instances"].scale(*ratio)labels["instances"].add_padding(padw, padh)return labels
解析
类文档字符串解释了 LetterBox 的主要功能:在保持宽高比的同时调整图像尺寸并添加填充,同时更新相应的标签和边界框。它还列出了类的属性和主要方法。
def init(self, new_shape=(640, 640), auto=False, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True, center=True, stride=32):
def call(self, labels=None, image=None):
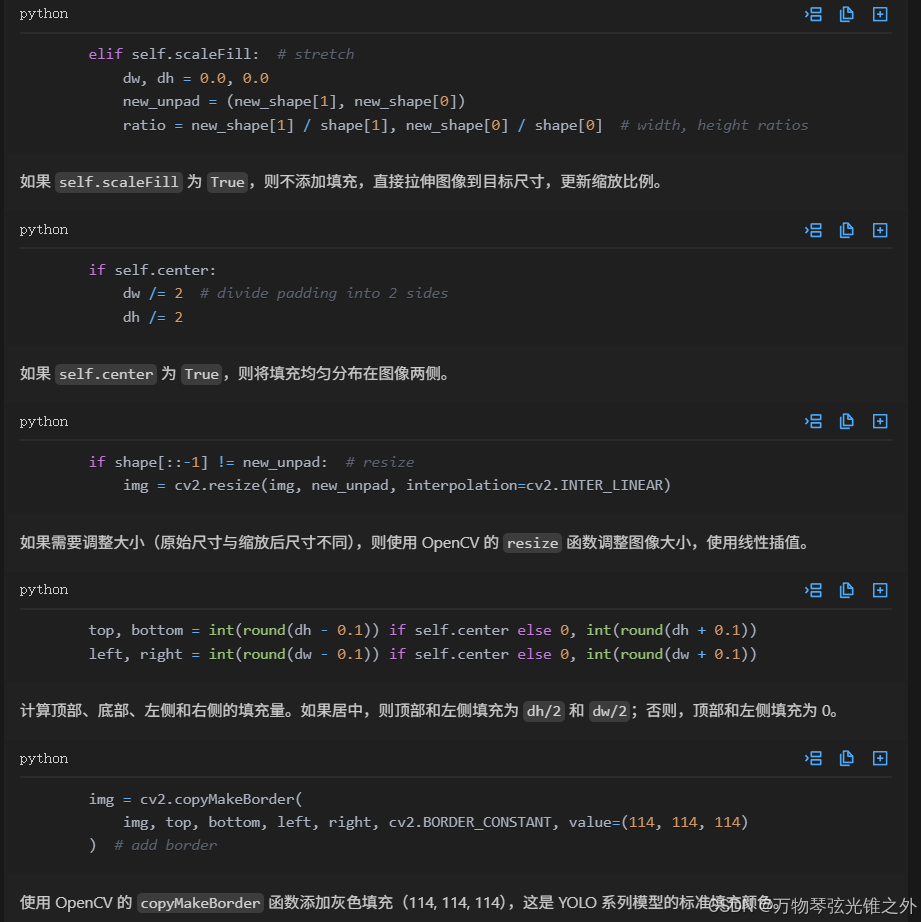
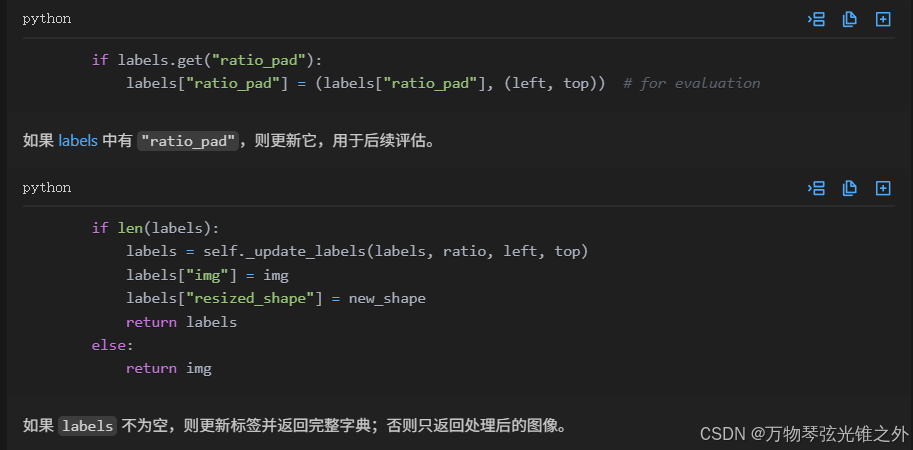
什么是top,bottom,left和right:

辅助方法
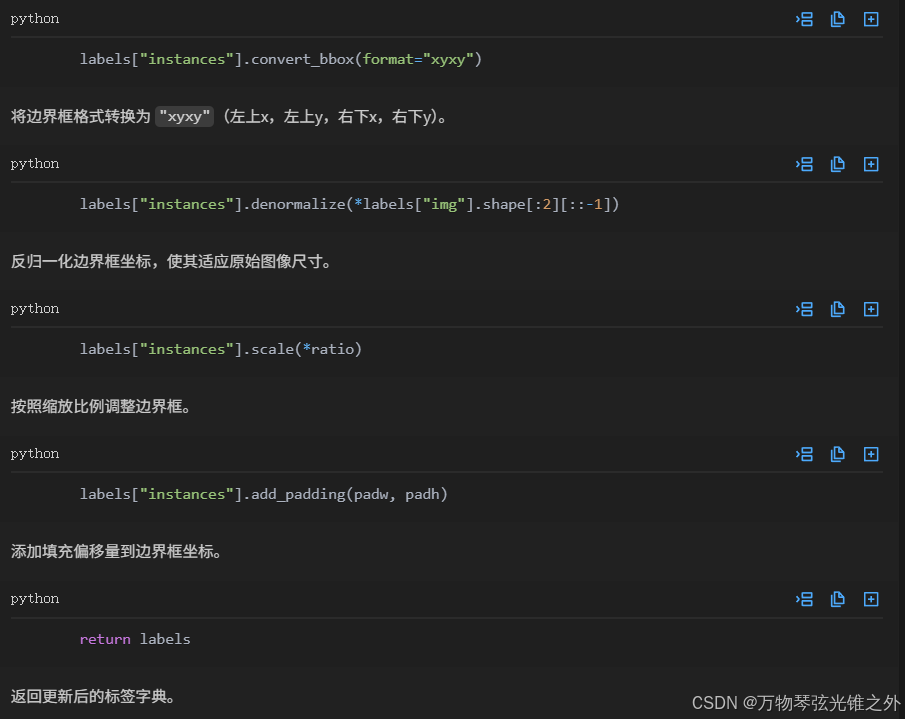
@staticmethoddef _update_labels(labels, ratio, padw, padh):
定义静态方法 _update_labels,用于在应用 letterboxing 后更新标签。
设计思路总结
保持宽高比:LetterBox 的核心功能是在调整图像尺寸时保持原始宽高比,避免图像变形,这对目标检测任务至关重要。
灵活的填充策略:
auto=True:确保填充尺寸是模型步幅的倍数
scaleFill=True:直接拉伸图像,不保持宽高比
center=True:图像居中,填充均匀分布
标签同步更新:在调整图像的同时,相应地更新边界框坐标,确保标注数据与图像匹配。
多任务支持:适用于目标检测、实例分割和姿态估计等多种计算机视觉任务。
高效实现:使用 OpenCV 进行图像处理,确保预处理速度高效。
这种预处理方法在 YOLO 系列模型中被广泛使用,是确保模型在不同尺寸输入上保持高性能的关键技术之一。
