[Agent可视化] docs | go/rust/py混构 | Temporal编排 | WASI沙箱
链接:Kocoro-lab/Shannon: Kubernetes/Linux of AI Agents - An enterprise-ready AI agent platform built with Rust for performance, Go for orchestration, Python for LLMs, and Solana for Web3 trust.
docs:Shannon平台
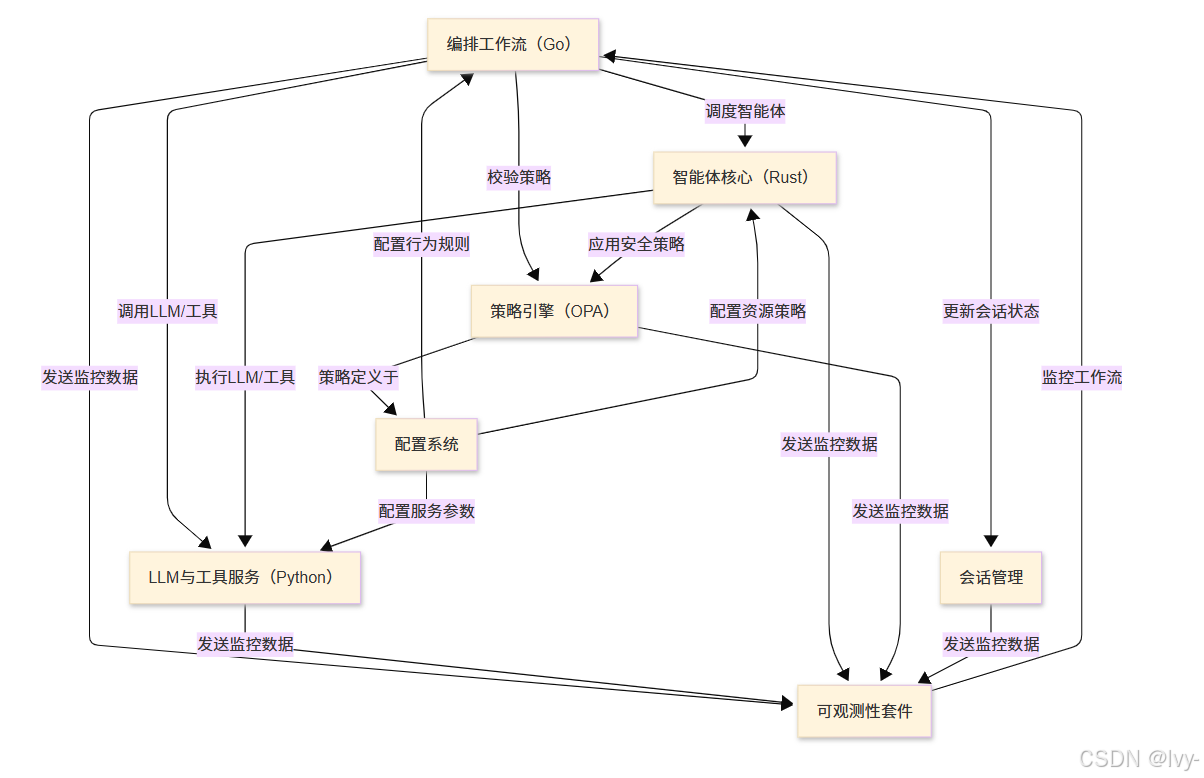
Shannon是一个生产就绪的平台,专为大规模构建和运行可靠AI智能体而设计(可视化)
它扮演着总指挥(Orchestration Workflows)的角色,负责分解复杂请求并协调多个安全智能体(Agent Core)在隔离沙箱中执行任务
这些智能体连接至智能AI模型与专用工具(LLM & Tooling Service),同时遵循中央规则集(Policy Engine),维护会话记忆(Session Management)
所有功能均可通过主控面板(Configuration System)配置,并由全方位监控套件(Observability Stack)实时追踪,确保性能、成本控制与安全性
总览
章节
- 配置系统
- LLM与工具服务(Python)
- 策略引擎(OPA)
- 智能体核心(Rust)
- 编排工作流(Go)
- 会话管理
- 可观测性套件
构造
根据 Shannon 项目的架构,多种编程语言之间的衔接主要通过以下几种方式实现:
1. 基于 Temporal 的工作流编排
https://temporal.io/
- Go 作为主要的编排层,负责整体的工作流管理
- Temporal 提供了跨语言的工作流引擎,允许不同语言的组件在同一个工作流中协作
- 通过 Temporal 的 SDK,各语言组件可以注册为 Workers 并参与工作流执行
2. WASI (WebAssembly System Interface) 沙箱
- Rust 编写的代理核心可以编译为 WebAssembly 模块
- WASI 提供了标准化的系统接口,使得 Rust 代码可以在沙箱环境中安全执行
- Go 编排层可以通过 WASI 运行时加载和执行 Rust 编译的 WASM 模块
3. HTTP/gRPC API 接口
- Python LLM 服务通过 REST API 或 gRPC 暴露服务接口
- Go 编排层通过网络调用访问 Python 提供的 LLM 功能
- 这种松耦合的方式允许各服务独立部署和扩展
4. 消息队列和事件系统
- 使用 Redis 作为消息中间件,实现异步通信
- 各语言组件通过发布/订阅模式进行事件驱动的交互
- 支持代理之间的消息传递和状态同步
5. 共享数据存储
- PostgreSQL 存储持久化数据和工作流状态
- Qdrant 向量数据库存储嵌入向量
- 各语言组件通过标准数据库协议访问共享数据
6. 标准化接口和协议
- 使用 OpenTelemetry 实现统一的可观察性
- Prometheus 指标收集,支持多语言客户端
- 通过标准协议确保各组件间的互操作性
架构优势
这种多语言架构设计的优势在于:
- 性能优化:Rust 提供高性能的代理执行,Go 提供高效的并发编排
- 生态利用:Python 拥有丰富的 AI/ML 生态系统
- 安全隔离:WASI 沙箱确保代理执行的安全性
- 可维护性:各组件职责清晰,可独立开发和部署
这种设计体现了现代云原生应用"选择合适工具解决特定问题"的理念,通过标准化接口和中间件实现了多语言系统的有机整合。
go/rust/py混编
在 Shannon 这样的多语言系统中,各语言并不是真正的"混合编程"
而是通过模块化架构和标准化接口实现协作。
让我详细解释各种衔接方式:
1. Rust + Go 的集成方式
方式一:CGO 调用 Rust 库
// Go 代码
/*
#cgo LDFLAGS: -L./lib -lagent_core
#include "agent.h"
*/
import "C"func ExecuteAgent(config string) string {cConfig := C.CString(config)defer C.free(unsafe.Pointer(cConfig))result := C.execute_agent(cConfig)return C.GoString(result)
}
// Rust 代码 (编译为 C 兼容库)
#[no_mangle]
pub extern "C" fn execute_agent(config: *const c_char) -> *mut c_char {let config_str = unsafe { CStr::from_ptr(config).to_str().unwrap() };let result = run_agent_logic(config_str);CString::new(result).unwrap().into_raw()
}
方式二:WASI WebAssembly 沙箱
// Go 加载和执行 WASM 模块
import "github.com/tetratelabs/wazero"func RunAgentInSandbox(wasmBytes []byte, input string) string {ctx := context.Background()runtime := wazero.NewRuntime(ctx)module, _ := runtime.Instantiate(ctx, wasmBytes)fn := module.ExportedFunction("execute_agent")result, _ := fn.Call(ctx, uint64(len(input)))return string(result)
}
// Rust 编译为 WASM
#[no_mangle]
pub extern "C" fn execute_agent(input_len: u32) -> u32 {// 代理执行逻辑let result = process_agent_task();result.len() as u32
}
2. Python + Go 的集成方式
方式一:HTTP/gRPC 服务调用
# Python LLM 服务
from fastapi import FastAPI
import openaiapp = FastAPI()@app.post("/llm/completion")
async def completion(request: CompletionRequest):response = await openai.ChatCompletion.acreate(model="gpt-4",messages=request.messages)return {"content": response.choices[0].message.content}
// Go 调用 Python 服务
type LLMClient struct {baseURL stringclient *http.Client
}func (c *LLMClient) GetCompletion(messages []Message) (string, error) {payload := CompletionRequest{Messages: messages}resp, err := c.client.Post(c.baseURL+"/llm/completion", "application/json", payload)// 处理响应...return result.Content, nil
}
方式二:嵌入式 Python 解释器
// 使用 go-python 库
import "github.com/sbinet/go-python"func CallPythonLLM(script string, args map[string]interface{}) string {py.Initialize()defer py.Finalize()module := py.PyImport_ImportModule("llm_service")function := module.GetAttrString("process_request")pyArgs := convertToPyDict(args)result := function.Call(pyArgs)return py.PyString_AsString(result)
}
3. Temporal 工作流编排
// Go Temporal Worker
func AgentWorkflow(ctx workflow.Context, request AgentRequest) (string, error) {// 1. 调用 Rust 代理进行预处理preprocessResult, err := workflow.ExecuteActivity(ctx, activities.RustPreprocess, request.Input).Get(ctx, nil)// 2. 调用 Python LLM 服务llmResult, err := workflow.ExecuteActivity(ctx, activities.PythonLLMCall, preprocessResult).Get(ctx, nil)// 3. 调用 Rust 代理进行后处理finalResult, err := workflow.ExecuteActivity(ctx, activities.RustPostprocess, llmResult).Get(ctx, nil)return finalResult, nil
}
# Python Temporal Activity
from temporalio import activity@activity.defn
async def python_llm_call(input_data: str) -> str:# 使用 Python AI/ML 生态import torchimport transformersmodel = transformers.AutoModel.from_pretrained("gpt-4")result = model.generate(input_data)return result
4. 消息队列异步通信
// Go 发布消息
func PublishAgentTask(task AgentTask) error {client := redis.NewClient(&redis.Options{Addr: "localhost:6379"})taskJSON, _ := json.Marshal(task)return client.Publish(ctx, "agent_tasks", taskJSON).Err()
}
# Python 订阅处理
import redis
import jsondef process_agent_tasks():r = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379)pubsub = r.pubsub()pubsub.subscribe('agent_tasks')for message in pubsub.listen():task = json.loads(message['data'])result = run_ml_inference(task)# 发布结果r.publish('agent_results', json.dumps(result))
5. 共享数据存储
// Rust 写入向量数据
use qdrant_client::prelude::*;async fn store_embeddings(vectors: Vec<Vec<f32>>) -> Result<()> {let client = QdrantClient::from_url("http://localhost:6334").build()?;let points: Vec<PointStruct> = vectors.into_iter().enumerate().map(|(id, vector)| PointStruct::new(id as u64, vector, payload)).collect();client.upsert_points_blocking("agents", points, None).await?;Ok(())
}
# Python 查询向量数据
from qdrant_client import QdrantClientdef search_similar_agents(query_vector):client = QdrantClient("localhost", port=6334)search_result = client.search(collection_name="agents",query_vector=query_vector,limit=10)return [hit.payload for hit in search_result]
设计原则
- 松耦合架构:各语言组件通过标准接口通信,而非直接调用
- 容器化部署:每个语言组件独立容器化,便于扩展和维护
- 标准化协议:使用 HTTP、gRPC、消息队列等标准协议
- 数据驱动:通过共享数据存储实现状态同步
- 异步处理:利用消息队列实现非阻塞的异步处理
这种架构让每种语言都能发挥其最大优势,同时保持系统的整体一致性和可维护性。
