AI(学习笔记第十课) 使用langchain的AI tool
文章目录
- AI(学习笔记第九课) 使用langchain的AI tool
- 学习内容:
- 1. 为什么需要使用`AI Tool`以及什么是`AI Tool`
- 1.1. 什么是`AI Tool`
- 1.2 整体概念(`database tool`):
- 1.3 整体概念(`get weather tool`):
- 2. 如何创建`AI Tool`
- 2.1 从`Function`即(`python function`)来创建
- 2.2 从`LangChain Runnables`来创建
- 2.2.1 langchain的runnables
- 2.2.2 示例代码
- 2.3 使用`Subclass BaseTool`来创建
- 3. 如何使用`chat model`来`call AI tool`
- 3.1 主要步骤
- 3.2 代码示例
- 3.3 代码示例执行结果
- 3.4 继续练习
AI(学习笔记第九课) 使用langchain的AI tool
- 为什么需要使用
AI tool - 什么是
AI tool - 如何创建
AI tool - 如何使用
chat model来call AI tool
学习内容:
- 为什么需要使用
AI tool以及什么是AI tool - 如何创建
AI tool - 如何使用
chat model来call AI tool
1. 为什么需要使用AI Tool以及什么是AI Tool
1.1. 什么是AI Tool
langchain中的tool是一个python的function,包含一个schema,定义函数function的name,description以及expected arguments。
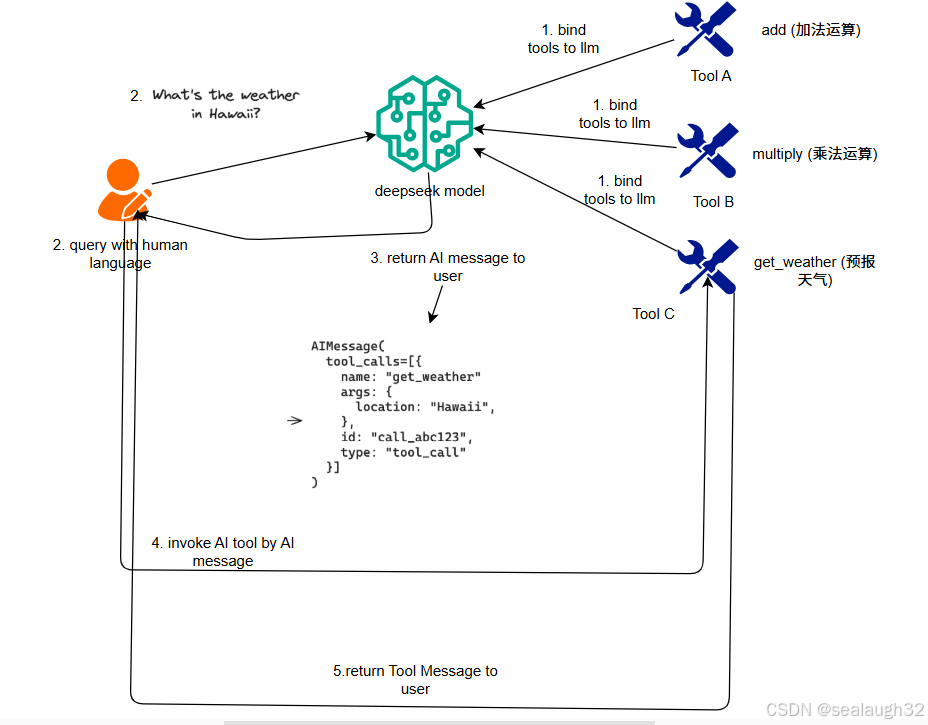
关键概念:
- 创建工具(
Tool Creation)
使用@tool这个Python的decorator进行tool的定义,一个tool就是关联这个function和schema的关联(association) - 绑定工具(
Tool Binding)
这里很关键,就是让modol(llm)知道工具的存在,所以,上面的创建tool这里,必须要定义tool的name,description以及需要的参数expected arguments。 - 呼出工具
Tool Calling
使用人类自然语言,对model(LLM)进行提问,如果合适,model(LLM)将返回AI Message,这里会包含将要执行的tool,以及需要的参数。 - 执行工具
Tool Executing
用户通过model(llm)提供的function以及arguments,来最终执行tool,并获得结果。
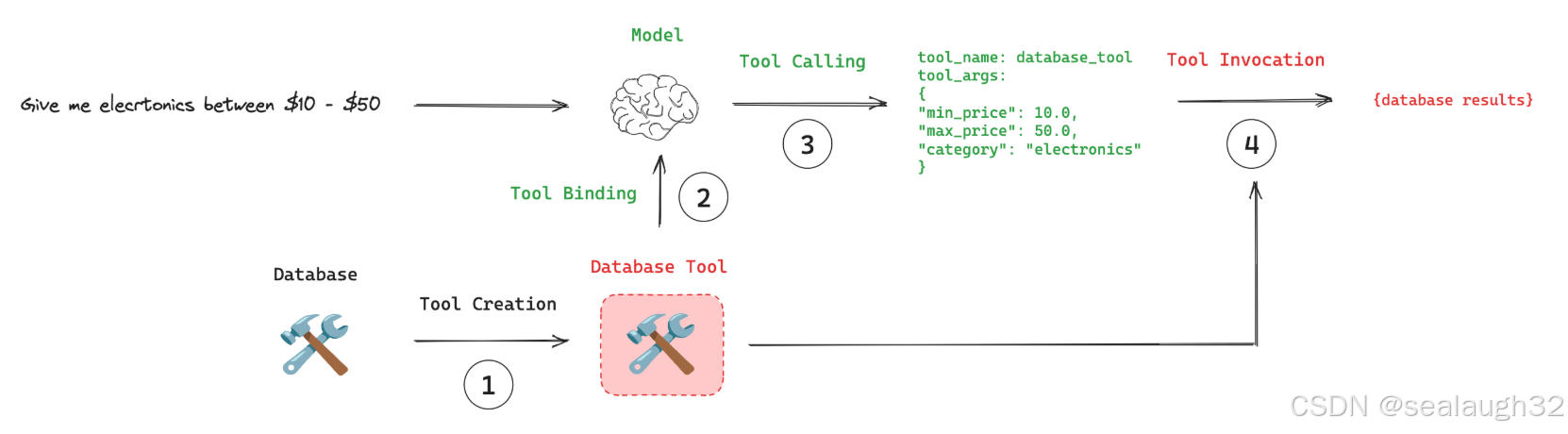
1.2 整体概念(database tool):
1.3 整体概念(get weather tool):
AI Tool能够让model(llm)能够像八爪鱼一样,伸出各个触角,让model(llm)不仅能单纯的回答问题,而且能够通过调用tool,动起来。了解了AI Tool的整体思路之后,开始动手!、
2. 如何创建AI Tool
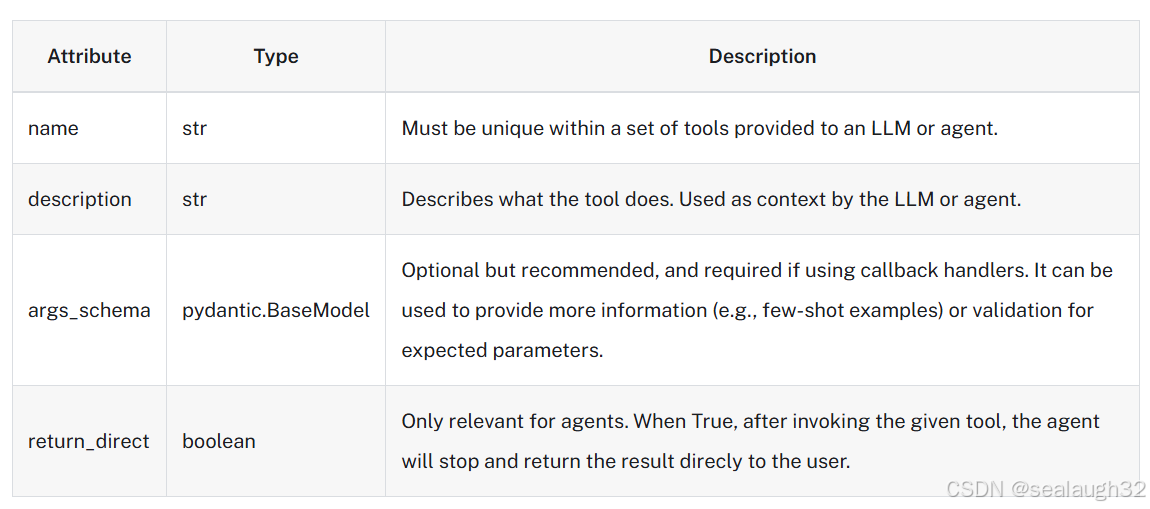
使用langchain来创建AI Tool的时候,需要提供如下信息。
langchain支持三种方法创建tool:
- 从
Function即(python function)来创建 - 从
LangChain Runnables来创建 - 从
BaseTool继承来创建
2.1 从Function即(python function)来创建
实例代码
from langchain_core.tools import tool@tool
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:"""Multiply two numbers."""return a * b# Let's inspect some of the attributes associated with the tool.
print(multiply.name)
print(multiply.description)
print(multiply.args)
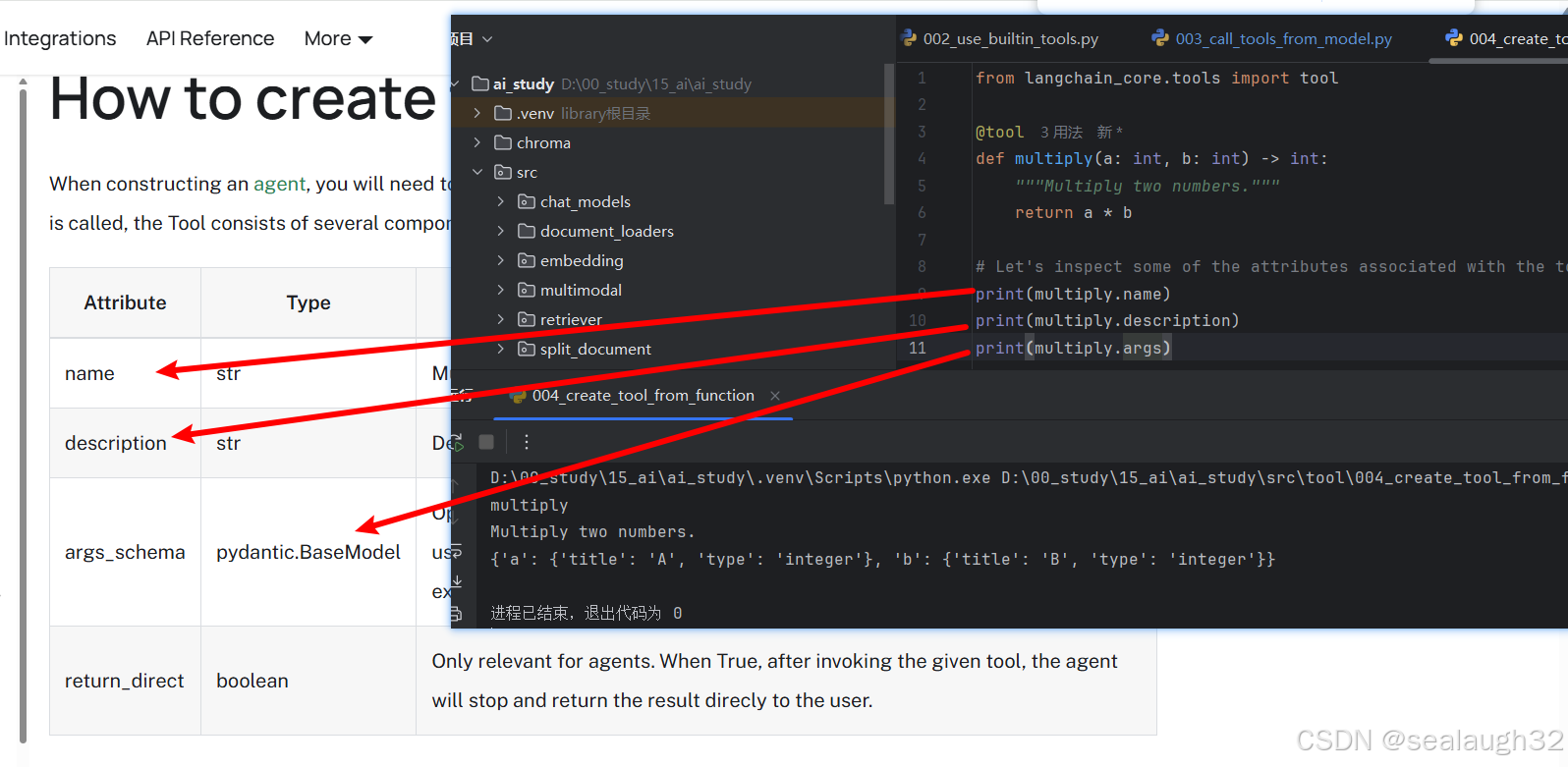
可以,看出这种方法比较简单,可以使用较少的代码就能够实现一个AI Tool。
2.2 从LangChain Runnables来创建
2.2.1 langchain的runnables
langchain’s runnables
这个是langchain的一个标准接口interface
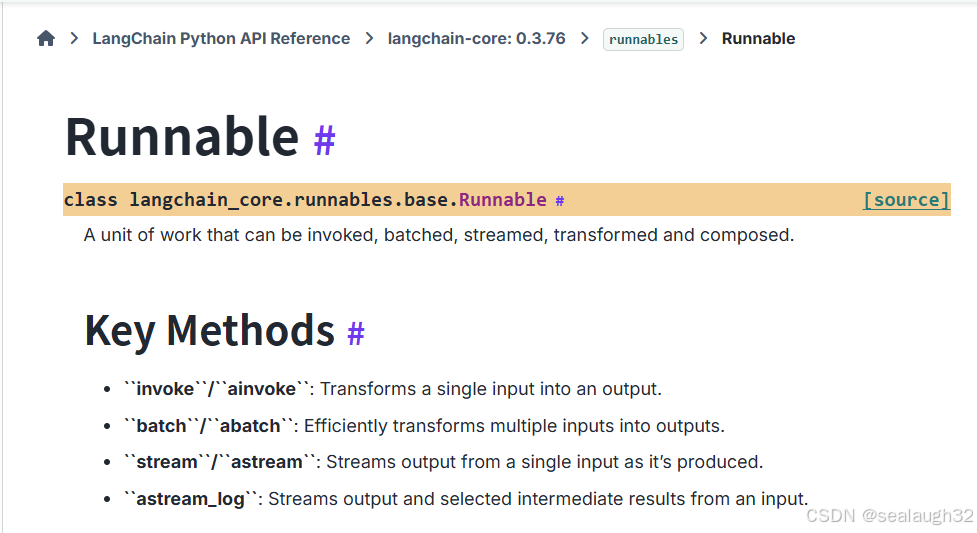
这里,使用一个简单的fake model进行一个演示。
2.2.2 示例代码
示例代码(create tool from langchain’s runnable)
from langchain_core.language_models import GenericFakeChatModel
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate# 修改提示模板以支持用户输入的问题
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", "You are a helpful assistant that responds in the style of {answer_style}."),("human", "{question}")
])# 使用 GenericFakeChatModel,可以设置多个响应消息
llm = GenericFakeChatModel(messages=iter(["Ahoy there! What be troublin' ye today?", # 海盗风格"Greetings! How may I assist you?", # 正式风格"Hey! What's up?", # 休闲风格"Salutations! How can I be of service?" # 古典风格
]))# 创建处理链
chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()# 测试链的交互功能
def chat_with_chain():print("=== 风格化聊天机器人 ===")print("可用的回答风格: pirate, formal, casual, classic")while True:try:# 获取用户输入style = input("\n选择回答风格: ").strip()question = input("请输入您的问题: ").strip()if question.lower() in ['quit', 'exit', 'bye']:print("再见!")break# 调用chain获取回答response = chain.invoke({"answer_style": style,"question": question})print(f"\n🤖 回答 ({style}风格): {response}")except KeyboardInterrupt:print("\n\n聊天结束!")breakexcept Exception as e:print(f"错误: {e}")# 作为工具使用(可选)
as_tool = chain.as_tool(name="StyleResponder",description="回答问题并根据指定风格进行回复。输入应该包含 'answer_style' 和 'question' 参数。"
)print("工具参数结构:", as_tool.args)
print("\n开始聊天...")
# chat_with_chain()
print(as_tool.name)
print(as_tool.description)
print(as_tool.args)
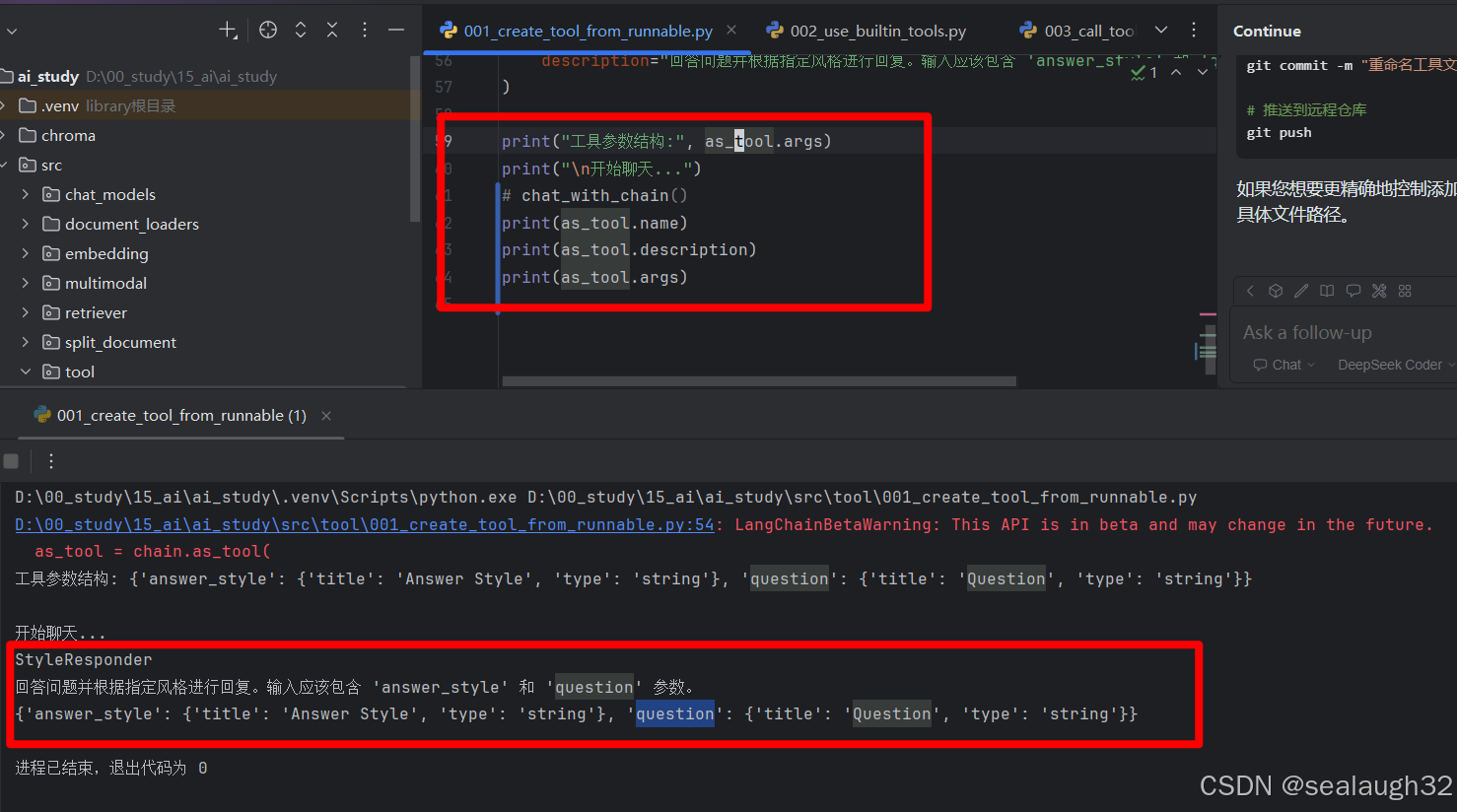
这样任何``langchain的runnable的子类对象都可以通过as_tool方法迅速转换成AI tool,非常方便。
2.3 使用Subclass BaseTool来创建
这种方法是代码量最多的方法,但是同样带来的好处是可以调节的细节更多,可以更加细腻描绘AI Tool。
create tool from base tool示例代码
from typing import Optionalfrom langchain_core.callbacks import (AsyncCallbackManagerForToolRun,CallbackManagerForToolRun,
)
from langchain_core.tools import BaseTool
from langchain_core.tools.base import ArgsSchema
from pydantic import BaseModel, Fieldclass CalculatorInput(BaseModel):a: int = Field(description="first number")b: int = Field(description="second number")# Note: It's important that every field has type hints. BaseTool is a
# Pydantic class and not having type hints can lead to unexpected behavior.
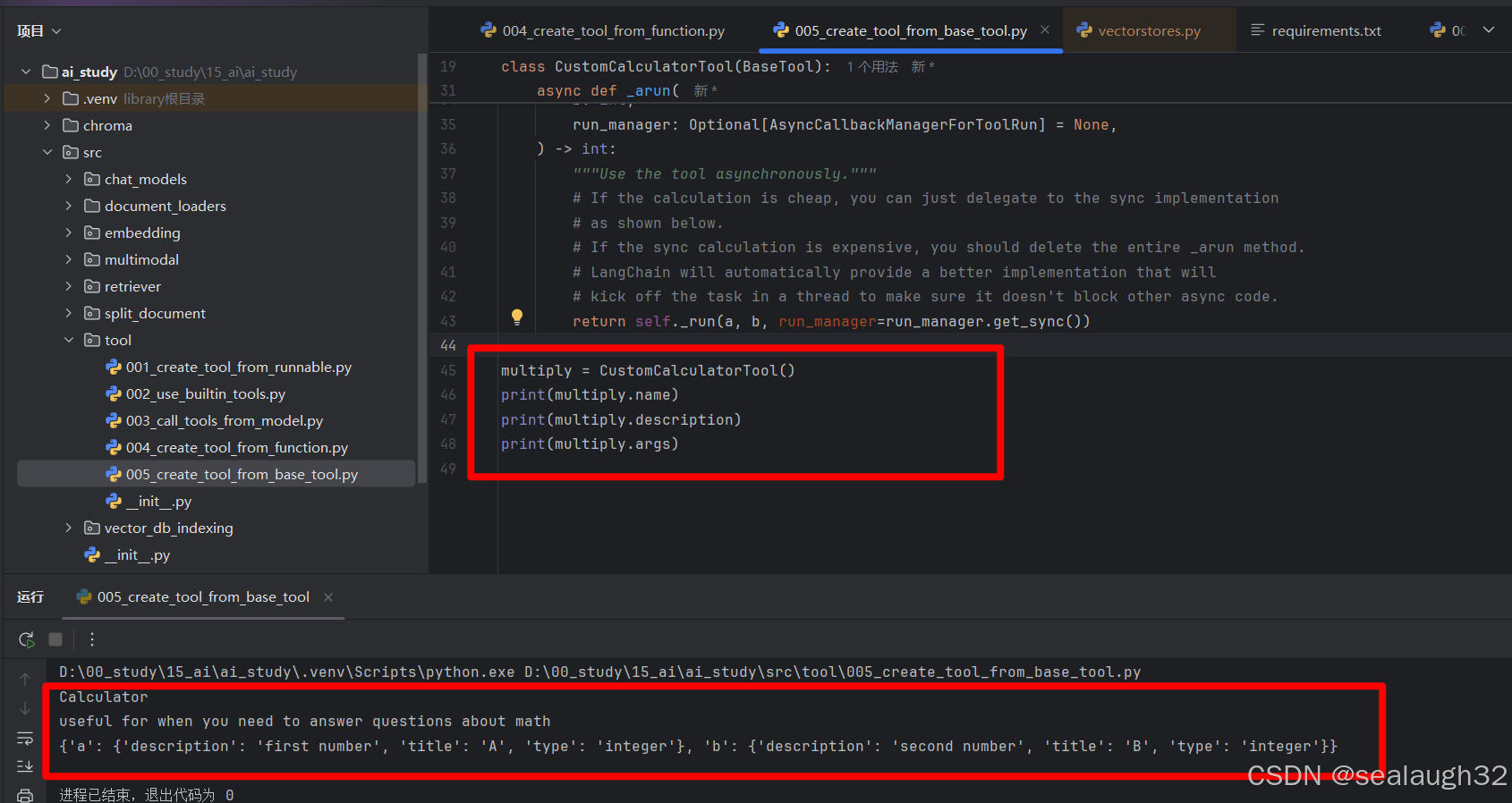
class CustomCalculatorTool(BaseTool):name: str = "Calculator"description: str = "useful for when you need to answer questions about math"args_schema: Optional[ArgsSchema] = CalculatorInputreturn_direct: bool = Truedef _run(self, a: int, b: int, run_manager: Optional[CallbackManagerForToolRun] = None) -> int:"""Use the tool."""return a * basync def _arun(self,a: int,b: int,run_manager: Optional[AsyncCallbackManagerForToolRun] = None,) -> int:"""Use the tool asynchronously."""# If the calculation is cheap, you can just delegate to the sync implementation# as shown below.# If the sync calculation is expensive, you should delete the entire _arun method.# LangChain will automatically provide a better implementation that will# kick off the task in a thread to make sure it doesn't block other async code.return self._run(a, b, run_manager=run_manager.get_sync())multiply = CustomCalculatorTool()
print(multiply.name)
print(multiply.description)
print(multiply.args)
执行后查看生成的AI Tool
3. 如何使用chat model来call AI tool
最后,是如何使用chat model进行AI Tool的调用。
3.1 主要步骤
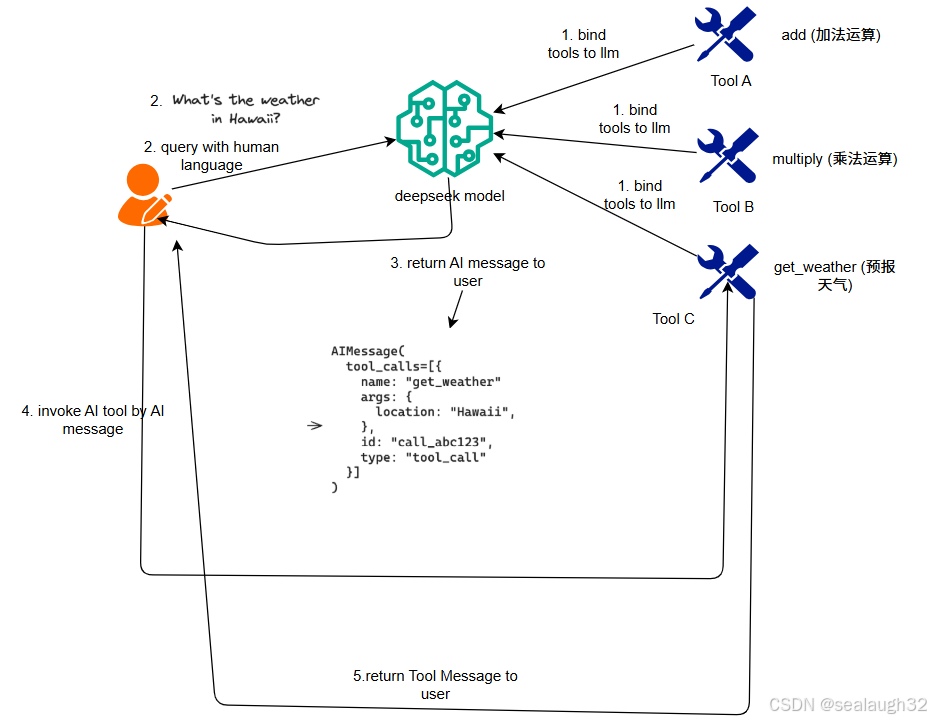
3.2 代码示例
call tool from model(llm)示例代码
import os
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
from langchain_core.tools import tool@tool
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:"""Adds a and b."""print("add was called\n")return a + b@tool
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:"""Multiplies a and b."""return a * btools = [add, multiply](os.environ.setdefault("DEEPSEEK_API_KEY","sk-XXXXXX"))from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_modelllm = init_chat_model("deepseek-chat", model_provider="deepseek")
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
query = ("6加上7等于多少")
messages = [HumanMessage(query)]
ai_msg = llm_with_tools.invoke(messages)
print(ai_msg.tool_calls)for tool_call in ai_msg.tool_calls:selected_tool = {"add": add, "multiply": multiply}[tool_call["name"].lower()]tool_msg = selected_tool.invoke(tool_call)messages.append(tool_msg)print(messages)
3.3 代码示例执行结果
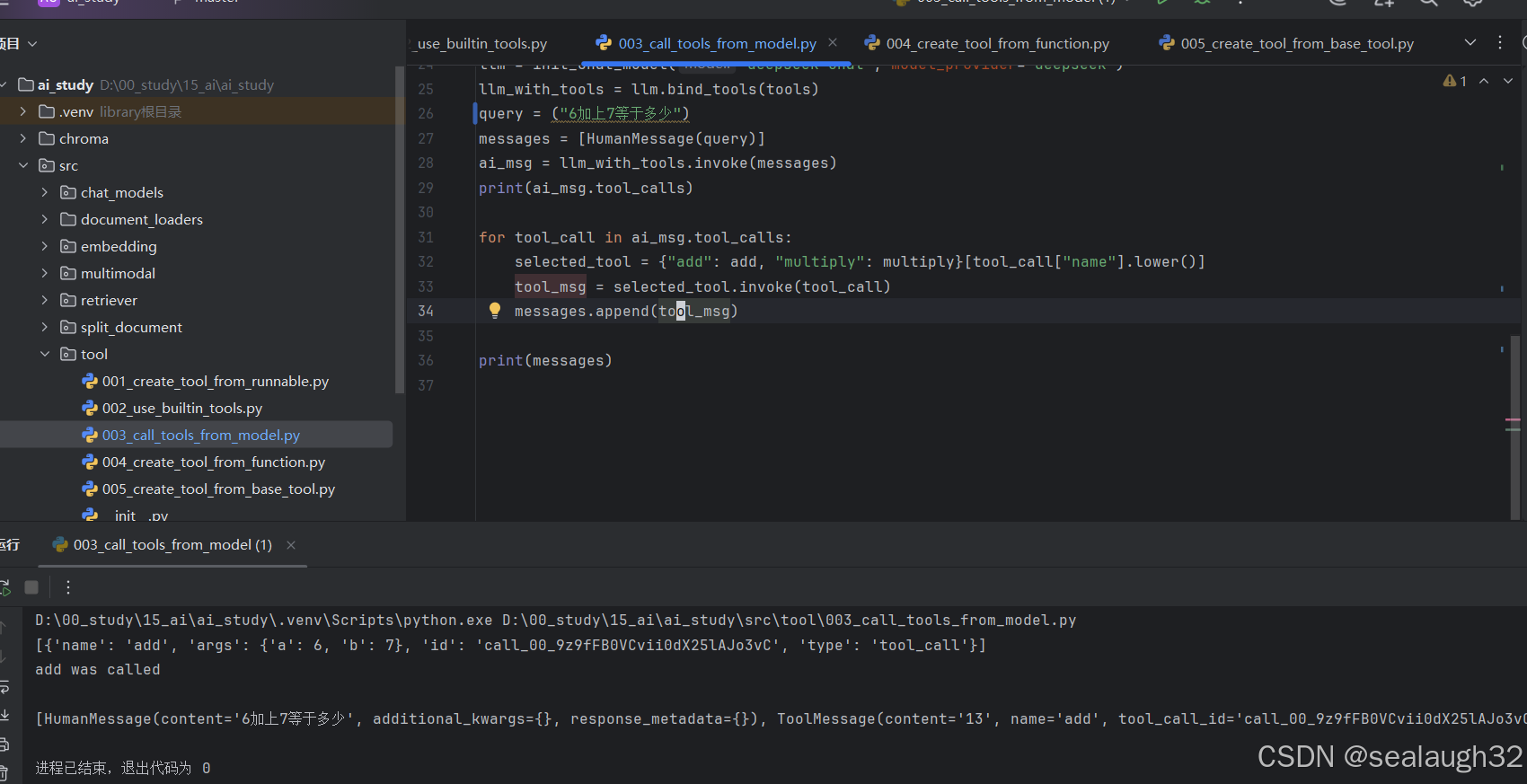
可以看出AI Tool被调用,model(llm)通过自然语言的提问,能够准确定位到tool。
3.4 继续练习
这里按照广度优先,下次继续练习multimodal