机器学习16:自监督式学习(Self-Supervised Learning)②
摘要
本周重点学习了自监督式学习中的两大代表性模型——BERT 与 GPT。BERT 通过“填空”和句子连贯性判断任务,学习上下文感知的词嵌入表示,能够有效处理一词多义问题,并在跨语言任务中表现出色。其嵌入向量能捕捉词汇语义和上下文信息,甚至可迁移至非文本任务(如 DNA 分类)。GPT 则采用自回归方式预测下一个 token,具备文本生成能力,并支持少样本、单样本和零样本学习,展现出强大的泛化能力。两者均为自监督学习的典型应用,推动了自然语言处理的发展。
Abstract
This week's focus was on self-supervised learning, particularly on two representative models: BERT and GPT. BERT learns context-aware word embeddings through "fill-in-the-blank" and sentence coherence tasks, effectively handling polysemy and performing well in cross-lingual tasks. Its embeddings capture semantic and contextual information and can even be transferred to non-text tasks such as DNA classification. GPT, on the other hand, uses an autoregressive approach to predict the next token, enabling text generation and supporting few-shot, one-shot, and zero-shot learning, demonstrating strong generalization capabilities. Both models are key applications of self-supervised learning and have significantly advanced the field of natural language processing.
一.BERT的用处
前面我们通过BERT来学习自监督式学习,了解了BERT主要是为了完成两件事“填空”以及判断两个句子前后是否连贯。那对于这两个简单的事件也就是说BERT完成的事情非常的简单但其为什么被应用广泛呢?
1.常见的理由
最常见的解释就是如下,对于BERT输入一串文字,每一个文字对应到BERT输出的一个向量,相反的这些向量也代表了对应输入的字,对于这些向量我们接下来称之为嵌入(embedding)。
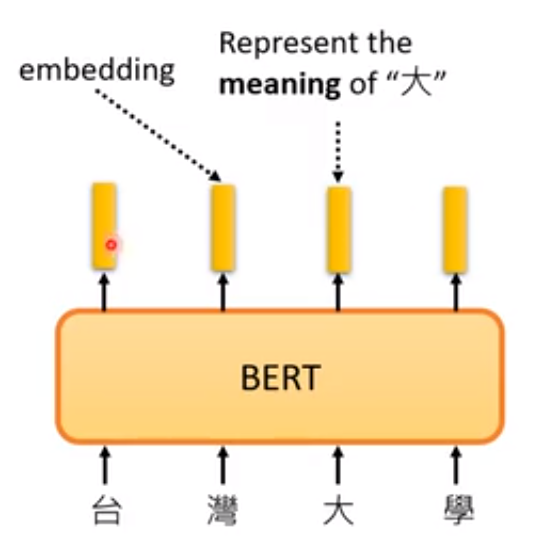
对于向量能够代表对应输入的字,具体来说就是将一些字对应的向量表示出来,就会发现两个字的意思越相近,其对应的向量就越接近。
