对文件的输入和输出
易错:
🎉使用 putchar 将字符输出到屏幕上显示,继续读取下一个字符。
主要使用于单个字符
putchar(ch);
(输出屏幕也可以用printf)
⚽ch=getchar( );
//接收最后输入的回车符
//这行代码的本意是读取并丢弃 scanf 输入文件名后留在缓冲区的换行符,
//但实际上 scanf 读取字符串时不会把换行符留在缓冲区,这行代码是多余的。
🎉// getchar 逐个读取字符,
ch=getchar( );
⚽ while(!feof(in)) //检查当前读写位置是否移到文件末端,不为1就不会读到末端
🎉putchar(10); //换行
⚽fclose(in); //关闭
fclose(out); //关闭
return 0;
🎉if((in=fopen(infile,"r"))==NULL)
{
printf("无法打开此文件\n"); exit(0);
}
⚽gets 函数不会检查输入字符串的长度,它会一直读取,直到遇到换行符(\n),并将换行符替换为字符串结束符\0。
🎉字符串之间的顺序排序
//排序算法:冒泡,选择
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++) { k=i;for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)if(strcmp(str[k],str[j])>0) k=j;//字符串之间比较用scr//>0,排在后面,ascll码值大if(k!=i){ strcpy(temp,str[i]); //字符串之间不能直接赋值strcpy(str[i],str[k]);strcpy(str[k],temp);}}⚽fputs("\n",fp);
🎉结构体数据在内存中是二进制形式存储的,
⚽数组名字本身就有地址
![]()
🎉有多少个学生,这里就要有多少,(循环除外)
例题
例10.1
从键盘输入一些字符,逐个把它们送到磁盘上去,直到用户输入一个“#”为止。
解题思路:用getchar函数从键盘逐个输入字符,然后用fputc函数写到磁盘文件即可。
![]()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>//用exit函数时加
int main()
{ FILE *fp;char ch,filename[10];//存放输入的文件名printf("请输入所用的文件名:");//没有说路径,源文件所在位置存放在一起scanf("%s",filename);if((fp=fopen(filename,"w"))==NULL) { printf("无法打开此文件\n"); exit(0); }ch=getchar( );//最后打完的enter消化掉//接收最后输入的回车符//这行代码的本意是读取并丢弃 scanf 输入文件名后留在缓冲区的换行符,//但实际上 scanf 读取字符串时不会把换行符留在缓冲区,这行代码是多余的。printf("请输入一个字符串(以#结束):");// getchar 逐个读取字符,ch=getchar( ); //只要读取的字符不是 #,就使用 fputc 将字符写入到之前打开的文件中,while(ch!='#') { fputc(ch,fp); //使用 putchar 将字符输出到屏幕上显示,继续读取下一个字符。putchar(ch); ch=getchar(); }fclose(fp); //关闭文件// putchar(10); //输出一个换行符/putchar(10) 输出一个换行符(ASCII 码 10 代表换行)return 0;
}例10.2
将一个磁盘文件中的信息复制到另一个磁盘文件中。 file1.dat->file2.dat解题思路:从file1.dat文件中逐个读入字符,然后逐个输出到file2.dat中。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main( )
{ FILE *in,*out; //读和写出去char ch,infile[10],outfile[10]; printf("输入读入文件的名字:");scanf("%s",infile); printf("输入输出文件的名字:");scanf("%s",outfile); if((in=fopen(infile,"r"))==NULL) {printf("无法打开此文件\n"); exit(0);}if((out=fopen(outfile,“w”))==NULL) {printf("无法打开此文件\n"); exit(0); }while(!feof(in)) //检查当前读写位置是否移到文件末端,不为1就不会读到末端{ ch=fgetc(in); fputc(ch,out); putchar(ch); //输出一份到屏幕上}putchar(10); //换行fclose(in); //关闭fclose(out); //关闭return 0;
}例10.3
♟️用到二维数组,一个字符串==一个单词,然后有好几个单词
♟️gets(str[i]);//键盘获得字符串,放到第i行(str[i][j] j=0)
♟️if(strcmp(str[k],str[j])>0) k=j;//字符串之间比较用scr
♟️if(k!=i)
{ strcpy(temp,str[i]); //字符串之间不能直接赋值
strcpy(str[i],str[k]);
strcpy(str[k],temp);}
从键盘读入若干个字符串,对它们按字母大小的顺序排序,然后把排好序的字符串送到磁盘文件中保存。
gets:

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{ FILE *fp;char str[3][10],temp[10]; //交换,也是数组//用二维数组存储,3行每行有10个字符,每个单词村一行int i,j,k,n=3;printf("Enter strings:\n"); for(i=0;i<n;i++) gets(str[i]);//键盘获得字符串,放到第i行//排序算法:冒泡,选择
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++) { k=i;for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)if(strcmp(str[k],str[j])>0) k=j;//字符串之间比较用scr//>0,排在后面,ascll码值大if(k!=i){ strcpy(temp,str[i]); //字符串之间不能直接赋值strcpy(str[i],str[k]);strcpy(str[k],temp);}}//选择符,记录要交换的位置,i在k里面,//升序,由小到大
if((fp=fopen("D:\\CC\\string.dat","w"))==NULL) {printf("can't open file!\n");exit(0);}printf("\nThe new sequence:\n");for(i=0;i<n;i++){ fputs(str[i],fp);//不带结束标志fputs("\n",fp); //则是向文件中写入一个换行符 \n ,目的是让每个写入文件的字符串独占一行,使文件内容更加清晰易读。printf("%s\n",str[i]); }return 0;
}问题1:

思考:
从文件string.dat中读回字符串,并在屏幕上显示,应如何编写程序?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{ FILE *fp; char str[3][10]; int i=0;if((fp=fopen("D:\\CC\\string.dat", "r"))==NULL) {printf("can't open file!\n");exit(0);}while(fgets(str[i],10,fp)!=NULL){ printf("%s",str[i]); i++; }fclose (fp);return 0;
}
例10.4
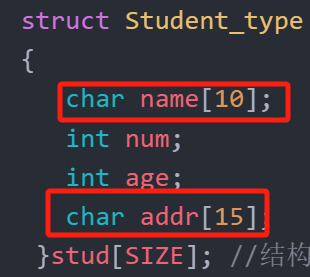
从键盘输入10个学生的有关数据(用结构体数组),然后把它们转存到磁盘文件上去。

#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 10
struct Student_type
{ char name[10];int num;int age;char addr[15];}stud[SIZE]; //结构体数组,长度为10,不在main函数定义,全局变量
void save( ) //不带任何参数,直接访问全局变量,
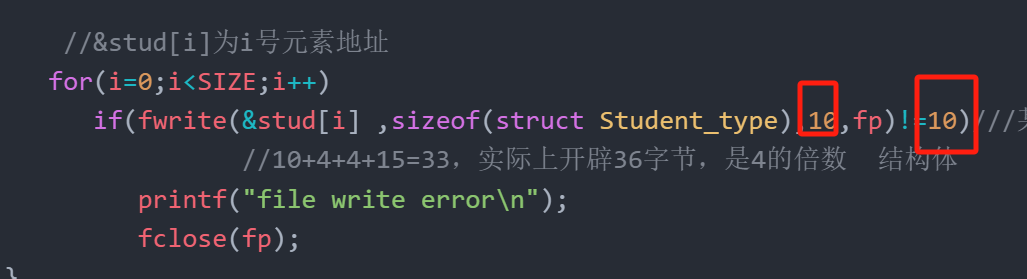
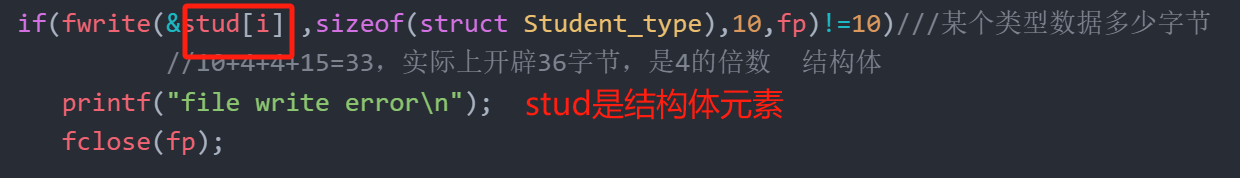
{ FILE *fp; int i;//wb为二进制if((fp=fopen("stu.dat","wb"))==NULL) { printf("cannot open file\n");return;}//&stud[i]为i号元素地址for(i=0;i<SIZE;i++)if(fwrite(&stud[i] ,sizeof(struct Student_type),1,fp)!=1)///某个类型数据多少字节//10+4+4+15=33,实际上开辟36字节,是4的倍数 结构体printf("file write error\n");fclose(fp);
}
int main()
{ int i;printf("enter data of students:\n");for(i=0;i<SIZE;i++) scanf("%s%d%d%s",stud[i].name,&stud[i].num,&stud[i].age,stud[i].addr);save( );return 0;
}

例10.5(1)rewind函数
有一个磁盘文件,内有一些信息。要求第一次将它的内容显示在屏幕上,第二次把它复制到另一文件上。

#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{ FILE *fp1,*fp2;fp1=fopen("file1.dat","r"); fp2=fopen("file2.dat","w"); while(!feof(fp1)) putchar(fgetc(fp1)); putchar(10); //输出到屏幕上rewind(fp1); //小指针又到开头while(!feof(fp1)) putc(getc(fp1),fp2); fclose(fp1); fclose(fp2);return 0;
}
putc(getc(fp1),fp2);

10.4.2随机读写
例10.6
在磁盘文件上存有10个学生的数据。要求将第1,3,5,7,9个学生数据输入计算机,并在屏幕上显示出来。要求:从例10.4中建立的“stu.dat”中读入数据
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct St
{ char name[10];int num;int age;char addr[15];
}stud[10]; int main()
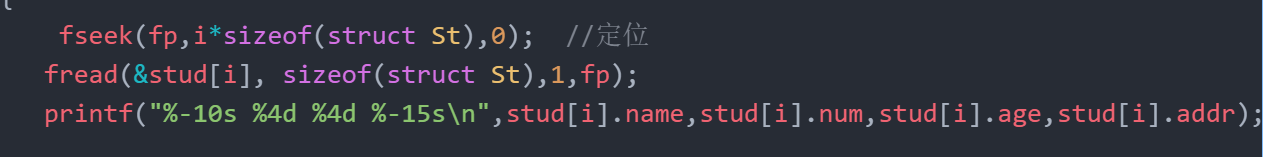
{ int i; FILE *fp; if((fp=fopen("stu.dat","rb"))==NULL) {printf("can not open file\n");exit(0);}for(i=0;i<10;i+=2){ //从1.3.5一直跳,不是按照顺序fseek(fp,i*sizeof(struct St),0); //定位fread(&stud[i], sizeof(struct St),1,fp); printf("%-10s %4d %4d %-15s\n",stud[i].name,stud[i].num,stud[i].age,stud[i].addr); }fclose(fp); return 0;
}

作业
作业5:
![]()
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{FILE *fp;char ch, filename[10];int word = 0, num = 0;printf("请输入文件名: ");scanf("%s", filename);getchar();if ((fp = fopen(filename, "r")) == NULL)
{printf("can't open file!\n");exit(0);
}while(!feof(fp)) { // 循环条件:未到达文件末尾ch = fgetc(fp); // 从文件中读取一个字符if (ch == ' ') // 如果当前字符是空格word = 0; // 标记“未在单词中”else if (word == 0) { // 如果当前字符不是空格,且之前的状态是“未在单词中”word = 1; // 标记“进入单词”num++; // 单词计数+1}
}printf("文件中的单词个数为:%d\n",num);fclose(fp);return 0;
}
int main() {FILE *in,*out;char ch,infile[10],outfile[10];char c;int i,sum=0 ,word=0;printf("输入读入文件的名字:");scanf("%s",infile);printf("输入输出文件的名字:");scanf("%s",outfile);if((in=fopen(infile,"r"))==NULL){printf("无法打开此文件\n");exit(0);}if((out=fopen(outfile,"w"))==NULL){printf("无法打开此文件\n");exit(0);}for(i=0;(c=fgetc(in))!=EOF;i++)if(c=='')word=0;else if(word==0 ){ word=1;sum++;}
printf("%d words\n",sum);
fprintf(out,"%d words\n",sum);
fclose(in);fclose(out);
return 0;}作业6
题目: 以二进制方式读入一个外部数据文件,并存储在结构体数组中
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 3struct Student_type
{char name[10];int num;int age;char addr[15];
} stud[SIZE];void save()
{FILE *fp;int i;if((fp=fopen("stu.dat","wb"))==NULL){printf("cannot open file\n");return;}if(fwrite(&stud[0], sizeof(struct Student_type), SIZE, fp) != SIZE)printf("file write error\n");fclose(fp);
}void print()
{FILE *fp;int i;if((fp=fopen("stu.dat","rb"))==NULL){printf("cannot open file\n");return;}struct Student_type student;for(i = 0; i < SIZE; i++){if(fread(&student, sizeof(struct Student_type), 1, fp) == 1){printf("Name: %s, Num: %d, Age: %d, Addr: %s\n",student.name, student.num, student.age, student.addr);}else{printf("file read error\n");break;}}fclose(fp);
}int main()
{int i;printf("enter data of students:\n");for(i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)scanf("%s %d %d %s", stud[i].name, &stud[i].num, &stud[i].age, stud[i].addr);save();printf("\nData saved to stu.dat. Now printing the data:\n");print();return 0;
}作业7
1.用正确的方法读取学生信息文件stu.txt的数据,并生成一个单链表(每个学生数据为一个节点)
2.输入一个学生的名字,在列表中删除该名字的节点,如果没有匹配到的节点,也输出提示信息。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>// 学生结构体定义
struct stu {char name[10];int num;int age;char addr[10];struct stu *next;
} aaa, b, c;int main() {// 初始化链表aaa.next = &b;b.next = &c;c.next = NULL;// 打开文件FILE *fp;if ((fp = fopen("D://stu2.txt", "rb")) == NULL) {printf("cannot open file\n");exit(0);}// 读取文件数据并打印链表struct stu *pt = &aaa; // 链表头指针struct stu *p = pt; // 遍历指针while (p != NULL) {fscanf(fp, "%s %d %d %s", p->name, &p->num, &p->age, p->addr);printf("%-10s %4d %4d %-15s\n", p->name, p->num, p->age, p->addr);p = p->next;}fclose(fp);// 用户输入要删除的姓名char name[10];printf("\n请输入要删除的学生姓名: ");gets(name);// 查找并删除节点p = pt;struct stu *prev = NULL; // 前驱节点指针if (strcmp(name, p->name) == 0) {pt = pt->next; // 删除头节点} else {while (p != NULL && strcmp(name, p->name) != 0) {prev = p;p = p->next;}if (p == NULL) {printf("找不到该学生!\n");return 0;}prev->next = p->next; // 删除中间或尾节点}// 打印删除后的链表printf("\n删除后的学生列表:\n");p = pt;while (p != NULL) {printf("%-10s %4d %4d %-15s\n", p->name, p->num, p->age, p->addr);p = p->next;}return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>// 定义学生结构体
typedef struct Student {char name[10];int num;int age;char addr[10];struct Student *next;
} Student;// 创建新节点
struct Student* creatNode(const char* name, int num, int age, const char* addr) {struct Student* p = (struct Student*)malloc(sizeof(struct Student));if (!p) {perror("内存分配失败");return NULL;}strcpy(p->name, name);p->num = num;p->age = age;strcpy(p->addr, addr);p->next = NULL;return p;
}// 从文件读取数据并创建链表
struct Student *realList(const char* filename) {FILE *fp = fopen(filename, "r");if (fp == NULL) {printf("cannot open this file\n");exit(0);}Student *head = NULL;Student *tail = NULL;char name[10];int num;int age;char addr[10];while (fscanf(fp, "%s %d %d %s", name, &num, &age, addr) == 4) {struct Student* p = creatNode(name, num, age, addr);if (head == NULL) {head = p;tail = p;} else {tail->next = p;tail = p;}}fclose(fp);return head;
}// 打印链表
void printList(Student* head) {Student* current = head;while (current != NULL) {printf("Name:%s,Num:%d,Age:%d,Addr:%s\n", current->name, current->num, current->age, current->addr);current = current->next;}
}// 释放链表内存
void freeList(Student* head) {Student* current = head;Student* next;while (current != NULL) {next = current->next;free(current);current = next;}
}// 删除指定学生名字节点的函数
struct Student* deleteStudentNodeByName(struct Student* head, const char* targetName) {struct Student* p = NULL;struct Student* q = head;while (q != NULL && strcmp(q->name, targetName) != 0) {p = q;q = q->next;}if (q == NULL) {printf("未找到名为 %s 的学生节点\n", targetName);return head;}if (p == NULL) {head = q->next;} else {p->next = q->next;}free(q);return head;
}int main() {const char* fpname = "stu.txt";Student *head = realList(fpname);if (head != NULL) {char targetName[10];printf("请输入要删除的学生名字: ");scanf("%s", targetName);head = deleteStudentNodeByName(head, targetName);printf("删除节点后的链表:\n");printList(head);freeList(head);}return 0;
}模板
输入字符+送到磁盘
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>//用exit函数时加
int main()
{ FILE *fp;char ch,filename[10];//存放输入的文件名printf("请输入所用的文件名:");//没有说路径,源文件所在位置存放在一起scanf("%s",filename);if((fp=fopen(filename,"w"))==NULL) { printf("无法打开此文件\n"); exit(0); }ch=getchar( );//输入字符printf("请输入一个字符串(以#结束):");// getchar 逐个读取字符,ch=getchar( ); // 送到磁盘while(ch!='#') { fputc(ch,fp); //使用 putchar 将字符输出到屏幕上显示,继续读取下一个字符。putchar(ch); ch=getchar(); }fclose(fp); return 0;
}打开文件
if ((fp=fopen("file1","r"))==NULL){printf("cannot open this file\n");exit(0);//人为中断执行}
磁盘文件中的信息复制到另一个磁盘文件中
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main( )
{ FILE *in,*out; //读和写出去char ch,infile[10],outfile[10]; printf("输入读入文件的名字:");scanf("%s",infile); printf("输入输出文件的名字:");scanf("%s",outfile); if((in=fopen(infile,"r"))==NULL) {printf("无法打开此文件\n"); exit(0);}if((out=fopen(outfile,“w”))==NULL) {printf("无法打开此文件\n"); exit(0); }while(!feof(in)) //检查当前读写位置是否移到文件末端,不为1就不会读到末端{ ch=fgetc(in); fputc(ch,out); putchar(ch); //输出一份到屏幕上}putchar(10); //换行fclose(in); //关闭fclose(out); //关闭return 0;
}