【LeetCode hot100|Week5】链表2
笔记用于个人复习和巩固,题解非原创,参考LeetCode官方题解以及各个大佬的解法,希望给大家带来帮助,同时笔记也能督促我学习进步
这周主要把链表剩余部分的题目刷了一遍

文章目录
- Week5
- D1
- 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
- D2
- 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
- D3
- 25. K 个一组翻转链表
- D4
- 138. 随机链表的复制
- D5
- 148. 排序链表
- D6
- 23. 合并 K 个升序链表
- 暴力
- 优化
Week5
D1
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
先计算链表长度,再循环得到要删除的前一个节点
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);int length = getLength(head);ListNode cur = dummy;for (int i = 1; i < length - n + 1; ++i) {cur = cur.next;}cur.next = cur.next.next;ListNode ans = dummy.next;return ans;}public int getLength(ListNode head) {int length = 0;while (head != null) {++length;head = head.next;}return length;}
}D2
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);dummyHead.next = head;ListNode temp = dummyHead;while (temp.next != null && temp.next.next != null) {ListNode node1 = temp.next;ListNode node2 = temp.next.next;temp.next = node2;node1.next = node2.next;node2.next = node1;temp = node1;}return dummyHead.next;}
}D3
25. K 个一组翻转链表
25. K 个一组翻转链表
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {// 统计节点个数int n = 0;for (ListNode cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {n++;}ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);ListNode p0 = dummy;ListNode pre = null;ListNode cur = head;// k 个一组处理for (; n >= k; n -= k) {for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { // 同 92 题ListNode nxt = cur.next;cur.next = pre; // 每次循环只修改一个 next,方便大家理解pre = cur;cur = nxt;}// 见视频ListNode nxt = p0.next;p0.next.next = cur;p0.next = pre;p0 = nxt;}return dummy.next;}
}D4
138. 随机链表的复制
138. 随机链表的复制
遍历两遍链表,第一次建立新的节点,第二次建立节点之间的联系
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {int val;Node next;Node random;public Node(int val) {this.val = val;this.next = null;this.random = null;}
}
*/class Solution {public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {if(head==null){return null;}Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();Node p = head;//创建新节点建立与原始节点的映射关系,map用于解决random节点的链接问题while (p != null) {map.put(p, new Node(p.val));p = p.next;}p = head;//将各个节点连接起来while (p != null) {Node newNode = map.get(p);newNode.next = map.get(p.next);newNode.random = map.get(p.random);p = p.next;}return map.get(head);//返回新的头节点}
}
D5
148. 排序链表
148. 排序链表
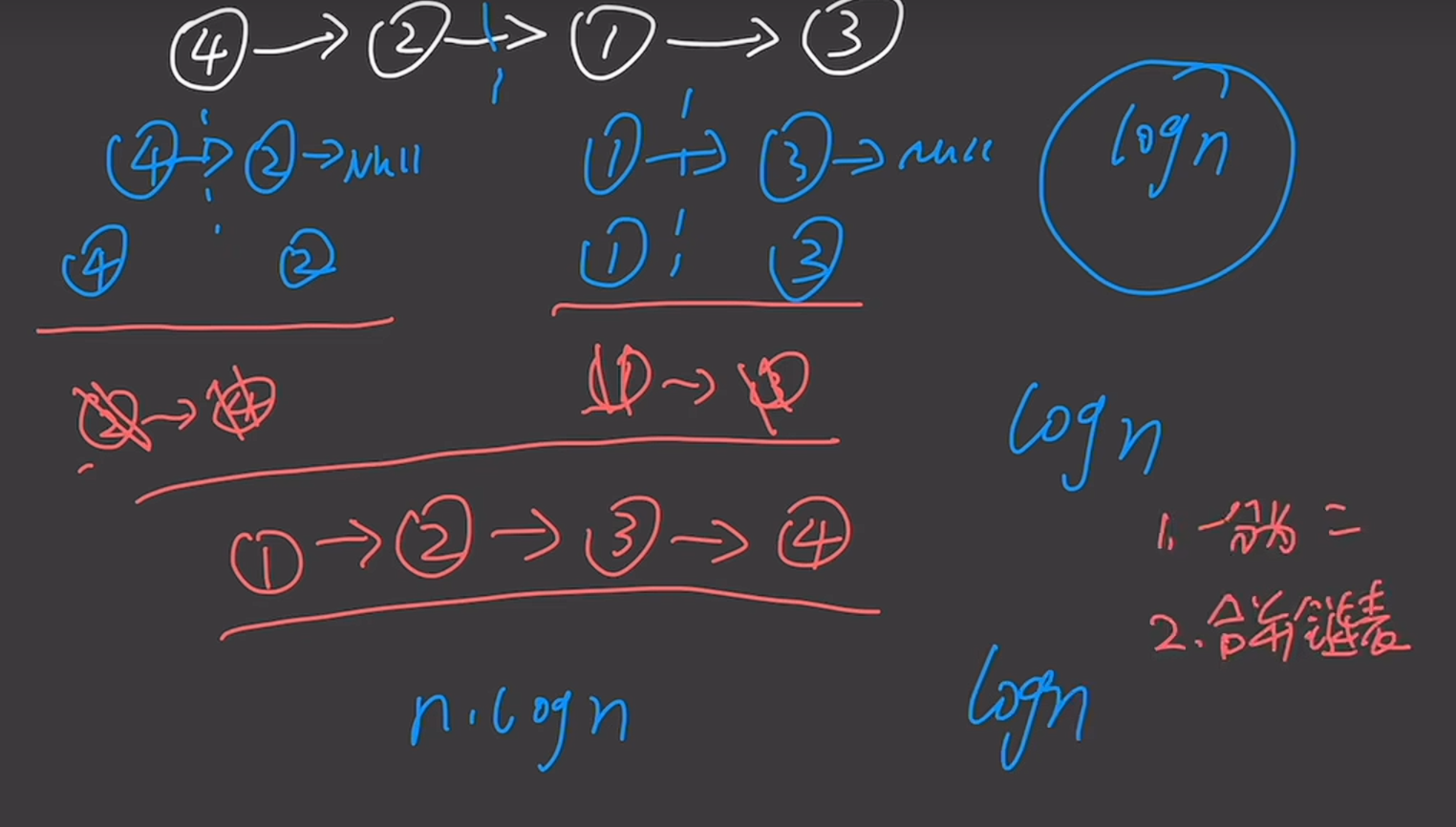
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {if(head == null||head.next == null){return head;}ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head.next;while(fast != null && fast.next != null){slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}ListNode second = slow.next;slow.next = null;ListNode first = head;first = sortList(first);second = sortList(second);return mergeList(first,second); }public ListNode mergeList(ListNode left,ListNode right){ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);ListNode tail = dummy;while(left != null && right != null){if(left.val < right.val){tail.next = left;left = left.next;}else{tail.next = right;right = right.next;}tail = tail.next;}if(left != null){tail.next = left;}else{tail.next = right;}return dummy.next;}
}
D6
23. 合并 K 个升序链表
23. 合并 K 个升序链表
暴力
遍历数组,依次合并
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {if(lists == null || lists.length == 0){return null;}ListNode result = null;for(ListNode list:lists){result = mergeTwoLists(result, list);}return result;}public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode left,ListNode right){ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);ListNode tail = dummy;while(left != null && right != null){if(left.val < right.val){tail.next = left;left = left.next;}else{tail.next = right;right = right.next;}tail = tail.next;}if(left != null)tail.next = left;else tail.next = right;return dummy.next;}
}
优化
两两合并
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {if(lists == null || lists.length == 0){return null;}while(lists.length > 1){List<ListNode> tempList = new ArrayList<>();for(int i = 0;i < lists.length;i += 2){ListNode l1 = lists[i];ListNode l2 = null;if(i + 1 < lists.length)l2 = lists[i + 1];tempList.add(mergeTwoLists(l1,l2));}lists = tempList.toArray(new ListNode[0]);}return lists[0];}public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode left,ListNode right){ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);ListNode tail = dummy;while(left != null && right != null){if(left.val < right.val){tail.next = left;left = left.next;}else{tail.next = right;right = right.next;}tail = tail.next;}if(left != null)tail.next = left;else tail.next = right;return dummy.next;}
}
Java 中链表(ListNode)的基本用法
- 链表节点定义
在 Java 中,链表通常由一个自定义的 ListNode 类表示:
public class ListNode {int val;ListNode next;// 构造函数ListNode() {}ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}
注意:Java 标准库没有内置的单向链表结构(LinkedList 是双向链表),所以我们常自己定义 ListNode。
- 创建链表
方法一:手动逐个创建节点
// 创建 1 -> 2 -> 3 的链表
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(2, node3);
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(1, node2);ListNode head = node1; // 头节点
方法二:使用循环创建
// 创建 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
int[] values = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
ListNode head = null;
ListNode tail = null;for (int val : values) {ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);if (head == null) {head = newNode;tail = newNode;} else {tail.next = newNode;tail = newNode;}
}
- 遍历链表
public void printList(ListNode head) {ListNode current = head;while (current != null) {System.out.print(current.val + " -> ");current = current.next;}System.out.println("null");
}// 调用
printList(head); // 输出: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> null
- 在链表末尾插入节点
public ListNode append(ListNode head, int val) {ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);if (head == null) {return newNode;}ListNode current = head;while (current.next != null) {current = current.next;}current.next = newNode;return head;
}
- 在链表头部插入节点
public ListNode prepend(ListNode head, int val) {ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);newNode.next = head;return newNode; // 新头节点
}
- 删除值为 val 的节点
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {// 使用虚拟头节点简化删除头节点的情况ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);dummy.next = head;ListNode prev = dummy;ListNode current = head;while (current != null) {if (current.val == val) {prev.next = current.next; // 跳过当前节点} else {prev = current;}current = current.next;}return dummy.next;
}
- 反转链表(经典操作)
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {ListNode prev = null;ListNode current = head;while (current != null) {ListNode next = current.next; // 保存下一个节点current.next = prev; // 反转指针prev = current; // 移动 prevcurrent = next; // 移动 current}return prev; // 新的头节点
}
- 查找链表中间节点(快慢指针)
public ListNode findMiddle(ListNode head) {if (head == null) return null;ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}return slow; // slow 就是中间节点
}
- 判断链表是否有环(快慢指针)
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) return false;ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;if (slow == fast) {return true; // 快慢指针相遇,说明有环}}return false;
}
- 使用 Java 内置的 LinkedList 类(双向链表)
虽然不是 ListNode,但 Java 提供了 java.util.LinkedList,可用于模拟链表操作:
import java.util.*;LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.addFirst(1); // 头插
list.addLast(2); // 尾插
list.add(1, 10); // 在索引1插入10
System.out.println(list); // [1, 10, 2]list.removeFirst();
list.removeLast();
注意:LinkedList 是双向链表,适合频繁插入删除,但做算法题时通常还是用 ListNode。
