ApplicationContext接口实现(三)
除了前面讲过的两种applicationContext接口实现类之外,还有基于java配置类的实现接口
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,这是一种比较常用的接口容器。
基于Java配置类的实现
1.准备实体类
static class Bean1{}static class Bean2{private Bean1 bean1;public void setBean1(Bean1 bean1){this.bean1 = bean1;}public Bean1 getBean1(){return bean1;}}2.准备配置类
使用@Configuration以及@Bean注解配置类,并且需要设置类之间的注入关系。
@Configurationstatic class Config{@Beanpublic Bean1 bean1(){return new Bean1();}@Beanpublic Bean2 bean2(Bean1 bean1){Bean2 bean2 = new Bean2();bean2.setBean1(bean1);return bean2;}}3.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类的使用
public static void testAnnotationConfigApplicationContext(){AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()){System.out.println(name);}System.out.println(context.getBean(Bean2.class).getBean1());}4.调用方法
public static void main(String[] args) {//testClassPathXmlApplicationContext();//testFileSystemXmlApplicationContext();/*DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();System.out.println("读取之前....");for(String name : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()){System.out.println(name);}XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);reader.loadBeanDefinitions(new FileSystemResource("src\\main\\resources\\a01.xml"));System.out.println("读取之后");for(String name : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()){System.out.println(name);}*/testAnnotationConfigApplicationContext();}输出结果:
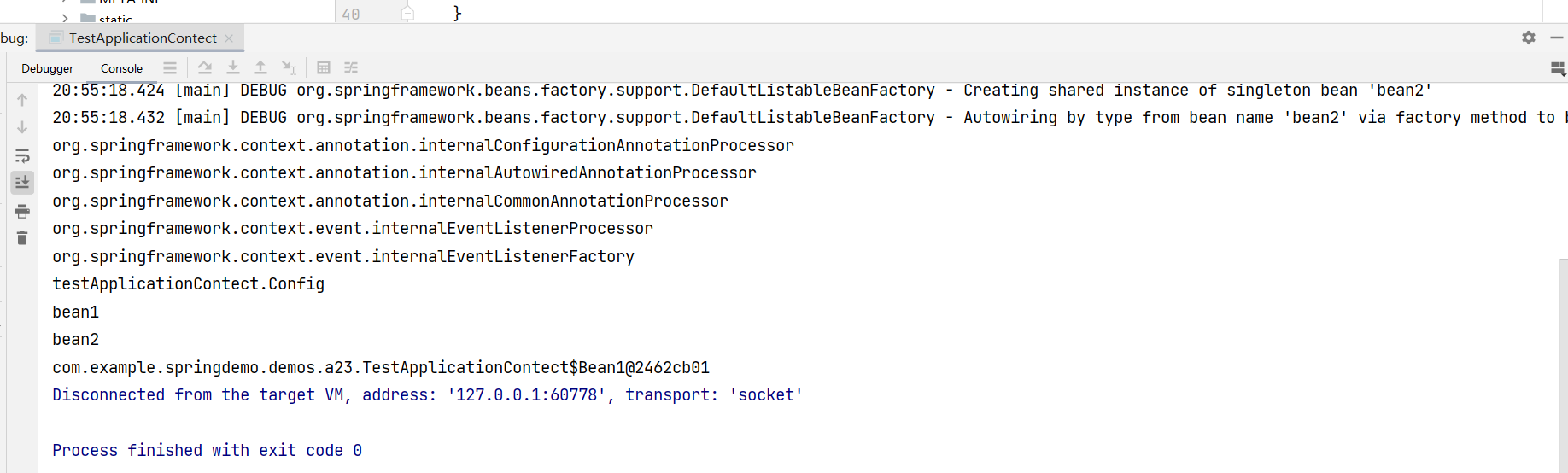
通过结果可以看到Spring容器里面注入了Config配置类以及Bean1和Bean2。并且还自带了一些后处理器。效果等于使用了下面的代码。
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(beanFactory);