【04】EPGF 架构搭建教程之 工具环境变量的配置
📝 EPGF 架构搭建教程之 工具环境变量的配置(路径自治 · 全局可控)
📅 更新时间:2025-09-21
🎯 目标:通过手动 PATH 配置实现全局工具链可见性,完成 路径自治,让 Python 各版本和工具链在系统全局可用
🔑 核心理念:路径可控、顺序可审计、冲突可避免
EPGF 白皮书】路径治理驱动的多版本 Python 架构—— Windows 环境治理与 AI 教学开发体系
Python 多版本环境治理理念驱动的系统架构设计——三维治理、四级隔离、五项自治 原则(路径治理升级修订 V 2.0 版)
【01】EPGF 架构搭建教程之 Anaconda 安装指南
【02】EPGF 架构搭建教程之 Python 多版本配置
【03】EPGF 架构搭建教程之 虚拟环境管理工具的安装
1. 教程定位:承上启下的关键步骤
在前两篇中,我们已经完成:
-
多版本 Python 环境:py308、py309、py310、py311、py312、py313
-
工具链安装:uv、poetry、hatch、pipenv、virtualenv、pipx、nox、tox、poetry-plugin-shell
本篇是 EPGF 架构中的“路径自治”落地篇,通过手动配置 PATH,将这些工具精准暴露到系统,既保证全局可见,又避免路径污染和优先级混乱。
📌 这一篇是后续“项目级本地化”和“PyCharm 实战演示”的前置准备,必须先完成。
2. 为什么手动配置 PATH 而不是默认勾选?
| 问题 | 默认做法 | EPGF 做法 | 好处 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PATH 自动添加 | 安装勾选“Add Anaconda to PATH” | 取消勾选,手动添加 | 避免安装器打乱 PATH 顺序 |
| 全局冲突 | 可能覆盖系统其他 Python | 精准控制优先级,谁在前谁在后 | 确保调用的是目标 py3xx 解释器 |
| 难以审计 | 安装器自动插入,不可见 | 所有路径手动添加,可审计 | 方便迁移、复制、复现 |
💡 核心理念:路径是 EPGF 架构的“控制面板”。只有我们亲手配置,才能实现路径自治。
详细配置过程(含快捷设置)参考:
EPGF 架构下的 Python 环境变量设置建议——Anaconda 路径精简后暴露 python 及工具到环境变量的配置记录 [三]
3. 系统环境变量 PATH 配置
建议将以下路径逐条添加到 系统环境变量 PATH:
D:\A
D:\A\Library\mingw-w64\bin
D:\A\Library\usr\bin
D:\A\Library\bin
D:\A\Scripts
D:\A\envs\py308
D:\A\envs\py309
D:\A\envs\py310
D:\A\envs\py311
D:\A\envs\py312
D:\A\envs\py313
| 路径 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| D:\A | 使 conda.exe 可全局调用 |
| D:\A\Library\mingw-w64\bin | 提供 GCC 编译工具链(如需编译 C/C++ 扩展) |
| D:\A\Library\usr\bin | 提供部分类 Unix 工具(如 patch、diff) |
| D:\A\Library\bin | 包含 DLL 动态链接库,运行时必需 |
| D:\A\Scripts | 提供 conda、pip、activate 等脚本 |
| D:\A\envs\py3xx | 暴露各版本 python.exe,便于 where python 查看 |
⚠ 建议顺序保持一致,避免先后颠倒导致调用非预期的解释器。
4. 用户环境变量 PATH 配置
在 用户环境变量 PATH 中添加以下路径,确保工具链的可执行文件可被调用:
D:\A\envs\py308\Scripts
D:\A\envs\py309\Scripts
D:\A\envs\py310\Scripts
D:\A\envs\py311\Scripts
D:\A\envs\py312\Scripts
D:\A\envs\py313\Scripts
| 路径 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| D:\A\envs\py3xx\Scripts | 暴露工具链(uv、poetry、hatch、pipenv 等)的可执行文件 |
💡 用户 PATH 用于暴露工具,不与系统 PATH 混放,便于分层治理。
5. 推荐使用 PowerToys 环境变量编辑器
微软 PowerToys 提供了可视化的环境变量管理器:
-
支持逐条添加和删除
-
可直接启用/禁用某条 PATH
-
无需重新打开 CMD 即时生效
🔗 PowerToys 官方下载
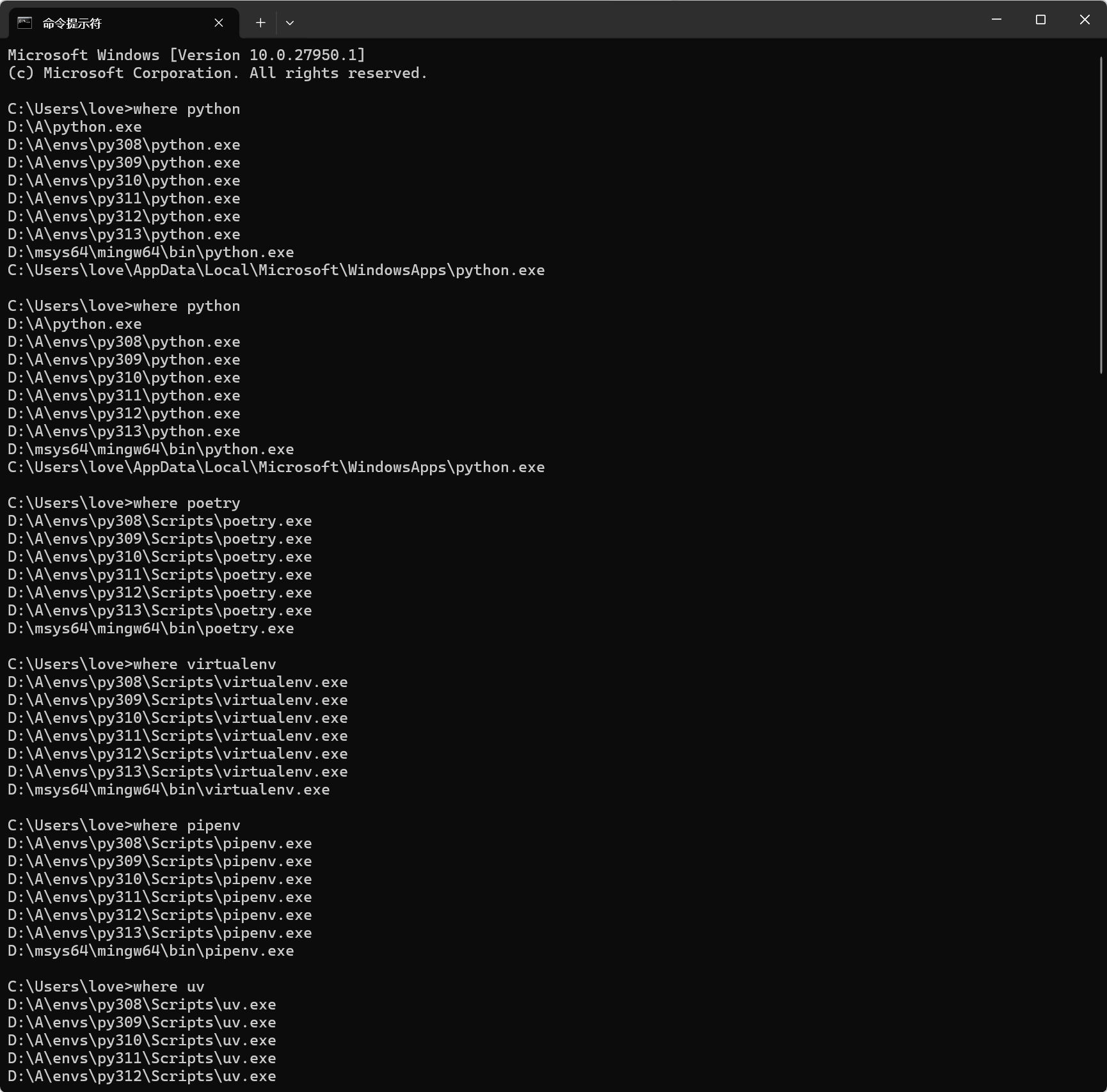
6. 验证 PATH 配置是否生效
打开终端,执行:
where python
where poetry
where virtualenv
where pipenv
where uv
where hatch
where pipx
where nox
where tox应看到:
-
输出中包含所有 py3xx 的 python.exe 路径
-
输出中包含 D:\A\envs\py3xx\Scripts\poetry.exe、uv.exe 等工具
✅ 如果缺少路径,说明 PATH 配置有误,需重新检查顺序。
7. 对应 EPGF 架构要点
| 架构维度 | 本篇落地 | 铺垫下一步 |
|---|---|---|
| 三维治理 → 路径治理 | 手动配置 PATH,路径顺序可控 | 保证后续创建 .venv 时不会冲突 |
| 四级隔离 → 第一级隔离 | 与系统全局隔离,但可控地暴露入口 | 项目级隔离可在此基础上叠加 |
| 五项自治 → 路径自治 | 所有路径透明可查,便于迁移复现 | 下一篇进入项目级本地化实践 |
8. 思维导图梳理
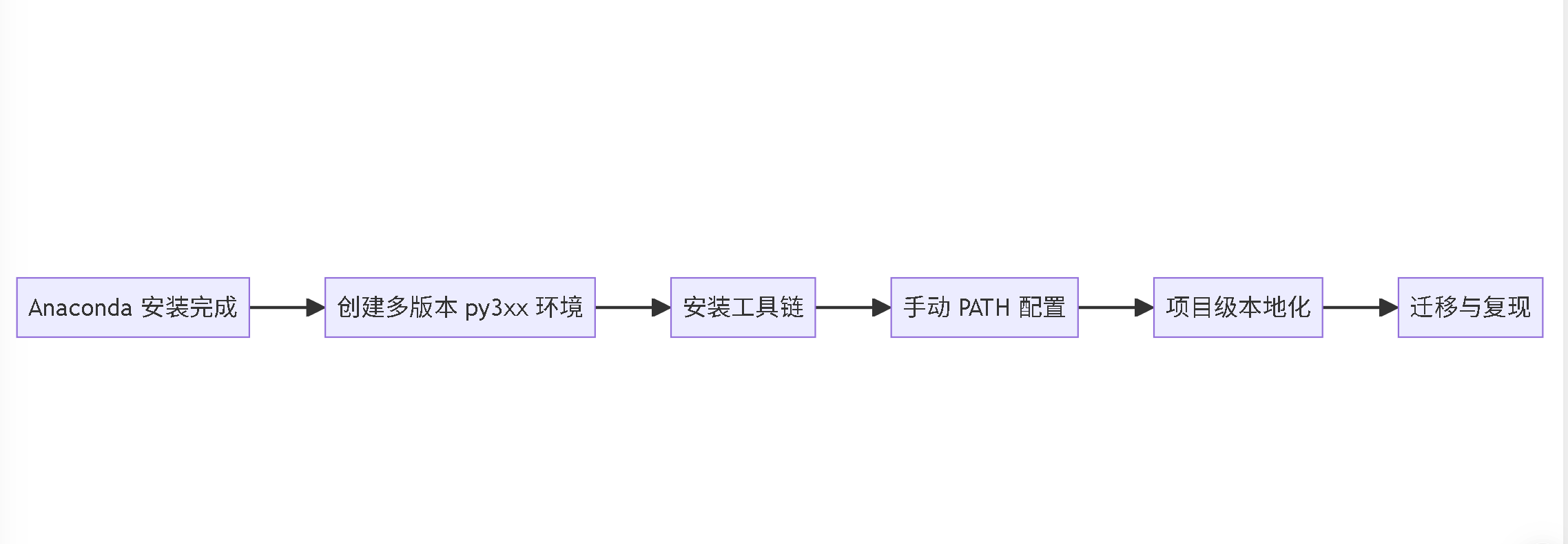
graph LRA[Anaconda 安装完成] --> B[创建多版本 py3xx 环境]B --> C[安装工具链]C --> D[手动 PATH 配置]D --> E[项目级本地化]E --> F[迁移与复现]
📌 PATH 配置是连接工具链层和项目层的关键环节。

9. 下一步行动
完成本篇后,系统已实现 路径自治,接下来可以进入:
-
项目级虚拟环境实战演示:用
python -m venv .venv创建项目内虚拟环境 -
本地化工具链(uv、poetry、hatch 等),实现项目自包含
附录:环境变量设置快捷脚本
说明:下列脚本用于将 EPGF 架构建议的
D:\A与各 py3xx 环境路径批量写入系统/用户 PATH(便于where python/where poetry等能列出所有版本与工具)。请在使用前认真阅读本章节并在受控环境中测试。
声明(必读):使用此脚本前,请确保您知晓脚本原理,请仔细核对路径,作者不对脚本使用之后产生的潜在不良后果负责。
使用前准备(强烈建议)
-
以管理员权限运行:修改系统 PATH 需要管理员权限(System / Machine 级别)。
-
备份当前 PATH(示例将备份文件放在
C:\):-
PowerShell 备份(推荐):
[Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path','Machine') | Out-File -FilePath C:\epgf_backup_system_path.txt -Encoding utf8 [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path','User') | Out-File -FilePath C:\epgf_backup_user_path.txt -Encoding utf8-
CMD/注册表备份(备用):
reg query "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" /v Path > C:\epgf_backup_system_path_reg.txt reg query "HKCU\Environment" /v Path > C:\epgf_backup_user_path_reg.txt -
-
先在一台机器上测试,确认行为与预期一致后再批量部署。
-
如果你的 PATH 已经非常长(历史遗留),强烈推荐使用 PowerShell 方案,因为
setx可能导致截断。
A. CMD 脚本(简单版 — 适合快速手动执行)
适用场景:单台机器快速执行;注意
setx的长度限制。
把下面保存为 epgf-set-path.cmd,以管理员身份运行(右键 → 以管理员身份运行):
@echo off
:: epgf-set-path.cmd
:: 以管理员权限运行echo 备份当前 PATH 到 C:\epgf_backup_system_path_reg.txt 和 C:\epgf_backup_user_path_reg.txt ...
reg query "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" /v Path > C:\epgf_backup_system_path_reg.txt
reg query "HKCU\Environment" /v Path > C:\epgf_backup_user_path_reg.txtecho 正在设置系统环境变量 PATH...
setx /M PATH "%PATH%;D:\A;D:\A\Library\mingw-w64\bin;D:\A\Library\usr\bin;D:\A\Library\bin;D:\A\Scripts;D:\A\envs\py308;D:\A\envs\py309;D:\A\envs\py310;D:\A\envs\py311;D:\A\envs\py312;D:\A\envs\py313"echo 正在设置用户环境变量 PATH...
setx PATH "%PATH%;D:\A\envs\py308\Scripts;D:\A\envs\py309\Scripts;D:\A\envs\py310\Scripts;D:\A\envs\py311\Scripts;D:\A\envs\py312\Scripts;D:\A\envs\py313\Scripts"echo 完成。请重新打开终端或注销/重启以使更改生效。
pause
注意 / 限制:
-
setx写入有长度限制(旧版 Windows 截断风险),且会把新的 PATH 写入注册表覆盖原值;在 PATH 很长时可能造成截断丢失旧值。 -
若不确定,请用 PowerShell 脚本(下文)或先备份再测试。
B. PowerShell 脚本(推荐 — 更安全、自动去重、避免截断)
把下面保存为 epgf-set-path.ps1,以管理员权限运行 PowerShell(例如:右键 PowerShell -> 以管理员身份运行,然后执行 .\epgf-set-path.ps1,或用 powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File .\epgf-set-path.ps1):
# epgf-set-path.ps1
# 以管理员权限运行# 备份当前 PATH 到文件
$systemPath = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path','Machine')
$userPath = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path','User')
$systemPath | Out-File C:\epgf_backup_system_path.txt -Encoding utf8
$userPath | Out-File C:\epgf_backup_user_path.txt -Encoding utf8# 要追加的系统路径(按优先级顺序)
$newSystemPaths = @('D:\A','D:\A\Library\mingw-w64\bin','D:\A\Library\usr\bin','D:\A\Library\bin','D:\A\Scripts','D:\A\envs\py308','D:\A\envs\py309','D:\A\envs\py310','D:\A\envs\py311','D:\A\envs\py312','D:\A\envs\py313'
)# 将新路径追加到系统 PATH,且避免重复
$sysParts = @()
if ($systemPath -ne $null -and $systemPath -ne '') { $sysParts = $systemPath -split ';' | ForEach-Object { $_.Trim() } | Where-Object { $_ -ne '' } }
foreach ($p in $newSystemPaths) {if (-not ($sysParts -contains $p)) {$sysParts += $p}
}
$newSystem = ($sysParts -join ';')
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('Path', $newSystem, 'Machine')# 用户 PATH —— 仅用于工具可执行文件(Scripts)
$newUserPaths = @('D:\A\envs\py308\Scripts','D:\A\envs\py309\Scripts','D:\A\envs\py310\Scripts','D:\A\envs\py311\Scripts','D:\A\envs\py312\Scripts','D:\A\envs\py313\Scripts'
)$userParts = @()
if ($userPath -ne $null -and $userPath -ne '') { $userParts = $userPath -split ';' | ForEach-Object { $_.Trim() } | Where-Object { $_ -ne '' } }
foreach ($p in $newUserPaths) {if (-not ($userParts -contains $p)) {$userParts += $p}
}
$newUser = ($userParts -join ';')
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('Path', $newUser, 'User')Write-Host "✅ PATH 设置完成。已备份到 C:\epgf_backup_system_path.txt 和 C:\epgf_backup_user_path.txt" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host "请重新打开 PowerShell 或注销/重启以使更改生效。"
优点:
-
自动去重(避免重复条目)
-
不会因长度问题被截断
-
便于回滚(因为已写入备份文件)
C. 回滚(恢复备份)示例
PowerShell 恢复(推荐):
# 以管理员权限运行
$oldSystem = Get-Content C:\epgf_backup_system_path.txt -Raw
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('Path', $oldSystem, 'Machine')$oldUser = Get-Content C:\epgf_backup_user_path.txt -Raw
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('Path', $oldUser, 'User')Write-Host "已恢复 PATH,请注销或重启以生效。" -ForegroundColor Yellow
CMD/注册表恢复(如使用过 reg 导出):
reg import C:\epgf_backup_system_path.reg
reg import C:\epgf_backup_user_path.reg
D. 验证(执行后检查)
在新的终端(必须是脚本执行后新打开的终端)中,运行:
where python
where poetry
where uv
期望示例输出(可见多个版本):
D:\A\python.exe
D:\A\envs\py308\python.exe
D:\A\envs\py309\python.exe
D:\A\envs\py310\python.exe
...
D:\A\envs\py310\Scripts\poetry.exe
D:\A\envs\py310\Scripts\uv.exe
若输出缺少预期路径,回到备份文件检查是否写入成功,或检查脚本是否以管理员权限运行。
E. 运行与权限小贴士
-
在 Windows 10/11 上,新开进程会读取新的 PATH;部分 GUI 进程需要注销或重启 Explorer 才能看到更新。
-
推荐步骤:以管理员运行 PowerShell,执行 PowerShell 脚本,打开新的 PowerShell / CMD 确认
where python。若仍未生效,注销或重启机器。 -
如果你的组织使用集中化管理工具(SCCM、Intune、Ansible 等),请使用这些工具分发并收集执行结果(避免手工操作错误)。
F. 企业/批量部署建议
-
对大量机器部署,优先使用
epgf-set-path.ps1(PowerShell)并通过运维平台下发执行。 -
在部署前把
C:\epgf_backup_system_path.txt存档到中央位置,便于大规模回滚。
再次提醒(重要):使用此脚本前,请确保您知晓脚本原理,请仔细核对路径,作者不对脚本使用之后产生的潜在不良后果负责。
