[数据结构] 二叉树
1 . 树形结构
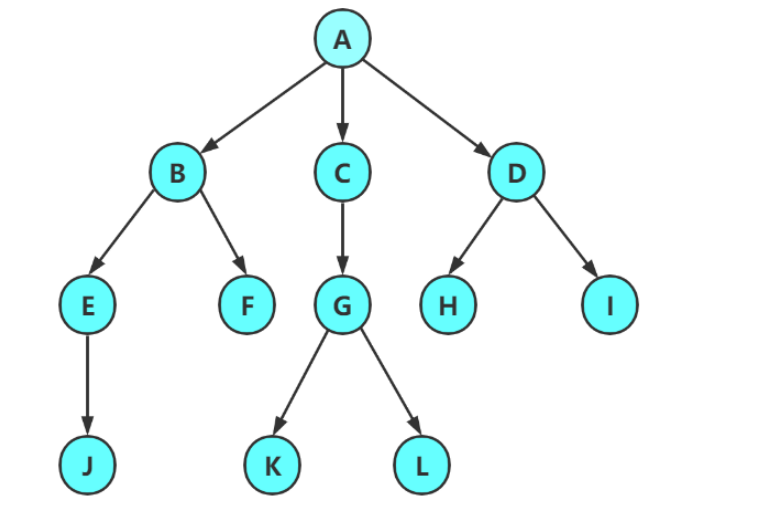
注意:
- 子树是不相交的
- 除了根节点外 , 每个结点有且仅有一个父节点
- 一棵N个结点的树有N-1条边
概念:
- 结点的度 : 一个结点含 子树的个数
- 树的度 : 一颗树种 , 所有结点 度的最大值
- 叶子结点或终端结点 : 度为0的结点
- 双亲结点或夫结点 : 若一个结点含有子节点 , 这个结点称为父节点
- 孩子结点或子节点 : 一个结点含有子树的的跟结点称为其子结点的父节点
- 根节点 : 一棵树种 , 没有双亲结点的结点
- 结点的层次 : 从根开始定义 , 根为第一层 , 根的子节点为第二层
- 树的高度或深度 : 树中结点的最大层次; 树的高度是树的最大深度
2 . 二叉树
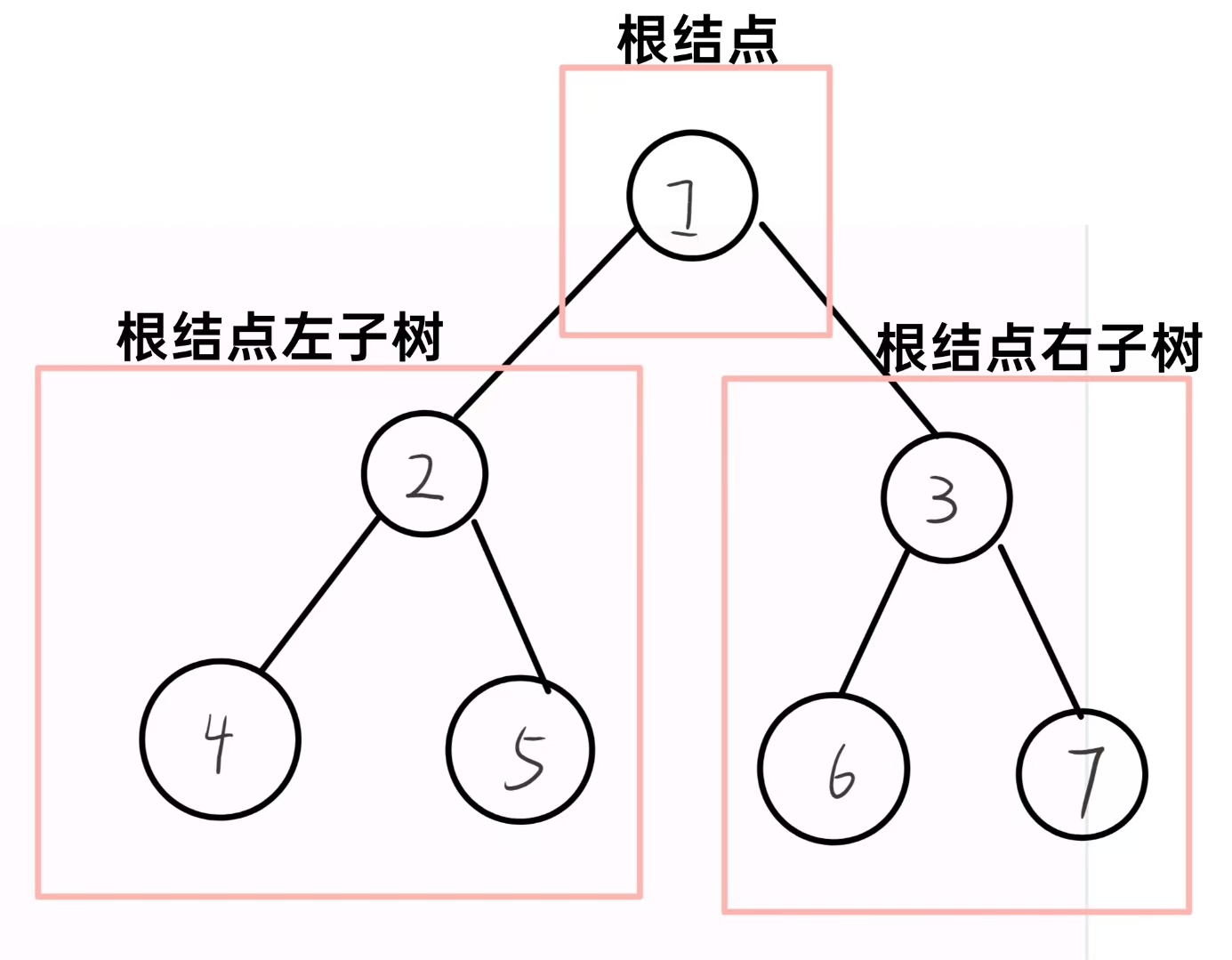
2.1 一颗二叉树是结点的一个有限集合
该集合 :
- 或者为空
- 或者是由一个根结点 加上两颗别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成
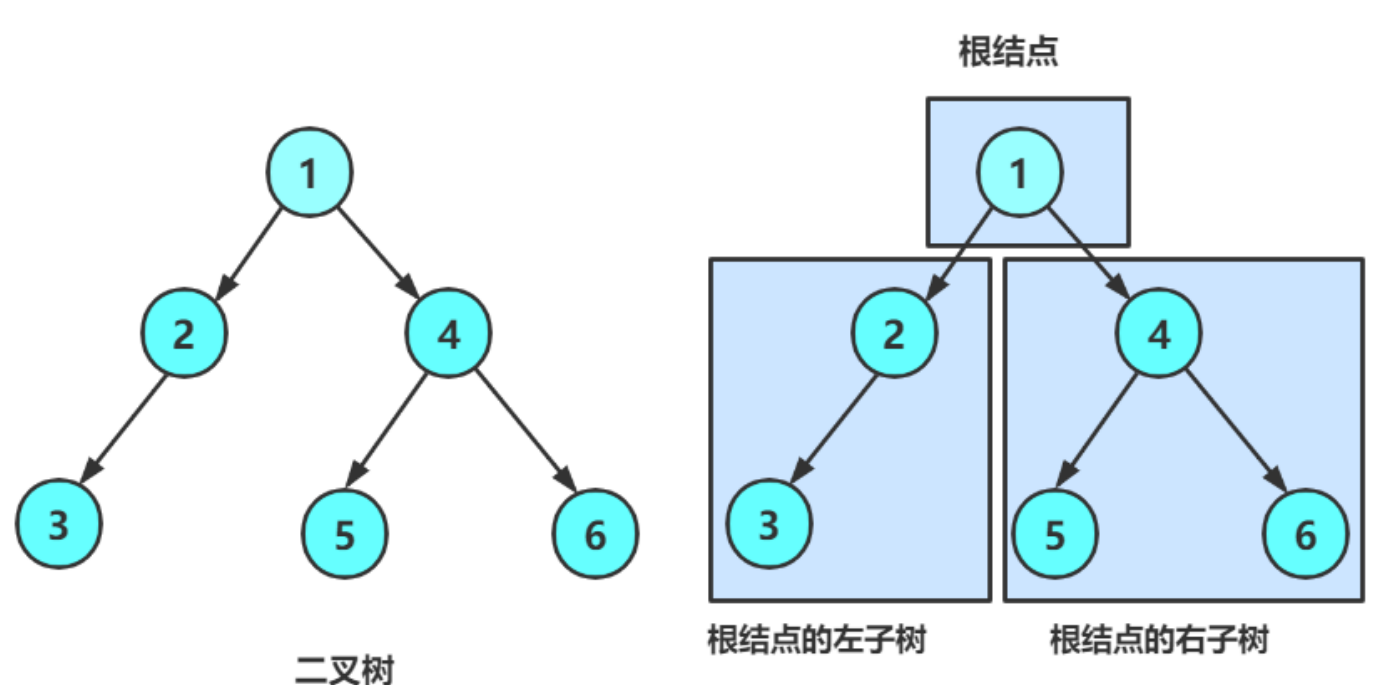
从上图看出 :
- 二叉树不存在度大于2 的结点
- 二叉树的子树有左右之分 , 次序不能颠倒 , 因此二叉树是有序树
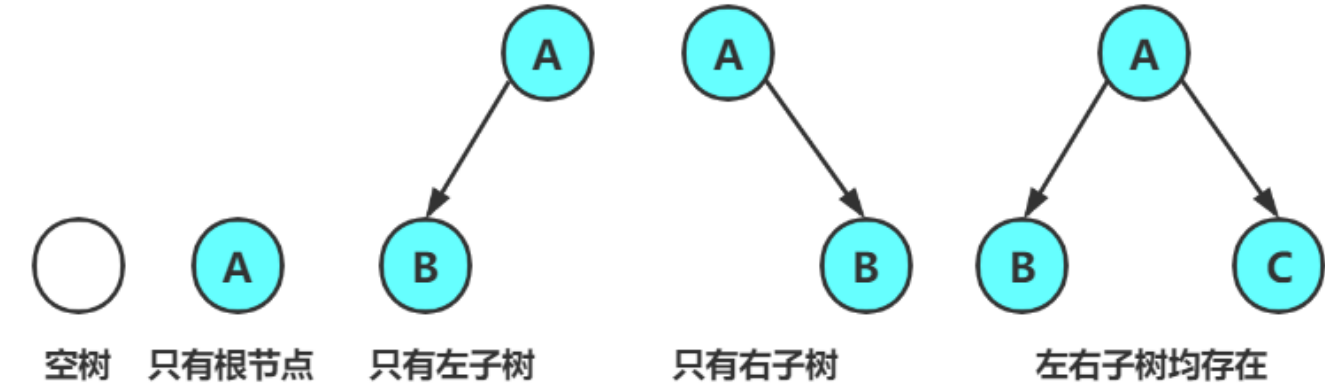
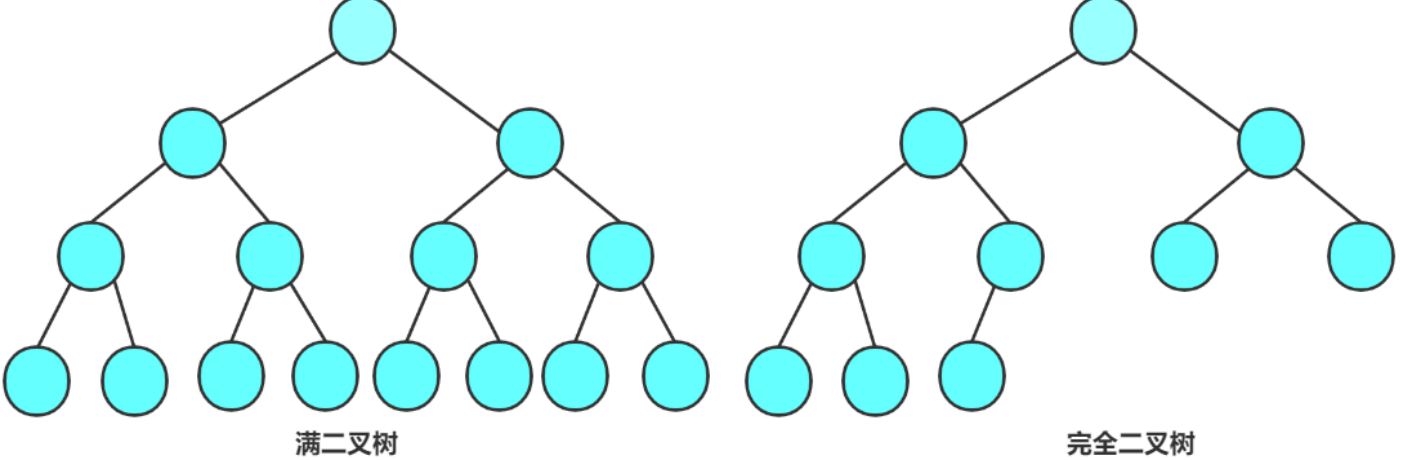
2.2 两种特殊的二叉树
满二叉树 : 一颗二叉树 , 如果每层的结点数都达到最大值 , 则这颗二叉树就是满二叉树.
- 如果一棵二叉树的层数为K , 且结点总数为2k-1, 则它就是二叉树
完全二叉树 : 完全二叉树是效率很高的数据结构 , 完全二叉树是由满二叉树印出来的
- 对于深度为K , 有N个结点的二叉树 , 当且仅当其每一个结点都与深度为K的满二叉树中编号从0至n-1的结点
- 从上到下 , 从左到右依次存放
- 满二叉树也是一种特殊的完全二叉树
2.3 二叉树的性质
1.若规定根节点的层数为1 , 则一颗非空二叉树的 第i层 上最多有 2i-1 (i>0)个结点
2.若规定只有根节点的二叉树的深度为1 , 则深度为 K 的二叉树的最大结点数是 2k-1(k>=0)
3.对任何一颗二叉树 , 如果其叶结点个数为 n0 , 则度为2 的非叶子结点个数为n2 , 则有n0 = n2 +1;简要证明如下
- 条件 : 一棵N个结点的树有N-1条边 ;
- 二叉树结点: 度为0 的结点有 n0 个 =>产生不了新的边
度为1 的结点有 n1 个 =>产生n1 个新边
度为2 的结点有 n2 个 =>产生2*n2 条新边
n0 + n1 + n2 =N ; n1 + 2 * n2 = N - 1 =>n2 + 1 = n0
4.具有 n 个结点的 完全二叉树 的深度 K 为 log2(n+1) 向上取整
5.对于具有 n 个结点的完全二叉树 , 如果按照从上到下 从左至右的顺序 对所有结点从0开始编号 , 则对于序号为i 的结点有:
- 若 i > 0 , 双亲序号 : (i-1)/2
- 若 2i+1<n , 右孩子序号 : 2i+1
- 若 2i+1>n , 左孩子序号 : 2i+2
2.4 二叉树的存储
- 二叉树的存储分为 ①顺序存储 和 ②类似于链表的链式存储
- 此处介绍的是二叉树的链式存储
- 二叉树的链式存储是通过一个个的结点的结点引用起来的
class Node2{int val;//数据域Node2 left;//左子树Node2 right;//左子树}
class Node3{int val;//数据域Node3 left;//左子树Node3 right ;//右子树Node3 parent;//当前结点的根节点
}2.5 二叉树的简单创建
public class BinaryTree {public class TreeNode{public int val;public TreeNode right;public TreeNode left;public TreeNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}private TreeNode root;public void creattree (){TreeNode node1 = new TreeNode(11);TreeNode node2 = new TreeNode(12);TreeNode node3 = new TreeNode(13);TreeNode node4 = new TreeNode(14);TreeNode node5 = new TreeNode(15);TreeNode node6 = new TreeNode(16);TreeNode node7 = new TreeNode(17);root = node1;node1.left = node2;node1.right = node3;node2.left = node4;node2.right = node5;node3.left = node6;node3.right = node7;}
}
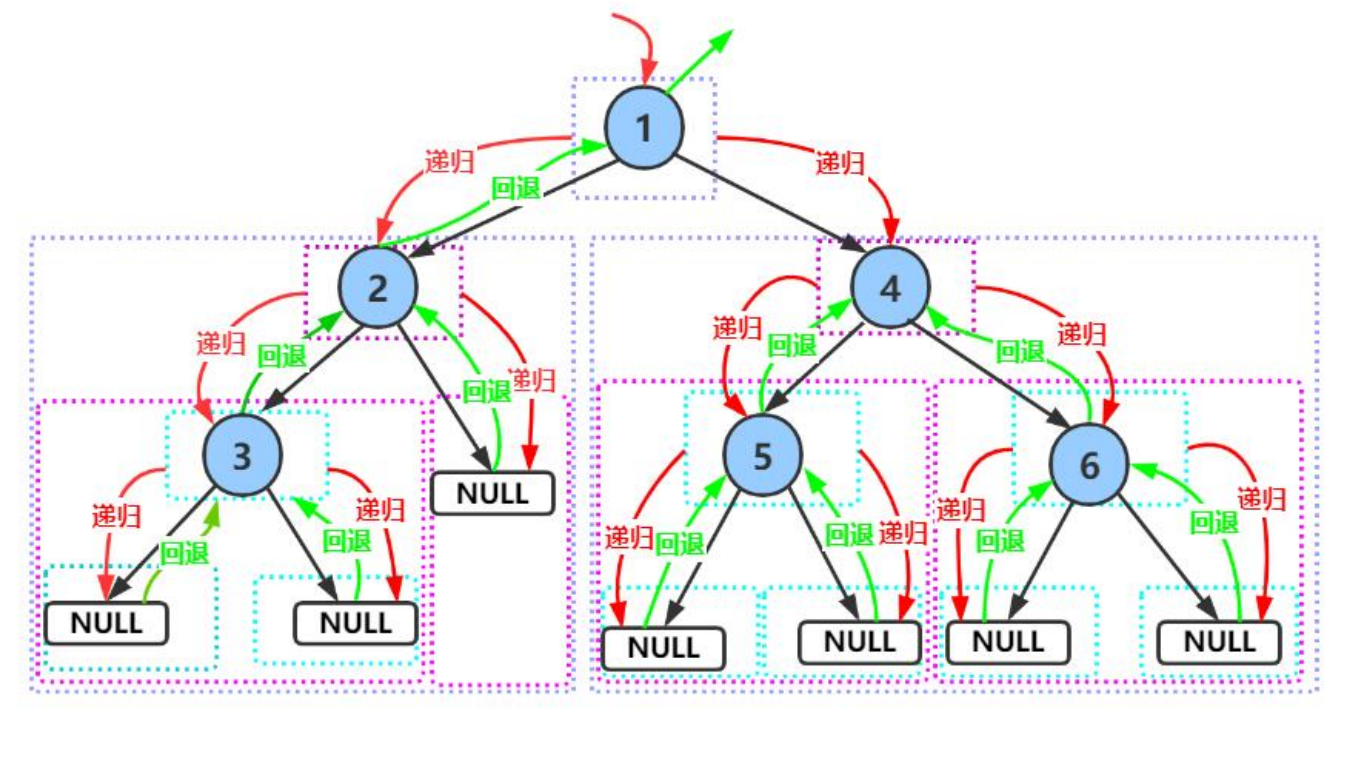
2.6 二叉树的遍历
- 前序遍历 : 访问根节点 -->根的左子树 -->根的右子树
- 中序遍历 : 根的左子树 -->根结点 -->根的右子树
- 后序遍历 : 根的左子树 -->根的右子树 -->根结点
例如上图的前中后序列分别是:
- 前序 : 1 2 4 5 3 6 7
- 中序 : 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
- 后序 : 4 5 2 6 7 3 1
代码:
前序遍历 :
①递归方式遍历
代码中先打印当前节点 (根),再递归遍历左子树,最后递归遍历右子树
public void preOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){return;
}
System.out.println(root);
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}中序遍历:
①递归方式遍历
代码中先递归遍历左子树,再打印当前节点 (根),最后递归遍历右子树
public void inOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){return;
}
inOrder(root.left);
System.out.println(root);
inOrder(root.right);
}后续遍历 :
①递归方式遍历
代码中先递归遍历左子树,再递归遍历右子树,最后打印当前节点 (根)
public void postOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){return;
}
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
System.out.println(root);
}层序遍历 :
从上而下 , 从左至右逐层访问树的结点的过程
设二叉树的根节点所在层数为 1 ,层序遍历就是从所在二叉树的根节点出发 , 首先访问第一层的树的根节点 , 然后从左至右访问第二层上的结点 , 接着是第三层 , 以此类推
层序遍历
public void levelOrderN(TreeNode root){
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode cur = root;
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){cur = queue.poll();System.out.println(cur);if(cur.left!=null){queue.offer(cur.left);}if(cur.right!=null){queue.offer(cur.right);}
}
}3 二叉树的基本操作
还是运用这颗 二叉树来测试
public class BinaryTree {public class TreeNode{public int val;public TreeNode right;public TreeNode left;public TreeNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}private TreeNode root;public void creattree (){TreeNode node1 = new TreeNode(11);TreeNode node2 = new TreeNode(12);TreeNode node3 = new TreeNode(13);TreeNode node4 = new TreeNode(14);TreeNode node5 = new TreeNode(15);TreeNode node6 = new TreeNode(16);TreeNode node7 = new TreeNode(17);root = node1;node1.left = node2;node1.right = node3;node2.left = node4;node2.right = node5;node3.left = node6;node3.right = node7;}
}
调用该构造方法
public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTree treeNode = new BinaryTree();BinaryTree.TreeNode root = treeNode.creatree();
}①获取树中结点的个数
public static int size = 0;
//获取树中结点的个数
public int size1(TreeNode root){if(root == null){return 0;
}
size++;
size1(root.left);
size1(root.right);return size;
}public int size2(TreeNode root){if(root == null){return 0;}return size2(root.left)+size2(root.right)+1;
}- size1( ) : 使用了静态变量
size来累计结点数量 ; 是运用递归的方式 来遍历二叉树 , 只要结点不为空就+1 - size2( ) : 是运用 结点个数 = 左子树结点个数 + 右子树结点个数 + 1(根节点)
测试 :
int a = treeNode.size1(root);
System.out.println(a);//7
int b = treeNode.size2(root);
System.out.println(b);//7② 获取叶子结点个数
//获取叶子结点个数
public static int LeafCount = 0;
public void getLeafNodeCount1(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){return ;
}
if(root.right == null && root.right == null){LeafCount++;
}getLeafNodeCount1(root.left);
getLeafNodeCount1(root.right);
}public int getLeafNodeCount2(TreeNode root){if(root == null){return 0;}if(root.right == null && root.right == null){return 1;}return getLeafNodeCount2(root.left)+getLeafNodeCount2(root.right);
}- 方法 1 使用了静态变量
LeafCount来累计叶子节点数量,需要读取该静态变量获取结果 - 方法 2 通过递归返回值累加叶子节点数量
测试 :
treeNode.getLeafNodeCount1(root);
System.out.println(treeNode.LeafCount);//4int c = treeNode.getLeafNodeCount2(root);
System.out.println(c);//4③ 获取第 K 层结点的个数
//获取第K层结点的个数
public int getKLeveNodeCount(TreeNode root,int k) {if (root == null) {return 0;}if (k == 1) {return 1;}return getKLeveNodeCount(root.right, k - 1) + getKLeveNodeCount(root.left, k - 1);}- 当遍历的时候到达第 K 层时 , 返回 1;
测试
int d = treeNode.getKLeveNodeCount(root,3);
System.out.println(d);
int d1 = treeNode.getKLeveNodeCount(root,2);
System.out.println(d1);※④ 获取二叉树高度
//二叉树的高度
public int getHeight(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){return 0;
}
int heightLeft = getHeight(root.left);
int heightRight = getHeight(root.right);
return Math.max(heightLeft,heightRight)+1;
}⑤ 检测值 为 value 的元素是否存在
//检测值 为 value 的元素是否存在
public TreeNode find(TreeNode root,int val){if(root == null) {return null;}if(root.val == val) {return root;}TreeNode leftT = find(root.left,val);if(leftT != null) {return leftT;}TreeNode rightT = find(root.right,val);if(rightT != null) {return rightT;}return null;
}⑥ 判断一颗二叉树是不是完全二叉树
//判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){return true;}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNode cur = root;if (cur != null) {return false;}else {break;}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()){TreeNode peek = queue.peek();if(peek!=null){return false;}queue.poll();
}
return true;
}4 二叉树的应用
- 表达式树:用于编译器解析算术表达式
- 哈夫曼树:用于数据压缩
- 决策树:用于机器学习和分类问题
- 堆:用于实现优先队列
5 注意事项
- 二叉树的操作时间复杂度通常为O(h),其中h为树的高度。平衡二叉树可以保证h为O(log n)。
- 递归实现可能导致栈溢出,对于深度较大的树,建议使用迭代方法
