Java数据结构 - 单链表的模拟实现
目录
- 1.基本介绍
- 1.1 基本的功能
- 1.2 节点
- 2.功能的实现
- 2.1 尾插法
- 2.2 头插法
- 2.3 索引插入
- 2.4 判断元素是否存在
- 2.5 删除第一次出现的关键值key的节点
- 2.6 删除所有key节点
- 2.7 获取长度
- 2.8 打印节点值
- 2.9 回收链表
- 2.10 功能测试
- 3.单链表的应用
- 3.1 反转一个单链表
- 2.3 给定x值划分
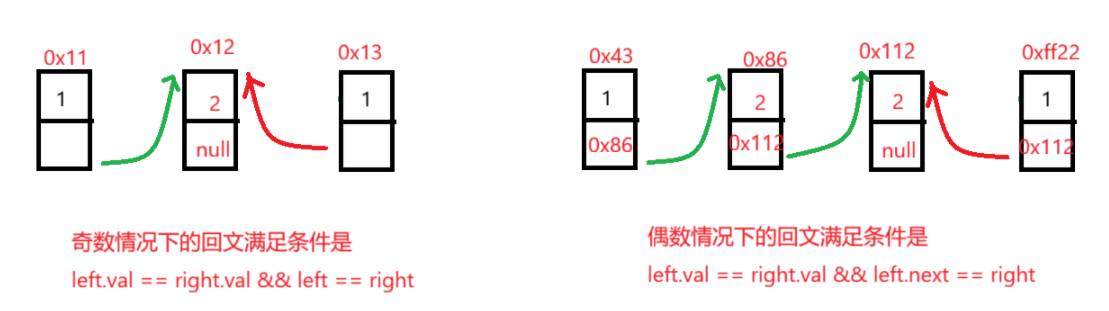
- 3.3 判断单链表是否是回文结构
- 3.4 判断环的入口点
- 4.代码链接
1.基本介绍
单链表是数据结构链表中的其中一种,与之对应的还有双链表,此处模拟实现的单链表主要实现其增删查改,搜索,遍历等功能。
1.1 基本的功能
// 1、⽆头单向⾮循环链表实现
public class SingleLinkedList {//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){} //尾插法
public void addLast(int data){}//任意位置插⼊,第⼀个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){} //查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){return false;} //删除第⼀次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){}//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){} //得到单链表的⻓度
public int size(){return -1;} //回收节点
public void clear() {}//遍历单链表
public void display() {}}
1.2 节点
单链表的实现是通过一个个的节点”连接“创建的,每一个节点由两部分组成,一部分存放节点值,一部分存放下一节点的地址,最后一个节点的下一个节点值为空。
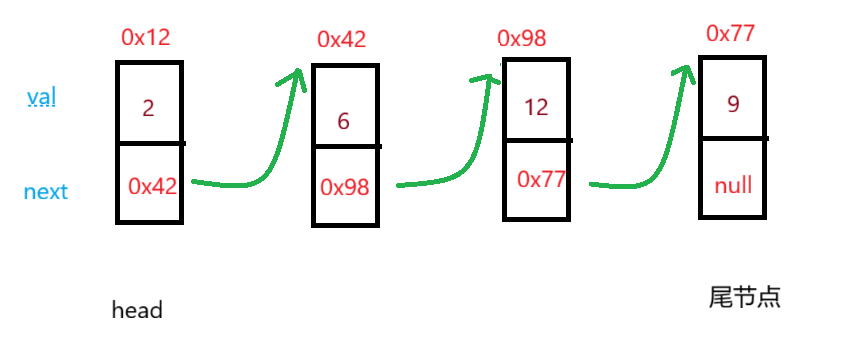
节点的使用可以先在类中创建一个静态内部类,每一次创建时将节点赋值
//节点static class Node{//成员变量int val;Node next;//构造方法public Node(int val){this.val = val;}}
2.功能的实现
2.1 尾插法
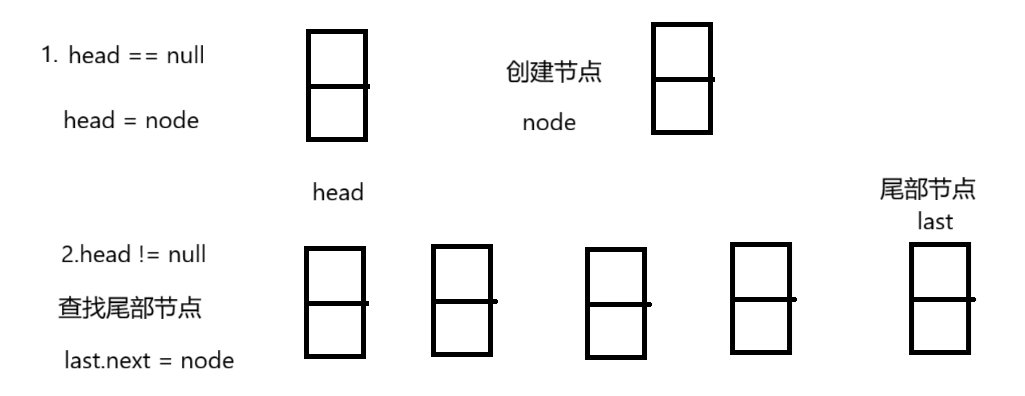
可先定义一个头节点引用,创建一个节点,如果发现头节点为null,将此节点引用赋值给头节点,否则将通过循环遍历链表,找到最后一个节点,将节点的next赋值为此节点。
//定义一个头节点Node head ;//尾插法public void addFirst(int data){//1.创建一个节点Node node = new Node(data);//2.判断if(head == null){head = node;}else{//遍历链表,创建一个搜索方法Node cur = searchNode(head);//cur为尾部节点cur.next = node;}}private Node searchNode(Node head){//为了不改变头节点的位置,创建一个临时引用Node tem = head;//通过遍历循环,尾部节点的next为nullwhile(tem.next != null){//进入循环说明该节点还不是尾部节点//将tem赋值为下一节点,直到不满之条件tem = tem.next;}//返回return tem;}
2.2 头插法
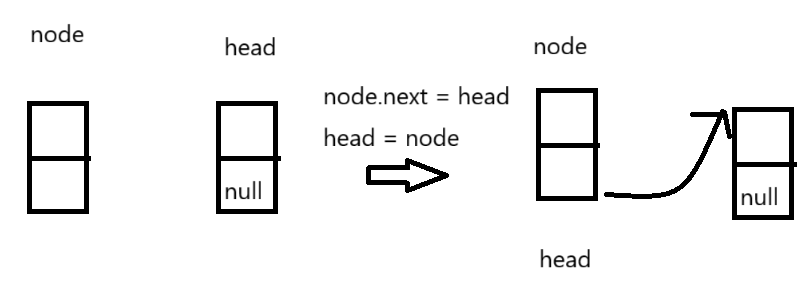
头插法需要分为两种情况,如果head节点为空,将创建的节点赋值给head,如果不为null,需要将新节点的next赋值为head,再将head赋值为node。
//头插法public void addFirst(int data){//1.创建节点Node node = new Node(data);//2.判断if(head == null){head = node;}else{node.next = head;head = node;}}
2.3 索引插入
根据下标的位置插入,分为三种情况:第一种,判断是否是头插,使用头插法;第二种,在尾部插入,可以调用已经实现的尾插法;第三种,在中将位置插入,需要找到插入位置前一个元素,修改前一个节点和node节点的next。

//节点数量int usedSize;//每次增加元素++//任意位置插⼊,第⼀个数据节点为0号下标public void addIndex(int index,int data){Node node = new Node(data);//1.判断是否为头插if(index == 0){addFirst(data);return;}//2.判断是否为尾插else if(index == usedSize){addLast(data);return;}//3.中间插入:找到插入位置的前一个元素Node prev = searchPrevNode(index);//node节点next赋值node.next = prev.next;//改变prev的nextprev.next = node;usedSize++;}private Node searchPrevNode(int index){Node tem = head;//例如获取索引2节点的前一个节点//2 > 1 tem为索引1节点 1 > 1为假while(index > 1){tem = tem.next;index--;}return tem;}
2.4 判断元素是否存在
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中public boolean contains(int key){//没有节点if(head == null) return false;//循环遍历Node tem = head;while(tem != null){//满足返回真if(tem.val == key) return true;//遍历下一节点tem = tem.next;}//不满足条件return false;}
2.5 删除第一次出现的关键值key的节点
//删除第⼀次出现关键字为key的节点public void remove(int key){if(head == null){System.out.println("没有值为" + key + "的节点");return;}//获取key节点Node ret = findNode(key);if(ret == null){System.out.println("没有值为" + key + "的节点");return;}//1.如果只有一个节点if(usedSize == 1){head = null;usedSize--;return;}//2.多个节点:删除头节点if(ret == head){head = ret.next;}//删除尾节点else if(ret.next == null){//找到前一个节点Node prev = findPrev(ret);prev.next = null;}//删除中间节点else{//找到前一个节点Node prev = findPrev(ret);prev.next = ret.next;}usedSize--;}private Node findPrev(Node key){Node tem = head;while(tem != null){if(tem.next == key) {return tem;}tem = tem.next;}//找不到return null;}
2.6 删除所有key节点
//删除所有值为key的节点public void removeAllKey(int key){if(head == null) return;Node tem = head;while(tem != null){if(tem.val == key){remove(key);}}}
2.7 获取长度
//得到单链表的⻓度public int size(){return usedSize;}
2.8 打印节点值
//遍历单链表public void display() {Node tem = head;if(tem != null){System.out.print(tem.val + " ");tem = tem.next;}}2.9 回收链表
//回收链表 public void clear() {//如过val值是引用数据类型,需要将每一个赋值为null/*Node tem = head;while(tem != null){tem.val = null;tem = tem.next;}*///最后将head赋值head = null;}
2.10 功能测试
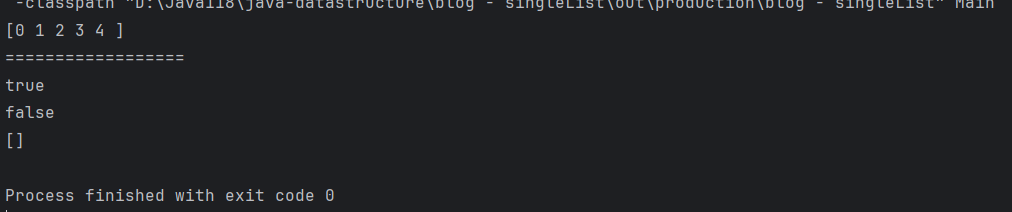
public class Main{public static void main(String[] args) {SingleLinkedList head = new SingleLinkedList();//增加//头插head.addFirst(2);head.addFirst(1);//尾插head.addLast(3);//索引插入head.addIndex(0,0);head.addIndex(4,4);//移除head.remove(3);//增加head.addIndex(3,3);//打印head.display();System.out.println("==================");head.remove(1);head.remove(2);head.remove(3);head.remove(4);//只剩下0元素head.addLast(0);head.addLast(0);//包含System.out.println(head.contains(0));//移除0head.removeAllKey(0);//不包含System.out.println(head.contains(0));//回收head.clear();head.display();}
}
3.单链表的应用
3.1 反转一个单链表
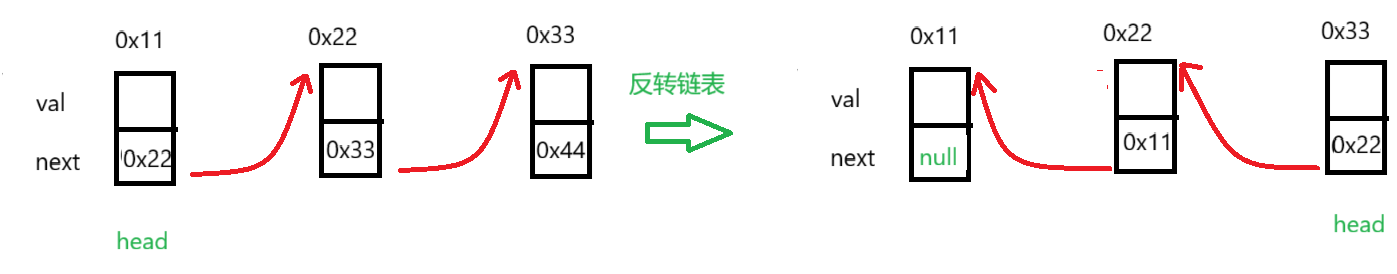
反转链表需要获取三个节点值,第一个是头节点,第二个是头节点的下一节点cur和cur节点的下一节点curNext,先改变头节点与下一节点的关系,再将头节点赋值为cur,cur节点赋值为curNext,直到循环结束。
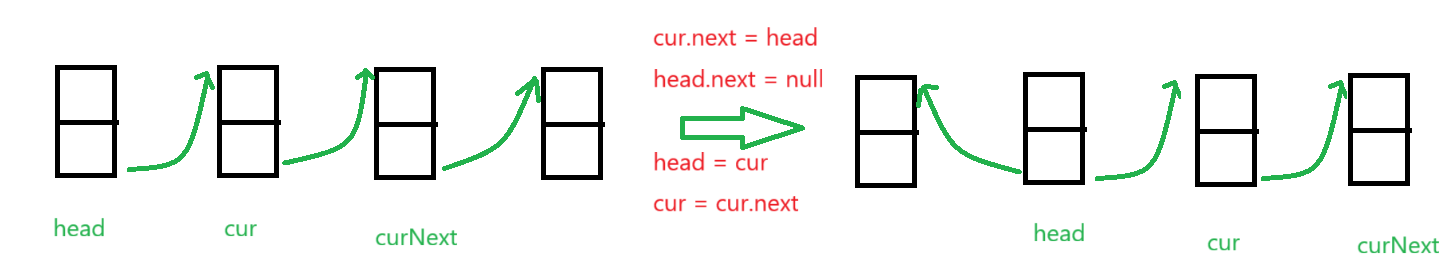
//反转单链表public void reverseSingleLinkedList(Node head){//没有元素或者只有一个节点if(head == null || usedSize == 1) return;//由多个元素Node tem = head;Node cur = head.next;//满足条件说明cur前面还有节点while(cur != null){//cur下一给节点Node curNext = cur.next;cur.next = tem;tem = cur;cur = curNext;}//head的next赋值为null,并将head赋值head.next = null;head = tem;}
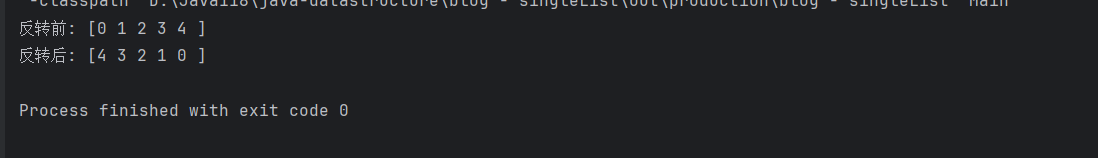
//测试public static void main(String[] args) {SingleLinkedList head = new SingleLinkedList();head.addFirst(2);head.addFirst(1);head.addLast(3);head.addIndex(0,0);head.addIndex(4,4);System.out.print("反转前: ");head.display();head.reverseSingleLinkedList(head.head);System.out.print("反转后: ");head.display();}
2.3 给定x值划分
给定一个单链表,将单链表小于x的划分在左边区域,大于x部分划分在右边区域,不改变原有顺序
可以定义两个节点h1和h2,遍历单链表,将小于x的节点由h1增加,大于x的节点由h2增加,最后合并h1和h2。
//给定x值分割后合并public void partition(int x){Node h1 = null;Node h2 = null;int usedSize1 = 0;//h1节点个数int usedSize2 = 0;//h2节点个数Node tem = head;//遍历链表while(tem != null){//h1添加if(tem.val < x) {//首次添加if(h1 == null){h1 = tem;}else{//找到末尾节点后添加Node last = searchLastNode(h1,usedSize1);last.next = tem;}usedSize1++;}//h2添加else {//首次添加if (h2 == null) {h2 = tem;} else {Node last = searchLastNode(h2, usedSize2);last.next = tem;}usedSize2++;}tem = tem.next;}//将h1 和 h2 合并:找到h1的尾部节点last,改变last.next = h2,Node last1 = searchLastNode(h1,usedSize1);last1.next = h2;//找到h2最后一个节点,将其next赋值为nullNode last2 = searchLastNode(h2,usedSize2);last2.next = null;}private Node searchLastNode(Node head,int size){//为了不改变头节点的位置,创建一个临时引用Node tem = head;//通过遍历循环,尾部节点的next为nullwhile(size > 1){//进入循环说明该节点还不是尾部节点//将tem赋值为下一节点,直到不满之条件tem = tem.next;size--;}//返回return tem;}
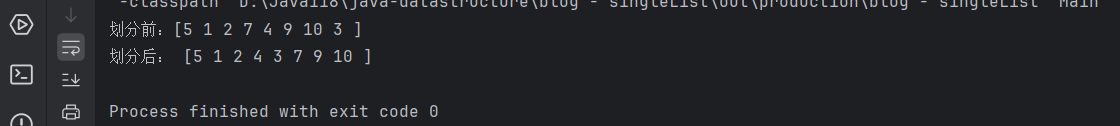
//测试public static void main(String[] args) {SingleLinkedList head = new SingleLinkedList();head.addLast(5);head.addLast(1);head.addLast(2);head.addLast(7);head.addLast(4);head.addLast(9);head.addLast(10);head.addLast(3);//按照6划分System.out.print("划分前:");head.display();System.out.print("划分后: ");head.partition(6);head.display();}
3.3 判断单链表是否是回文结构
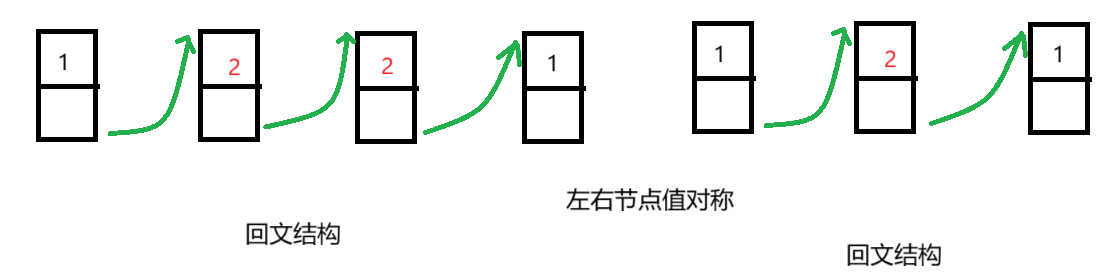
判断一个单链表是否是回文结构需要实现末尾节点可以往前遍历,第一步需要获取中间节点位置,将中间节点到尾部节点的方向改变,最后从头节点和尾部节点遍历判断。
1.获取中间节点,使用快慢双指针遍历单链表,开始时快慢双指针都是从头节点开始,随后快指针走两步,慢指针走一步,直到快指针走到末尾节点或尾节点后,此时快指针的路程是慢指针的两倍,慢指针的位置就是中间节点的位置。
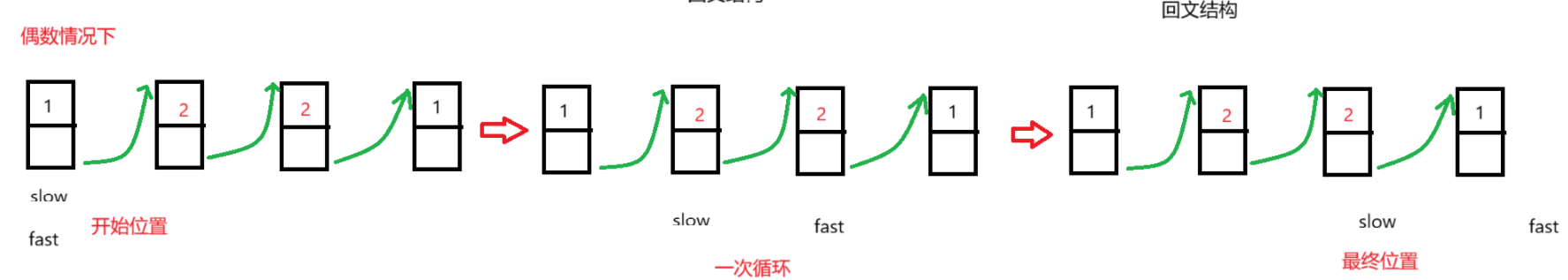
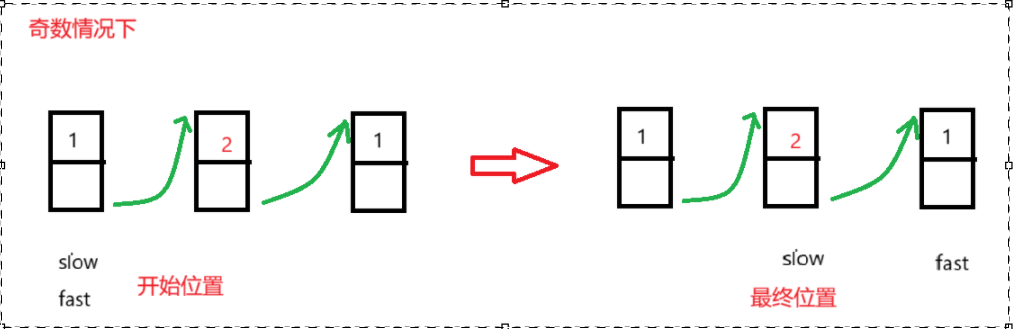
//获取中间节点public Node midNode(){//判断是否没有节点或者只有一个节点if(head == null || size() == 1){return null;}//定义快慢双指针Node slow = head;Node fast = head;//不能改变判断条件的位置,否则如果fast为null,//判断fast.next会发生空引用异常while(fast != null && fast.next != null){fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}
2.将中间位置和末尾位置节点改变方向,调用改变逆序单链表方法。
//2.逆序链表Node last = reverseSingleLinkedList(mid);
//反转单链表:返回新的headpublic Node reverseSingleLinkedList1(Node head){//没有元素或者只有一个节点if(head == null || usedSize == 1) return null;//由多个元素Node tem = head;Node cur = head.next;//满足条件说明cur前面还有节点while(cur != null){//cur下一给节点Node curNext = cur.next;cur.next = tem;tem = cur;cur = curNext;}head.next = null;return tem;}
3.判断回文
//获取中间节点public Node midNode(Node head){//判断是否没有节点或者只有一个节点if(head == null || head.next == null){return null;}//定义快慢双指针Node slow = head;Node fast = head;//不能改变判断条件的位置,否则如果fast为null,//判断fast.next会发生空引用异常while(fast != null && fast.next != null){fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}//反转单链表public Node reverseSingleLinkedList1(Node head){//没有元素或者只有一个节点if(head == null || usedSize == 1) return null;//由多个元素Node tem = head;Node cur = head.next;//满足条件说明cur前面还有节点while(cur != null){//cur下一给节点Node curNext = cur.next;cur.next = tem;tem = cur;cur = curNext;}head.next = null;return tem;}public boolean palindrome(Node head){//1.获取中间位置Node mid = midNode(head);//2.逆序链表Node right = reverseSingleLinkedList1(mid);//3.判断是否回文Node left = head;while(left != null){//不相等直接返回if(left.val != right.val){return false;}//相等并且head.next == last返回trueelse if( left == right || left.next == right){return true;}left = left.next;right = right.next;}return false;}
测试public static void main(String[] args) {SingleLinkedList head = new SingleLinkedList();head.addLast(1);head.addLast(2);head.addLast(3);head.addLast(3);head.addLast(2);head.addLast(1);System.out.println(head.palindrome(head.head));System.out.println("=================");SingleLinkedList head1 = new SingleLinkedList();head1.addLast(1);head1.addLast(2);head1.addLast(3);head1.addLast(2);head1.addLast(1);System.out.println(head.palindrome(head1.head));System.out.println("=================");SingleLinkedList head2 = new SingleLinkedList();head2.addLast(1);head2.addLast(1);head2.addLast(9);head2.addLast(4);head2.addLast(1);System.out.println(head.palindrome(head2.head));}
3.4 判断环的入口点
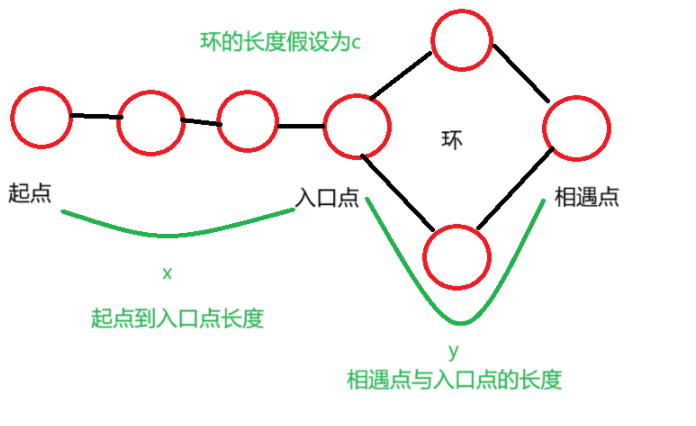
定义快慢双指针,从起点位置开始,快指针每一次走两步,慢指针每一次走一步,因为存在环循结构,快慢双指针都进入环后必定会相遇,将相遇点与入口点的位置长度假设为y,起点到入口点的位置长度为x,环行结构的长度为c,由以下推到可知:x = (n - 1) c + y

使用快慢双指针走到相遇点,使用慢指针从起始点开始,快指针从相遇点开始,以相同的速度开始走,当快指针和慢指针相遇,就是环入口(慢指针走x距离,相当于走(n-1)c + y距离,走n-1圈,还是在相遇点,再走y距离就到起始位置)。
//查找入口点public Node detectCycle(Node head){//先判断是否存在环形结构if(!existtCycle()){return null;}//定义快慢双指针Node slow = head;Node fast = head;//走到相遇点while(fast != null){fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;if(fast == slow) break;}//此时fast是相遇点,将slow从新赋值slow = head;while(slow != fast){slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next;}//相遇点return slow;}
public static Node createCycle(SingleLinkedList s){s.addLast(1);s.addLast(2);s.addLast(3);Node last1 = s.searchNode(s.head);s.addLast(2);s.addLast(1);Node last2 = s.searchNode(s.head);last2.next = last1;return s.head;}
测试用例:1 2 3 2 1(3 2 1 为环)
public class Main{public static void main(String[] args) {SingleLinkedList s = new SingleLinkedList();System.out.print("环的入口点val: ");System.out.println(s.detectCycle(s.createCycle(s)).val);}}