Kaggle 竞赛入门指南
一、账号注册
- https://www.kaggle.com/account/login?phase=emailRegister
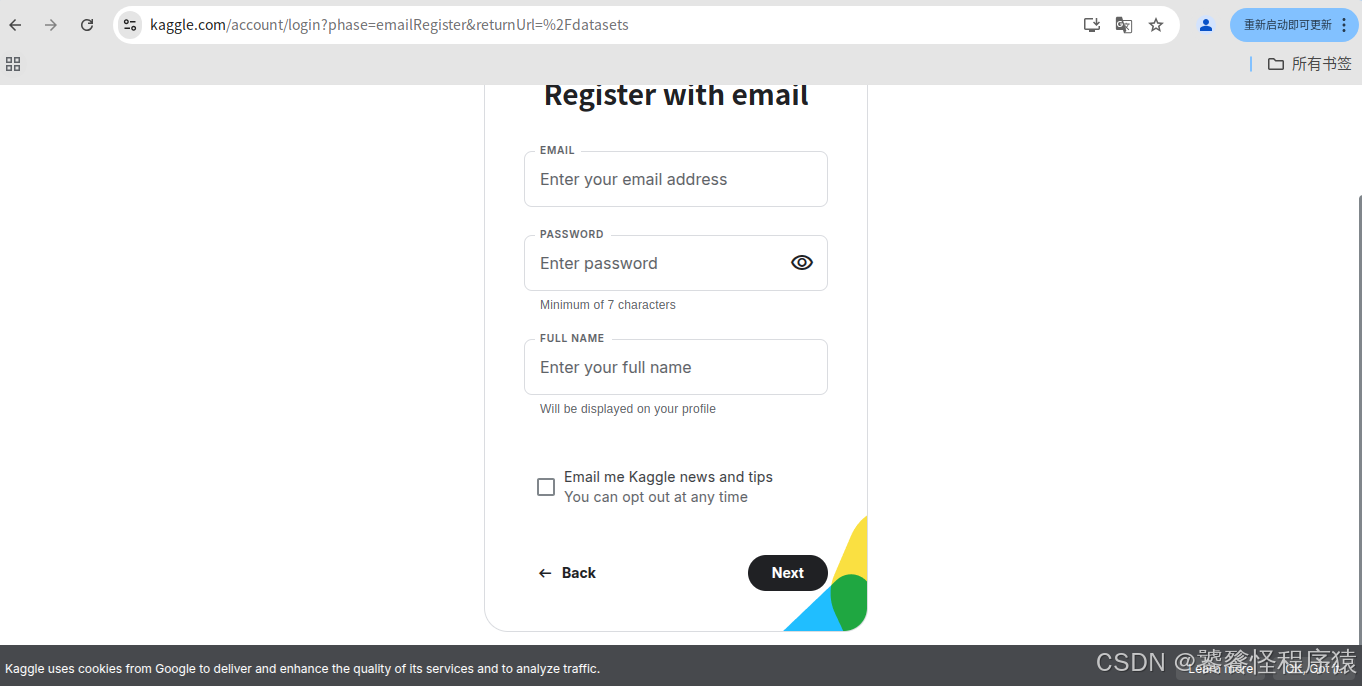
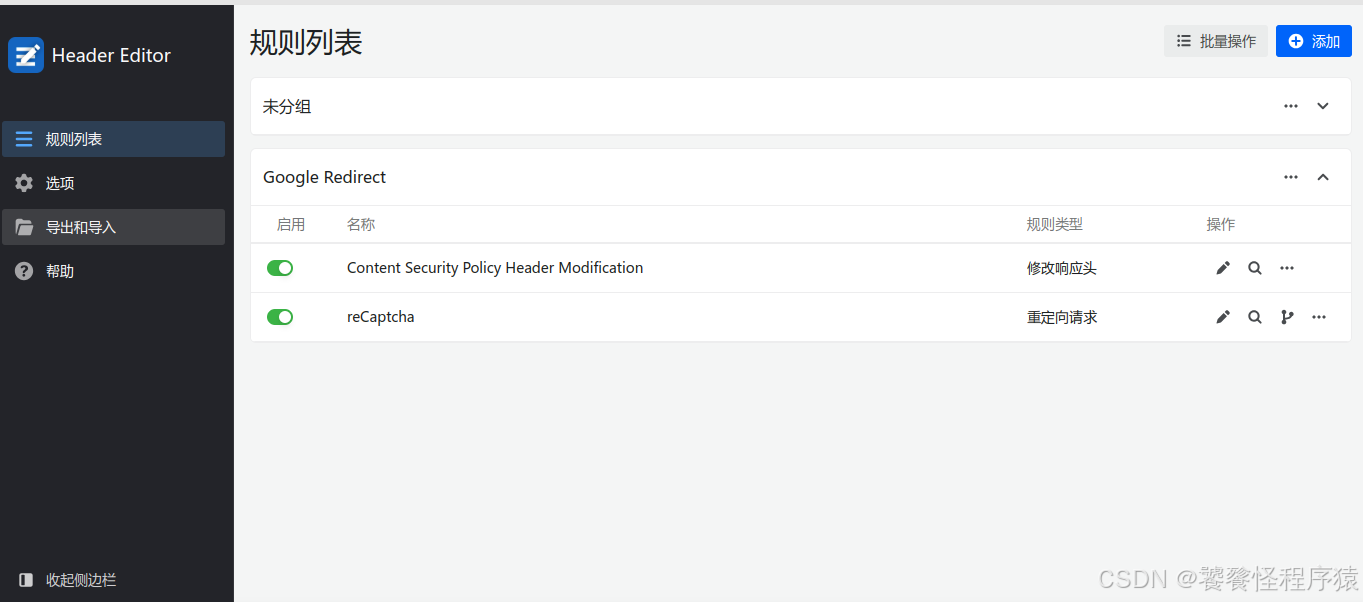
使用邮箱进行注册,但是通常会因为网络问题导致验证码无法正常显示,此时需要安装插件 Header Editor,将网页URL进行重定向,让验证码显示出来。
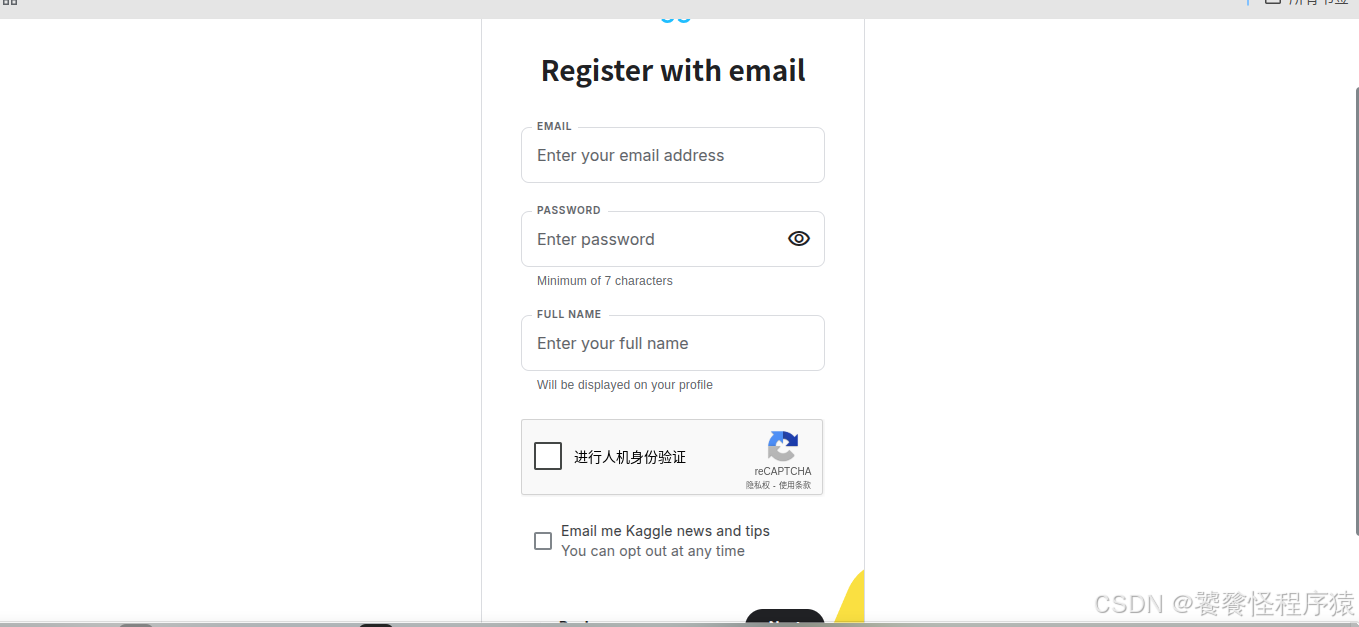
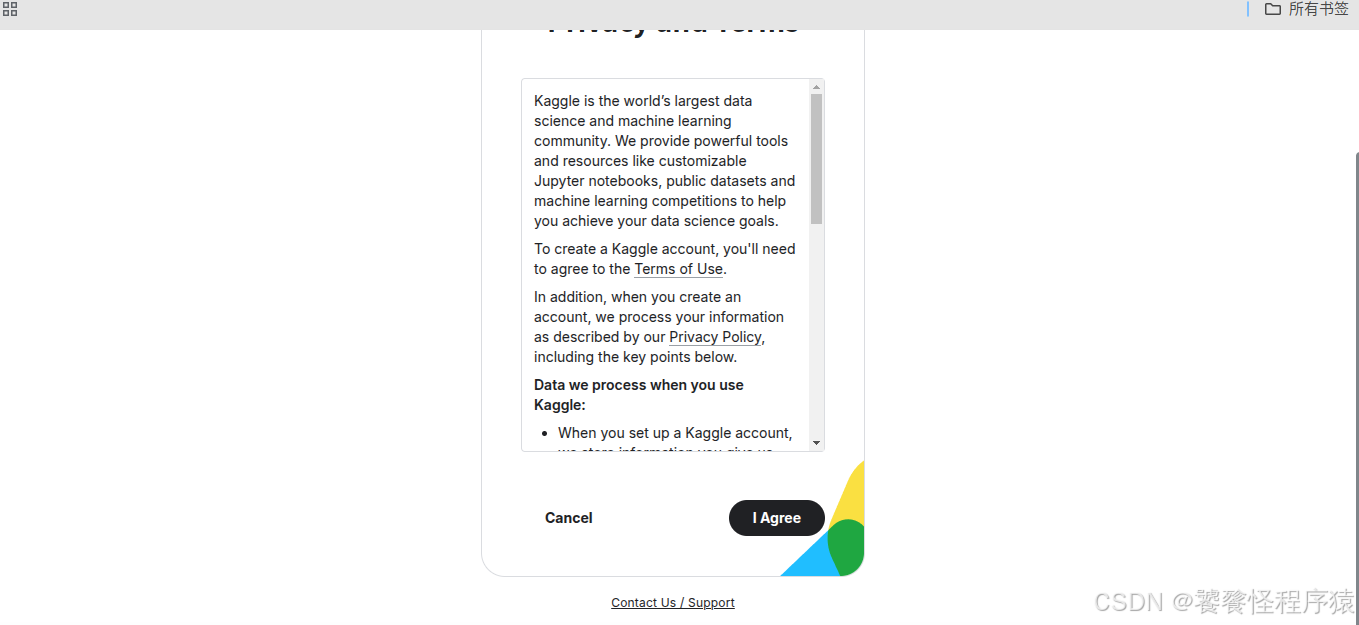
如图,到这里已经注册成功了。
二、竞赛入门
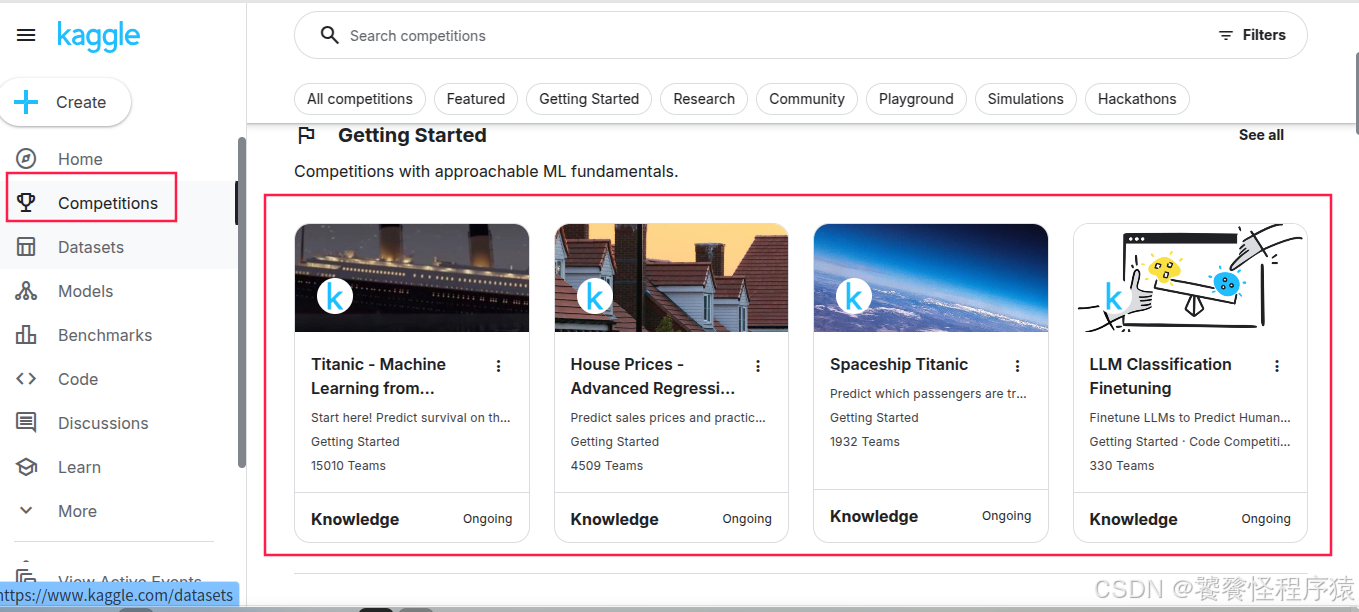
官方提供了一些入门级竞赛项目,非常容易上手,我们可以从这些赛事入手。
三、房价预测竞赛
例如,我们可以从 House Prices - Advanced Regression Techniques 这个赛事开始。
1、背景与任务
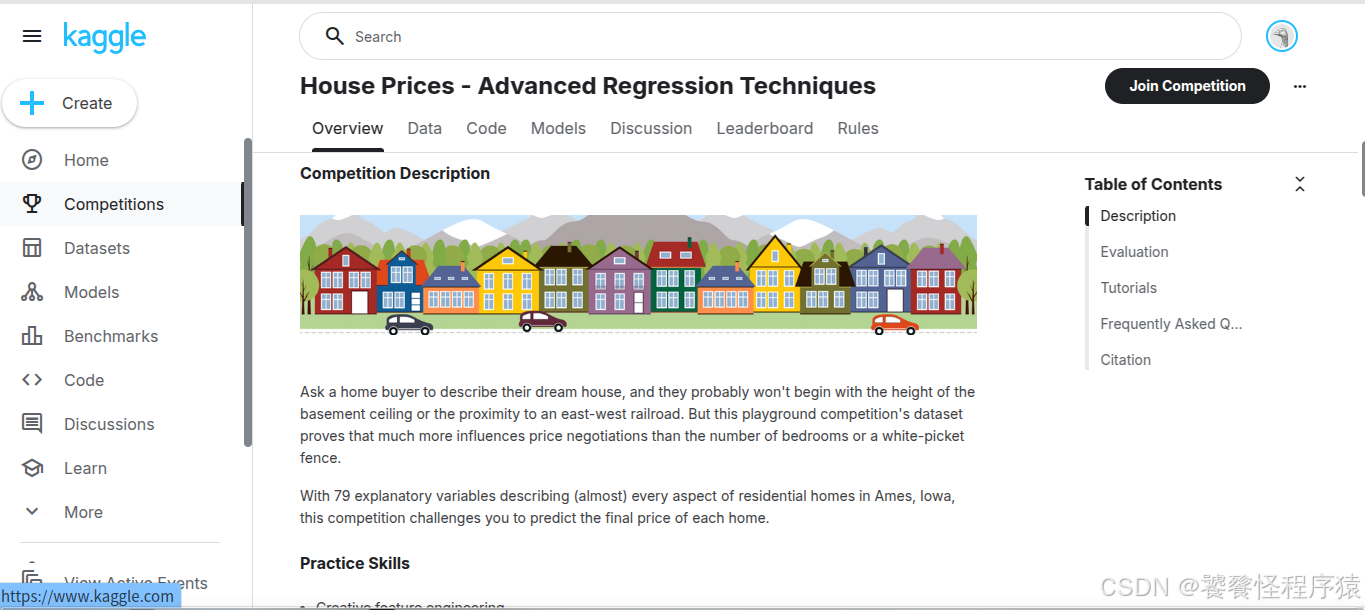
根据 Overview 页面的介绍,我们可以得知:购房者理想房屋描述与真实价格差异往往由多个因素决定,赛事提供了79个解释变量包含了住宅几乎各方面特征,希望参赛者能够使用这些特征进行最终房价预测。
2、数据集
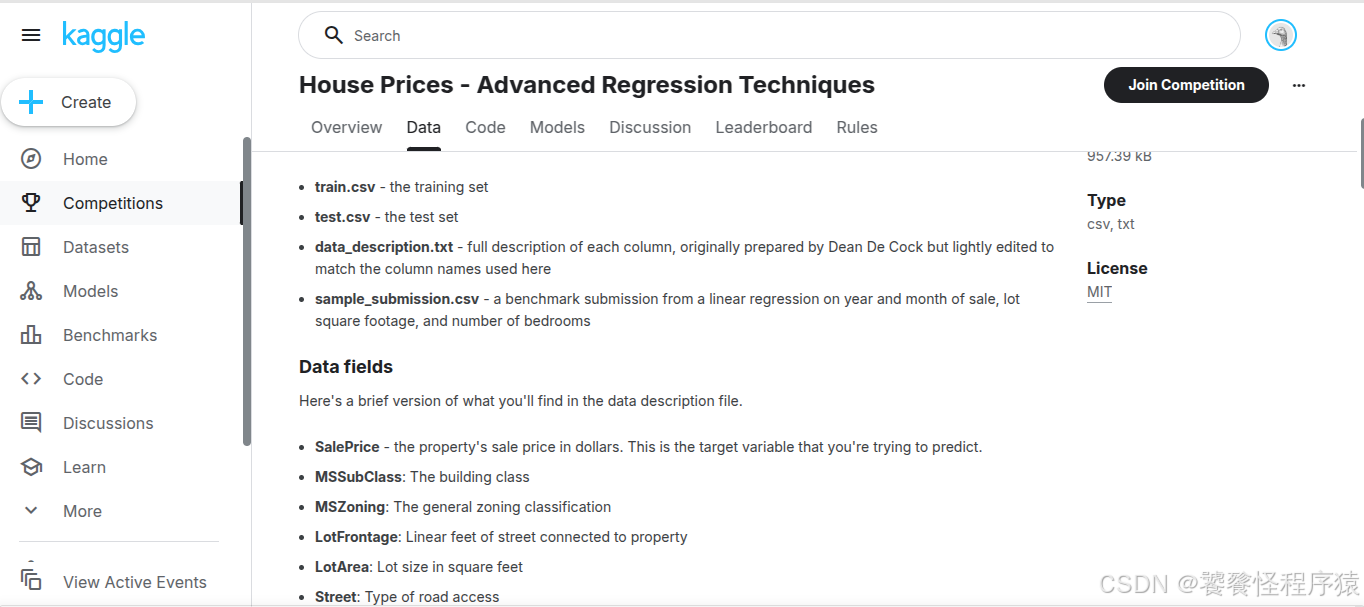
每个数据集的每个字段在 Data 页面都有具体说明:
3、Baseline
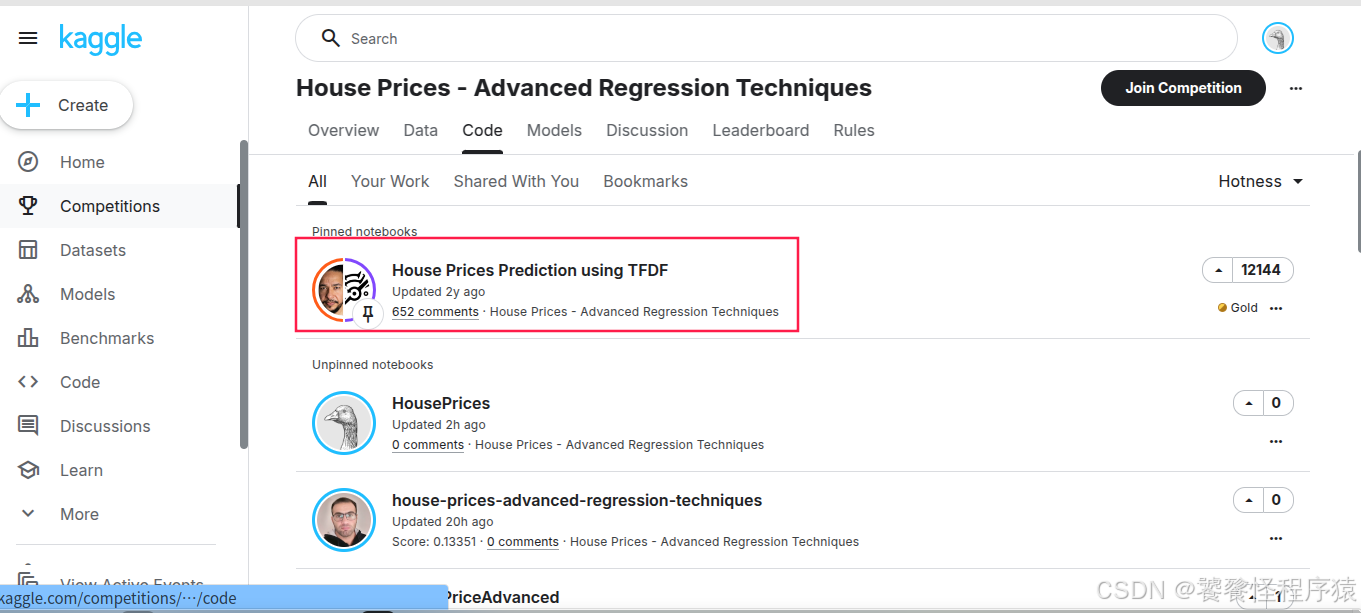
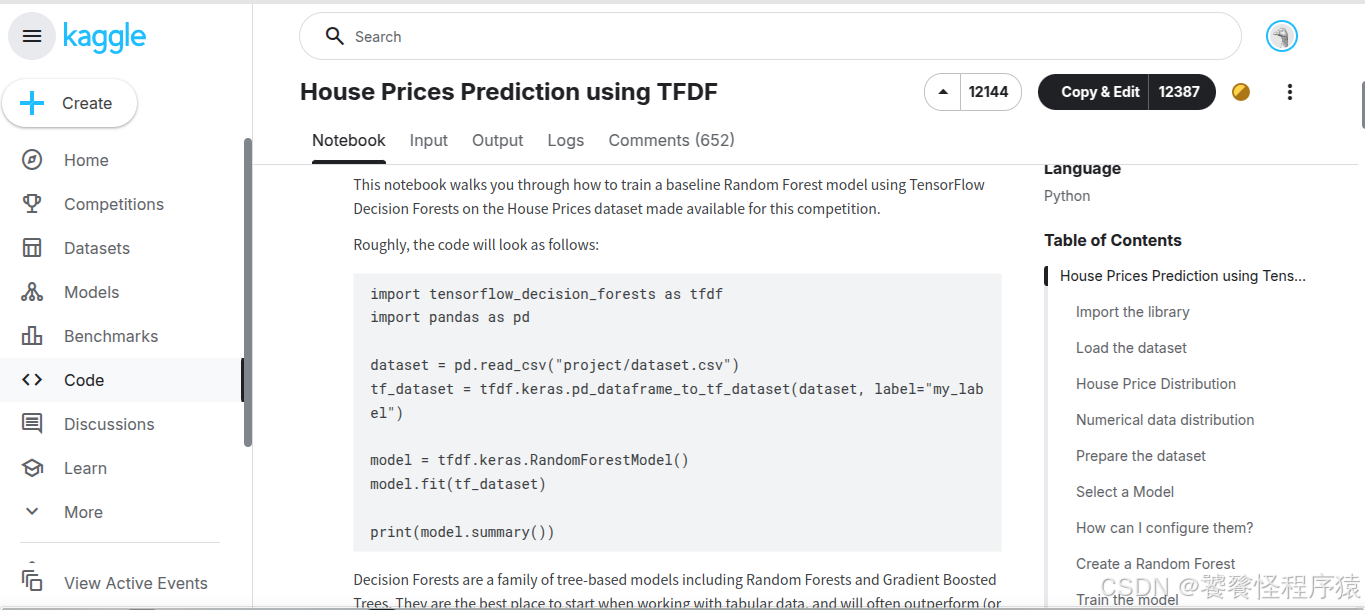
在 Code 页面中,House Prices Prediction using TFDF 是一个能够完成赛事任务的基础实现方案,同时也可以看到众多参赛者分享的 Notebook:
四、跑通Baseline
1、创建一个notebook
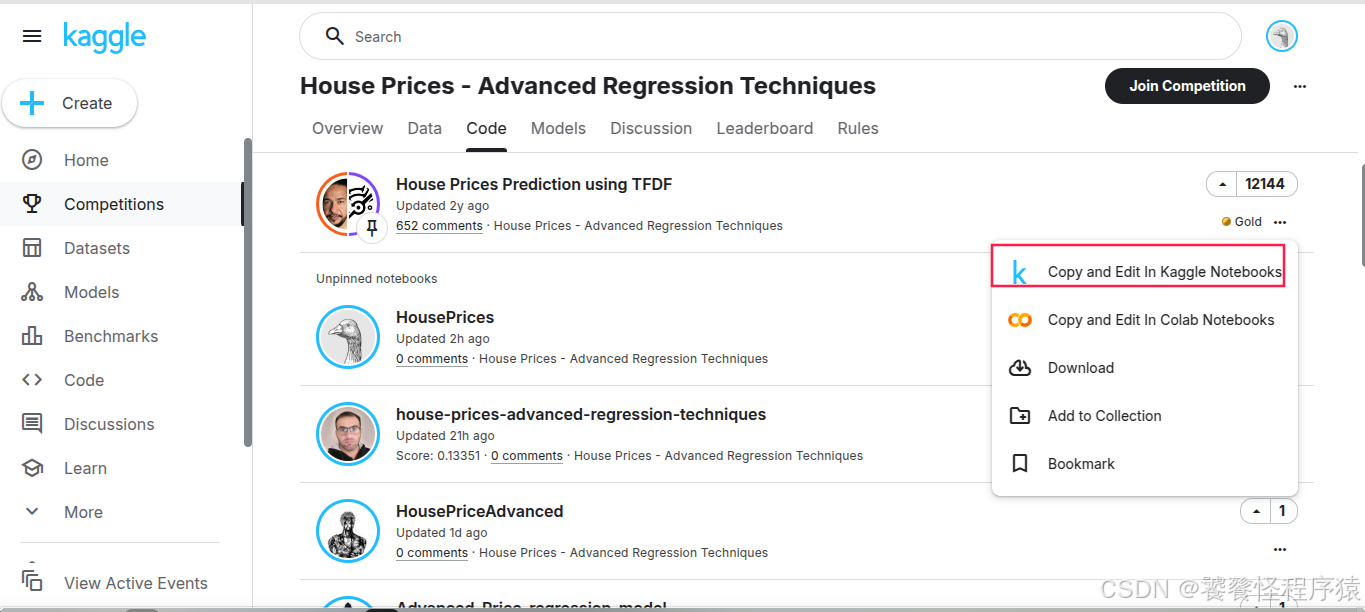
可以直接复制一份 Baseline 的 Notebook,也可以手动创建一个新的 Notebook:
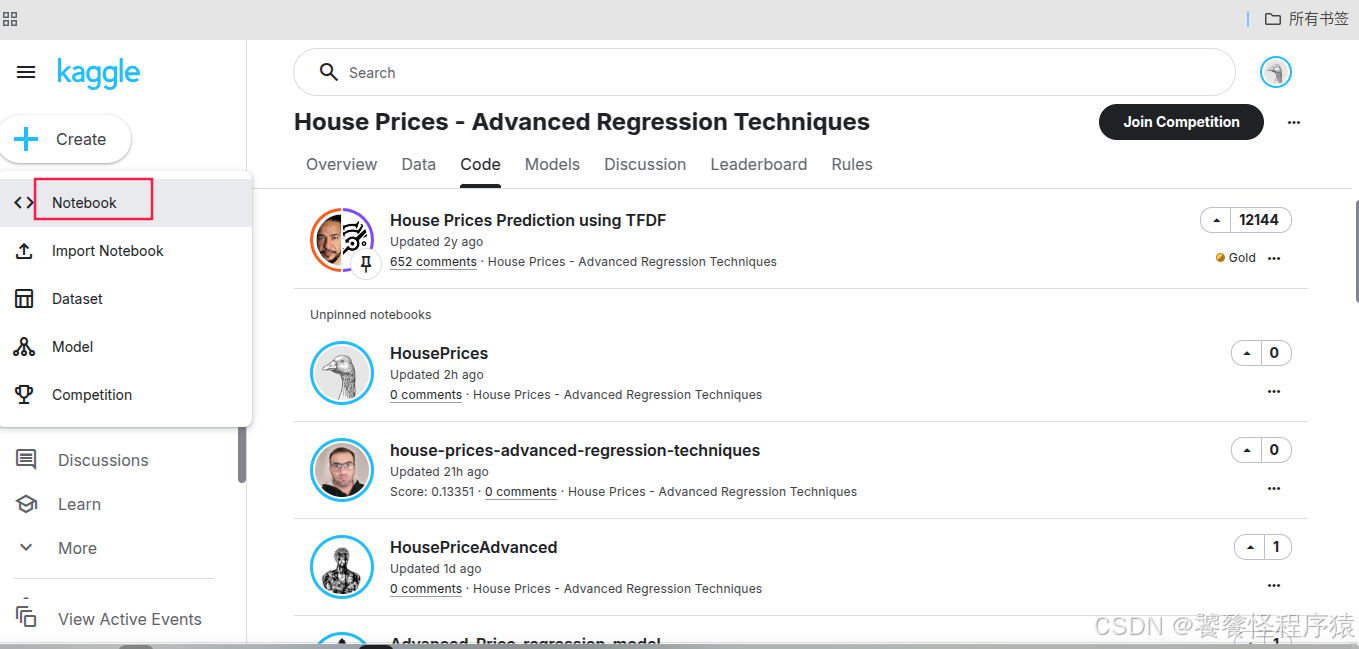
为了方便演示,这里直接复制一份 Baseline:
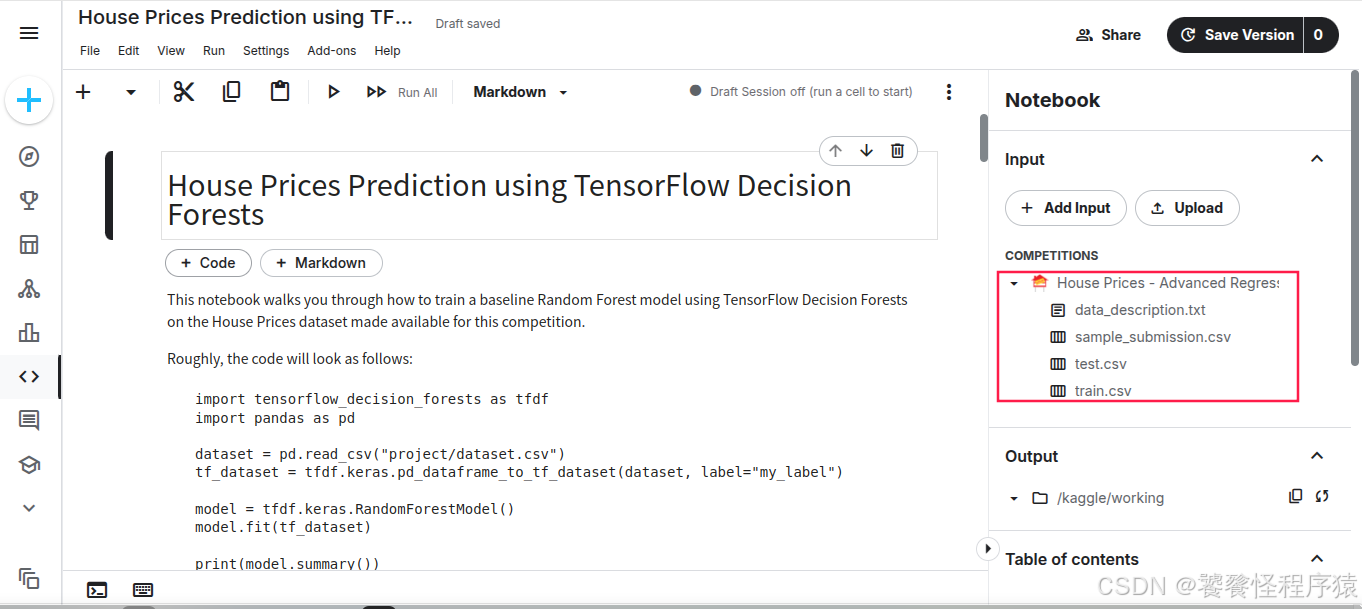
可以看到,该 Notebook 还自动引入了竞赛数据集,现在所有事情都可以在云端完成,无需本地搭建开发环境,非常方便。
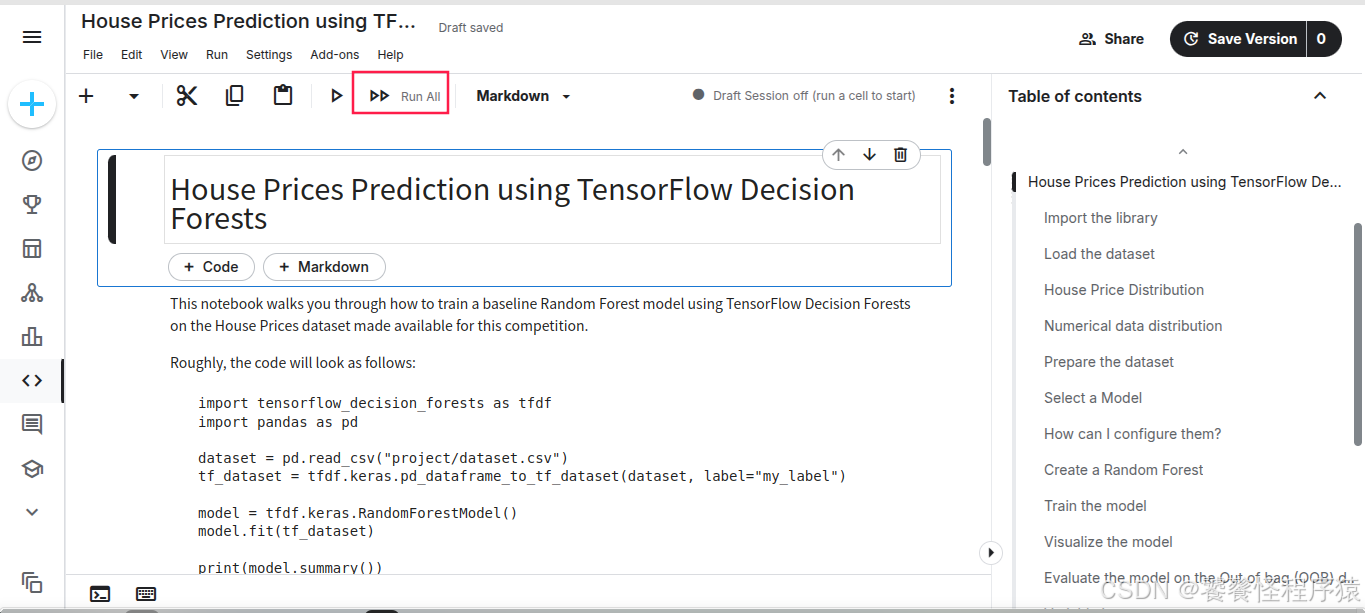
2、一键执行代码
3、提交预测结果
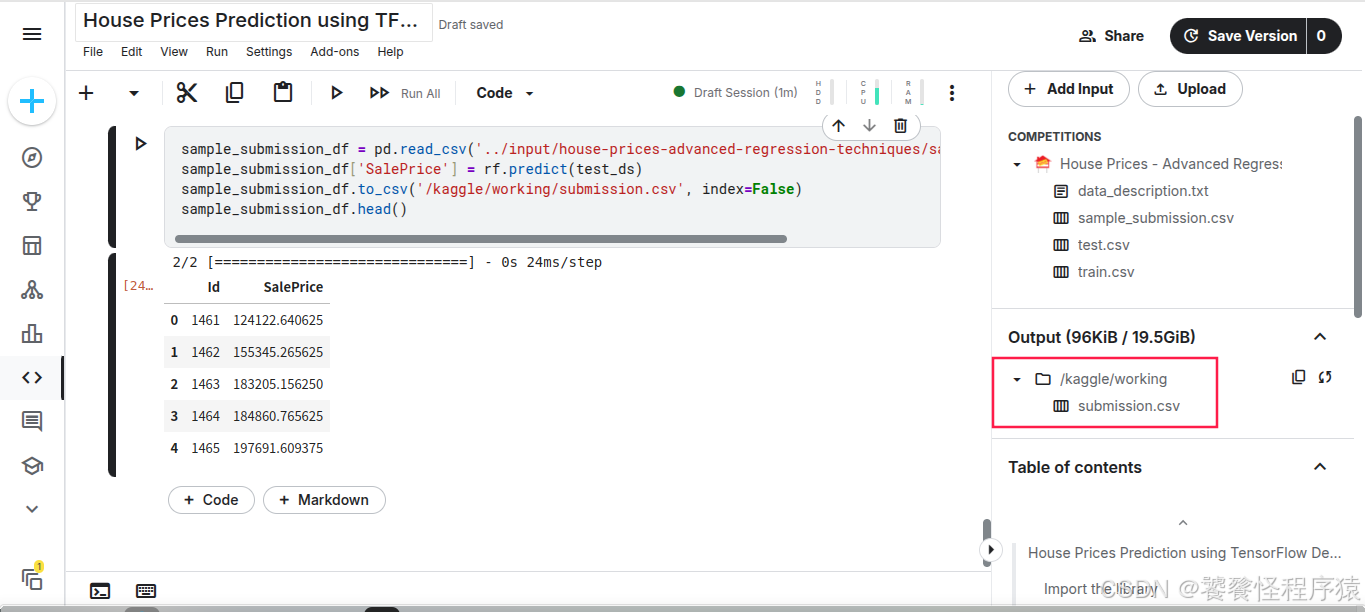
所有代码执行完毕之后,在 output 目录下生成 submission.csv 结果文件,该文件就是对房价进行预测后的结果文件。
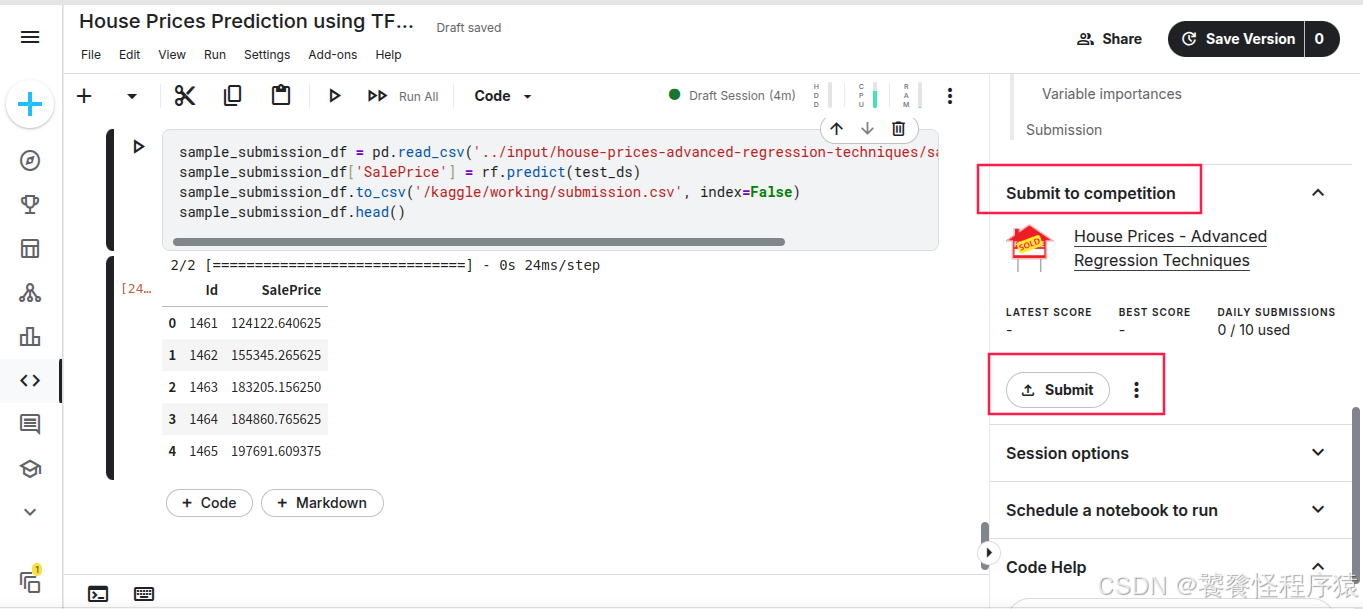
此时可以直接展开 Submit to competition 提交预测文件:
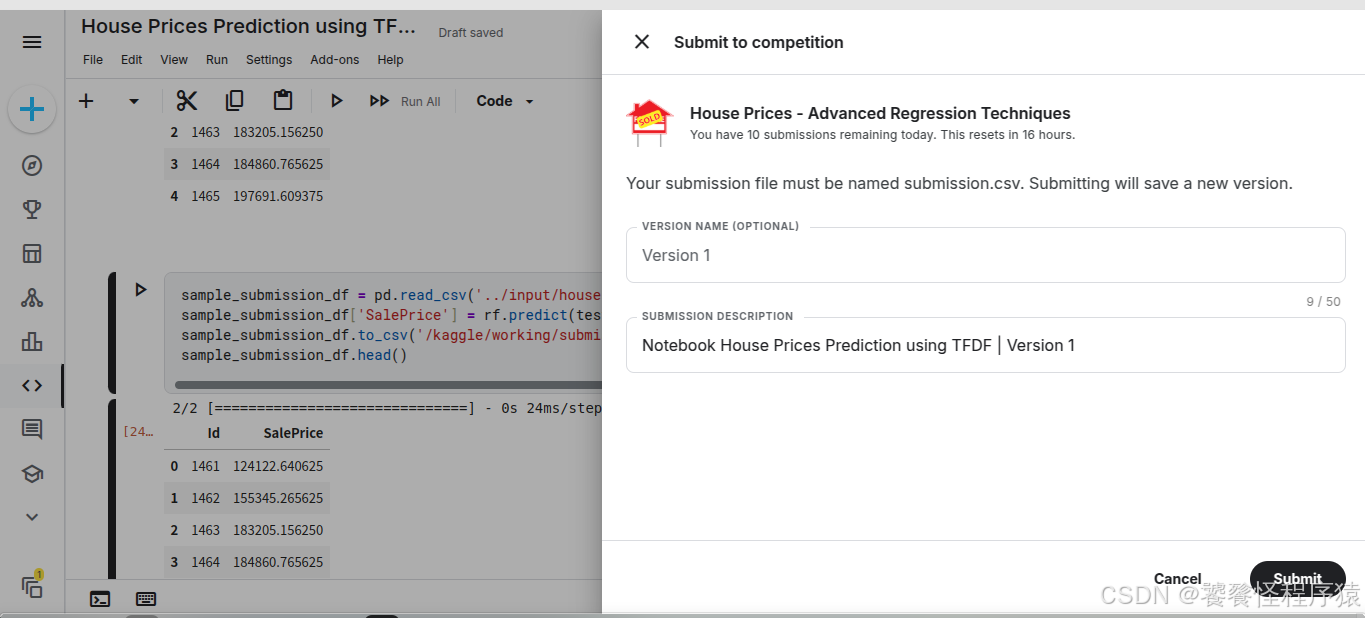
4、得分与排行榜
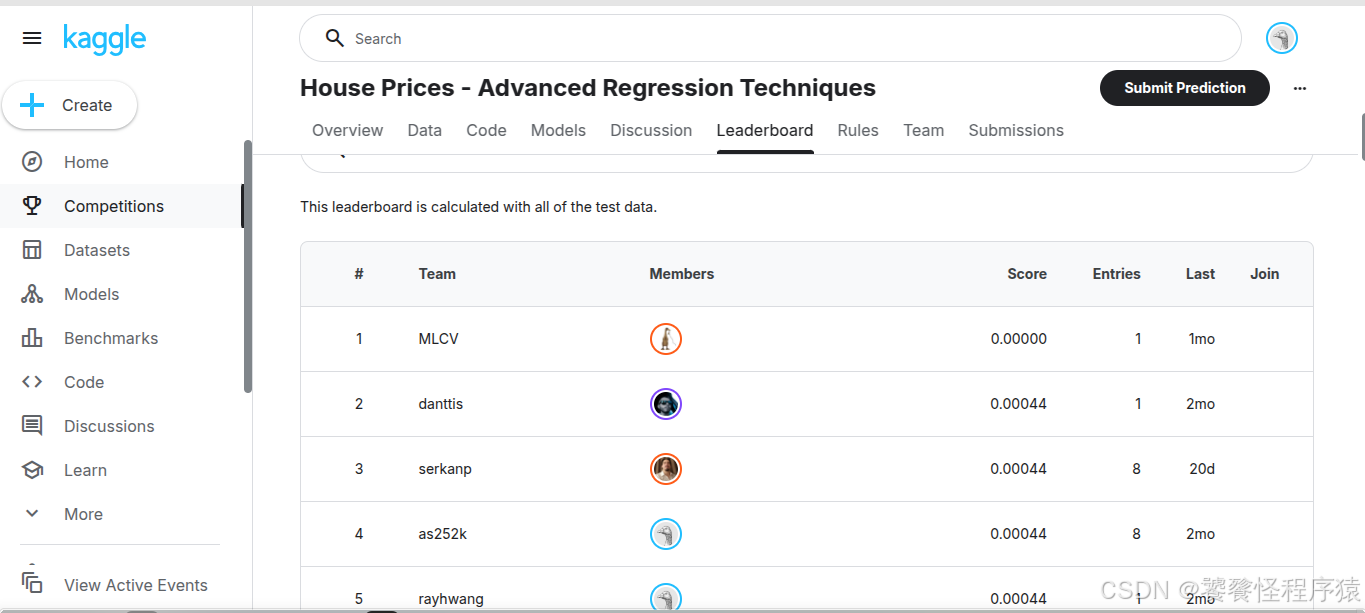
在赛事的 Leaderboard 页面可以查看自己的得分与名次:
五、Baseline拆解
Step1、导入依赖
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_decision_forests as tfdf
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# Comment this if the data visualisations doesn't work on your side
%matplotlib inline
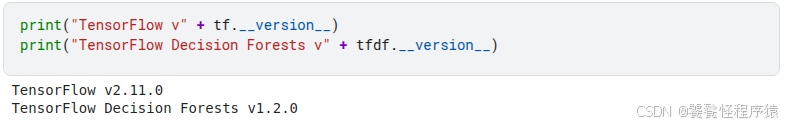
TensorFlow v2.11.0
TensorFlow Decision Forests v1.2.0
Step2、加载数据集
train_file_path = "../input/house-prices-advanced-regression-techniques/train.csv"
dataset_df = pd.read_csv(train_file_path)
print("Full train dataset shape is {}".format(dataset_df.shape))
Full train dataset shape is (1460, 81)
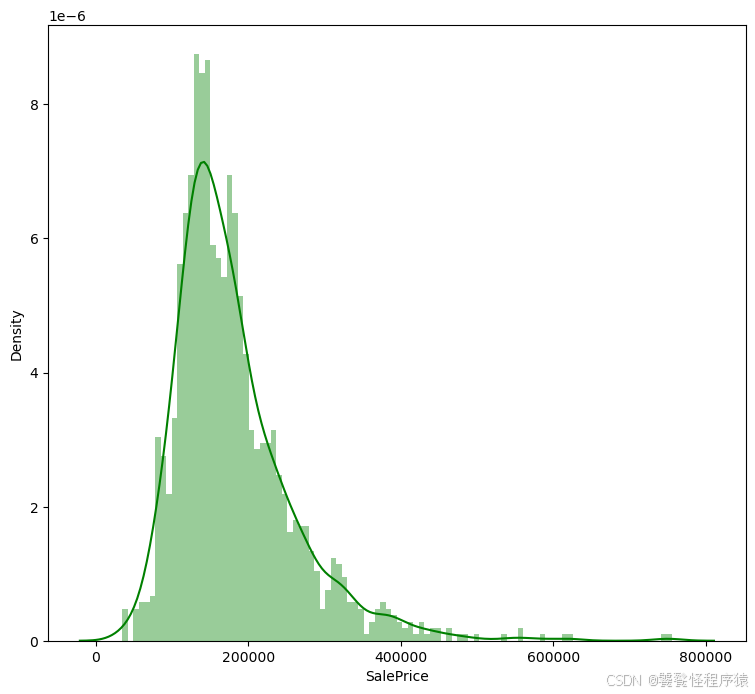
Step3、查看房价分布
print(dataset_df['SalePrice'].describe())
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 8))
sns.distplot(dataset_df['SalePrice'], color='g', bins=100, hist_kws={'alpha': 0.4});
count 1460.000000
mean 180921.195890
std 79442.502883
min 34900.000000
25% 129975.000000
50% 163000.000000
75% 214000.000000
max 755000.000000
Name: SalePrice, dtype: float64
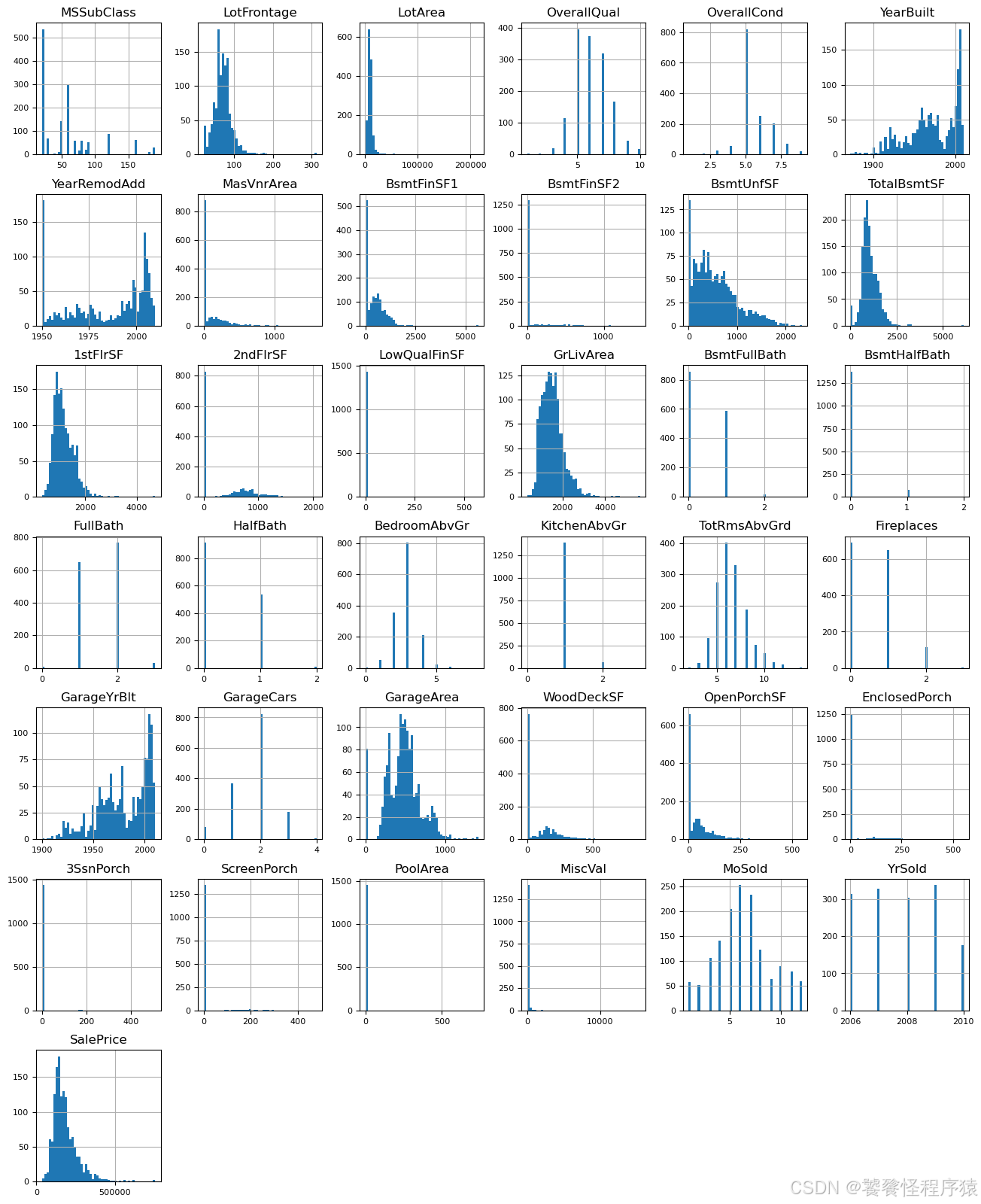
Step4、数值数据分布
list(set(dataset_df.dtypes.tolist()))df_num = dataset_df.select_dtypes(include = ['float64', 'int64'])
df_num.head()df_num.hist(figsize=(16, 20), bins=50, xlabelsize=8, ylabelsize=8);
Step5、划分数据集
import numpy as npdef split_dataset(dataset, test_ratio=0.30):test_indices = np.random.rand(len(dataset)) < test_ratioreturn dataset[~test_indices], dataset[test_indices]train_ds_pd, valid_ds_pd = split_dataset(dataset_df)
print("{} examples in training, {} examples in testing.".format(len(train_ds_pd), len(valid_ds_pd)))
label = 'SalePrice'
train_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(train_ds_pd, label=label, task = tfdf.keras.Task.REGRESSION)
valid_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(valid_ds_pd, label=label, task = tfdf.keras.Task.REGRESSION)
Step6、选择随机森林模型
rf = tfdf.keras.RandomForestModel(task = tfdf.keras.Task.REGRESSION)
rf.compile(metrics=["mse"]) # Optional, you can use this to include a list of eval metrics
Step7、训练模型
rf.fit(x=train_ds)
Step8、评估模型
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
logs = rf.make_inspector().training_logs()
plt.plot([log.num_trees for log in logs], [log.evaluation.rmse for log in logs])
plt.xlabel("Number of trees")
plt.ylabel("RMSE (out-of-bag)")
plt.show()
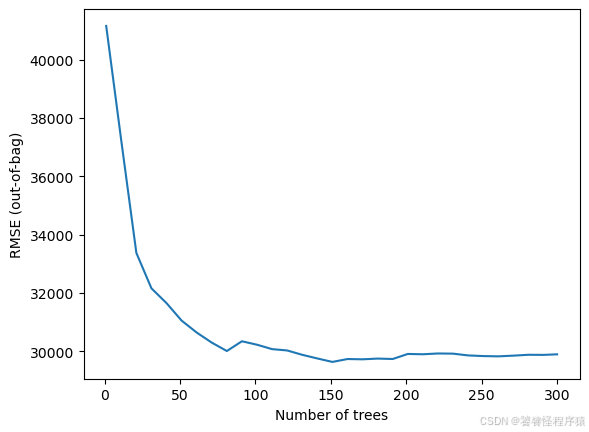
inspector = rf.make_inspector()
inspector.evaluation()
Evaluation(num_examples=1019, accuracy=None, loss=None, rmse=29893.939666232716, ndcg=None, aucs=None, auuc=None, qini=None)
evaluation = rf.evaluate(x=valid_ds,return_dict=True)for name, value in evaluation.items():print(f"{name}: {value:.4f}")
1/1 [==============================] - 1s 747ms/step - loss: 0.0000e+00 - mse: 698953728.0000
loss: 0.0000
mse: 698953728.0000
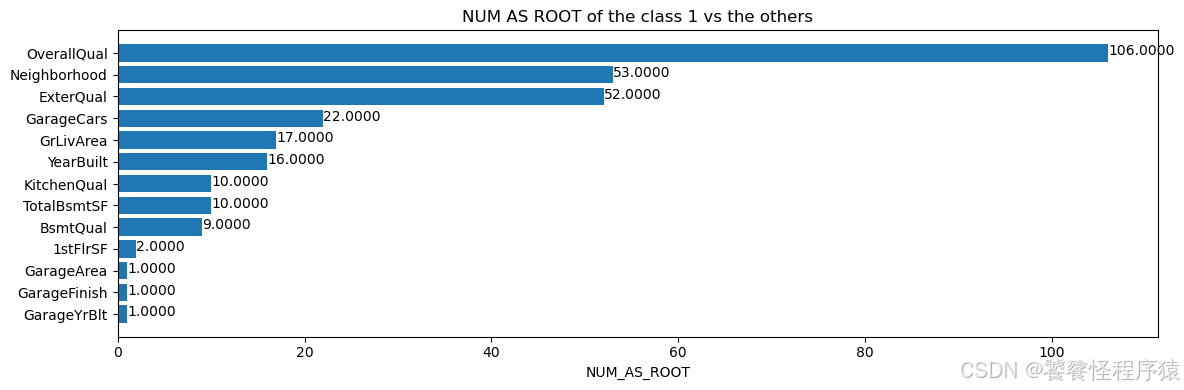
Step9、特征重要性
print(f"Available variable importances:")
for importance in inspector.variable_importances().keys():print("\t", importance)
Available variable importances:SUM_SCORENUM_AS_ROOTNUM_NODESINV_MEAN_MIN_DEPTH
inspector.variable_importances()["NUM_AS_ROOT"]
[("OverallQual" (1; #62), 106.0),("Neighborhood" (4; #59), 53.0),("ExterQual" (4; #22), 52.0),("GarageCars" (1; #32), 22.0),("GrLivArea" (1; #38), 17.0),("YearBuilt" (1; #76), 16.0),("KitchenQual" (4; #44), 10.0),("TotalBsmtSF" (1; #73), 10.0),("BsmtQual" (4; #14), 9.0),("1stFlrSF" (1; #0), 2.0),("GarageArea" (1; #31), 1.0),("GarageFinish" (4; #34), 1.0),("GarageYrBlt" (1; #37), 1.0)]
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))# Mean decrease in AUC of the class 1 vs the others.
variable_importance_metric = "NUM_AS_ROOT"
variable_importances = inspector.variable_importances()[variable_importance_metric]# Extract the feature name and importance values.
#
# `variable_importances` is a list of <feature, importance> tuples.
feature_names = [vi[0].name for vi in variable_importances]
feature_importances = [vi[1] for vi in variable_importances]
# The feature are ordered in decreasing importance value.
feature_ranks = range(len(feature_names))bar = plt.barh(feature_ranks, feature_importances, label=[str(x) for x in feature_ranks])
plt.yticks(feature_ranks, feature_names)
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()# TODO: Replace with "plt.bar_label()" when available.
# Label each bar with values
for importance, patch in zip(feature_importances, bar.patches):plt.text(patch.get_x() + patch.get_width(), patch.get_y(), f"{importance:.4f}", va="top")plt.xlabel(variable_importance_metric)
plt.title("NUM AS ROOT of the class 1 vs the others")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Step10、保存预测结果
test_file_path = "../input/house-prices-advanced-regression-techniques/test.csv"
test_data = pd.read_csv(test_file_path)
ids = test_data.pop('Id')test_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(test_data,task = tfdf.keras.Task.REGRESSION)preds = rf.predict(test_ds)
output = pd.DataFrame({'Id': ids,'SalePrice': preds.squeeze()})output.head()
sample_submission_df = pd.read_csv('../input/house-prices-advanced-regression-techniques/sample_submission.csv')
sample_submission_df['SalePrice'] = rf.predict(test_ds)
sample_submission_df.to_csv('/kaggle/working/submission.csv', index=False)
sample_submission_df.head()
Next Steps
微调模型,上分打榜。
