C++学习之STL学习:string类常用接口的模拟实现
上一篇博客我们学习了string类的常见应用,接下来我们将堆对它们的底层进行深入挖掘,并进行模拟实现
作者个人gitee主页:楼田莉子 (riko-lou-tian) - Gitee.com
感兴趣的可以自行去查看
目录
string实现的前置准备
string的构造/析构实现
string()的模拟实现
string(const char* str)的模拟实现
构造的合并
string的拷贝构造函数
赋值重载
string的析构实现
string函数的实现
size()的模拟实现
operator[]的模拟实现
迭代器模拟实现
正向迭代器
const正向迭代器
string的插入函数
reserve
pushback
append
+=运算符重载
insert
成员变量:npos
erase
pop_back
find
substr
clear函数
swap函数
流插入与流提取
流插入
流提取
getline函数
比较函数
<
<=
>
>=
==
!=
源代码
string实现的前置准备
首先我们需要三个文件
string.h:string实现的命名空间、类以及函数声明
string.cpp:string实现的方法
test.cpp:测试文件
string在底层上可以认为是一个字符顺序表。因此在底层上我们也像顺序表那样定义三个变量
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;同时在测试文件test.c需要将模拟实现与原装时间进行对比,但是这样就会与我们系统的string冲突。所以我们需要一个命名空间来包装它
//防止测试的时候与系统的string冲突,故用Boogiepop命名空间封装
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普
{class basic_string{public:private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;};
};命名空间可以在多个文件进行书写。多个文件的命名空间一般被认为是同一个命名空间(相当于被合并了)
我们要在三个文件中都用同一个命名空间包装起来。否则会冲突
string的构造/析构实现
string的构造方式常用的有三种:
string()、string(const char*str)、
string()的模拟实现
误区:不要这么初始化

测试:
string.cpp
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普{string::string():_str(nullptr), _size(0),_capacity(0){}string::string(const char* str){}const char*string:: c_str() const{return _str; }
}
string.h
#pragma once
//防止测试的时候与系统的string冲突,故用Boogiepop命名空间封装
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普{class string{public:string();string(const char* str);//用c_str来打印//之所以不先用流插入流提取是因为它们相对比较复杂,后面进行学习const char* c_str() const;private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;};
};test.cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普//三个文件的命名空间被认为是同一个命名空间
{void string_test1(){string s1;cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;}
};
int main()
{Boogiepop::string_test1();return 0;
}经过测试,程序崩溃

为什么会崩溃呢?
因为返回的_str是一个const类型的指针。const char*的指针与其他指针不同,其他指针都会按十六进制的地址去打印,但是const char* 不会。const char*更多指向一个串,对指向的空间上的内容,直到'\0'停止。但_str被初始化为nullptr,而且不能被修改,空指针直接的解引用就会报错。
正确的初始化方式为:
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普{string::string():_str(new char[1] {'\0'}), _size(0), _capacity(0){}string::string(const char* str){}const char*string:: c_str() const{return _str; }
}
string(const char* str)的模拟实现
string::string(const char* str):_str(new char[strlen(str) + 1])//strlen是不包含’\0‘的长度,_size(strlen(str)), _capacity(strlen(str))
{strcpy(_str, str);
}但是这么初始化并不好。因为strlen是在运行时候计算数值,连续调用三个strlen会让程序运行变得很慢。
那么我们是否可以这么改呢?
string::string(const char* str):_size(strlen(str)),_str(new char[_size + 1])//strlen是不包含’\0‘的长度, _capacity(_size)
{strcpy(_str, str);
}也是不可以的。
因为初始化列表是严格按照类中声明的顺序来的,声明的顺序为:
private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;我们可不可以将_size顺序调换呢?理论上确实可以解决这个问题。但是这样的程序是耦合的。改变的一个就会影响后面的。项目中应当极力避免的。
如果我们要改可以这样
string::string(const char* str):_size(strlen(str))//strlen是不包含’\0‘的长度
{_str=new char[_size + 1];_capacity=_size;strcpy(_str, str);
}构造的合并
我们也可以将两种构造方式合并。无参的构造和带参数的构造是可以合并的——写全缺省的构造函数
但是不能初始化为nullptr,程序会崩溃。可以初始化为'\0'或者
string.h
#pragma once
#include<string.h>//包含C语言的头文件
//防止测试的时候与系统的string冲突,故用Boogiepop命名空间封装
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普
{class string{public://string的构造函数//string();//合并了构造函数string(const char* str="");//用c_str来打印//之所以不先用流插入流提取是因为它们相对比较复杂,后面进行学习const char* c_str() const;private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;};
};
string.cpp
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普{//string的构造/*string::string():_str(new char[1] {'\0'}), _size(0), _capacity(0){ }*///string的合并string::string(const char* str):_size(strlen(str))//strlen是不包含’\0‘的长度{_str=new char[_size + 1];_capacity=_size;strcpy(_str, str);}const char*string:: c_str() const{return _str; }
}string的拷贝构造函数
string.h
//拷贝构造函数
string(const string& str);string.cpp
//拷贝构造函数
string::string(const string& str)
{}现代写法:
void string::swap(string& s)
{std::swap(_str, s._str);std::swap(_size, s._size);std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
string::string(const string& s)
{string tmp(s._str);swap(tmp);
}赋值重载
声明:
//赋值重载
string& operator=(const string& s);
//赋值重载
string& operator=(const string& s);
//赋值重载
string& operator=(const string tmp);方法一
//赋值重载
//方法一
string& string::operator=(const string& s)
{if (this != &s){char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1];memcpy(tmp, s._str, s._size + 1);delete[] _str;_str = tmp;_size = s._size;_capacity = s._capacity;}return *this;
}方法二
//方法二
string& string::operator=(const string& s)
{if (this != &s){string tmp(s);swap(tmp);}return *this;
}方法三
//方法三
string& string::operator=(string tmp)
{cout << "string& string::operator=(string tmp)" << endl;swap(tmp);return *this;
}string的析构实现
string.cpp
//string的析构
string::~string()
{delete[] _str;//用[]是因为中间可能用多个字符_str = nullptr;_size = 0;_capacity = 0;
}string函数的实现
size()的模拟实现
//size()函数
size_t string::size() const
{return _size;
}operator[]的模拟实现
char& string::operator[](size_t i)//可以写的operator[]()函数{assert(i< _size);//断言写的是为真的条件,为假会直接报错return _str[i];}const char& string::operator[](size_t i) const//只读的operator[]()函数{assert(i < _size);//断言写的是为真的条件,为假会直接报错return _str[i];}测试:
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普//三个文件的命名空间被认为是同一个命名空间
{void string_test1(){string s1;cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;string s2("hello world");cout<<s2.c_str()<<endl;for (size_t i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++){s2[i]++;cout<<s2[i]<<" ";}}
};
int main()
{Boogiepop::string_test1();return 0;
}结果为:

运行正常
迭代器模拟实现
正向迭代器
string.h
//迭代器
typedef char* iterator;
//正向迭代器
iterator begin();
iterator end();string.cpp
//正向迭代器
string::iterator string::begin()
{return _str;
}
string::iterator string::end()
{return _str + _size;
}测试:
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普//三个文件的命名空间被认为是同一个命名空间
{void string_test2(){const string s1("the song of the end world ");string::iterator it1 = s1.begin();while (it1 != s1.end()){cout<<*it1<<" ";it1++;}cout<<endl;}
};
int main()
{//Boogiepop::string_test1();Boogiepop::string_test2();return 0;
}这样是不通过的,因为涉及到了权限的放大,所以我们还需要模拟实现const迭代器
const正向迭代器
string.h
//迭代器
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
//正向迭代器
iterator begin();
iterator end();
//正向const迭代器
const_iterator begin() const;
const_iterator end() const;string.cpp
//正向const迭代器
string::const_iterator string::begin() const
{return _str;
}
string::const_iterator string::end() const
{return _str + _size;
}但是const迭代器目前只是简单实现,实际上const迭代器的实现十分复杂。需要后面的知识才能明白
string的插入函数
reserve
void string::reserve(size_t n)//扩容函数
{if (n > _capacity){char* new_str = new char[n + 1];strcpy(new_str, _str);delete[] _str;_str = new_str;_capacity = n;}
}pushback
string.cpp
void string::push_back(char c)//尾插函数
{if (_size >= _capacity){size_t new_capacity =_capacity == 0? 4 : _capacity *2;reserve(new_capacity);}_str[_size] = c;++_size;_str[_size] = '\0';
}test.cpp
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普//三个文件的命名空间被认为是同一个命名空间
{void string_test3(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;s1.push_back('!');cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;}
};
int main()
{Boogiepop::string_test3();return 0;
}测试成功’

append
void string::append(const char* str)
{size_t len = strlen(str);if (len + _size > _capacity){size_t new_capacity = len + _size <_capacity * 2? _capacity *2: len + _size;}strcpy(_str + _size, str);_size += len;
}+=运算符重载
string.h
string& operator+=(char ch);
string& operator+=(const char* str);string.cpp
string& string::operator+=(char ch){push_back(ch);return *this;}string& string::operator+=(const char* str){append(str);return *this;}测试:
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普//三个文件的命名空间被认为是同一个命名空间
{void string_test3(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;s1.push_back('!');cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;s1.append(" —— singer");cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;s1+= " —— singer";cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;s1+= '~';cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;}
};
int main()
{Boogiepop::string_test3();return 0;
}结果为:

测试均成功
insert
string.h
//插入函数
void insert(size_t pos, const char* str);
void insert(size_t pos, char ch);string.cpp
//插入函数void string::insert(size_t pos, char ch){assert(pos<=_size);if (_size >= _capacity){size_t new_capacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2;reserve(new_capacity);}//挪动数据//方案一:/* int end = _size;while (end >=(int) pos){_str[end + 1] = _str[end];--end;}*///方案二:size_t end = _size+1;while (end > pos){_str[end] = _str[end-1];--end;}_str[pos] = ch;++_size;}void string::insert(size_t pos, const char* str){assert(pos <= _size);size_t len = strlen(str);if (_size+len >= _capacity){size_t new_capacity =2*_capacity>len+_size? 2*_capacity : len + _size;reserve(new_capacity);}//挪动数据size_t end = _size+len;while (end >pos+len-1){_str[end] = _str[end-len];--end;}for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++){_str[pos + i] = _str[i];}}测试:
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普//三个文件的命名空间被认为是同一个命名空间
{void string_test5(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout << s1 << endl;s1.insert(0, "d");cout << s1 << endl;s1.insert(10, "singer");cout << s1 << endl;}
};
int main()
{Boogiepop::string_test5();return 0;
}测试结果为:
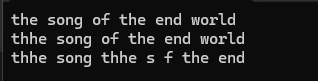
成员变量:npos
string.h
//定义成员变量npos
static const size_t npos = -1;
erase
string.h
//erase函数
string& erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);string.cpp
//定义成员变量nposstatic const size_t npos = -1;//erase函数string& string::erase(size_t pos, size_t len){assert(pos < _size);// 要删除的数据,大于pos后面的字符个数// pos后面全删if (len == npos || len >= (_size - pos)){_size = pos;_str[_size] = '\0';}else{size_t i = pos + len;memmove(_str + pos, _str + i, _size + 1 - i);_size -= len;}return *this;}test.cpp
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普//三个文件的命名空间被认为是同一个命名空间
{void string_test6(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout << s1 << endl;s1.erase(0, 4);cout << s1 << endl;}
};
int main()
{Boogiepop::string_test6();return 0;
}测试结果正确
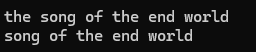
pop_back
string.h
//pop_back函数
void pop_back()string.cpp
//pop_back函数
void string::pop_back()
{assert(_size > 0);--_size;_str[_size] = '\0';
}test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普//三个文件的命名空间被认为是同一个命名空间
{void string_test6(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout << s1 << endl;s1.erase(0, 4);cout << s1 << endl;s1.pop_back();s1.pop_back();s1.pop_back();s1.pop_back();s1.pop_back();cout << s1 << endl;}
};
int main()
{Boogiepop::string_test6();return 0;
}测试结果正确
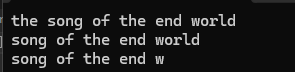
find
string.h
//查找函数
size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0);
size_t find(const char *str, size_t pos = 0 );string.cpp
//查找函数
size_t string::find(char ch, size_t pos )
{for (int i = pos; i < _size; i++){if (_str[i] == ch){return i;}}
}
size_t string::find(const char* str, size_t pos )
{const char* p = strstr(_str+pos, str);if (p == nullptr){return npos;}else{return p - _str;}
}test.cpp
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普//三个文件的命名空间被认为是同一个命名空间
{void string_test7(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout << s1 << endl;size_t P=s1.find("the");if (P != string::npos){cout<<"找到了,位置在:"<<P<<endl;}else{cout<<"没找到"<<endl;}size_t U = s1.find("o");if (U != string::npos){cout << "找到了,位置在: " << U << endl;}else{cout << "没找到" << endl;}}
};
int main()
{Boogiepop::string_test7();return 0;
}测试成功:

substr
string.h
//substr函数
string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;string.cpp
//substr函数
string string::substr(size_t pos , size_t len ) const
{if (len == npos || len > _size - pos){len=_size - pos;}string ret;ret.reserve(len);for (size_t i = 0;i < len;i++){ret+=_str[pos+i];}return ret;
}test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普//三个文件的命名空间被认为是同一个命名空间
{void string_test8(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout << s1 << endl;string s2=s1.substr(0, 4);cout << s2 << endl;string s3=s1.substr(10, 6);cout << s3 << endl;}
};
int main()
{Boogiepop::string_test8();return 0;
}测试结果:

clear函数
//清除函数
void string::clear()
{_size = 0;_str[0] = '\0';
}swap函数
void swap(string& x, string& y){x.swap(y);}流插入与流提取
流插入
string.h
//流插入
ostream& operator<< (ostream& out, const string& str);
//流提取
iostream& operator>> (iostream& in, string& str);在这里不必要使用友元函数来访问私有,因为访问c_str就足够访问内部的变量了
string.cpp
//流提取
ostream& operator<< (ostream& out, const string& str)
{out<<str.c_str();return out;
}但是这么写有一个漏洞
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普//三个文件的命名空间被认为是同一个命名空间
{void string_test4(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout<<s1<<endl;s1 += '\0';cout<<s1<<endl;s1 += '!';cout<<s1<<endl;}
};
int main()
{Boogiepop::string_test4();return 0;
}结果为:

不仅打印不出来'\0',而且连后面的'!'都无法打印出来了。
因此改变一下为:
//流插入
ostream& operator<< (ostream& out, const string& str)
{for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++){out<<str[i];}return out;
}c_str与C语言保持一致,遇到'\0'就停止了
流提取
get()是C++自己的函数,用来从输入流中读取一个字符
string.cpp
//流提取
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{s.clear();char buff[128];int i = 0;//get()是C++自己的函数,用来从输入流中读取一个字符char ch = in.get();while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n'){buff[i++] = ch;if (i == 127){buff[i] = '\0';s += buff;i = 0;}ch = in.get();}if (i > 0){buff[i] = '\0';s += buff;}return in;
}getline函数
string.cpp
istream& getline(istream& in, string& s, char delim){s.clear();char buff[128];int i = 0;char ch = in.get();while (ch != delim){buff[i++] = ch;if (i == 127){buff[i] = '\0';s += buff;i = 0;}ch = in.get();}if (i > 0){buff[i] = '\0';s += buff;}return in;}
比较函数
声明:
//比较函数
bool operator<(const string& s) const;
bool operator<=(const string& s) const;
bool operator>(const string& s) const;
bool operator>=(const string& s) const;
bool operator==(const string& s) const;
bool operator!=(const string& s) const;<
bool string::operator<(const string& s) const
{size_t i1 = 0, i2 = 0;while (i1 < _size && i2 < s._size){if (_str[i1] < s._str[i2]){return true;}else if (_str[i1] > s._str[i2]){return false;}else{++i1;++i2;}}<=
bool string::operator<=(const string& s) const
{return *this < s || *this == s;
}>
bool string::operator>(const string& s) const
{return !(s <= *this);
}>=
bool string::operator>=(const string& s) const
{return !(*this < s);
}==
bool string::operator==(const string& s) const
{size_t i1 = 0, i2 = 0;while (i1 < _size && i2 < s._size){if (_str[i1] != s[i2]){return false;}else{++i1;++i2;}}return i1 == _size && i2 == s._size;
}!=
bool string::operator!=(const string& s) const
{return !(*this == s);
}源代码
string.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream> #include<string.h>//包含C语言的头文件
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
//防止测试的时候与系统的string冲突,故用Boogiepop命名空间封装
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普
{class string{public://string的构造函数//string();//合并了构造函数string(const char* str="");//用c_str来打印//之所以不先用流插入流提取是因为它们相对比较复杂,后面进行学习//c_str()函数const char* c_str() const;//拷贝构造函数string(const string& s);//string的析构函数~string(); //赋值重载string& operator=(const string& s);//赋值重载string& operator=(const string& s);//赋值重载string& operator=(const string tmp);//size()函数size_t size() const;//operator[]()函数char& operator[](size_t i);//可以写的operator[]()函数const char& operator[](size_t i) const;//只读的operator[]()函数//迭代器typedef char* iterator;typedef const char* const_iterator;//正向迭代器iterator begin();iterator end();//正向const迭代器const_iterator begin() const;const_iterator end() const;//string插入相关的函数void reserve(size_t n);void push_back(char c);void append(const char* str);string& operator+=(char ch);string& operator+=(const char* str);//插入函数void insert(size_t pos, const char* str);void insert(size_t pos, char ch);//定义成员变量nposstatic const size_t npos=-1 ;//erase函数string& erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);//pop_back函数void pop_back();//查找函数size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0);size_t find(const char *str, size_t pos = 0 );//substr函数string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;//比较函数bool operator<(const string& s) const;bool operator<=(const string& s) const;bool operator>(const string& s) const;bool operator>=(const string& s) const;bool operator==(const string& s) const;bool operator!=(const string& s) const;//清除函数void clear();//swap函数void swap(string& s);private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;};//流插入ostream& operator<< (ostream& out, const string& str);//流提取istream& operator>> (istream& in, string& str);//getline函数istream& getline(istream& in, string& str, char delim='\n');
};
string.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普{//string的构造/*string::string():_str(new char[1] {'\0'}), _size(0), _capacity(0){ }*///string的合并string::string(const char* str):_size(strlen(str))//strlen是不包含’\0‘的长度{_str=new char[_size + 1];_capacity=_size;strcpy(_str, str);}void string::swap(string& s){std::swap(_str, s._str);std::swap(_size, s._size);std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);}//拷贝构造函数/*string::string(const string& s){_str = new char[s._size + 1];memcpy(_str,s._str, s._size + 1);_size = s._size;_capacity = s._capacity;}*///拷贝构造函数现代写法string::string(const string& s){string tmp(s._str);swap(tmp);}//string的析构string::~string(){delete[] _str;//用[]是因为中间可能用多个字符_str = nullptr;_size = 0;_capacity = 0;}//赋值重载//方法一string& string::operator=(const string& s){if (this != &s){char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1];memcpy(tmp, s._str, s._size + 1);delete[] _str;_str = tmp;_size = s._size;_capacity = s._capacity;}return *this;}//方法二string& string::operator=(const string& s){if (this != &s){string tmp(s);swap(tmp);}return *this;}//方法三string& string::operator=(string tmp){cout << "string& string::operator=(string tmp)" << endl;swap(tmp);return *this;}//c_str函数const char*string:: c_str() const{return _str; }//size()函数size_t string::size() const{return _size;}//operator[]()函数char& string::operator[](size_t i)//可以写的operator[]()函数{assert(i< _size);//断言写的是为真的条件,为假会直接报错return _str[i];}const char& string::operator[](size_t i) const//只读的operator[]()函数{assert(i < _size);//断言写的是为真的条件,为假会直接报错return _str[i];}//正向迭代器string::iterator string::begin(){return _str;}string::iterator string::end(){return _str + _size;}//正向const迭代器string::const_iterator string::begin() const{return _str;}string::const_iterator string::end() const{return _str + _size;}//string插入相关的函数void string::reserve(size_t n)//扩容函数{if (n > _capacity){char* new_str = new char[n + 1];memcpy(new_str, _str,_size + 1);delete[] _str;_str = new_str;_capacity = n;}}void string::push_back(char c)//尾插函数{if (_size >= _capacity){size_t new_capacity =_capacity == 0? 4 : _capacity *2;reserve(new_capacity);}_str[_size] = c;++_size;_str[_size] = '\0';}void string::append(const char* str){size_t len = strlen(str);if (len + _size > _capacity){size_t new_capacity = len + _size <_capacity * 2? _capacity *2: len + _size;}memcpy(_str + _size, str+1,len + 1);_size += len;}string& string::operator+=(char ch){push_back(ch);return *this;}string& string::operator+=(const char* str){append(str);return *this;}//插入函数void string::insert(size_t pos, char ch){assert(pos<=_size);if (_size >= _capacity){size_t new_capacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2;reserve(new_capacity);}//挪动数据//方案一:/* int end = _size;while (end >=(int) pos){_str[end + 1] = _str[end];--end;}*///方案二:size_t end = _size+1;while (end > pos){_str[end] = _str[end-1];--end;}_str[pos] = ch;++_size;}void string::insert(size_t pos, const char* str){assert(pos <= _size);size_t len = strlen(str);if (_size+len >= _capacity){size_t new_capacity =2*_capacity>len+_size? 2*_capacity : len + _size;reserve(new_capacity);}//挪动数据size_t end = _size+len;while (end >pos+len-1){_str[end] = _str[end-len];--end;}for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++){_str[pos + i] = _str[i];}}//定义成员变量nposstatic const size_t npos = -1;//erase函数string& string::erase(size_t pos, size_t len){assert(pos < _size);// 要删除的数据,大于pos后面的字符个数// pos后面全删if (len == npos || len >= (_size - pos)){_size = pos;_str[_size] = '\0';}else{size_t i = pos + len;memmove(_str + pos, _str + i, _size + 1 - i);_size -= len;}return *this;}//pop_back函数void string::pop_back(){assert(_size > 0);--_size;_str[_size] = '\0';}//查找函数size_t string::find(char ch, size_t pos ){for (int i = pos; i < _size; i++){if (_str[i] == ch){return i;}}}size_t string::find(const char* str, size_t pos ){const char* p = strstr(_str+pos, str);if (p == nullptr){return npos;}else{return p - _str;}}//substr函数string string::substr(size_t pos , size_t len ) const{if (len == npos || len > _size - pos){len=_size - pos;}string ret;ret.reserve(len);for (size_t i = 0;i < len;i++){ret+=_str[pos+i];}return ret;}//比较函数bool string::operator<(const string& s) const{size_t i1 = 0, i2 = 0;while (i1 < _size && i2 < s._size){if (_str[i1] < s[i2]){return true;}else if (_str[i1] > s[i2]){return false;}else{++i1;++i2;}}return i2<s._size;}bool string::operator<=(const string& s) const{return *this < s || *this == s;}bool string::operator>(const string& s) const{return !(s <= *this);}bool string::operator>=(const string& s) const{return !(*this < s);}bool string::operator==(const string& s) const{size_t i1 = 0, i2 = 0;while (i1 < _size && i2 < s._size){if (_str[i1] != s[i2]){return false;}else{++i1;++i2;}}return i1 == _size && i2 == s._size;}bool string::operator!=(const string& s) const{return !(*this == s);}//清除函数void string::clear(){_size = 0;_str[0] = '\0';}//swap函数void swap(string& x, string& y){x.swap(y);}//流插入ostream& operator<< (ostream& out, const string& str){for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++){out << str[i];}return out;}//流提取istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s){s.clear();char buff[128];int i = 0;//get()是C++自己的函数,用来从输入流中读取一个字符char ch = in.get();while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n'){buff[i++] = ch;if (i == 127){buff[i] = '\0';s += buff;i = 0;}ch = in.get();}if (i > 0){buff[i] = '\0';s += buff;}return in;}//getline函数istream& getline(istream& in, string& str, char delim ){str.clear();char buff[128];int i = 0;char ch = in.get();while (ch != delim){buff[i++] = ch;if (i == 127){buff[i] = '\0';str += buff;i = 0;}ch = in.get();}if (i > 0){buff[i] = '\0';str += buff;}return in;}
}
test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"string.h"
namespace Boogiepop//命名空间:不吉波普//三个文件的命名空间被认为是同一个命名空间
{void string_test1(){string s1;cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;string s2("hello world");cout<<s2.c_str()<<endl;for (size_t i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++){s2[i]++;cout<<s2[i]<<" ";}}void string_test2(){const string s1("the song of the end world ");string::const_iterator it1 = s1.begin();while (it1 != s1.end()){cout<<*it1<<" ";it1++;}cout<<endl;}void string_test3(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;s1.push_back('!');cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;s1.append(" —— singer");cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;s1+= " —— singer";cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;s1+= '~';cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;}void string_test4(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout<<s1<<endl;s1 += '\0';cout<<s1<<endl;s1 += '!';cout<<s1<<endl;cout<<s1.c_str()<<endl;s1 += " —— singer";cout << s1 << endl;}void string_test5(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout << s1 << endl;s1.insert(0, "d");cout << s1 << endl;s1.insert(10, "singer");cout << s1 << endl;}void string_test6(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout << s1 << endl;s1.erase(0, 4);cout << s1 << endl;s1.pop_back();s1.pop_back();s1.pop_back();s1.pop_back();s1.pop_back();cout << s1 << endl;}void string_test7(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout << s1 << endl;size_t P=s1.find("the");if (P != string::npos){cout<<"找到了,位置在:"<<P<<endl;}else{cout<<"没找到"<<endl;}size_t U = s1.find("o");if (U != string::npos){cout << "找到了,位置在: " << U << endl;}else{cout << "没找到" << endl;}}void string_test8(){string s1("the song of the end world ");cout << s1 << endl;string s2=s1.substr(0, 4);cout << s2 << endl;string s3=s1.substr(10, 6);cout << s3 << endl;}void string_test9(){string s1("the song of the end world "), s2("the song of the end world");string s3("the song of the end world"), s4("the song of the end worldX");string s5("the song of the end worldC "), s6("the song of the end world");cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;cout << (s3 < s4) << endl;cout << (s5 < s6) << endl;}void string_test10(){string s1("the song of the end world "), s2("the story of the end world");cout << s1 << s2 << endl;cin>>s1>>s2;cout << s1 << s2 << endl;}
};
int main()
{//Boogiepop::string_test1();//Boogiepop::string_test2();//Boogiepop::string_test3();//Boogiepop::string_test4();//Boogiepop::string_test5();//Boogiepop::string_test6();//Boogiepop::string_test7();//Boogiepop::string_test8();//Boogiepop::string_test9();Boogiepop::string_test10();return 0;
}本篇博客到此结束,希望通过string的模拟实现能对string有更深刻的理解。
下一篇我们将继续学习STL中vector的内容进行学习
在这里求一个点赞,谢谢
封面图自取:

