CSP-J教程——第一阶段——第六课:程序流程控制 - 循环结构(一)for循环
课程目标
- 理解循环的概念和用途
- 掌握for循环的语法结构
- 学会使用循环变量、循环条件和步长控制
- 能够使用for循环解决重复性任务
- 理解循环的执行流程
- 学会调试循环程序
第一部分:循环的概念(30分钟)
1.1 什么是循环?
生活比喻:
- 重复动作:像体育课跑步,绕操场跑5圈
- 计数任务:像数数从1数到100
- 批量处理:像给全班同学发作业本
1.2 为什么需要循环?
没有循环的困境:
// 想要输出5次"Hello"
cout << "Hello" << endl;
cout << "Hello" << endl;
cout << "Hello" << endl;
cout << "Hello" << endl;
cout << "Hello" << endl;// 想要计算1+2+3+...+100
int sum = 1 + 2 + 3 + ... + 100; // 要写100个数!
使用循环的便利:
// 使用循环输出5次"Hello"
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {cout << "Hello" << endl;
}// 使用循环计算1到100的和
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {sum += i;
}
1.3 循环的三要素
- 循环变量:控制循环次数的计数器
- 循环条件:决定循环是否继续执行的条件
- 步长:每次循环后循环变量的变化量
第二部分:for循环语法详解(50分钟)
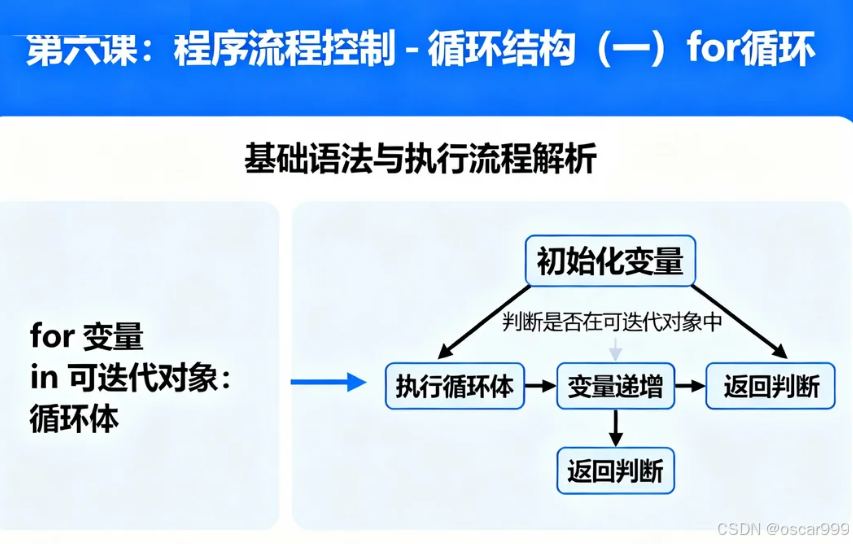
2.1 for循环的基本结构
语法:
for (初始化; 循环条件; 更新) {// 循环体:重复执行的代码
}
执行流程图:
开始循环↓
执行初始化↓
检查循环条件↓
条件为假 → 结束循环↓条件为真
执行循环体↓
执行更新↓
检查循环条件 → ...
2.2 第一个for循环程序
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {// 输出5次"Hello, World!"for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {cout << "Hello, World!" << endl;}cout << "循环结束!" << endl;return 0;
}
2.3 循环变量详解
循环变量的作用:
- 记录当前是第几次循环
- 可以在循环体中使用
- 控制循环的执行次数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {// 使用循环变量i来显示循环次数for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {cout << "这是第 " << i + 1 << " 次循环" << endl;cout << "循环变量 i 的值是: " << i << endl;cout << "---" << endl;}return 0;
}
2.4 循环条件详解
循环条件决定循环何时结束:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {// 从1数到10cout << "从1数到10: ";for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;// 从0数到9cout << "从0数到9: ";for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
2.5 步长控制详解
步长控制循环变量的变化方式和速度:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {// 每次增加1(默认)cout << "每次增加1: ";for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;// 每次增加2:输出偶数cout << "每次增加2: ";for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i += 2) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;// 倒计时:每次减少1cout << "倒计时: ";for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--) {cout << i << " ";}cout << "发射!" << endl;// 每次增加5cout << "5的倍数: ";for (int i = 0; i <= 50; i += 5) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
第三部分:for循环的多种形式(40分钟)
3.1 不同的初始化方式
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {// 方式1:在for循环内部声明循环变量(推荐)cout << "内部声明: ";for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;// 方式2:在外部声明循环变量cout << "外部声明: ";int j;for (j = 0; j < 3; j++) {cout << j << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "循环结束后j的值: " << j << endl; // 这里还可以访问jreturn 0;
}
3.2 不同的步长变化
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {// 递增步长cout << "递增步长(+3): ";for (int i = 0; i < 10; i += 3) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;// 递减步长cout << "递减步长(-2): ";for (int i = 10; i > 0; i -= 2) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;// 乘法步长(几何增长)cout << "乘法步长(×2): ";for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i *= 2) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;// 复杂步长cout << "复杂步长: ";for (int i = 0; i < 20; i = i * 2 + 1) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.3 使用变量控制循环
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int start, end, step;cout << "请输入循环的起始值: ";cin >> start;cout << "请输入循环的结束值: ";cin >> end;cout << "请输入步长: ";cin >> step;cout << "循环序列: ";for (int i = start; i <= end; i += step) {cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
3.4 循环变量的作用域
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {// 正确:在循环内部声明,避免命名冲突for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {cout << "第一个循环: " << i << endl;}// 可以再次使用i,因为上一个i的作用域已经结束for (int i = 10; i < 13; i++) {cout << "第二个循环: " << i << endl;}return 0;
}
第四部分:for循环的应用示例(50分钟)
4.1 数字求和
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int n, sum = 0;cout << "请输入一个正整数: ";cin >> n;// 计算1到n的和for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {sum += i; // 等价于 sum = sum + i;}cout << "1到" << n << "的和是: " << sum << endl;// 显示计算过程(可选)cout << "计算过程: 1";for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {cout << " + " << i;}cout << " = " << sum << endl;return 0;
}
4.2 乘法表生成
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int number;cout << "请输入要生成乘法表的数字: ";cin >> number;cout << number << "的乘法表:" << endl;cout << "==============" << endl;for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {cout << number << " × " << i << " = " << number * i << endl;}return 0;
}
4.3 寻找最大值和最小值
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int n, number, max, min;cout << "请输入数字的个数: ";cin >> n;if (n <= 0) {cout << "请输入有效的数字个数!" << endl;return 0;}cout << "请输入第1个数字: ";cin >> number;max = number; // 假设第一个数字是最大值min = number; // 假设第一个数字是最小值// 循环输入剩余数字并比较for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {cout << "请输入第" << i << "个数字: ";cin >> number;if (number > max) {max = number;cout << "更新最大值: " << max << endl;}if (number < min) {min = number;cout << "更新最小值: " << min << endl;}}cout << "\n=== 统计结果 ===" << endl;cout << "最大值: " << max << endl;cout << "最小值: " << min << endl;cout << "范围: " << max - min << endl;return 0;
}
4.4 统计字符
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main() {string text;int letterCount = 0, digitCount = 0, spaceCount = 0;cout << "请输入一段文本: ";getline(cin, text);// 统计文本中各种字符的个数for (int i = 0; i < text.length(); i++) {char ch = text[i];if ((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z')) {letterCount++;} else if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {digitCount++;} else if (ch == ' ') {spaceCount++;}}cout << "\n=== 字符统计结果 ===" << endl;cout << "总字符数: " << text.length() << endl;cout << "字母个数: " << letterCount << endl;cout << "数字个数: " << digitCount << endl;cout << "空格个数: " << spaceCount << endl;return 0;
}
4.5 质数判断
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int number;bool isPrime = true;cout << "请输入一个正整数: ";cin >> number;if (number <= 1) {isPrime = false;} else {// 检查从2到number-1是否有因数for (int i = 2; i < number; i++) {if (number % i == 0) {isPrime = false;cout << "发现因数: " << i << endl;break; // 发现一个因数就可以确定不是质数}}}if (isPrime) {cout << number << " 是质数" << endl;} else {cout << number << " 不是质数" << endl;}return 0;
}
第五部分:嵌套for循环(40分钟)
5.1 什么是嵌套循环?
在一个循环内部包含另一个循环
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {// 外层循环控制行for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {cout << "第" << i << "行: ";// 内层循环控制列for (int j = 1; j <= 4; j++) {cout << "(" << i << "," << j << ") ";}cout << endl; // 换行}return 0;
}
5.2 打印图案
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int rows;cout << "请输入行数: ";cin >> rows;// 打印直角三角形cout << "直角三角形:" << endl;for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {cout << "* ";}cout << endl;}cout << "\n正方形:" << endl;for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= rows; j++) {cout << "* ";}cout << endl;}return 0;
}
5.3 完整的乘法表
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;int main() {// 打印9×9乘法表cout << " ";for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {cout << setw(4) << i;}cout << endl;cout << " " << string(36, '-') << endl;for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {cout << i << " |";for (int j = 1; j <= 9; j++) {cout << setw(4) << i * j;}cout << endl;}return 0;
}
5.4 数字金字塔
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int n;cout << "请输入金字塔层数: ";cin >> n;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {// 打印前导空格for (int j = 1; j <= n - i; j++) {cout << " ";}// 打印左边数字(递增)for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {cout << j << " ";}// 打印右边数字(递减)for (int j = i - 1; j >= 1; j--) {cout << j << " ";}cout << endl;}return 0;
}
第六部分:常见错误与调试(30分钟)
6.1 常见错误类型
1. 无限循环
// 错误:循环条件永远为真
for (int i = 0; i >= 0; i++) {cout << "无限循环..." << endl;
}// 错误:忘记更新循环变量
for (int i = 0; i < 5;) { // 缺少i++cout << "卡住了..." << endl;
}
2. 循环变量作用域错误
// 错误:在循环外部访问循环变量
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {// 循环体
}
cout << i; // 错误:i已经不存在// 正确:在外部声明变量
int j;
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++) {// 循环体
}
cout << j; // 正确:可以访问j
3. 分号位置错误
// 错误:在for语句后面误加分号
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++); { // 这个分号导致循环体为空cout << "Hello" << endl; // 这行代码只执行一次!
}// 正确:不要加分号
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {cout << "Hello" << endl; // 这行代码执行5次
}
4. 边界条件错误
// 错误:少循环一次或多循环一次
for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) { // 循环6次:0,1,2,3,4,5cout << i << " ";
}for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) { // 循环4次:1,2,3,4cout << i << " ";
}
6.2 调试技巧
使用输出语句跟踪循环:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int sum = 0;cout << "开始循环..." << endl;for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {cout << "第" << i << "次循环开始" << endl;cout << " i = " << i << ", 当前sum = " << sum << endl;sum += i;cout << " 相加后sum = " << sum << endl;cout << "第" << i << "次循环结束" << endl;cout << "---" << endl;}cout << "循环结束,最终结果: " << sum << endl;return 0;
}
使用表格跟踪变量:
| 循环次数 | i的值 | sum的值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 开始前 | - | 0 | 初始化 |
| 第1次 | 1 | 1 | 0+1=1 |
| 第2次 | 2 | 3 | 1+2=3 |
| 第3次 | 3 | 6 | 3+3=6 |
| 第4次 | 4 | 10 | 6+4=10 |
| 第5次 | 5 | 15 | 10+5=15 |
练习与作业
基础练习(必做)
练习1:数字序列生成
编写程序生成以下序列:
- 1到100的所有整数
- 1到100的所有奇数
- 100到1的倒序数字
- 0到100的所有5的倍数
练习2:阶乘计算
输入一个正整数n,计算n的阶乘(n! = 1×2×3×…×n)
要求检查输入有效性(n≥0)
练习3:平均成绩计算
输入5个学生的成绩,计算平均分、最高分和最低分
挑战练习(选做)
挑战1:斐波那契数列
输出斐波那契数列的前n项:
1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, …
规律:每个数是前两个数之和
挑战2:数字金字塔进阶
输入行数n,输出以下格式的金字塔:
1232345434567654
567898765
挑战3:质数筛选
找出100以内的所有质数,使用嵌套循环实现
实验任务
任务1:循环变量实验
测试不同的循环变量初始化、条件和步长,观察循环次数和结果:
// 测试不同的循环条件
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) // 循环几次?
for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) // 循环几次?
for (int i = 5; i > 0; i--) // 循环几次?
任务2:嵌套循环实验
使用嵌套循环打印不同的图案:
- 直角三角形(左上、右上、左下、右下)
- 菱形
- 空心正方形
任务3:性能测试
测试循环大量数据时的性能:
// 测试计算1到1000000的和需要多长时间
#include <ctime>
// 使用clock()函数测量时间
学习总结
今天学到了:
- ✅ 循环的概念:重复执行特定任务
- ✅ for循环语法:初始化、条件、更新
- ✅ 循环变量:控制循环次数
- ✅ 循环条件:决定循环是否继续
- ✅ 步长控制:循环变量的变化方式
- ✅ 嵌套循环:循环内部的循环
- ✅ 调试技巧:跟踪循环执行过程
关键技能:
- 循环设计:确定循环三要素
- 模式识别:识别适合使用循环的问题
- 边界处理:正确处理循环的开始和结束
- 算法思维:使用循环解决数学问题
下一课预告:
下一节课我们将学习程序流程控制:循环结构(二),包括while和do-while循环,以及循环控制语句break和continue。
