学习:JavaScript(6)
Math(数学)对象
在 JavaScript 中, Math 对象提供了数学常数和函数的属性和方法。以下是 Math 对象的完整指南,涵盖常数、函数和实际应用。
1. Math 对象的基本特性
(1) 静态对象
Math不是构造函数,不能创建实例- 所有属性和方法都是静态的,直接通过
Math调用
(2) 常用数学常数
| 属性 | 值(近似) | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
Math.PI | 3.14159 | 圆周率 π |
Math.E | 2.71828 | 自然对数的底数 e |
Math.LN2 | 0.69315 | 2的自然对数 |
Math.LN10 | 2.30259 | 10的自然对数 |
Math.LOG2E | 1.44270 | 以2为底e的对数 |
Math.LOG10E | 0.43429 | 以10为底e的对数 |
Math.SQRT2 | 1.41421 | 2的平方根 |
Math.SQRT1_2 | 0.70711 | 1/2的平方根 |
2. Math 对象的常用方法
(1) 基本数学运算
| 方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
Math.abs(x) | 绝对值 | Math.abs(-5) → 5 |
Math.ceil(x) | 向上取整 | Math.ceil(4.2) → 5 |
Math.floor(x) | 向下取整 | Math.floor(4.8) → 4 |
Math.round(x) | 四舍五入 | Math.round(4.5) → 5 |
Math.trunc(x) | 去除小数部分 | Math.trunc(4.9) → 4 |
(2) 幂和开方运算
| 方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
Math.pow(x, y) | x的y次幂 | Math.pow(2, 3) → 8 |
Math.sqrt(x) | 平方根 | Math.sqrt(16) → 4 |
Math.cbrt(x) | 立方根 | Math.cbrt(27) → 3 |
Math.exp(x) | e的x次幂 | Math.exp(1) → 2.718 |
Math.log(x) | 自然对数 | Math.log(Math.E) → 1 |
Math.log10(x) | 以10为底的对数 | Math.log10(100) → 2 |
Math.log2(x) | 以2为底的对数 | Math.log2(8) → 3 |
(3) 三角函数
| 方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
Math.sin(x) | 正弦(弧度) | Math.sin(Math.PI/2) → 1 |
Math.cos(x) | 余弦(弧度) | Math.cos(Math.PI) → -1 |
Math.tan(x) | 正切(弧度) | Math.tan(Math.PI/4) → 1 |
Math.asin(x) | 反正弦 | Math.asin(1) → π/2 |
Math.acos(x) | 反余弦 | Math.acos(0) → π/2 |
Math.atan(x) | 反正切 | Math.atan(1) → π/4 |
Math.atan2(y, x) | 从x轴到点(x,y)的角度 | Math.atan2(1, 1) → π/4 |
(4) 最大值和最小值
| 方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
Math.max(...values) | 返回最大值 | Math.max(1, 3, 2) → 3 |
Math.min(...values) | 返回最小值 | Math.min(1, 3, 2) → 1 |
(5) 随机数生成
| 方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
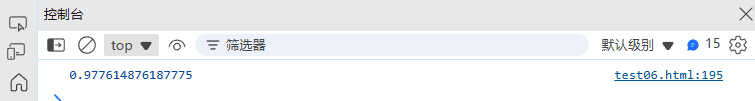
Math.random() | 生成0-1之间的随机数 | Math.random() → |
3. 角度和弧度转换
// 角度转弧度
function degreesToRadians(degrees) {return degrees * Math.PI / 180;
}// 弧度转角度
function radiansToDegrees(radians) {return radians * 180 / Math.PI;
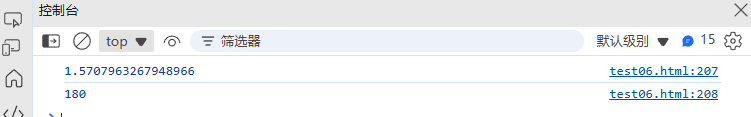
}console.log(degreesToRadians(90)); // 1.5708 (π/2)
console.log(radiansToDegrees(Math.PI)); // 180
4. 实际应用示例
(1) 生成随机数范围
// 生成 min-max 之间的随机整数
function randomInt(min, max) {return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
}// 生成 min-max 之间的随机浮点数
function randomFloat(min, max) {return Math.random() * (max - min) + min;
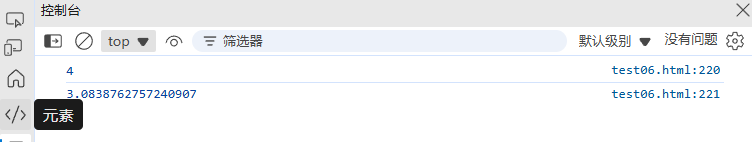
}console.log(randomInt(1, 10)); // 1-10的随机整数
console.log(randomFloat(1.5, 3.5)); // 1.5-3.5的随机浮点数
(2) 数字格式化
// 保留小数位数
function formatNumber(num, decimals = 2) {return Math.round(num * Math.pow(10, decimals)) / Math.pow(10, decimals);
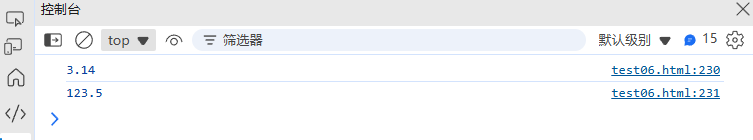
}console.log(formatNumber(3.14159, 2)); // 3.14
console.log(formatNumber(123.456, 1)); // 123.5
(3) 距离计算(勾股定理)
// 计算两点之间的距离
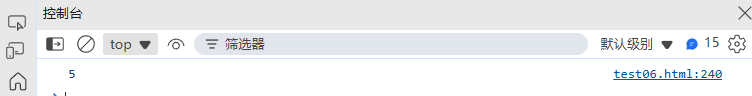
function distance(x1, y1, x2, y2) {const dx = x2 - x1;const dy = y2 - y1;return Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}console.log(distance(0, 0, 3, 4)); // 5
(4) 圆周运动
// 角度转弧度
function degreesToRadians(degrees) {return (degrees * Math.PI) / 180;
}function circularMotion(centerX, centerY, radius, angle) {const rad = degreesToRadians(angle);return {x: centerX + radius * Math.cos(rad),y: centerY + radius * Math.sin(rad)};
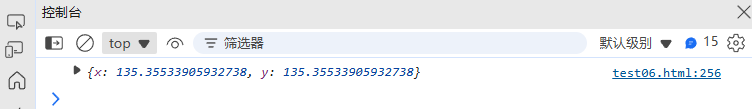
}const point = circularMotion(100, 100, 50, 45);
console.log(point); // { x: 135.36, y: 135.36 }
(5) 数值范围限制
// 将数值限制在指定范围内
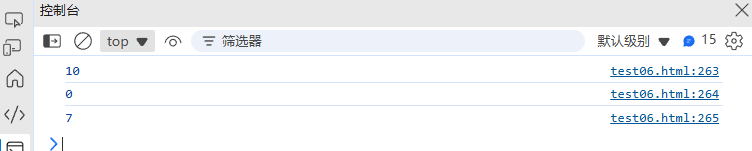
function clamp(value, min, max) {return Math.min(Math.max(value, min), max);
}console.log(clamp(15, 0, 10)); // 10
console.log(clamp(-5, 0, 10)); // 0
console.log(clamp(7, 0, 10)); // 7
(6) 百分比计算
// 计算百分比
function percentage(value, total) {return Math.round((value / total) * 100);
}// 从百分比还原数值
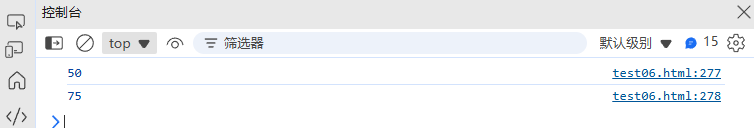
function fromPercentage(percent, total) {return Math.round((percent / 100) * total);
}console.log(percentage(75, 150)); // 50
console.log(fromPercentage(50, 150)); // 75
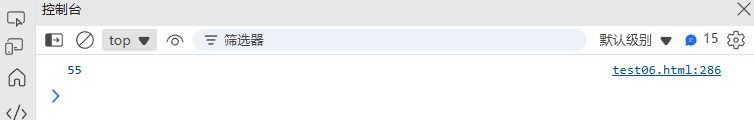
(7) 斐波那契数列
// 使用黄金比例公式计算斐波那契数
function fibonacci(n) {const phi = (1 + Math.sqrt(5)) / 2;return Math.round(Math.pow(phi, n) / Math.sqrt(5));
}console.log(fibonacci(10)); // 55
(8) 正态分布随机数
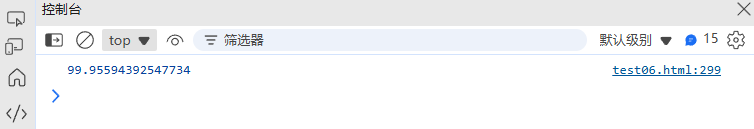
// 生成正态分布随机数(Box-Muller变换)
function normalRandom(mean = 0, stdDev = 1) {let u = 0, v = 0;while (u === 0) u = Math.random();while (v === 0) v = Math.random();const z = Math.sqrt(-2 * Math.log(u)) * Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * v);return z * stdDev + mean;
}console.log(normalRandom(100, 15)); // 近似正态分布的随机数
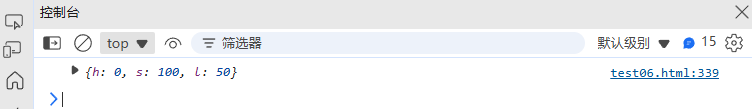
(9) 颜色转换(RGB ↔ HSL)
// RGB 转 HSL
function rgbToHsl(r, g, b) {r /= 255; g /= 255; b /= 255;const max = Math.max(r, g, b);const min = Math.min(r, g, b);const delta = max - min;let h = 0, s = 0, l = (max + min) / 2;if (delta !== 0) {s = l > 0.5 ? delta / (2 - max - min) : delta / (max + min);switch (max) {case r: h = (g - b) / delta + (g < b ? 6 : 0); break;case g: h = (b - r) / delta + 2; break;case b: h = (r - g) / delta + 4; break;}h /= 6;}return {h: Math.round(h * 360),s: Math.round(s * 100),l: Math.round(l * 100)};
}console.log(rgbToHsl(255, 0, 0)); // { h: 0, s: 100, l: 50 } (红色)
(10) 动画缓动函数
// 常用缓动函数
const easingFunctions = {// 线性linear: t => t,// 二次缓动easeInQuad: t => t * t,easeOutQuad: t => t * (2 - t),easeInOutQuad: t => t < 0.5 ? 2 * t * t : -1 + (4 - 2 * t) * t,// 正弦缓动easeInSine: t => 1 - Math.cos(t * Math.PI / 2),easeOutSine: t => Math.sin(t * Math.PI / 2),easeInOutSine: t => -(Math.cos(Math.PI * t) - 1) / 2,// 指数缓动easeInExpo: t => Math.pow(2, 10 * (t - 1)),easeOutExpo: t => 1 - Math.pow(2, -10 * t)
};// 使用示例
function animate(element, property, start, end, duration, easing = 'linear') {const startTime = Date.now();function update() {const elapsed = Date.now() - startTime;const progress = Math.min(elapsed / duration, 1);const eased = easingFunctions[easing](progress);const current = start + (end - start) * eased;element.style[property] = current + 'px';if (progress < 1) {requestAnimationFrame(update);}}update();
}

5. 最佳实践
使用
**运算符替代Math.pow()// 推荐(ES6+) const result = 2 ** 3; // 8// 传统方式 const result = Math.pow(2, 3); // 8处理浮点数精度问题
// 浮点数精度问题 console.log(0.1 + 0.2); // 0.30000000000000004// 解决方案 function preciseAdd(a, b) {const multiplier = Math.pow(10, Math.max(a.toString().split('.')[1]?.length || 0,b.toString().split('.')[1]?.length || 0));return (a * multiplier + b * multiplier) / multiplier; }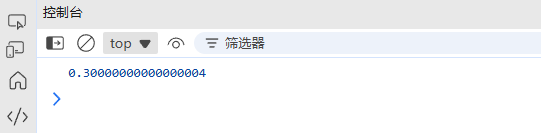
使用常量提高性能
// 缓存常用数学常数 const PI = Math.PI; const HALF_PI = PI / 2; const TWO_PI = PI * 2;
RegExp(正则表达式)对象
在 JavaScript 中, RegExp 对象用于模式匹配和文本处理。以下是正则表达式的完整指南,涵盖创建、语法、方法和实际应用。
1. RegExp 对象的基本特性
(1) 两种创建方式
// 字面量形式(推荐)
const regex1 = /pattern/flags;// 构造函数形式
const regex2 = new RegExp("pattern", "flags");
(2) 常用标志(flags)
| 标志 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
g | 全局匹配 | /a/g |
i | 忽略大小写 | /a/i |
m | 多行匹配 | /^a/m |
s | 点号匹配所有字符 | /a.b/s |
u | Unicode 模式 | /\u{1F600}/u |
y | 粘性匹配 | /a/y |
2. 正则表达式语法
(1) 基本元字符
| 元字符 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
. | 匹配任意单个字符(除换行符) | /.at/ 匹配 "cat", "hat" |
\d | 数字字符 | /\d/ 匹配 "0"-"9" |
\D | 非数字字符 | /\D/ 匹配非数字 |
\w | 单词字符(字母、数字、下划线) | /\w/ 匹配 "a-z", "A-Z", "0-9", "_" |
\W | 非单词字符 | /\W/ 匹配非字母数字下划线 |
\s | 空白字符 | /\s/ 匹配空格、制表符、换行符 |
\S | 非空白字符 | /\S/ 匹配非空白字符 |
(2) 字符类
// 字符集合
/[abc]/ // 匹配 a, b 或 c
/[a-z]/ // 匹配 a 到 z 的任意字符
/[^abc]/ // 匹配除 a, b, c 外的任意字符
/[0-9]/ // 匹配数字
(3) 量词
| 量词 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
* | 0次或多次 | /a*/ 匹配 "", "a", "aa" |
+ | 1次或多次 | /a+/ 匹配 "a", "aa" |
? | 0次或1次 | /a?/ 匹配 "", "a" |
{n} | 恰好n次 | /a{3}/ 匹配 "aaa" |
{n,} | 至少n次 | /a{2,}/ 匹配 "aa", "aaa" |
{n,m} | n到m次 | /a{2,4}/ 匹配 "aa", "aaa", "aaaa" |
(4) 边界和位置
| 符号 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
^ | 字符串开始 | /^a/ 匹配以a开头的字符串 |
$ | 字符串结束 | /a$/ 匹配以a结尾的字符串 |
\b | 单词边界 | /\bword\b/ 匹配独立的"word" |
\B | 非单词边界 | /\Bword\B/ 匹配非独立的"word" |
(5) 分组和捕获
// 分组
/(ab)+/ // 匹配 "ab", "abab", "ababab"// 捕获组
/(\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2})/ // 捕获年月日// 非捕获组
/(?:ab)+/ // 分组但不捕获// 命名捕获组
/(?<year>\d{4})-(?<month>\d{2})/ // 命名分组
(6) 选择符和断言
// 选择符
/cat|dog/ // 匹配 "cat" 或 "dog"// 正向先行断言
/\d+(?=元)/ // 匹配后面是"元"的数字// 负向先行断言
/\d+(?!元)/ // 匹配后面不是"元"的数字// 正向后行断言
/(?<=\$)\d+/ // 匹配前面是"$"的数字// 负向后行断言
/(?<!\$)\d+/ // 匹配前面不是"$"的数字
3. RegExp 对象的常用方法
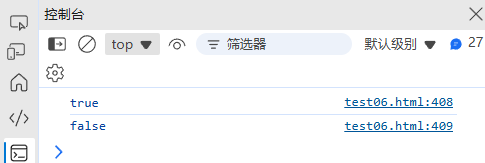
(1) test() - 测试匹配
const regex = /hello/i;
console.log(regex.test("Hello World")); // true
console.log(regex.test("Hi World")); // false
(2) exec() - 执行匹配
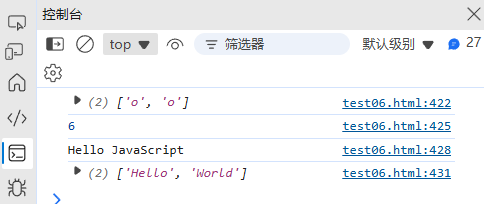
const regex = /(\w+)\s(\w+)/;
const result = regex.exec("Hello World");console.log(result[0]); // "Hello World" (完整匹配)
console.log(result[1]); // "Hello" (第一个捕获组)
console.log(result[2]); // "World" (第二个捕获组)
console.log(result.index); // 0 (匹配开始位置)
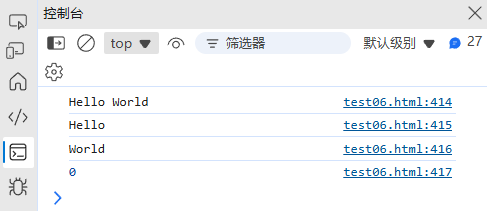
(3) 字符串方法结合正则
const str = "Hello World";// match() - 查找匹配
console.log(str.match(/o/g)); // ["o", "o"]// search() - 返回匹配位置
console.log(str.search(/World/)); // 6// replace() - 替换匹配内容
console.log(str.replace(/World/, "JavaScript")); // "Hello JavaScript"// split() - 分割字符串
console.log(str.split(/\s/)); // ["Hello", "World"]
4. 实际应用示例
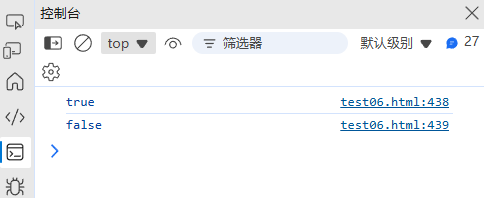
(1) 邮箱验证
function validateEmail(email) {const regex = /^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$/;return regex.test(email);
}console.log(validateEmail("test@example.com")); // true
console.log(validateEmail("invalid.email")); // false
(2) 手机号验证
function validatePhone(phone) {const regex = /^1[3-9]\d{9}$/;return regex.test(phone);
}console.log(validatePhone("13812345678")); // true
console.log(validatePhone("12345678901")); // false
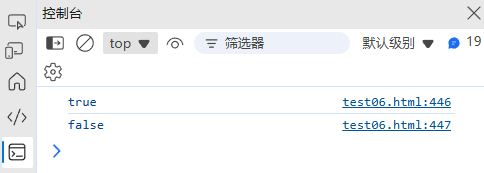
(3) 密码强度验证
function checkPasswordStrength(password) {const patterns = {length: /.{8,}/,upper: /[A-Z]/,lower: /[a-z]/,number: /\d/,special: /[!@#$%^&*()_+\-=\[\]{};':"\\|,.<>\/?]/};let score = 0;for (const pattern of Object.values(patterns)) {if (pattern.test(password)) score++;}return {score,strength: score < 3 ? "弱" : score < 5 ? "中" : "强"};
}console.log(checkPasswordStrength("Password123!")); // { score: 5, strength: "强" }
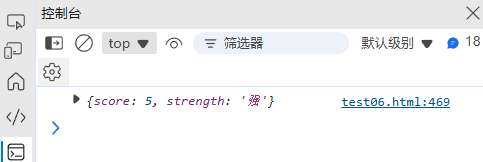
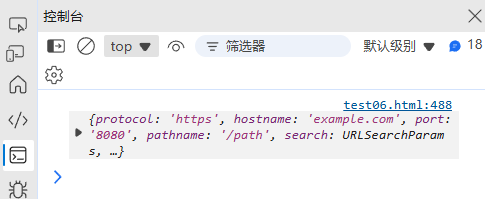
(4) URL 解析
function parseURL(url) {const regex = /^(https?):\/\/([^\/:]+)(?::(\d+))?([^?#]*)(?:\?([^#]*))?(?:#(.*))?$/;const match = url.match(regex);if (!match) return null;return {protocol: match[1],hostname: match[2],port: match[3] || (match[1] === "https" ? "443" : "80"),pathname: match[4] || "/",search: match[5] ? new URLSearchParams(match[5]) : null,hash: match[6] || ""};
}console.log(parseURL("https://example.com:8080/path?query=value#hash"));
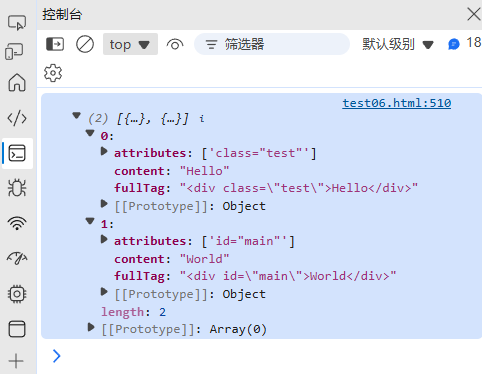
(5) HTML 标签提取
function extractTags(html, tagName) {const regex = new RegExp(`<${tagName}\\b[^>]*>(.*?)<\\/${tagName}>`, "gis");const matches = [];let match;while ((match = regex.exec(html)) !== null) {matches.push({fullTag: match[0],content: match[1],attributes: match[0].match(/\b(\w+)=["']([^"']*)["']/g) || []});}return matches;
}const html = '<div class="test">Hello</div><div id="main">World</div>';
console.log(extractTags(html, "div"));
(6) 日期格式转换
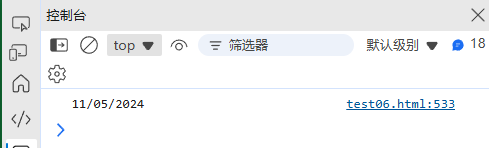
function formatDate(dateStr, fromFormat, toFormat) {const formatPatterns = {"YYYY-MM-DD": /^(\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2})$/,"MM/DD/YYYY": /^(\d{2})\/(\d{2})\/(\d{4})$/,"DD.MM.YYYY": /^(\d{2})\.(\d{2})\.(\d{4})$/};const match = dateStr.match(formatPatterns[fromFormat]);if (!match) return dateStr;const [, y, m, d] = match;const formats = {"YYYY-MM-DD": `${y}-${m}-${d}`,"MM/DD/YYYY": `${m}/${d}/${y}`,"DD.MM.YYYY": `${d}.${m}.${y}`};return formats[toFormat];
}console.log(formatDate("2024-11-05", "YYYY-MM-DD", "MM/DD/YYYY")); // "11/05/2024"
(7) 敏感词过滤
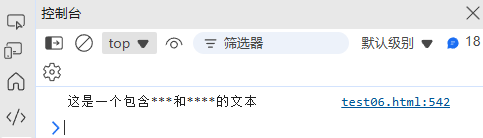
function filterSensitiveWords(text, sensitiveWords) {const regex = new RegExp(sensitiveWords.join("|"), "gi");return text.replace(regex, match => "*".repeat(match.length));
}const text = "这是一个包含敏感词和违规内容的文本";
const sensitive = ["敏感词", "违规内容"];
console.log(filterSensitiveWords(text, sensitive)); // "这是一个包含****和****的文本"
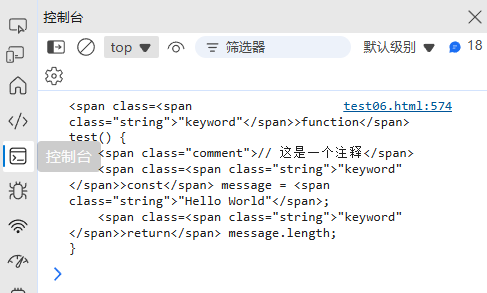
(8) 代码高亮
function highlightCode(code, language = "javascript") {const patterns = {javascript: {keyword: /\b(function|var|let|const|if|else|for|while|return)\b/g,string: /(["'`])(?:(?=(\\?))\2.)*?\1/g,comment: /\/\/.*$|\/\*[\s\S]*?\*\//gm,number: /\b\d+(\.\d+)?\b/g}};const langPatterns = patterns[language];if (!langPatterns) return code;let highlighted = code;for (const [type, pattern] of Object.entries(langPatterns)) {highlighted = highlighted.replace(pattern, match => `<span class="${type}">${match}</span>`);}return highlighted;
}const code = `function test() {// 这是一个注释const message = "Hello World";return message.length;
}`;console.log(highlightCode(code));
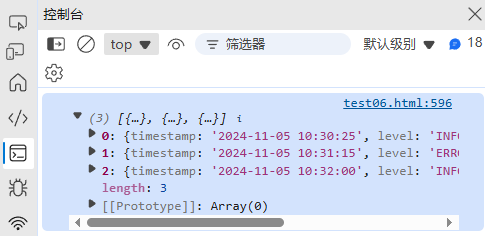
(9) 数据提取和清洗
function extractData(text, pattern) {const regex = new RegExp(pattern, "g");const results = [];let match;while ((match = regex.exec(text)) !== null) {results.push(match.groups || match.slice(1));}return results;
}const logText = `
2024-11-05 10:30:25 [INFO] User login: alice
2024-11-05 10:31:15 [ERROR] Database connection failed
2024-11-05 10:32:00 [INFO] User logout: alice
`;const logPattern = /(?<timestamp>\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2} \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}) \[(?<level>\w+)\] (?<message>.+)/;
console.log(extractData(logText, logPattern));
(10) 模板引擎
function simpleTemplate(template, data) {return template.replace(/\{\{(\w+)\}\}/g, (match, key) => {return data[key] !== undefined ? data[key] : match;});
}const template = "Hello, {{name}}! You have {{count}} new messages.";
const data = { name: "Alice", count: 5 };
console.log(simpleTemplate(template, data)); // "Hello, Alice! You have 5 new messages."
5. 最佳实践
使用字面量创建简单的正则表达式
// 推荐 const regex = /pattern/gi;// 不推荐(除非需要动态构建) const regex = new RegExp("pattern", "gi");缓存正则表达式对象
// 推荐(避免重复编译) const emailRegex = /^[^@]+@[^@]+\.[^@]+$/;// 不推荐(每次都会编译) function validateEmail(email) {return /^[^@]+@[^@]+\.[^@]+$/.test(email); }使用非贪婪匹配避免性能问题
// 贪婪匹配(可能匹配过多内容) const greedy = /<.*>/;// 非贪婪匹配(推荐) const nonGreedy = /<.*?>/;处理特殊字符转义
function escapeRegex(str) {return str.replace(/[.*+?^${}()|[\]\\]/g, '\\$&'); }const search = "file.txt"; const regex = new RegExp(escapeRegex(search), "gi");
6. 常见问题解决
(1) 多行匹配
const text = `Line 1
Line 2
Line 3`;// 匹配每行开头的 "Line"
const regex = /^Line/gm;
console.log(text.match(regex)); // ["Line", "Line", "Line"]
(2) Unicode 字符匹配
// 匹配中文字符
const chineseRegex = /[\u4e00-\u9fa5]/g;
console.log("Hello 世界".match(chineseRegex)); // ["世", "界"]// 匹配表情符号
const emojiRegex = /\p{Emoji}/gu;
console.log("Hello 😀 World 🌍".match(emojiRegex)); // ["😀", "🌍"]
(3) 性能优化
// 避免灾难性回溯
// 不好的模式(可能造成性能问题)
const badRegex = /(a+)+b/;// 好的模式
const goodRegex = /a+b/;
DOM(文档对象模型)
在 JavaScript 中,DOM(文档对象模型) 是 HTML 和 XML 文档的编程接口,它将文档表示为树形结构。以下是 DOM 的完整指南,涵盖节点操作、事件处理、遍历和实际应用。
1. DOM 的基本概念
(1) DOM 树结构
Document
└── html├── head│ ├── meta│ └── title└── body├── h1├── p└── div
(2) 节点类型
| 节点类型 | 数值常量 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
ELEMENT_NODE | 1 | 元素节点 |
TEXT_NODE | 3 | 文本节点 |
COMMENT_NODE | 8 | 注释节点 |
DOCUMENT_NODE | 9 | 文档节点 |
2. DOM 选择器
(1) 基本选择方法
// 单个元素选择
document.getElementById("myId");
document.querySelector(".myClass");// 多个元素选择
document.getElementsByClassName("myClass");
document.getElementsByTagName("div");
document.querySelectorAll("p.highlight");
(2) 选择器示例
// ID 选择器
const header = document.querySelector("#header");// 类选择器
const items = document.querySelectorAll(".item");// 属性选择器
const links = document.querySelectorAll("a[target='_blank']");// 组合选择器
const firstPara = document.querySelector("div.content > p:first-child");
3. DOM 节点操作
(1) 创建和添加节点
// 创建元素
const newDiv = document.createElement("div");
const newText = document.createTextNode("Hello World");// 添加节点
parentElement.appendChild(newDiv);
parentElement.insertBefore(newDiv, referenceElement);
parentElement.replaceChild(newDiv, oldChild);
(2) 修改节点内容
const element = document.getElementById("myElement");// 修改 HTML 内容
element.innerHTML = "<strong>新内容</strong>";// 修改文本内容
element.textContent = "纯文本内容";// 修改属性
element.setAttribute("class", "new-class");
element.className = "another-class";
element.id = "new-id";
(3) 删除节点
// 删除子节点
parentElement.removeChild(childElement);// 直接删除(现代方法)
element.remove();// 清空所有子节点
element.innerHTML = "";
while (element.firstChild) {element.removeChild(element.firstChild);
}
4. DOM 属性和样式
(1) 属性操作
<a href="https://blog.csdn.net/" target="_blank">示例链接</a><script>const link = document.querySelector("a");// 获取和设置属性link.getAttribute("href");link.setAttribute("href", "https://example.com");link.removeAttribute("target");// 检查属性link.hasAttribute("class");// data-* 属性link.dataset.id = "123";console.log(link.dataset.id); // "123"</script>
(2) 样式操作
const element = document.getElementById("myElement");// 直接修改样式
element.style.color = "red";
element.style.backgroundColor = "#f0f0f0";
element.style.fontSize = "16px";// 批量修改样式
Object.assign(element.style, {color: "blue",fontSize: "18px",margin: "10px"
});// 类名操作
element.classList.add("active");
element.classList.remove("inactive");
element.classList.toggle("hidden");
element.classList.contains("active");
5. DOM 遍历
(1) 父子关系遍历
const element = document.querySelector(".child");// 父节点
element.parentNode;
element.parentElement;// 子节点
element.childNodes; // 所有子节点(包括文本节点)
element.children; // 所有子元素节点
element.firstChild;
element.lastChild;
element.firstElementChild;
element.lastElementChild;
(2) 兄弟关系遍历
const element = document.querySelector(".middle");// 兄弟节点
element.previousSibling;
element.nextSibling;
element.previousElementSibling;
element.nextElementSibling;
(3) 遍历示例
<div id="container"><p>段落1</p><span>文本</span><p>段落2</p>
</div><script>// 获取一个父元素const element = document.querySelector("div");// 遍历所有子元素const children = Array.from(element.children);children.forEach((child) => {console.log(child.tagName);});// 查找特定祖先function findAncestor(element, selector) {while (element) {if (element.matches(selector)) {return element;}element = element.parentElement;}return null;}// 使用示例:查找某个元素的body祖先const someElement = document.querySelector("a");const bodyAncestor = findAncestor(someElement, "body");</script>
6. DOM 事件处理
(1) 事件监听
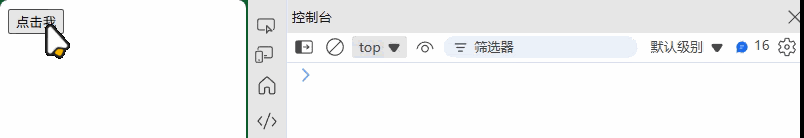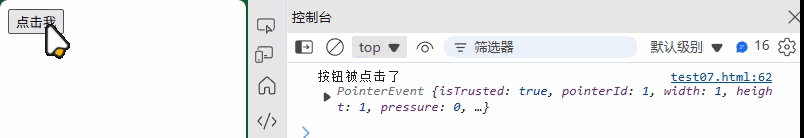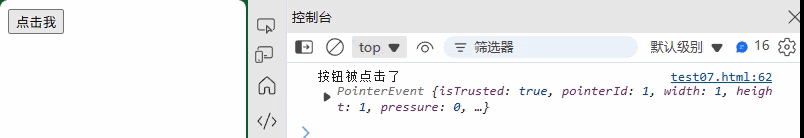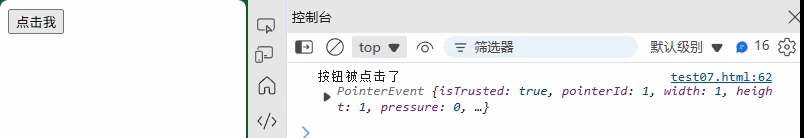
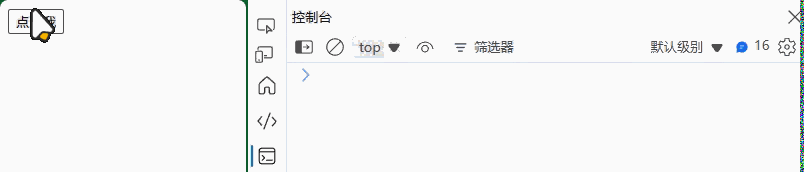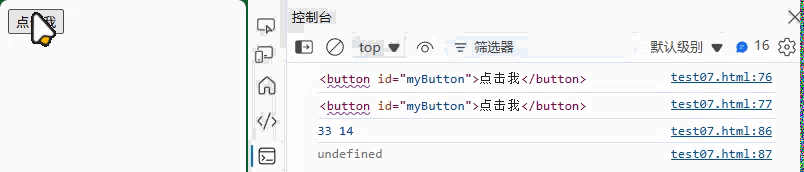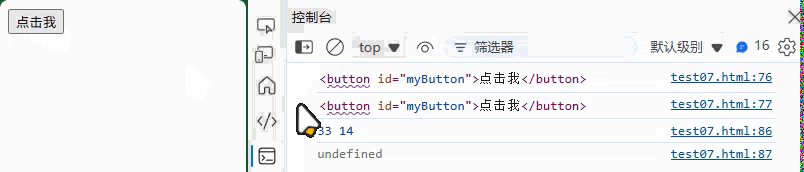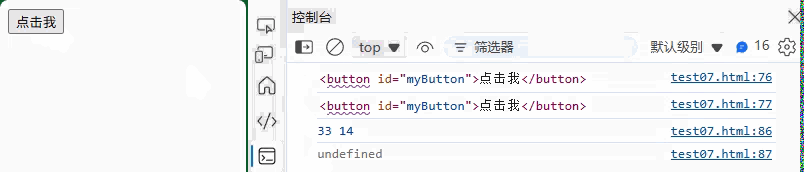
<button id="myButton">点击我</button>
const button = document.getElementById("myButton");// 添加事件监听器
button.addEventListener("click", function(event) {console.log("按钮被点击了", event);
});// 移除事件监听器
const handler = function() { console.log("点击"); };
button.addEventListener("click", handler);
button.removeEventListener("click", handler);
(2) 事件对象
// 获取一个元素(可以使用之前创建的按钮)
const element = document.getElementById("myButton");
element.addEventListener("click", function(event) {// 事件目标console.log(event.target); // 实际点击的元素console.log(event.currentTarget); // 绑定事件的元素// 阻止默认行为event.preventDefault();// 停止事件传播event.stopPropagation();// 事件信息console.log(event.clientX, event.clientY); // 鼠标位置console.log(event.key); // 键盘事件键名
});
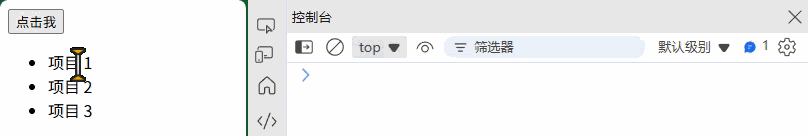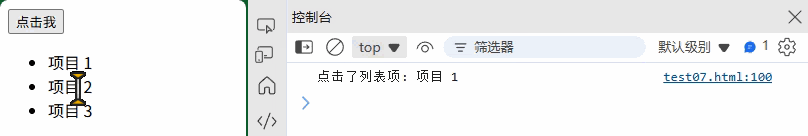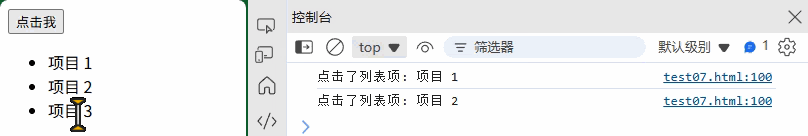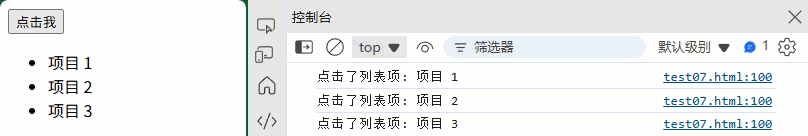
(3) 事件委托
<ul id="list"><li class="item">项目 1</li><li class="item">项目 2</li><li class="item">项目 3</li>
</ul>
// 在父元素上监听,处理动态添加的子元素
document.getElementById("list").addEventListener("click", function(event) {if (event.target.matches("li.item")) {console.log("点击了列表项:", event.target.textContent);}
});
(4) 常用事件类型
// 鼠标事件
element.addEventListener("click", handler);
element.addEventListener("dblclick", handler);
element.addEventListener("mouseenter", handler);
element.addEventListener("mouseleave", handler);
element.addEventListener("mousemove", handler);// 键盘事件
element.addEventListener("keydown", handler);
element.addEventListener("keyup", handler);
element.addEventListener("keypress", handler);// 表单事件
element.addEventListener("focus", handler);
element.addEventListener("blur", handler);
element.addEventListener("change", handler);
element.addEventListener("submit", handler);// 窗口事件
window.addEventListener("load", handler);
window.addEventListener("resize", handler);
window.addEventListener("scroll", handler);
7. DOM 操作最佳实践
(1) 性能优化
<ul id="list"></ul>
<div id="myElement">示例元素</div>
// 批量操作(使用 DocumentFragment)
const fragment = document.createDocumentFragment();
for (let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {const li = document.createElement("li");li.textContent = `项目 ${i}`;fragment.appendChild(li);
}
document.getElementById("list").appendChild(fragment);// 避免重排重绘
const element = document.getElementById("myElement");
element.style.display = "none"; // 隐藏元素
// 进行大量 DOM 操作
element.style.display = "block"; // 显示元素
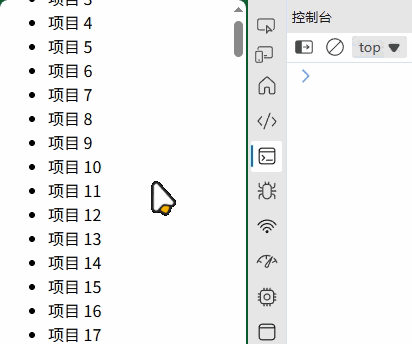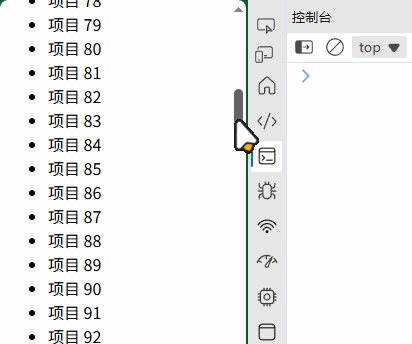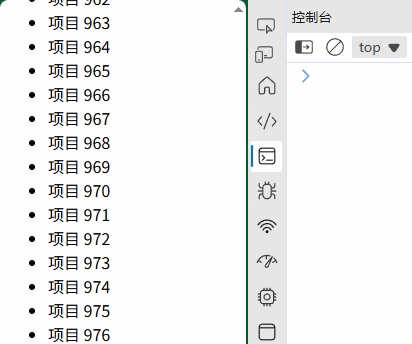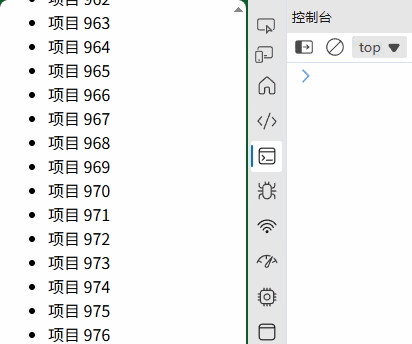
(2) 内存管理
// 移除事件监听器
function createComponent() {const element = document.createElement("div");const handler = () => console.log("点击");element.addEventListener("click", handler);// 清理函数return () => {element.removeEventListener("click", handler);element.remove();};
}
8. 实际应用示例
(1) 动态列表管理
<div id="myList"></div>
class ListManager {constructor(containerId) {this.container = document.getElementById(containerId);this.items = [];this.setupEvents();}setupEvents() {this.container.addEventListener("click", (event) => {if (event.target.matches(".delete-btn")) {this.deleteItem(event.target.closest(".item").dataset.id);}});this.container.addEventListener("input", (event) => {if (event.target.matches(".item-input")) {this.updateItem(event.target.closest(".item").dataset.id,event.target.value);}});}addItem(text) {const id = Date.now().toString();const item = {id,text,element: this.createItemElement(id, text)};this.items.push(item);this.container.appendChild(item.element);return id;}createItemElement(id, text) {const div = document.createElement("div");div.className = "item";div.dataset.id = id;div.innerHTML = `<input type="text" class="item-input" value="${text}"><button class="delete-btn">删除</button>`;return div;}deleteItem(id) {const index = this.items.findIndex(item => item.id === id);if (index !== -1) {this.items[index].element.remove();this.items.splice(index, 1);}}updateItem(id, text) {const item = this.items.find(item => item.id === id);if (item) {item.text = text;}}
}// 使用示例
const listManager = new ListManager("myList");
listManager.addItem("第一个项目");
listManager.addItem("第二个项目");
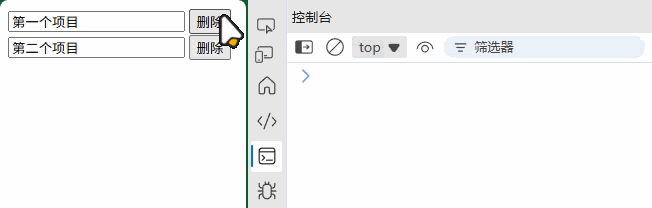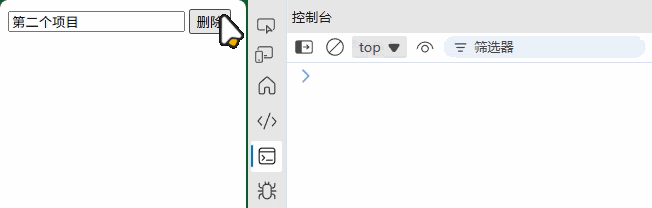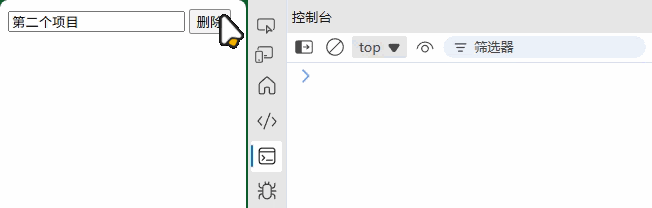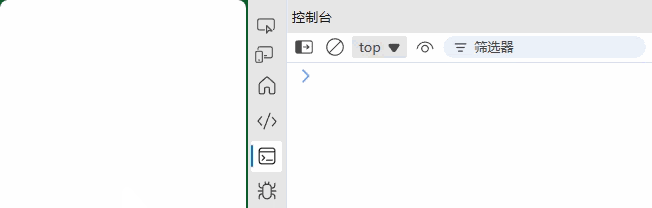
(2) 模态框组件
class Modal {constructor() {this.modal = null;this.isOpen = false;this.createModal();}createModal() {this.modal = document.createElement("div");this.modal.className = "modal";this.modal.innerHTML = `<div class="modal-content"><span class="close">×</span><div class="modal-body"></div></div>`;document.body.appendChild(this.modal);this.setupEvents();}setupEvents() {this.modal.querySelector(".close").addEventListener("click", () => {this.close();});this.modal.addEventListener("click", (event) => {if (event.target === this.modal) {this.close();}});document.addEventListener("keydown", (event) => {if (event.key === "Escape" && this.isOpen) {this.close();}});}open(content) {this.modal.querySelector(".modal-body").innerHTML = content;this.modal.style.display = "block";document.body.style.overflow = "hidden";this.isOpen = true;}close() {this.modal.style.display = "none";document.body.style.overflow = "";this.isOpen = false;}
}// 使用示例
const modal = new Modal();
modal.open("<h2>标题</h2><p>这是模态框内容</p>");
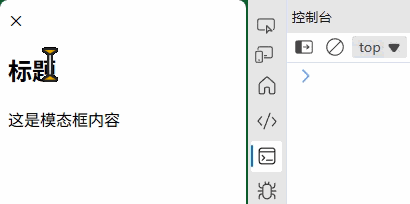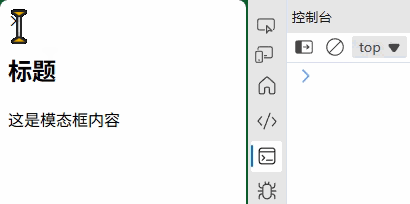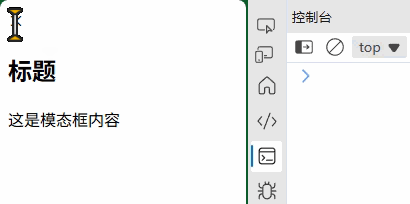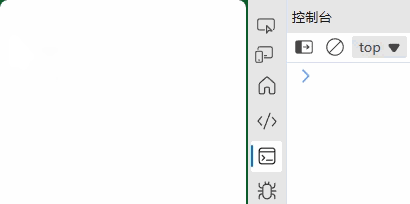
(3) 表单验证
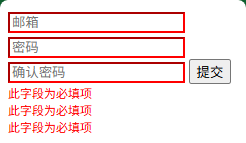
class FormValidator {constructor(formId) {this.form = document.getElementById(formId);this.fields = this.form.querySelectorAll("[data-validate]");this.errors = new Map();this.setupValidation();}setupValidation() {this.fields.forEach(field => {field.addEventListener("blur", () => this.validateField(field));field.addEventListener("input", () => this.clearError(field));});this.form.addEventListener("submit", (event) => {if (!this.validateForm()) {event.preventDefault();}});}validateField(field) {const value = field.value.trim();const rules = field.dataset.validate.split(" ");for (const rule of rules) {const error = this.checkRule(rule, value, field);if (error) {this.showError(field, error);return false;}}this.clearError(field);return true;}checkRule(rule, value, field) {switch (rule) {case "required":return value ? null : "此字段为必填项";case "email":return /^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/.test(value) ? null : "请输入有效的邮箱地址";case "minlength":const min = parseInt(field.dataset.minlength);return value.length >= min ? null : `至少需要 ${min} 个字符`;case "match":const matchField = document.getElementById(field.dataset.match);return value === matchField.value ? null : "密码不匹配";default:return null;}}showError(field, message) {this.clearError(field);const errorElement = document.createElement("div");errorElement.className = "error-message";errorElement.textContent = message;errorElement.style.color = "red";errorElement.style.fontSize = "12px";field.parentNode.appendChild(errorElement);field.style.borderColor = "red";this.errors.set(field, errorElement);}clearError(field) {const errorElement = this.errors.get(field);if (errorElement) {errorElement.remove();field.style.borderColor = "";this.errors.delete(field);}}validateForm() {let isValid = true;this.fields.forEach(field => {if (!this.validateField(field)) {isValid = false;}});return isValid;}
}// 使用示例
const validator = new FormValidator("myForm");
(4) 无限滚动
class InfiniteScroll {constructor(containerId, loadMoreCallback) {this.container = document.getElementById(containerId);this.loadMoreCallback = loadMoreCallback;this.isLoading = false;this.hasMore = true;this.setupScrollListener();this.loadInitialData();}setupScrollListener() {window.addEventListener("scroll", () => {if (this.shouldLoadMore() && !this.isLoading && this.hasMore) {this.loadMore();}});}shouldLoadMore() {const { scrollTop, scrollHeight, clientHeight } = document.documentElement;return scrollTop + clientHeight >= scrollHeight - 100; // 距离底部100px时加载}async loadMore() {this.isLoading = true;this.showLoadingIndicator();try {const newItems = await this.loadMoreCallback();if (newItems.length === 0) {this.hasMore = false;this.showNoMoreData();} else {this.appendItems(newItems);}} catch (error) {this.showError("加载失败");} finally {this.isLoading = false;this.hideLoadingIndicator();}}appendItems(items) {const fragment = document.createDocumentFragment();items.forEach(item => {const element = document.createElement("div");element.className = "item";element.textContent = item;fragment.appendChild(element);});this.container.appendChild(fragment);}showLoadingIndicator() {let indicator = this.container.querySelector(".loading-indicator");if (!indicator) {indicator = document.createElement("div");indicator.className = "loading-indicator";indicator.textContent = "加载中...";this.container.appendChild(indicator);}}hideLoadingIndicator() {const indicator = this.container.querySelector(".loading-indicator");if (indicator) {indicator.remove();}}showNoMoreData() {const message = document.createElement("div");message.className = "no-more-data";message.textContent = "没有更多数据了";this.container.appendChild(message);}showError(message) {const errorElement = document.createElement("div");errorElement.className = "error-message";errorElement.textContent = message;this.container.appendChild(errorElement);}loadInitialData() {this.loadMore();}
}// 使用示例
const infiniteScroll = new InfiniteScroll("content", async () => {// 模拟异步数据加载return new Promise(resolve => {setTimeout(() => {resolve(["新项目 " + Date.now()]);}, 1000);});
});
(5) 拖拽功能
<div class="draggable">可拖拽元素1</div><div class="draggable">可拖拽元素2</div>
class Draggable {constructor(element) {this.element = element;this.isDragging = false;this.offset = { x: 0, y: 0 };this.makeDraggable();}makeDraggable() {this.element.style.position = "absolute";this.element.style.cursor = "move";this.element.addEventListener("mousedown", this.onMouseDown.bind(this));document.addEventListener("mousemove", this.onMouseMove.bind(this));document.addEventListener("mouseup", this.onMouseUp.bind(this));}onMouseDown(event) {this.isDragging = true;const rect = this.element.getBoundingClientRect();this.offset.x = event.clientX - rect.left;this.offset.y = event.clientY - rect.top;this.element.style.zIndex = "1000";event.preventDefault();}onMouseMove(event) {if (!this.isDragging) return;const x = event.clientX - this.offset.x;const y = event.clientY - this.offset.y;this.element.style.left = x + "px";this.element.style.top = y + "px";}onMouseUp() {this.isDragging = false;this.element.style.zIndex = "";}
}// 使用示例
const draggableElements = document.querySelectorAll(".draggable");
draggableElements.forEach(element => new Draggable(element));
9. 现代 DOM API
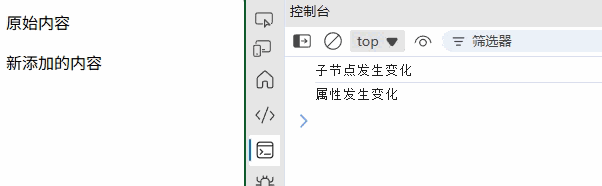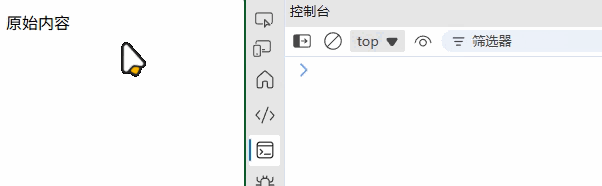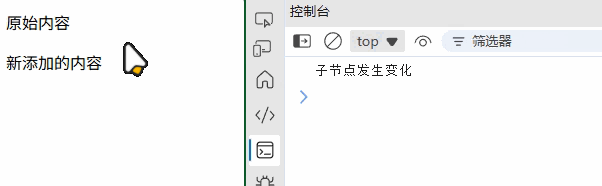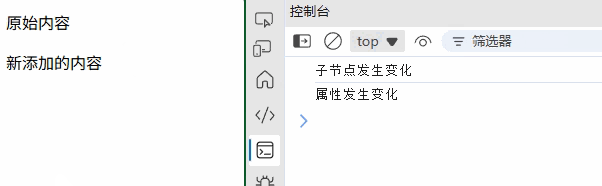
(1) MutationObserver
// 监听 DOM 变化
const observer = new MutationObserver((mutations) => {mutations.forEach(mutation => {if (mutation.type === 'childList') {console.log('子节点发生变化');}});
});observer.observe(document.getElementById('target'), {childList: true,attributes: true,subtree: true
});
(2) IntersectionObserver
// 监听元素进入视口
const io = new IntersectionObserver((entries) => {entries.forEach(entry => {if (entry.isIntersecting) {entry.target.classList.add('visible');}});
});document.querySelectorAll('.lazy-load').forEach(el => io.observe(el));
10. 兼容性和最佳实践
(1) 特征检测
// 检查浏览器支持
if ('querySelector' in document) {// 使用现代选择器
}if ('classList' in document.createElement('div')) {// 使用 classList API
}
(2) 性能监控
// 测量 DOM 操作性能
function measureDOMOperation(callback) {const start = performance.now();callback();const end = performance.now();console.log(`操作耗时: ${end - start}ms`);
}