IndexedDB开发示例:面向对象的方式
前言
代码经过了通义灵码和Deepseek的多次检查,不能说十分完美,但基本功能已经完善。
作为学习demo来用还是非常好的。
页面效果
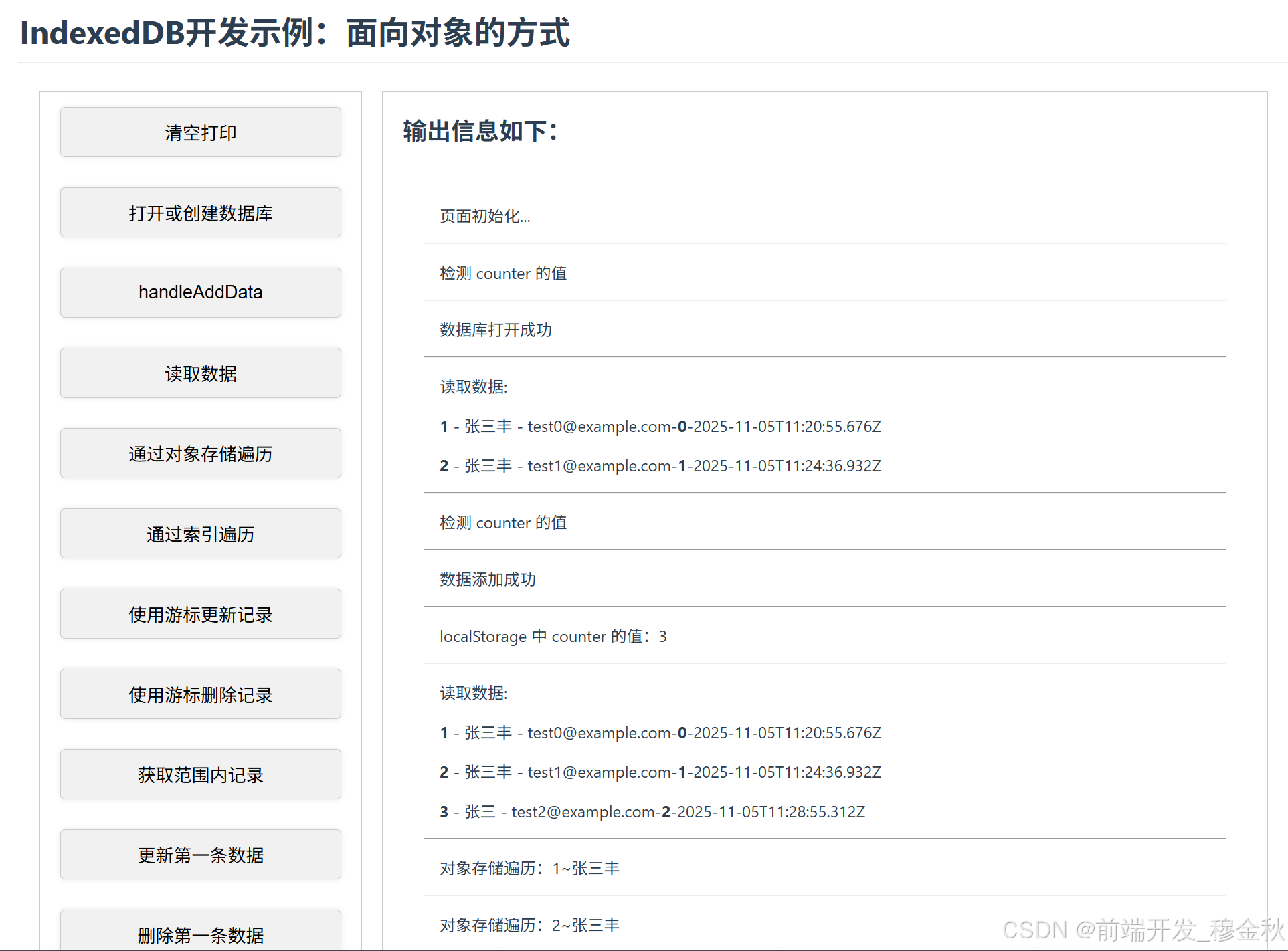
代码示例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN"><head><meta charset="utf-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>木木的学习笔记</title><link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/common.css" /><style>div.flexBox {min-height: 100%;width: 100%;box-sizing: border-box;padding: 20px;display: flex;flex-direction: row;justify-content: start;/* border: 1px solid #ccc; */div.left {border: 1px solid #ccc;display: flex;flex-direction: column;justify-content: start;button {display: block;min-width: 280px;height: 50px;background-color: #f1f1f1;border: 1px solid #ccc;cursor: pointer;font-size: 18px;margin: 15px 20px;padding: 5px 20px;border-radius: 5px;box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);transition: all 0.2s ease-in-out;outline: none;}}div.right {margin-left: 20px;padding: 20px;border: 1px solid #ccc;div#output {min-width: 800px;margin-top: 20px;border: 1px solid #ccc;padding: 20px;div {margin: 1rem; /* 1rem = 16px */}}}}</style></head><body><div class="container"><h1>IndexedDB开发示例:面向对象的方式</h1><hr /><div class="flexBox"><div class="left"><!-- 一些方法返回 Promise,但 HTML 中的调用没有处理 async/await。虽然这不会导致错误,但如果需要等待操作完成,应该考虑使用 async/await。 --><!-- HTML 中直接调用 async 方法时没有使用 await,这在某些场景下可能不是期望的行为。 --><button onclick="app.clearWrite()">清空打印</button><button onclick="app.openDB()">打开或创建数据库</button><button onclick="app.handleAddData()">handleAddData</button><button onclick="app.readData()">读取数据</button><button onclick="app.storeOpenCursor()">通过对象存储遍历</button><button onclick="app.indexOpenCursor()">通过索引遍历</button><button onclick="app.updateRecord()">使用游标更新记录</button><button onclick="app.deleteRecord()">使用游标删除记录</button><button onclick="app.getDataByKeyRange()">获取范围内记录</button><button onclick="app.updateData()">更新第一条数据</button><button onclick="app.deleteData()">删除第一条数据</button><button onclick="app.handleOpenKeyCursor()">handleOpenKeyCursor</button><button onclick="app.handleDeleteDatabase()">handleDeleteDatabase</button><button onclick="app.clearData()">清空所有数据</button><!-- 问题:async 方法在 HTML 中调用没有处理 Promise --><!-- 建议改为: --><!-- app.openDB() 确实返回一个 Promise,这部分是正确的 --><!-- <button onclick="app.openDB().catch(console.error)">打开或创建数据库</button> --><!-- Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'catch') at HTMLButtonElement.onclick --><!-- app.handleAddData() 不返回 Promise,它是一个普通的异步函数,没有显式返回 Promise --><!-- <button onclick="app.handleAddData().catch(console.error)">添加数据</button> --><!-- 问题:async 方法调用没有错误处理 --><!-- 方案1:添加全局错误处理 --><button onclick="app.handleAddDataByPromise().catch(handleError)">handleAddDataByPromise</button><!-- 方案2:修改所有方法返回 Promise --><button onclick="app.safeCall('handleAddData')">safeCall("handleAddData")</button><!-- 虽然 safeCall 方法可以处理 Promise,但直接调用 handleAddDataByPromise 更简单。 --><button onclick="app.handleAddDataByPromise()">handleAddDataByPromise</button></div><div class="right"><h2>输出信息如下:</h2><div id="output"></div></div></div></div><script>// 在类外部添加全局错误处理function handleError(error) {console.error("操作失败:", error.message);}// IndexedDB 操作类class IndexedDBManager {constructor(dbName = "MyTestDB", version = 1) {this.dbName = dbName;this.version = version;this.db = null; //数据库对象this.counter = 0; //counter 用于生成唯一的不重复的值this.init();}// 初始化init() {this.showOutput("页面初始化...");this.checkCounter();}// 添加安全调用方法// 统一方法实现,选择让所有方法返回 Promise 或使用 safeCallasync safeCall(methodName, ...args) {try {return await this[methodName](...args);} catch (error) {this.showOutput(`操作 ${methodName} 失败`);throw error;}}checkCounter() {this.showOutput("检测 counter 的值");// 从 localStorage 获取计数器值,如果不存在则默认为 0if (!localStorage.getItem("counter")) {localStorage.setItem("counter", "0");this.counter = 0;} else {// counter 变量会是字符串类型(如果没有经过 parseInt 转换),这可能导致后续的数学运算出现问题。// 添加默认值处理this.counter = parseInt(localStorage.getItem("counter")) || 0;}}// 重置计数器resetCounter() {this.counter = 0;localStorage.removeItem("counter"); // 删除localStorage中的counter}// 显示输出showOutput(msg) {document.getElementById("output").innerHTML += "<div>" + msg + "</div><hr/>";}// 清空输出clearWrite() {document.getElementById("output").innerHTML = "";}// 打开数据库(返回 Promise)openDB() {// 如果已经有打开的数据库,直接返回 resolved Promiseif (this.db) {this.showOutput("数据库已打开");return Promise.resolve(this.db);}return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {const request = indexedDB.open(this.dbName, this.version);request.onsuccess = (e) => {this.db = e.target.result;// 版本变更事件处理this.db.onversionchange = () => {// deleteDatabase() 删除数据库时也会触发this.db.close();this.showOutput("触发 onversionchange,数据库已关闭");};this.showOutput("数据库打开成功");resolve(this.db);};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("数据库打开失败");reject(e.target.error);};// 升级数据库request.onupgradeneeded = (e) => {this.showOutput("触发 onupgradeneeded :数据库升级");this.db = e.target.result;const transaction = e.target.transaction;let oldVersion = e.oldVersion;let newVersion = e.newVersion || this.db.version; // 兼容性处理this.showOutput(`数据库版本从 ${oldVersion} 升级到 ${newVersion}`);// 安全的迁移方式const migrateToVersion = (targetVersion) => {try {switch (targetVersion) {case 1:this.showOutput("执行版本1迁移: 初始化用户表");if (!this.db.objectStoreNames.contains("users")) {const store = this.db.createObjectStore("users", {keyPath: "id",autoIncrement: true,});store.createIndex("name", "name", { unique: false });store.createIndex("email", "email", { unique: false });store.createIndex("times", "times", { unique: true });this.showOutput("对象存储 users 创建成功");}break;case 2:this.showOutput("执行版本2迁移: 添加手机号索引");if (this.db.objectStoreNames.contains("users")) {const transaction = e.target.transaction;// transaction 可能为 nullif (transaction) {const store = transaction.objectStore("users");if (store && !store.indexNames.contains("phone")) {store.createIndex("phone", "phone", { unique: true });this.showOutput("对象存储 users 新字段 phone 创建成功");}} else {// 备用方案:在下一个事务中创建索引this.showOutput("警告:无法在当前事务中创建索引,将在后续操作中处理");}}break;case 3:this.showOutput("执行版本3迁移: 创建订单表");if (!this.db.objectStoreNames.contains("orders")) {// 检查对象存储是否已存在const store = this.db.createObjectStore("orders", { keyPath: "id" });store.createIndex("name", "name", { unique: false });store.createIndex("address", "address", { unique: false });this.showOutput("对象存储orders创建成功");} else {this.showOutput("对象存储orders已存在");}break;}} catch (error) {this.showOutput(`版本 ${targetVersion} 迁移失败}`);throw error;}};// 动态执行所有需要的迁移for (let v = oldVersion + 1; v <= newVersion; v++) {migrateToVersion(v);}};});}// 确保数据库已连接async ensureDB() {if (!this.db) {try {await this.openDB();} catch (error) {this.showOutput("数据库连接失败");throw error;}}}//修复问题:原方法 handleAddData()没有返回 Promise,但 HTML 中尝试使用 app.handleAddData().catch(handleError)async handleAddDataByPromise() {try {// 需要检测 localStorage counter 是否存在,因为清空时,localStorage 中的 counter 会被重置为 nullthis.checkCounter();// 创建唯一的数据项避免重复(呼应createIndex()中的 unique: true)const user = {name: "张三",email: "test" + this.counter + "@example.com",times: this.counter,createdAt: new Date().toISOString(),};return await this.addData(user); // 返回 Promise} catch (error) {this.showOutput("处理添加数据时发生错误");throw error;}}// 添加测试数据handleAddData() {// 需要检测 localStorage counter 是否存在,因为清空时,localStorage 中的 counter 会被重置为 nullthis.checkCounter();// 创建唯一的数据项避免重复(呼应createIndex()中的 unique: true)const user = {name: "张三",email: "test" + this.counter + "@example.com",times: this.counter,createdAt: new Date().toISOString(),};this.addData(user); // 没有返回这个 Promise}// 添加数据async addData(user) {try {await this.ensureDB();// 确保对象中没有 id 属性,因为使用了 autoIncrement:trueif ("id" in user) {delete user.id;}// 在 IndexedDB 中,事务模式决定了你可以在事务中执行哪些操作。主要有三种事务模式:readonly、readwrite、versionchange// 最佳实践:// 尽可能使用最低权限:只读操作使用 "readonly",需要写入时才使用 "readwrite"// 性能考虑:readonly 事务性能更好,因为它不需要锁定数据进行写入// 并发性:多个 readonly 事务可以同时运行,但 readwrite 事务会互相阻塞// 明确意图:使用合适的模式可以让代码意图更清晰const transaction = this.db.transaction(["users"], "readwrite"); // 读写权限// 获取对象存储const store = transaction.objectStore("users");// 添加数据const request = store.add(user);return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {request.onsuccess = () => {this.showOutput("数据添加成功");// counter++ 是后置递增操作,意味着它会先返回 counter 的当前值,然后再将 counter 增加 1。这可能导致 localStorage 中存储的值比预期的值小1。localStorage.setItem("counter", ++this.counter); // 更新 counter 的值到 localStoragethis.showOutput("localStorage 中 counter 的值:" + localStorage.getItem("counter"));this.readData();resolve();};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("数据添加失败");reject(e.target.error);};});} catch (error) {this.showOutput("添加数据时发生错误");throw error;}}// 读取数据async readData() {try {await this.ensureDB();const transaction = this.db.transaction(["users"], "readonly");const store = transaction.objectStore("users");const request = store.getAll();return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {request.onsuccess = (e) => {const users = e.target.result;let userP = "<p>读取数据:</p>";if (users.length > 0) {users.forEach((element) => {userP += `<p><b>${element.id}</b> - ${element.name} - ${element.email}-<b>${element.times}</b>-${element.createdAt}</p>`;});} else {userP += "<p>数据未添加或者已清空</p>";}this.showOutput(userP);resolve(users);};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("读取数据失败");reject(e.target.error);};});} catch (error) {this.showOutput("读取数据时发生错误");throw error;}}// reject(e.target.error);//// 这种写法是合理的,原因如下:// Promise 中的 reject():在 Promise 执行器内部,reject(e) 用于将 Promise 状态设置为 rejected,并传递错误信息。// 同步错误传播:throw e 用于在当前执行上下文中抛出错误,这对于同步错误处理是必要的。// 在 Promise 的执行器函数中,这两个语句的顺序是正确的:// 首先调用 reject(e) 将 Promise 状态设置为 rejected// 然后使用 throw e 确保错误在当前上下文中也被抛出// 不过需要注意的是,在 Promise 的执行器中,通常只需要 reject(e) 就足够了,因为 Promise 的消费者会通过 .catch() 或第二个参数处理错误。额外的 throw e 主要是为了确保错误也能被外层的 try-catch 捕获,或者在控制台中显示错误信息。// 所以这个顺序是正确的,没有问题。// 问题在于:一旦执行了 reject(e),如果这个 Promise 已经被某个 .catch() 或类似的错误处理机制所处理,那么紧接着的 throw e 就可能是多余的,甚至可能造成问题。如果没有外层的 try-catch,throw e 会导致未捕获的异常// 实际上,在 Promise 执行器内部,执行了 reject(e) 之后,再执行 throw e 是没有意义的,因为:// Promise 的状态已经确定(rejected)// throw e 不会被 Promise 机制捕获// 如果没有外层的 try-catch,throw e 会导致未捕获的异常// 所以,正确的做法应该是只使用 reject(e),或者根据具体需求重新组织代码结构。// 另外//// reject(e.target.error);//这行不会执行到,因为上面已经抛出异常了// 这段代码的书写顺序是不正确的。// 更新数据(更新第一条记录)async updateData() {try {await this.ensureDB();const transaction = this.db.transaction(["users"], "readwrite");const store = transaction.objectStore("users");// 先获取所有数据,找出第一条记录const request = store.getAll();return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {request.onsuccess = (e) => {const users = e.target.result;if (users.length > 0) {const user = users[0]; // 获取第一条记录// parseFloat() 是 JavaScript 中的一个内置函数,用于解析字符串并返回一个浮点数。// parseInt() 只解析整数部分// user.name = "李四" + parseInt(Math.random() * 1000);user.name = "李四";user.updatedAt = new Date().toISOString();// 更新const updateRequest = store.put(user);updateRequest.onsuccess = () => {this.showOutput("数据更新成功");this.readData();resolve();};updateRequest.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("数据更新失败");reject(e.target.error);};} else {this.showOutput("未找到要更新的数据");resolve();}};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("获取数据失败");reject(e.target.error);};});} catch (error) {this.showOutput("更新数据时发生错误");throw error;}}// 删除数据(删除第一条记录)async deleteData() {try {await this.ensureDB();const transaction = this.db.transaction(["users"], "readwrite");const store = transaction.objectStore("users"); // 获取对象仓库// 先获取所有数据,找出第一条记录//const request = store.getAll();// 使用 getAllKeys() 更高效const request = store.getAllKeys();return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {request.onsuccess = (e) => {const keys = e.target.result;if (keys.length > 0) {// 删除第一条记录// delete() 方法需要的是主键(key),而不是完整的对象。const request = store.delete(keys[0]);request.onsuccess = () => {this.showOutput("数据删除成功");this.readData();resolve();};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("数据删除失败");reject(e.target.error);};} else {this.showOutput("未找到要删除的数据");resolve();}};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("获取数据失败");reject(e.target.error);};});} catch (error) {this.showOutput("删除数据时发生错误");throw error;}}// 清空所有数据async clearData() {try {await this.ensureDB();const transaction = this.db.transaction(["users"], "readwrite");const store = transaction.objectStore("users");// IndexedDB中使用clear()方法清空所有数据后,再重新添加数据时,自增主键不会归零。如果需要重置主键,需要删除并重新创建对象存储。// store.clear() 方法的作用是删除该对象仓库中的所有数据记录。关键点在于:它只删除数据,而不会触碰或重置那个负责生成主键的内部计数器。const request = store.clear();return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {request.onsuccess = () => {this.showOutput("clearData 数据已清空");this.resetCounter();this.readData();resolve();};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("清空数据失败");reject(e.target.error);};});} catch (error) {this.showOutput("清空数据时发生错误");throw error;}}// deleteDatabase() 和 deleteObjectStore() 是 IndexedDB 中两个不同的方法,它们的作用范围和用途完全不同// deleteDatabase() 删除整个数据库(包括所有对象存储、索引和数据)// 删除整个数据库实例// 删除后需要重新创建数据库才能使用// 通常用于完全清理应用数据async handleDeleteDatabase() {return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {// 先关闭当前数据库连接if (this.db) {this.db.close();this.db = null;}const request = indexedDB.deleteDatabase(this.dbName);request.onsuccess = () => {this.showOutput("handleDeleteDatabase 数据库删除成功");this.resetCounter();resolve();};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("handleDeleteDatabase 删除数据库失败");reject(e.target.error);};});}// 通过对象存储遍历async storeOpenCursor() {try {await this.ensureDB();const transaction = this.db.transaction(["users"], "readonly");const store = transaction.objectStore("users");// 通过对象存储遍历const request = store.openCursor(); // 打开游标return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {request.onsuccess = (e) => {const cursor = e.target.result; // 获取游标if (cursor) {// 处理当前记录// 通过对象存储进行遍历时,key 和 primaryKey 是相同的,都表示对象的主键。this.showOutput("对象存储遍历:" + cursor.value.id + "~" + cursor.value.name);// 移动到下一条记录cursor.continue();} else {this.showOutput("没有数据或数据已全部遍历");resolve();}};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("通过对象存储遍历失败");reject(e.target.error);};});} catch (error) {this.showOutput("遍历数据时发生错误");throw error;}}// 通过索引遍历async indexOpenCursor() {try {await this.ensureDB();const transaction = this.db.transaction(["users"], "readonly");const store = transaction.objectStore("users");// 通过索引遍历// 在对象存储上调用index()方法,得到一个IDBIndex实例。const index = store.index("name"); // 假设数据中有一个 name 索引 { id: 1, name: "张三", email: "zhangsan@example.com" }// 索引非常像对象存储,可以创建新游标,与在对象存储上创建的游标一样。const request = index.openCursor(); // 通过索引遍历return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {request.onsuccess = (e) => {const cursor = e.target.result;if (cursor) {// cursor.key 索引字段的值 (如 "张三")// cursor.primaryKey 对象的主键// cursor.value 完整的对象// 通过索引(Index)创建游标时,key 表示索引键(当前索引字段的值),primaryKey 表示对象的主键。this.showOutput("索引遍历:" + cursor.value.id + "~" + cursor.value.name);cursor.continue();} else {this.showOutput("没有数据或数据已全部遍历");resolve();}};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("通过索引遍历失败");reject(e.target.error);};});} catch (error) {this.showOutput("索引遍历时发生错误");throw error;}}// 游标可用于更新个别记录。async updateRecord() {try {await this.ensureDB();const transaction = this.db.transaction(["users"], "readwrite");const store = transaction.objectStore("users");// 通过对象存储遍历const request = store.openCursor(); // 打开游标return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {request.onsuccess = (e) => {// 仅返回一条记录var cursor = e.target.result; // 返回IDBCursorWithValueif (cursor) {if (cursor.value.name == "张三") {cursor.value.name = "张三丰";var requestUpdate = cursor.update(cursor.value); // 更新记录requestUpdate.onsuccess = () => {this.showOutput("数据 <b>id = " + cursor.value.id + "</b> 更新成功!");resolve();};requestUpdate.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("更新失败");reject(e.target.error);};}cursor.continue(); // 继续遍历} else {this.readData();this.showOutput("没有数据或数据已全部遍历");resolve();}};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("查询失败");reject(e.target.error);};});} catch (error) {this.showOutput("更新记录时发生错误");throw error;}}// 调用delete()删除游标位置的记录,也会创建一个请求。// 如果事务没有修改对象存储的权限,update()和delete()都会报错。// 通过游标位置删除记录async deleteRecord() {try {await this.ensureDB();const transaction = this.db.transaction(["users"], "readwrite");const store = transaction.objectStore("users");var request = store.openCursor();return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {request.onsuccess = (e) => {var cursor = e.target.result;if (cursor) {if (cursor.value.name == "李四") {let request = cursor.delete(); // 删除记录request.onsuccess = () => {this.showOutput("数据 <b>id = " + cursor.value.id + "</b> 删除成功!");resolve();};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("删除失败");reject(e.target.error);};}cursor.continue();} else {this.showOutput("数据不存在或全部删除完毕");resolve();}};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("查询失败");reject(e.target.error);};});} catch (error) {this.showOutput("删除记录时发生错误");throw error;}}// 使用游标获取数据的方式受到了限制。// 使用键范围(Key Range)可以让游标更容易理解。// 键范围对应 IDBKeyRange 的实例。有4种方式指定键范围:only(),lowerBound(),upperBound(),bound()// 定义了范围之后,把它传给openCursor()方法,就可以得到位于该范围内的游标。async getDataByKeyRange() {try {await this.ensureDB();const transaction = this.db.transaction(["users"], "readonly");const store = transaction.objectStore("users");// bound 4个参数:1.开始值 2.结束值 3.是否跳过开始值 4.是否跳过结束值// 这个范围查询是基于主键的,主键是自增ID,可能没有在这个范围内的数据。// let keyRange = IDBKeyRange.bound(160, 170, true, true); // 创建一个范围: 160 < key < 170let keyRange;try {// IndexedDB 的自增主键默认从 1 开始,而不是 0。keyRange = IDBKeyRange.bound(1, 100); // 更可能有数据的范围} catch (error) {this.showOutput("创建键范围失败");throw error;}// 如果对象存储中有重复的记录,可能需要游标跳过那些重复的项。为此,可以给openCursor()传入第二个参数"nextunique"。var request = store.openCursor(keyRange);return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {request.onsuccess = (e) => {var cursor = e.target.result;if (cursor) {this.showOutput("找到了 <b>" + cursor.value.id + "~~" + cursor.value.name + "</b>");cursor.continue();} else {this.showOutput("没有符合条件的数据");resolve();}};request.onerror = (e) => {this.showOutput("发生错误:");reject(e.target.error);};});} catch (error) {this.showOutput("获取范围内记录时发生错误");throw error;}}// 使用openKeyCursor()也可以在索引上创建特殊游标,只返回每条记录的主键。async handleOpenKeyCursor() {try {await this.ensureDB();const transaction = this.db.transaction(["users"], "readonly");const store = transaction.objectStore("users");// const index = store.index("name"); // name索引const index = store.index("email"); // email索引// 通过对象存储遍历const request = index.openKeyCursor();return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {request.onsuccess = (e) => {const cursor = e.target.result;console.log(cursor);if (cursor) {this.showOutput(cursor.key);cursor.continue();} else {this.showOutput("没有数据或数据已全部遍历");}resolve();};request.onerror = (e) => {reject(e.target.error);};});} catch (error) {this.showOutput("测试键游标时发生错误");throw error;}}}// 创建应用实例const app = new IndexedDBManager();// 注意前++和后++的区别// let a = 1;// console.log(a++); //1// let b = 1;// console.log(++b); //2// 后续建议的改进// 添加加载状态 - 在异步操作期间禁用按钮// 数据验证 - 在添加数据前验证字段// 分页支持 - 对于大量数据的遍历// 备份功能 - 导出/导入 IndexedDB 数据</script></body>
</html>