『 数据库 』MySQL复习 - 从更新删除到分组聚合查询实践
文章目录
- 1 例表
- 1.1 student_scores 表
- 1.2 student_info 表
- 1.3 Oracle9i 经典测试用表 scottDB
- 2 UPDATE 更新
- 2.1 student_scores 表 - 对LiuYi的subject1_score更新为100
- 2.2 student_scores 表 - 对ChenEr的subject1_score更新为100, subject2_score 更新为55
- 2.3 student_scores 表 - 将 "subject1_score + subject2_score + subject3_score" 记录倒数三名的 subject1_score 加上 30
- 2.4 student_scores 表 - 将所有student的subject2_score更新为subject2_score*=2
- 3 DELETE 删除操作
- 3.1 student_scores 表 - 删除ZhangSan的相关记录
- 3.2 student_info 表 - 删除整张表数据
- 3.3 TRUNCATE 截断表
- 4 插入查询结果
- 5 聚合函数
- 5.1 student_info表 - 查询表内有多少条记录
- 5.2 对去重数据进行计数
- 5.3 student_scores表 - 统计 subject1_score 总分
- 5.4 查询出 subject3_score >70 的最小值
- 6 GROUP BY 语句 - 分组查询
- 6.1 scottDB_emp 表 - 查询每个部门的最高薪资和平均薪资
- 6.2 scottDB_emp 表 - 查询每个部门的每种岗位的最低薪资和平均薪资
- 6.3 显示平均工资低于2000的部门和它的平均工资
1 例表
该部分提供该篇文章所使用的表;
1.1 student_scores 表
CREATE TABLE `student_scores` (`student_id` char(8) NOT NULL,`student_name` varchar(20) NOT NULL,`student_gender` enum('man','woman') NOT NULL,`student_age` int unsigned DEFAULT NULL,`subject1_score` int NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',`subject2_score` int NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',`subject3_score` int NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',`total_score` int NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',`average_score` decimal(5,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00',PRIMARY KEY (`student_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;INSERT INTO `student_scores` (`student_id`, `student_name`, `student_gender`, `student_age`, `subject1_score`, `subject2_score`, `subject3_score`, `total_score`, `average_score`) VALUES
('20250001', 'LiuYi', 'man', 20, 85, 92, 78, 255, 85.00),
('20250002', 'ChenEr', 'woman', 19, 92, 88, 95, 275, 91.67),
('20250003', 'ZhangSan', 'man', 21, 76, 85, 82, 243, 81.00),
('20250004', 'LiSi', 'woman', 20, 88, 79, 91, 258, 86.00),
('20250005', 'WangWu', 'man', 22, 65, 72, 68, 205, 68.33),
('20250006', 'ZhaoLiu', 'woman', 19, 95, 96, 94, 285, 95.00),
('20250007', 'SunQi', 'man', 20, 82, 75, 79, 236, 78.67),
('20250008', 'ZhouBa', 'woman', 21, 0, 86, 90, 176, 58.67),
('20250009', 'WuJiu', 'man', 20, 78, 82, 76, 236, 78.67),
('20250010', 'ZhengShi', 'woman', 19, 91, 89, 93, 273, 91.00),
('20250011', 'FengShiyi', 'man', 21, 84, 0, 88, 172, 57.33),
('20250012', 'ChenShier', 'woman', 20, 79, 85, 81, 245, 81.67),
('20250013', 'ChuShisan', 'man', 22, 87, 91, 86, 264, 88.00),
('20250014', 'WeiShisi', 'woman', 19, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0.00),
('20250015', 'ShenShiwu', 'man', 20, 93, 87, 96, 276, 92.00);
1.2 student_info 表
CREATE TABLE `student_info` (`student_id` char(8) NOT NULL COMMENT '学生学号,主键',`student_name` varchar(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '学生姓名,不能为空',`student_age` int unsigned DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '学生年龄',`student_gender` enum('man','woman') DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '学生性别',`qq_number` varchar(15) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'QQ号,唯一约束,允许为空',`email` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱,唯一约束,允许为空',PRIMARY KEY (`student_id`),UNIQUE KEY `qq_number` (`qq_number`),UNIQUE KEY `email` (`email`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci COMMENT='学生基本信息表';INSERT INTO `student_info` (`student_id`, `student_name`, `student_age`, `student_gender`, `qq_number`, `email`) VALUES
('20250001', 'LiuYi', 20, 'man', '123456789', 'liuyi@example.com'),
('20250002', 'ChenEr', 19, 'woman', NULL, 'chener@example.com'),
('20250003', 'ZhangSan', 21, 'man', '987654321', NULL),
('20250004', 'LiSi', 20, 'woman', NULL, NULL),
('20250005', 'WangWu', 22, 'man', '555666777', 'wangwu@example.com'),
('20250006', 'ZhaoLiu', 19, 'woman', '888999000', 'zhaoliu@example.com'),
('20250007', 'SunQi', 20, 'man', NULL, 'sunqi@example.com'),
('20250008', 'ZhouBa', 21, 'woman', '111222333', NULL),
('20250009', 'WuJiu', 20, 'man', NULL, NULL),
('20250010', 'ZhengShi', 19, 'woman', '444555666', 'zhengshi@example.com');
1.3 Oracle9i 经典测试用表 scottDB
DROP database IF EXISTS `scott`;
CREATE database IF NOT EXISTS `scott` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;USE `scott`;DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `dept`;
CREATE TABLE `dept` (`deptno` int(2) unsigned zerofill NOT NULL COMMENT ' 部门编号 ',`dname` varchar(14) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' 部门名称 ',`loc` varchar(13) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' 部门所在地点 '
);DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `emp`;
CREATE TABLE `emp` (`empno` int(6) unsigned zerofill NOT NULL COMMENT '雇员编号',`ename` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '雇员姓名',`job` varchar(9) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '雇员职位',`mgr` int(4) unsigned zerofill DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '雇员领导编号',`hiredate` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '雇佣时间',`sal` decimal(7,2) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '工资月薪',`comm` decimal(7,2) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '奖金',`deptno` int(2) unsigned zerofill DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '部门编号'
);DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `salgrade`;
CREATE TABLE `salgrade` (`grade` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '等级',`losal` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '此等级最低工资',`hisal` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '此等级最高工资'
);insert into dept (deptno, dname, loc)
values (10, 'ACCOUNTING', 'NEW YORK');
insert into dept (deptno, dname, loc)
values (20, 'RESEARCH', 'DALLAS');
insert into dept (deptno, dname, loc)
values (30, 'SALES', 'CHICAGO');
insert into dept (deptno, dname, loc)
values (40, 'OPERATIONS', 'BOSTON');insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7369, 'SMITH', 'CLERK', 7902, '1980-12-17', 800, null, 20);insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7499, 'ALLEN', 'SALESMAN', 7698, '1981-02-20', 1600, 300, 30);insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7521, 'WARD', 'SALESMAN', 7698, '1981-02-22', 1250, 500, 30);insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7566, 'JONES', 'MANAGER', 7839, '1981-04-02', 2975, null, 20);insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7654, 'MARTIN', 'SALESMAN', 7698, '1981-09-28', 1250, 1400, 30);insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7698, 'BLAKE', 'MANAGER', 7839, '1981-05-01', 2850, null, 30);insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7782, 'CLARK', 'MANAGER', 7839, '1981-06-09', 2450, null, 10);insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7788, 'SCOTT', 'ANALYST', 7566, '1987-04-19', 3000, null, 20);insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7839, 'KING', 'PRESIDENT', null, '1981-11-17', 5000, null, 10);insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7844, 'TURNER', 'SALESMAN', 7698,'1981-09-08', 1500, 0, 30);insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7876, 'ADAMS', 'CLERK', 7788, '1987-05-23', 1100, null, 20);insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7900, 'JAMES', 'CLERK', 7698, '1981-12-03', 950, null, 30);insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7902, 'FORD', 'ANALYST', 7566, '1981-12-03', 3000, null, 20);insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7934, 'MILLER', 'CLERK', 7782, '1982-01-23', 1300, null, 10);insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (1, 700, 1200);
insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (2, 1201, 1400);
insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (3, 1401, 2000);
insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (4, 2001, 3000);
insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (5, 3001, 9999);2 UPDATE 更新
UPDATE 更新语法是对数据进行更新, 除了对数据进行更新以外, 我们通常也运行其对所查询到的结果进行列值更新;
-
语法
UPDATE table_name SET column = expr [, column = expr ...][WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] [LIMIT ...];
本质上对查询到的结果进行列值更新即筛选出需要更新的列并进行更新;
2.1 student_scores 表 - 对LiuYi的subject1_score更新为100
通过条件筛选出 student_name为LiuYi的数据更新其subject1_score为100;
mysql> select student_name, subject1_score from student_scores where student_name = 'LiuYi';
+--------------+----------------+
| student_name | subject1_score |
+--------------+----------------+
| LiuYi | 85 |
+--------------+----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> update student_scores set subject1_score = 100 where student_name ='LiuYi';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0mysql> select student_name, subject1_score from student_scores where student_name = 'LiuYi';
+--------------+----------------+
| student_name | subject1_score |
+--------------+----------------+
| LiuYi | 100 |
+--------------+----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)2.2 student_scores 表 - 对ChenEr的subject1_score更新为100, subject2_score 更新为55
与2.1相同, 唯一不同的是更新的column数量变多;
mysql> select student_name, subject1_score, subject2_score from student_scores where student_name ='ChenEr';
+--------------+----------------+----------------+
| student_name | subject1_score | subject2_score |
+--------------+----------------+----------------+
| ChenEr | 92 | 88 |
+--------------+----------------+----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> update student_scores set subject1_score=100, subject2_score = 55
where student_name = 'ChenEr';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0mysql> select student_name, subject1_score, subject2_score from student_scores where student_name ='ChenEr';
+--------------+----------------+----------------+
| student_name | subject1_score | subject2_score |
+--------------+----------------+----------------+
| ChenEr | 100 | 55 |
+--------------+----------------+----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2.3 student_scores 表 - 将 “subject1_score + subject2_score + subject3_score” 记录倒数三名的 subject1_score 加上 30
需要对subject1_score, subject2_score, subject3_score的和进行降序排序并使用LIMIT分页前三个;
将筛选出来的数据进行 subject1_score = subject1_score + 30;
mysql> select student_name, subject1_score, subject1_score+subject2_score+subject3_score as total from student_scores order by total asc limit 3;
+--------------+----------------+-------+
| student_name | subject1_score | total |
+--------------+----------------+-------+
| WeiShisi | 0 | 0 |
| FengShiyi | 84 | 172 |
| ZhouBa | 0 | 176 |
+--------------+----------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> update student_scores set subject1_score = subject1_score+30 order by subject1_score+subject2_score+subject3_score asc limit 3;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Rows matched: 3 Changed: 3 Warnings: 0mysql> select student_name, subject1_score, subject1_score+subject2_score+subject3_score as total from student_scores order by total asc limit 3;
+--------------+----------------+-------+
| student_name | subject1_score | total |
+--------------+----------------+-------+
| WeiShisi | 30 | 30 |
| FengShiyi | 114 | 202 |
| WangWu | 65 | 205 |
+--------------+----------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
由于记录被更新后, total排序发生变化, 因此两次查询结果不同, 但可以查询对应列的所有数据来验证已经修改成功;
mysql> select student_name, subject1_score, subject1_score+subject2_score+subject3_score as total from student_scores order by total asc;
+--------------+----------------+-------+
| student_name | subject1_score | total |
+--------------+----------------+-------+
| WeiShisi | 30 | 30 |
| FengShiyi | 114 | 202 |
| WangWu | 65 | 205 |
| ZhouBa | 30 | 206 |
| SunQi | 82 | 236 |
| WuJiu | 78 | 236 |
| ZhangSan | 76 | 243 |
| ChenShier | 79 | 245 |
| ChenEr | 100 | 250 |
| LiSi | 88 | 258 |
| ChuShisan | 87 | 264 |
| LiuYi | 100 | 270 |
| ZhengShi | 91 | 273 |
| ShenShiwu | 93 | 276 |
| ZhaoLiu | 95 | 285 |
+--------------+----------------+-------+
15 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2.4 student_scores 表 - 将所有student的subject2_score更新为subject2_score*=2
此处为全表更新, 通常全表更新需要慎用;
mysql> select student_name, subject2_score from student_scores;
+--------------+----------------+
| student_name | subject2_score |
+--------------+----------------+
| LiuYi | 92 |
| ChenEr | 55 |
| ZhangSan | 85 |
| LiSi | 79 |
| WangWu | 72 |
| ZhaoLiu | 96 |
| SunQi | 75 |
| ZhouBa | 86 |
| WuJiu | 82 |
| ZhengShi | 89 |
| FengShiyi | 0 |
| ChenShier | 85 |
| ChuShisan | 91 |
| WeiShisi | 0 |
| ShenShiwu | 87 |
+--------------+----------------+
15 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> update student_scores set subject2_score = subject2_score*2;
Query OK, 13 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Rows matched: 15 Changed: 13 Warnings: 0mysql> select student_name, subject2_score from student_scores;
+--------------+----------------+
| student_name | subject2_score |
+--------------+----------------+
| LiuYi | 184 |
| ChenEr | 110 |
| ZhangSan | 170 |
| LiSi | 158 |
| WangWu | 144 |
| ZhaoLiu | 192 |
| SunQi | 150 |
| ZhouBa | 172 |
| WuJiu | 164 |
| ZhengShi | 178 |
| FengShiyi | 0 |
| ChenShier | 170 |
| ChuShisan | 182 |
| WeiShisi | 0 |
| ShenShiwu | 174 |
+--------------+----------------+
15 rows in set (0.00 sec)
要注意的是, 在MySQL中不支持*=类似的这种写法;
mysql> update student_scores set subject2_score*=2;
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near '*=2' at line 1
mysql>
3 DELETE 删除操作
删除通常为删除表中的某一行记录;
-
语法
DELETE FROM table_name [WHERE ...] [ORDER BY ...] [LIMIT ...]
删除操作同样可以对已查询到的结果进行删除, 即筛选条件进行删除, 但是DELETE能删除的最小单位为行;
若是需要删除单元格内数据通常采用UPDATE语法更新该单元格数据为NULL;
3.1 student_scores 表 - 删除ZhangSan的相关记录
同样为筛选出对应的行, 并使用DELETE进行删除;
mysql> select * from student_scores\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************student_id: 20250001student_name: LiuYi
student_gender: manstudent_age: 20
subject1_score: 100
subject2_score: 184
subject3_score: 78total_score: 255average_score: 85.00
*************************** 2. row ***************************student_id: 20250002student_name: ChenEr
student_gender: womanstudent_age: 19
subject1_score: 100
subject2_score: 110
subject3_score: 95total_score: 275average_score: 91.67
*************************** 3. row ***************************student_id: 20250003student_name: ZhangSan
student_gender: manstudent_age: 21
subject1_score: 76
subject2_score: 170
subject3_score: 82total_score: 243average_score: 81.00
*************************** 4. row ***************************student_id: 20250004student_name: LiSi
student_gender: womanstudent_age: 20
subject1_score: 88
subject2_score: 158
subject3_score: 91total_score: 258average_score: 86.00
*************************** 5. row ***************************student_id: 20250005student_name: WangWu
student_gender: manstudent_age: 22
subject1_score: 65
subject2_score: 144
subject3_score: 68total_score: 205average_score: 68.33
*************************** 6. row ***************************student_id: 20250006student_name: ZhaoLiu
student_gender: womanstudent_age: 19
subject1_score: 95
subject2_score: 192
subject3_score: 94total_score: 285average_score: 95.00
*************************** 7. row ***************************student_id: 20250007student_name: SunQi
student_gender: manstudent_age: 20
subject1_score: 82
subject2_score: 150
subject3_score: 79total_score: 236average_score: 78.67
*************************** 8. row ***************************student_id: 20250008student_name: ZhouBa
student_gender: womanstudent_age: 21
subject1_score: 30
subject2_score: 172
subject3_score: 90total_score: 176average_score: 58.67
*************************** 9. row ***************************student_id: 20250009student_name: WuJiu
student_gender: manstudent_age: 20
subject1_score: 78
subject2_score: 164
subject3_score: 76total_score: 236average_score: 78.67
*************************** 10. row ***************************student_id: 20250010student_name: ZhengShi
student_gender: womanstudent_age: 19
subject1_score: 91
subject2_score: 178
subject3_score: 93total_score: 273average_score: 91.00
*************************** 11. row ***************************student_id: 20250011student_name: FengShiyi
student_gender: manstudent_age: 21
subject1_score: 114
subject2_score: 0
subject3_score: 88total_score: 172average_score: 57.33
*************************** 12. row ***************************student_id: 20250012student_name: ChenShier
student_gender: womanstudent_age: 20
subject1_score: 79
subject2_score: 170
subject3_score: 81total_score: 245average_score: 81.67
*************************** 13. row ***************************student_id: 20250013student_name: ChuShisan
student_gender: manstudent_age: 22
subject1_score: 87
subject2_score: 182
subject3_score: 86total_score: 264average_score: 88.00
*************************** 14. row ***************************student_id: 20250014student_name: WeiShisi
student_gender: womanstudent_age: 19
subject1_score: 30
subject2_score: 0
subject3_score: 0total_score: 0average_score: 0.00
*************************** 15. row ***************************student_id: 20250015student_name: ShenShiwu
student_gender: manstudent_age: 20
subject1_score: 93
subject2_score: 174
subject3_score: 96total_score: 276average_score: 92.00
15 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> delete from student_scores where student_name='ZhangSan';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)mysql> select * from student_scores where student_name = 'ZhangSan'\G
Empty set (0.00 sec)
3.2 student_info 表 - 删除整张表数据
删除整表操作, 通常情况下, 涉及到全表的操作都应该慎用;
mysql> create table student_todel as (select * from student_info); # 拷贝一张新表
Query OK, 10 rows affected (0.03 sec)
Records: 10 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0mysql> select * from student_todel;
+------------+--------------+-------------+----------------+-----------+----------------------+
| student_id | student_name | student_age | student_gender | qq_number | email |
+------------+--------------+-------------+----------------+-----------+----------------------+
| 20250001 | LiuYi | 20 | man | 123456789 | liuyi@example.com |
| 20250002 | ChenEr | 19 | woman | NULL | chener@example.com |
| 20250003 | ZhangSan | 21 | man | 987654321 | NULL |
| 20250004 | LiSi | 20 | woman | NULL | NULL |
| 20250005 | WangWu | 22 | man | 555666777 | wangwu@example.com |
| 20250006 | ZhaoLiu | 19 | woman | 888999000 | zhaoliu@example.com |
| 20250007 | SunQi | 20 | man | NULL | sunqi@example.com |
| 20250008 | ZhouBa | 21 | woman | 111222333 | NULL |
| 20250009 | WuJiu | 20 | man | NULL | NULL |
| 20250010 | ZhengShi | 19 | woman | 444555666 | zhengshi@example.com |
+------------+--------------+-------------+----------------+-----------+----------------------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> delete from student_todel;
Query OK, 10 rows affected (0.00 sec)mysql> select * from student_todel;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
通常情况下, 使用DELETE FROM语句不会重置AUTO_INCREMENT计数;
假设存在一张测试表;
mysql> show create table to_del\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************Table: to_del
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `to_del` (`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select * from to_del;
+----+----------+
| id | name |
+----+----------+
| 1 | ZhangSan |
| 2 | LiSi |
| 3 | WangWu |
+----+----------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
此时该表的auto_increment数值为4;
对该表执行DELETE操作并再次查看auto_increment值;
mysql> delete from to_del;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)mysql> select * from to_del;
Empty set (0.00 sec)mysql> show create table to_del\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************Table: to_del
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `to_del` (`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> insert into to_del(name) value('LiLi');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)mysql> select * from to_del;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 4 | LiLi |
+----+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
从上述操作中可以观察到, 使用DELETE语句并未重置AUTO_INCREMENT数值;
本质上清空表只是清空表内数据, 并不会对表结构产生影响;
3.3 TRUNCATE 截断表
在上文的 3.2 中提到, 实际上使用DELETE语法清空表操作并不会对表结构产生影响;
而TRUNCATE为截断表, 截断表可以对表内数据进行清除, 并影响表结构为初始状态, 这也包括AUTO_INCREMENT属性;
-
语法
TRUNCATE table_name;语句后跟上表名即可;
mysql> select * from to_del;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 4 | LiLi |
| 5 | LiLi |
| 6 | LiLi |
| 7 | LiLi |
| 8 | LiLi |
| 9 | LiLi |
| 10 | LiLi |
+----+------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> show create table to_del\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************Table: to_del
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `to_del` (`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=11 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> truncate to_del;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.07 sec)mysql> select * from to_del;
Empty set (0.00 sec)mysql> show create table to_del\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************Table: to_del
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `to_del` (`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
在这个示例中可以观察到, 当使用TRUNCATE对表进行截断后, 表内数据被清空, 对应的表结构也受到影响回归到初始状态;
当然需要注意的是, 通常情况下TRUNCATE语句是不能进行事务回滚的;
通常情况下, 大部分的表操作都会被MySQL中的一个记录日志记录, 这些记录可以被回滚, 而TRUNCATE不被这种日志记录系统所约束, 因此该操作无法回滚;
4 插入查询结果
假设一张表为存在重复数据的表;
mysql> show create table products\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************Table: products
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `products` (`id` int DEFAULT NULL,`name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select * from products;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 1 | Apple |
| 2 | Banana |
| 3 | Orange |
| 1 | Apple |
| 3 | Orange |
+------+--------+
5 rows in set (0.01 sec)
- 若是需要将数据去重该如何操作?
通常普遍的操作是将数据去重, 并将去重后的数据使用INSERT INTO插入;
通常情况下, INSERT INTO数据插入允许插入SELECT查询的结果(同一表结构下);
因此需要的操作是:
-
创建结构相同的表
mysql> create table products_1 like products; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)mysql> show create table products_1\G *************************** 1. row ***************************Table: products_1 Create Table: CREATE TABLE `products_1` (`id` int DEFAULT NULL,`name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci 1 row in set (0.01 sec) -
插入数据
mysql> insert into products_1 (select distinct * from products); Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec) Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0mysql> select * from products_1; +------+--------+ | id | name | +------+--------+ | 1 | Apple | | 2 | Banana | | 3 | Orange | +------+--------+ 3 rows in set (0.01 sec) -
对表进行
RENAME重命名mysql> rename table products to products_bak; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)mysql> rename table products_1 to products; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)mysql> select * from products; +------+--------+ | id | name | +------+--------+ | 1 | Apple | | 2 | Banana | | 3 | Orange | +------+--------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
这种操作通常被称为 “影子表替换”, 其最后采用的RENAME操作为原子性的, 这种情况下, 在未对原表进行操作时, 采用新表数据接收原表数据的筛选内容, 保证原表依旧能对服务提供服务;
而若是在原表进行替换时, 若是原表仍在对外提供服务, 可能会造成用户查不到数据等问题;
而RENAME操作本质上是原子操作, 对系统而言(尤其是Linux), 创建一个数据库是创建一个新的文件夹, 创建一张表结构则是创建一个新的文件, 而RENAME操作则是简单的对文件进行重命名move, 本身不涉及到文件的移动等操作;
当所有准备完毕后, 使用RENAME进行表名更换, 即为操作系统对文件进行move重命名;
由于是原子操作, 速度极快, 因此在两表交替名字时, 能做到完全的快速操作而不被服务或者用户察觉;
5 聚合函数
在MySQL中, 通常情况下存在一些函数, 这些函数能对表的一些数据进行操作, 并返回用户需要的结果;
-
常见的聚合函数有
函数 说明 COUNT([DISTINCT] expr)返回查询到的数据的 数量 SUM([DISTINCT] expr)返回查询到的数据的 总和, 不是数字没有意义 AVG([DISTINCT] expr)返回查询到的数据的 平均值, 不是数字没有意义 MAX([DISTINCT] expr)返回查询到的数据的 最大值, 不是数字没有意义 MIN([DISTINCT] expr)返回查询到的数据的 最小值, 不是数字没有意义
5.1 student_info表 - 查询表内有多少条记录
mysql> select count(*) from student_info;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 10 |
+----------+
调用聚合函数, 同时结果也可以进行AS重命名;
mysql> select count(*) as count_result from student_info;
+--------------+
| count_result |
+--------------+
| 10 |
+--------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)5.2 对去重数据进行计数
假设一张表及其表内记录为:
mysql> show create table products\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************Table: products
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `products` (`id` int DEFAULT NULL,`name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select * from products;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 1 | Apple |
| 2 | Banana |
| 3 | Orange |
| 1 | Apple |
| 3 | Orange |
+------+--------+
5 rows in set (0.01 sec)
若想计数去重后的结果时, 通常情况下无法使用下面这种语法:
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT *) FROM table_name;
这是一种错误的语法, 本质上DISTINCT可以理解为存在两种:
-
行级去重
DISTINCT在
SELECT语句中的去重, 应用于整个结果集, 通常只是为查询修饰;SELECT DISTINCT * FROM table_name; -
值级去重
DISTINCT在聚合函数中去重, 应用于单个表达式或列的去重;
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT column) FROM table_name;值级
DISTINCT必须嵌套函数使用, 且无法进行全列*修饰, 只能对单个column进行修饰;
因此此处的去重只能是通过值级去重后再被聚合函数计算;
mysql> select count(distinct id) from products;
+--------------------+
| count(distinct id) |
+--------------------+
| 3 |
+--------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
5.3 student_scores表 - 统计 subject1_score 总分
直接使用聚合函数SUM()即可;
mysql> select sum(subject1_score) from student_scores;
+---------------------+
| sum(subject1_score) |
+---------------------+
| 1132 |
+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
也可配合其他聚合函数或是直接使用AVG聚合函数计算平均分;
mysql> select sum(subject1_score)/count(*) as avg from student_scores; # 使用两个聚合函数计算出平均分
+---------+
| avg |
+---------+
| 80.8571 |
+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select avg(subject1_score) from student_scores; # 使用AVG聚合函数计算平均分
+---------------------+
| avg(subject1_score) |
+---------------------+
| 80.8571 |
+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
5.4 查询出 subject3_score >70 的最小值
可以使用两种解法:
-
使用
WHERE筛选出>70的内容并使用ORDER BY ... ASC进行排序后通过LIMIT进行分页即可mysql> select student_name, subject3_score from student_scores where subject3_score>70 order by subject3_score asc limit 1; +--------------+----------------+ | student_name | subject3_score | +--------------+----------------+ | WuJiu | 76 | +--------------+----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -
使用
WHERE条件筛选过后, 对结果进行MIN()聚合函数查询mysql> select min(subject3_score) from student_scores where subject3_score>70; +---------------------+ | min(subject3_score) | +---------------------+ | 76 | +---------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
6 GROUP BY 语句 - 分组查询
通常情况下, 在MySQL中的SELECT语句可以通过GROUP BY子句对指定列来分组查询;
在该模块中我们使用Oracle9i 经典测试用表 scottDB 进行基本演示;
通常在数据库中, 分组都是为了更好的进行聚合统计;
通常情况下一组数据表中可能已经对某些数据进行了分组, 但由于排序规则, 无法很好的将所分的组进行一系列的按组进行操作(查询),而GROUP BY语句则是用来做到这一点, 即将已经分组但未按组进行排列的数据按照对应的column进行分组, 从而进行更好的统计;
-
语法
SELECT column1, aggregate_function(column2) FROM table_name WHERE condition GROUP BY column1, column3 HAVING aggregate_condition ORDER BY column1;
假设有一堆不同颜色的小球, 需要计算每种颜色的小球的数量, 那么则需要进行先分组再聚合;
即:
- 将不同颜色的小球按照颜色进行区分(分组)
- 将区分出来的每种颜色小球计算他们的个数(聚合)
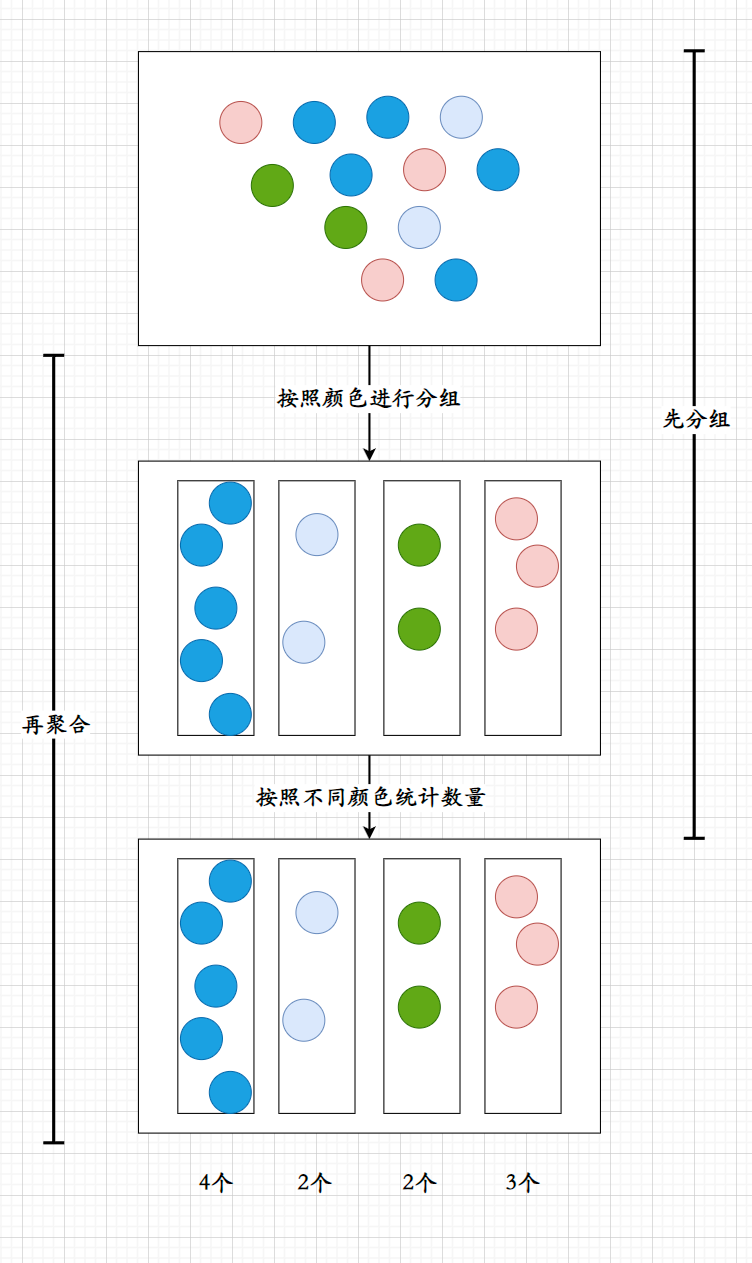
其中分组的作用即为GROUP BY语句, 聚合即为聚合函数等聚合操作;
通常情况下是为某列的不同行进行分组;
同时在使用GROUP BY语句进行分组时需要注意, 此时的SELECT语句后, 只能跟被分组的column或是被聚合函数所包裹的column;
6.1 scottDB_emp 表 - 查询每个部门的最高薪资和平均薪资
通常需要查询最高工资和平局工资可以使用MAX()和AVG聚合函数进行查询;
mysql> select max(sal) max, avg(sal) avg from emp ;
+---------+-------------+
| max | avg |
+---------+-------------+
| 5000.00 | 2073.214286 |
+---------+-------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
而此处需要按照每个部门来查询, 通常情况下GROUP BY可以对某个column进行分组;
如:
mysql> select deptno from emp;
+--------+
| deptno |
+--------+
| 20 |
| 30 |
| 30 |
| 20 |
| 30 |
| 30 |
| 10 |
| 20 |
| 10 |
| 30 |
| 20 |
| 30 |
| 20 |
| 10 |
+--------+
14 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select deptno from emp group by deptno;
+--------+
| deptno |
+--------+
| 20 |
| 30 |
| 10 |
+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec) 此处对deptno进行分组, 而将两个语句进行集合即为:
mysql> select max(sal) max, avg(sal), deptno from emp group by deptno;
+---------+-------------+--------+
| max | avg(sal) | deptno |
+---------+-------------+--------+
| 3000.00 | 2175.000000 | 20 |
| 2850.00 | 1566.666667 | 30 |
| 5000.00 | 2916.666667 | 10 |
+---------+-------------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
6.2 scottDB_emp 表 - 查询每个部门的每种岗位的最低薪资和平均薪资
与6.1需求类似,采用相同的方式, 即先分组, 再进行聚合统计;
mysql> select deptno, job, avg(sal) avg, min(sal) min from emp group by deptno, job;
+--------+-----------+-------------+---------+
| deptno | job | avg | min |
+--------+-----------+-------------+---------+
| 20 | CLERK | 950.000000 | 800.00 |
| 30 | SALESMAN | 1400.000000 | 1250.00 |
| 20 | MANAGER | 2975.000000 | 2975.00 |
| 30 | MANAGER | 2850.000000 | 2850.00 |
| 10 | MANAGER | 2450.000000 | 2450.00 |
| 20 | ANALYST | 3000.000000 | 3000.00 |
| 10 | PRESIDENT | 5000.000000 | 5000.00 |
| 30 | CLERK | 950.000000 | 950.00 |
| 10 | CLERK | 1300.000000 | 1300.00 |
+--------+-----------+-------------+---------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
这里分组为两列分组, 即分组条件为两列;
6.3 显示平均工资低于2000的部门和它的平均工资
这个查询内存在几个条件:
- 平均工资低于
2000的部门 - 这些部门的平均工资
通常我们可能使用WHERE语句来进行条件筛查:
select deptno, avg(sal) avg from emp group by deptno where avg<2000;
# 或是
select deptno, avg(sal) avg from emp group by deptno where avg(sal)<2000;
然而这个条件筛查的结果实际上的结果为如下:
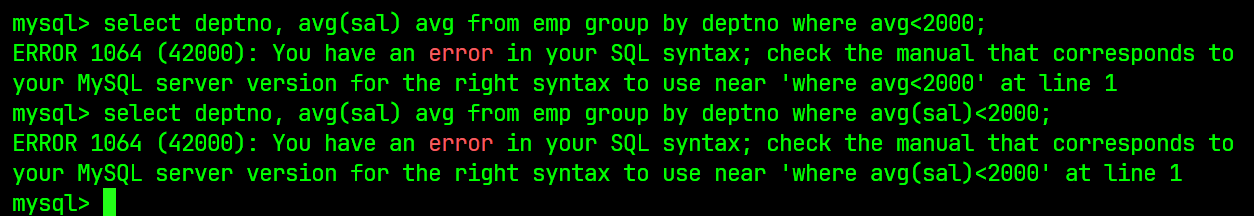
本质原因是WHERE条件筛查是针对未分组的数据, 其操作是在分组之前, 这里两条语句分别都出现了问题;
- 第一句SQL语句, 直接使用了
AS后别名avg进行WHERE条件筛查, 而此时的WHERE语句由于语句执行顺序, 无法认识到当前的avg - 第二句SQL语句直接在
WHERE语句后使用聚合函数, 而聚合函数通常只被允许在SELECT后使用;
因此这里我们采用使用HAVING的方式来完成语句;
mysql> select deptno, avg(sal) avg from emp group by deptno having avg<2000;
+--------+-------------+
| deptno | avg |
+--------+-------------+
| 30 | 1566.666667 |
+--------+-------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
此处的HAVING语句是为分组后聚合后的结果进行条件筛查, 其效果与WHERE类似, 甚至能达到WHERE 效果;
mysql> select deptno, ename from emp having deptno=20;
+--------+-------+
| deptno | ename |
+--------+-------+
| 20 | SMITH |
| 20 | JONES |
| 20 | SCOTT |
| 20 | ADAMS |
| 20 | FORD |
+--------+-------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
但因为其执行顺序和针对项不同, 我们必须在使用的时候严格区分HAVING与WHERE,不能将HAVING来代替WHERE;
通常执行的语句顺序为如下:
-
FROM: 选择表; -
WHERE: 过滤原始行(针对单行数据); -
GROUP BY: 分组过滤后的行; -
HAVING: 过滤分组后的结果(可以针对聚合); -
SELECT: 投影列,包括计算聚合和别名; -
ORDER BY: 排序最终结果;
假设我们在该题的基础上增加一个条件, 即岗位MANAGER不参与;
在这个条件下, 我们需要优先排除MANAGER岗位, 再进行分组聚合统计;
mysql> select deptno, avg(sal) avg from emp where job <> 'MANAGER' group by deptno having avg<2000;
+--------+-------------+
| deptno | avg |
+--------+-------------+
| 20 | 1975.000000 |
| 30 | 1310.000000 |
+--------+-------------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)
这里首先对job == 'MANAGER'的记录进行排除, 而后进行GROUP BY deptno分组, 分组后进行聚合计算AVG(sal), 最后HAVING avg<2000对聚合后的结果进行筛选;
在这里实际上每个中间过程都可以视为一张表,即在MySQL中的表,并不只是在磁盘中具体存在的表, 而是任何结果都是一张表, 可以将其理解为 “MySQL中一切皆为表” ;
