CS231n学习笔记1-4: Image Features
作业一-Q4: Image Features
文章目录
- 作业一-Q4: Image Features
- 本节任务
- 准备
- 代码详解
- 1. 规范化前置流程
- 2. features: HOG&HSV
- 3. softmax classifier
- 4. Question1: Classification Visualization
- 5. Train a TwoLayerNet
本节任务
- 理解 HOG 和 HSV hue histogram 的含义
- 实现并使用特征训练一个线性分类器
- 实现并使用特征训练一个 TwoLayerNet, 调参获取表现最优的模型
- 对比使用特征和图像像素的准确率
准备
补充 scipy 包:
pip install scipy
打开 features.ipynb 删除代码第一块(Google Drive).
代码详解
1. 规范化前置流程
全局设置: import, magic, pltSetting;
加载数据集: data = get_CIFAR10_data()
2. features: HOG&HSV
HOG&HSV: Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) & a color histogram using the hue channel in HSV
HOG(梯度方向直方图): 在图像的网格小单元上统计边缘梯度的方向分布(常见参数:9 个方向、8×8 像素为一单元),刻画了“轮廓/纹理”的形状信息,但不编码具体语义。
HSV Hue histogram(HSV 色相直方图): 将图像从 RGB 转到 HSV,仅对色相通道做直方图统计,关注颜色构成。
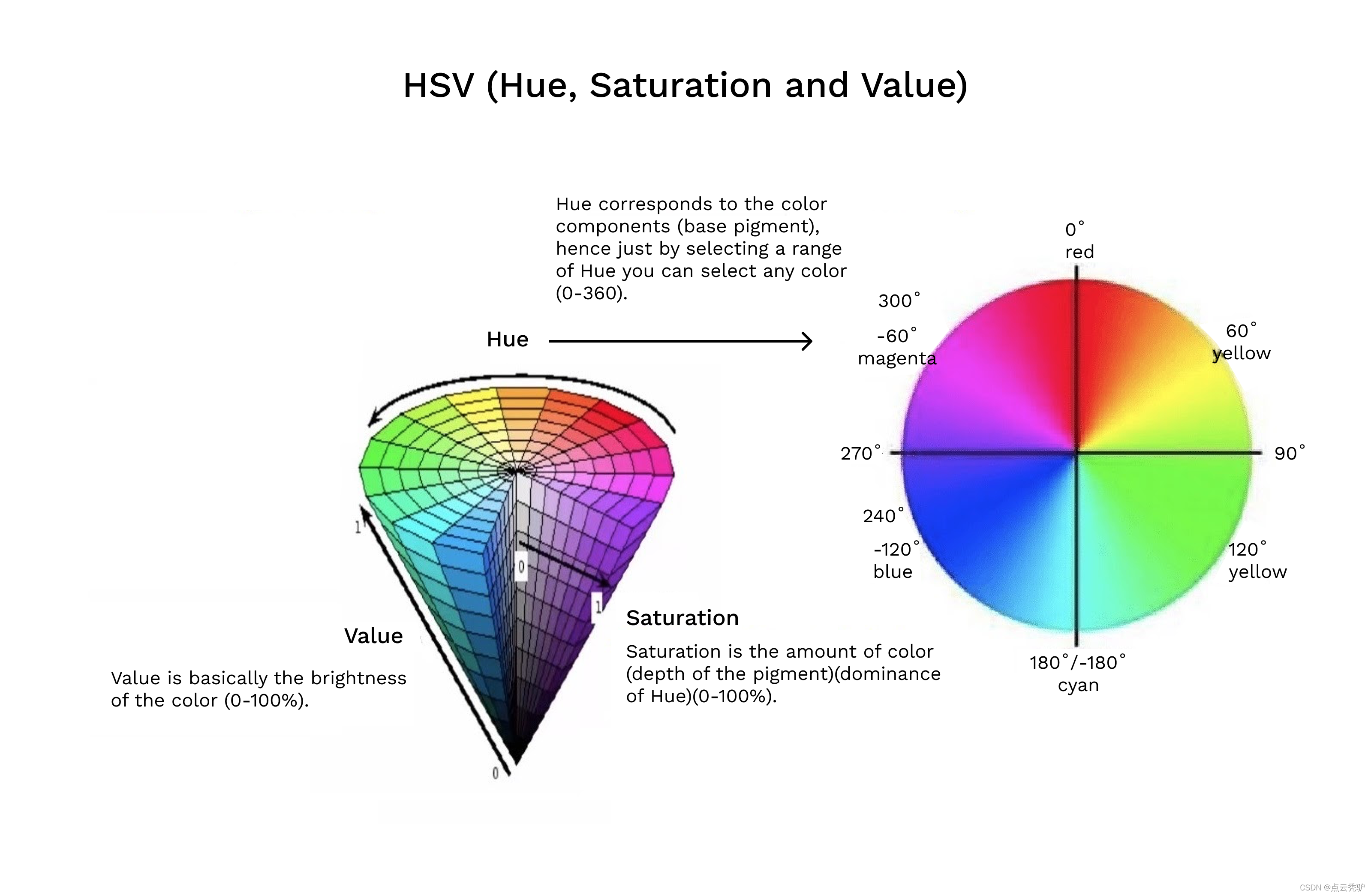
HSV 颜色系统
Hue 指色相,Saturation 指饱和度/彩度,Value 指色调/明度。
这里对图像在 Hue(色相)通道做直方图统计。在 HSV 模型中,用度数来描述色相,其中红色对应 0 度,绿色对应 120 度,蓝色对应 240 度。

HOG&HSV 可视化
为了更直观的理解,举例图像对 HOG 和 HSV hue histogram 可视化(非作业内容):
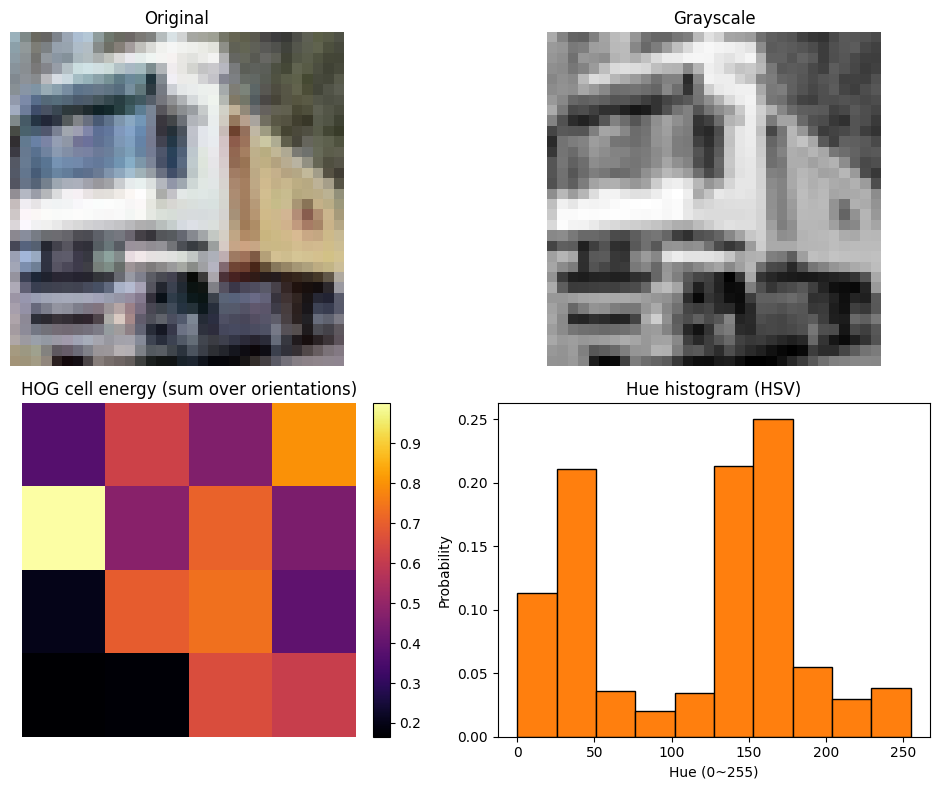
HOG:
亮块对应变化梯度大的纹理区域。比如卡车车头与车厢的边缘有大量垂直或水平边界,导致梯度大,产生更大的值。暗块对应纹理少、对比度低的区域。比如路面、车身有大面积的平坦或模糊,导致梯度小,能量低。
HSV hue histogram:
直方图对 HSV 的色相 H 做分箱(10 个 bin,范围 0~255)。车厢偏黄,在约 40~60 的 bin 有明显峰值。天空及反光的车窗带青蓝成分,约 130~180 的 bin 有峰值。车头大面积白和灰在 HSV 中色相不稳定,常被映射到靠近 0 的位置,0 附近会有一定计数,但一般不尖锐。
上面的 HOG 能量图是 9 个方向上各 8×8 cell 像素梯度能量图的总和。我们下面我们可视化 9 个方向上每个 8×8 cell 内各像素梯度幅值累加后的强度。
- 对每个像素算水平梯度 gx 和垂直梯度 gy,得到幅值 sqrt(gx2+gy2) 和方向 atan2(gy, gx)。
- 将方向量化到若干个角度区间,9 个方向覆盖 0°~180°,每个 bin 宽约 20°,图像标题为中心角度。在每个 8×8 的 cell 里把所有像素的梯度幅值累加到对应方向的 bin,就得到该 cell 的方向直方图。
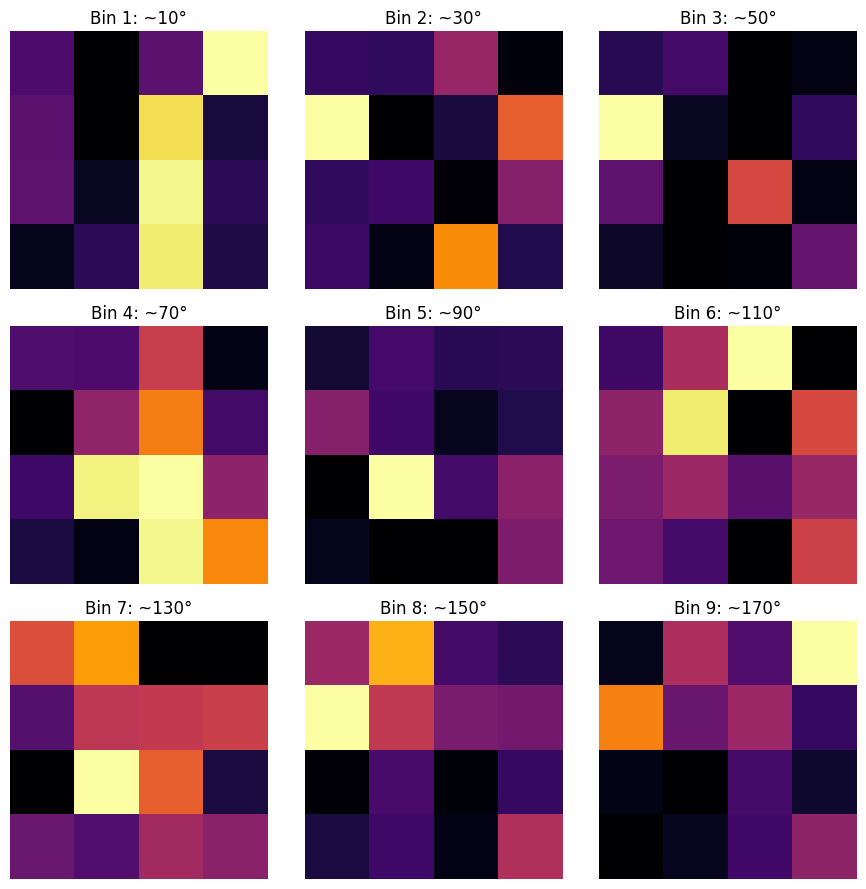
某个方向上第二行第一个 cell 有较高的像素梯度加和,加和或选择主方向得到总的梯度图,该 cell 还是较为明亮,判断该 cell 处有较为明显的边缘纹理。
提取特征
hog_feature(img): 将图像转灰度,按 8×8 cell 统计 9 个方向的梯度直方图,得到形状 4×4×9 = 144 维(CIFAR-10 为 32×32 像素)。
color_histogram_hsv(img, nbin): 把图像转 HSV,用色相 H 做直方图,得到 nbin 维。
extract_features 会对每张图依次调用列表里的函数,并把各自返回的一维向量“横向拼接”为一行,最终得到形状 (N, 144+nbin) 的矩阵。
3. softmax classifier
构建一个以 softmax+交叉熵损失为 loss 的线性分类器, 结构为一层 affine 层 + softmax.
# Use the validation set to tune the learning rate and regularization strengthfrom cs231n.classifiers.linear_classifier import Softmaxlearning_rates = [1e-7, 1e-6]
regularization_strengths = [5e5, 5e6]results = {}
best_val = -1
best_softmax = None################################################################################
# TODO: #
# Use the validation set to set the learning rate and regularization strength. #
# This should be identical to the validation that you did for the Softmax; save#
# the best trained classifer in best_softmax. If you carefully tune the model, #
# you should be able to get accuracy of above 0.42 on the validation set. #
################################################################################for lr in learning_rates:for reg in regularization_strengths:model = Softmax()loss_history = model.train(X_train_feats, y_train, lr, reg, num_iters=1000, batch_size=500, )y_train_pred = model.predict(X_train_feats)y_val_pred = model.predict(X_val_feats)train_acc = np.mean(y_train_pred == y_train)val_acc = np.mean(y_val_pred == y_val)if val_acc > best_val:best_val = val_accbest_softmax = modelresults[(lr, reg)] = (train_acc, val_acc)
# END# Print out results.
for lr, reg in sorted(results):train_accuracy, val_accuracy = results[(lr, reg)]print('lr %e reg %e train accuracy: %f val accuracy: %f' % (lr, reg, train_accuracy, val_accuracy))print('best validation accuracy achieved: %f' % best_val)
调整超参得到最高验证准确率为 0.434.
best validation accuracy achieved: 0.434000
4. Question1: Classification Visualization
分类可视化:

Inline question 1:
Describe the misclassification results that you see. Do they make sense?
描述这些误分类现象, 他们是否合理?
YourAnswer:\color{blue}{\textit Your Answer:}YourAnswer:
有相同轮廓、颜色或背景的类别可能会被混淆,比如猫和狗有着类似的轮廓、颜色和地面背景,鸟和飞机有这类似的天空背景。
他们是合理的,因为目前只使用了梯度直方图和颜色直方图特征,模型学习到的是轮廓和颜色特点,分类时也是基于这些信息。所以类似轮廓和颜色的图像会被分为一类导致误分类。
5. Train a TwoLayerNet
使用特征训练一个两层神经网络, 隐藏层维度大小为 500.
训练 TwoLayerNet 的代码如下, 主要工作在调参.
from cs231n.classifiers.fc_net import TwoLayerNet
from cs231n.solver import Solverinput_dim = X_train_feats.shape[1]
hidden_dim = 500
num_classes = 10data = {'X_train': X_train_feats,'y_train': y_train,'X_val': X_val_feats,'y_val': y_val,'X_test': X_test_feats,'y_test': y_test,
}net = TwoLayerNet(input_dim, hidden_dim, num_classes)
best_net = None################################################################################
# TODO: Train a two-layer neural network on image features. You may want to #
# cross-validate various parameters as in previous sections. Store your best #
# model in the best_net variable. #
################################################################################
lrs = [5e-1, 1e-1, 3e-2]
regs = [1e-3, 3e-3, 5e-3]
best_val_acc = -1for lr in lrs:for reg in regs:net = TwoLayerNet(input_dim, hidden_dim, num_classes, reg=reg)solver = Solver(net, data,update_rule='sgd',optim_config={'learning_rate': lr,},lr_decay=0.95,num_epochs=8, batch_size=200,print_every=1000)solver.train()if solver.best_val_acc > best_val_acc:best_val_acc = solver.best_val_accbest_net = netbest_lr = lrbest_reg = reg
print("Best val acc: ", best_val_acc, "\nBest lr: ", lr, "\nBest reg: ", reg)
# END
得到结果, 验证准确率为 0.595.
Best val acc: 0.595
Best lr: 0.03
Best reg: 0.005
更改层数为和上一节相同的 200 层, 得到验证准确率为 0.592.
Best val acc: 0.592
Best lr: 0.03
Best reg: 0.005
即使是将层数更改为 200 层, 验证准确率仍然能保持在 0.592. 相比上一节我们使用像素训练得到的验证准确率为 0.51, 这次在 epoch 和 batch size 都没有上一节大的情况下, 使用特征得到了更好的准确率. 因此我们得出结论: 使用有效的特征比如图片的 HOG 和 HSV hue hist 训练能够提升图片分类模型的性能.
