[iOS] YYModel 初步学习
[iOS] YYModel 初步学习
文章目录
- [iOS] YYModel 初步学习
- 前言
- YYModel 与其他第三方库的对比
- YYModel 的使用场景
- 简单的 Model 与 JSON
- Model 属性名和 JSON 中的 Key 不相同
- Model 包含其他 Model
- 容器类属性
- 黑名单与白名单
前言
iOS 开发中少不了各种各样的模型,不论是采用 MVC、MVP 还是 MVVM 设计模式都逃不过 Model。那么大家在使用 Model 的时候肯定遇到过一个问题,即接口传递过来的数据(一般是 JSON 格式)需要转换为 iOS 内我们能直接使用的模型(类)。iOS 开发早期第三方框架没有那么多,大家可能会手写相关代码,但是随着业务的扩展,模型的增多,这些没什么技术含量的代码只是在重复的浪费我们的劳动力而已。所以就会出现 YYModel 这一类的第三方库来解放我们的劳动力。
YYModel 与其他第三方库的对比
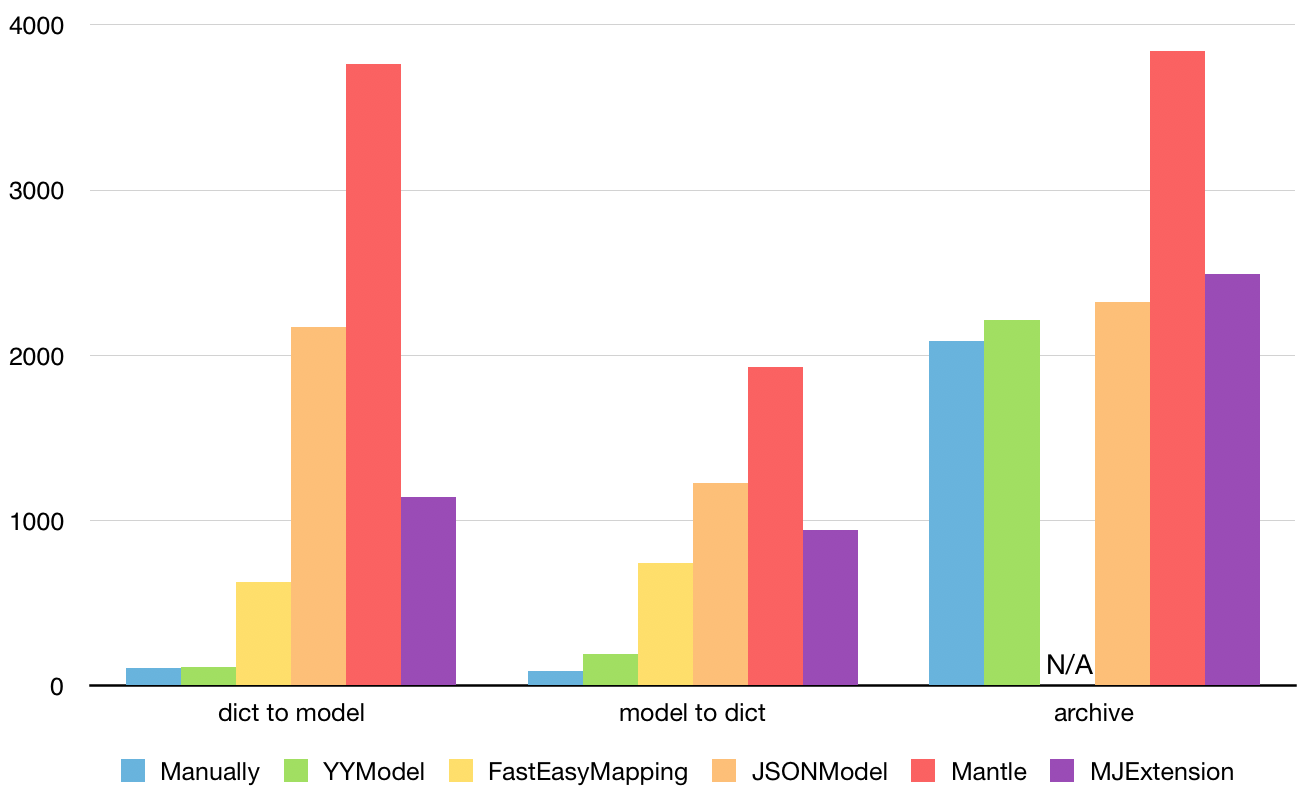
这里可以看出 YYmodel 的性能是超过了 JSONNModel 的,下文只会介绍到 YYModel 的使用。
YYModel 的使用场景
简单的 Model 与 JSON
// JSON:
{"uid":123456,"name":"Harry","created":"1965-07-31T00:00:00+0000"
}// Model:
@interface User : NSObject
@property UInt64 uid;
@property NSString *name;
@property NSDate *created;
@end
@implementation User
@end// Convert json to model:
User *user = [User yy_modelWithJSON:json];// Convert model to json:
NSDictionary *json = [user yy_modelToJSONObject];上面是最简单的 Model 的形式
当 JSON/Dictionary 中的对象类型与 Model 属性不一致时,YYModel 将会进行如下自动转换。自动转换不支持的值会被忽视。

Model 属性名和 JSON 中的 Key 不相同
// JSON:
{"n":"Harry Pottery","p": 256,"ext" : {"desc" : "A book written by J.K.Rowing."},"ID" : 100010
}// Model:
@interface Book : NSObject
@property NSString *name;
@property NSInteger page;
@property NSString *desc;
@property NSString *bookID;
@end
@implementation Book
//返回一个 Dict,将 Model 属性名对映射到 JSON 的 Key。
+ (NSDictionary *)modelCustomPropertyMapper {return @{@"name" : @"n",@"page" : @"p",@"desc" : @"ext.desc",@"bookID" : @[@"id",@"ID",@"book_id"]};
}
@end
你可以把一个或一组 JSON Key (Key path)映射到一个或多个属性。如果一个属性没有映射关系,那默认会使用相同属性名作为映射。
在 JSON->Model 的过程中:如果一个属性对应了多个 JSON Key,那么转换过程会按顺序查找,并使用第一个不为空的值。
在 Model->JSON 的过程中:如果一个属性对应了多个 JSON Key(Key path),那么转换过程仅会处理第一个 JSON Key(Key path);如果多个属性对应了同一个 JSON Key,则转换过程会使用其中任意一个不为空的值。
Model 包含其他 Model
@interface Condition : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign) NSInteger code;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *icon;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *text;
@end@interface CurrentWeather : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign) NSInteger cloud;
@property (nonatomic, strong) Condition *condition;
@property (nonatomic, assign) CGFloat temp_c;
@property (nonatomic, assign) CGFloat humidity;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *last_updated;
@end
容器类属性
@interface ForecastDay : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *date;
@property (nonatomic, strong) Astro *astro;
@property (nonatomic, strong) Day *day;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray<HourWeather *> *hour;
@end
@implementation ForecastDay
+ (NSDictionary *)modelContainerPropertyGenericClass {return @{@"hour" : [HourWeather class]};
}
@end
这里我们需要调用一下+ (NSDictionary *)modelContainerPropertyGenericClass这个方法,这个方法是让我们的NSArray或者NSSet这些容器知道里面的存储的元素是什么对象。
这里我们可以看到这里的数组里面存储的也是一个Model,所以我们在这个方法里面给他一个字典让这个属性对应Model的这个class,所以我们就可以让他进行一个Model的解析了。下面给出网络请求和YYModel数据结合
#import "ViewController.h"
#import <AFNetworking/AFNetworking.h>
#import "Model.h"
@interface ViewController ()@end@implementation ViewController- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];NSDictionary *cityDict = @{@"name": @"西安"};[self searchWearth:cityDict];
}
- (void) searchWearth: (NSDictionary *) city {NSString *cityName = city[@"name"];if (cityName.length == 0) {return;}NSString *apiKey = @"8950a91429864a60a7b105904252508";NSString *encodeQuery = [cityName stringByAddingPercentEncodingWithAllowedCharacters:[NSCharacterSet URLHostAllowedCharacterSet]];NSString *urlStr = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"https://api.weatherapi.com/v1/forecast.json?key=%@&q=%@&lang=zh&days=7", apiKey, encodeQuery];AFHTTPSessionManager *manager = [AFHTTPSessionManager manager];manager.requestSerializer = [AFJSONRequestSerializer serializer];[manager GET:urlStr parameters:nil headers:nil progress:nil success:^(NSURLSessionDataTask * _Nonnull task, id _Nullable responseObject) {if (![responseObject isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) {return;}NSDictionary *JSONDict = responseObject;WeatherResponse *response = [WeatherResponse yy_modelWithDictionary:JSONDict];
// NSLog(@"当前最高温度: %.1f, 天气: %@", response.current.temp_c, response.current.condition.text);
// NSLog(@"back JSON Task %@", responseObject);NSLog(@"%@", JSONDict);NSLog(@"%@", response.forecast.forecastday);} failure:^(NSURLSessionDataTask * _Nullable task, NSError * _Nonnull error) {NSLog(@"请求失败%@", error);}];
}@end下面是打印结果
("<ForecastDay: 0x600000c3c510>","<ForecastDay: 0x600000c3d110>","<ForecastDay: 0x600000c3d260>"
)
这里显示地址的原因是
- 打印数组时,NSArray 内部默认调用每个对象的 -description 方法。
- 如果模型类(ForecastDay)里没有重写 -description 方法,就只会显示 类名 + 内存地址(也就是你现在看到的效果)。
黑名单与白名单
@interface User
@property NSString *name;
@property NSUInteger age;
@end@implementation Attributes
// 如果实现了该方法,则处理过程中会忽略该列表内的所有属性
+ (NSArray *)modelPropertyBlacklist {return @[@"test1", @"test2"];
}
// 如果实现了该方法,则处理过程中不会处理该列表外的属性。
+ (NSArray *)modelPropertyWhitelist {return @[@"name"];
}
@end
-
避免无用属性被解析
有时模型里会有一些临时字段(比如缓存数据、运行时状态),它们并不来自 JSON,也不应该写回 JSON。
可以把这些属性加到 黑名单,YYModel 就不会去管它们。
-
提高安全性
如果后台返回了额外字段,而你的模型刚好有同名属性,可能会被覆盖。
用 白名单限制只解析你关心的属性,就不会意外污染数据。
上面是黑白名单的作用
