洞察未来:Temporal.io 如何赋能复杂模拟引擎的韧性与智能
引言:在分布式系统的迷雾中寻找确定性
在当今瞬息万变的数字化世界,构建能够长时间运行、处理复杂业务逻辑、并能从各种故障中优雅恢复的分布式应用程序,是每一个技术团队的终极挑战。传统的编程模型往往像在流沙上建造城堡——每当服务重启、网络波动、或者第三方API抽风,我们精心构建的逻辑链条就可能瞬间崩塌,留下半成品的数据、不一致的状态,以及用户体验的断裂。特别是在需要模拟复杂、长时间运行的智能体交互,甚至涉及多轮迭代、用户干预的系统(比如我们即将深入探讨的“昆仑镜”项目)中,这种脆弱性被无限放大。
想象一下以下场景:
- 一个电商平台的用户下单流程,涉及库存扣减、支付、物流通知、积分赠送等十几个步骤,其中任何一步都可能因为外部系统缓慢或失败而卡住。如果你只是简单地使用消息队列,如何确保所有步骤要么全部成功,要么全部回滚?如何处理长达数小时的支付等待?
- 一个金融风险评估系统,需要从多个数据源拉取数据,进行复杂的模型计算,然后人工审批,整个过程可能跨越数天。期间服务器可能重启多次,模型迭代升级。如何确保评估过程不中断、状态不丢失?
- 在AI领域,训练一个复杂的模型可能耗时数小时甚至数天,如果训练过程中计算节点故障,如何从上一个检查点精确恢复,而不是从头再来?
这些场景的共同特点是:长时间运行、有状态、业务逻辑复杂、对容错性要求极高。 面对这些挑战,我们迫切需要一种新的分布式编程范式,一种能够让我们像编写普通的单体应用一样,编写这些复杂、有状态的分布式业务流程,而无需深陷底层分布式系统复杂性的泥潭。
这就是 Temporal.io 横空出世的原因。它不仅仅是一个框架,更是一个 可靠的应用编排引擎,其核心理念是提供 持久化工作流(Durable Workflows)。它将分布式系统的“魔鬼细节”抽象化,让开发者可以专注于业务逻辑本身,而由Temporal来保证程序的“时间旅行”能力和“永生不死”的韧性。
1. Temporal.io 是什么?—— 持久化工作流的奥秘
Temporal.io 是一个开源的、可靠的应用编排引擎,常被称为“持久化工作流引擎”或“状态编排器”。它的核心目标是赋能开发者,让他们能够轻松地编写和运行长时间运行、复杂、有状态且容错的分布式应用程序,而无需担心底层的分布式系统复杂性。
核心思想:像编写普通代码一样编写分布式系统。
传统的分布式系统开发往往意味着大量的样板代码:消息队列的管理、重试逻辑、幂等性处理、状态持久化、并发控制、超时处理、分布式锁等等。这些底层细节不仅令人头疼,而且极易出错,导致系统脆弱。
Temporal 的出现,旨在颠覆这种现状。它通过以下方式实现了这一目标:
- 将复杂业务流程抽象为“工作流”(Workflows): 你可以将一个业务流程(例如,用户注册后的欢迎流程)编码为一个普通的函数。这个函数可以包含顺序执行的步骤、条件判断、循环、甚至等待外部事件(如用户点击邮件链接)的能力。
- 确保工作流的“持久化”和“容错性”: 一旦一个工作流被启动,Temporal Server 将负责其状态的持久化、并在任何故障发生时(如Worker崩溃、网络分区、数据库宕机),能够从上次中断的地方精确恢复,继续执行。这就像给你的程序赋予了“时间旅行”和“不死之身”的能力。
- 提供强大的编程抽象: Temporal 提供了高层次的编程抽象(如Workflow和Activity),让开发者可以用自己熟悉的语言(Go, Java, Python, TypeScript/JavaScript, PHP, Ruby)编写业务逻辑,而无需直接与消息队列、数据库或分布式协调服务打交道。
一个比喻:
想象你正在写一部史诗级的电影剧本,其中包含无数场景、角色、对话和复杂的时间线。
- 传统方式: 你每次只能写一小段,写完一个场景就得立即保存,担心电脑突然死机文字丢失。剧组人员也得时刻在线,一旦有人离开或设备故障,整个拍摄进度都得重新协调。如果你想检查某个特定时间的剧本状态,你可能需要翻阅一大堆草稿和会议记录。
- 有了Temporal: 你可以像写一个连贯的故事一样,一口气写完整个剧本。Temporal就像一个超级大脑和记录员,它会默默地为你记录下剧本的每一个字、每一个场景的变化(事件溯源/Event Sourcing)。无论你的电脑突然断电,还是剧组成员因为各种原因暂时离线,当他们回来时,Temporal都能精确地告诉你现在正在拍摄哪一幕,台词是什么,甚至能“回放”整个拍摄过程,让你随时了解剧本走到哪一步了。你还可以随时暂停拍摄(Pause Workflow),等待特定演员到位(Wait for Signal),甚至可以“快进”到某个关键情节(Conditional Logic / Signal handling)。
Temporal 就是这个负责确保你的“剧本”(Workflow)能够可靠且完整地被“拍摄”(执行)到底的超级大脑。它把分布式系统的各种恼人问题(如状态管理、故障恢复、超时、重试、并发、版本兼容)都隐藏在幕后,让你能够专注于创作(业务逻辑实现)。
2. Temporal.io 的核心概念:构建持久化系统的基石
要深入理解 Temporal,我们需要掌握其几个核心概念。它们共同构成了一个强大、灵活且高度容错的分布式应用编排框架。
2.1. Workflow (工作流)
Workflow 是 Temporal 中最核心的抽象,代表了一个端到端的业务流程。它是一个具有确定性、长时间运行、有状态且能从失败中恢复的程序。
核心特性:
-
确定性 (Determinism):
- 含义: Workflow 代码必须是确定性的。这意味着给定相同的输入和事件历史,Workflow 逻辑在任何 Worker 上的执行(重放)结果都必须完全一致。你不能在 Workflow 代码中直接使用随机数生成器、获取当前时间、发起网络请求或访问文件系统等非确定性操作。
- 为什么重要? Temporal 通过“事件溯源”(Event Sourcing)和“重放”(Replay)机制来保证 Workflow 的持久性和容错性。当 Worker 需要恢复 Workflow 状态或执行新指令时,Temporal Server 会将 Workflow 的完整事件历史发送给 Worker。Worker 接收到历史事件后,会从头开始重放 Workflow 代码,直到达到最新的状态。如果代码不确定,重放就会产生不同的结果,导致状态不一致和逻辑错误。
- 如何实现确定性? Temporal SDK 提供了
workflow包中一系列确定性的 API (如workflow.Now(),workflow.GetRandomKey(),workflow.ExecuteActivity(),workflow.Sleep()) 来替代非确定性的标准库函数。所有外部副作用(如数据库写入、API调用)都必须封装在 Activity 中。
-
持久性 (Durability):
- Workflow 的所有本地变量和状态都是持久化的。无论 Worker 进程崩溃、机器重启、网络中断,Workflow 的执行状态(包括当前正在执行的步骤、所有局部变量的值等)都会被 Temporal Server 自动保存和恢复。当 Worker 重新上线时,Workflow 会从上次中断的地方精确无缝地恢复执行。
- 这通过 Server 存储 Workflow 的事件历史来实现。每个 Workflow 命令(如调用 Activity, 创建 Timer, 完成 Activity)都会作为事件记录下来。
-
长时间运行 (Long-Running):
- Workflow 可以运行数分钟、数小时、数天、数月甚至数年。Temporal Server 会在 Workflow 处于等待状态时(例如等待 Activity 完成、等待定时器到期、等待外部信号),消耗极少的资源。
- 它不像传统线程那样在等待时占用内存和CPU,而是将Workflow的执行权交还给Server,一旦有事件驱动,Server通知Worker,Worker再恢复Workflow。
-
容错性 (Fault-Tolerant):
- Workflow 能够自动从各种故障中恢复,包括 Worker 崩溃、网络分区、Temporal Server 节点故障等。Temporal 会自动处理重试 Activity、恢复 Workflow 状态等底层复杂逻辑。
-
编程模型 (Programming Model):
- Workflow 函数本质上是一个普通的程序,可以包含循环、条件判断、变量声明、函数调用等。但这些函数调用都必须通过 Temporal SDK 提供的确定性API来完成。
- Workflow 函数不能直接执行 I/O 操作,所有 I/O 都必须委托给 Activity。
Workflow 的状态与生命周期:
- Run ID: 每次 Workflow 执行都会有一个唯一的 Run ID。
- Workflow ID: 一个业务实体(如用户ID、订单ID)通常对应一个唯一的 Workflow ID,可以被多次执行(不同 Run ID)。
- Open (运行中): Workflow 正在执行或等待某个事件。
- Completed (完成): Workflow 成功执行完毕。
- Failed (失败): Workflow 执行过程中遇到无法恢复的错误。
- Canceled (取消): Workflow 被外部请求取消。
- Terminated (终止): Workflow 被外部强制终止。
- ContinuedAsNew (继续为新): Workflow 将其当前状态传递给一个新的 Workflow 实例,然后当前实例终止。这用于处理非常长的链式 Workflow,避免历史事件过大。
2.2. Activity (活动)
Activity 是 Workflow 中执行实际业务逻辑(即具有副作用的非确定性操作)的最小单元。如果说 Workflow 负责“编排”,那么 Activity 就是负责“执行”。
核心特性:
-
非确定性 (Non-Deterministic OK):
- Activity 代码可以包含任何标准的、非确定性的操作,如数据库读写、API 调用、文件操作、随机数生成、获取当前系统时间等。这是因为 Activity 的执行结果会被记录在 Workflow 的事件历史中,Workflow 的重放只需要依赖这些已记录的结果,而非重新执行 Activity 本身。
- 这使得 Activity 成为与外部系统交互的理想场所。
-
重试和超时 (Retries and Timeouts):
- Temporal 提供了强大的重试机制。你可以为 Activity 配置重试策略,包括失败次数上限、重试间隔、指数退避等。当 Activity 执行失败(例如,外部 API 请求超时)时,Temporal 会根据策略自动重试,无需在 Activity 代码中手动编写重试逻辑。
- Deadlock Detection (死锁检测): Activity 可以设置三种超时机制:
StartToCloseTimeout: Activity 从调度时刻到完成(成功或失败)的最长时间。ScheduleToStartTimeout: Activity 从被调度到 Worker 开始执行的最长时间(处理 Worker 不可用或 Task Queue 拥堵情况)。HeartbeatTimeout: 如果 Activity 是长时间运行的(例如处理一个大文件),它可以定期向 Temporal Server 发送“心跳”信号。如果 Worker 在HeartbeatTimeout规定时间内没有发送心跳,Temporal 会认为 Activity 失败并进行重试。这可以有效检测 Worker 进程在执行期间的崩溃。
-
幂等性 (Idempotency):
- 由于 Activity 可能会被重试,因此设计 Activity 时需要考虑幂等性。即多次执行同一个 Activity 及其输入,其结果应与执行一次相同,且不会产生额外的副作用。
- 例如,一个扣款 Activity,在重试时如果无法保证幂等,可能会导致重复扣款。通常结合数据库事务ID或业务ID来实现幂等。
-
隔离性 (Isolation):
- 每个 Activity 作为一个独立的任务被 Worker 执行,其执行上下文与 Workflow 隔离。
-
异步性和并发性 (Asynchronous and Concurrency):
- Workflow 可以异步调度多个 Activity,并等待它们全部完成(fan-out/fan-in 模式)。Temporal Server 会管理这些并发 Activity 的生命周期。
何时使用 Activity:
- 与数据库进行读写交互。
- 调用外部服务(REST API, RPC)。
- 发送邮件、短信。
- 执行耗时且可能失败的计算任务。
- 任何具有副作用或非确定性的操作。
2.3. Worker (工作者)
Worker 是 Temporal 架构的执行单元。它是一个独立的进程,负责托管并执行 Workflow 和 Activity 代码。
核心功能:
- 轮询任务队列 (Poll Task Queues): Worker 不断从 Temporal Server 的特定 Task Queue 中拉取任务。任务可以是 Workflow Task(用于驱动 Workflow 状态机)或 Activity Task(用于执行 Activity)。
- 执行 Workflow 和 Activity (Execute Workflows and Activities): 当 Worker 接收到任务后,它会在本地的 JVM/Go Runtime/Node.js Runtime 上执行相应的 Workflow 或 Activity 函数。
- 向 Server 报告结果 (Report Results to Server): Worker 完成任务后,将结果(例如 Activity 的返回值、Workflow 的下一个命令)报告回 Temporal Server。
核心特性:
- 高度可扩展性 (Scalability): 你可以启动任意数量的 Worker 进程,它们可以运行在不同的机器、容器或 Pod 中。Temporal Server 会自动在所有轮询同一 Task Queue 的 Worker 之间负载均衡任务。
- 语言无关性 (Language Agnostic): Temporal 提供了多种语言的 SDK,意味着你可以用 Go Worker 执行 Go Workflow 和 Activity,用 Java Worker 执行 Java Workflow 和 Activity。甚至不同语言的 Worker 可以共同处理同一个 Task Queue 中的任务(如果任务定义兼容)。
- 无状态 (Stateless for a given execution): Worker 本身是无状态的(在处理单个 Workflow 或 Activity 任务时,它会从 Server 获取所有必要的信息,并在处理完毕后释放这些信息)。这意味着 Worker 可以随时停止、重启或替换,而不会影响正在运行的 Workflow 的状态。
- 版本管理 (Versioning): Worker 可以注册不同版本的 Workflow/Activity 代码。Temporal 提供了机制(如 Sticky Task Queues, Build ID based versioning)来确保正在运行的 Workflow 继续由兼容其版本的 Worker 来处理。
2.4. Task Queue (任务队列)
Task Queue 是 Temporal Server 用来连接 Workflow/Activity 任务生产者和 Worker 执行者的逻辑队列。它是一个轻量级的、多租户的机制,用于任务的负载均衡和路由。
核心特性:
- 解耦 (Decoupling): Task Queue 解耦了任务的产生(由 Workflow 或 Temporal Server)和任务的消费(由 Worker)。Workflow 不需要知道哪个 Worker 会执行特定的 Activity,只需要将其发送到某个 Task Queue。
- 负载均衡 (Load Balancing): 多个 Worker 可以同时轮询同一个 Task Queue。Temporal Server 会将任务均匀地分发给可用的 Worker,实现自动的负载均衡。
- 路由 (Routing): 你可以创建不同的 Task Queue,将特定类型的 Workflow 或 Activity 任务路由到专门的 Worker 组。例如,一个 Task Queue 用于 CPU 密集型任务,另一个用于 I/O 密集型任务。
- 命名 (Naming): Task Queue 只是一个字符串名称。它的存在是按需的,当有任务发布到某队列或 Worker 轮询某队列时,该队列即“出现”。
- Sticky Task Queue (粘性任务队列): Worker 可以维护最近访问的 Workflow 的本地缓存。这允许 Worker 在短时间内“粘性”地处理同一个 Workflow 的任务,减少与 Server 的网络往返,提高效率。这对于 Workflow 的重放尤其重要。
2.5. Client (客户端)
Client 是你应用程序中与 Temporal Server 交互的部分。它允许你启动、查询、发送信号、取消或终止 Workflow。
核心功能:
- 启动 Workflow (Start Workflow): Client 是 Workflow 执行的入口点。你可以通过 Client 调用
StartWorkflow来启动一个新的 Workflow 实例,并传递初始输入参数。 - 查询 Workflow (Query Workflow): Workflow 可以在运行时暴露内部状态,供 Client 查询。这是一种同步、非变更的操作,常用于获取 Workflow 的最新进度或结果。
- 发送信号到 Workflow (Signal Workflow): Signal 是一种异步、外部触发的事件,用于向正在运行的 Workflow 发送数据或指令。Workflow 可以定义 Signal 处理函数来响应该事件。例如,一个订单 Workflow 在等待用户支付时,可以接收一个“支付成功”的 Signal。
- 取消 Workflow (Cancel Workflow): Client 可以请求取消 Workflow。Workflow 内部可以捕获取消请求,并执行清理操作,然后优雅地退出。
- 终止 Workflow (Terminate Workflow): Client 可以强制性地终止 Workflow。这是一种不推荐的粗暴操作,Workflow 不会执行任何清理工作,直接停止。
- 查看 Workflow 状态 (Observe Workflow State): Client 可以使用 Temporal CLI 或 Temporal Web UI 查看 Workflow 的历史事件、当前状态和日志。
2.6. Temporal Server (服务端)
Temporal Server 是整个 Temporal 系统的核心大脑和持久性层。它负责存储 Workflow 的状态、调度任务、管理 Worker、处理故障恢复等。
核心组件 (高层视图):
- Frontend Gateway (前端网关): 接收所有来自 Client 和 Worker 的 RPC 请求(如启动 Workflow、完成 Activity、轮询任务等)。它执行认证、授权、速率限制等功能,并将请求路由到内部服务。
- History Service (历史服务): 这是 Temporal Server 的核心。它存储每个 Workflow 实例的完整事件历史。当 Worker 需要“重放”Workflow 代码时,History Service 就提供这些历史事件。它还负责管理 Workflow 的状态和定时器。
- Matching Service (匹配服务): 负责将任务匹配给可用的 Worker。当 Workflow 调度一个 Activity 或 Workflow Task 时,它会将其放入 Matching Service 管理的 Task Queue 中。Matching Service 会轮询注册到该 Task Queue 的 Worker,并将任务推送到这些 Worker。
- Worker Service (Worker 服务 - 仅在少数部署中出现,通常指的是 Server 内部的 worker): 在某些特定的部署架构中(例如,当 Server 负载很高或需要执行一些内部管理任务时),Server 内部也可能包含一些 Worker 角色。但通常我们讨论的 Worker 是指运行你业务代码的外部 Worker 进程。
- Persistence Layer (持久层): Temporal Server 将所有 Workflow 状态和事件历史持久化到数据库中。支持 PostgreSQL, MySQL, Cassandra 等。这是实现 Workflow 持久性和容错性的关键。
- Visibility Service (可见性服务): 提供 Workflow 的查询和列表功能,支持 Temporal Web UI 和 CLI。
核心机制:
- 事件溯源 (Event Sourcing): Workflow 的每一次状态变更(如 Activity 启动、Activity 完成、定时器触发)都被记录为一个不可变的事件,按时间顺序存储。Workflow 的当前状态可以通过重放这些事件来重建。
- 重放 (Replay): 当 Worker 处理 Workflow Task 时,会从头开始重放 Workflow 的事件历史,直到达到当前最新状态。这确保了在任何 Worker 上都能精确地恢复 Workflow 的状态。
- 隔离性 (Isolation): Temporal Server 与业务逻辑的 Worker 是完全隔离的。Server 负责协调,Worker 负责执行,两者互不影响。
扩展性与可用性:
Temporal Server 被设计为高度可扩展和高可用。每个核心组件都可以独立扩展。通过多个 Server 节点和持久化层的数据复制,Temporal 可以抵抗单个节点或组件的故障,确保 Workflow 的持续运行。
2.7. 其他重要概念
- Namespace (命名空间): 类似于多租户的概念。每个 Workflow 都运行在一个特定的 Namespace 中。Namespace 提供了逻辑隔离,不同的团队、项目或环境可以使用不同的 Namespace 来部署他们的 Workflow,互不干扰。这类似于 Kubernetes 的 Namespace。
- Timer (定时器): Workflow 可以设置定时器来等待一段时间后继续执行。例如
workflow.Sleep(duration)。Timer 是异步且持久化的。即使 Timer 到期时 Worker 不在线,Server 也会在 Worker 重新上线时触发 Workflow 继续执行。 - Child Workflow (子工作流): 一个 Workflow 可以启动另一个 Workflow 作为其子 Workflow。父 Workflow 可以等待子 Workflow 完成,并获取其结果。子 Workflow 具有自己的生命周期、事件历史和 ID。这对于构建模块化、可组合的复杂业务流程非常有用。
- ContinueAsNew (继续为新): 当一个 Workflow 运行时间过长,导致其事件历史非常庞大时,可以通过
workflow.ContinueAsNew来“重置”Workflow 的历史。它会启动一个新的 Workflow 实例,将当前 Workflow 的状态作为输入传递给新实例,然后旧实例完成。这有效地避免了单个 Workflow 历史过大带来的性能问题。 - Version (版本): Temporal 提供了 Workflow 和 Activity 代码版本管理的机制。
workflow.GetVersion允许 Workflow 在代码更新时,根据 Workflow 的运行历史,选择执行旧逻辑还是新逻辑,确保正在运行的 Workflow 实例不受代码变更影响,实现无中断的代码部署。
3. Temporal.io 在“昆仑镜”项目中的应用:从构想到现实的复杂模拟
在“昆仑镜”项目中,PRD (产品需求文档) 和 TSD (技术设计文档) 都明确指出,模拟过程将是一个复杂、长时间运行、需要精确控制和状态管理的任务。它不仅仅是一次性的计算,更需要支持多轮辩证循环,并且用户能够实时监控、介入控制(暂停、恢复、终止,甚至“快进”)。
让我们具体看看 Temporal 如何解决“昆仑镜”项目面临的挑战。
“昆仑镜”项目核心需求与挑战复盘:
-
PRD F-2.1 (综合引擎): 要求模拟能执行多轮辩证循环,支持暂停、恢复、终止和“快进”。
- 挑战:
- 长生命周期与状态持久化: 模拟可能跑几个小时甚至几天,如果服务器重启,所有状态(当前轮数、所有智能体状态、产生的假设和批判等)都会丢失。如何保证状态不丢失?
- 复杂流程编排: 多轮辩证,每轮内部又包含多个步骤(分析问题、提出假设、批判假设、评估结果)。如何清晰、可靠地编排这些复杂的顺序和并行逻辑?
- 外部控制点: 用户需要能实时“暂停”、“恢复”、“终止”模拟,甚至根据某种条件“快进”到下一个关键阶段。如何实现这些强大的外部控制能力?
- 容错性: 模拟过程中可能会调用各种外部AI服务、知识图谱API、数据存储。这些外部服务可能不稳定,如何处理它们的失败并自动重试?
- 挑战:
-
TSD P-2.3 (模拟状态与进度): 要求能够实时查看模拟的当前状态、已完成轮数、当前正在进行的步骤,以及生成的中间结果。
- 挑战:
- 实时可见性: 如何在不影响模拟性能的前提下,实时向外部系统暴露模拟的内部运行状态?
- 数据一致性: 确保报告的进度与实际模拟状态严格一致。
- 挑战:
-
TSD P-2.4 (数据持久化): 模拟过程中所有重要的中间结果和最终结果都需要持久化存储。
- 挑战:
- 事务性数据写入: 当模拟引擎产生新的假设或批判时,需要原子性地写入数据库。如果写入失败,如何处理?
- 数据量: 长时间运行的模拟可能会产生大量中间数据,如何高效持久化?
- 挑战:
如果直接用 Go 的 Goroutine、简单的状态机或消息队列组合来实现,会面临以下严峻挑战:
-
状态持久化 (State Persistence):
- 传统方案的痛点: Goroutine 崩溃或宿主机重启,内存中的所有状态即刻丢失。手动将所有中间状态频繁写入数据库会引入大量样板代码,影响性能,且极难保证写入的原子性与一致性。
- Temporal 如何解决:
SimulationWorkflow的内部状态(如当前轮数、所有智能体状态、产生的假设和批判的列表等)会自动被 Temporal Server 使用事件溯源机制持久化。无论 Worker 进程发生什么故障,只要有 Worker 重新上线并轮询相应的 Task Queue,Temporal 就能让 Workflow 从上次中断的地方精确恢复,无需任何手动 checkpointing 或恢复逻辑。 - “昆仑镜”例子: 在
SimulationWorkflow中,你可以定义一个 Go structSimulationContext包含CurrentRound,AgentStates,GeneratedHypotheses,Critiques等字段。当 Workflow 代码读取或更新这些字段时,Temporal 会自动将这些操作记录为事件。即便 Worker 重启,这些字段的值也会在重放 Workflow 历史时被重建。
-
错误处理与重试 (Error Handling and Retries):
- 传统方案的痛点: 调用外部 AI 服务(如 LLM API)或知识图谱查询可能因为网络波动、服务过载而失败。手动编写复杂的重试逻辑(指数退避、熔断)会污染业务代码,且难以统一管理。
- Temporal 如何解决: 将所有与外部服务交互的代码封装在 Activity 中(例如
AnalyzeIssueActivity,ProposeHypothesisActivity,IntegrateKnowledgeGraphActivity,StoreDecisionActivity)。Temporal 允许你为每个 Activity 定义强大的重试策略(例如最大尝试次数、初始延迟、最大延迟、退避乘数、特定错误不重试、心跳机制)。当 Activity 执行失败时,Temporal Server 会自动按照配置进行重试,大大简化了容错代码。 - “昆仑镜”例子:
ProposeHypothesisActivity调用 LLM 生成假设。如果 LLM API 返回 5xx 错误或连接超时,Activity 会自动根据预设策略(例如重试 5 次,每次间隔逐倍增加)进行重试。AnalyzeIssueActivity可能会因为处理复杂文本而耗时较长。通过设置HeartbeatTimeout,Worker 可以定期向 Server 发送心跳。如果 Activity 进程在长时间运行时崩溃,Server 会检测到心跳丢失,然后将该 Activity 标记为失败并调度重试到另一个 Worker。
-
长时间运行与资源效率 (Long-Running & Resource Efficiency):
- 传统方案的痛点: Goroutine 会一直占用内存和 CPU,即使它在等待外部事件或定时器。大量长时间运行的 Goroutine 会消耗大量系统资源。
- Temporal 如何解决: Workflow 在等待外部事件(如 Activity 完成、定时器到期、Signal 到来)时,会将其执行状态持久化到 Server,然后 Worker 进程可以释放当前 Workflow 的内存资源去处理其他任务。只有当外部事件触发时,Temporal Server 才会通知 Worker 唤醒 Workflow,重新加载历史并继续执行。这使得 Workflow 能够以极低的资源消耗长时间运行。
- “昆仑镜”例子: 模拟过程中,
SimulationWorkflow可能在等待一个定时器(例如,每隔 N 分钟检查一次模拟进度),或者等待用户发送的“恢复”信号。在这些等待期间,Worker 只需要占用极小的资源来轮询 Task Queue,而不会一直占用 CPU。
-
精确控制与用户交互 (Precise Control & User Interaction):
- 传统方案的痛点: 实现“暂停”、“恢复”、“终止”这类细粒度的外部控制会非常复杂,需要共享内存、通道通信或分布式协调服务,且难以保证一致性。
- Temporal 如何解决:
- 暂停/恢复: Workflow 可以使用
workflow.Sleep或workflow.Await结合workflow.GetSignalChannel来实现等待外部信号。当用户通过客户端发起“暂停”操作时,客户端发送PauseSignal。Workflow 接收到信号后,进入睡眠状态或等待另一个ResumeSignal。 - 终止: 客户端可以直接调用
TerminateWorkflow强制停止。更优雅的方式是发送一个CancelSignal,Workflow 内部捕获workflow.Is Canceled来执行清理操作并退出。 - 快进: Workflow 可以接收一个
FastForwardSignal,其中包含目标轮数或跳过的阶段。Workflow 内部逻辑根据此信号调整循环条件或跳过某些子 Workflow/Activity 的执行。
- 暂停/恢复: Workflow 可以使用
- “昆仑镜”例子:
SimulationWorkflow内部可以有一个workflow.GetSignalChannel来监听PauseSignal和ResumeSignal。当PauseSignal到来时,Workflow 进入一个循环,sleep短暂时间,然后检查ResumeSignal是否到来。FastForwardSignal可以携带targetRoundNumber。Workflow 在每次辩证循环开始前检查if currentRound < targetRoundNumber,如果成立,则continue到下一轮,直到达到目标轮数,从而跳过中间的详细处理。或者,更复杂地,通过workflow.ContinueAsNew携带简化模式的参数。
-
实时可见性与可观测性 (Real-time Visibility & Observability):
- 传统方案的痛点: 实时获取复杂流程的当前进度和状态通常需要建立复杂的日志聚合、指标监控和查询系统,并且状态可能不一致。
- Temporal 如何解决:
- Query Capabilities: Workflow 可以定义 Query Handler,允许客户端在 Workflow 运行时同步查询其内部状态。这是一个轻量级的读操作,不会改变 Workflow 状态,非常适合实时监控。
- Event History: Temporal Server 完整记录了 Workflow 的所有事件历史,可以通过 Temporal Web UI 或 CLI 方便地进行审计和调试。
- Metrics: Temporal Server 和 SDK 都会暴露大量 Prometheus/Grafana 兼容的指标,可以用于监控系统健康、性能和 Workflow 瓶颈。
- “昆仑镜”例子:
- 用户界面可以通过查询
SimulationWorkflow来获取currentRound,progressPercentage,latestHypothesis,timeElapsed等信息,满足 P-2.3 实时状态显示的需求。 - Ops 团队可以通过 Temporal Web UI 查看每个模拟实例的事件历史,了解某个模拟为何卡住,或某个 Activity 失败重试了多少次。
- 通过 Temporal 的指标监控,可以追踪平均模拟时长、Activity 失败率、Worker 负载等关键性能指标。
- 用户界面可以通过查询
-
可扩展性与弹性 (Scalability & Elasticity):
- 传统方案的痛点: 随着模拟数量的增加,如何弹性地扩展计算资源?Goroutine 的水平扩展需要手动管理。
- Temporal 如何解决: Worker 是无状态的,可以根据负载需要随时启动或关闭任意数量的 Worker 进程。Temporal Server 会自动在所有 Worker 之间进行任务负载均衡。这意味着你可以根据模拟任务的并发量,轻松地扩展 Worker 组,实现弹性伸缩。
- “昆仑镜”例子: 当有大量用户同时启动模拟时,可以自动增加承载
SimulationWorkflow和Activity的 Worker 实例数量,它们会自动注册到相应的 Task Queue 并开始处理任务,无需任何复杂配置。
基于 Temporal 的深度集成:
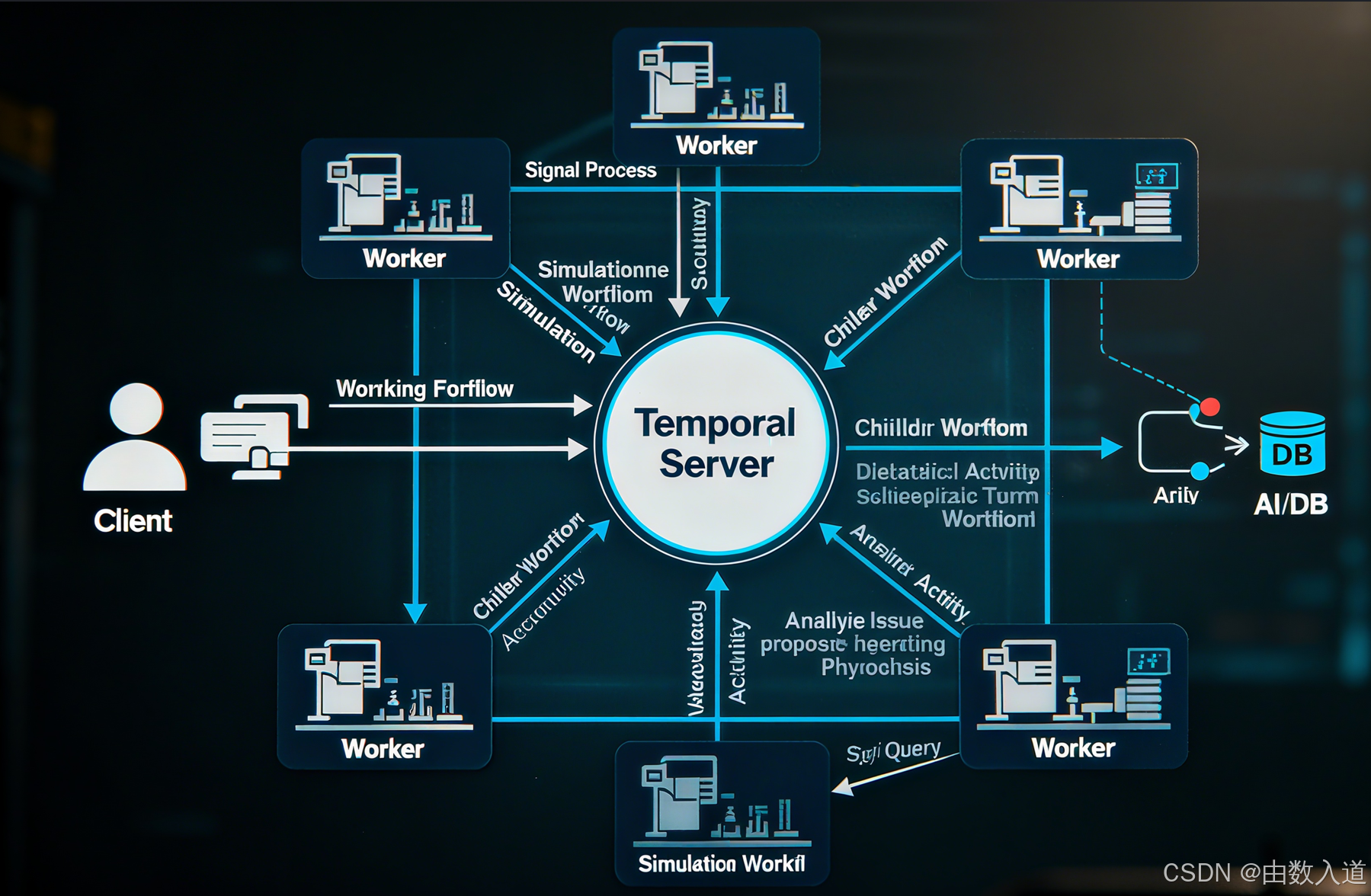
我们将定义一个父级工作流 SimulationWorkflow 来管理整个模拟生命周期,并使用子工作流 DialecticalTurnWorkflow 来处理每一轮的辩证过程。各个与外部 AI 服务和数据存储的交互则封装为 Activity。
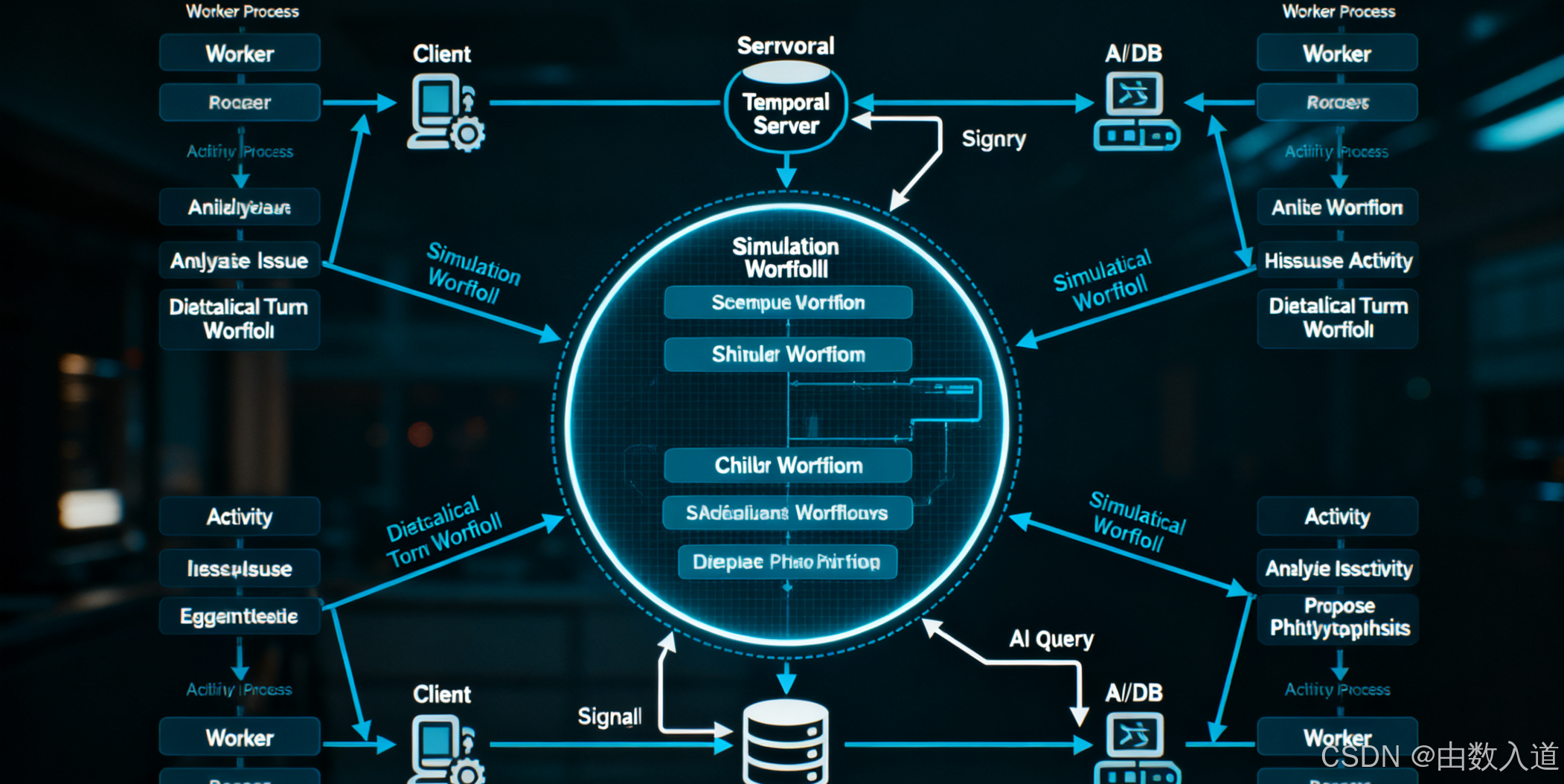
-
顶层工作流:
SimulationWorkflow- 职责: 管理整个模拟会话的生命周期。
- 输入: 模拟初始化参数(例如,初始问题、参与智能体配置、最大轮数)。
- 内部状态:
CurrentRound(当前轮数),AllHypotheses(所有已生成的假设),AllCritiques(所有已提出的批判),AgentStatus(各智能体状态),SimulationGlobalConfig(全局配置)。这些状态在 Workflow 代码中声明为变量,由 Temporal 自动持久化。 - 核心逻辑:
- 初始化模拟环境。
- 主循环:
for round := 1; round <= MaxRounds; round++ { ... }- 在每轮开始前,检查
FastForwardSignal或PauseSignal。 - 启动
DialecticalTurnWorkflow作为子工作流,处理当前轮次的辩证。 - 等待子工作流完成,获取本轮结果。
- 更新
AllHypotheses,AllCritiques等全局状态。 - 通过
workflow.UpsertSearchAttributes更新可见性属性,方便在 UI 中按进度查询。
- 在每轮开始前,检查
- 模拟结束,生成最终报告 (调用
GenerateFinalReportActivity)。
- 控制与交互:
- Query (查询): 提供
GetSimulationStatusQuery 处理函数,允许外部(如 UI)查询CurrentRound,latestHypothesis,progressPercentage,overallStatus。 - Signal (信号):
PauseSignal: 接收到后,Workflow 进入workflow.Await(func() bool { return isResumed })状态,直到ResumeSignal收到。ResumeSignal: 设置isResumed = true,解除暂停。FastForwardSignal(targetRound int): Workflow 记录targetRound,在循环中跳过中间的DialecticalTurnWorkflow执行,直到达到targetRound或超出。OverrideAgentParamSignal(agentID string, newConfig map[string]string): 允许在运行时动态调整某个智能体的行为参数。Workflow 接收到信号后,更新AgentStatus中的对应配置,后续的子工作流实例化时会使用新配置。
- Cancellation (取消): 客户端可以请求取消。Workflow 内部捕获
workflow.IsCanceled()在循环中优雅退出,执行一些清理 Activity (如CleanupTempResourcesActivity)。
- Query (查询): 提供
-
子工作流:
DialecticalTurnWorkflow- 职责: 负责单一轮次的辩证循环,将复杂过程分解。
- 输入:
RoundNumber、CurrentIssueContext、ExistingKnowledgeBase、AgentConfiguration。 - 输出:
RoundSummary(本轮产生的假设、批判、评估结果)。 - 核心逻辑:
- 调用
AnalyzeIssueActivity:分析当前问题上下文,调用外部知识图谱或 LLM 识别关键要素。 - 调用
ProposeHypothesisActivity:基于分析结果,由假设生成智能体调用 LLM 提出新的假设。 - 调用
CritiqueHypothesisActivity(并行执行): 多个批判智能体并行调用 LLM 对提出的假设进行批判。 - 调用
EvaluateOutcomeActivity:综合假设和批判,评估本轮的进展和结果。 - 调用
StoreRoundResultActivity:将本轮所有数据持久化到数据库。 - 处理 Activity 失败:每个 Activity 都配置了重试策略。例如,如果
ProposeHypothesisActivity调用 LLM 失败,Temporal 会自动重试,直到成功或达到最大重试次数。
- 调用
-
Activities (活动): 这些是与外部世界交互的实际执行单元。
-
AnalyzeIssueActivity(ctx context.Context, input AnalyzeIssueInput) (*AnalyzeIssueOutput, error)- 功能: 调用外部知识图谱服务或专业 LLM,对当前问题域进行深入分析,提取关键概念、关系和潜在矛盾。
- 复杂场景: 外部知识图谱 API 可能会有速率限制或偶尔的 503 错误。
- Temporal 优势: 配置
temporal.ActivityOptions,设置RetryPolicy(例如MaximumAttempts: 5,InitialInterval: time.Second * 5,BackoffCoefficient: 2.0,ExcludeForStatusCodes: []string{"400"})。如果 503 发生,Temporal 会自动指数退避重试;如果是 400 客户端错误,则直接失败。
-
ProposeHypothesisActivity(ctx context.Context, input ProposeHypothesisInput) (*ProposeHypothesisOutput, error)- 功能: 调用大型语言模型 (LLM) 生成新的假设。可能耗时较长。
- 复杂场景: LLM API 请求可能因网络延迟而卡顿,或者 LLM 本身处理时间较长。
- Temporal 优势: 设置
StartToCloseTimeout为较长时间 (例如 10 分钟)。同时,在 Activity 内部使用activity.Get Logger(ctx).Info("sending heartbeat")activity.RecordHeartbeat(ctx, "progress: " + currentStep)定期发送心跳。如果 Activity 进程在 LLM 调用期间因 Worker 崩溃而中断,Server 会检测到心跳丢失,然后重试该 Activity,Worker 会从头开始调用 LLM。
-
CritiqueHypothesisActivity(ctx context.Context, input CritiqueHypothesisInput) (*CritiqueHypothesisOutput, error)- 功能: 调用另一组 LLM(例如,不同专长的智能体)对提出的假设进行批判。
- 复杂场景: 可能会有多个批判智能体并行工作。
- Temporal 优势:
DialecticalTurnWorkflow可以使用workflow.ExecuteActivity的Async模式,同时启动多个CritiqueHypothesisActivity,然后用workflow.GetFutures()聚合所有结果(fan-out/fan-in 模式)。如果其中一个批判智能体返回不可用的结果,其 Activity 失败,Temporal 会自动重试它,不影响其他并行运行的 Activity。
-
EvaluateOutcomeActivity(ctx context.Context, input EvaluateOutcomeInput) (*EvaluateOutcomeOutput, error)- 功能: 基于所有假设和批判,由评估智能体判断本轮模拟的有效性和进展。
- 复杂场景: 可能需要复杂的计算或调用专有内部模型。
- Temporal 优势: 如果计算在 Activity 内部抛出 OOM 错误,Activity 会失败,并根据重试策略重新调度到另一个资源充足的 Worker 上。
-
StoreRoundResultActivity(ctx context.Context, input StoreRoundResultInput) error- 功能: 将本轮模拟的关键结果(假设、批判、评估)持久化到数据库。
- 复杂场景: 数据库写入时可能遇到死锁或短暂的网络故障。需要保证幂等性。
- Temporal 优势:
- 配置
RetryPolicy,处理数据库的瞬态错误。 - Activity 内部应该实现幂等性:例如,使用
RoundNumber和SimulationID作为写入的唯一键进行UPSERT操作,而不是简单的INSERT。这样即使 Activity 被重试多次,也不会导致重复数据。
- 配置
-
GenerateFinalReportActivity(ctx context.Context) (*FinalReportOutput, error)- 功能: 模拟完成后,调用报告生成服务,汇总所有数据,生成最终报告并存储。
- 复杂场景: 报告生成可能需要长时间的聚合计算。
- Temporal 优势: 如果报告服务暂时不可用,Temporal 会自动重试。对于长时间的报告生成,可以和
ProposeHypothesisActivity一样使用心跳机制。
-
“昆仑镜”场景分析:
-
动态代理行为调整:
- 需求: 模拟进行到一半,发现某个智能体的行为不合理,需要调整其参数(例如,批判的严格程度、假设的创新性)。
- Temporal 解决方案:
SimulationWorkflow定义一个OverrideAgentParamSignal。外部管理界面发送带有新参数的Signal。Workflow 收到信号后,更新其内部的AgentConfiguration状态。DialecticalTurnWorkflow在启动下一轮前,从父 Workflow 获取最新的AgentConfiguration,将其作为 Activity 的输入参数传递。这样,无需停止模拟,即可实现动态调整。
-
人机协作模式 (Human-in-the-Loop):
- 需求: 在某些关键决策点,人工专家需要介入审核或提供指导,例如,在某个假设被多个智能体批判后,需要人工确认是否继续深入研究此假设。
- Temporal 解决方案:
- 在
DialecticalTurnWorkflow中,在CritiqueHypothesisActivity之后,调度一个HumanApprovalActivity。 HumanApprovalActivity实际上不做任何计算,它会调用一个外部服务,将待审核的假设和批判发送给人类用户界面,然后进入一个长时间的等待状态,直到收到来自外部服务通过 Temporal Client 发送的HumanApprovedSignal或HumanRejectedSignal。activity.GetLogger(ctx).Info("Awaiting human approval...")并在内部使用activity.RecordHeartbeat确保 Activity 不会超时。- 当人类用户在界面上点击“同意”或“拒绝”时,后台服务通过 Temporal Client 向
SimulationWorkflow(或DialecticalTurnWorkflow本身)发送带结果的HumanApprovedSignal。Workflow 收到信号后,更新HumanApprovalActivity的状态,Activity 完成。 - Workflow 根据
HumanApprovalActivity返回的结果决定下一步是继续模拟还是修改策略。
- 在
-
多分支探索与回溯 (Exploration & Backtracking):
- 需求: 模拟过程中,某些决策点可能需要探索多个不同的方向(例如,针对一个问题提出多种截然不同的假设集合),然后评估哪条路径更有前景。甚至,如果某个路径被证明是死胡同,可能需要“回溯”到之前的某个决策点,重新探索。
- Temporal 思考:
- 多分支:
SimulationWorkflow可以通过workflow.ExecuteChildWorkflow启动多个子工作流,每个子工作流代表一个探索分支。每个子工作流在结束后将结果返回给父工作流。父工作流收集所有分支的结果,评估哪个最佳。 - 回溯: Temporal 本身不直接提供“回溯”功能,因为它强调工作流的线性历史。但可以通过几种方式模拟:
ContinueAsNew+ 状态传递: 如果要回溯到较早的状态开始新的探索,可以在当前 Workflow 中通过ContinueAsNew启动一个新的SimulationWorkflow,并传递一个“回溯点”的状态作为新 Workflow 的初始输入。新 Workflow 将从该回溯点开始执行,但实际上是一个全新的 Workflow 实例。- 条件逻辑 + 状态复用: 在
SimulationWorkflow中,如果探测到一个分支失败,可以利用之前 Query 记录的某些“检查点”状态,然后通过条件逻辑跳过一些 Activity,并从之前的检查点状态(通过 Workflow 变量或从 Activity 读取)重新开始新的子工作流迭代。这要求 Workflow 有意识地保存这些检查点状态。
- 多分支:
-
版本兼容性升级 (Version Compatibility Upgrade):
- 需求: “昆仑镜”项目是一个长期项目,Workflow 和 Activity 的逻辑会不断迭代。在有大量长时间运行的模拟实例时,如何升级代码而不中断现有模拟?
- Temporal 优势:
- Worker Versioning (Build ID): Temporal Server 可以根据 Worker 上报的
Build ID来标识 Worker 的代码版本。它会尽量将同一个 Workflow 的任务发送给带有相同Build ID的 Worker。当部署新版本 Worker 时,Server 会在 Task Queue 中“标记”旧版本 Worker 的任务,直到旧版本 Worker 完成(或超时),然后新版本的 Worker 可以逐步接管。 - Workflow Code Versioning (
workflow.SetVersion): 在 Workflow 代码内部,可以使用workflow.SetVersion(ctx, "feature-v1", workflow.DefaultVersion, 1)。当 Workflow 历史重放到这个点时,它会记录一个版本标记。当将来部署带新逻辑的 Workflow 代码时,可以通过检查这个版本标记 (workflow.GetVersion(ctx, "feature-v1", initialVersion, latestVersion)) 来判断是执行旧逻辑还是新逻辑。例如,if version >= 1 { // new logic } else { // old logic }。这对于处理复杂、长期运行的工作流演进至关重要。
- Worker Versioning (Build ID): Temporal Server 可以根据 Worker 上报的
通过这些具体而复杂的场景分析,我们可以看到 Temporal.io 如何在“昆仑镜”项目中,将传统分布式系统开发的各种“不可能任务”转化为可管理、可靠、且易于维护的实践。它不仅仅是提高了效率,更是为项目的健壮性和未来的可扩展性奠定了坚实基础。
4. 总结 Temporal.io 的优势和引入建议
Temporal.io 不仅仅是一个工具,它更是一种编程范式和思维方式的转变,旨在简化分布式系统中的复杂业务流程编排。
4.1. Temporal.io 的核心优势总结
-
极强的可靠性和容错性 (Extreme Reliability & Fault Tolerance):
- 持久化工作流: 即使所有 Worker 进程崩溃,Workflow 状态也不会丢失,在 Worker 恢复后能从中断处精确恢复。
- 自动重试机制: 为 Activity 提供灵活的重试策略,无需手动在业务代码中处理。
- 事务性保证: 通过事件溯源和重放机制,保证 Workflow 的执行是原子性的,提供端到端的可靠性。
-
简化分布式编程模型 (Simplified Distributed Programming Model):
- 抽象复杂性: 将分布式系统中的状态管理、并发控制、错误处理、超时等复杂问题抽象化,使开发者能够像编写单体应用一样编写分布式逻辑。
- 熟悉的语言: 支持多种主流编程语言 SDK,降低学习曲线。
- 清晰的业务逻辑: Workflow 代码专注于业务本身,Activity 处理外部交互,职责分离。
-
高可观测性 (High Observability):
- 完整事件历史: 每个 Workflow 实例的所有状态变更和事件都可审计,便于调试、排查问题。
- Web UI & CLI: 提供直观的 Web 界面和命令行工具,方便管理和监控 Workflow。
- 丰富的指标: Server 和 SDK 都暴露大量可配置的指标,便于集成到现有监控系统。
-
卓越的扩展性和效率 (Excellent Scalability & Efficiency):
- 水平扩展: Worker 和 Server 核心组件都可水平扩展,以应对高并发或大规模业务需求。
- 资源效率: Workflow 在等待时几乎不占用 Worker 资源,实现了长时间运行任务的低成本。
- 解耦: Task Queues 有效解耦了任务生产者和消费者。
-
强大的控制与灵活性 (Powerful Control & Flexibility):
- 任意控制流: 支持复杂逻辑(循环、条件、并行、子工作流),满足各种业务编排需求。
- 外部交互: Signals 和 Queries 提供强大的与外部系统异步/同步交互的能力。
- 版本兼容性: 优雅处理 Workflow 代码的迭代升级,不影响正在运行的实例。
4.2. 引入 Temporal.io 的建议
虽然 Temporal 优势显著,但并非适用于所有场景。理性地引入它,才能发挥其最大价值。
何时应该强烈考虑引入 Temporal.io:
- 业务流程复杂且关键: 核心业务流程涉及多个步骤,相互依赖,对原子性和容错性要求极高。
- 长时间运行的任务: 任务可能持续数小时、数天甚至更久,中间需要等待外部事件或人为干预。
- 有状态且需要持久化的流程: 流程需要在执行过程中维护复杂的状态,并且这些状态不能因服务故障而丢失。
- 需要与外部不确定性系统交互: 大量与第三方 API、数据库、消息队列等外部系统集成,需要强大的重试、超时和幂等性处理。
- 需要外部或人工干预的流程: 流程中包含暂停/恢复、审批、动态调整参数等人机交互环节。
- 分布式事务: 需要实现跨多个服务或数据的复杂分布式事务(补偿机制)。
- 希望简化开发和运维: 厌倦了自己手动编写和维护复杂的分布式状态机、重试逻辑、消息幂等性代码。
何时可能不需要 Temporal.io (反模式/替代方案):
- 简单的请求-响应 API: 对于无状态的、短时执行的微服务 API,使用 RPC 框架或 RESTful 服务即可。
- 简单消息队列处理: 对于仅是发送消息、触发一次性处理且无需复杂状态跟踪的场景,Kafka、RabbitMQ 等消息队列足以。
- 静态批处理任务: 对于一次性运行、无需中断和恢复的大数据批处理,MapReduce 或 Spark 更合适。
- 纯粹的 ETL 管道: 数据抽取、转换、加载,如果不需要复杂的回溯和分支逻辑,可以考虑 Airflow 等工作流调度工具。
- 资源极度受限的环境: Temporal Server 和 Worker 仍需要一定的资源开销,对于极度轻量的边缘计算或嵌入式设备,可能过于重量级。
- 学习曲线与运维成本: 引入 Temporal 意味着需要团队学习新的编程模型和概念,并需要考虑 Server 的运维(自建或使用 Temporal Cloud)。
“昆仑镜”项目的引入策略:
-
从小处着手,聚焦核心痛点:
- 首先将最复杂、最容易出错、最需要长生命周期的“模拟引擎的核心辩证循环”作为试点,使用 Temporal 进行重构。例如,从
DialecticalTurnWorkflow和其依赖的 Activities 开始。 - 逐步迁移或新增其他复杂业务流程。
- 首先将最复杂、最容易出错、最需要长生命周期的“模拟引擎的核心辩证循环”作为试点,使用 Temporal 进行重构。例如,从
-
团队培训与知识共享:
- 组织内部培训,让开发人员熟悉 Temporal 的核心概念、SDK 使用、最佳实践(尤其是确定性原则)。
- 建立内部代码规范和示例,便于团队快速上手。
-
基础设施规划:
- 部署选择: 考虑是自建 Temporal Server 集群(需要专业的运维团队来维护高可用、可扩展的 Cassandra/Postgres + Temporal Server)还是使用 Temporal Cloud (托管服务,降低运维负担)。对于“昆仑镜”这种核心且对稳定性要求极高的系统,推荐一开始就考虑 Temporal Cloud 或投入足够的运维资源自建高可用集群。
- 监控与报警: 整合 Temporal Server 和 Worker 的指标到现有监控系统(Prometheus/Grafana),配置关键报警。
- 日志: 确保 Workflow 和 Activity 的日志能够聚合、查询,便于调试。
-
测试策略:
- 单元测试: 编写针对 Workflow 和 Activity 逻辑的单元测试,特别是确保 Workflow 的确定性。Temporal SDK 提供了测试框架来模拟 Workflow 和 Activity 的执行环境。
- 集成测试: 测试 Workflow 与外部服务(通过 mock 或真实服务)的集成。
- 端到端测试: 从客户端启动 Workflow 到最终完成的完整流程测试,包括模拟各种故障场景。
-
版本管理:
- 规划 Workflow 和 Activity 代码的演进策略,特别是利用
workflow.SetVersion和 Worker Build ID 来实现平滑的代码升级。 - 定义好
Workflow ID和Task Queue的命名规范。
- 规划 Workflow 和 Activity 代码的演进策略,特别是利用
通过上述全面的分析,我们不难看出 Temporal.io 对于“昆仑镜”这类复杂、长时间运行、对容错性和状态管理有极高要求的项目而言,具有革命性的价值。它将从根本上提升系统的健壮性,降低开发和维护的复杂性,使“昆仑镜”能够以更可靠、更智能的方式运行其核心模拟引擎,最终实现其前瞻性的产品目标。
5. 使用步骤:在“昆仑镜”中落地 Temporal.io (Go 语言示例)
本节将提供一个基于 Go 语言的、完整的“昆仑镜”核心模拟流程的 Temporal 实现示例。我们将涵盖 Workflow 定义、Activity 实现、Worker 启动、Client 交互,以及如何实现暂停/恢复、查询状态等功能。
示例目标:
模拟“昆仑镜”中的一个简化版辩证循环:
- 分析问题 (
AnalyzeIssueActivity) - 提出假设 (
ProposeHypothesisActivity) - 多个实体并行批判假设 (
CritiqueHypothesisActivity) - 评估本轮结果 (
EvaluateOutcomeActivity) - 支持暂停、恢复、快进、查询状态。
前置条件:
- Go 1.18+
- Docker (用于运行 Temporal Server)
- 安装
temporal-cli:go install go.temporal.io/sdk/cmd/temporal@latest
5.1. 环境搭建 (Temporal Server Local Setup)
首先,我们需要一个 Temporal Server 实例。最简单的方式是使用 Docker Compose 启动。
-
创建
docker-compose.yml文件:version: '3.8'services:temporal:image: temporalio/sync-worker:1.20.1 # 使用一个包含Temporal Server和CLI的镜像ports:- "7233:7233" # Frontend Service- "8080:8080" # Web UIvolumes:- ./temporal_data:/etc/temporal/config # Persistent data, optional but good for testing stateenvironment:- TEMPORAL_CLI_ADDRESS=temporal:7233command: [ "start-dev", "--db-filename", "temporal.db", "--enable-time-skipping" ] # --enable-time-skipping simplifies testing timershealthcheck:test: [ "CMD-SHELL", "temporal --address temporal:7233 health" ]interval: 5stimeout: 5sretries: 5admin-tools:image: temporalio/sync-worker:1.20.1depends_on:temporal:condition: service_healthyenvironment:- TEMPORAL_CLI_ADDRESS=temporal:7233command: [ "sleep", "infinity" ] # Keep container alive for manual CLI accesstty: true # Enable TTY for interactive shell -
启动 Temporal Server:
在docker-compose.yml所在目录执行:docker-compose up -d等待片刻,直到所有服务都 healthy。可以通过访问
http://localhost:8080查看 Temporal Web UI。 -
注册 Namespace (第一次运行需要):
进入admin-tools容器执行命令,或直接使用temporal-cli:# 进入 admin-tools 容器 # docker-compose exec admin-tools bash # temporal --address temporal:7233 namespace register default# 或者直接使用本地安装的 temporal-cli temporal --address localhost:7233 namespace register default temporal --address localhost:7233 namespace update default --retention 30 # Set retention to 30 days我们将使用
defaultNamespace。
5.2. 项目结构
创建一个名为 kunlun_mirror 的 Go 项目:
kunlun_mirror/
├── workflow/
│ ├── simulation_workflow.go
│ └── dialectical_turn_workflow.go
├── activity/
│ └── smart_agent_activities.go
├── worker/
│ └── main.go
└── client/└── main.go
初始化 Go 模块:
cd kunlun_mirror
go mod init kunlun_mirror
go get go.temporal.io/sdk@latest
5.3. 定义数据结构与接口
首先,我们需要定义 Workflow 和 Activity 的输入输出数据结构以及它们的接口。
在 workflow/types.go (新建此文件,方便共享类型定义):
package workflowimport ("time"
)// SimulationContext 定义模拟的当前状态,将被工作流持久化
type SimulationContext struct {SimulationID stringCurrentRound intMaxRound intInitialIssue stringGeneratedHypotheses []string // 所有已生成的假设CritiquesByHypo map[string][]string // 每个假设的批判AgentConfig map[string]AgentConfiguration // 各智能体配置IsPaused bool // 暂停状态FastForwardTarget int // 快进目标轮次StatusMessage string // 最新状态消息StartTime time.TimeLastUpdateTime time.Time
}// AgentConfiguration 定义智能体配置
type AgentConfiguration struct {Name stringRole stringConfig map[string]string // 例如 {"creativity": "high", "strictness": "medium"}
}// GlobalWorkflowInput 启动 SimulationWorkflow 的输入
type GlobalWorkflowInput struct {SimulationID stringInitialProblem stringMaxRounds intAgents map[string]AgentConfiguration
}// SimulationStatusQuery 定义查询 Workflow 状态的响应
type SimulationStatusQuery struct {ID stringCurrentRound intMaxRound intProgress float64 // 0.0 - 1.0Status stringGeneratedHypotheses []stringActiveAgentCount intIsPaused boolLastUpdate time.TimeDuration string
}// PauseSignalInput 定义暂停信号的输入
type PauseSignalInput struct {Reason string
}// ResumeSignalInput 定义恢复信号的输入
type ResumeSignalInput struct {Reason string
}// FastForwardSignalInput 定义快进信号的输入
type FastForwardSignalInput struct {TargetRound int
}// OverrideAgentParamSignalInput 定义动态修改智能体参数信号的输入
type OverrideAgentParamSignalInput struct {AgentID stringNewConfig map[string]string
}// DialecticalTurnWorkflow 的输入和输出
type DialecticalTurnInput struct {SimulationID stringRoundNumber intIssueContext string // 当前轮次的问题描述AgentConfig map[string]AgentConfiguration
}type DialecticalTurnResult struct {RoundNumber intHypothesis stringCritiques map[string]string // 智能体ID -> 批判内容EvaluationResult stringSuccessful bool
}// Activity 的输入输出定义
type AnalyzeIssueInput struct {SimulationID stringRoundNumber intIssueContext stringAgentID string
}
type AnalyzeIssueOutput struct {KeyConcepts []stringSummary string
}type ProposeHypothesisInput struct {SimulationID stringRoundNumber intIssueContext stringKeyConcepts []stringAgentConfig AgentConfigurationAgentID string
}
type ProposeHypothesisOutput struct {Hypothesis string
}type CritiqueHypothesisInput struct {SimulationID stringRoundNumber intHypothesis stringIssueContext stringAgentConfig AgentConfigurationAgentID string
}
type CritiqueHypothesisOutput struct {CriticAgentID stringCritique stringSeverity float64 // 批判严重性
}type EvaluateOutcomeInput struct {SimulationID stringRoundNumber intHypothesis stringCritiques map[string]stringAgentID string
}
type EvaluateOutcomeOutput struct {Evaluation stringNextSteps stringIsValid bool // 本轮辩证是否有效推进
}type StoreRoundResultInput struct {SimulationID stringRoundResult DialecticalTurnResult
}
type StoreRoundResultOutput struct {Success bool
}
5.4. 实现 Activity
在 activity/smart_agent_activities.go (模拟与外部 AI 或 DB 服务的交互):
package activityimport ("context""fmt""log""math/rand""time""go.temporal.io/sdk/activity""kunlun_mirror/workflow" // 导入 workflow 包以使用其类型定义
)// Global Activity options (可以在 Worker 中通过注册时设置,也可以在 Workflow 中为每个 Activity 实例动态设置)// AnalyzeIssueActivity 模拟分析问题的活动
func AnalyzeIssueActivity(ctx context.Context, input workflow.AnalyzeIssueInput) (*workflow.AnalyzeIssueOutput, error) {logger := activity.GetLogger(ctx)logger.Info("AnalyzeIssueActivity started", "simulationID", input.SimulationID, "round", input.RoundNumber)// 模拟耗时和可能的失败if rand.Float64() < 0.1 { // 10% 几率失败,模拟网络或服务错误logger.Error("AnalyzeIssueActivity failed due to simulated network error.")return nil, fmt.Errorf("simulated network error during issue analysis for round %d", input.RoundNumber)}time.Sleep(time.Duration(2+rand.Intn(3)) * time.Second) // 模拟 2-4 秒的分析时间output := &workflow.AnalyzeIssueOutput{KeyConcepts: []string{"quantum computing", "AI ethics", "distributed consensus"},Summary: fmt.Sprintf("Analyzed issue for round %d: %s. Identified key concepts.", input.RoundNumber, input.IssueContext),}logger.Info("AnalyzeIssueActivity completed", "summary", output.Summary)return output, nil
}// ProposeHypothesisActivity 模拟提出假设的活动
func ProposeHypothesisActivity(ctx context.Context, input workflow.ProposeHypothesisInput) (*workflow.ProposeHypothesisOutput, error) {logger := activity.GetLogger(ctx)logger.Info("ProposeHypothesisActivity started", "simulationID", input.SimulationID, "round", input.RoundNumber, "agent", input.AgentID)// 模拟长时间运行的 Activity 和心跳机制for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {// 模拟每个步骤的计算time.Sleep(time.Duration(1+rand.Intn(2)) * time.Second)select {case <-ctx.Done():logger.Warn("ProposeHypothesisActivity cancelled.")return nil, ctx.Err()default:// 定期发送心跳,确保 Temporal Server 知道 Activity 仍在运行activity.RecordHeartbeat(ctx, fmt.Sprintf("progress: %d/5 steps done", i+1), "agent", input.AgentID)logger.Info(fmt.Sprintf("ProposeHypothesisActivity heartbeat: %d/5", i+1))}}if rand.Float64() < 0.05 { // 5% 几率失败logger.Error("ProposeHypothesisActivity failed due to simulated LLM error.")return nil, fmt.Errorf("simulated LLM generation error for round %d, agent %s", input.RoundNumber, input.AgentID)}hypothesis := fmt.Sprintf("Hypothesis by %s for round %d: Based on '%v', we propose a novel approach for '%s'.",input.AgentID, input.RoundNumber, input.KeyConcepts, input.IssueContext)output := &workflow.ProposeHypothesisOutput{Hypothesis: hypothesis}logger.Info("ProposeHypothesisActivity completed", "hypothesis", output.Hypothesis)return output, nil
}// CritiqueHypothesisActivity 模拟批判假设的活动
func CritiqueHypothesisActivity(ctx context.Context, input workflow.CritiqueHypothesisInput) (*workflow.CritiqueHypothesisOutput, error) {logger := activity.GetLogger(ctx)logger.Info("CritiqueHypothesisActivity started", "simulationID", input.SimulationID, "round", input.RoundNumber, "criticAgent", input.AgentID)time.Sleep(time.Duration(1+rand.Intn(2)) * time.Second) // 模拟 1-2 秒批判时间if rand.Float64() < 0.03 { // 3% 几率失败logger.Error("CritiqueHypothesisActivity failed due to simulated DB write error.")return nil, fmt.Errorf("simulated DB write error for critique by %s", input.AgentID)}critique := fmt.Sprintf("Critique by %s for round %d: '%s' has potential flaws related to '%s'. Severity: %.2f",input.AgentID, input.RoundNumber, input.Hypothesis,input.AgentConfig.Config["critic_focus"], rand.Float64()*10)output := &workflow.CritiqueHypothesisOutput{CriticAgentID: input.AgentID,Critique: critique,Severity: rand.Float64() * 10,}logger.Info("CritiqueHypothesisActivity completed", "critique", output.Critique)return output, nil
}// EvaluateOutcomeActivity 模拟评估本轮结果的活动
func EvaluateOutcomeActivity(ctx context.Context, input workflow.EvaluateOutcomeInput) (*workflow.EvaluateOutcomeOutput, error) {logger := activity.GetLogger(ctx)logger.Info("EvaluateOutcomeActivity started", "simulationID", input.SimulationID, "round", input.RoundNumber, "agent", input.AgentID)time.Sleep(time.Duration(1+rand.Intn(3)) * time.Second) // 模拟 1-3 秒评估时间// 模拟复杂评估,可能需要长时间运行if rand.Float64() < 0.08 { // 8% 几率失败logger.Error("EvaluateOutcomeActivity failed due to simulated complex calculation error.")return nil, fmt.Errorf("simulated calculation error for evaluation of round %d", input.RoundNumber)}// 简单的评估逻辑:如果批判的平均严重性很高,则认为本轮不是有效推进totalSeverity := 0.0for _, c := range input.Critiques {// 简单提取严重性,实际可能更复杂totalSeverity += rand.Float64() * 10 // 模拟解析或计算}avgSeverity := totalSeverity / float64(len(input.Critiques))isValid := avgSeverity < 5.0output := &workflow.EvaluateOutcomeOutput{Evaluation: fmt.Sprintf("Evaluation by %s for round %d: Hypothesis '%s' was %s. Avg critique severity: %.2f",input.AgentID, input.RoundNumber, input.Hypothesis,func() string {if isValid { return "effectively advanced" }return "identified significant flaws"}(), avgSeverity),NextSteps: fmt.Sprintf("Suggesting based on evaluation. Valid: %t", isValid),IsValid: isValid,}logger.Info("EvaluateOutcomeActivity completed", "evaluation", output.Evaluation, "isValid", output.IsValid)return output, nil
}// StoreRoundResultActivity 模拟存储本轮结果的活动(通常要求幂等性)
func StoreRoundResultActivity(ctx context.Context, input workflow.StoreRoundResultInput) (*workflow.StoreRoundResultOutput, error) {logger := activity.GetLogger(ctx)logger.Info("StoreRoundResultActivity started", "simulationID", input.SimulationID, "round", input.RoundResult.RoundNumber)// 模拟幂等性写入:检查是否已存在,如果存在则更新,不存在则插入resultKey := fmt.Sprintf("sim:%s:round:%d", input.SimulationID, input.RoundResult.RoundNumber)// 实际场景会是 DB 调用, 这里只是模拟time.Sleep(time.Duration(500+rand.Intn(1000)) * time.Millisecond) // 模拟 0.5-1.5 秒DB写入if rand.Float64() < 0.02 { // 2% 几率失败logger.Error("StoreRoundResultActivity failed due to simulated DB connection error.")return nil, fmt.Errorf("simulated DB connection error when storing round %d result", input.RoundResult.RoundNumber)}logger.Info("Round result stored successfully (simulated)", "key", resultKey)return &workflow.StoreRoundResultOutput{Success: true}, nil
}
Activity 重试策略:
在 Worker 注册活动时,或者在 Workflow 中调用 Activity 时,可以设置 ActivityOptions 来指定重试策略和超时。我们将在 Worker 端集中设置默认的 Activity 选项。
5.5. 实现 Workflow
我们将有两个 Workflow:SimulationWorkflow (顶层控制) 和 DialecticalTurnWorkflow (单轮辩证)。
在 workflow/dialectical_turn_workflow.go:
package workflowimport ("context""fmt""time""go.temporal.io/sdk/workflow"
)// DialecticalTurnWorkflowOptions 为子工作流定义Activity的默认选项
func dialecticalTurnActivityOptions(ctx workflow.Context) workflow.Context {return workflow.With ActivityOptions(ctx, workflow.ActivityOptions{StartToCloseTimeout: time.Minute * 5, // Activity 从开始到完成的最大时间ScheduleToStartTimeout: time.Minute * 1, // Activity 从调度到被Worker开始执行的最大时间HeartbeatTimeout: time.Second * 30, // 针对长时间运行Activity的心跳// 设置默认重试策略RetryPolicy: &temporal.RetryPolicy{InitialInterval: time.Second * 3, // 第一次重试的间隔BackoffCoefficient: 2.0, // 每次重试间隔翻倍MaximumInterval: time.Minute * 2, // 最大重试间隔MaximumAttempts: 5, // 最多重试 5 次NonRetryableErrorTypes: []string{ // 某些特定错误不重试"ValidationError", // 例如,输入参数错误,重试无意义},},})
}// DialecticalTurnWorkflowInfo 是子工作流的注册名称
const DialecticalTurnWorkflowInfo = "DialecticalTurnWorkflow"// DialecticalTurnWorkflow 实现单轮辩证过程
func DialecticalTurnWorkflow(ctx workflow.Context, input DialecticalTurnInput) (*DialecticalTurnResult, error) {logger := workflow.GetLogger(ctx)logger.Info("DialecticalTurnWorkflow started", "simulationID", input.SimulationID, "round", input.RoundNumber)// 设置 Activity 选项ao := dialecticalTurnActivityOptions(ctx)var analyzeOutput *AnalyzeIssueOutputerr := workflow.ExecuteActivity(ao, "AnalyzeIssueActivity", AnalyzeIssueInput{SimulationID: input.SimulationID,RoundNumber: input.RoundNumber,IssueContext: input.IssueContext,AgentID: "AnalyzerAgent",}).Get(ctx, &analyzeOutput)if err != nil {logger.Error("AnalyzeIssueActivity failed", "error", err)return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to analyze issue: %w", err)}logger.Info("Issue analyzed", "summary", analyzeOutput.Summary)var proposeOutput *ProposeHypothesisOutputproposerAgent := input.AgentConfig["ProposerAgent"]err = workflow.ExecuteActivity(ao, "ProposeHypothesisActivity", ProposeHypothesisInput{SimulationID: input.SimulationID,RoundNumber: input.RoundNumber,IssueContext: input.IssueContext,KeyConcepts: analyzeOutput.KeyConcepts,AgentConfig: proposerAgent,AgentID: proposerAgent.Name,}).Get(ctx, &proposeOutput)if err != nil {logger.Error("ProposeHypothesisActivity failed", "error", err)return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to propose hypothesis: %w", err)}logger.Info("Hypothesis proposed", "hypothesis", proposeOutput.Hypothesis)// 并行执行多个批判 Activityvar critiqueFutures []workflow.ChildWorkflowFuture // for future child workflow, but here for ActivitiescritiqueResults := make(map[string]string) // AgentID -> Critique// Collect all critic agentscriticAgents := make([]AgentConfiguration, 0)for _, agent := range input.AgentConfig {if agent.Role == "Critic" {criticAgents = append(criticAgents, agent)}}for _, agent := range criticAgents {fut := workflow.ExecuteActivity(ao, "CritiqueHypothesisActivity", CritiqueHypothesisInput{SimulationID: input.SimulationID,RoundNumber: input.RoundNumber,Hypothesis: proposeOutput.Hypothesis,IssueContext: input.IssueContext,AgentConfig: agent,AgentID: agent.Name,})critiqueFutures = append(critiqueFutures, fut)}// 等待所有批判 Activity 完成for i, fut := range critiqueFutures {var critiqueOutput CritiqueHypothesisOutputerr = fut.Get(ctx, &critiqueOutput)if err != nil {logger.Error("CritiqueHypothesisActivity failed", "error", err, "criticAgent", criticAgents[i].Name)// TODO: 可以选择是否允许部分批判失败,这里简化为所有失败都导致本轮失败return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to get critique from agent %s: %w", criticAgents[i].Name, err)}critiqueResults[critiqueOutput.CriticAgentID] = critiqueOutput.Critiquelogger.Info("Hypothesis critiqued", "by", critiqueOutput.CriticAgentID, "critique", critiqueOutput.Critique)}var evaluateOutput *EvaluateOutcomeOutputevaluatorAgent := input.AgentConfig["EvaluatorAgent"]err = workflow.ExecuteActivity(ao, "EvaluateOutcomeActivity", EvaluateOutcomeInput{SimulationID: input.SimulationID,RoundNumber: input.RoundNumber,Hypothesis: proposeOutput.Hypothesis,Critiques: critiqueResults,AgentID: evaluatorAgent.Name,}).Get(ctx, &evaluateOutput)if err != nil {logger.Error("EvaluateOutcomeActivity failed", "error", err)return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to evaluate outcome: %w", err)}logger.Info("Outcome evaluated", "evaluation", evaluateOutput.Evaluation, "isValid", evaluateOutput.IsValid)// 存储本轮结果err = workflow.ExecuteActivity(ao, "StoreRoundResultActivity", StoreRoundResultInput{SimulationID: input.SimulationID,RoundResult: DialecticalTurnResult{RoundNumber: input.RoundNumber,Hypothesis: proposeOutput.Hypothesis,Critiques: critiqueResults,EvaluationResult: evaluateOutput.Evaluation,Successful: evaluateOutput.IsValid,},}).Get(ctx, nil) // Get(ctx, nil) 表示不关心 Activity 的返回值if err != nil {logger.Error("StoreRoundResultActivity failed", "error", err)return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to store round result: %w", err)}logger.Info("Round results stored.")return &DialecticalTurnResult{RoundNumber: input.RoundNumber,Hypothesis: proposeOutput.Hypothesis,Critiques: critiqueResults,EvaluationResult: evaluateOutput.Evaluation,Successful: evaluateOutput.IsValid,}, nil
}
在 workflow/simulation_workflow.go:
package workflowimport ("context""fmt""time""go.temporal.io/sdk/workflow"
)// SimulationWorkflowInfo 是顶层工作流的注册名称
const SimulationWorkflowInfo = "SimulationWorkflow"// SimulationWorkflow 定义“昆仑镜”的整个模拟过程
func SimulationWorkflow(ctx workflow.Context, input GlobalWorkflowInput) (*SimulationContext, error) {logger := workflow.GetLogger(ctx)logger.Info("SimulationWorkflow started", "simulationID", input.SimulationID, "maxRounds", input.MaxRounds)// 1. 初始化模拟上下文,这是工作流的持久化状态simCtx := &SimulationContext{SimulationID: input.SimulationID,CurrentRound: 0,MaxRound: input.MaxRounds,InitialIssue: input.InitialProblem,GeneratedHypotheses: []string{},CritiquesByHypo: make(map[string][]string),AgentConfig: input.Agents,IsPaused: false,FastForwardTarget: 0,StatusMessage: "Initializing simulation...",StartTime: workflow.Now(ctx),}// 2. 注册查询处理器,用于实时查询工作流状态err := workflow.SetQueryHandler(ctx, "GetSimulationStatus", func() (SimulationStatusQuery, error) {progress := float64(simCtx.CurrentRound) / float64(simCtx.MaxRound)if simCtx.MaxRound == 0 {progress = 0}status := "Running"if simCtx.IsPaused {status = "Paused"} else if simCtx.CurrentRound == simCtx.MaxRound {status = "Completed"}activeAgents := 0for _, agent := range simCtx.AgentConfig {if agent.Name != "" { // 简单检查是否有配置activeAgents++}}return SimulationStatusQuery{ID: simCtx.SimulationID,CurrentRound: simCtx.CurrentRound,MaxRound: simCtx.MaxRound,Progress: progress,Status: status,GeneratedHypotheses: simCtx.GeneratedHypotheses,ActiveAgentCount: activeAgents,IsPaused: simCtx.IsPaused,LastUpdate: simCtx.LastUpdateTime,Duration: workflow.Now(ctx).Sub(simCtx.StartTime).Round(time.Second).String(),}, nil})if err != nil {logger.Error("Failed to set query handler", "error", err)return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to set query handler: %w", err)}// 3. 注册信号处理器,用于接收外部控制命令// 暂停信号_ = workflow.Set SignalHandler(ctx, "PauseSimulation", func(input PauseSignalInput) {simCtx.IsPaused = truesimCtx.StatusMessage = fmt.Sprintf("Simulation paused by external signal: %s", input.Reason)logger.Info("Simulation paused", "reason", input.Reason)})// 恢复信号_ = workflow.SetSignalHandler(ctx, "ResumeSimulation", func(input ResumeSignalInput) {simCtx.IsPaused = falsesimCtx.StatusMessage = fmt.Sprintf("Simulation resumed by external signal: %s", input.Reason)logger.Info("Simulation resumed", "reason", input.Reason)})// 快进信号_ = workflow.SetSignalHandler(ctx, "FastForwardSimulation", func(input FastForwardSignalInput) {if input.TargetRound > simCtx.CurrentRound && input.TargetRound <= simCtx.MaxRound {simCtx.FastForwardTarget = input.TargetRoundsimCtx.StatusMessage = fmt.Sprintf("Fast-forwarding to round %d...", input.TargetRound)logger.Info("Fast-forward signal received", "targetRound", input.TargetRound)} else {logger.Warn("Invalid fast-forward target round", "targetRound", input.TargetRound, "currentRound", simCtx.CurrentRound)}})// 调整智能体参数信号_ = workflow.SetSignalHandler(ctx, "OverrideAgentParam", func(input OverrideAgentParamSignalInput) {if agent, ok := simCtx.AgentConfig[input.AgentID]; ok {for k, v := range input.NewConfig {agent.Config[k] = v // 更新智能体配置}simCtx.AgentConfig[input.AgentID] = agentsimCtx.StatusMessage = fmt.Sprintf("Agent %s parameters overridden.", input.AgentID)logger.Info("Agent parameters overridden", "agentID", input.AgentID, "newConfig", input.NewConfig)} else {logger.Warn("Agent not found for parameter override", "agentID", input.AgentID)}})// 4. 主辩证循环for round := 1; round <= simCtx.MaxRound; round++ {simCtx.CurrentRound = roundsimCtx.LastUpdateTime = workflow.Now(ctx)simCtx.StatusMessage = fmt.Sprintf("Starting round %d...", round)logger.Info("Starting dialectical round", "round", round)// 检查暂停或快进状态err = handleWorkflowControls(ctx, simCtx)if err != nil {logger.Error("Workflow control handler failed", "error", err)return nil, err // 如果取消,直接退出}if simCtx.FastForwardTarget > 0 && round < simCtx.FastForwardTarget {logger.Info("Skipping round due to fast-forward", "currentRound", round, "targetRound", simCtx.FastForwardTarget)if round == simCtx.FastForwardTarget-1 { // 到达快进目标前一轮,重置快进目标simCtx.FastForwardTarget = 0 }continue}// 执行子工作流:单轮辩证childID := fmt.Sprintf("%s-round-%d", simCtx.SimulationID, round)cwo := workflow.ChildWorkflowOptions{WorkflowID: childID,}inputForTurn := DialecticalTurnInput{SimulationID: simCtx.SimulationID,RoundNumber: round,IssueContext: simCtx.InitialIssue, // 可以根据前几轮结果动态更新 IssueContextAgentConfig: simCtx.AgentConfig,}var roundResult DialecticalTurnResulterr = workflow.ExecuteChildWorkflow(workflow.WithChildOptions(ctx, cwo), DialecticalTurnWorkflowInfo, inputForTurn).Get(ctx, &roundResult)if err != nil {logger.Error("DialecticalTurnWorkflow failed", "round", round, "error", err)// TODO: 可以根据错误类型选择继续、重试本轮、或终止整个模拟simCtx.StatusMessage = fmt.Sprintf("Round %d failed: %v", round, err)return simCtx, fmt.Errorf("dialectical turn failed in round %d: %w", round, err)}// 更新总模拟状态simCtx.GeneratedHypotheses = append(simCtx.GeneratedHypotheses, roundResult.Hypothesis)simCtx.CritiquesByHypo[roundResult.Hypothesis] = make([]string, 0)for _, v := range roundResult.Critiques {simCtx.CritiquesByHypo[roundResult.Hypothesis] = append(simCtx.CritiquesByHypo[roundResult.Hypothesis], v)}simCtx.StatusMessage = fmt.Sprintf("Round %d completed. Latest hypothesis: %s", round, roundResult.Hypothesis)}// 5. 模拟完成simCtx.StatusMessage = "Simulation completed successfully."simCtx.LastUpdateTime = workflow.Now(ctx)logger.Info("SimulationWorkflow completed", "simulationID", input.SimulationID)return simCtx, nil
}// handleWorkflowControls 处理暂停/恢复/取消逻辑
func handleWorkflowControls(ctx workflow.Context, simCtx *SimulationContext) error {logger := workflow.GetLogger(ctx)// 处理取消请求if ctx.IsCanceled() {logger.Info("SimulationWorkflow cancelled.")simCtx.StatusMessage = "Simulation cancelled."return fmt.Errorf("workflow cancelled")}// 检查并等待暂停状态for simCtx.IsPaused {logger.Info("Workflow paused. Waiting for ResumeSimulation signal...")simCtx.StatusMessage = "Paused. Waiting for resume."// 等待信号,或短时间睡眠,以便检查是否被取消selector := workflow.NewSelector(ctx)resumeChannel := workflow.GetSignalChannel(ctx, "ResumeSimulation")selector.AddReceive(resumeChannel, func(c workflow.ReceiveChannel, more bool) {var signal ResumeSignalInputc.Receive(ctx, &signal) // 清空信号队列,以便下次正确判断simCtx.IsPaused = falsesimCtx.StatusMessage = fmt.Sprintf("Resumed from signal: %s", signal.Reason)logger.Info("Simulation resumed by signal.", "reason", signal.Reason)})// 增加一个短时 Timer,以便在接收信号的同时也能响应 Worker Shutdown 或 Workflow 取消timer := workflow.NewTimer(ctx, time.Second * 5)selector.AddFuture(timer, func(f workflow.Future) {// Timer 触发,什么也不做,继续循环检查 isPaused})selector.Select(ctx) // 等待信号或 timer// 再次检查是否被取消或恢复if ctx.IsCanceled() {logger.Warn("Workflow cancelled while paused.")simCtx.StatusMessage = "Cancelled while paused."return fmt.Errorf("workflow cancelled while paused")}}return nil
}Workflow 注意事项:
workflow.WithActivityOptions或workflow.WithChildOptions统一设置 Activity 或 Child Workflow 的默认行为。workflow.SetQueryHandler: 定义工作流运行时可被查询的状态。workflow.SetSignalHandler: 定义工作流接收外部信号的逻辑。workflow.NewSelector: 用于同时等待多个事件(如信号、定时器、Activity 完成等),实现复杂的控制流。workflow.Now(ctx)/workflow.Sleep(ctx, duration):Temporal 提供的确定性时间操作。workflow.IsCanceled():检查工作流是否被取消。
5.6. 实现 Worker
Worker 负责监听 Task Queue,并执行 Workflow 和 Activity。
在 worker/main.go:
package mainimport ("log""go.temporal.io/sdk/client""go.temporal.io/sdk/worker""kunlun_mirror/activity""kunlun_mirror/workflow"
)func main() {// 1. 创建 Temporal Client// For local development with docker-compose, use localhost:7233// In production, you'd use a real Temporal Cluster address and mTLS for security.c, err := client.Dial(client.Options{HostPort: client.Default=client.WorkerModeProduction: "localhost:7233",Namespace: "default", // Replace with your Namespace if different})if err != nil {log.Fatalf("Unable to create Temporal client: %v", err)}defer c.Close()// 2. 创建 Worker// Task Queue 可以是任意字符串,同一 Task Queue 上的 Worker 会共享任务taskQueue := "kunlun-mirror-task-queue"w := worker.New(c, taskQueue, worker.Options{// 配置 Activity 选项,例如默认重试策略// 例如,可以设置所有 Activity 的默认 StartToCloseTimeoutActivityOptions: client.ActivityOptions{StartToCloseTimeout: workflow.Duration(5 * time.Minute), // Make sure this is long enough for your longest activityScheduleToStartTimeout: workflow.Duration(time.Minute), // Optional, how long before trying another worker if not picked upHeartbeatTimeout: workflow.Duration(30 * time.Second), // For long-running ActivitiesRetryPolicy: &temporal.RetryPolicy{InitialInterval: time.Second * 2,BackoffCoefficient: 2.0,MaximumInterval: time.Minute * 2,MaximumAttempts: 5,NonRetryableErrorTypes: []string{}, // Custom non-retryable errors},},})// 3. 注册 Workflow 函数w.RegisterWorkflow(workflow.SimulationWorkflow)w.RegisterWorkflow(workflow.DialecticalTurnWorkflow) // 注册子工作流// 4. 注册 Activity 函数w.RegisterActivity(activity.AnalyzeIssueActivity)w.RegisterActivity(activity.ProposeHypothesisActivity)w.RegisterActivity(activity.CritiqueHypothesisActivity)w.RegisterActivity(activity.EvaluateOutcomeActivity)w.RegisterActivity(activity.StoreRoundResultActivity)// 5. 启动 Worker,它将开始轮询 Task Queuelog.Printf("Starting Worker on Task Queue: %s", taskQueue)err = w.Run(worker.InterruptCh())if err != nil {log.Fatalf("Worker exited with error: %v", err)}log.Println("Worker stopped.")
}Worker 注意事项:
client.Dial: 连接 Temporal Server。worker.New: 创建 Worker 实例,并指定其监听的Task Queue。w.RegisterWorkflow()/w.RegisterActivity(): 注册 Workflow 和 Activity 实现,让 Worker 知道如何执行这些函数。w.Run(worker.InterruptCh()): 启动 Worker。InterruptCh()允许 Worker 响应中断信号(如 Ctrl+C)进行优雅关闭。
5.7. 实现 Client
Client 负责启动 Workflow,发送信号,查询状态等。
在 client/main.go:
package mainimport ("bufio""context""fmt""log""os""strconv""strings""time""go.temporal.io/sdk/client""go.temporal.io/sdk/temporal""kunlun_mirror/workflow"
)func main() {// 1. 创建 Temporal Client// In production, you'd use a real Temporal Cluster address and mTLS for security.c, err := client.Dial(client.Options{HostPort: client.Default=client.WorkerModeProduction: "localhost:7233",Namespace: "default",})if err != nil {log.Fatalf("Unable to create Temporal client: %v", err)}defer c.Close()reader := bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)fmt.Println("\n---昆仑镜模拟控制台---")fmt.Println("1. 启动新模拟")fmt.Println("2. 连接现有模拟 (需要 Workflow ID)")fmt.Println("3. 退出")fmt.Print("请选择操作: ")choiceStr, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')choice := strings.TrimSpace(choiceStr)var simRunID stringvar simWorkflowID stringif choice == "1" {// 启动新模拟simWorkflowID = fmt.Sprintf("kunlun-mirror-sim-%d", time.Now().Unix())fmt.Printf("请输入初始问题 (例如: 量子计算伦理): ")initialProblem, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')initialProblem = strings.TrimSpace(initialProblem)fmt.Printf("请输入最大辩证轮数 (例如: 10): ")maxRoundsStr, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')maxRounds, _ := strconv.Atoi(strings.TrimSpace(maxRoundsStr))if maxRounds <= 0 {maxRounds = 10}// 定义智能体配置agentConfig := map[string]workflow.AgentConfiguration{"AnalyzerAgent": {Name: "AnalyzerAgent", Role: "Analyzer", Config: map[string]string{}},"ProposerAgent": {Name: "ProposerAgent", Role: "Proposer", Config: map[string]string{"creativity": "high"}},"CriticAgent1": {Name: "CriticAgent1", Role: "Critic", Config: map[string]string{"critic_focus": "logic"}},"CriticAgent2": {Name: "CriticAgent2", Role: "Critic", Config: map[string]string{"critic_focus": "ethics"}},"EvaluatorAgent":{Name: "EvaluatorAgent", Role: "Evaluator", Config: map[string]string{}},}workflowInput := workflow.GlobalWorkflowInput{SimulationID: simWorkflowID,InitialProblem: initialProblem,MaxRounds: maxRounds,Agents: agentConfig,}// 异步启动 WorkflowworkflowOptions := client.StartWorkflowOptions{ID: simWorkflowID,TaskQueue: "kunlun-mirror-task-queue",WorkflowRunTimeout: time.Hour * 24 * 7, // 允许最长运行 7 天RetryPolicy: &temporal.RetryPolicy{ // 如果 StartWorkflow 本身失败,重试InitialInterval: time.Second,BackoffCoefficient: 2.0,MaximumInterval: time.Minute,MaximumAttempts: 5,NonRetryableErrorTypes: []string{"InputValidationError"},},}we, err := c.ExecuteWorkflow(context.Background(), workflowOptions, workflow.SimulationWorkflowInfo, workflowInput)if err != nil {log.Fatalf("Unable to start Workflow: %v", err)}simRunID = we.GetRunID()fmt.Printf("--- 模拟已启动 ---\nWorkflow ID: %s\nRun ID: %s\n", simWorkflowID, simRunID)} else if choice == "2" {fmt.Print("请输入现有模拟的 Workflow ID: ")simWorkflowID, _ = reader.ReadString('\n')simWorkflowID = strings.TrimSpace(simWorkflowID)fmt.Print("请输入现有模拟的 Run ID (可选,留空则获取最新): ")simRunID, _ = reader.ReadString('\n')simRunID = strings.TrimSpace(simRunID)fmt.Printf("连接到 Workflow ID: %s, Run ID: %s\n", simWorkflowID, simRunID)} else {fmt.Println("退出。")return}for {fmt.Println("\n--- 模拟控制面板 ---")fmt.Println("1. 查询当前状态 (Query)")fmt.Println("2. 暂停模拟 (Signal)")fmt.Println("3. 恢复模拟 (Signal)")fmt.Println("4. 快进模拟到指定轮次 (Signal)")fmt.Println("5. 调整智能体参数 (Signal)")fmt.Println("6. 终止模拟 (Terminate)")// fmt.Println("7. 取消模拟 (Cancel)") // 注意 Cancel 和 Terminate 的区别fmt.Println("8. 查看最终结果 (Wait for Completion)")fmt.Println("9. 返回主菜单 / 退出")fmt.Print("请选择操作: ")opStr, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')op := strings.TrimSpace(opStr)switch op {case "1": // 查询状态var status workflow.SimulationStatusQueryqueryCtx, _ := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second*5)// GetWorkflow 函数可以直接指定 Workflow ID 和 Run ID 来获取 WorkflowClient 后续交互// 而不需要每次都 Call ExecuteWorkflowcurrWorkflow := c.GetWorkflow(context.Background(), simWorkflowID, simRunID) err := currWorkflow.Query(queryCtx, "GetSimulationStatus").Get(&status)if err != nil {if strings.Contains(err.Error(), "workflow is completed") {fmt.Println("错误:模拟已完成或已终止,无法查询。")} else {log.Printf("查询模拟状态失败: %v", err)}continue}fmt.Printf("\n--- 模拟当前状态 ---\n")fmt.Printf("ID: %s\n", status.ID)fmt.Printf("轮数: %d/%d (%.2f%%)\n", status.CurrentRound, status.MaxRound, status.Progress*100)fmt.Printf("状态: %s (已暂停: %v)\n", status.Status, status.IsPaused)fmt.Printf("活跃智能体: %d\n", status.ActiveAgentCount)if len(status.GeneratedHypotheses) > 0 {fmt.Printf("最新假设: %s\n", status.GeneratedHypotheses[len(status.GeneratedHypotheses)-1])}fmt.Printf("持续时间: %s\n", status.Duration)fmt.Printf("最后更新: %s\n", status.LastUpdate.Format("15:04:05"))case "2": // 暂停fmt.Print("请输入暂停原因: ")reason, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')reason = strings.TrimSpace(reason)signalInput := workflow.PauseSignalInput{Reason: reason}err := c.SignalWorkflow(context.Background(), simWorkflowID, simRunID, "PauseSimulation", signalInput)if err != nil {log.Printf("发送暂停信号失败: %v", err)continue}fmt.Println("暂停信号已发送。")case "3": // 恢复fmt.Print("请输入恢复原因: ")reason, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')reason = strings.TrimSpace(reason)signalInput := workflow.ResumeSignalInput{Reason: reason}err := c.SignalWorkflow(context.Background(), simWorkflowID, simRunID, "ResumeSimulation", signalInput)if err != nil {log.Printf("发送恢复信号失败: %v", err)continue}fmt.Println("恢复信号已发送。")case "4": // 快进fmt.Print("请输入目标轮次: ")targetRoundStr, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')targetRound, _ := strconv.Atoi(strings.TrimSpace(targetRoundStr))if targetRound <= 0 {fmt.Println("目标轮次必须大于0。")continue}signalInput := workflow.FastForwardSignalInput{TargetRound: targetRound}err := c.SignalWorkflow(context.Background(), simWorkflowID, simRunID, "FastForwardSimulation", signalInput)if err != nil {log.Printf("发送快进信号失败: %v", err)continue}fmt.Printf("快进信号已发送,目标轮次: %d。\n", targetRound)case "5": // 调整智能体参数fmt.Print("请输入要调整的智能体ID (例如: CriticAgent1): ")agentID, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')agentID = strings.TrimSpace(agentID)fmt.Print("请输入新的参数 (例如: strictness=high,creativity=medium): ")paramsStr, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')params := make(map[string]string)for _, p := range strings.Split(strings.TrimSpace(paramsStr), ",") {parts := strings.SplitN(p, "=", 2)if len(parts) == 2 {params[strings.TrimSpace(parts[0])] = strings.TrimSpace(parts[1])}}if len(params) == 0 {fmt.Println("未输入有效参数。")continue}signalInput := workflow.OverrideAgentParamSignalInput{AgentID: agentID,NewConfig: params,}err := c.SignalWorkflow(context.Background(), simWorkflowID, simRunID, "OverrideAgentParam", signalInput)if err != nil {log.Printf("发送智能体参数调整信号失败: %v", err)continue}fmt.Printf("智能体 '%s' 参数调整信号已发送。\n", agentID)case "6": // 终止ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second*5)defer cancel()err := c.TerminateWorkflow(ctx, simWorkflowID, simRunID, "User terminated simulation from console.")if err != nil {log.Printf("终止模拟失败: %v", err)} else {fmt.Println("模拟已终止。")}return/* // 取消功能需要 Workflow 内部配合处理 ctx.Done()case "7": // 取消ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second*5)defer cancel()err := c.CancelWorkflow(ctx, simWorkflowID, simRunID)if err != nil {log.Printf("取消模拟失败: %v", err)} else {fmt.Println("取消信号已发送。")}return*/case "8": // 等待完成并获取结果fmt.Printf("正在等待模拟 %s 完成...\n", simWorkflowID)var finalContext workflow.SimulationContexterr := c.GetWorkflow(context.Background(), simWorkflowID, simRunID).Get(context.Background(), &finalContext)if err != nil {if temporal.IsCanceledError(err) {fmt.Println("模拟已被取消。")} else if temporal.IsTerminatedError(err) {fmt.Println("模拟已被终止。")} else {log.Printf("获取最终结果失败: %v", err)}} else {fmt.Printf("\n--- 模拟最终结果 ---\n")fmt.Printf("最终状态: %s\n", finalContext.StatusMessage)fmt.Printf("完成轮数: %d/%d\n", finalContext.CurrentRound, finalContext.MaxRound)fmt.Printf("所有假设 (%d): \n", len(finalContext.GeneratedHypotheses))for _, h := range finalContext.GeneratedHypotheses {fmt.Printf("- %s\n", h)if critiques, ok := finalContext.CritiquesByHypo[h]; ok {for _, c := range critiques {fmt.Printf(" -> %s\n", c)}}}}returncase "9":fmt.Println("退出控制面板。")returndefault:fmt.Println("无效操作,请重试。")}}
}
Client 注意事项:
client.ExecuteWorkflow: 启动新的 Workflow 实例。client.GetWorkflow: 获取一个正在运行的 Workflow 实例的句柄,以便后续操作(查询、发送信号、取消、终止)。workflow.Query(...): 同步查询 Workflow 的当前状态。client.SignalWorkflow(...): 异步向 Workflow 发送信号。client.TerminateWorkflow(...): 粗暴地终止 Workflow。wfRun.Get(...): 等待 Workflow 完成并获取其最终结果。
5.8. 运行示例
-
启动 Temporal Server (如果尚未启动):
cd kunlun_mirror/ docker-compose up -d # 等待服务健康,并通过 http://localhost:8080 检查 Web UI temporal --address localhost:7233 namespace register default --rd 1 -
启动 Worker:
打开一个新的终端窗口:cd kunlun_mirror/worker go run main.goWorker 将开始监听
kunlun-mirror-task-queue。 -
运行 Client:
打开第三个终端窗口:cd kunlun_mirror/client go run main.go按照 Client 提示进行操作。
交互示例流程:
- 选择
1. 启动新模拟,输入问题和轮数。 - Client 将打印 Workflow ID 和 Run ID。
- 选择
1. 查询当前状态,观察模拟进度。你会看到Round X/Y (Z%)正在推进。 - 选择
2. 暂停模拟,输入原因。 - 再次
1. 查询当前状态,你会看到状态: Paused。Worker 终端可能也会打印 Workflow 暂停的日志。 - 选择
3. 恢复模拟,输入原因。 - 再次
1. 查询当前状态,模拟将继续推进。 - 选择
4. 快进模拟,输入一个目标轮次(例如总共 10 轮,当前第 3 轮,输入 7)。 - 查询状态,你会看到轮次快速增加,跳过了中间的 Activity 执行。
- 选择
5. 调整智能体参数,为CriticAgent1调整strictness=very_high。 - (可选)如果你想暴力停止模拟,选择
6. 终止模拟。 - 选择
8. 查看最终结果,Client 会一直等待直到模拟完成(或被终止),然后打印最终状态和所有生成的假设。
通过这个详细的Go语言示例,你已经能够亲手体验到 Temporal.io 在构建复杂、有状态、可控的分布式工作流方面的强大能力。从环境搭建到代码实现,再到实际交互,每一个步骤都展示了 Temporal 如何将分布式系统的复杂性转化为简单、可靠的编程模型。
