Kotlin-基础语法练习四
接上一篇博客
函数
Kotlin - 函数
在Kotlin中,函数用于封装可多次执行的一段行为。函数可以接受输入参数、返回值,并提供一种将复杂逻辑封装到可重用代码块中的方法。
什么是函数?
函数是执行特殊任务的代码单元。在编程中,该函数用于将代码分解为更小的模块,从而使程序更易于管理。
我们可以调用sum(x, y)任意次数,它将返回两个数的和。因此,该函数避免了代码的重复,使代码更具可重用性。
函数示例
fun sum(a: Int, b: Int): Int {Int c = a + breturn c
}
函数中的参数
函数参数是指传递给函数以供进一步处理的元素,函数在接收到这些参数后,会对其进行操作。
在上述示例中,有两个参数:
a为 Integer(整数)
b为 Integer(整数)
这个过程就是将数据传递给函数进行处理,函数根据这些参数执行相应的操作。
函数体
在函数体中,我们执行要在函数中执行的操作,如上例所示:
val c = a + b
返回值
返回值是在函数中执行操作后返回的值。在上面的例子中,c是返回的值。
Kotlin中的函数类型
在Kotlin中,有两种类型的函数:
•用户自定义功能
•标准库功能
1. Kotlin用户定义函数
由用户定义的函数称为用户定义函数。如我们所知,要把一个大的程序分成小的模块,我们需要定义函数。每个定义的函数都有自己的属性,比如函数名、函数返回类型、传递给函数的参数数量等。
创建自定义功能
在Kotlin中,函数可以在顶部声明,而不需要创建一个类来保存函数,这是我们在Java或Scala等其他语言中习惯做的。通常,我们将函数定义为:
fun fun_name(a: data_type, b: data_type, ......): return_type {// other codesreturn
}
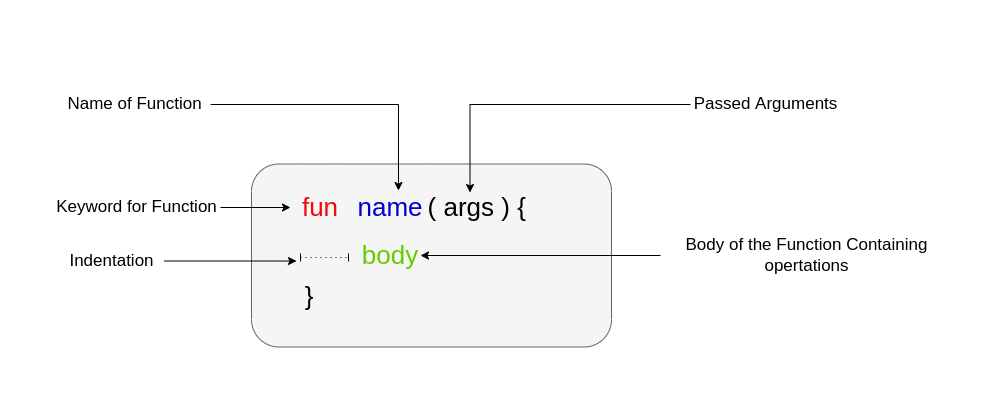
- fun:定义函数的关键字。
- fun_name:稍后用来调用该函数的函数名。
- a: data_type:这里,a是传递的参数,data_type指定参数的数据类型,如整数或字符串。
- return_type:指定函数返回的数据值类型。
- {…}:花括号代表一段代码。
Kotlin函数mul()将具有相同类型参数的两个数字相乘:
fun mul(num1: Int, num2: Int): Int {var number = num1.times(num2)return number
}
解释:我们在上面定义了一个以fun关键字开头的函数,它的返回类型是Integer。
mul() is the name of the function
num1 and num2 are names of the parameters being accepted by the function and both are Integer type.
Kotlin函数student()有不同类型的参数:
fun student(name: String , roll_no: Int , grade: Char) {println("Name of the student is : $name")println("Roll no of the student is: $roll_no")println("Grade of the student is: $grade")
}
调用用户自定义函数
fun mul(a: Int, b: Int): Int {var number = a.times(b)return number
}fun main(args: Array<String>) {var result = mul(3,5)println("The multiplication of two numbers is: $result")
}
Output:
The multiplication of two numbers is: 15
Kotlin程序通过传递所有参数来调用student()函数:
fun student( name: String , grade: Char , roll_no: Int) {println("Name of the student is: $name")println("Grade of the student is: $grade")println("Roll no of the student is: $roll_no")}fun main(args: Array<String>) {val name = "Praveen"val rollno = 25val grade = 'A'student(name,grade,rollno)student("Gaurav",'B',30)
}
Output:
Name of the student is: Praveen
Grade of the student is: A
Roll no of the student is: 25
Name of the student is: Gaurav
Grade of the student is: B
Roll no of the student is: 30
2. Kotlin标准库函数
下面是标准库函数的实现:
fun main(args: Array<String>) {var sum = arrayOf(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10).sum()println("The sum of all the elements of an array is: $sum")
}
Output:
在下面的程序中,我们将使用rem()来查找余数。
fun main(args: Array<String>) {var num1 = 26var num2 = 3var result = num1.rem(num2)println("The remainder when $num1 is divided by $num2 is: $result")
}
Output:
The remainder when 26 is divided by 3 is: 2
不同标准库函数的列表及其用法:
•sqrt():用于计算一个数的平方根。
•print():用于将消息打印到标准输出。
•rem():求一个数除以另一个数的余数。
•toInt():将数字转换为整数值。
•readline():用于标准输入。
•compareTo():比较两个数字并返回一个布尔值
Kotlin函数的优缺点
优点
- 模块化:函数提供了一种将代码模块化并将其分解为更小、更易于管理的部分的方法。这使您的代码更具可读性、可维护性,并且更易于测试。
- 可重用性:函数可以从代码中的多个位置调用,使代码易于重用并避免重复。
- 提高可读性:函数提供了一种将复杂逻辑封装到可重用代码块中的方法,这可以使您的代码更具可读性,更易于理解。
- 改进的抽象:函数可以用来抽象
缺点
- 开销:函数会增加代码的大小,并增加执行代码所需的内存量,尤其是在有很多函数的情况下。
- 调试:如果您的函数中有复杂的逻辑,函数会使调试变得更加困难,特别是如果您有多个相互调用的函数。
Kotlin | 默认参数和命名参数
在大多数编程语言中,我们需要指定函数在调用该函数时接受的所有参数,但在Kotlin中,我们不需要指定函数在调用该函数时接受的所有参数,因此这是最重要的功能之一。我们可以摆脱这个约束,使参数可选,即在调用函数时传递参数或不传递参数。在Kotlin中,函数参数使用逗号分隔,并使用Pascal符号定义,即:
name:data_type.
在Kotlin中,默认参数允许您为函数参数指定默认值。这意味着,如果在调用函数时没有显式地传递参数,则它将使用默认值。
fun greet(name: String = "World") {println("Hello, $name!")
}// Call with argument
greet("John") // Output: Hello, John!// Call without argument
greet() // Output: Hello, World!
Kotlin中的命名参数允许您按名称而不是按位置向函数传递参数。这在调用具有许多参数的函数或希望使代码更具可读性时非常有用。
fun printName(firstName: String, lastName: String) {println("First name: $firstName, Last name: $lastName")
}// Call with named arguments
printName(lastName = "Doe", firstName = "John") // Output: First name: John, Last name: Doe
Kotlin中有两种类型的参数
1. 默认参数
调用函数时不传递参数
Example:
// default arguments in function definition name, standard and roll_no
fun student(name: String="Ram", standard: String="IX" , roll_no: Int=11) { println("Name of the student is: $name")println("Standard of the student is: $standard")println("Roll no of the student is: $roll_no")
}fun main(args: Array<String>) {val name_of_student = "Raj"val standard_of_student = "VIII"val roll_no_of_student = 25student() // passing no arguments while calling student
}
Name of the student is: Ram
Standard of the student is: IX
Roll no of the student is: 11
在调用函数时传递部分参数
Example:
// default arguments in function definition name,standard and roll_no
fun student( name: String="Ram", standard: String="IX" , roll_no: Int=11 ) {println("Name of the student is: $name")println("Standard of the student is: $standard")println("Roll no of the student is: $roll_no")
}fun main(args: Array<String>) {val name_of_student = "Raj"val standard_of_student = "VIII"val roll_no_of_student = 25// passing only two arguments name and standard of studentstudent(name_of_student,standard_of_student)
}
Name of the student is: Raj
Standard of the student is: VIII
Roll no of the student is: 11
在调用函数时传递所有参数
// default arguments in function definition name, standard and roll_no
fun student( name: String="Ram", standard: String="IX" , roll_no: Int=11 ) {println("Name of the student is: $name")println("Standard of the student is: $standard")println("Roll no of the student is: $roll_no")
}fun main(args: Array<String>) {val name_of_student = "Raj"val standard_of_student = "VIII"val roll_no_of_student = 25//passing all the arguments of student name,//standard and roll_no in same order as defined in functionstudent(name_of_student,standard_of_student,roll_no_of_student)
}
Name of the student is: Raj
Standard of the student is: VIII
Roll no of the student is: 25
2. 命名参数
通过以随机顺序传递参数来调用student()的Kotlin程序
Example:
// default arguments in function definition name,standard and roll_no
fun student( name: String="Praveen", standard: String="IX" , roll_no: Int=11 ) {println("Name of the student is: $name")println("Standard of the student is: $standard")println("Roll no of the student is: $roll_no")
}fun main(args: Array<String>) {val name_of_student = "Gaurav"val standard_of_student = "VIII"val roll_no_of_student = 25// passing the argument name_of_student to name// and roll_no_of_student to standardstudent(name_of_student,roll_no_of_student)
}
Output:
Argument type mismatch: actual type is 'Int', but 'String' was expected.
使用参数名调用student()的Kotlin程序
Example:
// default arguments in function definition
// name,standard and roll_no
fun student( name: String="Ram", standard: String="IX" , roll_no: Int=11 ) {println("Name of the student is: $name")println("Standard of the student is: $standard")println("Roll no of the student is: $roll_no")
}fun main(args: Array<String>) {val name_of_student = "Raj"val standard_of_student = "VIII"val roll_no_of_student = 25// passing the arguments with name as defined in functionstudent(name=name_of_student,roll_no=roll_no_of_student)
}
Output:
Name of the student is: Raj
Standard of the student is: IX
Roll no of the student is: 25
Kotlin 递归
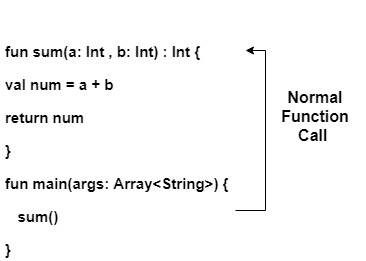
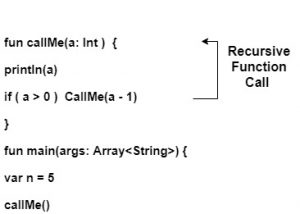
在这里,我们将学习Kotlin递归函数。像其他编程语言一样,我们可以在Kotlin中使用递归。调用自身的函数称为递归函数,这种重复的过程称为递归。无论何时调用函数,都有两种可能:
普通函数调用
递归函数调用
示例1:在不使用终止条件的情况下求一个数的阶乘
package function// Kotlin program of factorial using recursion
fun Fact(num: Int):Long{return num*Fact(num-1) // no terminate condition
}
//main method
fun main()
{println("Factorial of 5 is: " + Fact(5))// Recursive call
}
Output:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.StackOverflowErrorat function.TestFuncKt.Fact(TestFunc.kt:5)at function.TestFuncKt.Fact(TestFunc.kt:5)at function.TestFuncKt.Fact(TestFunc.kt:5)
示例2:使用终止条件查找一个数的阶乘
package function// Kotlin program of factorial using recursion
fun Fact(num: Int):Long{return if(num==1) num.toLong() else num*Fact(num-1) // no terminate condition
}
//main method
fun main()
{println("Factorial of 5 is: " + Fact(5))// Recursive call
}
Output:
Factorial of 5 is: 120
阶乘程序的工作流程

示例3:使用递归找到数组元素的和
package function// two parameters passed an array and size of array
fun sum(args: Array<Int>, index: Int): Int
{return if (index <= 0) 0else(sum(args, index - 1)+ args[index - 1]) // recursive function call
}fun main()
{// array initializationval array = arrayOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)// size of arrayval n = array.sizeval result = sum(array, n) // normal function callprintln("The sum of array elements is: $result")
}
Output:
The sum of array elements is: 55
递归的优点:
- 提高代码可读性和可维护性:递归函数通常使代码更加简洁,尤其对于复杂问题,易于理解。
- 便于实现算法:许多算法,如汉诺塔(Tower of Hanoi),可以通过递归方式轻松实现。
- 可重用性:递归函数通常能够在类似问题中重用,从而减少了重复编写代码的需求。
递归的缺点:
- 增加内存使用:每次递归调用都会将新的函数调用压入调用栈,可能导致栈溢出错误,尤其是在处理大数据集时。
- 性能问题:递归算法通常比迭代算法更慢,因为它们需要更多的内存和CPU周期。
Kotlin 尾递归
在传统的递归调用中,我们首先执行递归调用,然后获取递归调用的返回值并计算结果。但是在尾部递归中,我们首先执行计算,然后执行递归调用,将当前步骤的结果传递给下一个递归调用。最后,递归和尾递归都给出了相同的输出。尾递归必须遵循的规则是,递归调用应该是方法的最后一次调用。
使用尾部递归的好处
- 在尾递归中,函数调用是函数执行的最后一步,且当前函数没有剩余操作需要执行。因此,无需将当前函数调用保存在栈内存中,编译器可以将该栈空间用于下一个递归调用。
- 在尾递归中,程序执行过程中不会发生栈溢出错误(StackOverflowError)。
示例1:使用尾递归找到一个数字的阶乘
// Kotlin program of factorial using tail-recursion
fun Fact(num: Int, x:Int):Long{return if(num==1) // terminate conditionx.toLong()elseFact(num-1,x*num) //tail recursion
}fun main() {var n = 1var result = Fact(5,n)println("Factorial of 5 is: $result")
}
Output:
Factorial of 5 is: 120
上述程序的运行情况

示例2:使用尾递归找到数组元素的和
// two parameters passed an array and size of array
fun sum(args: Array<Int> , index:Int, s : Int = 0 ):Int{return if(index<=0) selse sum(args ,index-1, s + args[index-1]) // tail-recursion
}fun main() {// array initializationval array = arrayOf(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10)// size of arrayval n = array.sizeval result = sum(array,n) // normal function callprintln("The sum of array elements is: $result")
}
Output:
The sum of array elements is: 55
Kotlin 中的 Lambda 表达式和匿名函数
Lambda表达式
语法:
val lambda_name : Data_type = { argument_List -> code_body }
Example:
val sum = {a: Int , b: Int -> a + b}
在 Kotlin 中,lambda 表达式包含了一个可选部分,除了代码体 (code_body) 之外。以下是去除可选部分后的 lambda 表达式。
val sum:(Int,Int) -> Int = { a, b -> a + b}
注意:我们并不总是需要一个变量,因为它可以直接作为参数传递给函数。.
访问Lambda表达式
fun main(args: Array<String>) {val company = { println("Hello")}// invoking functions:// Method1company() // Method2company.invoke()
}
Output:
Hello
Hello
使用lambda表达式的程序
// with type annotation in lambda expression
val sum1 = { a: Int, b: Int -> a + b }// without type annotation in lambda expression
val sum2:(Int,Int)-> Int = { a , b -> a + b}fun main(args: Array<String>) {val result1 = sum1(2,3)val result2 = sum2(3,4)println("The sum of two numbers is: $result1")println("The sum of two numbers is: $result2")// directly print the return value of lambda// without storing in a variable.println(sum1(5,7))
}
Output:
The sum of two numbers is: 5
The sum of two numbers is: 7
12
lambda中的类型推断
Kotlin的类型推断帮助编译器计算lambda表达式的类型。下面是lambda表达式,我们可以用它来计算两个整数的和
val sum = {a: Int , b: Int -> a + b}
在这里,Kotlin编译器将其作为一个函数进行自求值,该函数接受两个Int类型的形参并返回Int值。
(Int,Int) -> Int
val sum1 = { a: Int, b: Int ->val num = a + bnum.toString() //convert Integer to String
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {val result1 = sum1(2,3)println("The sum of two numbers is: $result1")
}
Output:
The sum of two numbers is: 5
在上面的程序中,Kotlin编译器将其自求值为一个接受两个整数值并返回String的函数。
(Int,Int) -> String
lambdas中的类型声明
必须显式声明lambda表达式的类型。如果lambda没有返回值,则可以使用:Unit
模式 (Input) -> Output
返回类型的Lambda示例:
val lambda1: (Int) -> Int = {a -> a * a}
val lambda2: (String,String) -> String = { a , b -> a + b }
val lambda3: (Int)-> Unit = {print(Int)}
Lambdas可以用作类扩展:
val lambda4: String.(Int) -> String = {this + it}
使用lambdas作为类扩展时的程序
val lambda4 : String.(Int) -> String = { this + it }fun main(args: Array<String>) {val result = "Hello".lambda4(50)print(result)
}
Output:
Hello50
it:单个参数的隐式名称
使用lambda函数的简写形式
val numbers = arrayOf(1,-2,3,-4,5)fun main(args: Array<String>) {println(numbers.filter { it > 0 })
}
Output:
[1, 3, 5]
从lambda表达式返回一个值
通过lambda函数返回String值
val find =fun(num: Int): String{
if(num % 2==0 && num < 0) {return "Number is even and negative"}else if (num %2 ==0 && num >0){return "Number is even and positive"}else if(num %2 !=0 && num < 0){return "Number is odd and negative"}else {return "Number is odd and positive"}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {val result = find(112)println(result)
}
Output:
Number is even and positive
匿名函数
例1:作为表达式的函数体
fun(a: Int, b: Int) : Int = a * b
例2:函数体作为块
fun(a: Int, b: Int): Int {val mul = a * breturn mul
}
返回类型和参数:
- 1、返回类型和参数也以与普通函数相同的方式指定,但如果可以从上下文中推断出参数,则可以省略它们。
- 2、 如果函数是表达式,可以从函数中自动推断函数的返回类型;如果是体块,则必须为匿名函数显式指定返回类型。
程序调用匿名函数
// anonymous function with body as an expression
val anonymous1 = fun(x: Int, y: Int): Int = x + y// anonymous function with body as a block
val anonymous2 = fun(a: Int, b: Int): Int {val mul = a * breturn mul}fun main(args: Array<String>) {//invoking functionsval sum = anonymous1(3,5)val mul = anonymous2(3,5)println("The sum of two numbers is: $sum")println("The multiply of two numbers is: $mul")
}
Output:
The sum of two numbers is: 8
The multiply of two numbers is: 15
Lambda 表达式与匿名函数的区别
唯一的区别在于非本地返回的行为。没有标签的 return 语句总是从使用 fun 关键字声明的函数中返回。这意味着,在 Lambda 表达式中的 return 会导致从外部函数返回,而在匿名函数中的 return 只会导致从匿名函数本身返回。
Kotlin 内联函数
//待续
Kotlin 中的中缀函数表示法
//待续
Kotlin 高阶函数
//待续
