ffplay数据读取线程
简介
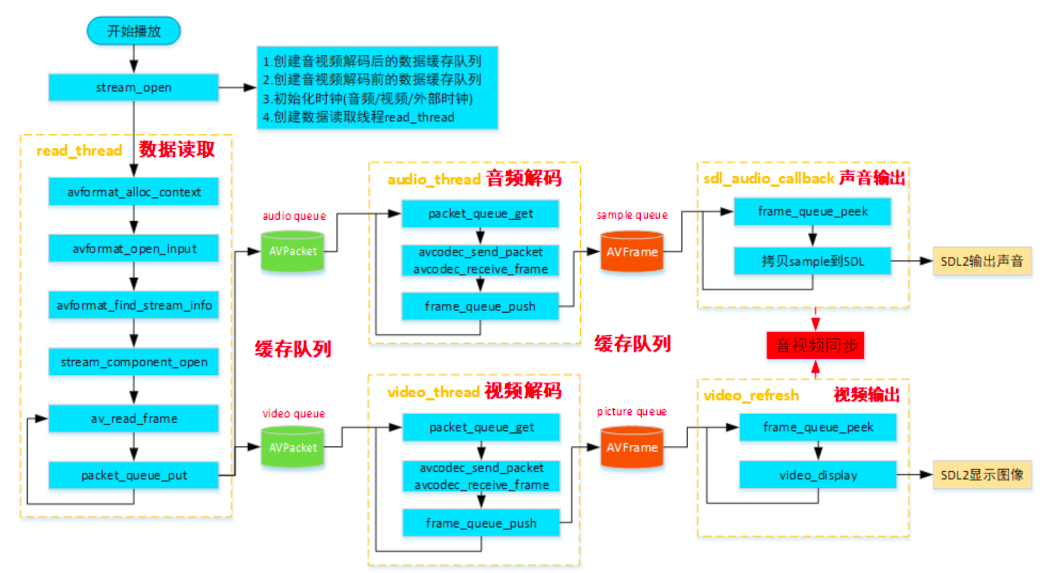
从ffplay框架分析我们可以看到,ffplay有专⻔的线程read_thread()读取数据,且在调⽤av_read_frame
读取数据包之前需要做例如打开⽂件,查找配置解码器,初始化⾳视频输出等准备阶段,主要包括三⼤步
骤:
- 准备⼯作
- For循环读取数据
- 退出线程处理
准备工作
- avformat_alloc_context 创建上下⽂
- ic->interrupt_callback.callback = decode_interrupt_cb;
- avformat_open_input打开媒体⽂件
- avformat_find_stream_info 读取媒体⽂件的包获取更多的stream信息
- 检测是否指定播放起始时间,如果指定时间则seek到指定位置avformat_seek_file
- 查找查找AVStream,讲对应的index值记录到st_index[AVMEDIA_TYPE_NB];
- 根据⽤户指定来查找流avformat_match_stream_specifier
- 使⽤av_find_best_stream查找流
- 从待处理流中获取相关参数,设置显示窗⼝的宽度、⾼度及宽⾼⽐
- stream_component_open打开⾳频、视频、字幕解码器,并创建相应的解码线程以及进⾏对应输出参 数的初始化
avformat_alloc_context() 创建上下文
调用 avformat_alloc_context()创建解复用器上下文
// 创建上下⽂结构体,这个结构体是最上层的结构体,表示输⼊上下⽂
ic = avformat_alloc_context();
最终该ic 赋值给VideoState的ic变量
is->ic = ic; // videoState的ic指向分配的ic
ic->interrupt_callback
// 设置中断回调函数,如果出错或者退出,就根据⽬前程序设置的状态选择继续check或者直接退出
// 当执⾏耗时操作时,会调⽤interrupt_callback.callback
// 回调函数中返回1则代表ffmpeg结束耗时操作退出当前函数的调⽤
// 回调函数中返回0则代表ffmpeg内部继续执⾏耗时操作,直到完成既定的任务(⽐如读取到既定的数据包)
ic->interrupt_callback.callback = decode_interrupt_cb;
ic->interrupt_callback.opaque = is;
interrupt_callback⽤于ffmpeg内部在执⾏耗时操作时检查调⽤者是否有退出请求,避免⽤户退出请求没
有及时响应。
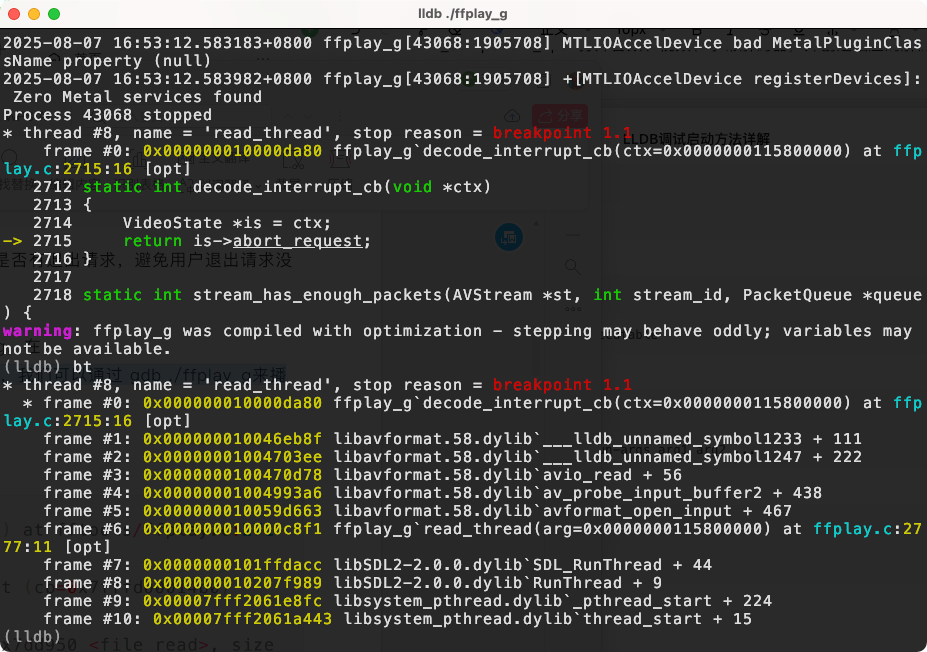
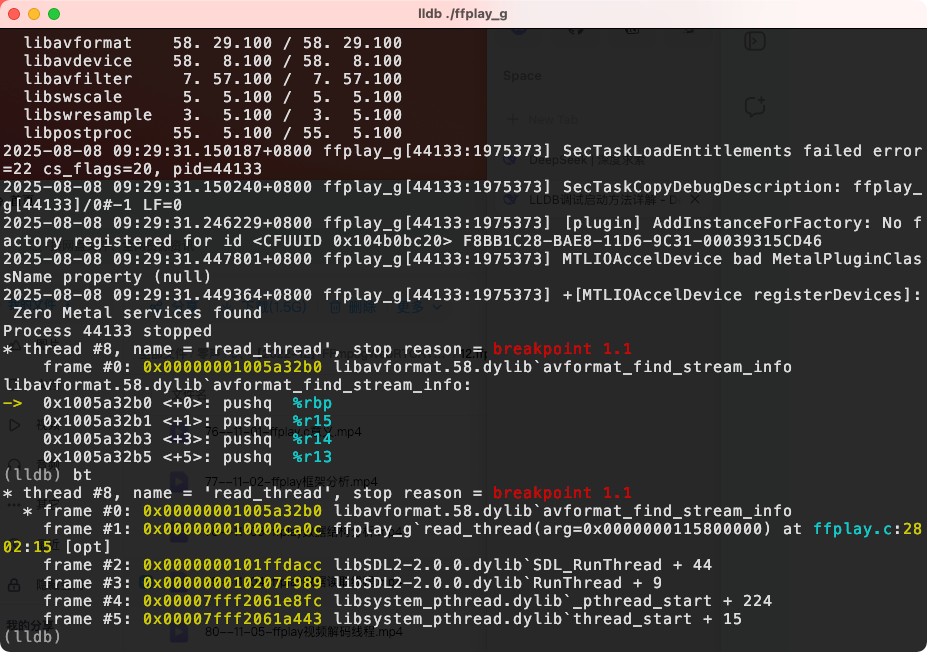
怎么去测试在哪⾥触发?
在 ffmpeg-4.2.1⽬录下有ffplay_g,我们可以通过 lldb ./ffplay_g来播 放视频,然后在decode_interrupt_cb打断点。
avformat_open_input 触发
avformat_find_stream_info 触发
avformat_open_input()打开媒体文件
函数原型:
/*** Open an input stream and read the header. The codecs are not opened.* The stream must be closed with avformat_close_input().** @param ps Pointer to user-supplied AVFormatContext (allocated by avformat_alloc_context).* May be a pointer to NULL, in which case an AVFormatContext is allocated by this* function and written into ps.* Note that a user-supplied AVFormatContext will be freed on failure.* @param url URL of the stream to open.* @param fmt If non-NULL, this parameter forces a specific input format.* Otherwise the format is autodetected.* @param options A dictionary filled with AVFormatContext and demuxer-private options.* On return this parameter will be destroyed and replaced with a dict containing* options that were not found. May be NULL.** @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on failure.** @note If you want to use custom IO, preallocate the format context and set its pb field.*/
int avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext **ps, const char *url, ff_const59 AVInputFormat *fmt, AVDictionary **options);
avformat_open_input⽤于打开输⼊⽂件(对于RTMP/RTSP/HTTP⽹络流也是⼀样,在ffmpeg内部都抽象为URLProtocol,这⾥描述为⽂件是为了⽅便与后续提到的AVStream的流作区分),读取视频⽂件的基本信息。
需要提到的两个参数是fmt和options。通过fmt可以强制指定视频⽂件的封装,options可以传递额外参数给封装(AVInputFormat)。
avformat_find_stream_info()
在打开了⽂件后,就可以从AVFormatContext中读取流信息了。⼀般调⽤avformat_find_stream_info获取完整的流信息。为什么在调⽤了avformat_open_input后,仍然需要调⽤avformat_find_stream_info才能获取正确的流信息呢?看下注释:
/*** Read packets of a media file to get stream information. This* is useful for file formats with no headers such as MPEG. This* function also computes the real framerate in case of MPEG-2 repeat* frame mode.* The logical file position is not changed by this function;* examined packets may be buffered for later processing.** @param ic media file handle* @param options If non-NULL, an ic.nb_streams long array of pointers to* dictionaries, where i-th member contains options for* codec corresponding to i-th stream.* On return each dictionary will be filled with options that were not found.* @return >=0 if OK, AVERROR_xxx on error** @note this function isn't guaranteed to open all the codecs, so* options being non-empty at return is a perfectly normal behavior.** @todo Let the user decide somehow what information is needed so that* we do not waste time getting stuff the user does not need.*/
int avformat_find_stream_info(AVFormatContext *ic, AVDictionary **options);
该函数是通过读取媒体⽂件的部分数据来分析流信息。在⼀些缺少头信息的封装下特别有⽤,⽐如说MPEG(⾥应该说ts更准确)(FLV⽂件也是需要读取packet 分析流信息)。⽽被读取⽤以分析流信息的数据可能被缓存,供av_read_frame时使⽤,在播放时并不会跳过这部分packet的读取。
监测是否指定播放起始时间
如果指定时间则seek到指定位置avformat_seek_file。
可以通过 ffplay -ss 设置起始时间,时间格式hh:mm:ss,⽐如:
ffplay -ss 00:00:30 test.flv # 则是从30秒的起始位置开始播放
查找 AVStream
⼀个媒体⽂件,对应有0n个⾳频流、0n个视频流、0~n个字幕流,⽐如这⾥我们⽤了2_audio.mp4是有2个⾳频流,1个视频流。
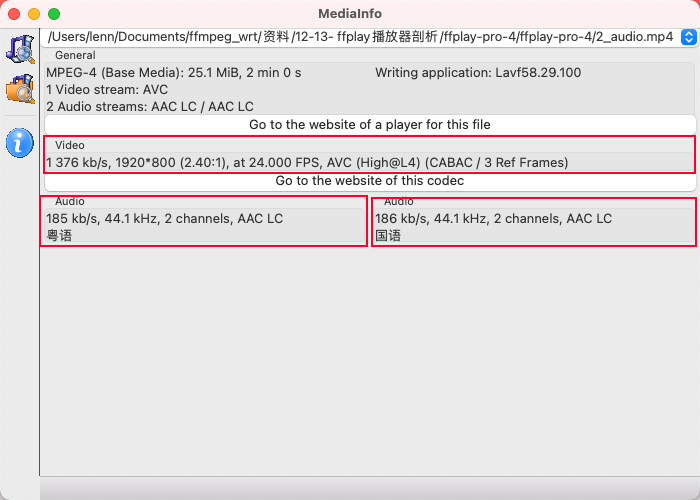
具体现在那个流进⾏播放我们有两种策略:
- 在播放起始指定对应的流
- 使⽤缺省的流进⾏播放
在播放起始指定对应的流
{ "ast", OPT_STRING | HAS_ARG | OPT_EXPERT, { &wanted_stream_spec[AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO] }, "select desired audio stream", "stream_specifier" },
{ "vst", OPT_STRING | HAS_ARG | OPT_EXPERT, { &wanted_stream_spec[AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO] }, "select desired video stream", "stream_specifier" },
{ "sst", OPT_STRING | HAS_ARG | OPT_EXPERT, { &wanted_stream_spec[AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE] }, "select desired subtitle stream", "stream_specifier" },
- -ast n 指定⾳频流(⽐如我们在看电影时,有些电影可以⽀持普通话和英⽂切换,此时可以⽤该命令进⾏选择)
- -vst n 指定视频流
- -vst n 指定字幕流
将对应的index值记录到st_index[AVMEDIA_TYPE_NB];
使⽤缺省的流进⾏播放
如果我们没有指定,则ffplay主要是通过<font style="color:rgb(38,38,38);">av_find_best_stream</font>来选择,其原型为:
/*** Find the "best" stream in the file.* The best stream is determined according to various heuristics as the most* likely to be what the user expects.* If the decoder parameter is non-NULL, av_find_best_stream will find the* default decoder for the stream's codec; streams for which no decoder can* be found are ignored.** @param ic media file handle* @param type stream type: video, audio, subtitles, etc.* @param wanted_stream_nb user-requested stream number,* or -1 for automatic selection* @param related_stream try to find a stream related (eg. in the same* program) to this one, or -1 if none* @param decoder_ret if non-NULL, returns the decoder for the* selected stream* @param flags flags; none are currently defined* @return the non-negative stream number in case of success,* AVERROR_STREAM_NOT_FOUND if no stream with the requested type* could be found,* AVERROR_DECODER_NOT_FOUND if streams were found but no decoder* @note If av_find_best_stream returns successfully and decoder_ret is not* NULL, then *decoder_ret is guaranteed to be set to a valid AVCodec.*/
int av_find_best_stream(AVFormatContext *ic,enum AVMediaType type,int wanted_stream_nb,int related_stream,AVCodec **decoder_ret,int flags);
- 如果⽤户没有指定流,或指定部分流,或指定流不存在,则主要由av_find_best_stream发挥作⽤。
- 如果指定了正确的wanted_stream_nb,⼀般情况都是直接返回该指定流,即⽤户选择的流。
- 如果指定了相关流,且未指定⽬标流的情况,会在相关流的同⼀个节⽬中查找所需类型的流,但⼀般结果,都是返回该类型第1个流。
通过 AVCodecParameters 和 av_guess_sample_aspect_ratio 计算出显示窗口宽、高
// 从待处理流中获取相关参数,设置显示窗口的宽度,高度及宽度高比
if (st_index[AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO] >= 0) {AVStream *st = ic->streams[st_index[AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO]];AVCodecParameters *codecpar = st->codecpar;AVRational sar = av_guess_sample_aspect_ratio(ic, st, NULL);if (codecpar->width)// 设置显示窗口的大小和宽高比set_default_window_size(codecpar->width, codecpar->height, sar);
}
具体流程如上所示,这⾥实质只是设置了default_width、default_height变量的⼤⼩,没有真正改变窗⼝的⼤⼩。真正调整窗⼝⼤⼩是在视频显示调⽤video_open()函数进⾏设置。
stream_component_open()
经过以上步骤,⽂件打开成功,且获取了流的基本信息,并选择⾳频流、视频流、字幕流。接下来就可以 所选流对应的解码器了。
/* open the streams */
// 打开视频、⾳频解码器。在此会打开相应解码器,并创建相应的解码线程。
if (st_index[AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO] >= 0) {stream_component_open(is, st_index[AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO]);
}ret = -1;
if (st_index[AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO] >= 0) {ret = stream_component_open(is, st_index[AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO]);
}
if (is->show_mode == SHOW_MODE_NONE)//选择怎么显示,如果视频打开成功,就显示视频画⾯,否则,显示⾳频对应的频谱图is->show_mode = ret >= 0 ? SHOW_MODE_VIDEO : SHOW_MODE_RDFT;if (st_index[AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE] >= 0) {stream_component_open(is, st_index[AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE]);
}
⾳频、视频、字幕等流都要调⽤stream_component_open,他们直接有共同的流程,也有差异化的流程,差异化流程使⽤switch进⾏区分。具体原型:
static int stream_component_open(VideoState *is, int stream_index);
逐步分析:
// 为解码器分配一个编解码器上下文
avctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(NULL);
if (!avctx)return AVERROR(ENOMEM);ret = avcodec_parameters_to_context(avctx, ic->streams[stream_index]->codecpar);
if (ret < 0)goto fail;
// 设置pkt_timebase
avctx->pkt_timebase = ic->streams[stream_index]->time_base;
先通过 avcodec_alloc_context3分配解码器上下文 AVCodecContext,然后通过 avcodec_parameters_to_context把所选流的解码参数赋值给 avctx,最后设置 time_base。
avcodec_parameters_to_context 解码时用,avcodec_parameters_from_context 用来编码
// 根据codec_id查找解码器
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(avctx->codec_id);switch(avctx->codec_type){// 获取指定解码器名字,如果没有设置则为NULLcase AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO : is->last_audio_stream = stream_index; forced_codec_name = audio_codec_name; // 获取指定解码器名字break;case AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE: is->last_subtitle_stream = stream_index; forced_codec_name = subtitle_codec_name; // 获取指定解码器名字break;case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO : is->last_video_stream = stream_index; forced_codec_name = video_codec_name; // 获取指定解码器名字break;
}
if (forced_codec_name)codec = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name(forced_codec_name);
if (!codec) {if (forced_codec_name) av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_WARNING,"No codec could be found with name '%s'\n", forced_codec_name);else av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_WARNING,"No decoder could be found for codec %s\n", avcodec_get_name(avctx->codec_id));ret = AVERROR(EINVAL);goto fail;
}
这段主要是通过 <font style="color:rgb(38,38,38);">avcodec_find_decoder</font> 找到所需解码器(AVCodec)。如果⽤户有指定解码器,则设置 <font style="color:rgb(38,38,38);">forced_codec_name</font>,并通过 <font style="color:rgb(38,38,38);">avcodec_find_decoder_by_name</font> 查找解码器。找到解码器后,就可以通过 <font style="color:rgb(38,38,38);">avcodec_open2</font> 打开解码器了。forced_codec_name对应到⾳频、视频、字幕不同的传⼊的解码器名字,如果有设置,⽐如:
ffplay -acodec aac xx.flv
此时audio_codec_name被设置为"aac",则相应的forced_codec_name为“aac”。
最后,是一个大的 switch-case:
switch (avctx->codec_type) {
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO:
#if CONFIG_AVFILTER{AVFilterContext *sink;is->audio_filter_src.freq = avctx->sample_rate;is->audio_filter_src.channels = avctx->channels;is->audio_filter_src.channel_layout = get_valid_channel_layout(avctx->channel_layout, avctx->channels);is->audio_filter_src.fmt = avctx->sample_fmt;// 准备音频输出if ((ret = configure_audio_filters(is, afilters, 0)) < 0)goto fail;sink = is->out_audio_filter;sample_rate = av_buffersink_get_sample_rate(sink);nb_channels = av_buffersink_get_channels(sink);channel_layout = av_buffersink_get_channel_layout(sink);}
#elsesample_rate = avctx->sample_rate;nb_channels = avctx->channels;channel_layout = avctx->channel_layout;
#endif/* prepare audio output */if ((ret = audio_open(is, channel_layout, nb_channels, sample_rate, &is->audio_tgt)) < 0)goto fail;is->audio_hw_buf_size = ret;is->audio_src = is->audio_tgt;is->audio_buf_size = 0;is->audio_buf_index = 0;/* init averaging filter */// 初始化averaging滤镜,非audio master时使用is->audio_diff_avg_coef = exp(log(0.01) / AUDIO_DIFF_AVG_NB);is->audio_diff_avg_count = 0;/* since we do not have a precise anough audio FIFO fullness,we correct audio sync only if larger than this threshold */is->audio_diff_threshold = (double)(is->audio_hw_buf_size) / is->audio_tgt.bytes_per_sec;is->audio_stream = stream_index; // 获取audio的stream索引is->audio_st = ic->streams[stream_index]; // 获取audio的stream指针// 初始化ffplay封装的音频解码器decoder_init(&is->auddec, avctx, &is->audioq, is->continue_read_thread);if ((is->ic->iformat->flags & (AVFMT_NOBINSEARCH | AVFMT_NOGENSEARCH | AVFMT_NO_BYTE_SEEK)) && !is->ic->iformat->read_seek) {is->auddec.start_pts = is->audio_st->start_time;is->auddec.start_pts_tb = is->audio_st->time_base;}// 启动音频解码线程if ((ret = decoder_start(&is->auddec, audio_thread, "audio_decoder", is)) < 0)goto out;SDL_PauseAudioDevice(audio_dev, 0);break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO:is->video_stream = stream_index;is->video_st = ic->streams[stream_index];decoder_init(&is->viddec, avctx, &is->videoq, is->continue_read_thread);if ((ret = decoder_start(&is->viddec, video_thread, "video_decoder", is)) < 0)goto out;is->queue_attachments_req = 1;break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE:is->subtitle_stream = stream_index;is->subtitle_st = ic->streams[stream_index];decoder_init(&is->subdec, avctx, &is->subtitleq, is->continue_read_thread);if ((ret = decoder_start(&is->subdec, subtitle_thread, "subtitle_decoder", is)) < 0)goto out;break;
default:break;
}
即根据具体的流类型,作特定的初始化。但不论哪种流,基本步骤都包括了ffplay封装的解码器的初始化和启动解码器线程:
- decoder_init 初始化解码器
- d->avctx = avctx 绑定解码器上下文
- d->queue = queue 绑定对应的 packet 队列
- d->empty_queue_cond = empty_queue_cond 绑定 VideoState 的 continue_read_thread,当解码线程没有 packet 可读时唤醒 read_thread 赶紧读取数据
- d->start_pts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE 初始化 start_pts
- d->pkt_serial = -1 初始化 pkt_serial
- decoder_start 启动解码器
- packet_queue_start 启动对应的 packet 队列
- SDL_CreateThread 创建对应的解码线程
需要注意的是,对应⾳频⽽⾔,这⾥还初始化了输出参数,这块在讲⾳频输出的时候再重点展开。
For 循环读取线程
主要包括以下步骤:
- 检测是否退出
- 检测是否暂停/继续
- 检测是否需要seek
- 检测video是否为attached_pic
- 检测队列是否已经有⾜够数据
- 检测码流是否已经播放结束
a. 是否循环播放
b. 是否⾃动退出 - 使⽤av_read_frame读取数据包
- 检测数据是否读取完毕
- 检测是否在播放范围内
- 到这步才将数据插⼊对应的队列
监测是否退出
if(is->abort_request)break;
当退出事件发⽣时,调⽤do_exit() -> stream_close() -> 将is->abort_request置为1。退出该for循环,并最终退出该线程。
监测是否暂停/继续
这⾥的暂停、继续只是对⽹络流有意义
// 2 检测是否暂停/继续
if (is->paused != is->last_paused) {is->last_paused = is->paused;if (is->paused)is->read_pause_return = av_read_pause(ic);elseav_read_play(ic);
}
av_read_pause
static int rtsp_read_pause(AVFormatContext *s)
{RTSPState *rt = s->priv_data;RTSPMessageHeader reply1, *reply = &reply1;if (rt->state != RTSP_STATE_STREAMING)return 0;else if (!(rt->server_type == RTSP_SERVER_REAL && rt->need_subscription)) {ff_rtsp_send_cmd(s, "PAUSE", rt->control_uri, NULL, reply, NULL);if (reply->status_code != RTSP_STATUS_OK) {return ff_rtsp_averror(reply->status_code, -1);}}rt->state = RTSP_STATE_PAUSED;return 0;
}
av_read_play
static int rtsp_read_play(AVFormatContext *s)
{RTSPState *rt = s->priv_data;RTSPMessageHeader reply1, *reply = &reply1;int i;char cmd[1024];av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "hello state=%d\n", rt->state);rt->nb_byes = 0;if (rt->lower_transport == RTSP_LOWER_TRANSPORT_UDP) {for (i = 0; i < rt->nb_rtsp_streams; i++) {RTSPStream *rtsp_st = rt->rtsp_streams[i];/* Try to initialize the connection state in a* potential NAT router by sending dummy packets.* RTP/RTCP dummy packets are used for RDT, too.*/if (rtsp_st->rtp_handle &&!(rt->server_type == RTSP_SERVER_WMS && i > 1))ff_rtp_send_punch_packets(rtsp_st->rtp_handle);}}if (!(rt->server_type == RTSP_SERVER_REAL && rt->need_subscription)) {if (rt->transport == RTSP_TRANSPORT_RTP) {for (i = 0; i < rt->nb_rtsp_streams; i++) {RTSPStream *rtsp_st = rt->rtsp_streams[i];RTPDemuxContext *rtpctx = rtsp_st->transport_priv;if (!rtpctx)continue;ff_rtp_reset_packet_queue(rtpctx);rtpctx->last_rtcp_ntp_time = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;rtpctx->first_rtcp_ntp_time = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;rtpctx->base_timestamp = 0;rtpctx->timestamp = 0;rtpctx->unwrapped_timestamp = 0;rtpctx->rtcp_ts_offset = 0;}}if (rt->state == RTSP_STATE_PAUSED) {cmd[0] = 0;} else {snprintf(cmd, sizeof(cmd),"Range: npt=%"PRId64".%03"PRId64"-\r\n",rt->seek_timestamp / AV_TIME_BASE,rt->seek_timestamp / (AV_TIME_BASE / 1000) % 1000);}ff_rtsp_send_cmd(s, "PLAY", rt->control_uri, cmd, reply, NULL);if (reply->status_code != RTSP_STATUS_OK) {return ff_rtsp_averror(reply->status_code, -1);}if (rt->transport == RTSP_TRANSPORT_RTP &&reply->range_start != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {for (i = 0; i < rt->nb_rtsp_streams; i++) {RTSPStream *rtsp_st = rt->rtsp_streams[i];RTPDemuxContext *rtpctx = rtsp_st->transport_priv;AVStream *st = NULL;if (!rtpctx || rtsp_st->stream_index < 0)continue;st = s->streams[rtsp_st->stream_index];rtpctx->range_start_offset =av_rescale_q(reply->range_start, AV_TIME_BASE_Q,st->time_base);}}}rt->state = RTSP_STATE_STREAMING;return 0;
}
检查是否需要 seek
// 监测是否seek
if (is->seek_req) { // 监测是否seek请求int64_t seek_target = is->seek_pos;int64_t seek_min = is->seek_rel > 0 ? seek_target - is->seek_rel + 2: INT64_MIN;int64_t seek_max = is->seek_rel < 0 ? seek_target - is->seek_rel - 2: INT64_MAX;
// FIXME the +-2 is due to rounding being not done in the correct direction in generation
// of the seek_pos/seek_rel variablesret = avformat_seek_file(is->ic, -1, seek_min, seek_target, seek_max, is->seek_flags);if (ret < 0) {av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR,"%s: error while seeking\n", is->ic->url);} else {if (is->audio_stream >= 0) { // 音频流packet_queue_flush(&is->audioq); // 清空packet队列数据// 放入flush pkt,用来开启新的播放序列,解码器读取到flush_pkt也清空解码器packet_queue_put(&is->audioq, &flush_pkt);}if (is->subtitle_stream >= 0) { // 字幕流packet_queue_flush(&is->subtitleq);packet_queue_put(&is->subtitleq, &flush_pkt);}if (is->video_stream >= 0) { // 视频流packet_queue_flush(&is->videoq);packet_queue_put(&is->videoq, &flush_pkt);}if (is->seek_flags & AVSEEK_FLAG_BYTE) {set_clock(&is->extclk, NAN, 0);} else {set_clock(&is->extclk, seek_target / (double)AV_TIME_BASE, 0);}}is->seek_req = 0;is->queue_attachments_req = 1;is->eof = 0;if (is->paused)// 如果本身是pause状态则显示一帧继续暂停step_to_next_frame(is);
}
主要的seek操作通过avformat_seek_file完成(该函数的具体使⽤在播放控制seek时做详解)。根据avformat_seek_file的返回值,如果seek成功,需要:
监测 video 是否为 attached_pic
// 检测video是否为attached_pic
if (is->queue_attachments_req) {// attached_pic附带图片。比如一些MP3,AAC音频文件附带的专辑封面,所以需要注意的是音频文件// 不一定只存在音频流本身if (is->video_st && is->video_st->disposition & AV_DISPOSITION_ATTACHED_PIC) {AVPacket copy = { 0 };if ((ret = av_packet_ref(©, &is->video_st->attached_pic)) < 0)goto fail;packet_queue_put(&is->videoq, ©);packet_queue_put_nullpacket(&is->videoq, is->video_stream);}is->queue_attachments_req = 0;
}
AV_DISPOSITION_ATTACHED_PIC是⼀个标志。如果⼀个流中含有这个标志的话,那么就是说这个流是 *.mp3等 ⽂件中的⼀个 <font style="color:rgb(38,38,38);">Video Stream</font>。并且该流只有⼀个 <font style="color:rgb(38,38,38);">AVPacket</font>,也就是 <font style="color:rgb(38,38,38);">attached_pic</font>。这个 <font style="color:rgb(38,38,38);">AVPacket</font>中所存储的内容就是这个 *.mp3等 ⽂件的封⾯图⽚。
因此,也可以很好的解释了⽂章开头提到的为什么 <font style="color:rgb(38,38,38);">st->disposition & AV_DISPOSITION_ATTACHED_PIC</font>这个操作可以决定是否可以继续向缓冲区中添加 <font style="color:rgb(38,38,38);">AVPacket</font>。
监测队列是否已经有足够数据
⾳频、视频、字幕队列都不是⽆限⼤的,如果不加以限制⼀直往队列放⼊packet,那将导致队列占⽤⼤量 的内存空间,影响系统的性能,所以必须对队列的缓存⼤⼩进⾏控制。
PacketQueue默认情况下会有⼤⼩限制,达到这个⼤⼩后,就需要等待10ms,以让消费者——解码线程 能有时间消耗。
if (infinite_buffer<1 &&(is->audioq.size + is->videoq.size + is->subtitleq.size > MAX_QUEUE_SIZE|| (stream_has_enough_packets(is->audio_st, is->audio_stream, &is->audioq) &&stream_has_enough_packets(is->video_st, is->video_stream, &is->videoq) &&stream_has_enough_packets(is->subtitle_st, is->subtitle_stream, &is->subtitleq)))) {/* wait 10 ms */SDL_LockMutex(wait_mutex);SDL_CondWaitTimeout(is->continue_read_thread, wait_mutex, 10);SDL_UnlockMutex(wait_mutex);continue;
}
缓冲区满有两种可能:
- audioq,videoq,subtitleq三个PacketQueue的总字节数达到了MAX_QUEUE_SIZE(15M,为什么 是15M?这⾥只是⼀个经验计算值,⽐如4K视频的码率以50Mbps计算,则15MB可以缓存2.4秒,从 这么计算实际上如果我们真的是播放4K⽚源,15MB是偏⼩的数值,有些⽚源⽐较坑 同⼀个⽂件位置 附近的pts差值超过5秒,此时如果视频要缓存5秒才能做同步,那15MB的缓存⼤⼩就不够了)
- ⾳频、视频、字幕流都已有够⽤的包(stream_has_enough_packets),注意:3者要同时成⽴
第⼀种好理解,看下第⼆种中的stream_has_enough_packets:
static int stream_has_enough_packets(AVStream *st, int stream_id, PacketQueue *queue) {return stream_id < 0 || // 没有该流queue->abort_request || // 请求退出(st->disposition & AV_DISPOSITION_ATTACHED_PIC) || // 是ATTACHED_PIC// 满足PacketQueue总时长为0或总时长不超过1squeue->nb_packets > MIN_FRAMES && (!queue->duration || av_q2d(st->time_base) * queue->duration > 1.0);
}
有这么几种情况包是够用的:
- 流没有打开(stream_id < 0),没有相应的流返回逻辑true
- 有退出请求(queue->abort_request)
- 配置了AV_DISPOSITION_ATTACHED_PIC
- packet队列内包个数⼤于MIN_FRAMES(>25),并满⾜PacketQueue总时⻓为0或总时⻓超过1s
检测码流是否播放结束
使用 av_read_frame 读取数据包
读取数据包很简单,但要注意传⼊的packet,av_read_frame不会释放其数据,⽽是每次都重新申请数据。
// 读取媒体数据,得到的是⾳视频分离后、解码前的数据
ret = av_read_frame(ic, pkt); // 调⽤不会释放pkt的数据,都是要⾃⼰去释放
检测数据是否读取完毕
if (ret < 0) {if ((ret == AVERROR_EOF || avio_feof(ic->pb)) && !is->eof) {// 插入空包说明码流数据读取完毕了,刷空包是为了从解码器把所有帧都读出来if (is->video_stream >= 0)packet_queue_put_nullpacket(&is->videoq, is->video_stream);if (is->audio_stream >= 0)packet_queue_put_nullpacket(&is->audioq, is->audio_stream);if (is->subtitle_stream >= 0)packet_queue_put_nullpacket(&is->subtitleq, is->subtitle_stream);is->eof = 1; // 文件读取完毕}if (ic->pb && ic->pb->error)break;SDL_LockMutex(wait_mutex);SDL_CondWaitTimeout(is->continue_read_thread, wait_mutex, 10);SDL_UnlockMutex(wait_mutex);continue; // 继续循环 保证线程运行
} else {is->eof = 0;
}
数据读取完毕后,放对应⾳频、视频、字幕队列插⼊“空包”,以通知解码器冲刷buffer,将缓存的所有数据都解出来frame并去出来。
然后继续在for{}循环,直到收到退出命令,或者loop播放,或者seek等操作。
检测是否在播放范围内
播放器可以设置:-ss 起始位置,以及 -t 播放时⻓
// 监测是否在播放范围内
stream_start_time = ic->streams[pkt->stream_index]->start_time;
pkt_ts = pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE ? pkt->dts : pkt->pts;
pkt_in_play_range = duration == AV_NOPTS_VALUE ||(pkt_ts - (stream_start_time != AV_NOPTS_VALUE ? stream_start_time : 0)) *av_q2d(ic->streams[pkt->stream_index]->time_base) -(double)(start_time != AV_NOPTS_VALUE ? start_time : 0) / 1000000<= ((double)duration / 1000000);
从流获取的参数:
- stream_start_time:是从当前流AVStream->start_time获取到的时间,如果没有定义具体的值则默认为AV_NOPTS_VALUE,即该值是⽆效的;那stream_start_time有意义的就是0值;
- pkt_ts:当前packet的时间戳,pts有效就⽤pts的,pts⽆效就⽤dts的;
ffplay 播放的参数
- duration:使⽤"-t value"指定的播放时⻓,默认值AV_NOPTS_VALUE,即该值⽆效不⽤参考
- start_time:使⽤“-ss value”指定播放的起始位置,默认AV_NOPTS_VALUE,即该值⽆效不⽤参考
当没有指定duration播放时⻓时,很显然duration == AV_NOPTS_VALUE的逻辑值为1,所以pkt_in_play_range为1;
当duration被指定(-t value)且有效时,主要判断
(pkt_ts - (stream_start_time != AV_NOPTS_VALUE ? stream_start_time : 0)) *
av_q2d(ic->streams[pkt->stream_index]->time_base) -
(double)(start_time != AV_NOPTS_VALUE ? start_time : 0) / 1000000
<= ((double)duration / 1000000);
实质就是当前时间戳 pkt_ts - start_time 是否 < duration,这⾥分为:
- stream_start_time是否有效:有效就⽤实际值,⽆效就是从0开始
- start_time 是否有效,有效就⽤实际值,⽆效就是从0开始
- 即是pkt_ts - stream_start_time - start_time < duration
将数据插入队列
if (pkt->stream_index == is->audio_stream && pkt_in_play_range) {packet_queue_put(&is->audioq, pkt);
} else if (pkt->stream_index == is->video_stream && pkt_in_play_range&& !(is->video_st->disposition & AV_DISPOSITION_ATTACHED_PIC)) {packet_queue_put(&is->videoq, pkt);
} else if (pkt->stream_index == is->subtitle_stream && pkt_in_play_range) {packet_queue_put(&is->subtitleq, pkt);
} else {av_packet_unref(pkt); // 不如队列直接释放
}
参考资料:https://github.com/0voice
