【C++】类和对象1
1. 类和对象上
1.1 类的定义
1.1.1 类的定义格式

// 数据和方法封装放到了一起,都在类里面
// 封装的本质体现了更严格的规范管理
class Stack
{
public:// 成员函数void Init(int capacity = 4){_a = nullptr; // malloc_top = 0;_capacity = capacity;}void Push(int x){}private:// 成员变量int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;//int capacity_;////member//int m_capacity;//int mCapacity;
};面向对象三大特性:封装,继承,多态
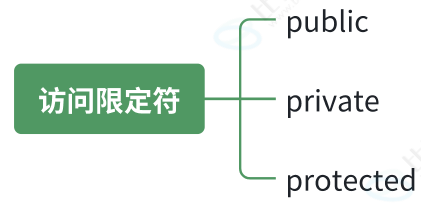
1.1.2 访问限定符

1.1.3 类域
- 类定义了一个新的作用域,类的所有成员都在类的作用域中,在类体外定义成员时,需要使用 :: 作用域操作符指明成员属于哪个类域。
- 类域影响的是编译的查找规则,下面程序中Init如果不指定类域Stack,那么编译器就把Init当成全局函数,那么编译时,找不到array等成员的声明/定义在哪里,就会报错。指定类域Stack,就是知道Init是成员函数,当前域找不到的array等成员,就会到类域中去查找。
1.2 实例化
1.2.1 实例化概念
1.2.2 对象大小
类的成员函数,成员函数的指针是不需要存储的,函数指针是一个地址,调用函数被编译成汇编指令【call地址】,其实编译器在编译链接时,就要找到函数的地址,不是在运行时找,只有动态多态是在运行时找,就需要存储函数地址。
类实例化的对象也要符合内存对齐的规则

class Stack
{
public:// 成员函数void Init(int n = 4){}//private:// 成员变量,声明int* array; // 4 8 4size_t capacity; // 8 8 size_t top; // 8 8 8
};int main()
{// 定义,类实例化对象Stack s1;s1.top = 0;s1.Init();Stack s2;s1.top = 1;s2.Init(100);cout << sizeof(s1) << endl; //24cout << sizeof(Stack) << endl; //24return 0;
}
class A
{
public:void Print(){cout << _ch << endl;}
private:char _ch;int _i;
};class B
{
public:void Print(){//...}
};class C
{};int main()
{cout << sizeof(A) << endl; //4// 开1byte为了占位,不存储实际数据,表示对象存在过cout << sizeof(B) << endl; //1cout << sizeof(C) << endl; //1B b1;B b2;cout << &b1 << endl; //00000037F8EFF6D4cout << &b2 << endl; //00000037F8EFF6D4return 0;
}
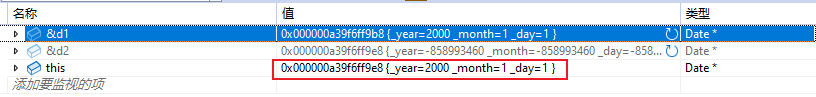
1.2.3 this指针

class Date
{
public://void Init(Date* const this, int year, int month, int day)void Init(int year, int month, int day){cout << this << endl;//const保护this不能修改//this = nullptr;//this->_year = year;this->_year = year;this->_month = month;_day = day;}void Print(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}
private:// 这里只是声明,没有开空间int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1;Date d2;// d1.Init(&d1, 2025, 7, 31);d1.Init(2025, 7, 31);//d2.Init(&d2, 2025, 7, 31);d2.Init(2025, 9, 1);d1.Print();d2.Print();return 0;
}2. 类和对象中
2.1 类的默认成员函数
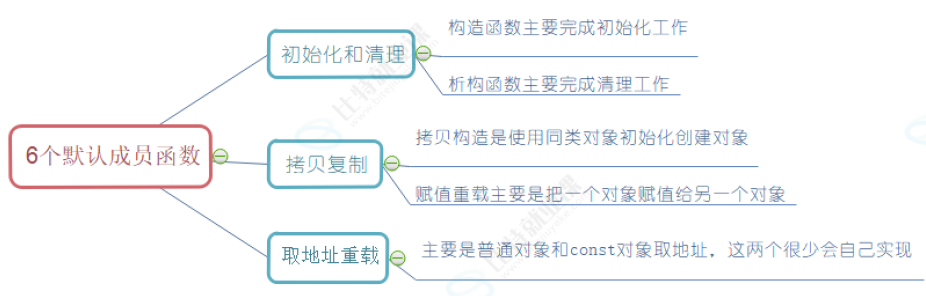
默认成员函数就是用户没有显式实现,编译器会自动生成的成员函数称为默认成员函数。一个类,我们不写的情况下编译器会默认生成以下6个默认成员函数,需要注意的是这6个中最重要的是前4个,最后两个取地址重载不重要,我们稍微了解一下即可。其次就是C++11以后还会增加两个默认成员函数,移动构造和移动赋值,这个我们后面再讲解。默认成员函数很重要,也比较复杂,我们要从两个方面去学习:
- 第一:我们不写时,编译器默认生成的函数行为是什么,是否满足我们的需求。
- 第二:编译器默认生成的函数不满足我们的需求,我们需要自己实现,那么如何自己实现?
2.2 构造函数
构造函数是特殊的成员函数,需要注意的是,构造函数虽然名称叫构造,但是构造函数的主要任务并不是开空间创建对象(我们常使用的局部对象是栈帧创建时,空间就开好了),而是对象实例化时初始化对象。构造函数的本质是要替代我们以前Stack和Date类中写的Init函数的功能,构造函数自动调用的特点就完美的替代的了Init。


说明:C++把类型分成内置类型(基本类型)和自定义类型。内置类型就是语言提供的原生数据类型,如:int/char/double/指针等,自定义类型就是我们使用class/struct等关键字自己定义的类型。
class Date
{
public://1. 无参构造函数//Date() //{// _year = 2000;// _month = 1;// _day = 1;//}// 2. 带参构造函数,不是默认构造函数//Date(int year, int month, int day) //{// _year = year;// _month = month;// _day = day;//}// 3. 全缺省构造函数Date(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void Print() {cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;};int main() {//函数声明/*Date func();*/Date d1; //2000/1/1Date d2 = Date(2025, 9, 9); //2025/9/9d1.Print();d2.Print();
}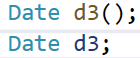
注意:如果通过无参构造函数创建对象时,对象后面不用跟括号,否则编译器无法区分这里是函数声明还是实例化对象
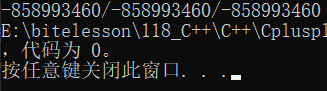
对于第七点,编译器默认生成的构造,对于内置变量的初始化没有要求:
class Date {
public:void Print() {cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day;}
private://内置类型int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main() {Date d1;d1.Print();return 0;
}
对于自定义类型的成员变量,要求调用这个自定义成员变量的默认构造函数,如果这个自定义成员变量没有默认构造函数,则会报错,否则用初始化列表解决(后续讲到)
自定义成员变量有默认构造函数:
class Stack {
public:Stack(){_a = nullptr;_top = 0;_capacity = 0;}private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};// 两个栈实现一个队列
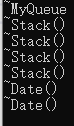
class MyQueue
{
private:// 自定义类型Stack _pushst;Stack _popst;};int main() {MyQueue q;return 0;
}如果自定义类型没有默认构造函数,则会报错:
class Date {
public:void Print() {cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day;}
private://内置类型int _year;int _month;int _day;
};class Stack {
public:Stack(int n){_a = nullptr;_top = 0;_capacity = 0;}private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};// 两个栈实现一个队列
class MyQueue
{
private:// 自定义类型Stack _pushst;Stack _popst;};int main() {Date d1;d1.Print();MyQueue q;return 0;
}
自定义成员的默认构造函数中如果有内置类型:
class Date {
public:void Print() {cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day;}
private://内置类型int _year;int _month;int _day;
};class Stack {
public:Stack(){_a = nullptr;_top = 0;_capacity = 0;}private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};// 两个栈实现一个队列
class MyQueue
{
private:// 自定义类型Stack _pushst;Stack _popst;int _size;};int main() {Date d1;d1.Print();MyQueue q;return 0;
}内置函数初始化的变量:
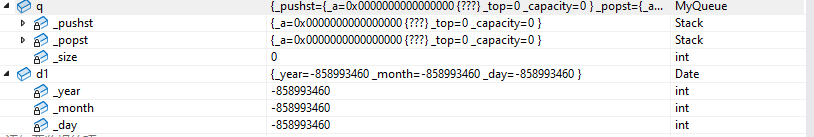
2.3 析构函数
析构函数与构造函数功能相反,析构函数不是完成对对象本身的销毁,比如局部对象是存在栈帧的,函数结束栈帧销毁,他就释放了,不需要我们管,C++规定对象在销毁时会自动调用析构函数,完成对象中资源的清理释放工作。析构函数的功能类比我们之前Stack实现的Destroy功能,而像Date没有Destroy,其实就是没有资源需要释放,所以严格说Date是不需要析构函数的。


后定义的先析构
//析构函数
class Date {
public:Date(int year=2000, int month=1, int day=1) {_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void Print() {cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}//日期类的析构函数可以不写,因为没有资源释放的需求~Date(){cout << "~Date()" << _day;}private://内置类型int _year;int _month;int _day;
};class Stack {
public:Stack(){_a = nullptr;_top = 0;_capacity = 0;}private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};int main() {Date d1;Date d2;return 0;
}
对于第五点:
//析构函数
class Date {
public:Date(int year=2000, int month=1, int day=1) {_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void Print() {cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}//日期类的析构函数可以不写,因为没有资源释放的需求~Date(){cout << "~Date()" << _day;}private://内置类型int _year;int _month;int _day;
};class Stack {
public:Stack(int n = 4){_a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);//检查a是否开辟成功_top = 0;_capacity = n;}// 有资源申请,自己写析构~Stack() {if (_a) {cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = 0;_capacity = 0;}}private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};// 两个栈实现一个队列
class MyQueue
{
private:// 自定义类型Stack _pushst;Stack _popst;int _size;};int main() {Date d1;Date d2;Stack s1;Stack s2(10);MyQueue q;return 0;
}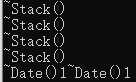
对于第六点,对于自定义类型成员,显示写析构和不显示写析构,默认生成都会去调用自定义类型成员的析构,就是为了保证资源不会泄露
对于括号匹配问题,C和C++的区别

2.4 拷贝构造
如果一个构造函数的第一个参数是自身类类型的引用,且任何额外的参数都有默认值,则此构造函数也叫做拷贝构造函数,也就是说拷贝构造是一个特殊的构造函数。
拷贝构造的特点:

class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}Date(Date& d) {_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};// 自定义类型传值传参要调用拷贝构造
void Func(Date d)
{}
//void Func(Date& d)
//{
//
//}int main()
{Date d1(2025, 8, 1);// 拷贝构造,拷贝同类型的对象完成初始化Date d2(d1);Func(d1);
}
传值传参需要调用拷贝构造
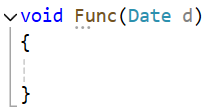

这个Func(d1),d1传给Func里的d,需要先调用拷贝构造,再进去Func函数(先完成传参这个动作)
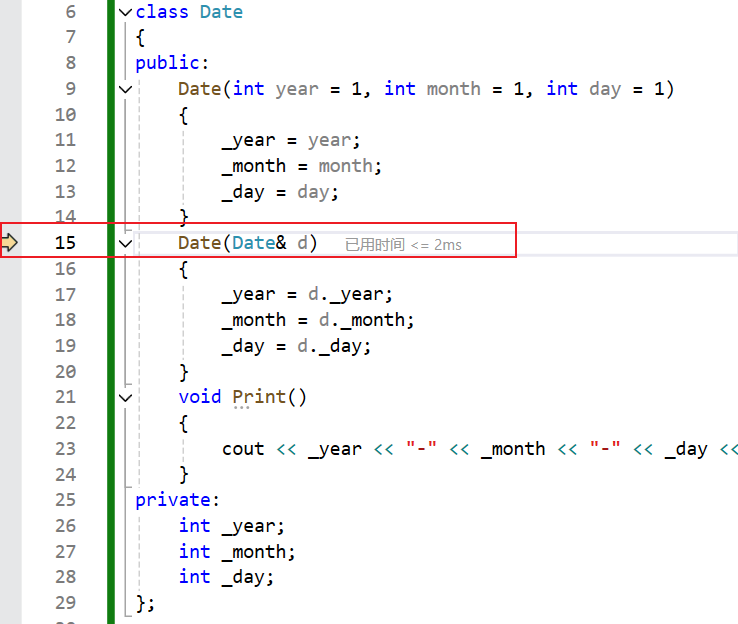
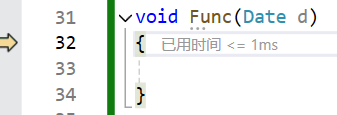
如果是引用传参,就不需要调用拷贝构造,直接进来就调用函数
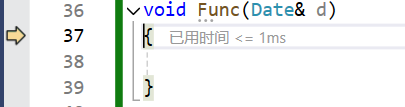

如果拷贝构造是传值传参,则会出现无穷递归的情况
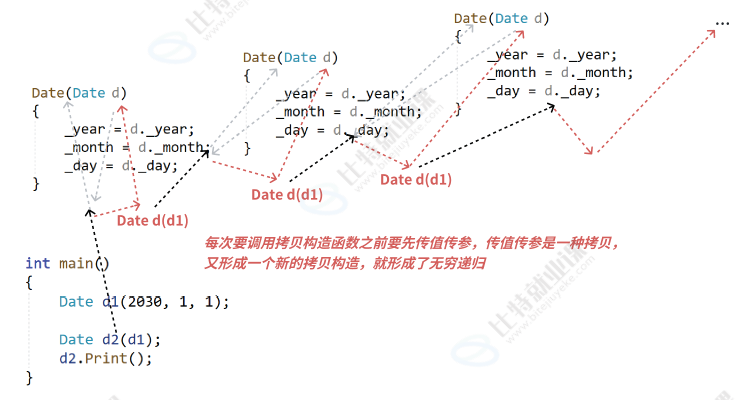
如果使用引用传参,就不会出现这个问题,建议引用传参都要加const,加const方便传参,权限可以平移,也可以缩小,但不能放大
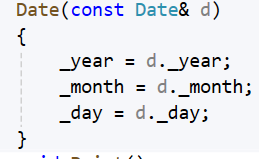
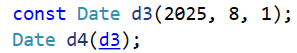
如果不加,就会出现权限放大的问题:
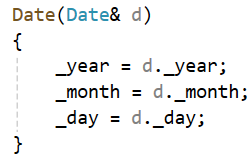
![]()

栈Stack的拷贝构造(出错情况):
typedef int STDataType;
class Stack
{
public:Stack(int n = 4){_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * n);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc申请空间失败");return;}_capacity = n;_top = 0;}// Stack st2(st1);//Stack(const Stack& s)//{// _a = s._a;// _capacity = s._capacity;// _top = s._top;//}Stack(const Stack& s){_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * s._capacity);if (_a == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}memcpy(_a, s._a, s._top * sizeof(STDataType));_capacity = s._capacity;_top = s._top;}void Push(STDataType x){if (_top == _capacity){int newcapacity = _capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(_a, newcapacity *sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}_a = tmp;_capacity = newcapacity;}_a[_top++] = x;}~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}
private:STDataType* _a;size_t _capacity;size_t _top;
};class MyQueue
{
private:Stack _pushst;Stack _popst;
};void Func( const Date& d)
{}
// 自定义类型传值传参要调用拷贝构造
//void Func(Date d)
//{
//
//}int main()
{Date d1(2025, 8, 1);// 拷贝构造,拷贝同类型的对象完成初始化Date d2(d1);Func(d1);const Date d3(2025, 8, 1);Date d4(d3);Stack st1;st1.Push(1);st1.Push(2);st1.Push(3);Stack st2(st1);MyQueue q1;MyQueue q2(q1);}


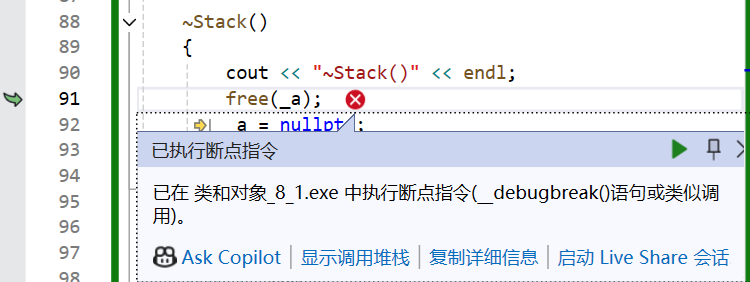
发生如下报错(程序出现内存相关的问题):
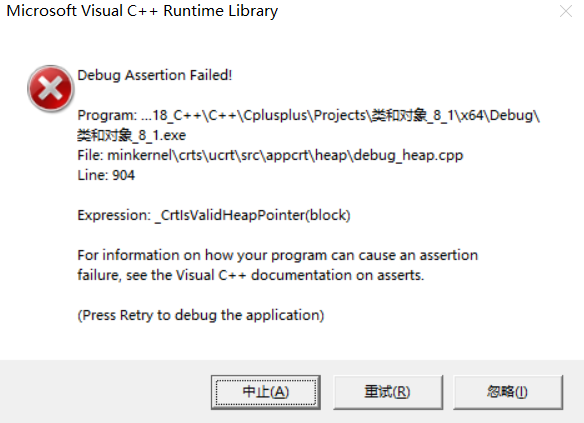
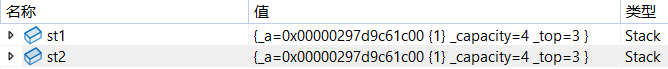
出了作用域调析构

第二次free挂了
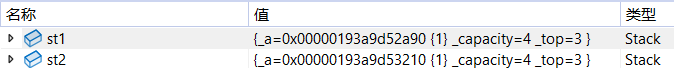
 上面的情况是浅拷贝/值拷贝,只把对象的值拷贝过去,一个对象的修改会影响另一个对象,浅拷贝的时候, 指向的是同一块空间
上面的情况是浅拷贝/值拷贝,只把对象的值拷贝过去,一个对象的修改会影响另一个对象,浅拷贝的时候, 指向的是同一块空间
如果是内置类型,可以用浅拷贝,但如果是自定义的类型,尤其是有指向的资源,就得用深拷贝,深拷贝指向的是不同的空间

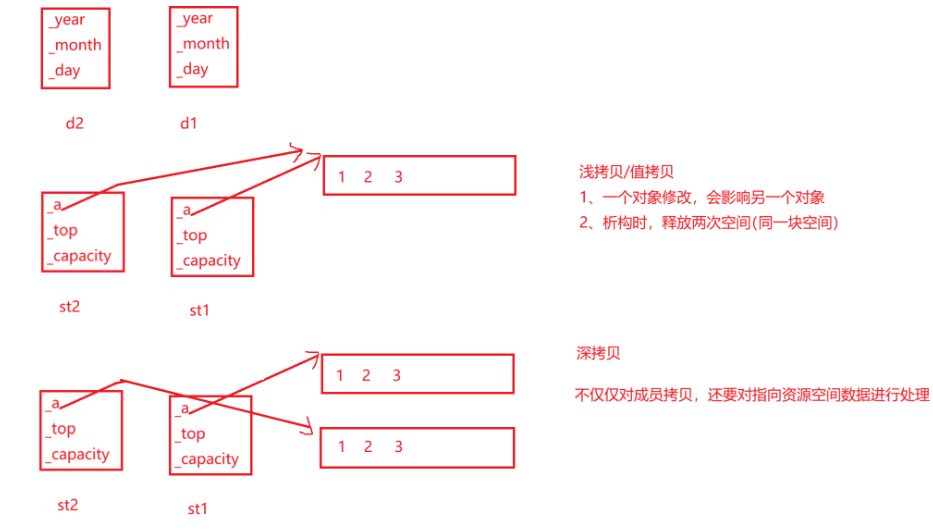
对于第四点,Date类可以调用默认的拷贝构造,因为都是内置类型,但是Stack必须自己写一个拷贝构造,原因如上,MyQueue类也可以调用默认的拷贝构造,因为对自定义类型成员变量会调用他的拷贝构造,也就是说会调用Stack的拷贝构造。一个类的析构和拷贝构造通常是绑定在一起的
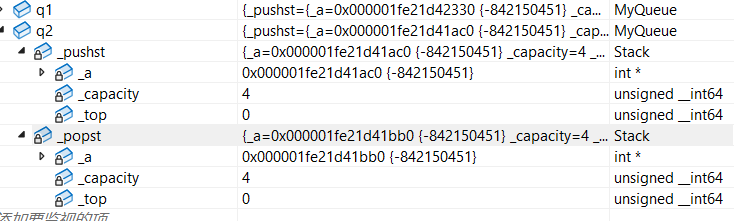
栈的传引用返回(会出现野指针的现象):
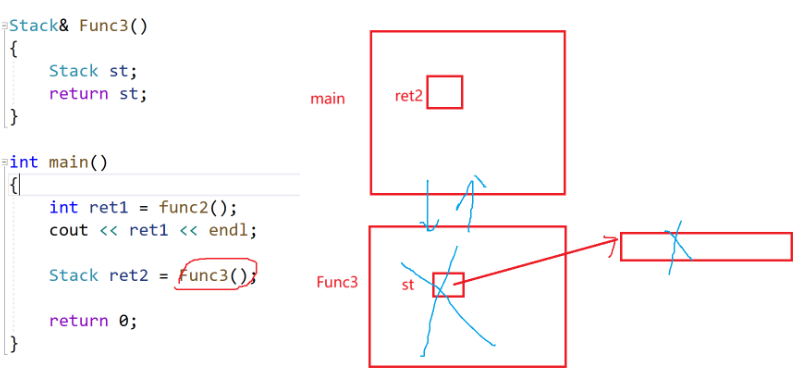
如果是传值返回,会调用拷贝构造

以下两种形式都是拷贝构造

第二行这样写就有点怪
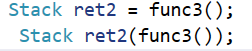
2.5 赋值运算符重载
2.5.1 运算符重载
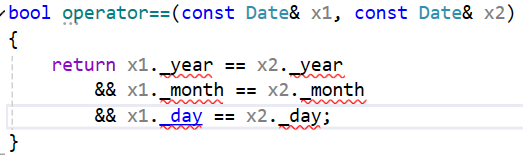
如果运算符重载函数在类外,而类内的成员变量为private修饰,那么成员变量就会不可访问,所以一般运算符重载函数写在类内
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}//其实还有个形参thisbool operator==(const Date& d){return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1(2025, 8, 1);Date d2(2025, 10, 1);cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;d1.operator==(d2);return 0;
}
成员函数的指针要指明域
void func1()
{cout << "void func()" << endl;
}class A
{
public:void func2(){cout << "A::func()" << endl;}
};int main()
{// 普通函数指针void(*pf1)() = func1;(*pf1)();// A类型成员函数的指针void(A::*pf2)() = &A::func2;A aa;(aa.*pf2)();return 0;
}
void(A::*pf2)() = &A::func2;A前面加&相当于是一种C++规定

![]()
2.5.2 赋值运算符重载

拷贝构造和赋值运算符重载的区别:
请牢牢记住赋值重载完成两个已经存在的对象直接的拷贝赋值
而拷贝构造用于一个对象拷贝初始化给另一个要创建的对象
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}// Date d4(d3);Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}// d1 = d3 = d5// d1 = d1Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1(2025, 8, 1);Date d2(d1);// 一定注意,这个是拷贝构造Date d4 = d1;Date d3(2025, 10, 1);d1 = d3;Date d5(2025, 9, 1);d1 = d3 = d5;d1 = d1;return 0;
}2.6 日期类的实现
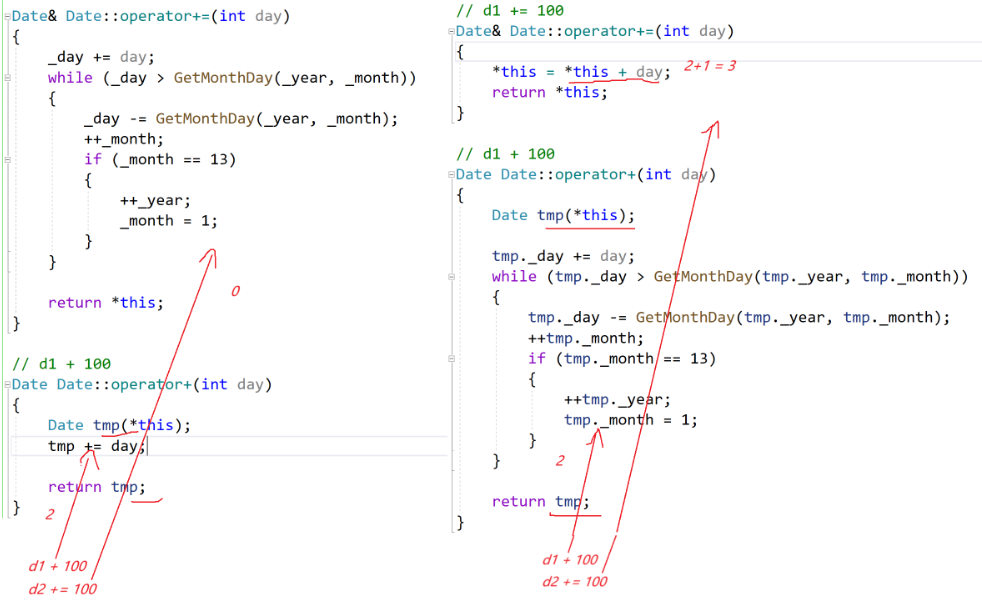
要实现日期类的加减法,加法思路如下,向月份进位(30/31天,二月份另算),减法思路类似,向月份借位(30/31天,二月份另算)

拷贝次数如下图所示:
代码:
Date.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public://全缺省参数在只函数声明或者函数定义Date(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1);void Print();int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){assert(month > 0 && month < 13);int MonthDayArray[13] = { -1, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)){return 29;}else{return MonthDayArray[month];}}bool operator<(const Date& d);bool operator<=(const Date& d);bool operator>(const Date& d);bool operator>=(const Date& d);bool operator==(const Date& d);bool operator!=(const Date& d);// d1 += 天数Date& operator+=(int day);Date operator+(int day);// d1 -= 天数Date& operator-=(int day);Date operator-(int day);// d1 - d2int operator-(const Date& d);// ++d1 -> d1.operator++()Date& operator++();// d1++ -> d1.operator++(0)// 为了区分,构成重载,给后置++,强行增加了一个int形参// 这里不需要写形参名,因为接收值是多少不重要,也不需要用// 这个参数仅仅是为了跟前置++构成重载区分Date operator++(int);Date& operator--();Date operator--(int);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
Date.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Date.h"Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;
};void Date::Print()
{cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}//原始写法,完整的
// d1 += 100
//Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
//{
// _day += day;
// while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
// {
// _day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
// ++_month;
// if (_month == 13) {
// ++_year;
// _month = 1;
// }
// }
// return *this;
//}
//
//// d1+100
//Date& Date::operator+(int day)
//{
// Date& tmp(*this);
//
// tmp._day += day;
//
// while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
// {
// tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
// ++tmp._month;
// if (tmp._month == 13) {
// ++tmp._year;
// tmp._month = 1;
// }
// }
// return tmp;
//
//}//另外一种写法一
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);++_month;if (_month == 13){++_year;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}// d1 + 100
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp += day;return tmp;
}//// 另一种写法二
//// d1 += 100
//Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
//{
// *this = *this + day;
// return *this;
//}
//
//Date& Date::operator+(int day)
//{
// Date& tmp(*this);
// tmp._day += day;
// while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
// {
// tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
// ++tmp._month;
// if (tmp._month == 13) {
// ++tmp._year;
// tmp._month = 1;
// }
// }
// return tmp;
//}// 前置++ 和后置++
// 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{*this += 1;return *this;
}
// 后置++, 为了和前置++进行区分达到重载,形参中添加int, 但这个int不起作用
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this += 1;return tmp;
}// 日期类的减法
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{//if (day < 0) //减法变加法//{// return *this += _day;//}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){--_month;_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month); //借上个月的天数if (_month == 0) {--_year;_month = 12;}}return *this;
}Date Date::operator-(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp -= day;return tmp;
}Test.cpp
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 日期类的实现
#include"Date.h"int main()
{// 日期加法//Date d1(2025, 8, 1);//Date d2 = d1 += 100;//d1.Print(); //2025-11-9//d2.Print(); //2025-11-9//Date d3(2025, 8, 1);//Date d4 = d3 + 100;//d3.Print(); //2025-8-1//d4.Print(); //2025-11-9//前置++和后置++//Date d1(2025, 8, 1);////Date ret1 = d1.operator++(10); // 显示调用,实参只要是整形就可以//Date ret1 = d1++;//ret1.Print(); //2025-8-1//d1.Print(); //2025-8-2////Date d2(2025, 8, 1);//Date ret2 = ++d2;////Date ret2 = d2.operator++();//ret2.Print(); //2025-8-2//d2.Print(); //2025-8-2// 日期类的减法Date d1(2025, 11, 9);Date d2 = d1 -= 100;d1.Print(); //2025 - 8 - 1d2.Print(); //2025 - 8 - 1Date d3(2025, 11, 9);Date d4 = d3 - 100;d3.Print(); //2025-11-9d4.Print(); //2025 - 8 - 1return 0;}