IDEA使用Maven和MyBatis简化数据库连接(实现篇)
目录
MyBatis官网:从 XML 中构建 SqlSessionFactory
一、引入MyBatis:
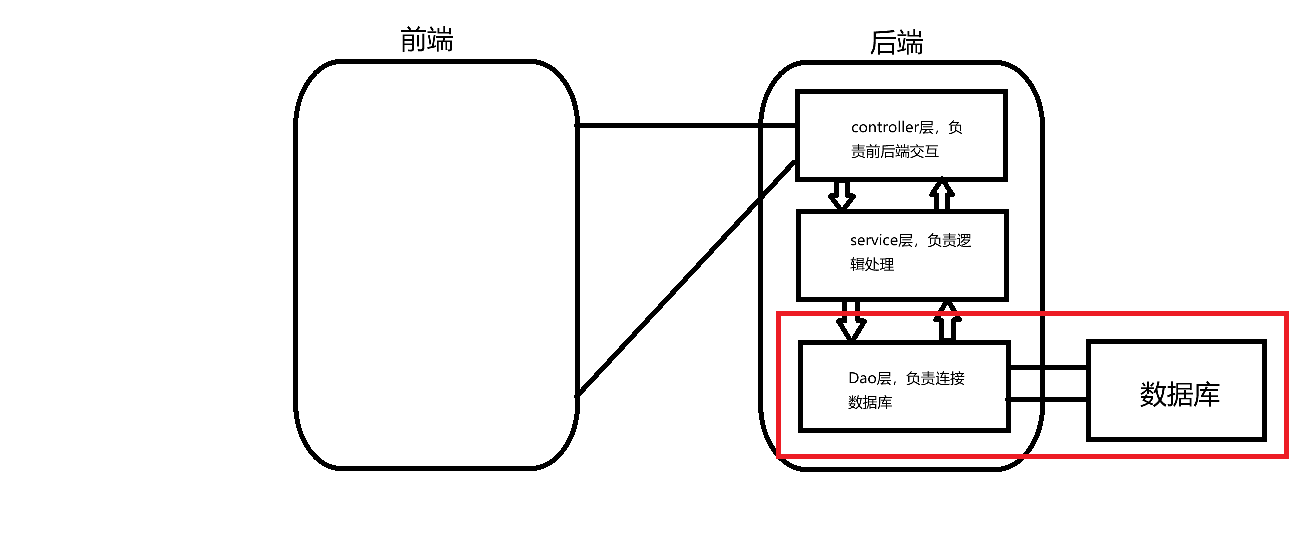
1.后端对于前端数据的处理和反馈大致分为三个层:controller层负责前后端交互,service层负责进行逻辑处理,Dao层也叫持久层,负责连接数据库。
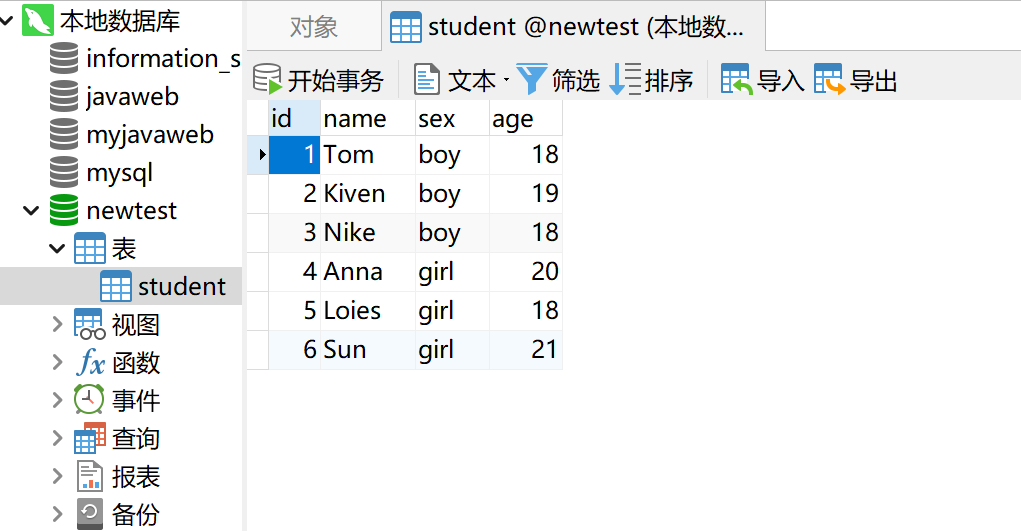
2.打开数据库,创建一个新的数据库并创建一个新的表来方便实验(我取的数据库名为“newtest”,表名为“student”的学生表)。在表中添加id、name、sex、age几个字段并填写数据:
3.打开pom.配置文件,在dependencies标签中导入mybatis和mysql的相关包(不需要实际导入,只需要拿到“坐标”):
具体引入的内容:
(1). 引入MyBatis的3.4.5的版本的坐标,保证是MyBatis
(2). 引入MySQL驱动的jar包,5.1.6版本,保证能够连接到数据库
(3). 引入Junit单元测试的jar包
(4). 引入log4j的jar包,1.2.12版本(需要引入log4j.properties的配置文件)
在dependencies中填写:
<dependencies>
<!--mybatis核心包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.10</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 日志 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>导入成功后,点击右上角的M标志刷新:
二、测试:
1.创建实体类:数据库映射到程序中还需要借助entity层,用于存储对应数据库中的信息(类对表,属性对应字段)。在main-->java-->com.newFile目录下创建一个“dao”包和“entity”包。在entity中创建students实体类(表名与类名无关,但字段名与属性名相关)。
填写属性和封装方法:
private int id;private String name;private int age;private String sex;public int getId() {return id;}public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getSex() {return sex;}public void setSex(String sex) {this.sex = sex;}//toString方法@Overridepublic String toString() {return "students{" +"id=" + id +", name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +", sex='" + sex + '\'' +'}';}2.在dao中编写一个接口作为规范:在dao目录下创建一个名为“StudentDao”的接口文件(名字可以任取),我们先编写一个findAll方法测试:
package com.newFile.dao;
//引入students包
import com.newFile.entity.students;
//引入list
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentDao {//定义findAll方法查找所有内容public List<students> findAll();
}3.创建接口的实现类:在main目录下创建一个resources资源目录,资源目录中存放着所有接口的实现类。再在resources中创建一个mapper目录存放接口的实现类(方便后续配置),在mapper目录下创建一个xml配置文件并通过配置文件创建接口的实现类,将配置文件命名为“StudentDao”并写入:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.newFile.dao.StudentDao"></mapper>再在resources目录下创建一个主配置文件命名为“SqlMapConfig.xml”并填入:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configurationPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration><environments default="mysql"><environment id="mysql"><!--配置事务的类型,使用本地事务策略--><transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager><!--是否使用连接池 POOLED表示使用链接池,UNPOOLED表示不使用连接池--><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/><!--student为数据库名--><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/newtest"/><!--这里写你mysql数据库的用户名和密码--><property name="username" value="root"/><property name="password" value="root"/></dataSource></environment></environments><mappers><!--实现类的路径--><mapper resource="mapper/StudentDao.xml"></mapper></mappers>
</configuration>在接口实现文件的“mapper”标签中就可以写sql语句了,实现的是findAll方法:
<select id="findAll" resultType="com.newFile.entity.students">select * from student
</select>其中:(应该传入包装类型的类全名)
1.id表示接口中定义的对应方法
2.parameterType表示方法需要传入的参数
3.resultType表示返回值的类型
4.测试:
MyBatis官网:从 XML 中构建 SqlSessionFactory
每个基于 MyBatis 的应用都是以一个 SqlSessionFactory 的实例为核心的。SqlSessionFactory 的实例可以通过 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 获得。而 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 则可以从 XML 配置文件或一个预先配置的 Configuration 实例来构建出 SqlSessionFactory 实例。
从 XML 文件中构建 SqlSessionFactory 的实例非常简单,建议使用类路径下的资源文件进行配置。 但也可以使用任意的输入流(InputStream)实例,比如用文件路径字符串或 file:// URL 构造的输入流。MyBatis 包含一个名叫 Resources 的工具类,它包含一些实用方法,使得从类路径或其它位置加载资源文件更加容易。
SqlSession 是 MyBatis 框架的核心接口,用于执行 SQL 语句、管理事务以及获取映射器(Mapper)实例,是应用程序与持久层交互的直接入口。
1.在Test测试类中创建run方法:
public void run() throws IOException {//主配置文件路径String resourcePath = "SqlMapConfig.xml";//加载主配置文件,为了拿到SqlSessionFactoryInputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resourcePath);//拿到SqlSessionFactory对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);//创建SqlSessionSqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();//通过SqlSession对象创建studentDao接口的代理对象studentDao mapper = session.getMapper(studentDao.class);//通过代理访问接口中的方法List<students> arr = mapper.findAll();//打印输出for(students student : arr){System.out.println(student);}}2.创建Test对象并执行run方法:
Test test = new Test();
test.run();输出结果:
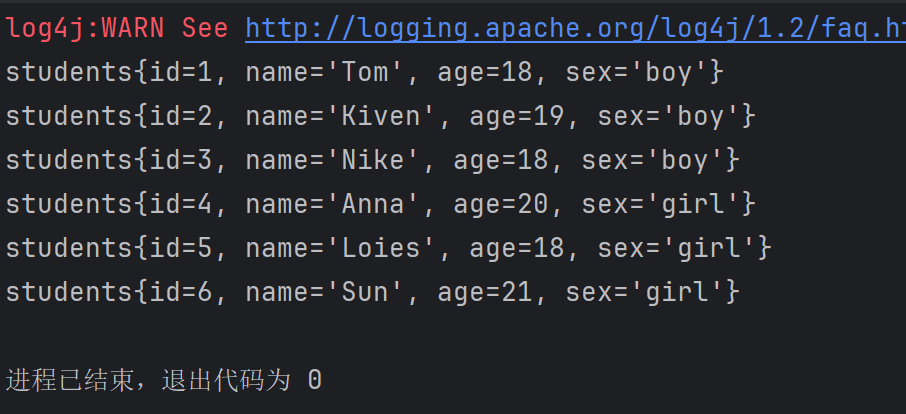
第一个sql查询就成功了。
