GFSK调制解调介绍(蓝牙GFSK BT=0.5)
一. GFSK 概念
高斯频移键控(GFSK)是一种数字调制技术,它在FSK的基础上增加了高斯滤波处理,使频谱更加紧凑,减少带外辐射。GFSK广泛应用于蓝牙、无线传感器网络等低功耗通信系统中。
- FSK: 用一种载波频率来表示数字
1(称为mark频率),用另一种载波频率来表示数字0(称为space频率)。例如,1用12kHz表示,0用8kHz表示。 - 高斯滤波: GFSK在进行FSK调制之前,先对原始的数字基带信号进行一道高斯低通滤波处理。这一步是GFSK的核心和命名来源。
- 目的: 为什么要加这个滤波器?未经处理的数字信号是方波,其频谱很宽,边带很大。直接用它去调制频率会产生非常宽的频谱,既浪费带宽又容易干扰相邻信道。高斯滤波器可以平滑方波的跳变沿,使其没有陡峭的跳变,从而极大地压缩调制后的信号频谱,提高频谱效率。
- 调制指数: 定义为
h = 2 * ΔF * T。其中ΔF是峰值频偏(载波频率最大变化量)。h=0.5意味着ΔF = 0.25 / T。调制指数决定了1和0对应频率之间的最小间隔。h=0.5是最小频移键控(MSK) 的条件,能提供最佳的频谱效率和误码性能平衡。
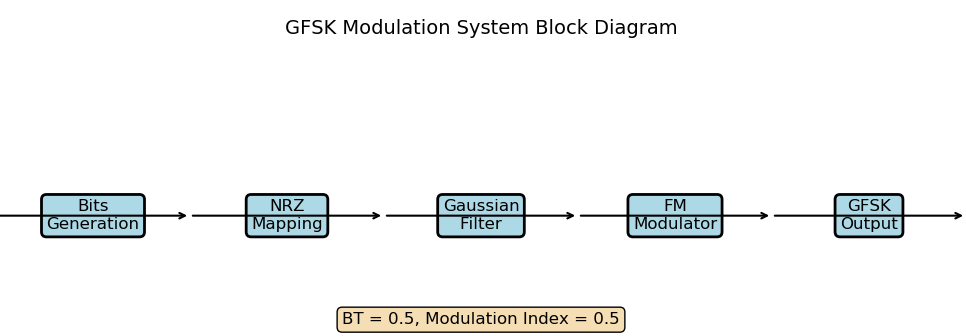
整个流程大概如下:
优点:
- 高频谱效率
- 恒包络特性(发射机功率放大器可以工作在非线性区而不会失真,效率高)
- 抗干扰能力强
二. GFSK 调制流程
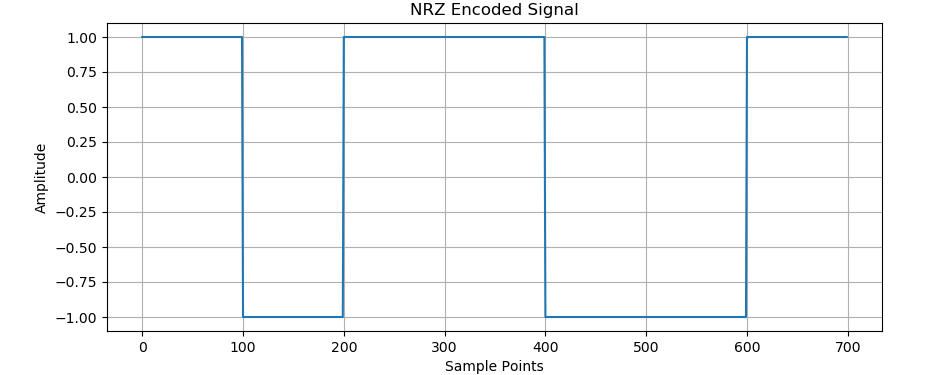
1. 生成基带NRZ信号
将输入的二进制比特流(例如 [1, 0, 1, 1, 0])转换为非归零码(NRZ)。通常用 +1 表示比特 1,用 -1 表示比特 0。
这块比较好理解,我们直接上python代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef nrz_encode(bits, samples_per_bit):"""将二进制比特流转换为NRZ信号:param bits: 二进制比特序列:param samples_per_bit: 每个比特的采样点数:return: NRZ信号"""signal = np.array([]) # 初始化一个空数组,用于存储生成的信号for bit in bits: # 遍历输入的每一个比特# 如果比特为1,生成一个长度为samples_per_bit的全1数组(表示高电平)# 如果比特为0,生成一个长度为samples_per_bit的全-1数组(表示低电平)symbol = np.ones(samples_per_bit) if bit == 1 else -np.ones(samples_per_bit)signal = np.concatenate((signal, symbol)) # 将当前比特的信号连接到总信号中return signal # 返回完整的NRZ信号# 示例使用
bits = [1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1] # 定义要编码的二进制序列
samples_per_bit = 100 # 设置每个比特用100个采样点表示
nrz_signal = nrz_encode(bits, samples_per_bit) # 调用函数生成NRZ信号# 绘制结果
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4)) # 创建图形窗口,设置大小
plt.plot(nrz_signal) # 绘制NRZ信号
plt.title('NRZ Encoded Signal') # 设置标题
plt.xlabel('Sample Points') # 设置x轴标签
plt.ylabel('Amplitude') # 设置y轴标签
plt.grid(True) # 显示网格
plt.show() # 显示图形可以看到原始的数据位[1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1]
下图就是把1变为1,0变为-1
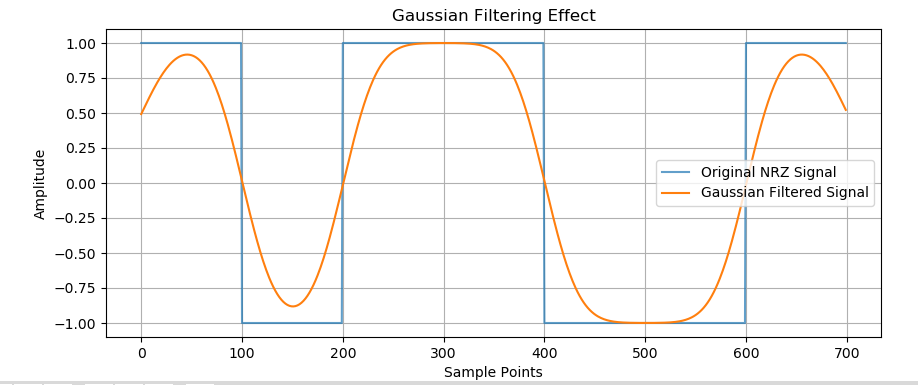
2. 高斯低通滤波
将NRZ信号通过一个截止频率由 BT 乘积决定的高斯低通滤波器。这一步将尖锐的方波脉冲平滑成类似高斯形状的脉冲。
BT乘积: 这是高斯滤波器的一个关键参数。B是滤波器的3dB带宽,T是符号周期(1/比特率)。BT值越小,滤波器带宽越窄,平滑效果越强,但过多的平滑可能会导致码间串扰(ISI)。BT=0.5是一个非常经典和常用的值(例如,蓝牙技术就使用它)。
我们先来看下BT=0.5的python代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef gaussian_filter(signal, bt_product, samples_per_bit):"""Apply Gaussian low-pass filter:param signal: Input signal:param bt_product: Bandwidth-time product (BT):param samples_per_bit: Number of samples per bit:return: Filtered signal"""# Calculate filter length and standard deviationfilter_length = 4 * samples_per_bit # Filter lengthstd_dev = np.sqrt(np.log(2)) / (2 * np.pi * bt_product) * samples_per_bit# Create Gaussian filter using NumPyx = np.arange(-filter_length//2, filter_length//2)gauss_filter = np.exp(-x**2 / (2 * std_dev**2))gauss_filter = gauss_filter / np.sum(gauss_filter) # Normalize# Apply filterfiltered_signal = np.convolve(signal, gauss_filter, mode='same')return filtered_signal# Generate NRZ signal
def nrz_encode(bits, samples_per_bit):"""Convert binary bit stream to NRZ signal:param bits: Binary bit sequence:param samples_per_bit: Number of samples per bit:return: NRZ signal"""signal = np.array([])for bit in bits:symbol = np.ones(samples_per_bit) if bit == 1 else -np.ones(samples_per_bit)signal = np.concatenate((signal, symbol))return signal# Example usage
bits = [1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1]
samples_per_bit = 100
nrz_signal = nrz_encode(bits, samples_per_bit)bt_product = 0.5 # Bandwidth-time product
filtered_signal = gaussian_filter(nrz_signal, bt_product, samples_per_bit)# Plot results
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4))
plt.plot(nrz_signal, alpha=0.7, label='Original NRZ Signal')
plt.plot(filtered_signal, label='Gaussian Filtered Signal')
plt.title('Gaussian Filtering Effect')
plt.xlabel('Sample Points')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()我们已经在前面介绍了NRZ,我们来介绍下高斯滤波器函数
def gaussian_filter(signal, bt_product, samples_per_bit):"""Apply Gaussian low-pass filter:param signal: Input signal:param bt_product: Bandwidth-time product (BT):param samples_per_bit: Number of samples per bit:return: Filtered signal"""# Calculate filter length and standard deviationfilter_length = 4 * samples_per_bit # Filter lengthstd_dev = np.sqrt(np.log(2)) / (2 * np.pi * bt_product) * samples_per_bit# Create Gaussian filter using NumPyx = np.arange(-filter_length//2, filter_length//2)gauss_filter = np.exp(-x**2 / (2 * std_dev**2))gauss_filter = gauss_filter / np.sum(gauss_filter) # Normalize# Apply filterfiltered_signal = np.convolve(signal, gauss_filter, mode='same')return filtered_signal功能解释:
参数说明:
signal:输入的NRZ信号bt_product:带宽时间积,控制滤波器的带宽(值越小,滤波器越窄)samples_per_bit:每个比特的采样点数
滤波器设计:
filter_length:滤波器长度设为比特长度的4倍std_dev:计算高斯函数的标准差,基于带宽时间积和采样点数
std_dev = np.sqrt(np.log(2)) / (2 * np.pi * bt_product) * samples_per_bit
这部分对应高斯滤波器的3dB带宽与标准差的关系。对于高斯滤波器,3dB带宽 $B$ 与标准差 $\sigma$ 的关系为:
![]()
- 创建高斯滤波器核:使用高斯函数公式
exp(-x²/(2σ²))
![]()
- 归一化滤波器:确保滤波后信号的总能量不变
gauss_filter = gauss_filter / np.sum(gauss_filter)
这确保了滤波器系数的总和为1,保持信号的直流分量不变,符合低通滤波器的特性。这相当于:
![]()
滤波操作:
- 使用
np.convolve对输入信号和高斯滤波器进行卷积
filtered_signal = np.convolve(signal, gauss_filter, mode='same')
这实现了高斯滤波的数学运算:
![]()
mode='same'确保输出信号长度与输入相同
然后我们来看看不同BT值生成的波形
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef gaussian_filter(signal, bt_product, samples_per_bit):"""Apply Gaussian low-pass filter:param signal: Input signal:param bt_product: Bandwidth-time product (BT):param samples_per_bit: Number of samples per bit:return: Filtered signal"""# Calculate filter length and standard deviationfilter_length = 4 * samples_per_bit # Filter lengthstd_dev = np.sqrt(np.log(2)) / (2 * np.pi * bt_product) * samples_per_bit# Create Gaussian filter using NumPyx = np.arange(-filter_length//2, filter_length//2)gauss_filter = np.exp(-x**2 / (2 * std_dev**2))gauss_filter = gauss_filter / np.sum(gauss_filter) # Normalize# Apply filterfiltered_signal = np.convolve(signal, gauss_filter, mode='same')return filtered_signal# Generate NRZ signal
def nrz_encode(bits, samples_per_bit):"""Convert binary bit stream to NRZ signal:param bits: Binary bit sequence:param samples_per_bit: Number of samples per bit:return: NRZ signal"""signal = np.array([])for bit in bits:symbol = np.ones(samples_per_bit) if bit == 1 else -np.ones(samples_per_bit)signal = np.concatenate((signal, symbol))return signal# Example usage
bits = [1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1]
samples_per_bit = 100
nrz_signal = nrz_encode(bits, samples_per_bit)# Selected BT values for comparison
bt_values = [0.2, 0.5, 0.8]
colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue']
line_styles = ['-', '--', '-.']# Create figure
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))# Plot original signal
plt.plot(nrz_signal, 'k-', linewidth=2, label='Original NRZ Signal')# Apply Gaussian filter with different BT values and plot
for i, bt in enumerate(bt_values):filtered_signal = gaussian_filter(nrz_signal, bt, samples_per_bit)plt.plot(filtered_signal, color=colors[i], linestyle=line_styles[i], linewidth=2, label=f'BT = {bt}')# Customize plot
plt.title('Gaussian Filtering with Different BT Values', fontsize=16)
plt.xlabel('Sample Points', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('Amplitude', fontsize=12)
plt.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=10)
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()# Add annotation to explain BT effect
plt.annotate('Lower BT = More filtering (smoother)\nHigher BT = Less filtering (sharper)', xy=(0.02, 0.98), xycoords='axes fraction',fontsize=10, ha='left', va='top',bbox=dict(boxstyle='round', facecolor='wheat', alpha=0.8))# Highlight the differences at specific points
bit_transitions = [i * samples_per_bit for i in range(len(bits) + 1)]
for transition in bit_transitions:plt.axvline(x=transition, color='gray', linestyle=':', alpha=0.5)plt.show()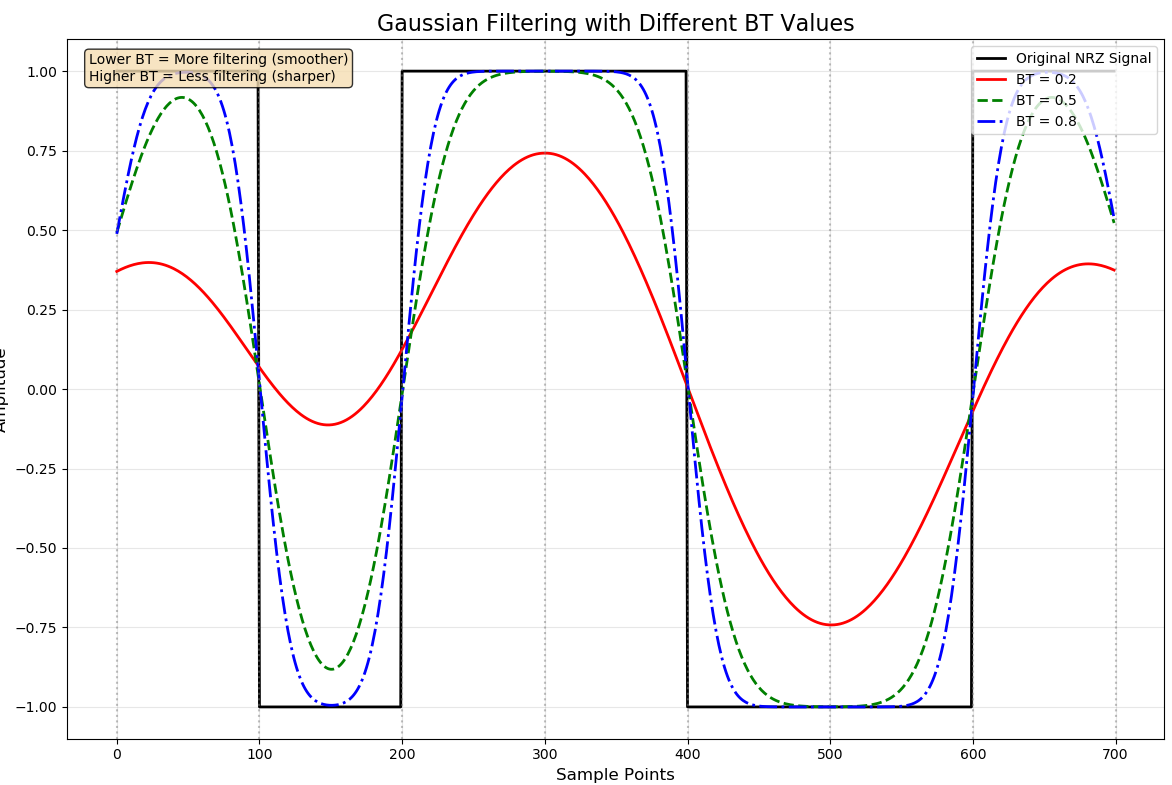
3. 频率调制
用滤波后的平滑信号去控制压控振荡器(VCO)的频率。
- 滤波后信号的每个采样点值
x[n]被当作瞬时频偏。 - 瞬时频偏
f_dev[n] = (调制指数 * 比特率) * x[n] / 2(因为NRZ信号的幅值是±1)。 - 瞬时相位
phi[n]是瞬时频率的积分:phi[n] = 2 * pi * f_dev[n] * dt的累积和,其中dt是采样间隔。
4. 生成射频信号
最终输出的GFSK信号是余弦(或正弦)载波,其相位由积分后的瞬时相位决定: s[n] = cos(2 * pi * fc * t[n] + phi[n])。
5. 完整gfsk代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef gaussian_filter(BT, samples_per_bit, L=4):"""生成高斯滤波器BT: 带宽比特周期积samples_per_bit: 每比特采样数L: 滤波器长度(以符号周期为单位)"""# 计算滤波器参数T = 1 # 归一化符号周期B = BT / T # 带宽alpha = np.sqrt(np.log(2)) / (2 * np.pi * B * T) # 高斯滤波器参数# 生成时间轴t = np.arange(-L/2, L/2, 1/samples_per_bit)# 计算高斯脉冲响应h = (1 / (alpha * np.sqrt(2 * np.pi))) * np.exp(-t**2 / (2 * alpha**2))# 归一化滤波器h = h / np.sum(h)return hdef gfsk_modulate(bits, BT=0.5, samples_per_bit=100, f_dev=0.5):"""GFSK调制器bits: 输入比特序列BT: 带宽比特周期积samples_per_bit: 每比特采样数f_dev: 频率偏移(相对于符号率)"""# 将比特转换为NRZ格式 (0 -> -1, 1 -> 1)nrz_bits = np.array([1 if bit == 1 else -1 for bit in bits])# 上采样upsampled = np.zeros(len(bits) * samples_per_bit)for i, bit in enumerate(nrz_bits):upsampled[i*samples_per_bit:(i+1)*samples_per_bit] = bit# 生成高斯滤波器gaussian_taps = gaussian_filter(BT, samples_per_bit)# 应用高斯滤波器filtered = np.convolve(upsampled, gaussian_taps, mode='same')# 计算相位变化phase = np.zeros(len(filtered))for i in range(1, len(filtered)):phase[i] = phase[i-1] + 2 * np.pi * f_dev * filtered[i] / samples_per_bit# 生成GFSK信号t = np.arange(len(phase)) / samples_per_bitgfsk_signal = np.cos(2 * np.pi * t + phase)# 生成IQ信号I = np.cos(phase)Q = np.sin(phase)return gfsk_signal, phase, filtered, I, Q# 输入比特序列
bits = [1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1]# 生成GFSK信号
gfsk_signal, phase, filtered, I, Q = gfsk_modulate(bits, BT=0.5, samples_per_bit=100)# 计算频谱 - 使用NumPy的FFT
N = len(gfsk_signal)
freq = np.fft.fftfreq(N, d=1/100) # 采样率为100Hz
spectrum = np.abs(np.fft.fftshift(np.fft.fft(gfsk_signal)))**2
spectrum_db = 10 * np.log10(spectrum / np.max(spectrum) + 1e-10) # 转换为dB,避免log(0)# 绘制结果
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 12))# 绘制原始比特(方波)
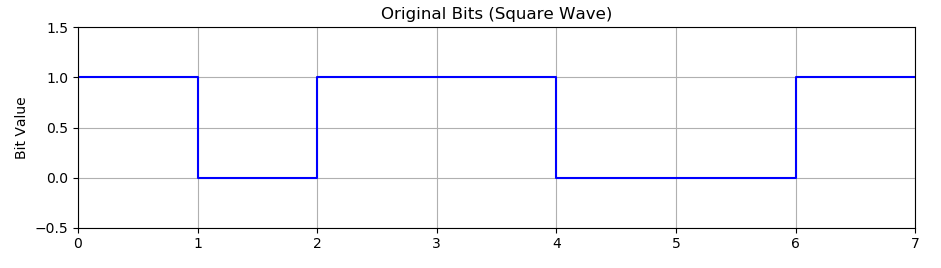
plt.subplot(4, 2, 1)
bit_times = np.arange(len(bits) + 1)
plt.step(bit_times, bits + [bits[-1]], 'b-', where='post')
plt.title('Original Bits (Square Wave)')
plt.ylabel('Bit Value')
plt.grid(True)
plt.ylim(-0.5, 1.5)
plt.xlim(0, len(bits))# 绘制滤波后的信号
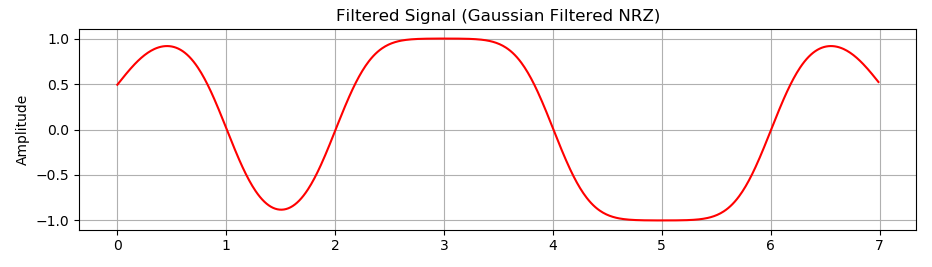
plt.subplot(4, 2, 2)
t_filtered = np.arange(len(filtered)) / 100.0
plt.plot(t_filtered, filtered, 'r-')
plt.title('Filtered Signal (Gaussian Filtered NRZ)')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.grid(True)# 绘制相位变化
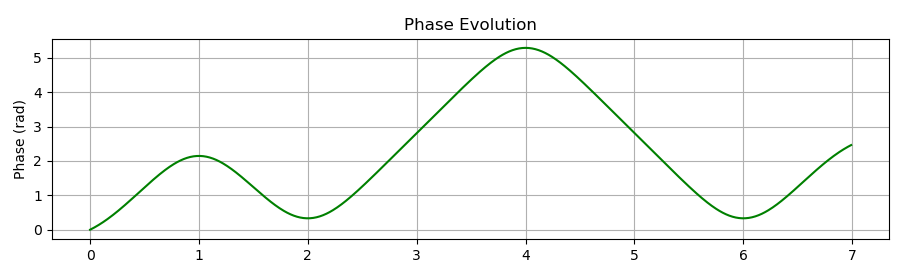
plt.subplot(4, 2, 3)
t_phase = np.arange(len(phase)) / 100.0
plt.plot(t_phase, phase, 'g-')
plt.title('Phase Evolution')
plt.ylabel('Phase (rad)')
plt.grid(True)# 绘制GFSK信号
plt.subplot(4, 2, 4)
t_signal = np.arange(len(gfsk_signal)) / 100.0
plt.plot(t_signal, gfsk_signal, 'm-')
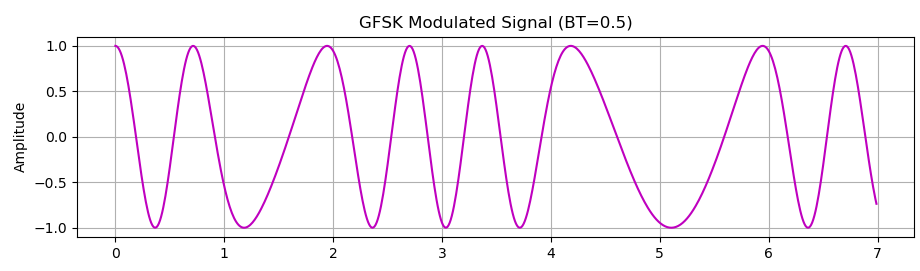
plt.title('GFSK Modulated Signal (BT=0.5)')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.grid(True)# 绘制IQ信号
plt.subplot(4, 2, 5)
t_iq = np.arange(len(I)) / 100.0
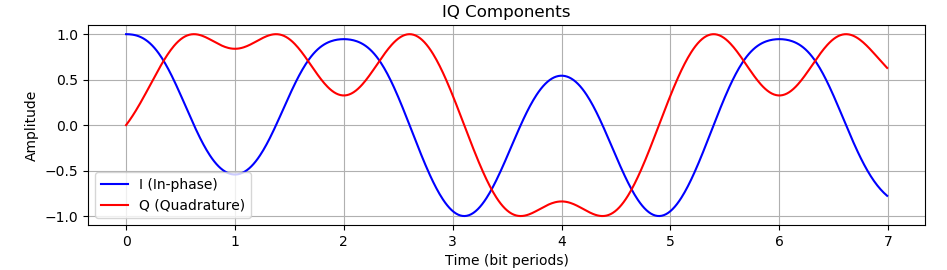
plt.plot(t_iq, I, 'b-', label='I (In-phase)')
plt.plot(t_iq, Q, 'r-', label='Q (Quadrature)')
plt.title('IQ Components')
plt.xlabel('Time (bit periods)')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)# 绘制星座图
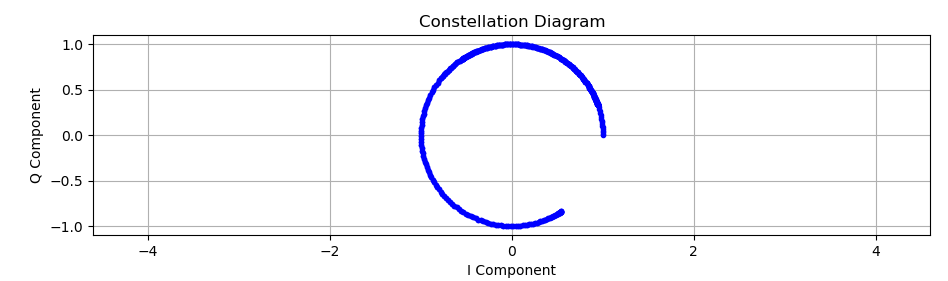
plt.subplot(4, 2, 6)
plt.plot(I, Q, 'b.')
plt.title('Constellation Diagram')
plt.xlabel('I Component')
plt.ylabel('Q Component')
plt.axis('equal')
plt.grid(True)# 绘制频谱图
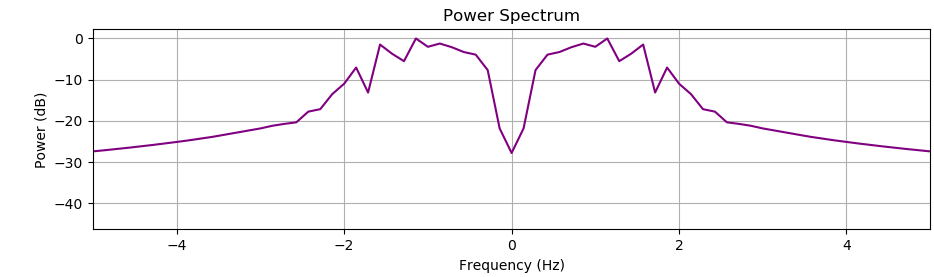
plt.subplot(4, 2, 7)
plt.plot(np.fft.fftshift(freq), spectrum_db, 'purple')
plt.title('Power Spectrum')
plt.xlabel('Frequency (Hz)')
plt.ylabel('Power (dB)')
plt.grid(True)
plt.xlim(-5, 5) # 限制频率范围以更好地观察主瓣# 绘制时频谱图
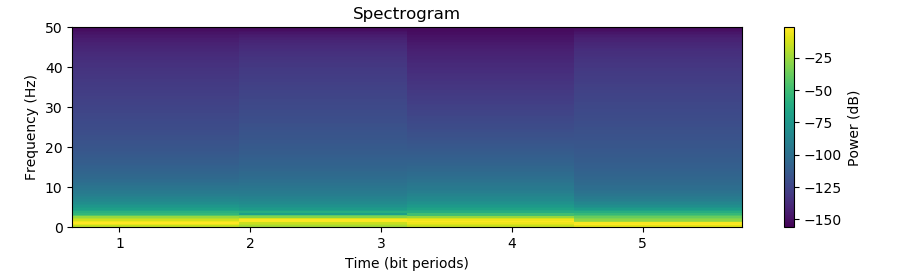
plt.subplot(4, 2, 8)
# 使用Matplotlib的specgram函数,它不依赖SciPy
plt.specgram(gfsk_signal, Fs=100, NFFT=256, noverlap=128, cmap='viridis')
plt.title('Spectrogram')
plt.xlabel('Time (bit periods)')
plt.ylabel('Frequency (Hz)')
plt.colorbar(label='Power (dB)')plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()- 原始比特(方波显示):使用阶梯图显示原始比特序列
- 滤波后的信号:显示经过高斯滤波后的NRZ信号
- 相位演变:显示调制过程中的相位变化
- GFSK调制信号:显示最终的GFSK调制信号
- IQ分量:显示GFSK信号的同相(I)和正交(Q)分量
- 星座图:显示I和Q分量的散点图,形成星座图
- 功率谱:显示GFSK信号的频谱特性
- 时频谱图:显示信号频率随时间的变化
绘制原始比特(方波)
绘制滤波后的信号
绘制相位变化
绘制GFSK信号
绘制IQ信号
绘制星座图
绘制频谱图
绘制时频谱图