系统编程day08-存储映射与共享内存
1.存储映射
存储映射 I/O (Memory-mapped I/O) 使一个磁盘文件与存储空间中的一个缓冲区相映射。于是当从缓冲区中取数据,就相当于读文件中的相应字节。于此类似,将数据存入缓冲区,则相应的字节就自动写入文件。这样,就可在不适用 read 和write 函数的情况下,使用地址(指针)完成 I/O 操作。
1.1存储映射函数mmap
函数原型:
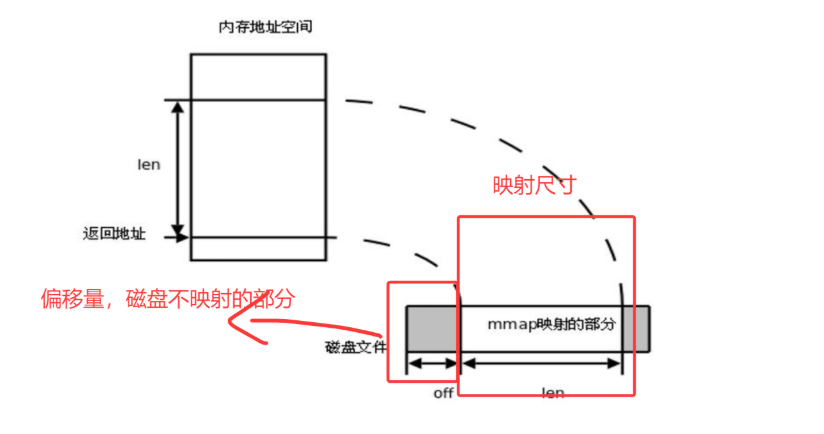
void *mmap(void *addr, size_t length, int prot, int flags,int fd, off_t offset);参数解释:
addr:指定的开始映射的内存地址,一般传入NULL,让系统自行分配
length:映射尺寸,字节位单位
prot:权限
PROT_READ 可读
PROT_WRITE 可写
flag:
MAP_SHARED 共享的 -- 对映射区的修改会影响源文件
MAP_PRIVATE 私有的
fd 文件描述符 需要打开一个文件
offset 指定一个偏移位置 ,从该位置开始映射,一般为0
1.2munmap函数
munmap函数:释放内存映射,仅仅释放当前进程,与其他进程无关
int munmap(void *addr, size_t length);参数解释:
addr 映射区的首地址
length 映射区的长度
1.3truncate函数
int truncate(const char *path, off_t length);对文件进行扩容。否则无法进行存储数据。
参数:
path:要扩容的文件
length:扩容的大小
1.4读写代码案例
写案例:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <string.h>int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{int fd = open("temp",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0664); //1.打开一个文件if (fd <0 ){perror("open()");return 0;}//2. 扩容,以往的操作是通过读写操作,但是此时是为了映射,所以后续不会读,也不会写,如果不扩容,大小一直是0int ret = truncate("temp",sizeof(long)*2);printf("%d\n",ret);//3mmap进行映射 void * p = mmap(NULL,16,PROT_WRITE | PROT_READ,MAP_SHARED,fd,0);//4地址强转 char *buff = (char *)p; //转换完就可以存入数据,那其他进程如果从这个内存读取数据可以直接都走strcpy(buff,"hello mmap");return 0;
}读案例:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <string.h>int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{int fd = open("temp",O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0664); //1.打开一个文件if (fd <0 ){perror("open()");return 0;}//2. 扩容,以往的操作是通过读写操作,但是此时是为了映射,所以后续不会读,也不会写,如果不扩容,大小一直是0int ret = truncate("temp",sizeof(long)*2);printf("%d\n",ret);//3mmap进行映射 void * p = mmap(NULL,16,PROT_WRITE | PROT_READ,MAP_SHARED,fd,0);//4地址强转 char *buff = (char *)p; //转换完就可以存入数据,那其他进程如果从这个内存读取数据可以直接都走printf("收到数据%s\n",buff);return 0;
}2.共享内存
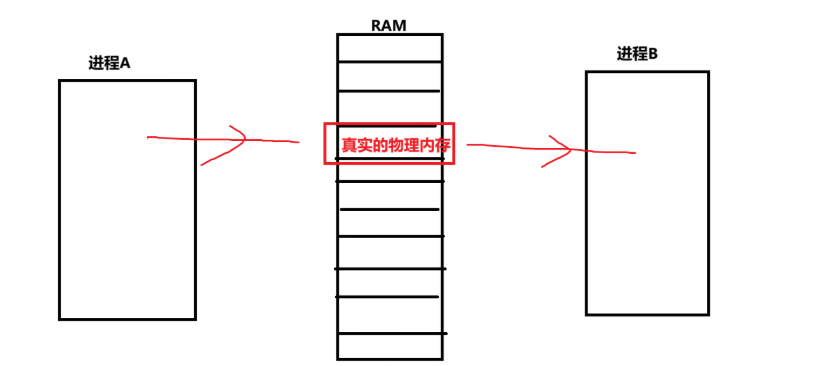
贡献内存允许两个或多个进程共享给定的存储区域。
2.1共享内存特点
1、共享内存是进程间共享数据的一种最快的方法。 一个进程向共享的内存区域写入了数据,共享这个内存区域的所有进程就可以立刻看到其中的内容。
2、使用共享内存要注意的是多个进程之间对一个给定存储区访问的互斥。 若一个进程正在向共享内存区写数据,则在它做完这一步操作前,别的进程不应当去读、写这些数据。
2.2共享内存的API
用共享内存进行通信,就好像两个人越好了在公园见面
比如两个人约好在公园的3号长椅见面。
公园:相当与内存
3号长椅:相当于key值
创建共享内存函数:shmget
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmget(key_t key, size_t size,int shmflg);功能:
创建或打开一块共享内存区
参数:
key:IPC 键值
size:该共享存储段的长度(字节)
shmflg:标识函数的行为及共享内存的权限。
IPC_CREAT:如果不存在就创建
IPC_EXCL:如果已经存在则返回失败
位或权限位:共享内存位或权限位后可以设置共享内存的访问权限,格式和 open 函数的 mode_t 一样,但可执行权限未使用。
返回值:
成功:返回共享内存标识符
失败:返回-1
shell命令查看共享内存标识符:
查看消息队列: ipcs -q
产看共享内存:ipcs -m
删除共享内存 ipcrm -m shmid
代码案例:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//获取一个唯一的key,用来帮助两个进程定位到同一个区域key_t key = ftok("/home/qf",254);printf("key:%u\n",key);//建立共享内存 int shmid = shmget(key,4096,IPC_CREAT |0666);if (shmid < 0){perror("shmget()");return 0;}printf("shmid:%u\n",shmid);//获取共享内存的内存标识符//放数据或者拿取数据return 0;
}shmat(映射函数):将真实的物理内存与进程中的虚拟内存地址关联起来
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr,int shmflg);功能:
将一个共享内存段映射到调用进程的数据段中。
参数:
shmid:共享内存标识符。
shmaddr:共享内存映射地址(若为 NULL 则由系统自动指定),推荐使用 NULL。
shmflg:共享内存段的访问权限和映射条件
0:共享内存具有可读可写权限。
SHM_RDONLY:只读。
SHM_RND:(shmaddr 非空时才有效)没有指定 SHM_RND 则此段连接到 shmaddr 所指定的地址上(shmaddr 必需页对齐)。指定了 SHM_RND 则此段连接到 shmaddr- shmaddr%SHMLBA 所表示的地址上。
返回值:
成功:返回共享内存段映射地址
失败:返回 -1
解除共享内存映射:断开真实物理内存与虚拟内存的联系
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmdt(const void *shmaddr);参数:shmaddr 共享内存映射的地址
2.3读写代码案例
写:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//获取一个唯一的key,用来帮助两个进程定位到同一个区域key_t key = ftok("/home/qf",254);printf("key:%u\n",key);//建立共享内存 int shmid = shmget(key,4096,IPC_CREAT |0666);if (shmid < 0){perror("shmget()");return 0;}printf("shmid:%u\n",shmid);//建立物理内存与进程中虚拟内存的链接char *buff = (char *)shmat(shmid,NULL,0); //系统自己分配内存,而且0代表可读可写strcpy(buff,"倒计时十五分钟下班");//放数据或者拿取数据shmdt(buff);//断开当前进程与共享内存的链接return 0;
}读:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//获取一个唯一的key,用来帮助两个进程定位到同一个区域key_t key = ftok("/home/qf",254);printf("key:%u\n",key);//建立共享内存 int shmid = shmget(key,4096,IPC_CREAT |0666);if (shmid < 0){perror("shmget()");return 0;}printf("shmid:%u\n",shmid);//建立物理内存与进程中虚拟内存的链接char *buff = (char *)shmat(shmid,NULL,0); //系统自己分配内存,而且0代表可读可写printf("%s\n",buff);shmdt(buff);//断开当前进程与共享内存的链接return 0;}2.4共享内存控制函数
共享内存控制函数:shmctl:
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd,struct shmid_ds *buf);功能:共享内存空间的控制。
参数:
shmid:共享内存标识符。
cmd:函数功能的控制。
buf:shmid_ds 数据类型的地址,用来存放或修改共享内存的属性。
cmd:函数功能的控制
IPC_RMID:删除。
IPC_SET:设置 shmid_ds 参数。
IPC_STAT:保存 shmid_ds 参数。
SHM_LOCK:锁定共享内存段(超级用户)。
SHM_UNLOCK:解锁共享内存段。
返回值:
成功返回 0
失败返回 -1
SHM_LOCK 用于锁定内存,禁止内存交换。并不代表共享内存被锁定后禁止其它进程访问。其真正的意义是:被锁定的内存(物理内存)不允许被交换到虚拟内存中。这样做的优势在于让共享内存一直处于内存中,从而提高程序性能
