29.线程的互斥与同步(三)
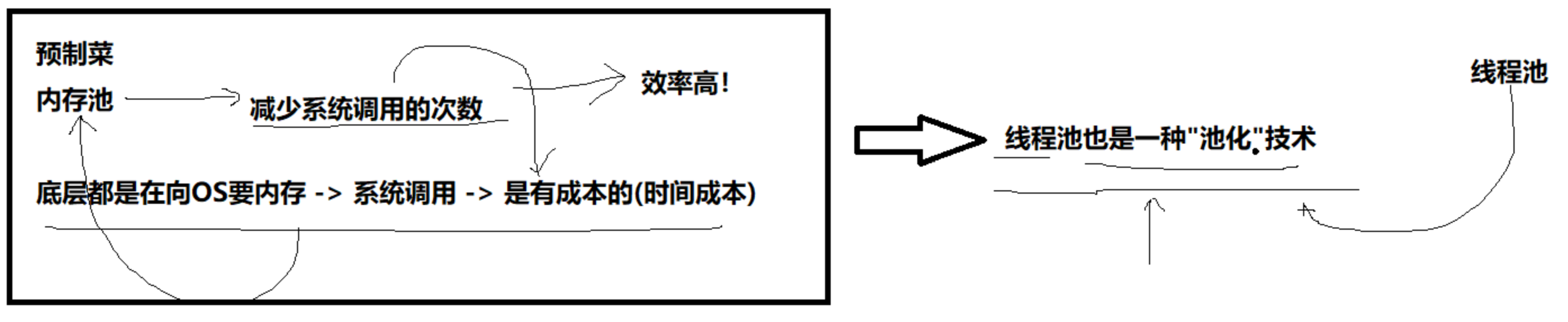
池化技术:预制,减少系统调用的次数,提高效率。
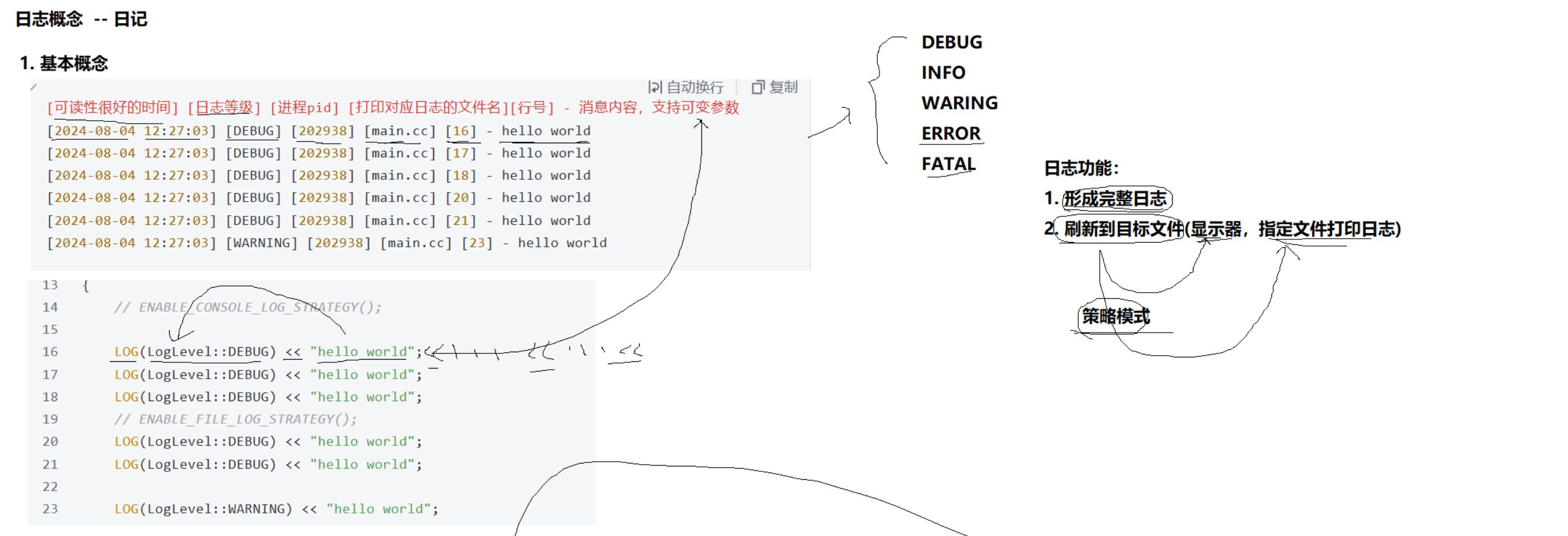
日志
完整代码:
#ifndef __LOG_HPP__ #define __LOG_HPP__#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <filesystem> #include <fstream> #include <memory> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <ctime> #include "Mutex.hpp"namespace LogModule {using namespace MutexModule;// 日志刷新策略class LogStrategy{public:~LogStrategy() = default;virtual void SyncLog(const std::string &message) = 0;};// 控制台刷新class ConsoleLogStrategy : public LogStrategy{public:ConsoleLogStrategy(){}~ConsoleLogStrategy(){}virtual void SyncLog(const std::string &message) override{MutexGuard mutexguard(_mutex);std::cout << message << std::endl;}private:Mutex _mutex;};static const std::string default_path = "./log";static const std::string default_file = "my.log";static const std::string sep = "\r\n";// 文件刷新class FileLogStrategy : public LogStrategy{public:FileLogStrategy(const std::string &path = default_path, const std::string &file = default_file): _path(path), _file(file){{// 保证多线程时的线程安全MutexGuard mutexguard(_mutex);// 如果已经存在目录,返回if (std::filesystem::exists(_path))return;try{// 创建目录结构std::filesystem::create_directories(_path);}catch (const std::filesystem::filesystem_error &e){std::cerr << e.what() << std::endl;}}}~FileLogStrategy(){}virtual void SyncLog(const std::string &message) override{std::string pathname = _path + (_path.back() == '/' ? "" : "/") + _file;// 以追加方式打开文件std::ofstream ofs(pathname, std::ios::app);ofs << message << sep;ofs.close();}private:std::string _path;std::string _file;Mutex _mutex;};enum class LogLevel{DEBUG,INFO,WARNING,ERROR,FATAL};std::string GetLevel(LogLevel level){switch (level){case LogLevel::DEBUG:return "DEBUG";case LogLevel::INFO:return "INFO";case LogLevel::WARNING:return "WARNING";case LogLevel::ERROR:return "ERROR";case LogLevel::FATAL:return "FATAL";default:return "UNKNOWN";}}std::string GetTime(){time_t timestamp = time(nullptr);struct tm data;localtime_r(×tamp, &data);char buff[128];snprintf(buff, 128, "%4d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d",data.tm_year + 1900,data.tm_mon + 1,data.tm_mday,data.tm_hour,data.tm_min,data.tm_sec);return buff;}class Log{public:Log(){}~Log(){}void EnableConsoleLogStrategy(){_sl = std::make_unique<ConsoleLogStrategy>();}void EnableFileLogStrategy(){_sl = std::make_unique<FileLogStrategy>();}// 格式化的左边消息class LogInfo{public:LogInfo(Log *log, LogLevel level, const std::string &filename, const unsigned int line): _time(GetTime()), _level(level), _pid(getpid()), _filename(filename), _line(line), _log(log){std::stringstream ss;ss << "[" << _time << "] "<< "[" << GetLevel(_level) << "] "<< "[" << _pid << "] "<< "[" << _filename << "] "<< "[" << _line << "] "<< "- ";_message = ss.str();}// LogInfo销毁时,刷新~LogInfo(){if (_log->_sl){_log->_sl->SyncLog(_message);}}template <typename T>LogInfo &operator<<(const T &data){std::stringstream ss;ss << data;_message += ss.str();return *this;}private:std::string _time; // 时间,年月日时分秒LogLevel _level; // 日志等级pid_t _pid; // 进程pidstd::string _filename; // 打印日志对应的文件名unsigned int _line; // 行号std::string _message; // 整条信息,左边+右边// Log的指针Log *_log;};// 重载函数调用,用仿函数的形式调用,且隐式传递自己的this指针// 返回LogInfo的匿名对象,生命周期只有一行,一行结束就调用析构,刷新。LogInfo operator()(LogLevel level, const std::string &filename, const unsigned int line){return LogInfo(this, level, filename, line);}private:std::unique_ptr<LogStrategy> _sl; // 策略基类指针};Log log; #define Enable_Console_log_Strategy() log.EnableConsoleLogStrategy() #define Enable_File_log_Strategy() log.EnableFileLogStrategy() #define LOG(level) log(level, __FILE__, __LINE__) }#endif效果:
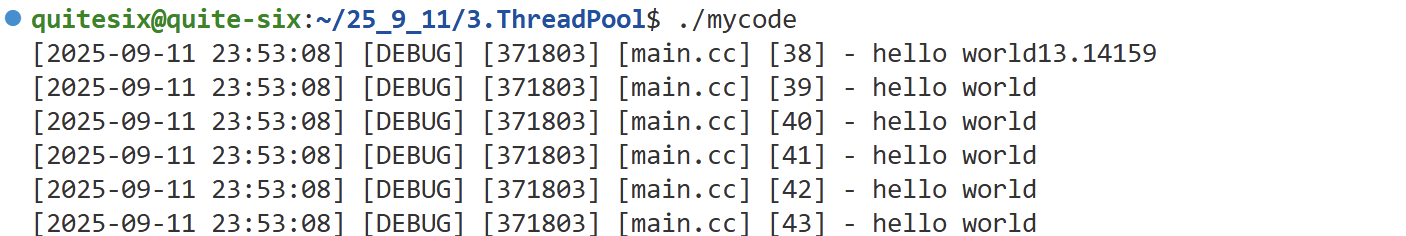
调用:
Enable_Console_log_Strategy();
Enable_File_log_Strategy();
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "hello world";
细节点1:
时间相关函数<time.h>
struct tm *localtime_r(const time_t *timep, struct tm *result);
参数timep为时间戳,可通过time(nullptr);获取
参数result为输出型参数
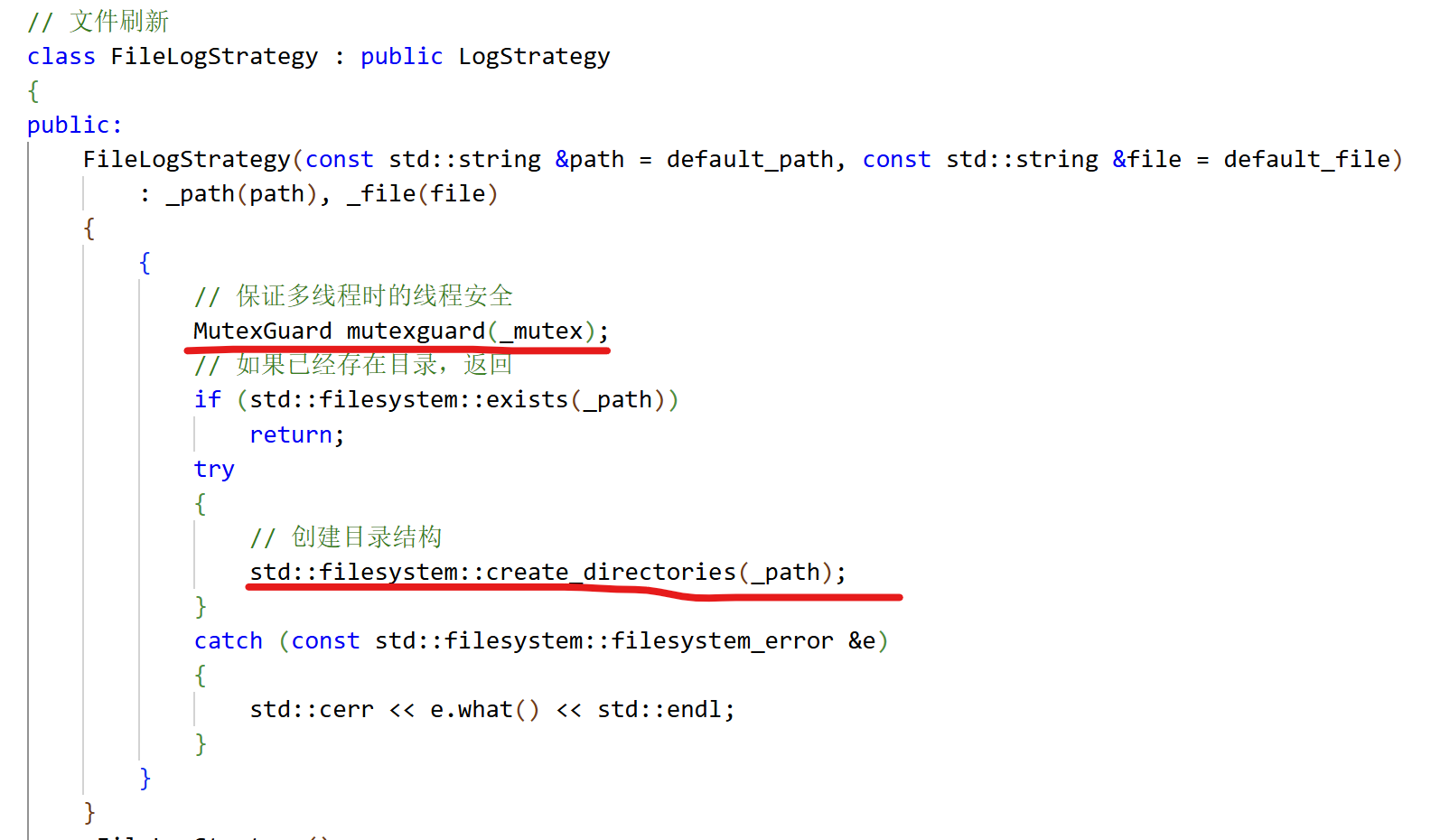
细节点2:
多线程情况下,目录结构为临界资源,需要加锁。同样的,显示器文件也要加锁。
细节点3:
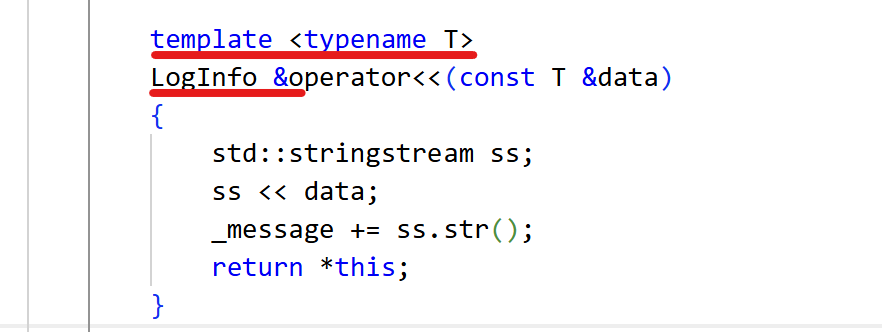
对于日志右边信息处理时,为了使用便利。重载流插入,并以模板的形式,支持stringstream流插入支持的类型。返回值返回引用,用于连续多次插入。
细节点4:
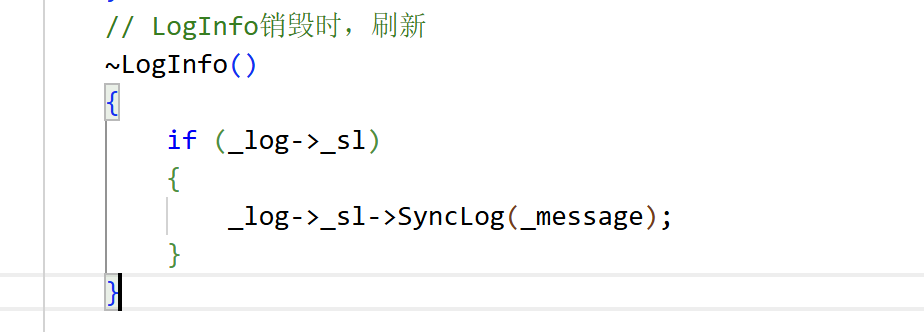
采用返回LogInfo的匿名对象,生命周期只有一行,一行结束就调用析构,析构中在设置刷新,就可以达到一行一行刷新日志的目的。
细节点5:
Log.hpp中定义一个全局的Log类型的变量。
采用宏替换和预处理的两个宏:__FILE__(文件名),__LINE__(行号)
使得使用更加便利和雅观。