Java入门级教程15——实现交替打印、JUC并发包之栅栏机制、制作验证码
目录
1.实现交替打印(使用synchronized关键字)
1.1 基础交替打印
1.2 模拟交替爬取页数
1.3 实践存钱与消费
2.实现交替打印(使用明锁lock)
2.1 基础交替打印
2.2 多个线程交替打印
2.3 实践多个线程交替打印(使用synchronized关键字)
3.JUC的安全并发包机制
3.1 包含
3.2 利用栅栏机制模拟包车
3.3 利用栅栏机制模拟学生到齐上课
4.制作验证码——java spi机制
1.实现交替打印(使用synchronized关键字)
1.1 基础交替打印
① PrintChar类(核心控制类)
package com.hy.chapter1;public class PrintChar {// 控制线程执行顺序的标志位:false→A线程执行,true→B线程执行private boolean flag = false;// 打印"A"的方法(供A线程调用)public void showA() {synchronized (this) { // 以当前PrintChar实例为锁,保证线程安全while (true) { // 无限循环,持续打印// 如果flag为true,说明此时该B线程执行,A线程进入等待if (this.flag) { try {this.wait(); // 释放锁,进入等待状态,等待被唤醒} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 打印"A"(此时flag为false,轮到A线程执行)System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":A");try {Thread.sleep(1000); // 暂停1秒,直观看到交替效果} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}this.flag = true; // 切换标志位:接下来轮到B线程执行this.notify(); // 唤醒等待在当前锁上的线程(此时唤醒B线程)}}}// 打印"B"的方法(供B线程调用)public void showB() {synchronized (this) { // 与showA使用同一个锁(当前PrintChar实例)while (true) { // 无限循环,持续打印// 如果flag为false,说明此时该A线程执行,B线程进入等待if (!this.flag) { try {this.wait(); // 释放锁,进入等待状态,等待被唤醒} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 打印"B"(此时flag为true,轮到B线程执行)System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":B");try {Thread.sleep(1000); // 暂停1秒,直观看到交替效果} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}this.flag = false; // 切换标志位:接下来轮到A线程执行this.notify(); // 唤醒等待在当前锁上的线程(此时唤醒A线程)}}}
}② UserThreadA类(打印 "A" 的线程)
package com.hy.chapter1;public class UserThreadA extends Thread {PrintChar p; // 持有PrintChar实例的引用(共享对象)// 构造方法:接收PrintChar实例,保证与B线程共享同一个对象public UserThreadA(PrintChar p) {this.p = p;}@Overridepublic void run() {this.p.showA(); // 线程启动后,调用PrintChar的showA()方法打印"A"}
}③ UserThreadB类(打印 "B" 的线程)
package com.hy.chapter1;public class UserThreadB extends Thread {PrintChar p; // 持有同一个PrintChar实例的引用public UserThreadB(PrintChar p) {this.p = p;}@Overridepublic void run() {this.p.showB(); // 线程启动后,调用PrintChar的showB()方法打印"B"}
}④ Test类(程序入口)
package com.hy.chapter1;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建一个PrintChar实例(核心共享对象,A、B线程通过它通信)PrintChar p = new PrintChar();// 创建A、B线程,传入同一个PrintChar实例(保证锁对象一致)UserThreadA a = new UserThreadA(p);UserThreadB b = new UserThreadB(p);// 启动两个线程a.start();b.start();}
}输出结果:
Thread-0:A
Thread-1:B
Thread-0:A
Thread-1:B
...
1.2 模拟交替爬取页数
① PrintChar类(核心控制类)
package com.hy.chapter2;public class PrintChar {// 控制标识位private boolean flag = false;public void showA() {synchronized (this) {for (int i = 1; i <= 35; i += 2) {if (this.flag) {try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "页码为: " + i);// 调用爬虫类的方法,传入的参数是页码 ,奇数try {Thread.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}this.flag = true;this.notify();}}}public void showB() {synchronized (this) {for (int i = 2; i <= 35; i += 2) {if (!this.flag) {try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "页码为: " + i);// 调用爬虫类的方法,传入的参数是页码 偶数try {Thread.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}this.flag = false;this.notify();}}}}② UserThreadA类(打印 "A" 的线程)
package com.hy.chapter2;public class UserThreadA extends Thread {PrintChar p;public UserThreadA(PrintChar p) {this.p = p;}public void run() {this.p.showA();}}
③ UserThreadB类(打印 "B" 的线程)
package com.hy.chapter2;public class UserThreadB extends Thread {PrintChar p;public UserThreadB(PrintChar p) {this.p = p;}public void run() {this.p.showB();}}
④ Test类(程序入口)
package com.hy.chapter2;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {PrintChar p = new PrintChar();UserThreadA a = new UserThreadA(p);UserThreadB b = new UserThreadB(p);a.start();b.start();}}
输出结果:
Thread-0页码为: 1
Thread-1页码为: 2
Thread-0页码为: 3
Thread-1页码为: 4...
1.3 实践存钱与消费
儿子消费(账户金额低于一个阈值),爸爸存钱(自动打款)
① PrintChar类(核心控制类)
package com.hy.chapter2_2;public class PrintChar {// 控制标识位private boolean flag = false;private int money = 100;public void showA() {synchronized (this) {while (true) {if (this.flag) {try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}if (this.money < 300) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":父亲打款500");this.money += 500;System.out.println("当前儿子余额为:" + this.money);}try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}this.flag = true;this.notify();}}}public void showB() {synchronized (this) {while (true) {if (!this.flag) {try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}if (this.money >= 300) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":儿子消费300");this.money -= 300;System.out.println("当前儿子余额为:" + this.money);}try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}this.flag = false;this.notify();}}}}② UserThreadA类(打印 "A" 的线程)
package com.hy.chapter2_2;public class UserThreadA extends Thread {PrintChar p;public UserThreadA(PrintChar p) {this.p = p;}public void run() {this.p.showA();}}
③ UserThreadB类(打印 "B" 的线程)
package com.hy.chapter2_2;public class UserThreadB extends Thread {PrintChar p;public UserThreadB(PrintChar p) {this.p = p;}public void run() {this.p.showB();}}
④ Test类(程序入口)
package com.hy.chapter2_2;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {PrintChar p = new PrintChar();UserThreadA a = new UserThreadA(p);UserThreadB b = new UserThreadB(p);a.start();b.start();}}
输出结果:
Thread-0:父亲打款500
当前儿子余额为:600
Thread-1:儿子消费300
当前儿子余额为:300
Thread-1:儿子消费300
当前儿子余额为:0
Thread-0:父亲打款500
当前儿子余额为:500
Thread-1:儿子消费300
当前儿子余额为:200...
2.实现交替打印(使用明锁lock)
2.1 基础交替打印
① PrintChar类(核心控制类)
package com.hy.chapter3;import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;public class PrintChar {// 控制标识位private boolean flag = false;private Lock lock;private Condition con;public PrintChar(Lock lock) {this.lock = lock;this.con = lock.newCondition();}public void showA() {try {lock.lock();while (true) {if (this.flag) {try {this.con.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",A");Thread.sleep(2000);this.flag = true;this.con.signal();}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}}public void showB() {try {lock.lock();while (true) {if (!this.flag) {try {this.con.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",B");Thread.sleep(2000);this.flag = false;this.con.signal();}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}}
}
② UserThreadA类(打印 "A" 的线程)
package com.hy.chapter3;public class UserThreadA extends Thread {PrintChar p;public UserThreadA(PrintChar p) {this.p = p;}public void run() {this.p.showA();}}
③ UserThreadB类(打印 "B" 的线程)
package com.hy.chapter3;public class UserThreadB extends Thread {PrintChar p;public UserThreadB(PrintChar p) {this.p = p;}public void run() {this.p.showB();}}
④ Test类(程序入口)
package com.hy.chapter3;import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();PrintChar p = new PrintChar(lock);UserThreadA a = new UserThreadA(p);UserThreadB b = new UserThreadB(p);a.start();b.start();}}
输出结果:
Thread-0:A
Thread-1:B
Thread-0:A
Thread-1:B
...
2.2 多个线程交替打印
① PrintChar类(核心控制类)
package com.hy.chapter4;import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;public class PrintChar {// 计数器变量private int num = 0;Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();// 创建一个监视器Condition c1 = lock.newCondition();Condition c2 = lock.newCondition();Condition c3 = lock.newCondition();// 5次Apublic void showA() {while (true) {lock.lock();if (num != 0) {try {this.c1.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",A");}try {Thread.sleep(2000);num = 1;this.c2.signal();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}lock.unlock();}}// 10次Bpublic void showB() {while (true) {lock.lock();if (num != 1) {try {this.c2.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",B");}try {Thread.sleep(2000);num = 2;this.c3.signal();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}lock.unlock();}}// 15次Cpublic void showC() {while (true) {lock.lock();if (num != 2) {try {this.c3.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",C");}try {Thread.sleep(2000);num = 0;this.c1.signal();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}lock.unlock();}}}② UserThreadA类(打印 "A" 的线程)
package com.hy.chapter4;public class UserThreadA extends Thread {PrintChar p;public UserThreadA(PrintChar p) {this.p = p;}public void run() {this.p.showA();}}
③ UserThreadB类(打印 "B" 的线程)
package com.hy.chapter4;public class UserThreadB extends Thread {PrintChar p;public UserThreadB(PrintChar p) {this.p = p;}public void run() {this.p.showB();}}
④ UserThreadC类(打印 "C" 的线程)
package com.hy.chapter4;public class UserThreadC extends Thread {PrintChar p;public UserThreadC(PrintChar p) {this.p = p;}public void run() {p.showC();}}
⑤ Test类(程序入口)
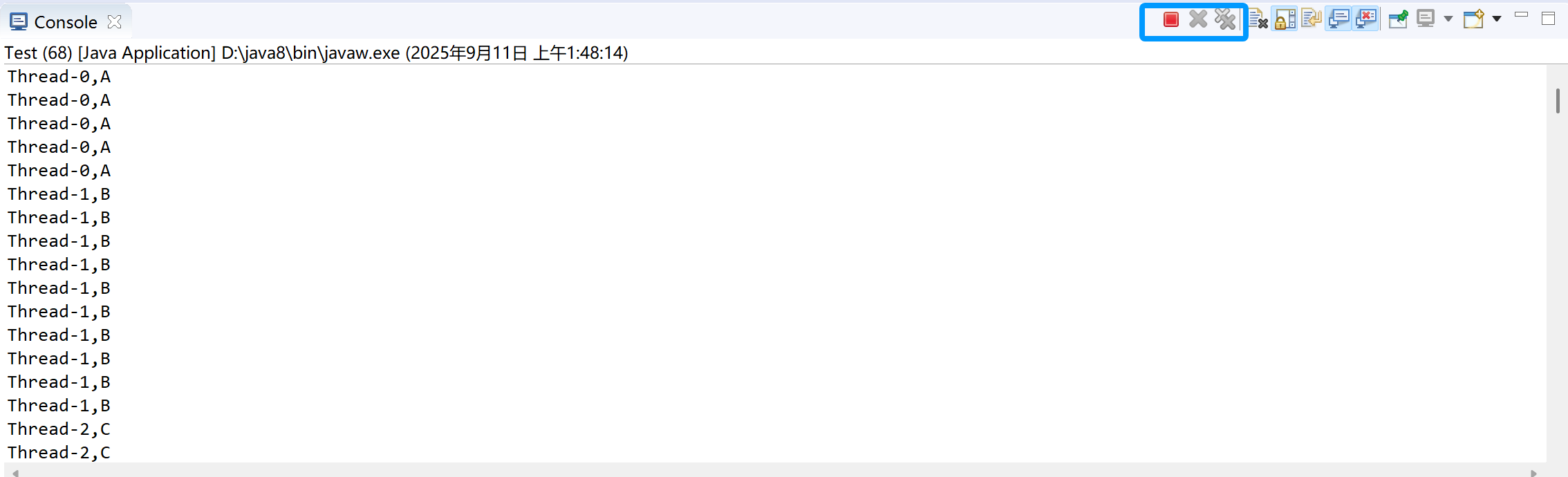
package com.hy.chapter4;/*** 一个线程打印5个A,通知另外一个线程打印10次的B,通知第三个线程打印15次的C * * Lock机制**/public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {PrintChar p = new PrintChar();UserThreadA a = new UserThreadA(p);UserThreadB b = new UserThreadB(p);UserThreadC c = new UserThreadC(p);a.start();b.start();c.start();}}
输出结果;
2.3 实践多个线程交替打印(使用synchronized关键字)
① PrintChar类(核心控制类)
package com.hy.chapter4_2;public class PrintChar {// 计数器变量(标志位):0→A执行,1→B执行,2→C执行private int num = 0;// 打印5次A(对应原逻辑的showA())public void showA() {while (true) { // 无限循环,持续执行// 1. 加锁:用当前PrintChar实例作为锁对象,保证线程互斥synchronized (this) {// 2. 检查标志位:若num≠0(不是A的执行时机),则释放锁并等待// 用while而非if,防止「虚假唤醒」(唤醒后标志位可能已变化)while (num != 0) {try {this.wait(); // 等价于原Condition的await(),释放锁并阻塞} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 3. 执行打印逻辑:打印5次Afor (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",A");}// 4. 切换执行权:更新标志位+唤醒下一个线程(B)try {Thread.sleep(2000); // 暂停2秒,直观展示交替效果num = 1; // 下一轮轮到B执行(标志位设为1)this.notifyAll(); // 等价于原Condition的signal(),唤醒等待在当前锁上的线程} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}// 5. 释放锁:synchronized块结束后自动释放,无需手动解锁(对比原Lock的unlock())}}}// 打印10次B(对应原逻辑的showB())public void showB() {while (true) {synchronized (this) { // 与showA()共用同一个锁对象(当前PrintChar实例)// 检查标志位:若num≠1(不是B的执行时机),则等待while (num != 1) {try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 执行打印逻辑:打印10次Bfor (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",B");}// 切换执行权:更新标志位+唤醒下一个线程(C)try {Thread.sleep(2000);num = 2; // 下一轮轮到C执行(标志位设为2)this.notifyAll(); } catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}// 打印15次C(对应原逻辑的showC())public void showC() {while (true) {synchronized (this) { // 共用同一个锁对象// 检查标志位:若num≠2(不是C的执行时机),则等待while (num != 2) {try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 执行打印逻辑:打印15次Cfor (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",C");}// 切换执行权:更新标志位+唤醒下一个线程(A)try {Thread.sleep(2000);num = 0; // 下一轮回到A执行(标志位重置为0)this.notifyAll(); } catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
}② UserThreadA类(打印 "A" 的线程)
③ UserThreadB类(打印 "B" 的线程)
④ UserThreadC类(打印 "C" 的线程)
⑤ Test类(程序入口)
输出结果:
同上
注意:notify()改为notifyAll()(解决 “唤醒错位”)
① this.notify()的特性是随机唤醒一个等待在锁上的线程,可能出现 “唤醒非目标线程” 的问题(例如 A 唤醒 A 自己,导致 B、C 长期等待)。
② 改为this.notifyAll()后,会唤醒所有等待在当前锁上的线程,确保 “下一个该执行的线程”(如 A 执行后唤醒 B,B 执行后唤醒 C)一定能被唤醒,避免 C 长期等待不打印的情况。
3.JUC的安全并发包机制
3.1 包含
由JDK1.5以后推出的,是对于多线程并发的一个新包。
- Lock属于 明锁机制、需要手动的释放锁。
- 栅栏机制,围栏,一个线程运行到一个点,线程停止运行,直到其它所有的线程都达到这个点,所有线程才重新运行,只能获取一个任务,栅栏可以复用。
- 闭锁机制
- 信号量机制
- 无锁机制
- 交换机制
- 队列机制
- JDK内置线程池机制,手写线程池
3.2 利用栅栏机制模拟包车
通过 CyclicBarrier(循环屏障)模拟了 “旅游包车,每满 4 人发车” 的场景(28 人共需 7 辆车)。核心利用 CyclicBarrier 的 “线程等待 - 共同触发” 特性,实现多线程间的同步协作。
package com.hy.chapter5;import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;/*** * 研学,旅游公司包车,一个车做4个同学,坐满就发车; 总共有28个人,怎么控制和实现?**/public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {CyclicBarrier cb = new CyclicBarrier(4, () -> {System.out.println("已经有4个同学了,就发车吧, 旅游车已经启动出发");});for (int i = 0; i < 28; i++) {Runnable r = () -> {System.out.println("学生来报道............");// 设置一个CyclicBarrier的屏障点try {cb.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {e.printStackTrace();}};try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e1) {e1.printStackTrace();}new Thread(r).start();}}}
输出结果:
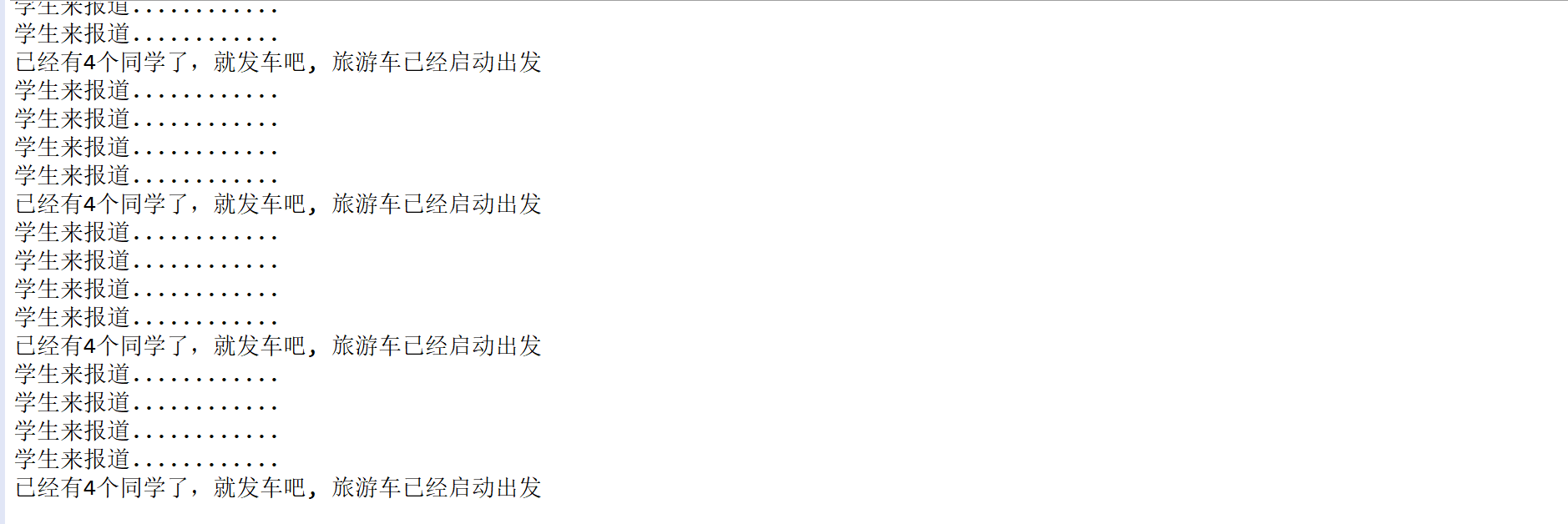
3.3 利用栅栏机制模拟学生到齐上课
package com.hy.chapter6;import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;public class StuRunnable implements Runnable {String name;int runTime;CyclicBarrier cb;public StuRunnable(String name, int runTime, CyclicBarrier cb) {this.name = name;this.runTime = runTime;this.cb = cb;}@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("每个学生从家到学校的时间是不一样的,正在赶路....");try {Thread.sleep(this.runTime * 1000);// 设置一个屏蔽点,就是阈值,所有的学生的线程交互等待this.cb.await();System.out.println(this.name + ",同学们起立问好");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
package com.hy.chapter6;public class TeacherRunnable implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("老师等学生到齐,我们才开始上课");try {Thread.sleep(2000);System.out.println("同学们,正式上课");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
package com.hy.chapter6;import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {CyclicBarrier cb = new CyclicBarrier(3, new TeacherRunnable());new Thread(new StuRunnable("张三", 30, cb)).start();new Thread(new StuRunnable("李四", 20, cb)).start();new Thread(new StuRunnable("王五", 15, cb)).start();}
}
输出结果:
每个学生从家到学校的时间是不一样的,正在赶路....
每个学生从家到学校的时间是不一样的,正在赶路....
每个学生从家到学校的时间是不一样的,正在赶路....
老师等学生到齐,我们才开始上课
同学们,正式上课
李四,同学们起立问好
王五,同学们起立问好
张三,同学们起立问好
4.制作验证码——java spi机制
package com.hy.interfaces;public interface ICode {public String makeCode();}
package com.hy.interfaces.impl;import java.util.Random;import com.hy.interfaces.ICode;public class ChineseCodeImpl implements ICode {private String[] nums = { "赵", "钱", "孙", "李", "王", "五", "马", "六", "天", "地" };public String makeCode() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubString code = "";for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {String s = nums[new Random().nextInt(nums.length)];if (!code.contains(s)) {code += s;} else {i--;}}return code;}}package com.hy.interfaces.impl;import java.util.Random;import com.hy.interfaces.ICode;public class NumberCodeImpl implements ICode {private String[] nums = { "0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9" };public String makeCode() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubString code = "";for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {String s = String.valueOf(new Random().nextInt(nums.length));if (!code.contains(s)) {code += s;} else {i--;}}return code;}}
package com.hy.javaspi;import com.hy.interfaces.ICode;
import com.hy.service.CodeServiceFactory;public class App {public static void main(String[] args) {while (true) {String checkCode = CodeServiceFactory.createCode(ICode.class);System.out.println("获取的验证码为:" + checkCode);try {Thread.sleep(6000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}
}
package com.hy.service;import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.ServiceLoader;import com.hy.interfaces.ICode;/*** Java面向对象 Java多线程 70% Java反射和注解* * @author hy**/public class CodeServiceFactory {public static String createCode(Class targetClass) {// 服务发现,是通过一个接口的策略文件来动态加载的ServiceLoader s = ServiceLoader.load(targetClass);Iterator its = s.iterator();ICode code = null;while (its.hasNext()) {// 实现子类的动态绑定code = (ICode) its.next();}String checkCode = code.makeCode();return checkCode;}
}
com.hy.interfaces.impl.NumberCodeImpl
#com.hy.interfaces.impl.ChineseCodeImpl