Linux-信号量
文章目录
- 信号量
- 概述
- 信号量相关函数
- sem_init函数
- sem_destroy函数
- sem_wait 信号量P操作(减1)
- sem_post信号量V操作(加1)
- gem_getvalue 获取信号量的值
- 练习一
- 练习二
- 练习三
信号量
概述
信号量广泛用于进程或线程间的同步和互斥,信号量本质上是一个非负的整数计数器,它被用来控制对公共资源的访问。
编程时可根据操作信号量值的结果判断是否对公共资源具有访问的权限,当信号量值大于 0 时,则可以访问,否则将阻塞。
PV 原语是对信号量的操作,一次 P 操作使信号量减1,一次 V 操作使信号量加1。
信号量主要用于进程或线程间的同步和互斥这两种典型情况。
信号量数据类型为:sem_t。
信号量用于互斥:
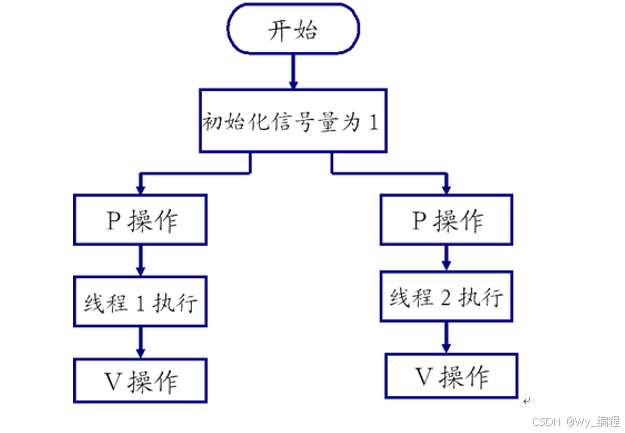
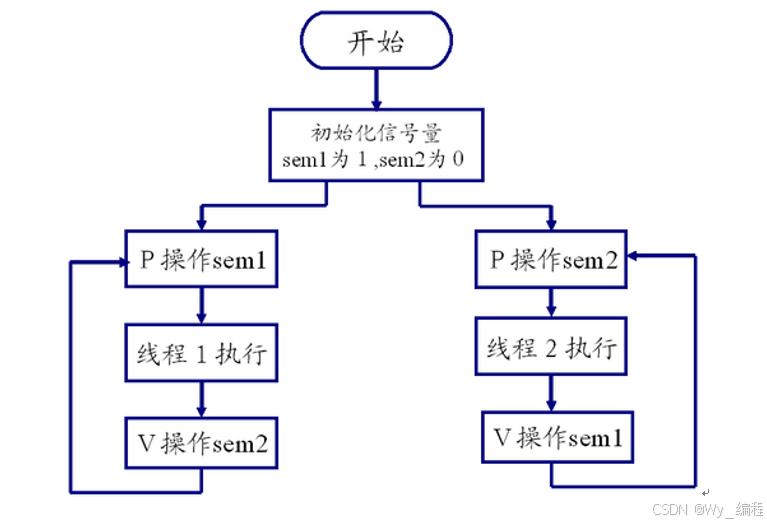
信号量用于同步:
信号量相关函数
sem_init函数
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
功能:创建一个信号量并初始化它的值。一个无名信号量在被使用前必须先初始化。
参数:sem:信号量的地址。pshared:等于 0,信号量在线程间共享(常用);不等于0,信号量在进程间共享。value:信号量的初始值。
返回值:成功:0失败: - 1
sem_destroy函数
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);
功能:删除 sem 标识的信号量。
参数:sem:信号量地址。
返回值:成功:0失败: - 1
sem_wait 信号量P操作(减1)
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);
功能:将信号量的值减 1。操作前,先检查信号量(sem)的值是否为 0,若信号量为 0,此函数会阻塞,直到信号量大于 0 时才进行减 1 操作。
参数:sem:信号量的地址。
返回值:成功:0失败: - 1
int sem_trywait(sem_t *sem);以非阻塞的方式来对信号量进行减 1 操作。若操作前,信号量的值等于 0,则对信号量的操作失败,函数立即返回。
int sem_timedwait(sem_t *sem, const struct timespec *abs_timeout);限时尝试将信号量的值减 1abs_timeout:绝对时间
abs_timeout补充说明:
struct timespec {
time_t tv_sec; /* seconds / // 秒
long tv_nsec; / nanosecondes*/ // 纳秒
}
time_t cur = time(NULL); //获取当前时间。
struct timespec t; //定义timespec 结构体变量t
t.tv_sec = cur + 1; // 定时1秒
sem_timedwait(&cond, &t);
sem_post信号量V操作(加1)
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);
功能:将信号量的值加 1 并发出信号唤醒等待线程(sem_wait())。
参数:sem:信号量的地址。
返回值:成功:0失败:-1
gem_getvalue 获取信号量的值
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_getvalue(sem_t *sem, int *sval);
功能:获取 sem 标识的信号量的值,保存在 sval 中。
参数:sem:信号量地址。sval:保存信号量值的地址。
返回值:成功:0失败:-1
练习一
信号量实现打印机效果
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h> #include <semaphore.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>sem_t sem;void print(const char *str)
{while(*str){printf("%c", *str);fflush(stdout);str++;usleep(50000);}
}void *PrintA(void *arg)
{//申请资源sem_wait(&sem);print("hello");//释放资源sem_post(&sem);pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *PrintB(void *arg)
{sem_wait(&sem);print("world");sem_post(&sem);pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int test01()
{int ret = -1;pthread_t tid1 = -1;pthread_t tid2 = -1;ret = sem_init(&sem, 0, 1);if(0 != ret){printf("sem_init failed\n");goto err0;}ret = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, PrintA, NULL);if(0 != ret){printf("pthread_create failed\n");goto err0;}ret = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, PrintB, NULL);if(0 != ret){printf("pthread_create failed\n");goto err0;}pthread_join(tid1, NULL);pthread_join(tid2, NULL);sem_destroy(&sem);printf("\n");return 0;
err0:return 1;}练习二
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>//表示可以存放产品的容器
sem_t sem_producer;//表示可以消费产品的个数
sem_t sem_customer;pthread_mutex_t mutex;typedef struct _node_t
{int data;struct _node_t *next;
}node_t;node_t *head = NULL;//生产者
void *producer(void *arg)
{node_t *new = NULL;while(1){//申请资源 ,存放产品的容器sem_wait(&sem_producer);pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);new = malloc(sizeof(node_t));if(NULL == new){printf("malloc failed\n");pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);break;}memset(new, 0, sizeof(node_t));new->data = random() % 100 + 1;new->next = head;head = new;printf("-------生产者生产了产品 %d\n", new->data);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//可以卖的产品个数加1sem_post(&sem_customer);sleep(random() % 3 + 1);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}
//消费者
void *customer(void *arg)
{node_t *tmp = NULL;while(1){//申请资源,产品的个数sem_wait(&sem_customer);pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//删除链表第一个节点tmp = head;head = head->next;printf("消费者消费产品 %d\n", tmp->data);free(tmp);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//释放资源,容器的个数sem_post(&sem_producer);sleep(random() % 3 + 1);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int test01()
{int ret = -1;pthread_t tid1 = -1;pthread_t tid2 = -1;srandom(time(NULL));ret = sem_init(&sem_producer, 0, 4);if(0 != ret){printf("sem_init failed\n");goto err0;} ret =sem_init(&sem_customer, 0, 0);if(0 != ret){printf("sem_init failed\n");goto err0;}ret = pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);if(0 != ret){printf("pthread_mutex_init failed\n");goto err0;}//生产者线程ret = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, producer, NULL);if(0 != ret){printf("pthread_create failed\n");goto err0;}//消费者线程ret = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, customer, NULL);if(0 != ret){printf("pthread_create failed\n");goto err0;}pthread_join(tid1, NULL);pthread_join(tid2, NULL);pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);sem_destroy(&sem_producer);sem_destroy(&sem_customer);return 0;
err0:return 1;
}练习三
哲学家吃饭
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex[5];
void* dine(void* arg)
{int num = (int)arg;int left, right;
if(num < 4){// 前4个人,右手拿自己筷子right = num;left = num+1;}else if(num == 4){// 最后一个人,右手拿别人筷子right = 0;left = num;}
// 吃饭while(1){// 右手加锁pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex[right]);// 尝试抢左手筷子if(pthread_mutex_trylock(&mutex[left]) == 0){// 吃面。。。printf("%c 正在吃面。。。。。。\n", num+'A');// 吃完放筷子pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex[left]);}// 解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex[right]);sleep(rand()%5);}
}
int main(int argc, const char* argv[])
{pthread_t p[5];
for(int i=0; i<5; ++i){pthread_mutex_init(&mutex[i], NULL);}
for(int i=0; i<5; ++i){pthread_create(&p[i], NULL, dine, (void*)i);}
for(int i=0; i<5; ++i){pthread_join(p[i], NULL);}for(int i=0; i<5; ++i){pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex[i]);}return 0;
}
