CAS 浅析
什么是 CAS ?
Compare And Swap 的缩写,中文翻译成比较并交换,实现并发算法时常用到的一种技术。
它包含三个操作数-----内存位置、预期原值、更新值
执行 CAS 操作的时候,将内存位置的值与预期原值做比较,如果相同则处理器会自动将该位置值更新为新值,如果不匹配,处理器不做任何操作,多个线程同时执行 CAS 操作只有一个会成功
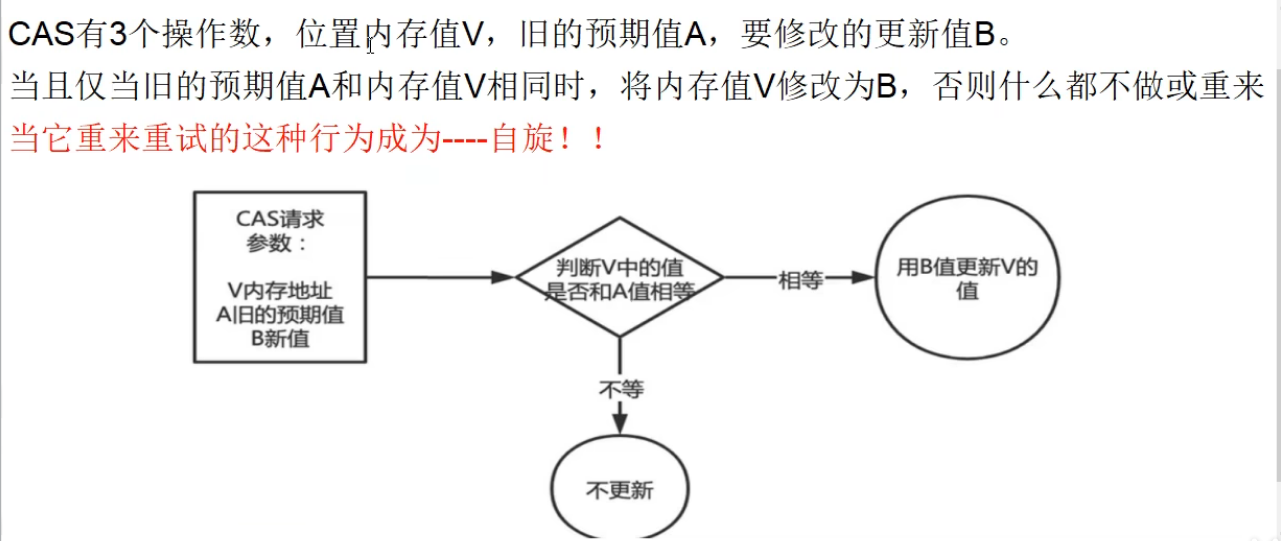
CAS 为什么能又不加锁又能保证数据一致和安全呢?
答案是硬件级别的保证 由 JVM 底层 C++ 实现的 UnSafe 类来实现



CAS 和自旋
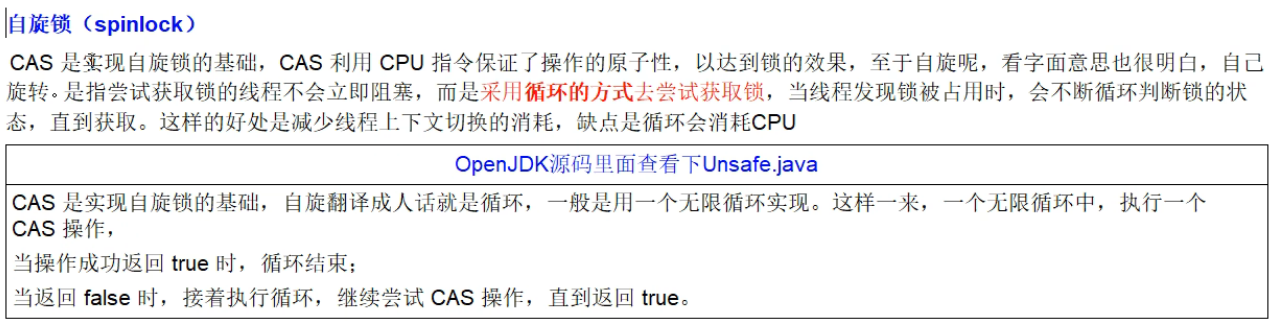
自旋锁的 demo
public class BaseTest {AtomicReference<Thread> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>();public void lock(){Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "/t" + "------ come in");while (!atomicReference.compareAndSet(null,thread)){}}public void unlock(){Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();atomicReference.compareAndSet(thread,null);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "/t" + "解锁成功");}public static void main(String[] args) {BaseTest baseTest = new BaseTest();new Thread(()->{baseTest.lock();try{TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}baseTest.unlock();},"A").start();try{TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);}catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}new Thread(()->{baseTest.lock();baseTest.unlock();},"B").start();}}
CAS 的两大缺点:
循环时间长开销大
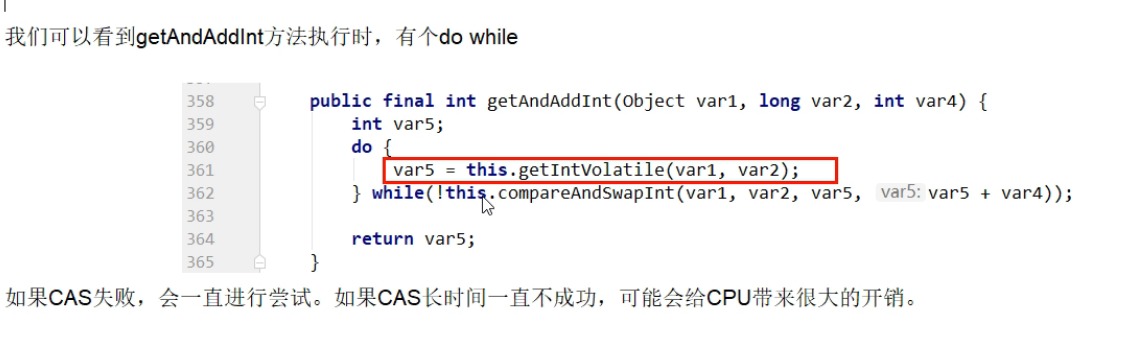
ABA 问题

想要解决 ABA 问题可以引入版本号机制或戳记流水,可以直接使用 Java 中的 AtomicStampedReference 实现
