101. 孤岛的总面积
101. 孤岛的总面积
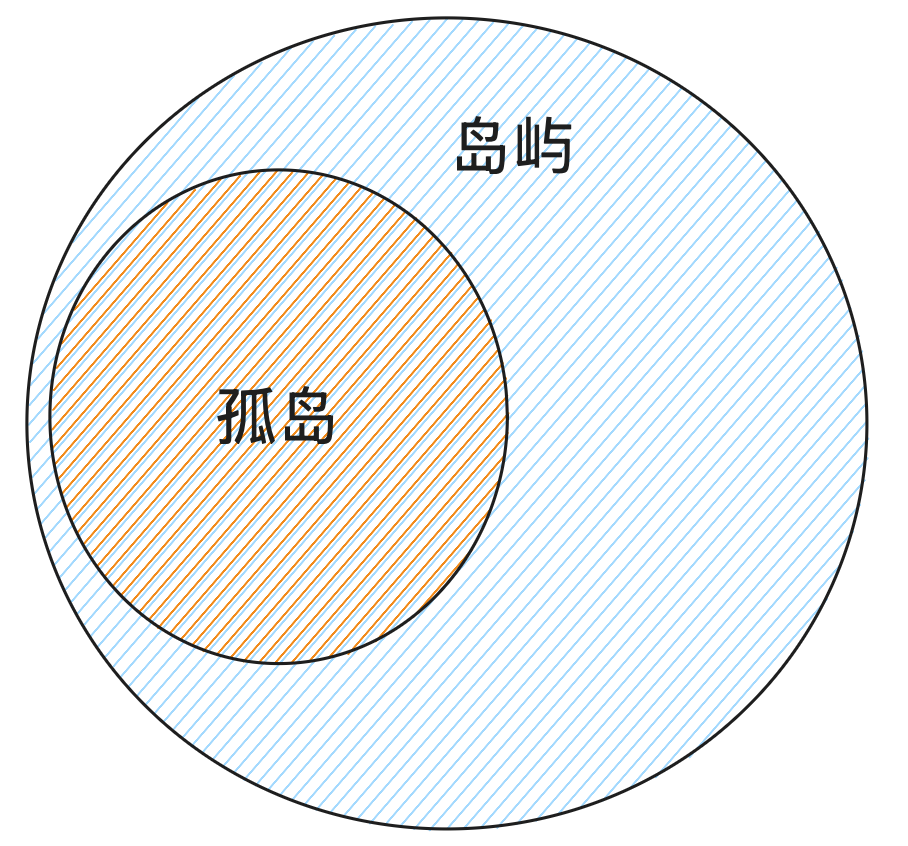
孤岛和岛屿的区别在于孤岛的陆地不能接触到边界。
思路:
先从边界开始遍历操作,构造一个bfs / dfs 来将接壤边界的岛屿全都转为海洋,后续再通过100. 求岛屿的面积做法去求孤岛的面积,累加就得到了孤岛的总面积。
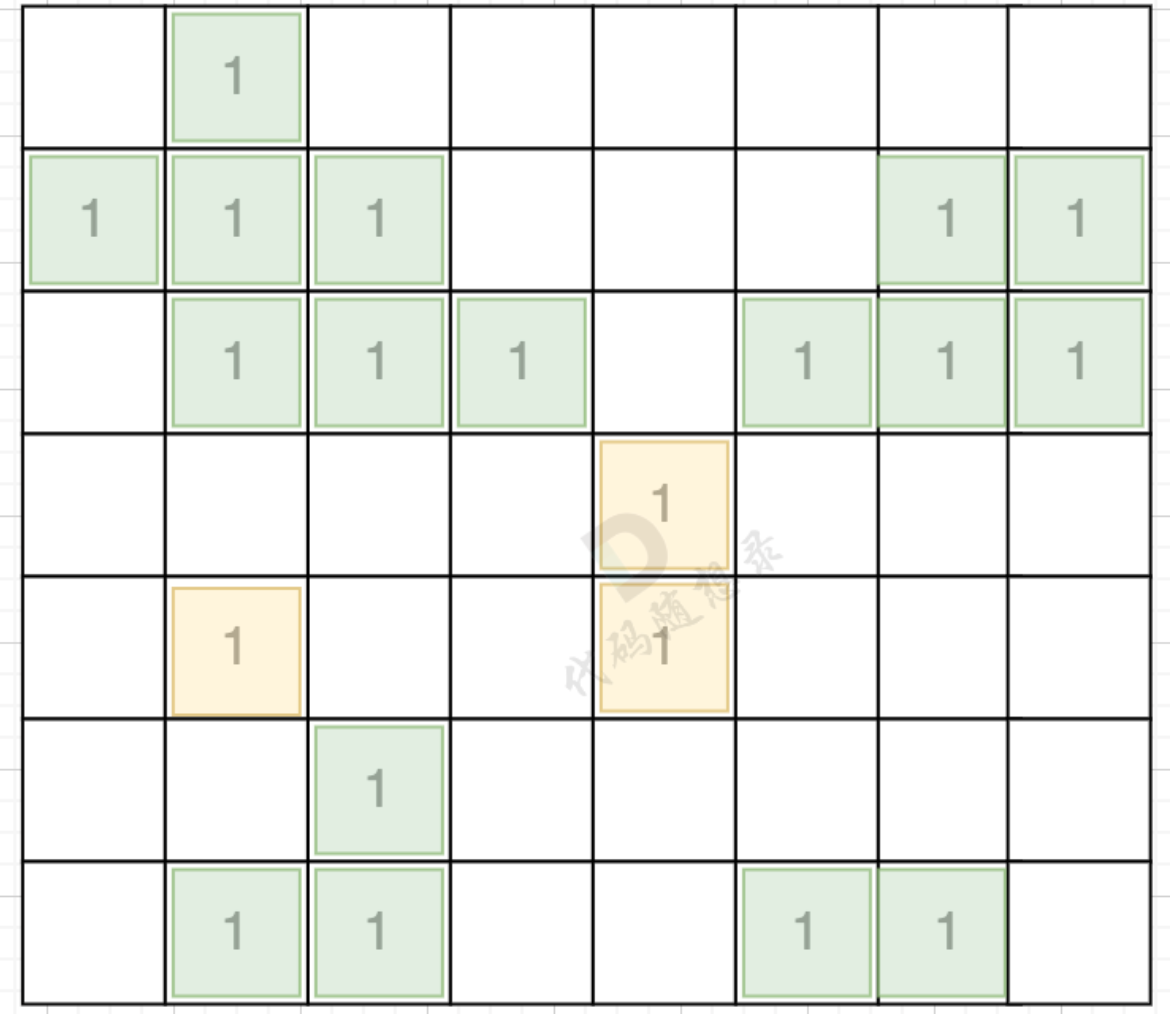
BFS广度搜索解法
手撕Code
## 孤岛和岛屿的区别在与岛屿可以是矩阵的边缘,但孤岛一定是在矩阵内部。 岛屿 >= 孤岛from collections import deque
directions = [[1,0],[0,1],[-1,0],[0,-1]]def main():row, line = map(int,input().split())graph = []visited = [[False]*line for _ in range(row)]for _ in range(row):per_row = list(map(int, input().split()))graph.append(per_row)result = 0for i in range(row): ## 对第一列和最后一列的接壤边界的陆地改为海洋if visited[i][0] == False and graph[i][0] == 1:bfs_zero(graph, visited, i, 0)if visited[i][line-1] == False and graph[i][line-1] == 1:bfs_zero(graph, visited, i, line-1)for j in range(line): ## 对第一行和最后一行的接壤边界的陆地改为海洋if visited[0][j] == False and graph[0][j] == 1:bfs_zero(graph, visited, 0, j)if visited[row-1][j] == False and graph[row-1][j] == 1:bfs_zero(graph, visited, row-1, j)result = 0for i in range(row):for j in range(line):if visited[i][j] == False and graph[i][j] == 1:area = bfs(graph,visited,i,j)result += areaprint(result)def bfs_zero(graph, visited, x, y): ### 目的:把靠近边缘的陆地变成海洋queue = deque([])queue.append([x,y])visited[x][y] = Truewhile queue:cur_x, cur_y = queue.popleft()for i, j in directions:next_x = cur_x + inext_y = cur_y + jif next_x < 0 or next_x >= len(graph) or next_y < 0 or next_y >= len(graph[0]):continueif visited[next_x][next_y] == False and graph[next_x][next_y] == 1:visited[next_x][next_y] = Truegraph[next_x][next_y] = 0queue.append([next_x,next_y])def bfs(graph, visited, x, y):queue = deque([])queue.append([x,y])visited[x][y] = Truecount = 1while queue:cur_x, cur_y = queue.popleft()for i, j in directions:next_x = cur_x + inext_y = cur_y + jif next_x < 0 or next_x >= len(graph) or next_y < 0 or next_y >= len(graph[0]):continueif visited[next_x][next_y] == False and graph[next_x][next_y] == 1:count += 1visited[next_x][next_y] = Truequeue.append([next_x,next_y])return countif __name__ == "__main__":main()
简洁版Code
思路:一视同仁,当遍历到陆地时就将陆地改为海洋,只不过我的遍历顺序是先从边界开始遍历,因此先接触到边界的岛屿被置成了海洋,随后遍历矩阵内部,在一边将孤岛置为海洋的同时一边计算孤岛的面积。
## 孤岛和岛屿的区别在与岛屿可以是矩阵的边缘,但孤岛一定是在矩阵内部。 岛屿 >= 孤岛from collections import deque
directions = [[1,0],[0,1],[-1,0],[0,-1]]def main():row, line = map(int,input().split())graph = []visited = [[False]*line for _ in range(row)]for _ in range(row):per_row = list(map(int, input().split()))graph.append(per_row)### 简洁部分体现,先对边界的陆地进行bfs广搜,将边界的置为海洋的逻辑移入bfs中for i in range(row): ## 对第一列和最后一列的接壤边界的陆地改为海洋if graph[i][0] == 1:bfs(graph, visited, i, 0)if graph[i][line-1] == 1:bfs(graph, visited, i, line-1)for j in range(line): ## 对第一行和最后一行的接壤边界的陆地改为海洋if graph[0][j] == 1:bfs(graph, visited, 0, j)if graph[row-1][j] == 1:bfs(graph, visited, row-1, j)
### 上述并没有输出岛屿面积,因此不会影响到我最终面积的计算。如果确实需要输出,也可以将输出结果在这里重新置为0,从而忽略掉接壤到边界的岛屿面积计算。result = 0for i in range(row):for j in range(line):if visited[i][j] == False and graph[i][j] == 1:area = bfs(graph,visited,i,j)result += areaprint(result)
### 遍历完图后,相当于将整个地图都改为海洋了,只不过我是从边界开始进行bfs,所以是先把接壤边界的岛屿置为海洋,后续在一边求孤岛面积的同时一边将孤岛也给置为海洋def bfs(graph, visited, x, y):queue = deque([])queue.append([x,y])visited[x][y] = Truegraph[x][y] = 0count = 1while queue:cur_x, cur_y = queue.popleft()for i, j in directions:next_x = cur_x + inext_y = cur_y + jif next_x < 0 or next_x >= len(graph) or next_y < 0 or next_y >= len(graph[0]):continueif visited[next_x][next_y] == False and graph[next_x][next_y] == 1:count += 1visited[next_x][next_y] = Truequeue.append([next_x,next_y])return countif __name__ == "__main__":main()
DFS深度搜索解法
## 孤岛和岛屿的区别在与岛屿可以是矩阵的边缘,但孤岛一定是在矩阵内部。 岛屿 >= 孤岛from collections import deque
directions = [[1,0],[0,1],[-1,0],[0,-1]]def main():row, line = map(int,input().split())graph = []visited = [[False]*line for _ in range(row)]for _ in range(row):per_row = list(map(int, input().split()))graph.append(per_row)for i in range(row): ## 对第一列和最后一列的接壤边界的陆地改为海洋if graph[i][0] == 1:dfs(graph, visited, i, 0)if graph[i][line-1] == 1:dfs(graph, visited, i, line-1)for j in range(line): ## 对第一行和最后一行的接壤边界的陆地改为海洋if graph[0][j] == 1:dfs(graph, visited, 0, j)if graph[row-1][j] == 1:dfs(graph, visited, row-1, j)result = 0for i in range(row):for j in range(line):if visited[i][j] == False and graph[i][j] == 1:area = dfs(graph,visited,i,j)result += areaprint(result)def dfs(graph, visited, x, y):cur_x = xcur_y = yvisited[cur_x][cur_y] = Truegraph[cur_x][cur_y] = 0area = 1for i, j in directions:next_x = cur_x + inext_y = cur_y + jif next_x < 0 or next_x >= len(graph) or next_y < 0 or next_y >= len(graph[0]):continueif visited[next_x][next_y] == False and graph[next_x][next_y] == 1:visited[next_x][next_y] = Truearea += dfs(graph, visited, next_x, next_y)return areaif __name__ == "__main__":main()