前端工程化:Vue3(一)
本文为个人学习笔记整理,仅供交流参考,非专业教学资料,内容请自行甄别
文章目录
- 一、插值
- 二、指令
- 2.1、v-html
- 2.2、v-on
- 2.3、v-if
- 2.4、v-for
- 2.5、v-bind
- 2.6、v-model
- 三、响应式编程
- 3.1、Ref
- 3.2、Reactive
- 四、Watch
一、插值
插值分为对象插值和属性插值,是对于页面上元素进行动态填充的手段,使用{{}}占位符。
<script setup lang="ts">let name = "test"let car = {brand:"brand",price: 999999}
</script><template><h3>属性插值:{{name}}</h3><h3>对象插值:{{car.brand}},{{car.price}}</h3>
</template><style scoped></style>

二、指令
常见的v-if,v-bind,v-model等都是vue的指令。
2.1、v-html
v-html的作用是向指定节点中渲染包含html结构的内容,如果想要在页面上展示msg中定义的样式,仅仅使用{{}},会将msg整体解析成一个文本,需要使用v-html对于样式进行解析:
<script setup lang="ts">
let msg = "<p style='color: olivedrab'> 测试指令 </p>"
</script><template><h2><div>{{ msg }}</div></h2><h2><div v-html="msg"></div></h2>
</template><style scoped></style>

两者的对比
2.2、v-on
v-on指令放置在元素上以附加事件监听器,最常见的是监听鼠标点击事件:
<script setup lang="ts">
function buy(){alert("购买成功")
}
</script><template><!-- once:条件,本条件代表不刷新页面只能点击一次--><button v-on:click.once="buy">绑定事件</button><br/></template><style scoped></style>
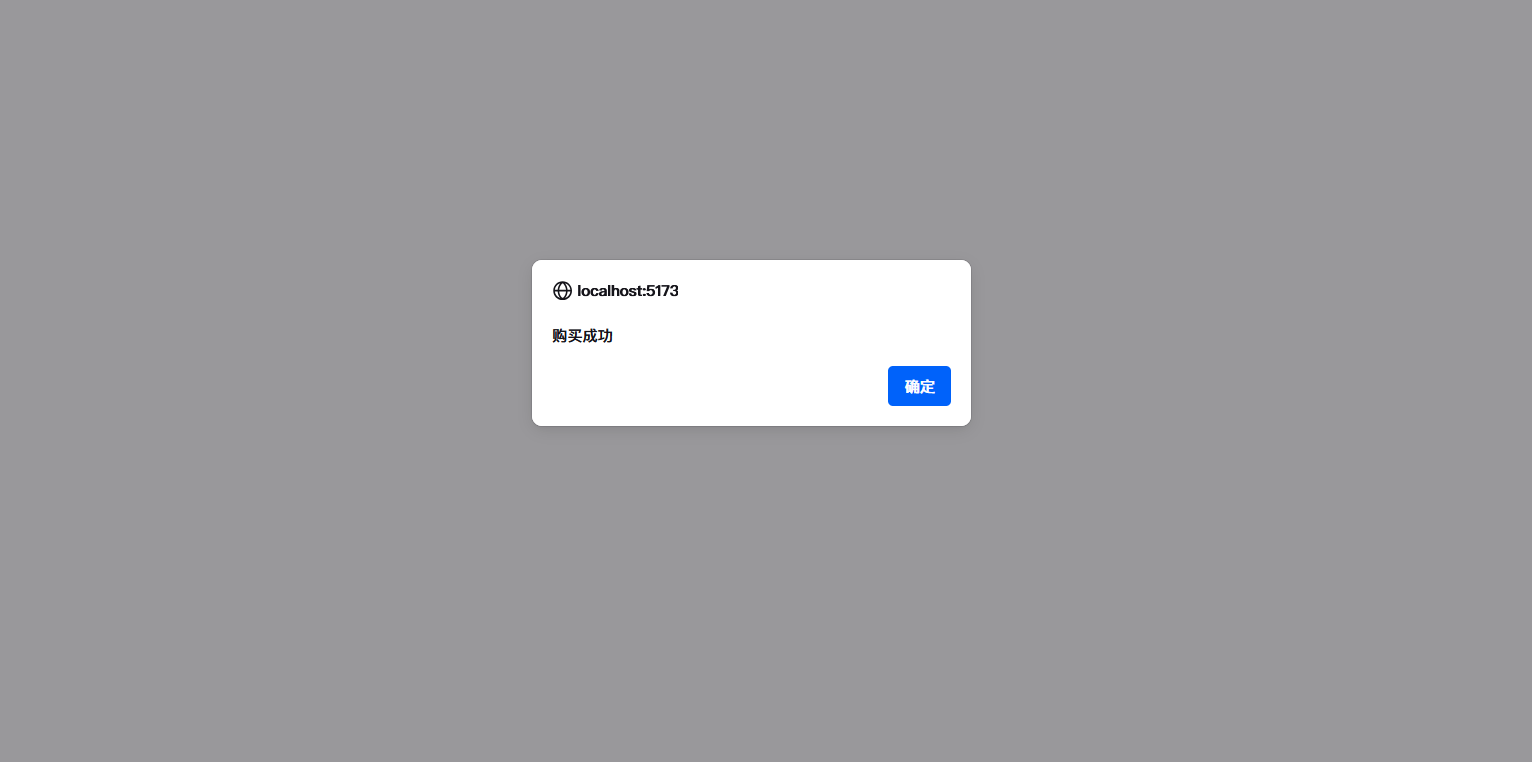
v-on: 的简写形式是 @。例如@Click='""
2.3、v-if
v-if通常用于进行条件判断,例如控制在某个条件下,按钮展示或者隐藏:
<script setup lang="ts">
let price = 1000
</script><template>
<!-- v-if--><span style="color: #2fffa5" v-if="price >= 1000">条件1</span><span style="color: cadetblue" v-if="price<1000">条件2</span>
</template><style scoped></style>

2.4、v-for
v-for用于对数组中的元素进行循环,并且支持获取索引号:
<script setup lang="ts">
let cats = ["布偶猫","蓝猫","奶牛猫"]
</script><template>
<!--v-for --><li v-for="(f,i) in cats ">{{f}} + 索引 + {{i}}</li>
</template><style scoped></style>

2.5、v-bind
v-bind用于单向绑定,将js表达式的结果,绑定到HTML元素的属性上。数据流向是js表达式 -> HTML元素。例如我定义了一个url,想要跳转百度,如果直接使用href:
<script setup lang="ts">
let url = "https://www.baidu.com"
</script><template><a href="url">跳转百度</a>
<!-- <br/>-->
</template><style scoped></style>

未能成功解析url地址
需要使用v-bind指令进行动态渲染:
<a v-bind:href="url">跳转百度</a>
Vue 在编译模板时,会自动把:<a v-bind:href="url">跳转百度</a>渲染成<a href="https://www.baidu.com">跳转百度</a>,而不是将url当做字符串进行处理。v-bind同样可以进行简化为:的形式:
<a :href="url">跳转百度</a>
区别于v-model的双向绑定,如果表单使用单向绑定,那么HTML元素-> js表达式的数据流向,是不会生效的。
2.6、v-model
v-model是进行双向绑定的指令。 双向绑定指的是数据变化引起页面变化,页面变化也会引起数据变化。
<script setup lang="ts">
import {reactive} from "vue";const data = reactive({username: "zhangsan",agree: true
})
</script><template><!-- 单向绑定:数据变化引起页面变化--><!-- 双向绑定:数据变化引起页面变化,页面变化也会引起数据变化--><!-- 所以表单要使用双向绑定--><div><label>请输入姓名</label><input v-model="data.username"/></div><div><label>结果展示</label><div>{{ data.username }}</div></div><div><label>同意协议</label><input type="checkbox" v-model="data.agree"></div><div><label>结果展示</label><div>{{ data.agree }}</div></div>
</template><style scoped></style>
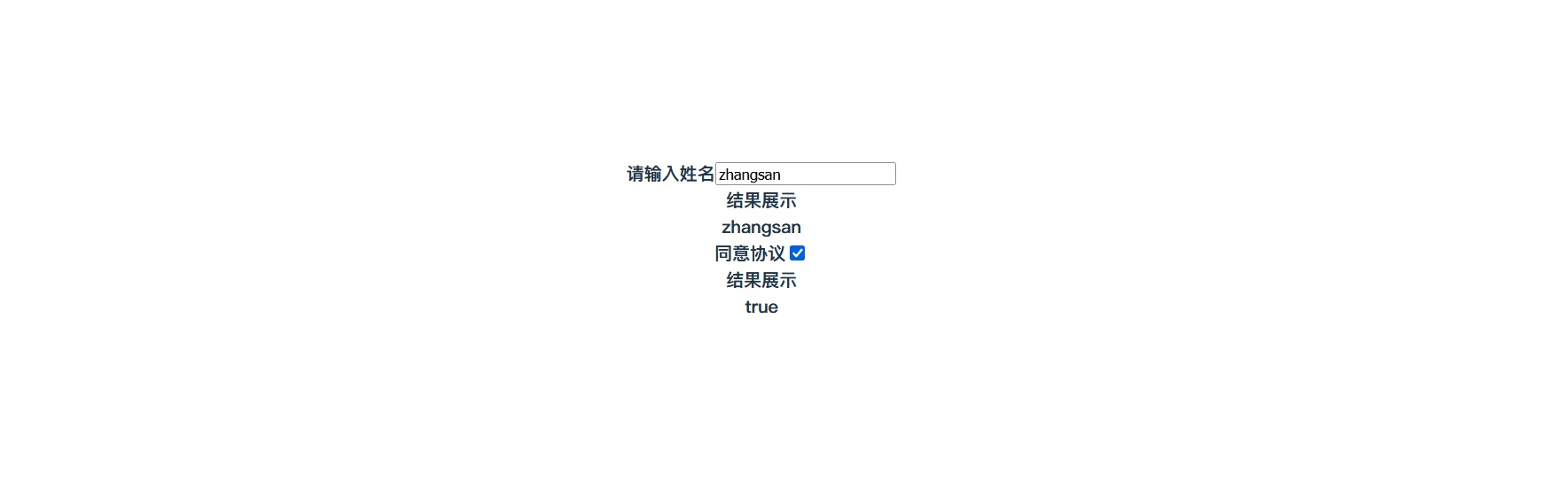
在JS中定义对象初始化的数据,页面上可以正常展示
修改页面上的数据,js中对象的属性值也会更改:

三、响应式编程
在v-bind解析url的案例中,如果想要再通过一个按钮绑定单击事件,让url的值发生过改变,常规的写法:
<script setup lang="ts">let url = "https://www.baidu.com"//修改时,需要用valuefunction changeUrl(){url = "https://www.taobao.com"alert(url)}</script><template><a :href="url">点击跳转,地址:{{url}}</a><button @click="changeUrl()">改变地址</button>
</template><style scoped></style>
页面上点击按钮,弹出的url虽然变更了,但是实际上的url属性并没有变更,点击跳转依旧能跳转到www.baidu.com
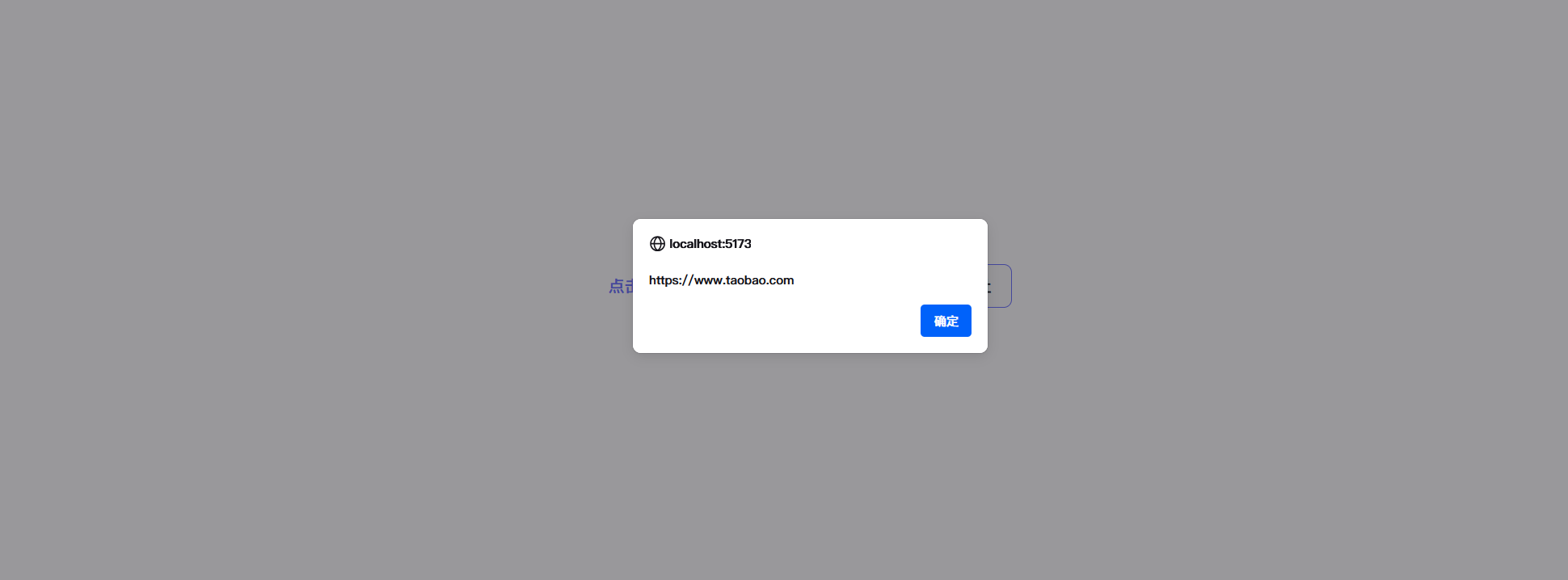

这是 Vue 3 的设计核心:只有响应式数据,模板中的绑定才会随着数据变化自动更新Vue 无法追踪普通变量(用 let 或 const 声明的变量)什么时候改变了,因此模板不会重新渲染。
要完成数据的同步变更,需要引入响应式的API
3.1、Ref
Ref是响应式的API其一,可以支持包装对象,也可以包装具体的属性:
<script setup lang="ts">import {ref} from "vue";//使用ref进行包装let url = ref("https://www.baidu.com");//修改时,需要用valuefunction changeUrl(){url.value = "https://www.taobao.com"alert(url.value)}</script><template><a :href="url">点击跳转,地址:{{url}}</a><button @click="changeUrl()">改变地址</button>
</template><style scoped></style>
使用Ref进行包装,实际上Vue 创建了一个响应式对象,需要在js中使用.value取出原始对象进行处理。在模板中用到 url,Vue 会追踪它的依赖。当你 url.value = ... 时,Vue 触发模板重新渲染。

点击改变地址后,页面上的url同步变更,点击后跳转到新链接
使用Ref包装对象;
<script setup lang="ts">import {ref} from "vue";let cat = ref({name:"布偶猫",price:2000})function changePrice(){cat.value.price = cat.value.price + 1000}</script><template><h3>{{cat.name}}</h3><h3>{{cat.price}}</h3><button @click="changePrice">变更价格</button>
</template><style scoped></style>
3.2、Reactive
Reactive是另一个响应式编程的API,它只支持对于对象进行包装,并且在处理时无需使用.value:
<script setup lang="ts">import {reactive} from "vue";//reactive只能包装对象,并且可以不用使用.value进行处理let cat = reactive( {name:"布偶猫",price:3000})function addPrice(){cat.price = cat.price + 100}
</script><template><h2>价格:{{cat.price}}</h2><button @click="addPrice()">加价</button>
</template><style scoped></style>
四、Watch
Watch的作用是添加一个监听器,当被监听的属性或者对象发生改变时,执行其中的逻辑:
<script setup lang="ts">
import {computed, reactive, watch} from "vue";let cat = reactive({name: "布偶猫",price: 2000,number: 1
})//计算总价
let totalPrice = computed(() => cat.price * cat.number)watch(cat, (value, oldValue, onCleanup) => {console.log("目前的数量" + value.number)console.log("旧的数量" + oldValue.number)if (value.number > 3) {alert("不能同时拥有三只以上的布偶猫")cat.number = 3}
})</script><template><h2>{{ cat.name }}</h2><h2>{{ cat.price }}</h2><h2>{{ cat.number }}</h2><button @click="cat.price = cat.price + 1000">加价</button><button @click="cat.number = cat.number + 1">加量</button><h2>{{ totalPrice }}</h2>
</template><style scoped></style>
