IO流-字节流-FileOutputStream
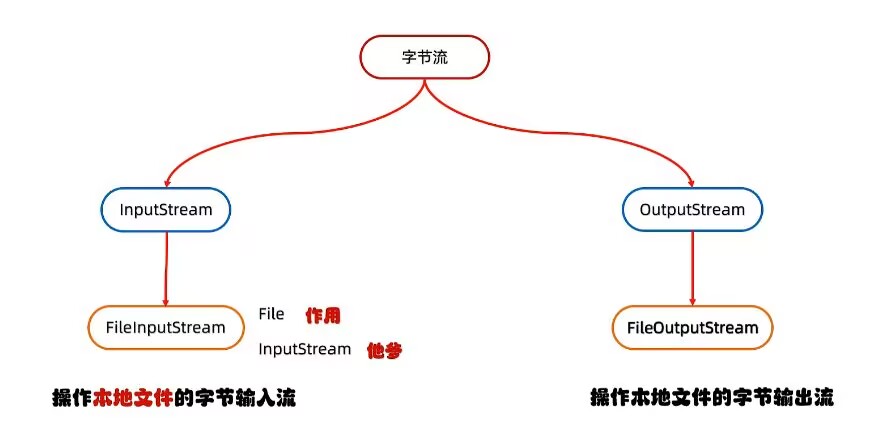
FileOutputStream: 操作本地文件的字节输出流,可以把程序中的数据写到本地文件中。
书写步骤:
①创建字节输出流对象
②写数据
③释放资源
public class ByteStreamDemo01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.创建对象//写出 输出流 OutputStream//本地文件 FileFileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("a.txt");//2.写出数据fos.write(97);System.out.println("======================");fos.write(57);fos.write(55);//3.释放资源fos.close();}
}FileOutputStream书写细节:
①创建字节输出流对象
细节1:参数是字符串表示的路径或者File对象都是可以的
细节2:如果文件不存在会创建一个新的文件, 但是要保证父级路径是存在的。
细节3:如果文件已经存在,则会清空文件
②写数据
细节: write方法的参数是整数,但是实际上写到本地文件中的是整数在ASCI上对应的字符
③释放资源
细节:每次使用完流之后都要释放资源
FileOutputStream写数据的3种方法:
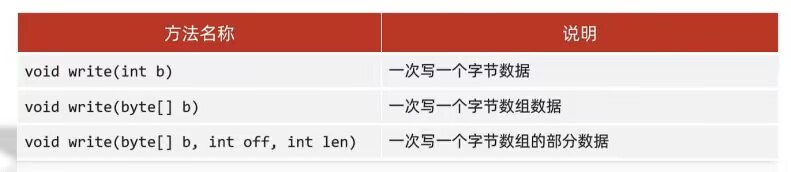
public class ByteStreamDemo02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*void write(int b) 一次写一个字节数据void write(byte[] b) 一次写一个字节数组数据void write(byte[] b ,int off, int len) 一次写一个字节数组的部分数据*/FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("a.txt");//fos.write(97);//fos.write(98);byte[] bytes={97,98,99,100,101};// fos.write(bytes);fos.write(bytes,1,2);fos.close();}
}
换行和续写:
换行:再次写出一个换行符就可以了
Windows: \r\n
Linux: \n
Mac: \r
在Windows操作系统当中,Java对回车换行进行了优化,虽然完整的是\r\n,但是写其中一个\r或者\n也可以实现,因为Java在底层会补全。
public class ByteStreamDemo03 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建对象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("a.txt");//写出数据String str1 = "haoxiangnimenya";byte[] bytes1 = str1.getBytes();//字符串变字节数组fos.write(bytes1);//再2写一个换行符就好了String wrap = "\r\n";byte[] bytes2 =wrap.getBytes();//字符串变字节数组fos.write(bytes2);String str2 = "aiaiai";byte[] bytes3 = str2.getBytes();//字符串变字节数组fos.write(bytes3);//释放资源fos.close();}
}续写:打开续写开关即可
开关位置:创建对象的第二个参数
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("a.txt",true);
默认是false:表示关闭续写,此时创建对象会清空文件
手动传递true:表示打开续写,此时创建对象不会清空
