状态管理V2装饰器大合集
@ObservedV2装饰器和@Trace装饰器:类属性变化观测
@ObservedV2装饰器与@Trace装饰器用于装饰类以及类中的属性,使得被装饰的类和属性具有深度观测的能力:
- @ObservedV2装饰器与@Trace装饰器需要配合使用,单独使用@ObservedV2装饰器或@Trace装饰器没有任何作用。
- 被@Trace装饰器装饰的属性property变化时,仅会通知property关联的组件进行刷新。
- 在嵌套类中,嵌套类中的属性property被@Trace装饰且嵌套类被@ObservedV2装饰时,才具有触发UI刷新的能力。
- 在继承类中,父类或子类中的属性property被@Trace装饰且该property所在类被@ObservedV2装饰时,才具有触发UI刷新的能力。
- 未被@Trace装饰的属性用在UI中无法感知到变化,也无法触发UI刷新。
- @ObservedV2的类实例目前不支持使用JSON.stringify进行序列化。
- 使用@ObservedV2与@Trace装饰器的类,需通过new操作符实例化后,才具备被观测变化的能力。
状态管理V1版本对嵌套类对象属性变化直接观测的局限性
现有状态管理V1版本无法实现对嵌套类对象属性变化的直接观测。
@Observed
class Father {son: Son;constructor(name: string, age: number) {this.son = new Son(name, age);}
}
@Observed
class Son {name: string;age: number;constructor(name: string, age: number) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {@State father: Father = new Father('John', 8);build() {Row() {Column() {Text(`name: ${this.father.son.name} age: ${this.father.son.age}`).fontSize(50).fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold).onClick(() => {this.father.son.age++;})}.width('100%')}.height('100%')}
}
在上述代码中,点击Text组件增加age的值时,不会触发UI刷新。原因在于现有的状态管理框架无法观测到嵌套类中属性age的值变化。V1版本的解决方案是使用@ObjectLink装饰器与自定义组件来实现观测。
@Observed
class Father {son: Son;constructor(name: string, age: number) {this.son = new Son(name, age);}
}
@Observed
class Son {name: string;age: number;constructor(name: string, age: number) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}
}
@Component
struct Child {@ObjectLink son: Son;build() {Row() {Column() {Text(`name: ${this.son.name} age: ${this.son.age}`).fontSize(50).fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold).onClick(() => {this.son.age++;})}.width('100%')}.height('100%')}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {@State father: Father = new Father('John', 8);build() {Column() {Child({son: this.father.son})}}
}
通过这种方式虽然能够实现对嵌套类中属性变化的观测,但是当嵌套层级较深时,代码将会变得十分复杂,易用性差。因此推出类装饰器@ObservedV2与成员变量装饰器@Trace,增强对嵌套类中属性变化的观测能力。
观察变化
使用**@ObservedV2装饰的类中被@Trace装饰的属性具有被观测变化的能力**,当该属性值变化时,会触发该属性绑定的UI组件刷新。
- 在嵌套类中使用@Trace装饰的属性具有被观测变化的能力
@ObservedV2class Son {@Trace age: number = 100;}class Father {son: Son = new Son();}@Entry@ComponentV2struct Index {father: Father = new Father();build() {Column() {// 当点击改变age时,Text组件会刷新Text(`${this.father.son.age}`).onClick(() => {this.father.son.age++;})}}} - 在继承类中使用@Trace装饰的属性具有被观测变化的能力。
@ObservedV2class Father {@Trace name: string = 'Tom';}class Son extends Father {}@Entry@ComponentV2struct Index {son: Son = new Son();build() {Column() {// 当点击改变name时,Text组件会刷新Text(`${this.son.name}`).onClick(() => {this.son.name = 'Jack';})}}} - 类中使用@Trace装饰的静态属性具有被观测变化的能力。
@ObservedV2class Manager {@Trace static count: number = 1;}@Entry@ComponentV2struct Index {build() {Column() {// 当点击改变count时,Text组件会刷新Text(`${Manager.count}`).onClick(() => {Manager.count++;})}}}
限制条件
- 非@Trace装饰的成员属性用在UI上无法触发UI刷新。
- @ObservedV2仅能装饰class,无法装饰自定义组件。
- @Trace不能用在没有被@ObservedV2装饰的class上。
- @Trace是class中属性的装饰器,不能用在struct中。
- @ObservedV2、@Trace不能与@Observed、@Track混合使用。
- 使用@ObservedV2与@Trace装饰的类不能和@State等V1的装饰器混合使用,编译时报错。
- 继承自@ObservedV2的类无法和@State等V1的装饰器混用,运行时报错。
- @ObservedV2的类实例目前不支持使用JSON.stringify进行序列化。
- 使用@ObservedV2与@Trace装饰器的类,需通过new操作符实例化后,才具备被观测变化的能力。
@ComponentV2装饰器:自定义组件
@ComponentV2主要配合状态管理V2使用。
和@Component装饰器一样,@ComponentV2装饰器用于装饰自定义组件
限制条件
- 在@ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件中,开发者仅可以使用全新的状态变量装饰器,包括@Local、@Param、@Once、@Event、@Provider、@Consumer等。
- @ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件暂不支持LocalStorage等现有自定义组件的能力。
- 无法同时使用@ComponentV2与@Component装饰同一个struct结构。
- @ComponentV2支持一个可选的boolean类型参数freezeWhenInactive,来实现组件冻结功能。
@Local装饰器:组件内部状态
为了实现对@ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件中变量变化的观测,开发者可以使用@Local装饰器装饰变量。
@Local表示组件内部的状态,使得自定义组件内部的变量具有观测变化的能力:
- 被@Local装饰的变量无法从外部初始化,因此必须在组件内部进行初始化。
- 当被@Local装饰的变量变化时,会刷新使用该变量的组件。
- @Local支持观测number、boolean、string、Object、class等基本类型以及Array、Set、Map、Date等内嵌类型。
- @Local的观测能力仅限于被装饰的变量本身。当装饰简单类型时,能够观测到对变量的赋值;当装饰对象类型时,仅能观测到对对象整体的赋值;当装饰数组类型时,能观测到数组整体以及数组元素项的变化;当装饰Array、Set、Map、Date等内嵌类型时,可以观测到通过API调用带来的变化。
- @Local支持null、undefined以及联合类型。
状态管理V1版本@State装饰器的局限性
状态管理V1使用@State装饰器定义组件中的基础状态变量,该状态变量常用来作为组件内部状态,在组件内使用。但由于@State装饰器又能够从外部初始化,因此无法确保@State装饰变量的初始值一定为组件内部定义的值。
| @State | @Local | |
|---|---|---|
| 参数 | 无。 | 无。 |
| 从父组件初始化 | 可选。 | 不允许外部初始化。 |
| 观察能力 | 能观测变量本身以及一层的成员属性,无法深度观测。 | 能观测变量本身,深度观测依赖@Trace装饰器。 |
| 数据传递 | 可以作为数据源和子组件中状态变量同步。 | 可以作为数据源和子组件中状态变量同步。 |
class ComponentInfo {name: string;count: number;message: string;constructor(name: string, count: number, message: string) {this.name = name;this.count = count;this.message = message;}
}
@Component
struct Child {@State componentInfo: ComponentInfo = new ComponentInfo('Child', 1, 'Hello World'); // 父组件传递的componentInfo会覆盖初始值build() {Column() {Text(`componentInfo.message is ${this.componentInfo.message}`)}}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {build() {Column() {Child({componentInfo: new ComponentInfo('Unknown', 0, 'Error')})}}
}
上述代码中,可以通过在初始化Child自定义组件时传入新的值来覆盖作为内部状态变量使用的componentInfo。但Child自定义组件并不能感知到componentInfo从外部进行了初始化,这不利于自定义组件内部状态的管理。因此推出@Local装饰器表示组件的内部状态。
观察变化
使用@Local装饰的变量具有观测变化的能力。当装饰的变量发生变化时,会触发该变量绑定的UI组件刷新。
- 当装饰的变量类型为boolean、string、number时,可以观察到对变量赋值的变化。
@Entry@ComponentV2struct Index {@Local count: number = 0;@Local message: string = 'Hello';@Local flag: boolean = false;build() {Column() {Text(`${this.count}`)Text(`${this.message}`)Text(`${this.flag}`)Button('change Local').onClick(()=>{// 当@Local装饰简单类型时,能够观测到对变量的赋值this.count++;this.message += ' World';this.flag = !this.flag;})}}} - 当装饰的变量类型为类对象时,仅可以观察到对类对象整体赋值的变化,无法直接观察到对类成员属性赋值的变化,对类成员属性的观察依赖@ObservedV2和@Trace装饰器。注意,API version 19之前,@Local无法和@Observed装饰的类实例对象混用。API version 19及以后,支持部分状态管理V1V2混用能力,允许@Local和@Observed同时使用,详情见状态管理V1V2混用文档。
- 当装饰简单类型数组时,可以观察到数组整体或数组项的变化。
- 当装饰的变量是嵌套类或对象数组时,@Local无法观察深层对象属性的变化。对深层对象属性的观测依赖@ObservedV2与@Trace装饰器。
- 当装饰内置类型时,可以观察到变量整体赋值及API调用带来的变化。
限制条件
- @Local装饰器只能在@ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件中使用。
- @Local装饰的变量表示组件内部状态,不允许从外部传入初始化。
@ComponentV2struct ChildComponent {@Local message: string = 'Hello World';build() {}}@ComponentV2struct MyComponent {build() {ChildComponent({ message: 'Hello' }) // 错误用法,编译时报错}}
@Param:组件外部输入
为了增强子组件接受外部参数输入的能力,开发者可以使用@Param装饰器。
@Param不仅可以接受组件外部输入,还可以接受@Local的同步变化。
@Param表示组件从外部传入的状态,使得父子组件之间的数据能够进行同步:
- @Param装饰的变量支持本地初始化,但不允许在组件内部直接修改。
- 被@Param装饰的变量能够在初始化自定义组件时从外部传入,当数据源也是状态变量时,数据源的修改会同步给@Param。
- @Param可以接受任意类型的数据源,包括普通变量、状态变量、常量、函数返回值等。
- @Param装饰的变量变化时,会刷新该变量关联的组件。
- @Param支持对基本类型(如number、boolean、string、Object、class)、内嵌类型(如Array、Set、Map、Date),以及null、undefined和联合类型进行观测。
- 对于复杂类型如类对象,@Param会接受数据源的引用。在组件内可以修改类对象中的属性,该修改会同步到数据源。
- @Param的观测能力仅限于被装饰的变量本身。
状态管理V1版本接受外部传入的装饰器的局限性
状态管理V1存在多种可接受外部传入的装饰器,常用的有@State、@Prop、@Link、@ObjectLink。这些装饰器使用有限制且不易区分,不当使用会导致性能问题。
@Observed
class Region {x: number;y: number;constructor(x: number, y: number) {this.x = x;this.y = y;}
}
@Observed
class Info {region: Region;constructor(x: number, y: number) {this.region = new Region(x, y);}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {@State info: Info = new Info(0, 0);build() {Column() {Button('change Info').onClick(() => {this.info = new Info(100, 100);})Child({region: this.info.region,regionProp: this.info.region,infoProp: this.info,infoLink: this.info,infoState: this.info})}}
}
@Component
struct Child {@ObjectLink region: Region;@Prop regionProp: Region;@Prop infoProp: Info;@Link infoLink: Info;@State infoState: Info = new Info(1, 1);build() {Column() {Text(`ObjectLink region: ${this.region.x}-${this.region.y}`)Text(`Prop regionProp: ${this.regionProp.x}-${this.regionProp.y}`)}}
}
在上面的示例中
@State仅能在初始化时接收info的引用,改变info之后无法同步。
@State属性在初始化时(组件创建时)会接收外部传入的引用(如infoState初始化为父组件的info),此时infoState和父组件的info指向同一个对象。- 当父组件的
info被重新赋值为一个新对象(new Info(100, 100))时,父组件的info指向了新的内存地址,但子组件的infoState仍然保持对旧对象的引用(因为@State不会自动感知数据源的引用被替换)。
@Prop虽然能够进行单向同步,但是对于较复杂的类型来说,深拷贝性能较差。
浅拷贝 vs 深拷贝
- 浅拷贝:只指的是创建一个新对象,其中包含原始对象的引用(指针),并没有真正将原始对象的数据复制到新对象中,因此新对象与原始对象共享部分或全部数据。
- 深拷贝:指的是创建一个新对象,并递归地将原始对象的数据复制到新对象中,因此新对象与原始对象之间不存在数据共享。
@Link能够接受传入的引用进行双向同步,但它必须要求数据源也是状态变量,因此无法接受info中的成员属性region。
@ObjectLink能够接受类成员属性,但是要求该属性类型必须为**@Observed**装饰的类。
装饰器的不同限制使得父子组件之间的传值规则复杂、不易使用。因此推出@Param装饰器,表示组件从外部传入的状态。
观察变化
使用@Param装饰的变量具有被观测变化的能力。当装饰的变量发生变化时,会触发该变量绑定的UI组件刷新。
- 当装饰的变量类型为boolean、string、number类型时,可观察数据源同步变化。
@Entry@ComponentV2struct Index {@Local count: number = 0;@Local message: string = 'Hello';@Local flag: boolean = false;build() {Column() {Text(`Local ${this.count}`)Text(`Local ${this.message}`)Text(`Local ${this.flag}`)Button('change Local').onClick(()=>{// 对数据源的更改会同步给子组件this.count++;this.message += ' World';this.flag = !this.flag;})Child({count: this.count,message: this.message,flag: this.flag})}}}@ComponentV2struct Child {@Require @Param count: number;@Require @Param message: string;@Require @Param flag: boolean;build() {Column() {Text(`Param ${this.count}`)Text(`Param ${this.message}`)Text(`Param ${this.flag}`)}}} - 当装饰的变量类型为类对象时,仅可以观察到对类对象整体赋值的变化,无法直接观察到对类成员属性赋值的变化,对类成员属性的观察依赖@ObservedV2和@Trace装饰器。
- 装饰的变量为简单类型数组时,可观察数组整体或数组项变化。
- 当装饰的变量是嵌套类或对象数组时,@Param无法观察深层对象属性的变化。对深层对象属性的观测依赖@ObservedV2与@Trace装饰器。
- 装饰的变量为内置类型时,可观察变量整体赋值和API调用的变化。
限制条件
- @Param装饰器只能在@ComponentV2装饰器的自定义组件中使用。
- @Param装饰的变量表示组件外部输入,需要初始化。支持使用本地初始值或外部传入值进行初始化。当存在外部传入值时,优先使用外部传入值。不允许既不使用本地初始值,也不使用外部传入值。
- 使用@Param装饰的变量在子组件中无法被直接修改。但是,如果装饰的变量是对象类型,在子组件中可以修改对象的属性。
@Once:初始化同步一次
想要实现仅从外部初始化一次且不接受后续同步变化的能力,可以使用@Once装饰器搭配@Param装饰器。
@Once装饰器在变量初始化时接受外部传入值进行初始化,后续数据源更改不会同步给子组件:
- @Once必须搭配@Param使用,单独使用或搭配其他装饰器使用都是不允许的。
- @Once不影响@Param的观测能力,仅针对数据源的变化做拦截。
- @Once与@Param装饰变量的先后顺序不影响使用功能。
- @Once与@Param搭配使用时,可以在本地修改@Param变量的值。
限制条件
- @Once仅在@ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件中与@Param搭配使用。
@ComponentV2struct MyComponent {@Param @Once onceParam: string = 'onceParam'; // 正确用法@Once onceStr: string = 'Once'; // 错误用法,@Once无法单独使用@Local @Once onceLocal: string = 'onceLocal'; // 错误用法,@Once不能与@Local一起使用}@Componentstruct Index {@Once @Param onceParam: string = 'onceParam'; // 错误用法} - @Once与@Param的先后顺序无关,可以写成@Param @Once也可以写成@Once @Param。
@ComponentV2struct MyComponent {@Param @Once param1: number;@Once @Param param2: number;}
使用场景
变量仅初始化同步一次
@Once用于期望变量仅初始化同步数据源一次,之后不再继续同步变化的场景。
@ComponentV2
struct ChildComponent {@Param @Once onceParam: string = '';build() {Column() {Text(`onceParam: ${this.onceParam}`)}}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct MyComponent {@Local message: string = 'Hello World';build() {Column() {Text(`Parent message: ${this.message}`)Button('change message').onClick(() => {this.message = 'Hello Tomorrow';})ChildComponent({ onceParam: this.message })}}
}
本地修改@Param变量
当@Once与@Param结合使用时,可以解除@Param无法在本地修改的限制,并能够触发UI刷新。此时,使用@Param和@Once的效果类似于@Local,但@Param和@Once还能接收外部传入的初始值。
@ObservedV2
class Info {@Trace name: string;constructor(name: string) {this.name = name;}
}
@ComponentV2
struct Child {@Param @Once onceParamNum: number = 0;@Param @Once @Require onceParamInfo: Info;build() {Column() {Text(`Child onceParamNum: ${this.onceParamNum}`)Text(`Child onceParamInfo: ${this.onceParamInfo.name}`)Button('changeOnceParamNum').onClick(() => {this.onceParamNum++;})Button('changeParamInfo').onClick(() => {this.onceParamInfo = new Info('Cindy');})}}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Index {@Local localNum: number = 10;@Local localInfo: Info = new Info('Tom');build() {Column() {Text(`Parent localNum: ${this.localNum}`)Text(`Parent localInfo: ${this.localInfo.name}`)Button('changeLocalNum').onClick(() => {this.localNum++;})Button('changeLocalInfo').onClick(() => {this.localInfo = new Info('Cindy');})Child({onceParamNum: this.localNum,onceParamInfo: this.localInfo})}}
}
@Event装饰器:规范组件输出
为了实现子组件向父组件要求更新@Param装饰变量的能力,开发者可以使用@Event装饰器。使用**@Event装饰回调方法**是一种规范,表明子组件需要传入更新数据源的回调。
@Event主要配合@Param实现数据的双向同步。
由于@Param装饰的变量在本地无法更改,使用@Event装饰器装饰回调方法并调用,可以实现更新数据源的变量,再通过**@Local的同步机制**,将修改同步回@Param装饰的变量,以此达到主动更新@Param装饰变量的效果。
@Event用于装饰组件对外输出的方法:
- @Event装饰的回调方法中参数以及返回值由开发者决定。
- @Event装饰非回调类型的变量不会生效。当@Event没有初始化时,会自动生成一个空的函数作为默认回调。
- 当@Event未被外部初始化,但本地有默认值时,会使用本地默认的函数进行处理。
@Param标志着组件的输入,表明该变量受父组件影响,而@Event标志着组件的输出,可以通过该方法影响父组件。使用@Event装饰回调方法是一种规范,表明该回调作为自定义组件的输出。父组件需要判断是否提供对应方法用于子组件更改@Param变量的数据源。
限制条件
- @Event只能用在@ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件中。当装饰非方法类型的变量时,不会有任何作用。
使用场景
更改父组件中变量
使用@Event可以更改父组件中变量,当该变量作为子组件@Param变量的数据源时,该变化会同步回子组件的@Param变量。
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Index {@Local title: string = 'Title One';@Local fontColor: Color = Color.Red;build() {Column() {Child({title: this.title,fontColor: this.fontColor,changeFactory: (type: number) => {if (type == 1) {this.title = 'Title One';this.fontColor = Color.Red;} else if (type == 2) {this.title = 'Title Two';this.fontColor = Color.Green;}}})}}
}@ComponentV2
struct Child {@Param title: string = '';@Param fontColor: Color = Color.Black;@Event changeFactory: (x: number) => void = (x: number) => {};build() {Column() {Text(`${this.title}`).fontColor(this.fontColor)Button('change to Title Two').onClick(() => {this.changeFactory(2);})Button('change to Title One').onClick(() => {this.changeFactory(1);})}}
}
值得注意的是,使用**@Event修改父组件的值是立刻生效的**,但从父组件将变化同步回子组件的过程是异步的,即在调用完@Event的方法后,子组件内的值不会立刻变化。这是因为@Event将子组件值实际的变化能力交由父组件处理,在父组件实际决定如何处理后,将最终值在渲染之前同步回子组件。
@Provider装饰器和@Consumer装饰器:跨组件层级双向同步
@Provider和@Consumer用于跨组件层级数据双向同步,可以使得开发者不用拘泥于组件层级。
@Provider和@Consumer提供了跨组件层级数据双向同步的能力。
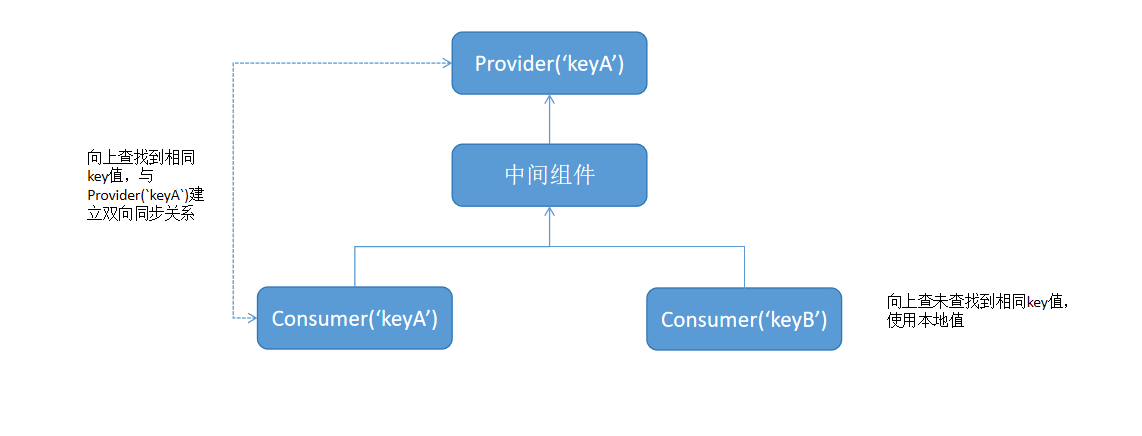
- @Provider和@Consumer强依赖自定义组件层级,@Consumer会因为所在组件的父组件不同,而被初始化为不同的值。
- @Provider和@Consumer相当于把组件粘合在一起了,从组件独立角度考虑,应减少使用@Provider和@Consumer。
@Provider和@Consumer vs @Provide和@Consume能力对比
| 能力 | V2装饰器@Provider和@Consumer | V1装饰器@Provide和@Consume |
|---|---|---|
| @Consume® | 必须本地初始化,当找不到@Provider时使用本地默认值。 | API version 20以前,@Consume禁止本地初始化,当找不到对应@Provide的时候,会抛出异常;从API version 20开始,@Consume支持设置默认值,如果没有设置默认值,且找不到对应@Provide时,会抛出异常。 |
| 支持类型 | 支持function。 | 不支持function。 |
| 观察能力 | 仅能观察自身赋值变化,如果要观察嵌套场景,配合@Trace一起使用。 | 观察第一层变化,如果要观察嵌套场景,配合@Observed和@ObjectLink一起使用。 |
| alias和属性名 | alias是唯一匹配的key,缺省时默认属性名为alias。 | alias和属性名都为key,优先匹配alias,匹配不到可以匹配属性名。 |
| @Provide® 从父组件初始化 | 不允许。 | 允许。 |
| @Provide®支持重载 | 默认开启,即@Provider可以重名,@Consumer向上查找最近的@Provider。 | 默认关闭,即在组件树上不允许有同名@Provide。如果需要重载,则需要配置allowOverride。 |
@Provider和@Consumer接受可选参数aliasName,没有配置参数时,使用属性名作为默认的aliasName。
@ComponentV2
struct Parent {// 未定义aliasName, 使用属性名'str'作为aliasName@Provider() str: string = 'hello';
}@ComponentV2
struct Child {// 定义aliasName为'str',使用aliasName去寻找// 能够在Parent组件上找到, 使用@Provider的值'hello'@Consumer('str') str: string = 'world';
}
@ComponentV2
struct Parent {// 定义aliasName为'alias'@Provider('alias') str: string = 'hello';
}@ComponentV2 struct Child {// 定义aliasName为 'alias',找到@Provider并获得值'hello'@Consumer('alias') str: string = 'world';
}
@ComponentV2
struct Parent {// 定义aliasName为'alias'@Provider('alias') str: string = 'hello';
}@ComponentV2
struct Child {// 未定义aliasName,使用属性名'str'作为aliasName// 没有找到对应的@Provider,使用本地值'world'@Consumer() str: string = 'world';
}
使用限制
- @Provider和@Consumer为自定义组件的属性装饰器,只能装饰自定义组件内的属性,不能装饰class的属性。
- @Provider和@Consumer为状态管理V2装饰器,只能在@ComponentV2中使用,不能在@Component中使用。
- @Provider和@Consumer只支持本地初始化,不支持外部传入初始化。
使用场景
@Provider和@Consumer装饰复杂类型,配合@Trace一起使用
- @Provider和@Consumer只能观察到数据本身的变化。如果需要观察其装饰的复杂数据类型的属性变化,必须配合@Trace一起使用。
- 装饰内置类型:Array、Map、Set、Date时,可以观察到某些API的变化,观察能力同@Trace。
@ObservedV2
class User {@Trace name: string;@Trace age: number;constructor(name: string, age: number) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}
}
const data: User[] = [new User('Json', 10), new User('Eric', 15)];
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Parent {@Provider('data') users: User[] = data;build() {Column() {Child()Button('add new user').onClick(() => {this.users.push(new User('Molly', 18));})Button('age++').onClick(() => {this.users[0].age++;})Button('change name').onClick(() => {this.users[0].name = 'Shelly';})}}
}@ComponentV2
struct Child {@Consumer('data') users: User[] = [];build() {Column() {ForEach(this.users, (item: User) => {Column() {Text(`name: ${item.name}`).fontSize(30)Text(`age: ${item.age}`).fontSize(30)Divider()}})}}
}
@Monitor装饰器:状态变量修改监听
为了增强状态管理框架对状态变量变化的监听能力,开发者可以使用@Monitor装饰器对状态变量进行监听。
Monitor装饰器用于监听状态变量修改,使得状态变量具有深度监听的能力:
- @Monitor装饰器支持在@ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件中使用,未被状态变量装饰器**@Local、@Param、@Provider、@Consumer、@Computed**装饰的变量无法被@Monitor监听到变化。
- @Monitor装饰器支持在类中与@ObservedV2、@Trace配合使用,不允许在未被@ObservedV2装饰的类中使用@Monitor装饰器。未被@Trace装饰的属性无法被@Monitor监听到变化。
- 当观测的属性变化时,@Monitor装饰器定义的 将被调用。判断属性是否变化使用的是严格相等(===),当严格相等判断的结果是false(即不相等)的情况下,就会触发@Monitor的回调。当在一次事件中多次改变同一个属性时,将会使用初始值和最终值进行比较以判断是否变化。
- 单个@Monitor装饰器能够同时监听多个属性的变化,当这些属性在一次事件中共同变化时,只会触发一次@Monitor的回调方法。
- @Monitor装饰器具有深度监听的能力,能够监听嵌套类、多维数组、对象数组中指定项的变化。对于嵌套类、对象数组中成员属性变化的监听要求该类被@ObservedV2装饰且该属性被@Trace装饰。
- 当@Monitor监听整个数组时,更改数组的某一项不会被监听到。无法监听内置类型(Array、Map、Date、Set)的API调用引起的变化。
- 在继承类场景中,可以在父子组件中对同一个属性分别定义@Monitor进行监听,当属性变化时,父子组件中定义的@Monitor回调均会被调用。
- 和@Watch装饰器类似,开发者需要自己定义回调函数,区别在于**@Watch装饰器将函数名作为参数,而@Monitor直接装饰回调函数**。@Monitor与@Watch的对比可以查看@Monitor与@Watch的对比。
状态管理V1版本@Watch装饰器的局限性
现有状态管理V1版本无法实现对对象、数组中某一单个属性或数组项变化的监听,且无法获取变化之前的值。
@Observed
class Info {name: string = 'Tom';age: number = 25;
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {@State @Watch('onInfoChange') info: Info = new Info();@State @Watch('onNumArrChange') numArr: number[] = [1,2,3,4,5];onInfoChange() {console.info(`info after change name: ${this.info.name}, age: ${this.info.age} `);}onNumArrChange() {console.info(`numArr after change ${this.numArr}`);}build() {Row() {Column() {Button('change info name').onClick(() => {this.info.name = 'Jack';})Button('change info age').onClick(() => {this.info.age = 30;})Button('change numArr[2]').onClick(() => {this.numArr[2] = 5;})Button('change numArr[3]').onClick(() => {this.numArr[3] = 6;})}.width('100%')}.height('100%')}
}
上述代码中,点击"change info name"更改info中的name属性或点击"change info age"更改age时,均会触发info注册的@Watch回调。点击"change numArr[2]"更改numArr中的第3个元素或点击"change numArr[3]"更改第4个元素时,均会触发numArr注册的@Watch回调。在这两个回调中,由于无法获取数据更改前的值,在业务逻辑更加复杂的场景下,无法准确知道是哪一个属性或元素发生了改变从而触发了@Watch事件,这不便于开发者对变量的更改进行准确监听。因此推出@Monitor装饰器实现对对象、数组中某一单个属性或数组项变化的监听,并且能够获取到变化之前的值。
监听变化
在@ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件中使用@Monitor
- @Monitor监听的变量需要被@Local、@Param、@Provider、@Consumer、@Computed装饰,未被状态变量装饰器装饰的变量在变化时无法被监听。@Monitor可以同时监听多个状态变量,这些变量名之间用","隔开。
@Entry@ComponentV2struct Index {@Local message: string = 'Hello World';@Local name: string = 'Tom';@Local age: number = 24;@Monitor('message', 'name')onStrChange(monitor: IMonitor) {monitor.dirty.forEach((path: string) => {console.info(`${path} changed from ${monitor.value(path)?.before} to ${monitor.value(path)?.now}`);});}build() {Column() {Button('change string').onClick(() => {this.message += '!';this.name = 'Jack';})}}} - @Monitor监听的状态变量为类对象时,仅能监听对象整体的变化。监听类属性的变化需要类属性被@Trace装饰。
class Info {name: string;age: number;constructor(name: string, age: number) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}}@Entry@ComponentV2struct Index {@Local info: Info = new Info('Tom', 25);@Monitor('info')infoChange(monitor: IMonitor) {console.info(`info change`);}@Monitor('info.name')infoPropertyChange(monitor: IMonitor) {console.info(`info name change`);}build() {Column() {Text(`name: ${this.info.name}, age: ${this.info.age}`)Button('change info').onClick(() => {this.info = new Info('Lucy', 18); // 能够监听到})Button('change info.name').onClick(() => {this.info.name = 'Jack'; // 监听不到})}}}
在@ObservedV2装饰的类中使用@Monitor
- @Monitor监听的对象属性需要被@Trace装饰,未被@Trace装饰的属性的变化无法被监听。@Monitor可以同时监听多个属性,这些属性之间用","隔开。
@ObservedV2class Info {@Trace name: string = 'Tom';@Trace region: string = 'North';@Trace job: string = 'Teacher';age: number = 25;// name被@Trace装饰,能够监听变化@Monitor('name')onNameChange(monitor: IMonitor) {console.info(`name change from ${monitor.value()?.before} to ${monitor.value()?.now}`);}// age未被@Trace装饰,不能监听变化@Monitor('age')onAgeChange(monitor: IMonitor) {console.info(`age change from ${monitor.value()?.before} to ${monitor.value()?.now}`);}// region与job均被@Trace装饰,能够监听变化@Monitor('region', 'job')onChange(monitor: IMonitor) {monitor.dirty.forEach((path: string) => {console.info(`${path} change from ${monitor.value(path)?.before} to ${monitor.value(path)?.now}`);})}}@Entry@ComponentV2struct Index {info: Info = new Info();build() {Column() {Button('change name').onClick(() => {this.info.name = 'Jack'; // 能够触发onNameChange方法})Button('change age').onClick(() => {this.info.age = 26; // 不能够触发onAgeChange方法})Button('change region').onClick(() => {this.info.region = 'South'; // 能够触发onChange方法})Button('change job').onClick(() => {this.info.job = 'Driver'; // 能够触发onChange方法})}}} - @Monitor可以监听深层属性的变化,该深层属性需要被@Trace装饰。
@ObservedV2class Inner {@Trace num: number = 0;}@ObservedV2class Outer {inner: Inner = new Inner();@Monitor('inner.num')onChange(monitor: IMonitor) {console.info(`inner.num change from ${monitor.value()?.before} to ${monitor.value()?.now}`);}}@Entry@ComponentV2struct Index {outer: Outer = new Outer();build() {Column() {Button('change num').onClick(() => {this.outer.inner.num = 100; // 能够触发onChange方法})}}} - 在继承类场景下,可以在继承链中对同一个属性进行多次监听。
@ObservedV2class Base {@Trace name: string;// 基类监听name属性@Monitor('name')onBaseNameChange(monitor: IMonitor) {console.info(`Base Class name change`);}constructor(name: string) {this.name = name;}}@ObservedV2class Derived extends Base {// 继承类监听name属性@Monitor('name')onDerivedNameChange(monitor: IMonitor) {console.info(`Derived Class name change`);}constructor(name: string) {super(name);}}@Entry@ComponentV2struct Index {derived: Derived = new Derived('AAA');build() {Column() {Button('change name').onClick(() => {this.derived.name = 'BBB'; // 能够先后触发onBaseNameChange、onDerivedNameChange方法})}}}
通用监听能力
- @Monitor支持对数组中的项进行监听,包括多维数组,对象数组。@Monitor无法监听内置类型(Array、Map、Date、Set)的API调用引起的变化。当@Monitor监听数组整体时,只能观测到数组整体的赋值。可以通过监听数组的长度变化来判断数组是否有插入、删除等变化。当前仅支持使用"."的方式表达深层属性、数组项的监听。
- 对象整体改变,但监听的属性不变时,不触发@Monitor回调。
- 在一次事件中多次改变被@Monitor监听的属性,以最后一次修改为准。
限制条件
- 不建议在一个类中对同一个属性进行多次@Monitor的监听。当一个类中存在对一个属性的多次监听时,只有最后一个定义的监听方法会生效。
- 当@Monitor传入多个路径参数时,以参数的全拼接结果判断是否重复监听。全拼接时会在参数间加空格,以区分不同参数。例如,‘ab’, ‘c’的全拼接结果为’ab c’,‘a’, ‘bc’的全拼接结果为’a bc’,二者全拼接不相等。以下示例中,Monitor 1、Monitor 2与Monitor 3都监听了name属性的变化。由于Monitor 2与Monitor 3的入参全拼接相等(都为’name position’),因此Monitor 2不生效,仅Monitor 3生效。当name属性变化时,将同时触发onNameAgeChange与onNamePositionChangeDuplicate方法。但请注意,Monitor 2与Monitor 3的写法仍然被视作在一个类中对同一个属性进行多次@Monitor的监听,这是不建议的。
@ObservedV2class Info {@Trace name: string = 'Tom';@Trace age: number = 25;@Trace position: string = 'North';@Monitor('name', 'age') // Monitor 1onNameAgeChange(monitor: IMonitor) {monitor.dirty.forEach((path: string) => {console.info(`onNameAgeChange path: ${path} change from ${monitor.value(path)?.before} to ${monitor.value(path)?.now}`);});}@Monitor('name', 'position') // Monitor 2onNamePositionChange(monitor: IMonitor) {monitor.dirty.forEach((path: string) => {console.info(`onNamePositionChange path: ${path} change from ${monitor.value(path)?.before} to ${monitor.value(path)?.now}`);});}// 重复监听name、position,仅最后定义的生效@Monitor('name', 'position') // Monitor3onNamePositionChangeDuplicate(monitor: IMonitor) {monitor.dirty.forEach((path: string) => {console.info(`onNamePositionChangeDuplicate path: ${path} change from ${monitor.value(path)?.before} to ${monitor.value(path)?.now}`);});}}@Entry@ComponentV2struct Index {info: Info = new Info();build() {Column() {Button('change name').onClick(() => {this.info.name = 'Jack'; // 同时触发onNameAgeChange与onNamePositionChangeDuplicate方法})}}} - @Monitor的参数需要为监听属性名的字符串,仅可以使用字符串字面量、const常量、enum枚举值作为参数。**如果使用变量作为参数,仅会监听@Monitor初始化时,变量值所对应的属性。当更改变量时,@Monitor无法实时改变监听的属性,即@Monitor监听的目标属性从初始化时便已经确定,无法动态更改。**不建议开发者使用变量作为@Monitor的参数进行初始化。
- 建议开发者避免在@Monitor中再次更改被监听的属性,这会导致无限循环。
@ObservedV2class Info {@Trace count: number = 0;@Monitor('count')onCountChange(monitor: IMonitor) {this.count++; // 应避免这种写法,会导致无限循环}}
@Monitor与@Watch对比
@Monitor与@Watch的用法、功能对比如下:
| @Watch | @Monitor | |
|---|---|---|
| 参数 | 回调方法名。 | 监听状态变量名、属性名。 |
| 监听目标数 | 只能监听单个状态变量。 | 能同时监听多个状态变量。 |
| 监听能力 | 跟随状态变量观察能力(一层)。 | 跟随状态变量观察能力(深层)。 |
| 能否获取变化前的值 | 不能获取变化前的值。 | 能获取变化前的值。 |
| 监听条件 | 监听对象为状态变量。 | 监听对象为状态变量或为@Trace装饰的类成员属性。 |
| 使用限制 | 仅能在@Component装饰的自定义组件中使用。 | 能在@ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件中使用,也能在@ObservedV2装饰的类中使用。 |
使用场景
监听深层属性变化
@Monitor可以监听深层属性的变化,并能够根据更改前后的值做分类处理。
下面的示例中监听了属性value的变化,并根据变化的幅度改变Text组件显示的样式。
@ObservedV2
class Info {@Trace value: number = 50;
}
@ObservedV2
class UIStyle {info: Info = new Info();@Trace color: Color = Color.Black;@Trace fontSize: number = 45;@Monitor('info.value')onValueChange(monitor: IMonitor) {let lastValue: number = monitor.value()?.before as number;let curValue: number = monitor.value()?.now as number;if (lastValue != 0) {let diffPercent: number = (curValue - lastValue) / lastValue;if (diffPercent > 0.1) {this.color = Color.Red;this.fontSize = 50;} else if (diffPercent < -0.1) {this.color = Color.Green;this.fontSize = 40;} else {this.color = Color.Black;this.fontSize = 45;}}}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Index {textStyle: UIStyle = new UIStyle();build() {Column() {Text(`Important Value: ${this.textStyle.info.value}`).fontColor(this.textStyle.color).fontSize(this.textStyle.fontSize)Button('change!').onClick(() => {this.textStyle.info.value = Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1;})}}
}
@Computed装饰器:计算属性
当开发者使用相同的计算逻辑重复绑定在UI上时,为了防止重复计算,可以使用@Computed计算属性。计算属性中的依赖的状态变量变化时,只会计算一次。这解决了UI多次重用该属性导致的重复计算和性能问题。如下面例子。
@Computed
get sum() {return this.count1 + this.count2 + this.count3;
}
Text(`${this.count1 + this.count2 + this.count3}`) // 计算this.count1 + this.count2 + this.count3
Text(`${this.count1 + this.count2 + this.count3}`) // 重复计算this.count1 + this.count2 + this.count3
Text(`${this.sum}`) // 读取@Computed sum的缓存值,节省上述重复计算
Text(`${this.sum}`) // 读取@Computed sum的缓存值,节省上述重复计算
@Computed为方法装饰器,装饰getter方法。@Computed会检测被计算的属性变化,当被计算的属性变化时,@Computed只会被求解一次。不推荐在@Computed中修改变量,错误的使用会导致数据无法被追踪或appfreeze等问题。
但需要注意,对于简单计算,不建议使用计算属性,因为计算属性本身也有开销。对于复杂的计算,@Computed能带来性能收益。
@Computed
get varName(): T {return value;
}
使用限制
- @Computed为方法装饰器,仅能装饰getter方法。
- @Computed装饰的方法只有在初始化,或者其被计算的状态变量改变时,才会发生重新计算。不建议开发者在@Computed装饰的getter方法中做除获取数据外其余的逻辑操作,如下面例子。
@Entry@ComponentV2struct Page {@Local firstName: string = 'Hua';@Local lastName: string = 'Li';@Local showFullNameRequestCount: number = 0;private fullNameRequestCount: number = 0;@Computedget fullName() {console.info('fullName');// 不推荐在@Computed的计算中做赋值逻辑,因为@Computed本质是一个getter访问器,用来节约重复计算// 在这个例子中,fullNameRequestCount仅代表@Computed计算次数,不能代表fullName被访问的次数this.fullNameRequestCount++;return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName;}build() {Column() {Text(`${this.fullName}`) // 获取一次fullNameText(`${this.fullName}`) // 获取一次fullName,累计获取两次fullName,但是fullName不会重新计算,读取缓存值// 点击Button,获取fullNameRequestCount次数Text(`count ${this.showFullNameRequestCount}`)Button('get fullName').onClick(() => {this.showFullNameRequestCount = this.fullNameRequestCount;})}}} - 在@Computed装饰的getter方法中,不能改变参与计算的属性,以防止重复执行计算属性导致的appfreeze。
- @Computed不能和双向绑定!!连用,@Computed装饰的是getter访问器,不会被子组件同步,也不能被赋值。开发者自己实现的计算属性的setter不生效,且产生编译时报错。
@ComponentV2struct Child {@Param double: number = 100;@Event $double: (val: number) => void;build() {Button('ChildChange').onClick(() => {this.$double(200);})}}@Entry@ComponentV2struct Index {@Local count: number = 100;@Computedget double() {return this.count * 2;}// @Computed装饰的属性是只读的,开发者自己实现的setter不生效,编译时报错。set double(newValue : number) {this.count = newValue / 2;}build() {Scroll() {Column({ space: 3 }) {Text(`${this.count}`)// 错误写法,@Computed装饰的属性是只读的,无法与双向绑定连用,编译时报错。Child({ double: this.double!! })}}}} - @Computed为状态管理V2提供的能力,只能在@ComponentV2和@ObservedV2中使用。
- 多个@Computed一起使用时,警惕循环求解,以防止计算过程中的死循环。
@Type装饰器:标记类属性的类型
为了实现序列化类时不丢失属性的复杂类型,开发者可以使用@Type装饰器装饰类属性。
@Type的目的是标记类属性,配合PersistenceV2使用,防止序列化时类丢失。在阅读本文档前,建议提前阅读:PersistenceV2。
@Type标记类属性,使得类属性序列化时不丢失类型信息,便于类的反序列化
使用限制
- 只能用在**@ObservedV2**装饰的类中,不能用在自定义组件中。
class Sample {data: number = 0;}@ObservedV2class Info {@Type(Sample)@Trace sample: Sample = new Sample(); // 正确用法}@Observedclass Info2 {@Type(Sample)sample: Sample = new Sample(); // 错误用法,不能用在@Observed装饰的类中,编译时报错}@ComponentV2struct Index {@Type(Sample)sample: Sample = new Sample(); // 错误用法,不能用在自定义组件中,编译时报错build() {}} - 不支持collections.Set、collections.Map等类型。
- 不支持非built-in类型。如[PixelMap、NativePointer、ArrayList等Native类型。
- 不支持简单类型。如string、number、boolean等。
- 不支持构造函数含参的类。
使用场景
持久化数据
import { PersistenceV2, Type } from '@kit.ArkUI';@ObservedV2
class SampleChild {@Trace childNumber: number = 1;
}@ObservedV2
class Sample {// 对于复杂对象需要@Type修饰,确保反序列化成功,去掉@Type会反序列化值失败。@Type(SampleChild)// 对于没有初值的类属性,经过@Type修饰后,需要手动保存,否则持久化失败。// 无法使用@Type修饰的类属性,必须要有初值才能持久化。@Trace sampleChild?: SampleChild = undefined;
}@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct TestCase {@Local sample: Sample = PersistenceV2.connect(Sample, () => new Sample)!;build() {Column() {Text('childNumber value:' + this.sample.sampleChild?.childNumber).onClick(() => {this.sample.sampleChild = new SampleChild();this.sample.sampleChild.childNumber = 2;PersistenceV2.save(Sample);}).fontSize(30)}}
}
@ReusableV2装饰器:组件复用
为了降低反复创建销毁自定义组件带来的性能开销,开发者可以使用@ReusableV2装饰@ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件,达成组件复用的效果。
在阅读本文前,建议提前阅读:@Reusable装饰器:组件复用。
@ReusableV2用于装饰V2的自定义组件,表明该自定义组件具有被复用的能力:
-
@ReusableV2仅能装饰V2的自定义组件,即@ComponentV2装饰的自定义组件。并且仅能将@ReusableV2装饰的自定义组件作为V2自定义组件的子组件使用。
-
@ReusableV2同样提供了aboutToRecycle和aboutToReuse的生命周期,在组件被回收时调用aboutToRecycle,在组件被复用时调用aboutToReuse,但与@Reusable不同的是,aboutToReuse没有入参。
-
在回收阶段,会递归地调用所有子组件的aboutToRecycle回调(即使子组件未被标记可复用);在复用阶段,会递归地调用所有子组件的aboutToReuse回调(即使子组件未被标记可复用)。
-
@ReusableV2装饰的自定义组件会在被回收期间保持冻结状态,即无法触发UI刷新、无法触发@Monitor回调,与freezeWhenInactive标记位不同的是,在解除冻结状态后,不会触发延后的刷新。
复用阶段的冻结
在之前的复用中,V1组件在复用池中仍能响应更新,这会对性能带来一定的负面影响,需要开发者使用组件冻结能力,才能够使V1组件在复用池中时不响应更新。针对这一点,V2组件在复用时将会被自动冻结,不会响应在回收期间发生的变化。这一个期间包括aboutToRecycle,即aboutToRecycle中的修改不会刷新到UI上,也不会触发@Computed以及@Monitor。冻结状态将持续到aboutToReuse前,即aboutToReuse及之后的变量更改,才会正常触发UI刷新、@Computed重新计算以及@Monitor的调用。 -
@ReusableV2装饰的自定义组件会在复用时自动重置组件内状态变量的值、重新计算组件内@Computed以及与之相关的@Monitor。不建议开发者在aboutToRecycle中更改组件内状态变量,详见复用前的组件内状态变量重置。
复用前的组件内状态变量重置
与@Reusable不同的是,@ReusableV2在复用前会重置组件中的状态变量以及相关的@Computed、@Monitor的内容。在复用的过程当中,所有的V2自定义组件,无论是否被标记了@ReusableV2,都会经历这一个重置过程。装饰器 重置方法 @Local 直接使用定义时的初始值重新赋值。 @Param 如果有外部传入则使用外部传入值重新赋值,否则用本地初始值重新赋值。注意:@Once装饰的变量同样会被重置初始化一次。 @Event 如果有外部传入则使用外部传入值重新赋值,否则用本地初始值重新赋值。如果本地没有初始值,则生成默认的空实现。 @Provider 直接使用定义时的初始值重新赋值。 @Consumer 如果有对应的@Provider则直接使用@Provider对应的值,否则使用本地初始值重新赋值。 @Computed 使用当前最新的值重新计算一次,如果使用到的变量还未被重置,将会使用重置前的值,因此推荐开发者将@Computed定义在所使用的变量之后。 @Monitor 在上述所有变量重置完成之后触发。重置过程中产生的变量变化不会触发@Monitor回调,仅更新IMonitorValue中的before值。重置过程中不产生变化的赋值不会触发@Monitor的重置。 常量 包括readonly的常量,不重置。 -
V1和V2的复用组件可在一定规则下混用。
-
不建议开发者嵌套滥用@ReusableV2装饰器,这可能会导致复用效率降低以及内存开销变大。
@ReusableV2 // 装饰ComponentV2的自定义组件
@ComponentV2
struct ReusableV2Component {@Local message: string = 'Hello World';build () {Column() {Text(this.message)}}
}
接口
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Index {build() {Column() {ReusableV2Component().reuse({reuseId: () => 'reuseComponent'}) // 使用'reuseComponent'作为reuseIdReusableV2Component().reuse({reuseId: () => ''}) // 使用空字符串将默认使用组件名'ReusableV2Component'作为reuseIdReusableV2Component() // 未指定reuseId将默认使用组件名'ReusableV2Component'作为reuseId}}
}
@ReusableV2
@ComponentV2
struct ReusableV2Component {build() {}
}
