<MySQL——L1>
<MySQL——L1>
文章目录
- <MySQL——L1>
- 1.DQL( Data Query Language )数据查询语言 select
- 1.1基本查询
- 1.2条件查询
- 1.3排序查询
- 1.4常见函数
- 1.5分组函数
- 1.6SQL92标准(用的少)
- 1.7SQL99标准
- 1.8联合查询
- 1.9子查询
- 1.10分页查询
- 1.11select题目练习-01
- 1.12select题目练习-02
1.DQL( Data Query Language )数据查询语言 select
1.1基本查询
-- DQL( Data Query Language ):数据查询语言 select ########################## 一、基本查询 ############################
/*1.语法select 查询列表 from 表; 查询列表:字段、表达式、常量、函数等2.执行顺序from -> select
*/########################## 案例 ############################-- 一、查询常量
select 10;-- 二、查询表达式
select version(); -- 查看数据库版本8.0.28
select database(); -- 查看当前数据库testdql2509-- 三、查询单个字段
select first_name from employees; -- 四、查询多个字段
select first_name,last_name from employees; -- 五、查询所有字段
select * from employees; -- 慎用*,会面向全表查询-- 六、查询函数(调用函数,获取返回值)
-- concat(字段1,字段2,...) 拼接函数
select concat(first_name,' & ',last_name) from employees;-- 七、给查询字段起别名
#方式一:使用as关键字
select concat(first_name,' & ',last_name) as name from employees;
#方式二:使用空格
select concat(first_name,' & ',last_name) 姓名 from employees;-- 八、+的作用
-- 1.两个操作数都是数值型,执行加法操作
select 1+2;
-- 2.其中一个操作数为字符型,一个操作数为数值,则将字符型数据强制转换成数值型,如果无法转换,则直接当做0处理
select '12a'+3; -- 15
select 'a12'+3; -- 3
-- 3.其中一个操作数为null,结果为null (null是无穷大)
select null+3; -- null
select first_name , commission_pct , salary , commission_pct*salary 提成 from employees;-- 九、distinct的使用,去除重复记录
#需求:查询员工涉及到的部门编号
select distinct department_id from employees;-- 十、查看表的结构
desc employees;########################## 作业 ############################-- 1.下面的语句是否可以执行成功select last_name , job_id , salary as salfrom employees;
select last_name , job_id , salary as sal from employees;
-- 2.下面的语句是否可以执行成功select * from employees;
select * from employees;
-- 3.找出下面语句中的错误select employee_id , last_name,salary* 12 “ANNUAL SALARY”from employees;
-- 中文 ,“”
select employee_id , last_name,salary* 12 "ANNUAL SALARY" from employees;
-- 4.显示表departments的结构,并查询其中的全部数据
desc departments;
select * from departments;
-- 5.显示出表employees中的全部job_id(不能重复)
select distinct job_id from employees;
-- 6.显示出表employees的全部列,各个列之间用逗号连接,列头显示成OUT_PUT
select CONCAT_WS(',',employee_id,first_name,last_name,phone_number,job_id,salary,commission_pct,manager_id,
department_id,hiredate) AS OUT_PUT from employees;
1.2条件查询
-- DQL( Data Query Language ):数据查询语言 select ########################## 二、条件查询 ############################
/*1.语法select 查询列表 from 表 where 筛选条件;2.执行顺序from -> where -> select
*/########################## 案例 ############################-- 一、按关系表达式筛选 关系运算符:> < >= <= = <> 补充:也可以使用!=,但不建议
#案例1:查询部门编号不是100的员工信息
select * from employees where department_id!=100;
select * from employees where department_id<>100;
#案例2:查询工资<15000的姓名、工资
select first_name , salary from employees where salary<15000;-- 二、按逻辑表达式筛选 逻辑运算符:and or not 补充:也可以使用&& || ! ,但不建议
#案例1:查询部门编号不是 50-100之间员工姓名、部门编号、邮箱
select first_name , department_id , email
from employees
where department_id<50 or department_id>100;select first_name , department_id , email
from employees
where department_id not between 50 and 100;#案例2:查询奖金率>0.03 或者 员工编号在60-110之间的员工信息
select employee_id , first_name , commission_pct
from employees
where commission_pct>0.03 or employee_id between 60 and 110;-- 三、模糊查询 like/not like
-- %任意模糊匹配 _占位,模糊匹配一个位置 \转义字符 escape指定符号充当转义字符
#案例1:查询姓名中包含字符a的员工信息
select first_name from employees where first_name like '%a%';
#案例2:查询姓名中包含最后一个字符为e的员工信息
select first_name from employees where first_name like '%e';
#案例3:查询姓名中包含第一个字符为e的员工信息
select first_name from employees where first_name like 'e%';
#案例4:查询姓名中包含第三个字符为x的员工信息
select first_name from employees where first_name like '__x%';
#案例5:查询姓名中包含第二个字符为_的员工信息
select last_name from employees where last_name like '_\_%';
select last_name from employees where last_name like '_$_%' escape '$';-- 四、查询某字段的值是否属于指定的列表之内 in/not in
#案例1:查询部门编号是30/50/90的员工名、部门编号
select first_name , department_id
from employees
where department_id in(30 , 50 , 90);#案例2:查询工种编号不是SH_CLERK或IT_PROG的员工信息
select first_name , job_id
from employees
where job_id not in ('SH_CLERK' , 'IT_PROG');-- 五、判断某个字段的值是否介于指定的区间范围 between and/not between and
#案例1:查询部门编号是30-90之间的部门编号、员工姓名
select first_name , department_id
from employees
where department_id between 30 and 90;#案例2:查询年薪不是100000-200000之间的员工姓名、工资、年薪
select first_name , salary , salary*12 年薪
from employees
where salary*12 not between 100000 and 200000;#查询员工姓名、工资、总收入
#IFNULL(字段,值1) 若字段为null,则取值1,否则为原来的值
select first_name , salary , commission_pct ,salary*12 年薪 ,salary*(1+IFNULL(commission_pct,0))*12 总收入
from employees;-- 六、查询是null字段 is null , 查询不是null字段 is not null
#案例1:查询没有奖金的员工信息
select *
from employees
where commission_pct is null;#案例2:查询有奖金的员工信息
select *
from employees
where commission_pct is not null;########################## 作业 ############################
-- 1.查询工资大于12000的员工姓名和工资
select first_name,last_name,salary
from employees
where salary > 12000;
-- 2.查询员工号为176的员工的姓名和部门号和年薪
select first_name,last_name,department_id,salary*12 as annual_salary
from employees
where employee_id=176;
-- 3.选择工资不在5000到12000的员工的姓名和工资
select first_name,last_name,salary
from employees
where salary not between 5000 and 12000;
-- 4.选择在20或50号部门工作的员工姓名和部门号 #####select first_name,last_name,department_id
from employees
where department_id in (20 ,50);-- 5.选择公司中没有管理者的员工姓名及job_id #####
select first_name,last_name,job_id
from employees
where manager_id is null;-- 6.选择公司中有奖金的员工姓名,工资和奖金级别 #####
select first_name,last_name,salary, commission_pct
from employees
where commission_pct is not null;-- 7.选择员工姓名的第三个字母是a的员工姓名
select first_name,last_name
from employees
where first_name like '__a%';SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM employees
WHERE SUBSTRING(first_name, 3, 1) = 'a';-- 8.选择姓名中有字母a和e的员工姓名 #####
select first_name,last_name
from employees
where first_name like '%a%e%' or first_name like '%e%a%';SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM employees
WHERE first_name LIKE '%a%e%' OR first_name LIKE '%e%a%'OR last_name LIKE '%a%e%' OR last_name LIKE '%e%a%';
-- 9.显示出表employees表中first_name 以'e'结尾的员工信息
select *
from employees
where first_name like '%e';
-- 10.显示出表employees部门编号在80-100之间的姓名、职位
select first_name,last_name, job_id,department_id
from employees
where department_id between 80 and 100;
-- 11.显示出表employees的manager_id 是100,101,110 的员工姓名、职位
select first_name,last_name, job_id,manager_id
from employees
where manager_id in(100,101,110);
1.3排序查询
-- DQL( Data Query Language ):数据查询语言 select ########################## 三、排序查询 ############################
/*1.语法select 查询列表 from 表 where 筛选条件 order by 排序列表 asc/desc;注意:排序列表可以是单个字段、多个字段、表达式、函数、列数、以及以上的组合默认升序asc 、降序desc2.执行顺序from -> where -> select -> order by
*/########################## 案例 ############################-- 一、按单个字段排序
#案例1:将员工编号>120的员工信息进行工资的升序
select *
from employees
where employee_id>120
order by salary;#案例2:将员工编号>120的员工信息进行工资的降序
select *
from employees
where employee_id>120
order by salary desc;-- 二、按表达式排序
#案例:对有奖金的员工,按年薪降序
select first_name , salary , commission_pct , salary*12
from employees
where commission_pct is not null
order by salary*12 desc;-- 三、按别名排序
#案例:对有奖金的员工,按年薪降序
select first_name , salary , commission_pct , salary*12 as yearSalary
from employees
where commission_pct is not null
order by yearSalary desc;-- 四、按函数的结果排序
#案例:按姓名的字数长度进行升序
select first_name , LENGTH(first_name) '字节数', CHAR_LENGTH(first_name) '字符数'
from employees
order by CHAR_LENGTH(first_name);-- UTF-8占3个字节 LENGTH()字节数 CHAR_LENGTH()字符数
select '李四' , LENGTH('李四') , CHAR_LENGTH('李四');-- 五、按多个字段排序
#案例:查询员工的姓名、工资、部门编号,先按工资升序,再按部门编号降序
select first_name , salary , department_id
from employees
order by salary , department_id desc;-- 六、按列数排序(不做要求)
#案例:按第二列排序
select * from employees order by 2;
select first_name from employees order by first_name;########################## 作业 ############################
-- 1.查询员工的姓名和部门号和年薪,按年薪降序按姓名升序
select first_name,last_name,department_id,salary*12 as annual_salary
from employees
order by annual_salary desc,first_name asc;
-- 2.选择工资不在8000到17000的员工的姓名和工资,按工资降序
select first_name,department_id,salary
from employees
where salary not between 8000 and 17000
order by salary desc;
-- 3.查询邮箱中包含e的员工信息,并先按邮箱的字节数降序,再按部门号升序select *
from employees
where email like '%e%'
order by CHAR_LENGTH(email) desc,department_id;1.4常见函数
-- DQL( Data Query Language ):数据查询语言 select ########################## 四、常见函数 ############################
/*1.语法select 查询列表 from 表 where 筛选条件 order by 排序列表 asc/desc;2.执行顺序from -> where -> select -> order by
*/########################## 1.案例-字符函数 ############################
-- 1、CONCAT 拼接字符
-- 语法:CONCAT(str1,str2,...) 将多个字符串进行拼接
select (first_name,' - ',last_name) name
from employees;select first_name
from employees
where first_name like CONCAT('%','a','%');-- 2、LENGTH 获取字节长度
-- 3、CHAR_LENGTH 获取字符个数
select 'abc' , LENGTH('abc') '字节长度', CHAR_LENGTH('abc') '字符个数';
select '李思思' , LENGTH('李思思') '字节长度' , CHAR_LENGTH('李思思') '字符个数';-- 4、INSERT 插入新字符串
-- 语法:INSERT(str,pos,len,newstr) 第一个参数:字符串 第二个参数:起始下标位置 第三个参数:替换的长度 第四个参数:插入新字符串
select first_name , INSERT(first_name,1,3,'A') from employees;-- 5、SUBSTRING 截取子串 注意:起始索引从1开始
-- 语法:SUBSTRING(str FROM pos FOR len) 第一个参数:字符串 第二个参数:起始下标位置 第三个参数:截取的长度
select first_name ,SUBSTRING(first_name , 1 , 3) from employees;
select first_name ,SUBSTRING(first_name FROM 1 FOR 3) from employees;-- 6、UPPER/LOWER 变大写/变小写
#案例:查询员工表的姓名,要求格式:姓首字符大写,其他字符小写,名所有字符大写,且姓和名之间用_分割,最后起别名“OUTPUT”
select CONCAT(UPPER(SUBSTRING(first_name,1,1)),LOWER(SUBSTRING(first_name,2)),' _ ' , UPPER(last_name)) OUTPUT from employees;-- 7、LEFT/RIGHT 截取子串
-- 语法:LEFT(str,len) 从左边截取 第一个参数:字符串 第二个参数:截取的长度
-- 语法:RIGHT(str,len) 从右边截取 第一个参数:字符串 第二个参数:截取的长度
select first_name , LEFT(first_name,3) , RIGHT(first_name,2)from employees;-- 8、LPAD/RPAD 左填充/右填充
-- 语法:LPAD(str,len,padstr) 用字符串pad对str最左边进行填充,直到str的长度为len个字符
-- 语法:RPAD(str,len,padstr) 用字符串pad对str最右边进行填充,直到str的长度为len个字符
select first_name , LPAD(first_name, 10,'AA') , RPAD(first_name, 10 ,'BB') from employees;-- 9、TRIM去前后指定的字符,默认是去空格
-- 用法:TRIM([remstr FROM] str) 默认去除左右空格
-- 用法:LTRIM(str) 默认去除左边空格
-- 用法:RTRIM(str) 默认去除右边空格
-- 用法:TRIM([{BOTH | LEADING | TRAILING} [remstr] FROM] str)
-- 第一个参数:BOTH两边移除,LEADING左边移除,TRAILING右边移除 第二个参数:remstr移除的字符串 第三个参数:FROM关键字 第四个参数:操作的字符串
select ' abc ' , LENGTH(' abc ') , TRIM(' abc ') , LENGTH(TRIM(' abc ')) ;
select ' abc ' , LENGTH(' abc ') , LTRIM(' abc ') , LENGTH(LTRIM(' abc ')) ;
select '###abc###' , LENGTH('###abc###') , TRIM(LEADING '#' FROM '###abc###') , LENGTH(TRIM(LEADING '#' FROM '###abc###')) ;-- 10、REPEAT(str,count) 第一个参数:操作的字符串 第二个参数:重复的次数
select 'abc' , REPEAT('abc',3);-- 11、REPLACE(str,from_str,to_str) 第一个参数:操作的字符串 第二个参数:将要替换的字符串 第三个参数:替换成字符串
select 'abcabc' , REPLACE('abcabc','a','AAA');-- 12、STRCMP 比较两个字符大小
SELECT STRCMP('A','B');
SELECT STRCMP('Abc','aBc');-- 13、INSTR获取字符第一次出现的索引
select INSTR('abcabc','b');-- 14、SUBSTR(str FROM pos)
select first_name , SUBSTR(first_name , 1 , 2) , SUBSTR(first_name , 2) from employees;########################## 2.案例-数学函数 ############################
-- 1、ABS 绝对值
select ABS(-10);-- 2、CEIL 向上取整 返回>=该参数的最小整数
select CEIL(12.3);
select CEIL(12.7);
select CEIL(-12.3);-- 3、FLOOR 向下取整,返回<=该参数的最大整数
select FLOOR(12.3);
select FLOOR(12.7);
select FLOOR(-12.3);-- 4、ROUND 四舍五入
select ROUND(12.3);
select ROUND(12.7);-- 5、TRUNCATE 截断
select TRUNCATE(12.66666,1); -- 12.6-- 6、MOD 取余
select MOD(10,3);-- 7、RAND() 返回0~1的随机值
select RAND();-- 随机数
select UUID() , LENGTH(UUID()); -- 12ee1471-becc-11f0-9a59-d06578850010
select UUID_SHORT() , LENGTH(UUID_SHORT()); -- 101595235888398336########################## 3.案例-日期时间函数 ############################-- 1、NOW() 系统当前时间
-- 2、CURDATE() 系统当前日期
-- 3、CURTIME() 系统当前时间
-- CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() 系统时间戳
select now(); -- 2025-11-11 15:34:59
select CURDATE(); -- 2025-11-11
select CURTIME(); -- 15:34:59
select CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(); -- 2025-11-11 15:35:49select YEAR(now());
select MONTH(now());
select DAY(now());
select HOUR(now());
select MINUTE(now());
select SECOND(now()); select WEEK(now()); -- 返回一年中的第几周
select WEEKDAY(now()); -- 返回周几,周1是0,周2是1,。。。周日是6-- 4、DATEDIFF(date1,date2) 返回date1 - date2的日期间隔
-- TIMEDIFF(time1, time2) 返回time1 - time2的时间间隔
select first_name , hiredate , ABS(DATEDIFF(hiredate,NOW())) from employees where first_name='William';-- 5、DATE_FORMAT(datetime ,fmt) 按照字符串fmt格式化日期datetime值
#案例:查看100号员工入职日期
select hiredate , DATE_FORMAT(hiredate,'%y%m%d') , DATE_FORMAT(hiredate,'%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s') from employees where employee_id=100;-- 6、STR_TO_DATE 按指定格式解析字符串为日期类型
#案例:查看1998年6月以前入职的员工信息
select first_name , hiredate from employees where hiredate < STR_TO_DATE('1998年6月15日','%Y年%m月%d日');-- 7、DATE_ADD(datetime, INTERVALE expr type) 返回与给定日期时间相差INTERVAL时间段的日期时间
/*使用 DATE_ADD(NOW(),INTERVAL 1 MONTH) 这个函数来进行修改时间第一个参数是要修改的时间;第二个参数固定写法;第三个参数的修改的值 : 如果正数就是加,负数就是减;第四个参数可填YEAR,MONTH,DAY,HOUR,MINUTE,SECOND;
*/
SELECT DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 YEAR); SELECT DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL -1 YEAR); #可以是负数SELECT DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL '1_1' YEAR_MONTH); #需要单引号########################## 4.案例-流程控制函数 ############################
-- 1、IF函数
#需求:如果有奖金,则显示最终奖金,如果没有,则显示0
-- IF(expr1,expr2,expr3) 根据expr1条件是否成立,若成立取expr2,若不成立取expr3
-- IFNULL(expr1,expr2) 根据expr1是否为null,为null则取expr2,若不为null取本身expr1
select commission_pct , IFNULL(commission_pct,0) , IF(commission_pct is null,0,commission_pct) from employees;-- 2、CASE函数
/*情况1 :类似于switch语句,可以实现等值判断CASE 表达式WHEN 值1 THEN 结果1WHEN 值2 THEN 结果2...ELSE 结果nEND
*/
#案例:部门编号是30,工资显示为2倍;部门编号是50,工资显示为3倍;部门编号是60,工资显示为4倍;否则不变;
#显示部门编号,新工资, 旧工资
select department_id , salary 旧工资 ,(case department_idwhen 30 then salary*2when 50 then salary*3when 60 then salary*4else salary end ) 新工资
from employees;/*情况2:类似于多重IF语句,实现区间判断CASEWHEN 条件1 THEN 结果1WHEN 条件2 THEN 结果2...ELSE 结果nEND
*/
#案例:如果工资>20000,显示级别A;工资>15000,显示级别B;工资>10000,显示级别C;否则,显示D
select salary ,
case
when salary>20000 then 'A'
when salary>15000 then 'B'
when salary>10000 then 'C'
else 'D'
end 级别
from employees;########################## 5.案例-分组(聚合)函数 ############################
-- 案例:查询员工信息表中,所有员工的工资和、工资平均值、最低工资、最高工资、有工资的个数-- count() 函数
#添加筛选条件
-- 案例1:查询emp表中记录数
select count(*) from employees; -- 107
select count(first_name) from employees; -- 107
select count(department_id) from employees; -- 106 department_id是null,count()计数会自动去处null值-- 案例2:查询emp表中有佣金的人数
select count(commission_pct) from employees; -- 35-- 案例3:查询emp表中月薪大于2500的人数
select count(*) from employees where salary>2500;-- 案例4:查询有领导的人数
select count(*) from employees where manager_id is not null;#其它用途
-- 案例5:统计结果集的行数,推荐使用count(*)。需求:查询员工表中30号部门的人数
select count(*) from employees where department_id=30;-- 案例6:搭配distinct实现去重的统计。需求:查询有员工的部门个数
select count(DISTINCT department_id) from employees;
locations
-- SUM() 求和函数
-- 案例7:查询所有员工月薪和
-- AVG() 平均值函数
-- 案例8:统计所有员工平均工资
-- MAX() 和 MIN() 最大值和最小值函数
-- 案例9:查询最高工资和最低工资
select sum(salary) '月薪和' , avg(salary) '平均工资' , max(salary) '最高工资' , min(salary) '最低工资' , count(salary) '有工资的个数' from employees;########################## 作业 ############################
######## 常见函数作业 ########
-- 1. 显示系统时间(注:日期+时间)
select now();
select now() as current_datetime;
-- 2. 查询员工号,姓名,工资,以及工资提高百分之 20%后的结果(new salary) #####
/*别名"new salary"中有一个空格,SQL中如果别名包含空格或特殊字符,通常需要用引号(单引号或双引号,根据数据库系统而定)括起来。
写法1:"new salary"
写法2:`new salary`
写法3:new_salary
*/select employee_id,first_name,last_name,salary,salary*1.2 as new salary from employees; -- 别名写法报错select employee_id,first_name,last_name,salary,salary*1.2 as `new salary` from employees;
select employee_id,first_name,last_name,salary,salary*1.2 as "new salary" from employees;
select employee_id,first_name,last_name,salary,salary*1.2 as new_salary from employees;
-- 3. 将员工的姓名按首字母排序,并写出姓名的长度(length) #########SELECT first_name, last_name, LENGTH(CONCAT(first_name, last_name)) AS name_length
FROM employees
ORDER BY SUBSTRING(first_name, 1, 1);
-- 4. 做一个查询,产生下面的结果 ##########
-- <last_name> earns <salary> monthly but wants <salary*3>
-- Dream Salary
-- King earns 24000 monthly but wants 72000
select CONCAT(last_name,' earns ',salary,' monthly but wants ',salary*3) as "Dream Salary"
from employees
where last_name = 'K_ing';-- 5. 使用 case-when,按照下面的条件: #############
-- job grade
-- AD_PRES A
-- ST_MAN B
-- IT_PROG C
-- SA_REP D
-- ST_CLERK E
-- 产生下面的结果
-- Last_name Job_id Grade
-- king AD_PRES Aselect last_name as "Last_name",job_id as "Job_id",case job_idwhen 'AD_PRES' then 'A'when 'ST_MAN ' then 'B 'when 'IT_PROG' then 'C'when 'SA_REP' then 'D 'when 'ST_CLERK' then 'E'else 'OTHER'end as Grade
from employees
where last_name='K_ing';######## 分组函数作业 ########
-- 1. 查询公司员工工资的最大值,最小值,平均值,总和
select MAX(salary),MIN(salary),AVG(salary),SUM(salary)
from employees;SELECT MAX(salary) AS max_salary,MIN(salary) AS min_salary,AVG(salary) AS avg_salary,SUM(salary) AS sum_salary
FROM employees;
-- 2. 查询员工表中的最大入职时间和最小入职时间的相差天数 (DIFFRENCE)
select DATEDIFF(MAX(hiredate),MIN(hiredate))
from employees;SELECT DATEDIFF(MAX(hiredate), MIN(hiredate)) AS DIFFRENCE
FROM employees;
-- 3. 查询部门编号为 90 的员工个数
select count(*)
from employees
where department_id = 90;SELECT COUNT(*) AS employee_count
FROM employees
WHERE department_id = 90;1.5分组函数
-- DQL( Data Query Language ):数据查询语言 select ########################## 五、分组查询 ############################
/*1.语法select 查询列表 from 表 where 筛选条件 group by 分组列表 having 分组后筛选 order by 排序列表;2.执行顺序from -> where -> group by -> having -> select -> order by3.注意点 3.1 select查询列表,查询列表要么是分组函数 (min、max、sum、avg、count) , 要么是group by后面的分组字段3.2 where 筛选条件 group by 分组列表 ,针对于原来数据进行筛选3.3 group by 分组列表 having 分组后筛选 , 针对于分组后产生的数据进行筛选
*/########################## 案例 ############################-- 1)简单的分组
#案例1:查询每个工种的员工平均工资
select job_id , avg(salary)
from employees
group by job_id;#案例2:查询每个领导的手下人数
select manager_id , count(*)
from employees
group by manager_id;-- 2)可以实现分组前的筛选
#案例1:查询邮箱中包含a字符的每个部门的最高工资
select department_id , max(salary)
from employees
where email like '%a%'
group by department_id;#案例2:查询每个领导手下有奖金的员工的平均工资
select manager_id , avg(salary)
from employees
where commission_pct is not null
group by manager_id;-- 3)可以实现分组后的筛选
#案例1:查询哪个部门的员工个数>5
select department_id , count(*)
from employees
group by department_id
having count(*)>5;#案例2:每个工种有奖金的员工的最高工资>12000的工种编号和最高工资
select job_id , max(salary)
from employees
where commission_pct is not null
group by job_id
HAVING max(salary)>12000;#案例3:领导编号>102的每个领导手下的最低工资大于5000的最低工资
select manager_id , min(salary)
from employees
where manager_id>102
group by manager_id
having min(salary)>5000;-- 4)可以实现排序
#案例:查询没有奖金的员工的最高工资>6000的工种编号和最高工资,按最高工资升序
select job_id , max(salary)
from employees
where commission_pct is null
group by job_id
HAVING max(salary)>6000
order by max(salary);-- 5)按多个字段分组
#案例:查询每个工种每个部门的最低工资,并按最低工资降序。提示:工种和部门都一样,才是一组
select job_id , department_id , min(salary)
from employees
group by job_id , department_id
order by min(salary) desc;########################## 作业 ############################-- 1.查询各job_id的员工工资的最大值,最小值,平均值,总和,并按job_id升序 #########
select job_id,MAX(salary),MIN(salary),AVG(salary),SUM(salary)
from employees
group by job_id
order by job_id;SELECT job_id,MAX(salary) AS max_salary,MIN(salary) AS min_salary,AVG(salary) AS avg_salary,SUM(salary) AS sum_salary
FROM employees
GROUP BY job_id
ORDER BY job_id;
-- 2.查询员工最高工资和最低工资的差距(DIFFERENCE) #########
select MAX(salary) - MIN(salary) from employees;SELECT MAX(salary) - MIN(salary) AS DIFFERENCE
FROM employees;
-- 3.查询各个管理者手下员工的最低工资,其中最低工资不能低于6000,没有管理者的员工不计算在内
select manager_id,MIN(salary)
from employees
where manager_id is not null
group by manager_id
having MIN(salary) >= 6000;SELECT manager_id, MIN(salary) AS min_salary
FROM employees
WHERE manager_id IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY manager_id
HAVING MIN(salary) >= 6000;
-- 4.查询所有部门的编号,员工数量和工资平均值,并按平均工资降序
select department_id,COUNT(*),AVG(salary)
from employees
group by department_id
order by AVG(salary) desc;SELECT department_id,COUNT(*) AS employee_count,AVG(salary) AS avg_salary
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY department_id
ORDER BY avg_salary DESC;
-- 5.选择具有各个job_id的员工人数
select job_id,count(*)
from employees
group by job_id;SELECT job_id, COUNT(*) AS employee_count
FROM employees
GROUP BY job_id;
1.6SQL92标准(用的少)
########################## SQL92标准 - 内连接 ############################
/*1.语法select 查询列表 from 表1 别名 , 表2 别名 , 表3 别名where 连接条件 and 筛选条件group by 分组列表having 分组后筛选条件order by 排序列表;2.执行顺序from -> where先执行连接条件再执行筛选条件 -> group by -> having -> select -> order by
*/############# 案例 - 等值连接 ##############
-- 1、多表等值查询
#案例1:查询女神名和对应的男神名
select g.`name` , b.`name`
from girl g , boy b
where g.boyfriend_id = b.id;#案例2:查询员工名和对应的部门名
select e.first_name , d.department_name
from employees e , departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id;-- 2、为表起别名
#查询员工名、工种号、工种名
select e.first_name , e.job_id , j.job_title
from employees e , jobs j
where e.job_id = j.job_id;-- 3、两个表的顺序可以调换
#查询员工名、工种号、工种名
select e.first_name , e.job_id , j.job_title
from jobs j , employees e
where e.job_id = j.job_id;-- 4、可以加筛选
#案例1:查询有奖金的员工名、部门名
select e.first_name , d.department_name
from employees e , departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id and e.commission_pct is not null;#案例2:查询城市名中第二个字符为o的部门名和城市名
select d.department_name , l.city
from departments d , locations l
where d.location_id = l.location_id and l.city like '_o%';-- 5、可以加分组
#案例1:查询每个城市的部门个数
select l.city , COUNT(*)
from departments d , locations l
where d.location_id = l.location_id
GROUP BY l.city;#案例2:查询有奖金的每个部门的部门名和部门的领导编号和该部门的最低工资
select d.department_name '部门名', max(d.manager_id) '领导编号', min(salary) '最低工资'
from employees e , departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id and e.commission_pct is not null
group by d.department_name;-- 6、可以加排序
#案例:查询每个工种的工种名和员工的个数,并且按员工个数降序
select j.job_title , count(*) c
from employees e , jobs j
where e.job_id = j.job_id
group by j.job_title
order by c desc;-- 7、可以实现三表连接?
#案例1:查询员工名、部门名和所在的城市
select e.first_name , d.department_name , l.city
from employees e , departments d , locations l
where e.department_id = d.department_id and d.location_id = l.location_id;#案例2:查询员工名、部门名和所在的城市,要求城市名称以s开头,并且按照部门名称降序。
select e.first_name , d.department_name deptname , l.city
from employees e , departments d , locations l
where e.department_id = d.department_id and d.location_id = l.location_id and l.city like 's%'
order by deptname desc;############# 案例 - 非等值连接 ##############
#案例:查询员工的工资和工资级别
select e.first_name , e.salary , g.grade_level
from employees e , job_grades g
where e.salary BETWEEN g.lowest_sal and g.highest_sal
order by e.salary;############# 案例 - 自连接 ##############
#案例:查询员工名和上级的名称
select e.first_name '员工' , m.first_name '领导'
from employees e , employees m
where e.manager_id = m.employee_id;1.7SQL99标准
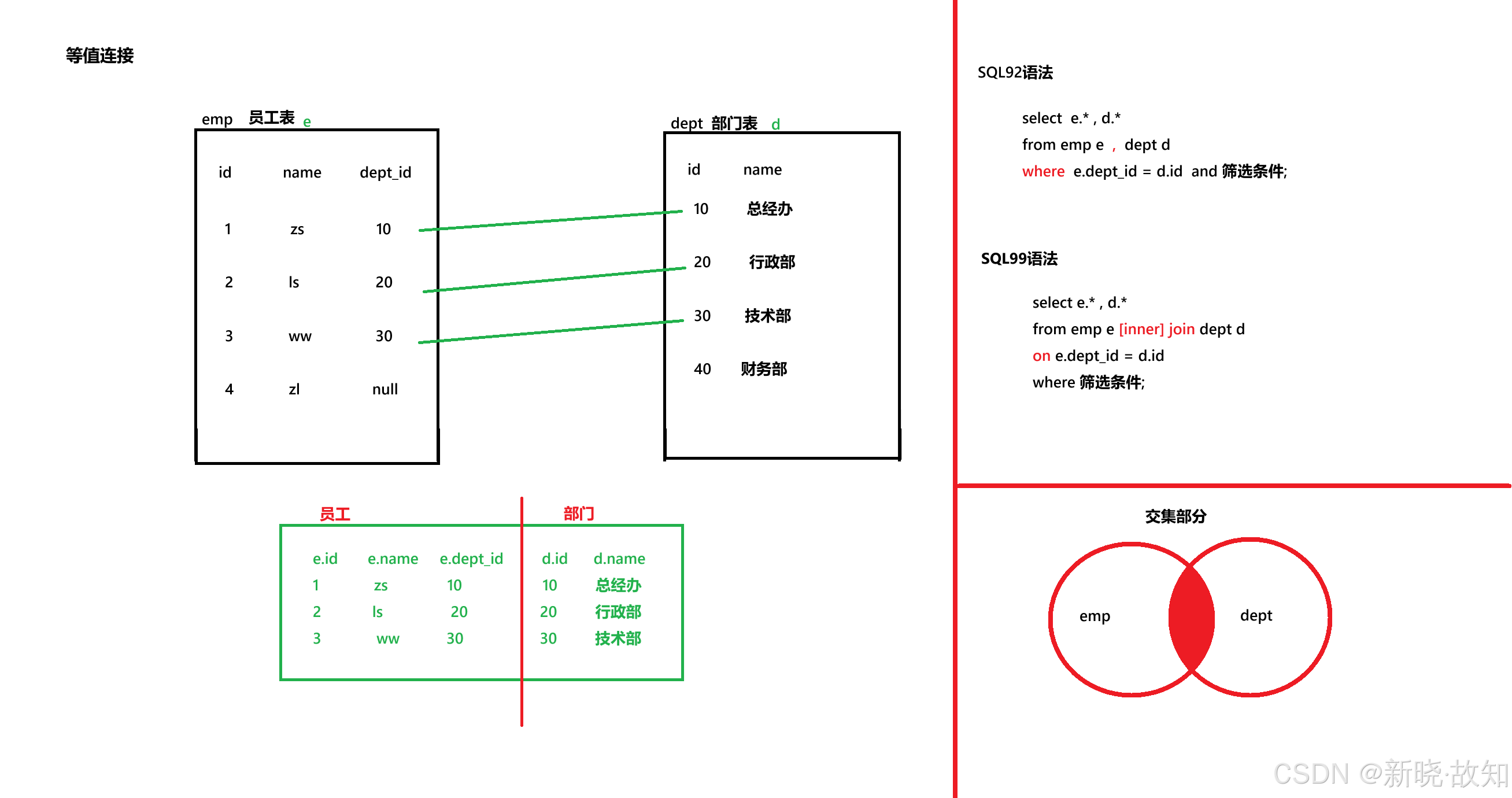
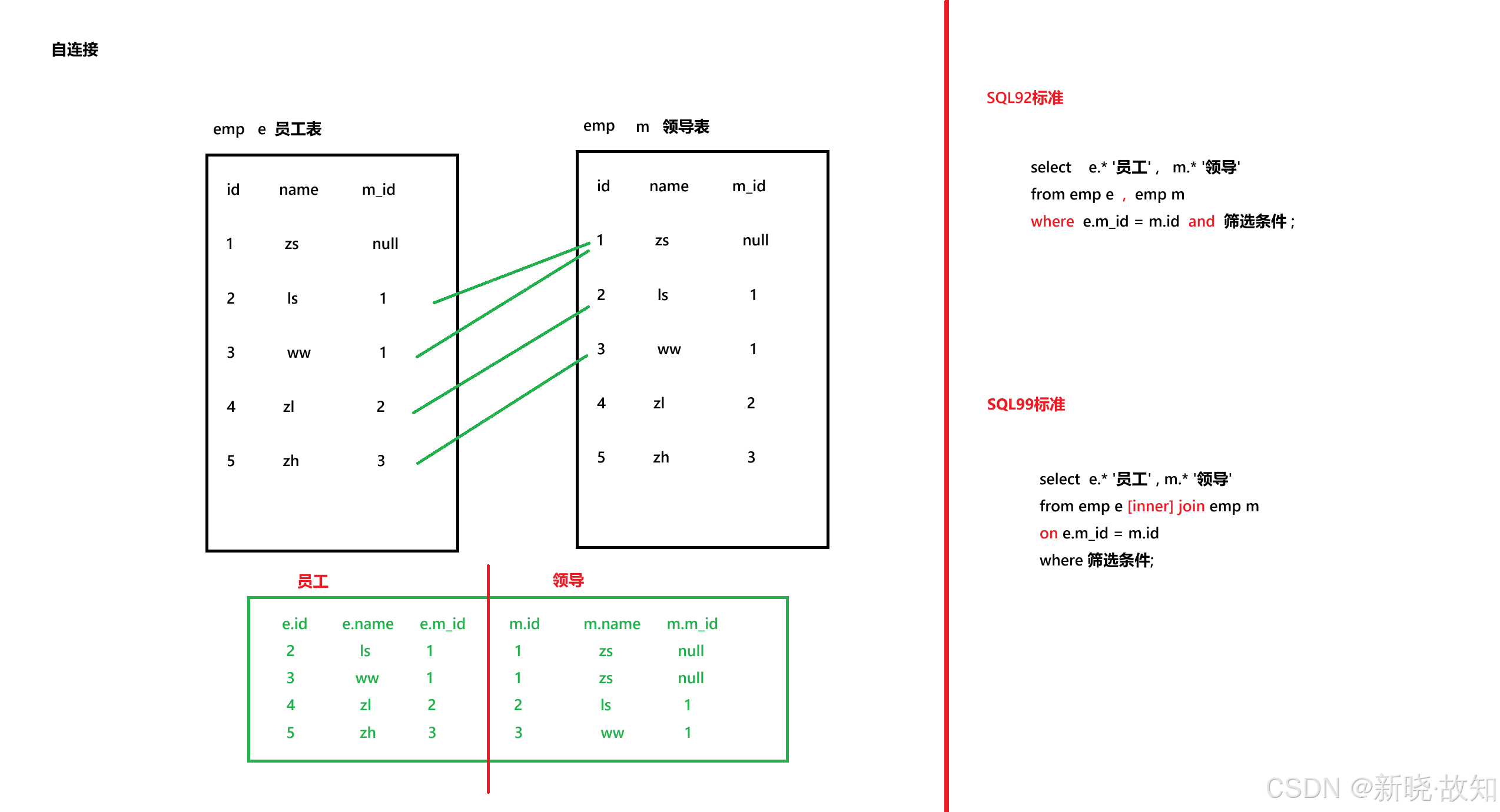
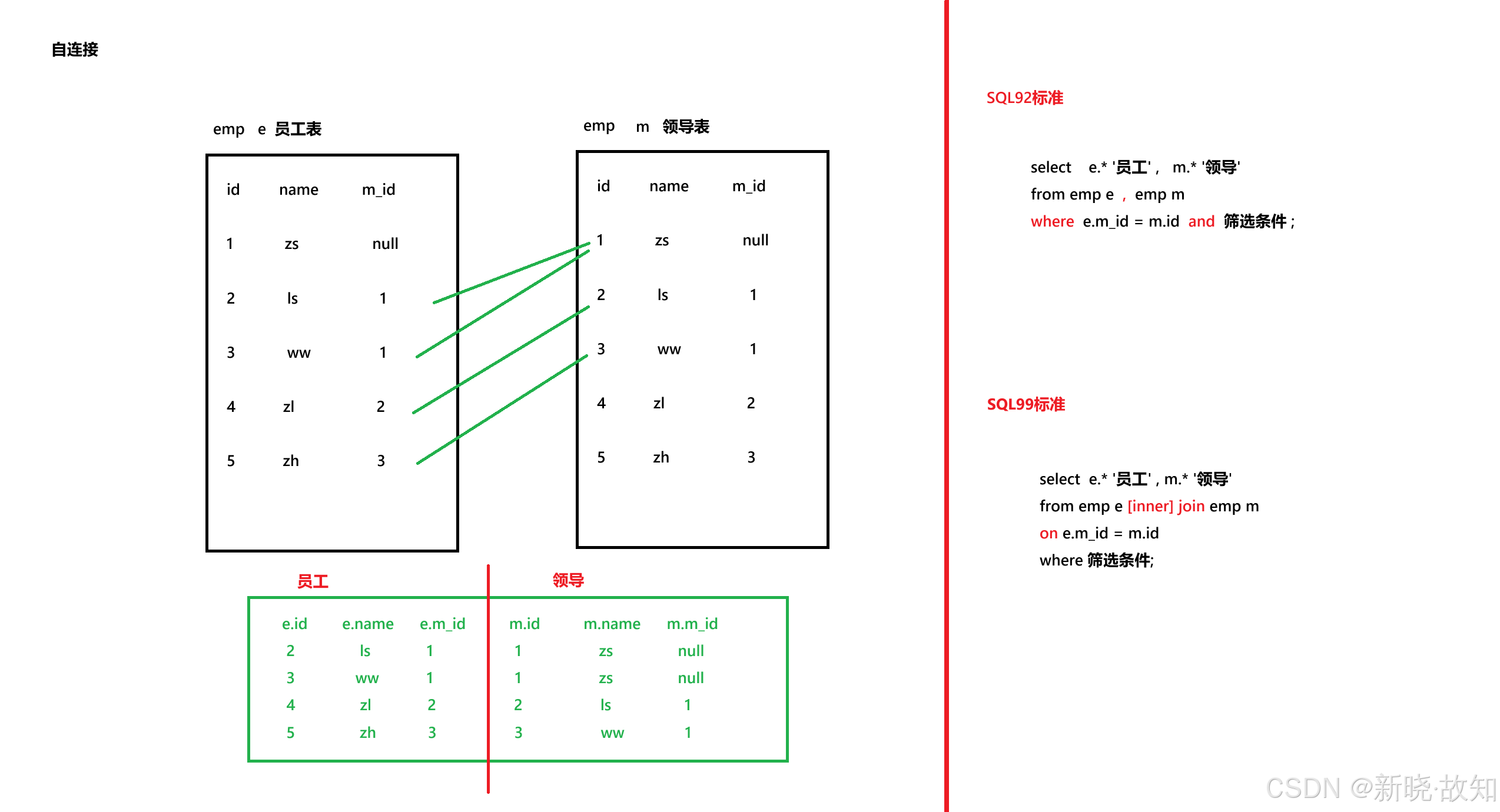
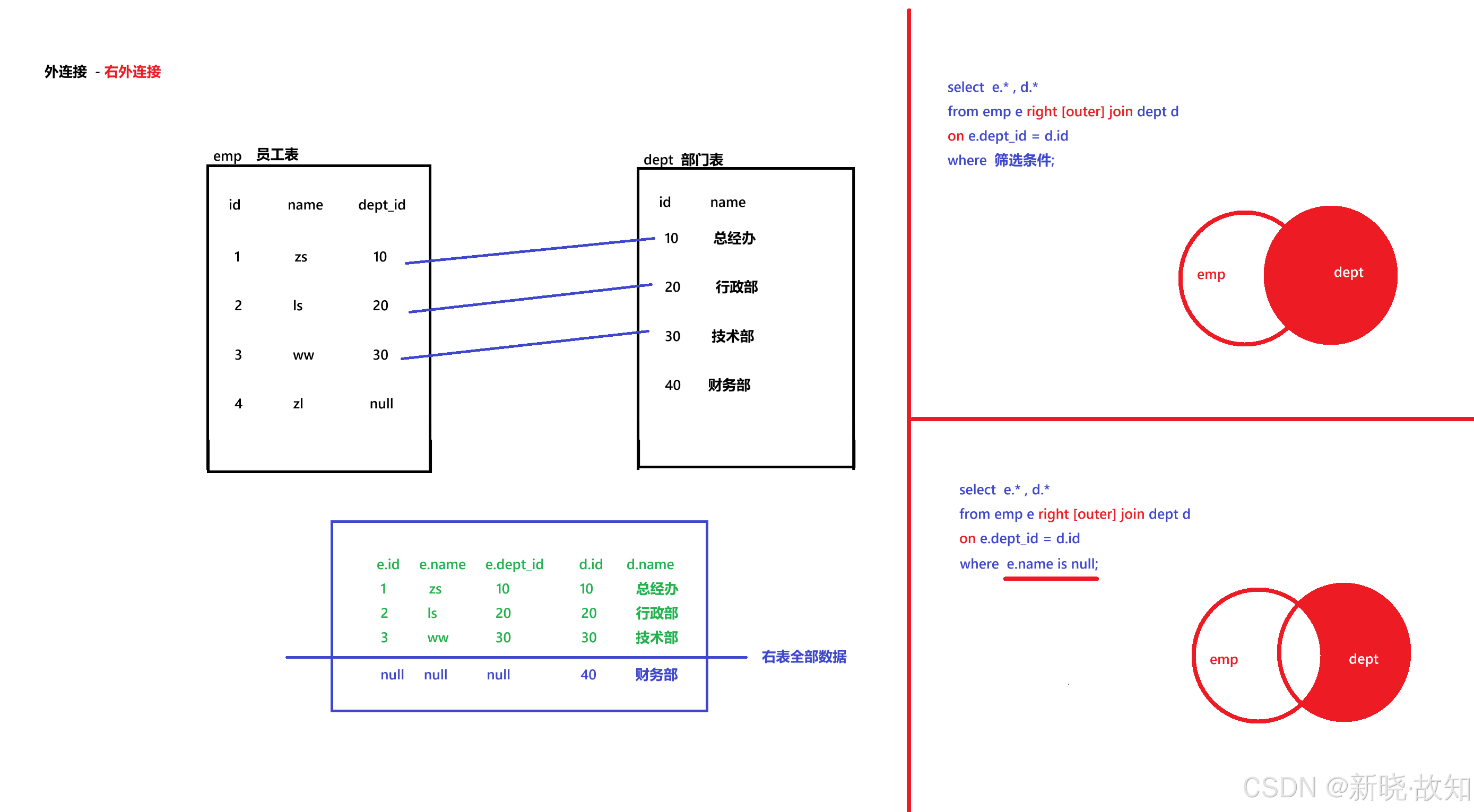

########################## SQL99标准 - 内连接 ############################
/*1.语法select 查询列表 from 表1 别名 [inner] join 表2 别名 [inner] join 表3 别名on 连接条件where 筛选条件group by 分组列表having 分组后筛选条件order by 排序列表;2.执行顺序from -> on执行连接条件 -> where执行筛选条件 -> group by -> having -> select -> order by
*/#--------------- 案例 - 等值连接 ---------------#
-- 1.简单连接
#案例:查询员工名和部门名
select e.first_name '员工名', d.department_name '部门名'
from employees e join departments d
on e.department_id = d.department_id;-- 2.添加筛选条件
#案例:查询部门编号>100的部门名和所在的城市名
select d.department_name ,l.city
from departments d join locations l
on d.location_id = l.location_id
where d.department_id>100;-- 3.添加分组
#案例:查询每个城市的部门个数
select l.city , count(d.department_id)
from departments d join locations l
on d.location_id = l.location_id
group by l.city;-- 4.添加分组+排序
#案例:查询部门中员工个数>10的部门名,并按员工个数降序
select d.department_name , count(*) '员工个数'
from employees e join departments d
on e.department_id = d.department_id
group by e.department_id
having count(*)>10
order by count(*) desc;#--------------- 案例 - 非等值连接 ---------------#
#案例:查询部门编号在10-90之间的员工的工资级别,并按级别进行分组
select j.grade_level , count(*) '员工人数'
from employees e join job_grades j
on e.salary BETWEEN j.lowest_sal and j.highest_sal
where e.department_id BETWEEN 10 and 90
group by j.grade_level;#--------------- 案例 - 自连接 ---------------#
#案例:查询员工名和对应的领导名
select e.first_name '员工' , m.first_name '领导'
from employees e join employees m
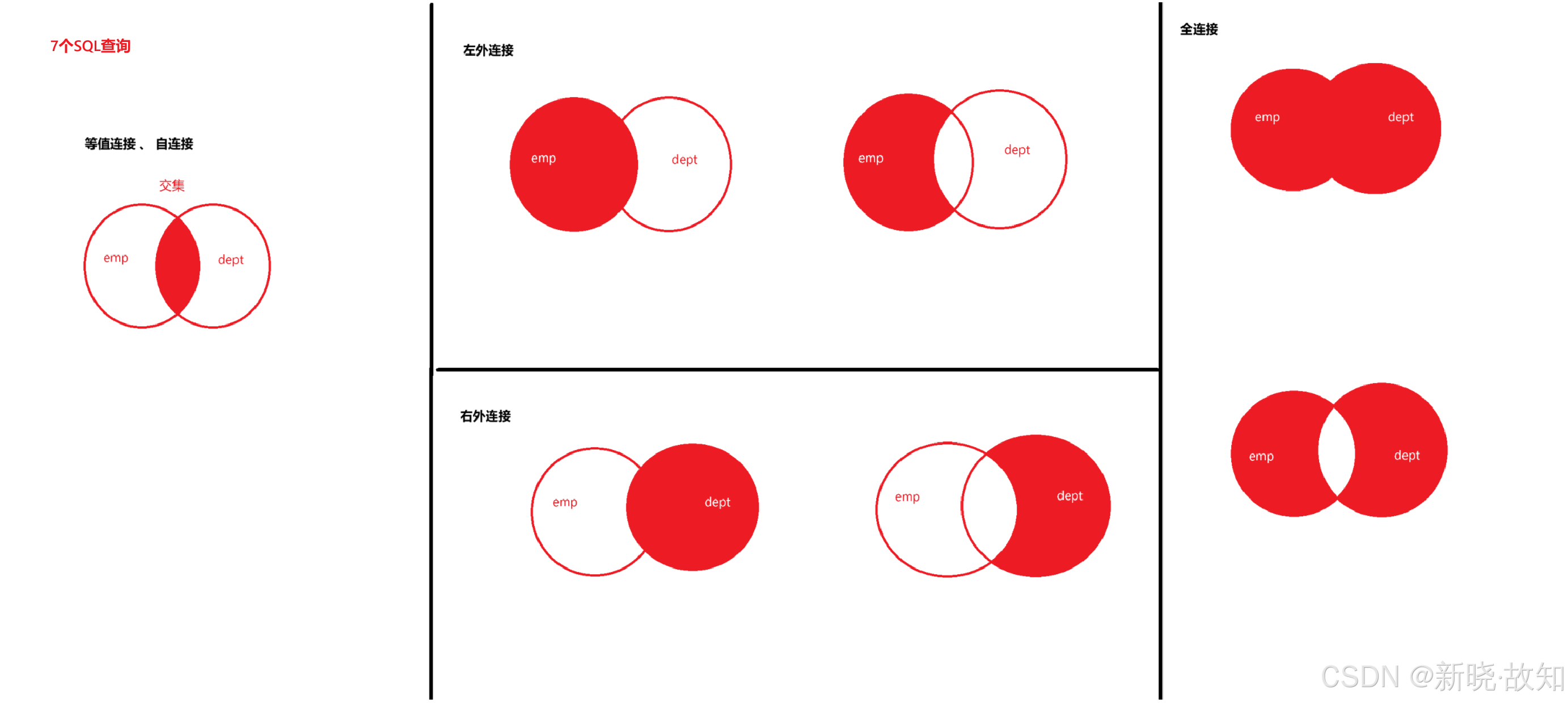
on e.manager_id = m.employee_id;########################## SQL99标准 - 外连接 ############################
/*1.语法select 查询列表 from 表1 别名 left | right | full [outer] join 表2 别名on 连接条件where 筛选条件group by 分组列表 having 分组后筛选条件order by 排序列表;2.执行顺序from -> on执行连接条件 -> where执行筛选条件 -> group by -> having -> select -> order by
*/#--------------- 案例 - 左外连接 & 右外连接 ---------------#
#案例1:查询所有女神记录,以及对应的男神名,如果没有对应的男神,则显示为null
-- 左连接
select g.* , b.*
from girl g left join boy b
on g.boyfriend_id = b.id;
-- 右连接
select g.* , b.*
from boy b right join girl g
on g.boyfriend_id = b.id;#案例2:查哪个女神没有男朋友
-- 左连接
select g.* , b.*
from girl g left join boy b
on g.boyfriend_id = b.id
where b.id is null;-- 右连接
select g.* , b.*
from boy b right join girl g
on g.boyfriend_id = b.id
where b.name is null;#案例3:查哪个男神没有女朋友
-- 左连接
select g.* , b.*
from boy b left join girl g
on g.boyfriend_id = b.id
where g.id is null;-- 右连接
select g.* , b.*
from girl g right join boy b
on g.boyfriend_id = b.id
where g.id is null;#案例4:查询哪个部门没有员工,并显示其部门编号和部门名
select d.department_id , d.department_name
from employees e right join departments d
on e.department_id = d.department_id
where e.employee_id is null;#案例5:查询城市名包含a字符的哪个城市没有部门,并按城市名降序
select l.city
from departments d right join locations l
on d.location_id = l.location_id
where d.department_name is null and l.city like '%a%'
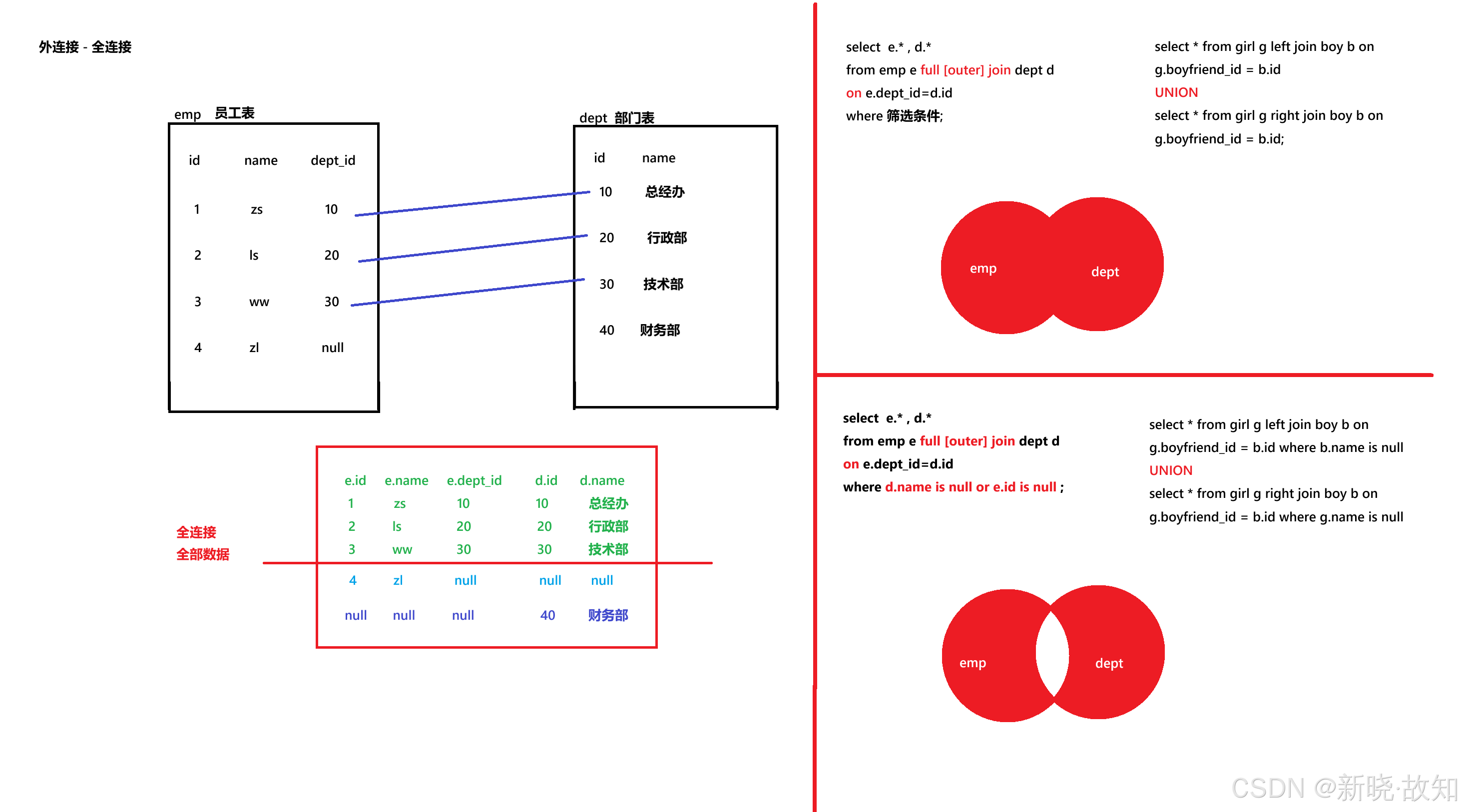
order by l.city desc;#--------------- 案例 - 全连接 ---------------#
/*1.语法select 查询列表 from 表1 别名 left | right | full [outer] join 表2 别名on 连接条件where 筛选条件group by 分组列表 having 分组后筛选条件order by 排序列表;2.执行顺序from -> on执行连接条件 -> where执行筛选条件 -> group by -> having -> select -> order by注意:全连接就是将表中所有记录都查询出来,且不允许重复。注:此处不支持。全外连接 = 内连接查询的结果 + 表1中有但表2中没有的记录 + 表2中有但表1中没有的记录
*/
#需求1:查询所有男生和女生数据
select g.* , b.*
from girl g full join boy b
on g.boyfriend_id = b.id;#需求2:查询所有没有女朋友的男生和 没有男朋友的女生数据
select g.* , b.*
from girl g full join boy b
on g.boyfriend_id = b.id
where g.name is null or b.id is null;########################## SQL99标准 - 交叉连接 ############################
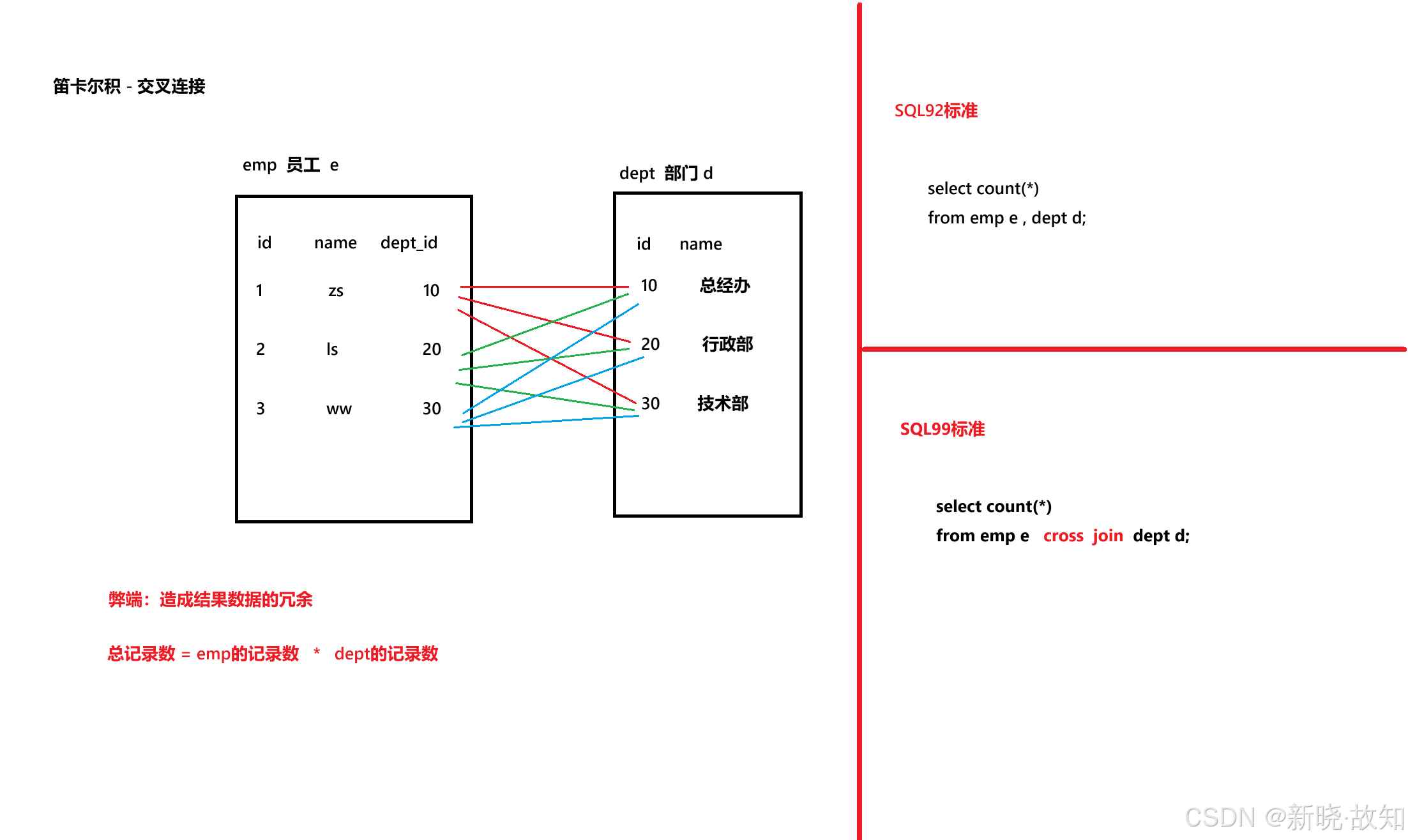
-- 笛卡尔积(交叉连接) 总记录数 = girl表中的记录数*boy表中的记录数
select count(*)
from girl , boy; -- 13*7select count(*)
from girl cross join boy; -- 13*7########################## SQL99标准 - 自然连接 ############################
-- 自然连接 两张连接的表中字段名称和类型完全一致的列作为条件,且数据一致
select g.* , b.*
from girl g NATURAL join boy b; ########################## 作业 ############################
########内连接########
-- 1. 显示所有员工的姓名,部门号和部门名称。
SELECT e.first_name,e.last_name,e.department_id,d.department_name
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id;-- 2. 查询 90 号部门员工的 job_id 和 90 号部门的 location_id
SELECT e.job_id,d.location_id
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id
WHERE e.department_id = 90;-- 3. 选择所有有奖金的员工的last_name , department_name , location_id , city
SELECT e.last_name,d.department_name,d.location_id,l.city
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id
INNER JOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_id
WHERE e.commission_pct IS NOT NULL;-- 4. 选择city在Toronto工作的员工的last_name , job_id , department_id , department_name
SELECT e.last_name,e.job_id,e.department_id,d.department_name
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id
INNER JOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_id
WHERE l.city = 'Toronto';-- 5.查询每个工种、每个部门的部门名、工种名和最低工资
SELECT d.department_name, j.job_title, MIN(e.salary) as min_salary
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id
INNER JOIN jobs j ON e.job_id = j.job_id
GROUP BY d.department_name, j.job_title, d.department_id, j.job_id;-- 6.查询每个国家下的部门个数大于 2 的国家编号
SELECT l.country_id, COUNT(d.department_id) as dept_count
FROM departments d
INNER JOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_id
GROUP BY l.country_id
HAVING COUNT(d.department_id) > 2;-- 7、选择指定员工的姓名,员工号,以及他的管理者的姓名和员工号,结果类似于下面的格式
-- employees Emp# manager Mgr#
-- kochhar 101 king 100
SELECTe.last_name AS employees,e.employee_id AS "Emp#",m.last_name AS manager,m.employee_id AS "Mgr#"
FROMemployees eINNER JOIN employees m ON e.manager_id = m.employee_id;
########外连接########
-- 一、查询编号>3 的女神的男朋友信息,如果有则列出详细,如果没有,用 null 填充
SELECT g.*,b.*
FROM girl g
LEFT JOIN boy b ON g.boyfriend_id = b.id
WHERE g.id > 3;-- 二、查询哪个城市没有部门
SELECT l.city,d.department_id
FROM locations l
LEFT JOIN departments d ON l.location_id = d.location_id
WHERE d.department_id IS NULL;-- 三、查询部门名为 SAL 或 IT 的员工信息
SELECT e.*
FROM employees e
LEFT JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id
WHERE d.department_name IN('SAL','IT');SELECT e.*
FROM employees e
INNER JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id
WHERE d.department_name IN ('Sal', 'IT');
1.8联合查询
########################## SQL99标准 - 全连接 ############################
/*1.语法select 查询列表 from 表1 别名 left | right | full [outer] join 表2 别名on 连接条件where 筛选条件group by 分组列表 having 分组后筛选条件order by 排序列表;2.执行顺序from -> on执行连接条件 -> where执行筛选条件 -> group by -> having -> select -> order by注意:全连接就是将表中所有记录都查询出来,且不允许重复。注:此处不支持。全外连接 = 内连接查询的结果 + 表1中有但表2中没有的记录 + 表2中有但表1中没有的记录
*/
#需求1:查询所有男生和女生数据
select g.* , b.*
from girl g full join boy b
on g.boyfriend_id = b.id;#需求2:查询所有没有女朋友的男生和 没有男朋友的女生数据
select g.* , b.*
from girl g full join boy b
on g.boyfriend_id = b.id
where g.name is null or b.id is null;########################## 联合查询 ############################
/*1.语法select 查询列表 from 表1 别名 where 筛选条件UNION | UNION ALLselect 查询列表 from 表2 别名 where 筛选条件;2.特点多条待联合查询的语句的查询列表的列数必须一致否则报错:1222 - The used SELECT statements have a different number of columns建议:查询的字段类型、字段含义最好一致
*/#需求1:查询所有男生和女生数据
select * from girl g left join boy b on g.boyfriend_id = b.id
UNION
select * from girl g right join boy b on g.boyfriend_id = b.id;#需求2:查询所有没有女朋友的男生和 没有男朋友的女生数据
select * from girl g left join boy b on g.boyfriend_id = b.id where b.name is null
UNION
select * from girl g right join boy b on g.boyfriend_id = b.id where g.name is null;#案例1:查询所有国家的年龄>20岁的用户信息
select * from chinese where age > 20
UNION
select * from japanese where jage > 20
UNION
select * from usa where uage > 20;#案例2:查询所有国家的用户姓名和年龄
select name , age from chinese
UNION
select jname , jage from japanese
UNION
select uname , uage from usa;#案例3:union自动去重/union all 可以支持重复项
select name , age from chinese
UNION ALL
select jname , jage from japanese
UNION ALL
select uname , uage from usa;############# 面试题 - union和union all区别 #############
-- union 联合查询,实现去重查询
-- union all 联合查询,实现全部查询,包含重复项########################## 作业 ############################
# 作业1:查询出所有女神及男神信息
SELECT g.*, b.* FROM girl g LEFT JOIN boy b ON g.boyfriend_id = b.id
UNION
SELECT g.*, b.* FROM girl g RIGHT JOIN boy b ON g.boyfriend_id = b.id;# 作业2:查询出没有男朋友的女神信息和没有女朋友的男神信息
SELECT * FROM girl g LEFT JOIN boy b ON g.boyfriend_id = b.id WHERE b.id IS NULL
UNION
SELECT * FROM girl g RIGHT JOIN boy b ON g.boyfriend_id = b.id WHERE g.id IS NULL;# 作业3:查询出所有员工及部门信息
SELECT * FROM employees e LEFT JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id
UNION
SELECT * FROM employees e RIGHT JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id;# 作业4:查询出没有部门的员工信息及没有员工的部门信息
SELECT * FROM employees e LEFT JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id WHERE d.department_id IS NULL
UNION
SELECT * FROM employees e RIGHT JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id WHERE e.employee_id IS NULL;# 作业5:查询出所有部门及区域信息
SELECT * FROM departments d LEFT JOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_id
UNION
SELECT * FROM departments d RIGHT JOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_id;# 作业6:查询出没有城市的部门及没有部门的城市信息
SELECT * FROM departments d LEFT JOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_id WHERE l.city IS NULL
UNION
SELECT * FROM departments d RIGHT JOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_id WHERE d.department_id IS NULL;
1.9子查询
########################## SQL99标准 - 全连接 ############################
/*按子查询出现的位置进行分类:1、select后面要求:子查询的结果为单行单列(标量子查询)2、from后面要求:子查询的结果可以为多行多列3、where或having后面要求:子查询的结果必须为单列;单行子查询;多行子查询其中where或having后面是重点:单行子查询,特点:子查询的结果集只有一行一列,符号:= > < != <> 多行子查询,特点:子查询的结果集有多行一列,符号:in 、not in、 any、 all 4、exists后面要求:子查询结果必须为单列(相关子查询)
*/
-- 一、放在where或having后面
-- 1.单行子查询
#案例1:谁的工资比 Abel 高?
select salary from employees where last_name = 'Abel';select * from employees where salary > (select salary from employees where last_name = 'Abel');#案例2:返回job_id与141号员工相同,salary比143号员工多的员工姓名,job_id 和工资
select job_id from employees where employee_id=141;
select salary from employees where employee_id=143;select first_name , job_id , salary
from employees
where job_id = (select job_id from employees where employee_id=141) and salary>(select salary from employees where employee_id=143);#案例3:返回公司工资最少的员工的last_name,job_id和salary
select min(salary) from employees;select last_name , job_id , salary
from employees
where salary = (select min(salary) from employees);#案例4:查询最低工资大于50号部门最低工资的部门id和其最低工资
select department_id ,min(salary) from employees GROUP BY department_id;
select min(salary) from employees group by department_id HAVING department_id=50;select department_id , min(salary)
from employees
group by department_id
HAVING min(salary) > (select min(salary) from employees group by department_id HAVING department_id=50);-- 2.多行子查询
#案例1:返回location_id是1400或1700的部门中的所有员工姓名
select department_id from departments where location_id=1400 or location_id=1700;select first_name , last_name
from employees
where department_id in (select distinct department_id from departments where location_id=1400 or location_id=1700);#案例2:返回其它部门中比job_id为‘IT_PROG’部门任一工资低的员工的员工号、姓名、job_id 以及salary
select salary from employees where job_id='IT_PROG';select employee_id , first_name , job_id , salary
from employees
where salary < any(select salary from employees where job_id='IT_PROG');#案例3:返回其它部门中比job_id为‘IT_PROG’部门所有工资都低的员工的员工号、姓名、job_id 以及salary
select salary from employees where job_id='IT_PROG';select employee_id , first_name , job_id , salary
from employees
where salary <(select min(salary) from employees where job_id='IT_PROG');select employee_id , first_name , job_id , salary
from employees
where salary < all(select salary from employees where job_id='IT_PROG');#案例4:使用子查询实现城市为Toronto的,且工资>10000的员工姓名
select d.department_id from departments d join locations l on d.location_id = l.location_id where l.city='Seattle';select first_name , salary , department_id
from employees
where salary>10000 and department_id in (select d.department_id from departments d join locations l on d.location_id = l.location_id where l.city='Seattle');-- 二、放在select后面
#案例:查询部门编号是50的员工个数
select count(*) from employees where department_id=50;select (select count(*) from employees where department_id=50) '员工个数';-- 三、放在from后面
#案例:查询每个部门的平均工资的工资级别
-- 结果是多行多列,当作新表进行子查询
select department_id ,avg(salary) from employees group by department_id;select s.department_id ,s.sal , j.grade_level
from (select department_id ,avg(salary) sal from employees group by department_id) s join job_grades j
on s.sal BETWEEN j.lowest_sal and j.highest_sal;-- 四、放在exists后面
#案例1 :查询有无名字叫“Abel”的员工信息
select * from employees where last_name = 'Abel';
select * from employees where first_name = 'Abel';-- 返回1代表存在
select EXISTS(select * from employees where last_name = 'Abel');
-- 返回0代表不存在
select EXISTS(select * from employees where first_name = 'Abel');#案例2:查询没有女朋友的男神信息
select *
from girl g right join boy b
on g.boyfriend_id = b.id
where g.id is null;-- EXISTSselect *
from boy b
where EXISTS(select b.id from girl g where g.boyfriend_id=b.id)=0;-- NOT EXISTSselect *
from girl g join boy b
on g.boyfriend_id = b.id;select *
from boy b
where NOT EXISTS(select b.id from girl g where g.boyfriend_id=b.id);########################## 作业 ############################-- 1. 查询和 Zlotkey 相同部门的员工姓名和工资
SELECT department_id FROM employees WHERE last_name = 'Zlotkey';SELECT first_name,last_name,salary,department_id FROM employees WHERE department_id = (SELECT department_id FROM employees WHERE last_name = 'Zlotkey');-- 2. 查询工资比公司平均工资高的员工的员工号,姓名和工资。
SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees;SELECT employee_id,first_name,last_name,salary FROM employees WHERE salary > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees);
-- 3. 查询各部门中工资比本部门平均工资高的员工的员工号, 姓名和工资
SELECT department_id, AVG(salary) as avg_sal
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY department_id;SELECT e.employee_id, e.first_name, e.last_name, e.salary
FROM employees e
WHERE e.department_id IS NOT NULLAND e.salary > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees WHERE department_id = e.department_id
);
-- 4. 查询和姓名中包含字母 u 的员工在相同部门的员工的员工号和姓名
-- 先找出姓名包含'u'的员工所在部门
SELECT DISTINCT department_id
FROM employees
WHERE first_name LIKE '%u%' OR last_name LIKE '%u%';-- 查询这些部门的所有员工
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IN (SELECT DISTINCT department_id FROM employees WHERE first_name LIKE '%u%' OR last_name LIKE '%u%'
);
-- 5. 查询在部门的 location_id 为 1700 的部门工作的员工的员工号
-- 先找出location_id为1700的部门
SELECT department_id
FROM departments
WHERE location_id = 1700;-- 查询在这些部门工作的员工
SELECT employee_id
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IN (SELECT department_id FROM departments WHERE location_id = 1700
);-- 6. 查询管理者是 King 的员工姓名和工资
-- 先找出姓King的管理者的员工ID
SELECT employee_id
FROM employees
WHERE last_name = 'K_ing';-- 查询这些管理者下属的员工
SELECT first_name, last_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE manager_id IN (SELECT employee_id FROM employees WHERE last_name = 'K_ing'
);-- 7. 查询工资最高的员工的姓名,要求 first_name 和 last_name 显示为一列,列名为 姓.名-- 先找出最高工资
SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees;-- 查询拿最高工资的员工,合并姓名
SELECT CONCAT(first_name, ' ', last_name) as 姓名
FROM employees
WHERE salary = (SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees
);
1.10分页查询
########################## 分页查询 ############################
/*1.语法select 查询列表from 表1 别称 left | right | [outer | inner] join 表2 on 连接条件where 筛选条件group by 分组列表 having 分组后筛选order by 排序列表 asc | desclimit 起始值 , 每页展示记录数;2.执行顺序from -> join -> on -> where -> group by -> having -> select -> order by -> limit3.特点①起始条目索引如果不写,默认是0②limit后面支持两个参数- 参数1:显示的起始条目索引- 参数2:条目数
*/
/*分页页面中提供的数据1.当前页码 now2.上一页 now-13.下一页 now+1数据库中提供的数据1.总记录数 select count(*) from 表 where 条件; -> myCounts2.展示数据 select * from 表 where 条件 limit begin,size; -> list计算1.起始值 begin -> 0,5 5,5 10,5 -> begin = (now-1)*size2.总页数 myPages -> myPages = myCounts%size==0 ? myCounts/size : myCounts/size
*/########################## 案例 #############################案例1:查询员工信息表的前5条
-- 第一页
select *
from employees
limit 5;-- 第三页
select *
from employees
limit 10,5;#案例2:查询第11条——第20条的员工信息
-- 第一页 0,10 第二页 11,10
select *
from employees
limit 11,10;#案例3:查询有奖金的工资最高的前三名员工名、工资、奖金、部门编号 TopN
select first_name , salary , commission_pct , department_id
from employees
where commission_pct is not null
limit 3;#案例4:查询年薪最高的前10名 TopN
select first_name , salary , salary*12 '年薪'
from employees
order by salary*12 desc
limit 10;#案例5:使用分页查询实现,查询员工信息表中部门为50号的工资最低的5名员工信息 TopN
select first_name , department_id ,salary
from employees
where department_id=50
order by salary
limit 5;#案例6:查询员工表中薪资排第二的员工信息
select first_name , department_id ,salary
from employees
order by salary desc
limit 1,1;########################## 作业 ############################
-- 1. 查询工资最低的员工信息: last_name, salary
SELECT last_name,salary
FROM employees
WHEREsalary IN(SELECT MIN(salary)FROM employees);SELECT last_name,salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary
LIMIT 1;-- 2. 查询平均工资最低的部门信息
SELECT *
FROM departments
WHERE department_id =(SELECT department_idFROM employeesGROUP BY department_idORDER BY AVG(salary)LIMIT 1);-- 3. 查询平均工资最低的部门信息和该部门的平均工资
select d.* , avg(e.salary)
from employees e join departments d
on e.department_id = d.department_id
group by department_id
order by avg(e.salary)
limit 1;-- 4. 查询平均工资最高的job 信息
select j.* , avg(e.salary)
from employees e join jobs j
on e.job_id = j.job_id
group by job_id
order by avg(e.salary) desc
limit 1;-- 5. 查询平均工资高于公司平均工资的部门有哪些?
select avg(salary) from employees;
select department_id , avg(salary) from employees group by department_id;select s2.department_id , s2.a
from (select avg(salary) a from employees )s1 ,(select department_id , avg(salary) a from employees group by department_id)s2
where s1.a < s2.a;-- 6. 查询出公司中所有manager 的详细信息
select DISTINCT manager_id from employees where manager_id is not null;
select * from employees where employee_id in (select DISTINCT manager_id from employees where manager_id is not null);select DISTINCT m.first_name '领导'
from employees e RIGHT join employees m
on e.manager_id = m.employee_id
where e.employee_id is not null;-- 7. 各个部门中最高工资中最低的那个部门的最低工资是多少
select department_id , max(salary)
from employees
group by department_id
order by max(salary) limit 1;
select e.*
from employees e
where department_id = (select department_id from employees group by department_id order by max(salary) limit 1)
order by e.salary
limit 1;-- 8. 查询平均工资最高的部门的manager 的详细信息: last_name, department_id, email, salary
select department_id , avg(salary)
from employees
group by department_id
order by avg(salary) desc
limit 1; -- 90 19333.333333select manager_id
from departments
where department_id = (select department_id from employees group by department_id order by avg(salary) desc limit 1); -- 100-- K_ing 90 SKING 24000.00
select last_name, department_id, email, salary
from employees
where employee_id = (select manager_id
from departments
where department_id = (select department_id from employees group by department_id order by avg(salary) desc limit 1));1.11select题目练习-01
########################## select语句-01题目版 ####################################select语句-01题目版########
-- 【1.整表查询】
-- 例子1:desc 查看表结构;
desc employees;
-- 【2.单表查询】
-- 例子2:查询employees前三个列的内容?
select employee_id,first_name,last_name from employees;
-- 例子3:显示部门中的所有内容?
select * from departments;
-- 例子4:显示每位员工的全名?
select CONCAT(first_name,' ',last_name) as full_name from employees;-- 例子5:员工全名 is in department 部门编号?
select CONCAT(first_name, ' ', last_name) as full_name, department_id from employees;
-- 例子6:列出每个员工的年薪?
select employee_id,first_name,last_name,salary*12 as annual_salary
from employees;
-- 例子7:列出每个员工的一年的总收入?
select employee_id,first_name,last_name,(salary*12)+IFNULL(commission_pct*salary*12,0) as total_income
from employees;-- 例子8:列出所有部门的种类?(distinct去除重复的)
select distinct department_id
from employees;
-- 例子9:列出各部门有什么不同的职位?(distinct去除重复的)
select distinct department_id,job_id
from employees;-- 【3.限定查询】
-- 例子10: 列出50部门的员工的employee_id,名字,salary,和部门号?(条件查询where)
select employee_id,first_name,last_name,salary,department_id
from employees
where department_id = 50;
-- 例子11: 找出工资高于12000元的员工的年薪?
select employee_id,first_name,last_name,salary*12 as annual_salary
from employees
where salary > 12000;
-- 例子12: 找出年薪高于120000元的员工?
select employee_id,first_name,last_name,salary*12
as annual_salary
from employees
where salary*12 > 12000;
-- 例子13: 找出90部门年薪高于120000元的员工?
select employee_id,first_name,last_name,salary,salary*12 as annual_salary
from employees
where department_id = 90 and salary*12 > 120000;-- 例子14: 找出‘Steven’每个月的工资?
select first_name,last_name,salary
from employees
where first_name = 'Steven';
-- 例子15: 把所有职位为‘ST_CLERK’的员工列出?
select *
from employees
where job_id = 'ST_CLERK';
-- 例子16: 找出工资在10000-20000之间的员工?
select *
from employees
where salary between 10000 and 20000;
-- 例子17: 找出30, 60, 90 部门的员工的工资?in(30,60,90) 或 or
select employee_id,first_name,last_name,salary,department_id
from employees
where department_id in (30 ,60 , 90);-- 例子18: 列出哪些员工没有提成?
select *
from employees
where commission_pct is null;-- 例子19: 列出不在30, 60, 90 部门的员工的工资?
select employee_id,first_name,last_name,salary,department_id
from employees
where department_id not in (30 ,60 , 90);
-- 例子20: 列出 60, 90 部门工资大于10000元的员工信息?
select *
from employees
where department_id in (60,90)
having salary > 10000;select *
from employees
where department_id in (60,90) and salary > 10000;-- 【4. 模糊查询】
-- _表示匹配任意一个字符,汉字占一个字符,%是指任意多个字符 ; escape '\' 表示将_或者%,转义成普通字符
-- 例子21:找出first_name第二个字母是 e 的员工信息?
select *
from employees
where first_name like '_e%';SELECT * FROM employees WHERE SUBSTRING(first_name, 2, 1) = 'e';
-- 例子22:列出当前DataBase下所有含有字母e的表?
-- show tables from 库名 like 条件;
show tables from testsql2509 like '%e%';
SHOW TABLES LIKE '%e%';
-- 例子23:找出入职时间是 92年的所有员工信息? #########
select *
from employees
where year(hiredate) = 1992; -- 【5. 排序查询 降序是desc,升序是asc,默认升序】
-- 例子24: 按工资降序显示员工的信息?
select *
from employees
order by salary desc;
-- 例子25: 按提成升序显示员工的信息?
select *
from employees
order by commission_pct;
-- 例子26: 先工资降序,再按提成升序显示员工?
select *
from employees
order by salary desc,commission_pct;
-- 例子27: 按年薪降序显示员工?
select *,salary * 12 as annual_salary
from employees
order by annual_salary desc;-- 6.常见函数
-- 【6.1字符函数:操作字符串的函数】
-- 例子28:当不知道‘Steven’在数据库是大小写的时,找出‘Steven’的工资?
select first_name,last_name,salary
from employees
where UPPER(first_name) = 'STEVEN';
-- 例子29:列出每个员工名字(last_name)的最后两个字符? #######
select last_name, SUBSTRING(last_name, -2) as last_two_chars
from employees;-- 【6.3日期函数】
-- 例子31:查出下一天、下一分钟、下一秒的时间
SELECT DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 DAY) AS next_day,DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 MINUTE) AS next_minute,DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 SECOND) AS next_second;-- 例子32:求某天是星期几
SELECT DAYNAME(NOW()) AS day_of_week;-- 例子33:找出今年的天数SELECT DAYOFYEAR(CONCAT(YEAR(NOW()), '-12-31')) AS days_in_year;-- 例子34:今天是一年的第几天
SELECT DAYOFYEAR(NOW()) AS day_of_year;-- 例子35:闰年的处理方法(如何判断闰年?)
select year(NOW()) as current_year,case when (year(NOW()) % 4 = 0 and year(NOW()) % 100 != 0) or (year(NOW()) % 400 = 0) then '闰年'else '平年'end as leap_year;-- 例子36:按照'%Y%m%d %H%i%s'的格式,输出50部门员工的入职时间?
select DATE_FORMAT(hiredate, '%Y%m%d %H%i%s') as formatted_hiredate
from employees
where department_id = 50;-- 例子37:列出4月份入职的员工?SELECT * FROM employees WHERE MONTH(hiredate) = 4;
-- 例子38:求出下个月的1号?SELECT DATE_FORMAT(DATE_ADD(LAST_DAY(NOW()), INTERVAL 1 DAY), '%Y-%m-01') AS next_month_first;
-- 例子39:找出92年上半年入职的员工信息? 92年01月~92年06月SELECT * FROM employees
WHERE YEAR(hiredate) = 1992 AND MONTH(hiredate) BETWEEN 1 AND 6;
-- 例子40:找出15号后入职的员工信息?SELECT * FROM employees WHERE DAY(hiredate) > 15;
-- 【6.4组函数:传进去一堆值,只返回一个值,默认对null去除】
-- 例子42:列出提成的平均值?
select AVG(commission_pct) as avg_commission
from employees;-- 例子43:列出提成的最大值?SELECT MAX(commission_pct) AS max_commission FROM employees;
-- 例子44:求出有提成的员工个数?
SELECT COUNT(*) AS employees_with_commission
FROM employees
WHERE commission_pct IS NOT NULL;-- 例子45:求出80部门的平均工资?(只显示平均工资)SELECT AVG(salary) AS avg_salary FROM employees WHERE department_id = 80;-- 【8.执行顺序: from --> where --> group by --> having --> select --> order by】-- 【7.分组查询 group by表示根据什么条件进行分组,having表示限定分组条件】
-- 例子46:求出50部门的平均工资?(显示部门号、平均工资)
SELECT department_id, AVG(salary) AS avg_salary
FROM employees
WHERE department_id = 50
GROUP BY department_id;
-- 例子47:求出各部门的平均工资?
select department_id,AVG(salary) as avg_salary
from employees
group by department_id;
-- 例子48:求出各职位的平均工资?(要求:列出职位名称和平均工资)
select job_id,AVG(salary) as avg_salary
from employees
group by job_id;
-- 例子49:求出各部门不同职位的平均工资?
select department_id,job_id,AVG(salary) as avg_salary
from employees
group by department_id,job_id;
-- 例子50:求出各部门的平均工资? (要求显示:区域名称、部门编号、部门名称、平均工资)?
SELECT l.city, d.department_id, d.department_name, AVG(e.salary) AS avg_salary
FROM employees e
JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id
JOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_id
GROUP BY l.city, d.department_id, d.department_name;1.12select题目练习-02
########################## select语句-02题目版 ############################-- 等值连接
-- 例子52:列出员工名字和部门名字?SELECT e.first_name, e.last_name, d.department_name
FROM employees e
JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id;-- 例子53:列出部门号、部门名称、城市名称?
SELECT d.department_id,d.department_name,l.city
FROM departments d
JOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_id;
-- 例子54:列出Seattle城市有多少个部门?
SELECT l.city,COUNT(d.department_id)
FROM locations l
JOIN departments d ON l.location_id=d.location_id
WHERE l.city = 'Seattle';
-- 例子55:列出Steven在哪个城市上班?SELECT e.first_name, e.last_name, l.city
FROM employees e
JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id
JOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_id
WHERE e.first_name = 'Steven';
-- 例子56:列出Seattle城市有多少员工?
SELECT COUNT(employee_id)
FROM employees e
JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id
JOIN locations l ON l.location_id = d.location_id
WHERE l.city = 'Seattle';SELECT COUNT(*) as emp_count
FROM employees e
JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id
JOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_id
WHERE l.city = 'Seattle';
-- 例子57:列出Oxford城市营销部门Sal有那些员工?SELECT e.first_name, e.last_name, e.job_id
FROM employees e
JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id
JOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_id
WHERE l.city = 'Oxford' AND d.department_name = 'Sal';-- 自连接
-- 例子58:列出员工名称和领导名称的对应关系?
SELECT e.first_name as employee_name, e.last_name as employee_last,m.first_name as manager_name, m.last_name as manager_last
FROM employees e
LEFT JOIN employees m ON e.manager_id = m.employee_id;
-- 例子59:Diana的领导是谁?SELECT m.first_name, m.last_name
FROM employees e
JOIN employees m ON e.manager_id = m.employee_id
WHERE e.first_name = 'Diana';
-- 例子60:Steven是谁的领导?
SELECT e.first_name, e.last_name
FROM employees e
JOIN employees m ON e.manager_id = m.employee_id
WHERE m.first_name = 'Steven';
-- 例子61:请问哪些员工是领导?SELECT DISTINCT m.first_name, m.last_name
FROM employees e
JOIN employees m ON e.manager_id = m.employee_id;-- 外连接
-- 例子62:列出员工和领导的对应关系,包含‘Steven’SELECT e.first_name as employee_name, e.last_name as employee_last,m.first_name as manager_name, m.last_name as manager_last
FROM employees e
LEFT JOIN employees m ON e.manager_id = m.employee_id
WHERE e.first_name = 'Steven' OR m.first_name = 'Steven';
-- 例子63:列出哪些人是员工?(或者)哪些员工不是领导? 18 + 89 = 107
-- 哪些员工不是领导
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id NOT IN (SELECT DISTINCT manager_id FROM employees WHERE manager_id IS NOT NULL
);-- 1.单列单行
-- 例子64.求出谁的工资最低?
-- 步骤1:先找出最低工资
SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employees;-- 步骤2:查询拿最低工资的员工
SELECT first_name, last_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary = (SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employees);-- 例子65.谁和"Neena"坐同一个职位?
-- 步骤1:先找出Neena的职位
SELECT job_id FROM employees WHERE first_name = 'Neena';-- 步骤2:查询相同职位的其他员工
SELECT first_name, last_name, job_id
FROM employees
WHERE job_id = (SELECT job_id FROM employees WHERE first_name = 'Neena')
AND first_name != 'Neena';-- 例子66.哪些部门的平均工资比30部门的平均工资高?
-- 步骤1:先计算30部门的平均工资
SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees WHERE department_id = 30;-- 步骤2:查询各部门平均工资并与30部门比较
SELECT department_id, AVG(salary) as avg_salary
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY department_id
HAVING AVG(salary) > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees WHERE department_id = 30);-- 例子67.找出与 'Steven' 同部门的员工信息?
-- 步骤1:先找出Steven所在的部门
SELECT department_id FROM employees WHERE first_name = 'Steven';-- 步骤2:查询这些部门的员工
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IN (SELECT department_id FROM employees WHERE first_name = 'Steven');-- 例子68.找出比 'Susan' 早入职的员工?
-- 步骤1:先找出Susan的入职日期
SELECT hiredate FROM employees WHERE first_name = 'Susan';-- 步骤2:查询比Susan早入职的员工
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE hiredate < (SELECT hiredate FROM employees WHERE first_name = 'Susan');-- 2.单列多行
-- 例子69.哪些人是领导?
-- 步骤1:先找出所有管理者的ID
SELECT DISTINCT manager_id FROM employees WHERE manager_id IS NOT NULL;-- 步骤2:查询这些管理者的信息
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id IN (SELECT DISTINCT manager_id FROM employees WHERE manager_id IS NOT NULL);-- 例子70.哪些部门有员工?
-- 步骤1:先找出有员工的部门ID
SELECT DISTINCT department_id FROM employees WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL;-- 步骤2:查询这些部门的信息
SELECT department_id, department_name
FROM departments
WHERE department_id IN (SELECT DISTINCT department_id FROM employees WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL);-- 例子71.哪些部门没有员工?
-- 步骤1:先找出有员工的部门ID
SELECT DISTINCT department_id FROM employees WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL;-- 步骤2:查询不在这些部门列表中的部门
SELECT department_id, department_name
FROM departments
WHERE department_id NOT IN (SELECT DISTINCT department_id FROM employees WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL);-- 例子72.哪些人是员工?(哪些人不是领导)
-- 步骤1:先找出所有管理者的ID
SELECT DISTINCT manager_id FROM employees WHERE manager_id IS NOT NULL;-- 步骤2:查询不是管理者的员工
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id NOT IN (SELECT DISTINCT manager_id FROM employees WHERE manager_id IS NOT NULL);-- 例子73.查询和50部门员工职位相同的所有员工的姓名?
-- 步骤1:先找出50部门的所有职位
SELECT DISTINCT job_id FROM employees WHERE department_id = 50;-- 步骤2:查询有这些职位的员工
SELECT first_name, last_name, job_id
FROM employees
WHERE job_id IN (SELECT DISTINCT job_id FROM employees WHERE department_id = 50);-- 3.多列子查询
-- 例子74.哪些员工的工资和本部门的平均工资一致?
-- 步骤1:先计算每个部门的平均工资
SELECT department_id, AVG(salary) as avg_salary
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY department_id;-- 步骤2:查询工资等于本部门平均工资的员工
SELECT e.first_name, e.last_name, e.salary, e.department_id
FROM employees e
WHERE (e.department_id, e.salary) IN (SELECT department_id, AVG(salary)FROM employeesWHERE department_id IS NOT NULLGROUP BY department_id
);-- 例子75.哪些员工是在Seattle工作,请打印出全名,部门名,薪资?
-- 步骤1:先找出在Seattle的部门
SELECT department_id
FROM departments d
JOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_id
WHERE l.city = 'Seattle';-- 步骤2:查询在这些部门工作的员工
SELECT CONCAT(e.first_name, ' ', e.last_name) as full_name, d.department_name, e.salary
FROM employees e
JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id
WHERE e.department_id IN (SELECT department_id FROM departments dJOIN locations l ON d.location_id = l.location_idWHERE l.city = 'Seattle'
);-- TopN查询:
-- 例子76:请找出公司中工资前5的员工的信息?SELECT first_name, last_name, salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary DESC
LIMIT 5;
-- 分页
-- 例子77:请找出所有员工工资由高到低中,第3条到第10条员工的全名和工资信息?
SELECT CONCAT(first_name, ' ', last_name) as full_name, salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary DESC
LIMIT 2, 8; -- 跳过前2条,取8条(第3-10条)-- 1. 查询工资最低的员工信息: last_name, salary
SELECT last_name, salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary ASC
LIMIT 1;-- 2. 查询平均工资最低的部门信息
SELECT department_id
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY department_id
ORDER BY AVG(salary) ASC
LIMIT 1;SELECT d.*
FROM departments d
WHERE d.department_id = (SELECT department_idFROM employeesWHERE department_id IS NOT NULLGROUP BY department_idORDER BY AVG(salary) ASCLIMIT 1
);-- 3. 查询平均工资最低的部门信息和该部门的平均工资
SELECT department_id, AVG(salary) as avg_salary
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY department_id
ORDER BY avg_salary ASC
LIMIT 1;SELECT d.*, dept_avg.avg_salary
FROM departments d
JOIN (SELECT department_id, AVG(salary) as avg_salaryFROM employeesWHERE department_id IS NOT NULLGROUP BY department_idORDER BY avg_salary ASCLIMIT 1
) dept_avg ON d.department_id = dept_avg.department_id;-- 4. 查询平均工资最高的 job 信息
SELECT job_id
FROM employees
GROUP BY job_id
ORDER BY AVG(salary) DESC
LIMIT 1SELECT j.*
FROM jobs j
WHERE j.job_id = (SELECT job_idFROM employeesGROUP BY job_idORDER BY AVG(salary) DESCLIMIT 1
);-- 5. 查询平均工资高于公司平均工资的部门有哪些?
SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees;SELECT department_id,AVG(salary)
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY department_id
HAVING AVG(salary) > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees)
ORDER BY AVG(salary) DESC
LIMIT 0,10;SELECT department_id, AVG(salary) as dept_avg_salary
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY department_id
HAVING AVG(salary) > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees)
ORDER BY dept_avg_salary DESC
LIMIT 0, 10;-- 6. 查询出公司中所有 manager 的详细信息SELECT DISTINCT m.*
FROM employees e
JOIN employees m ON e.manager_id = m.employee_id
ORDER BY m.employee_id
LIMIT 0, 100; -- 7. 各个部门中最高工资中最低的那个部门的最低工资是多少
SELECT MIN(salary) as min_salary
FROM employees
WHERE department_id = (SELECT department_idFROM employeesWHERE department_id IS NOT NULLGROUP BY department_idORDER BY MAX(salary) ASCLIMIT 1
);-- 8. 查询平均工资最高的部门的 manager 的详细信息: last_name, department_id, email, salary
SELECT m.last_name, m.department_id, m.email, m.salary
FROM employees m
WHERE m.employee_id = (SELECT d.manager_idFROM departments dWHERE d.department_id = (SELECT department_idFROM employeesWHERE department_id IS NOT NULLGROUP BY department_idORDER BY AVG(salary) DESCLIMIT 1)
);