Java_LinkedHashSet源码分析
说明:
1)LinkedHashSet是HashSet的子类
2)LinkedHashSet底层是一个LinkedHashMap,底层维护了一个数组 + 双向链表
3)LinkedHashSet根据元素的hashCode值来决定元素的存储位置,同时使用链表来维护元素的次序,这使得元素看起来是以插入顺序保存的(也就是说取出顺序和添加顺序是一样的,即存储位置无序,取出有序)
4)LinkedHashSet不允许添加重复元素
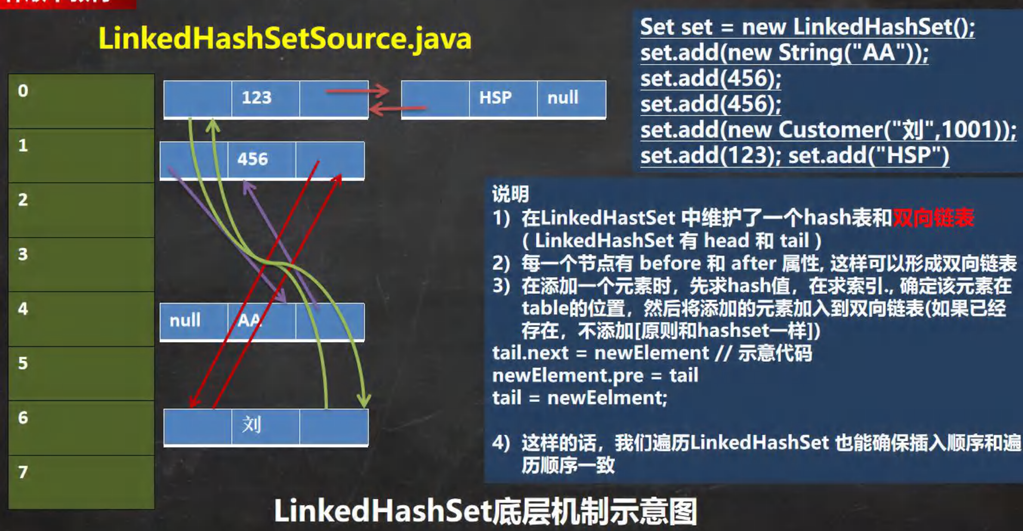
源码分析:
1)在LinkedHashset中维护了一个hash表和双向链表(LinkedHashSet由head和tail)
2)每一个节点由before和after属性,这样可以形成双向链表
3)在添加一个元素时,先求hash值,再求索引,确定该元素在table的位置,然后将添加的元素加入到双向链表(如果已经存在,则不添加【原则和hashset一样】)
tail.next = newElement; //示意代码
newElement.pre = tail;
tail = newElement;
4)这样的话,我们遍历LinkedHashSet也能确保插入顺序和遍历顺序一致
package com.CollectionStu_.Set_;import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class LinkedHashSetSource {public static void main(String[] args) {//分析LinkerHashSet底层机制Set set = new LinkedHashSet();set.add(new String("AA"));set.add(456);set.add(456);set.add(new Customer("刘", 1001));set.add(123);set.add("HSP");System.out.println("set=" + set);//set=[AA, 456, Customer{name='刘', no=1001}, 123, HSP]//解读:/*1.LinkedHashSet 加入顺序和取出元素/数据 的顺序一致2.LinkedHashSet底层维护的是一个LikedHashMap(HashMap的子类)3,LinkedHashMap底层结构(数组 + 双向链表)4.添加第一次时,直接将 数组table扩容到16,存放的结点类型是 LinkedHashMap$Entry5.数组HashMap$Node[] 存放的元素/数据是LinkedHashMap$Entry 类型//继承关系是在内部类完成的 Entry源码:static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {Entry<K,V> before, after;Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {super(hash, key, value, next);}}* Node也是一个静态内部类6.然后还是进入到前一章讲的HashMap中的putval中进行比较和赋值*/}
}
class Customer {private String name;private int no;public Customer(String name, int no) {this.name = name;this.no = no;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Customer{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", no=" + no +'}';}
}