JS原型和原型链
文章目录
- 深入面向对象
- 1. 构造函数
- 2. 原型
- 3. constructor属性
- 4. 对象原型(指向原型对象)
- 5. 原型继承
- 6. 原型链
- 7. 构造函数应用
- 学习总结
深入面向对象
面向对象编程(oop):灵活,代码可复用,容易维护和开发,适合多人合作的大型项目
特性:继承,封装,多态

1. 构造函数
JS通过构造函数实现封装 ,构造方法存在一个浪费内存的问题(存储复杂类型的时候)
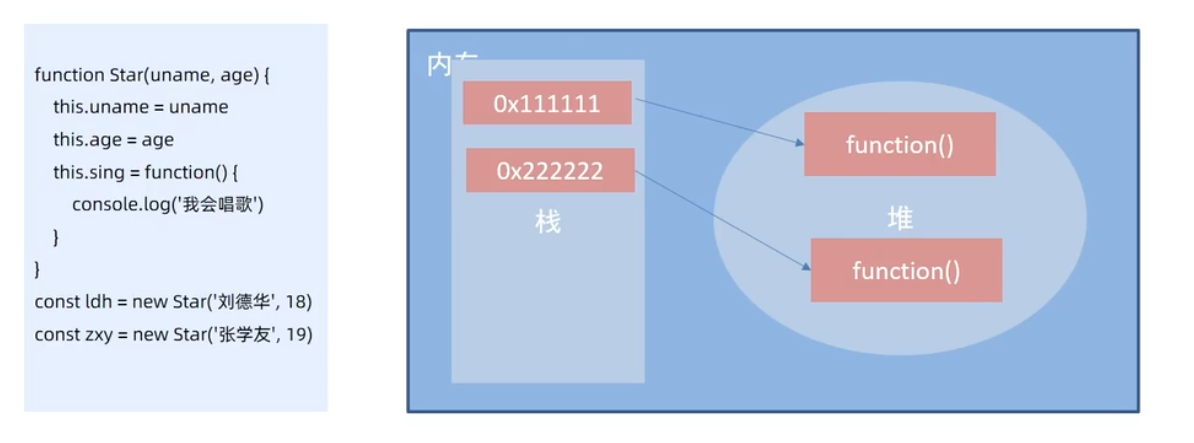
如何解决?:原型
2. 原型
- 构造函数通过原型分配的函数是所有对象共享的
- JavaScript规定,每一个构造函数都有一个prototype属性,指向另一个对象,所以我们也称为原型对象
- 这个对象可以挂载函数,对象实例化不会多次创建原型上函数,节约内存
- 我们可以把那些不变的方法,直接定义在prototype对象上,这样所有对象的实例就可以共享这些方法
- 构造函数和原型对象中的this都指向实例化的对象
- 公共的属性写在构造函数里,公共的方法写在原型上
let that
function Student(name, price) {that=thisthis.name = name;this.price = price;}
console.log(Student.prototype)
//原型对象中的this指向实例对象
Student.prototype.setName = function (name) {console.log(this)this.name = name;
}
var s = new Student('Tom', 12);
// 构造函数中的this就是实例对象s
console.log(that===s)//True
s.setName()
Student.prototype:

//this应用:封装一个求出的数组中最大最小值的方法Array.prototype.max = function(){return Math.max(...this)}const arr9 = [1, 2, 3]console.log(arr9.max())//3
3. constructor属性
- 每个原型对象里面都有一个constructor属性(constructor构造函数)
- 作用:该属性指向该原型对象的构造函数
- 如果有多个对象的方法,我们可以给原型对象采取对象形式赋值,但是这样就会覆盖构造函数原型对象的内容,这样修改后的原型对象constructor就不再指向当前构造函数了,此时,我们可以在修改后的原型对象中,添加一个和constructor来指向原来的构造函数
function Student(name, price) {this.name = name;this.price = price;}console.log(Student.prototype)// Student.prototype.sing = function () {// console.log('I am singing')// }// Student.prototype.dance = function () {// console.log('I am dancing')// }Student.prototype = {//还有让constructor重新指回原型对象的构造函数constructor: Student,sing: function () {console.log('I am singing')},dance: function () {console.log('I am dancing')}}var s = new Student('Tom', 12);console.log(Student.prototype.constructor === Student)//True
4. 对象原型(指向原型对象)
对象都会有一个属性:__proto__指向构造函数的prototype原型对象,之所以我们对象可以使用构造函数prototype原型对象的属性和方法,就是因为有__proto__原型的存在
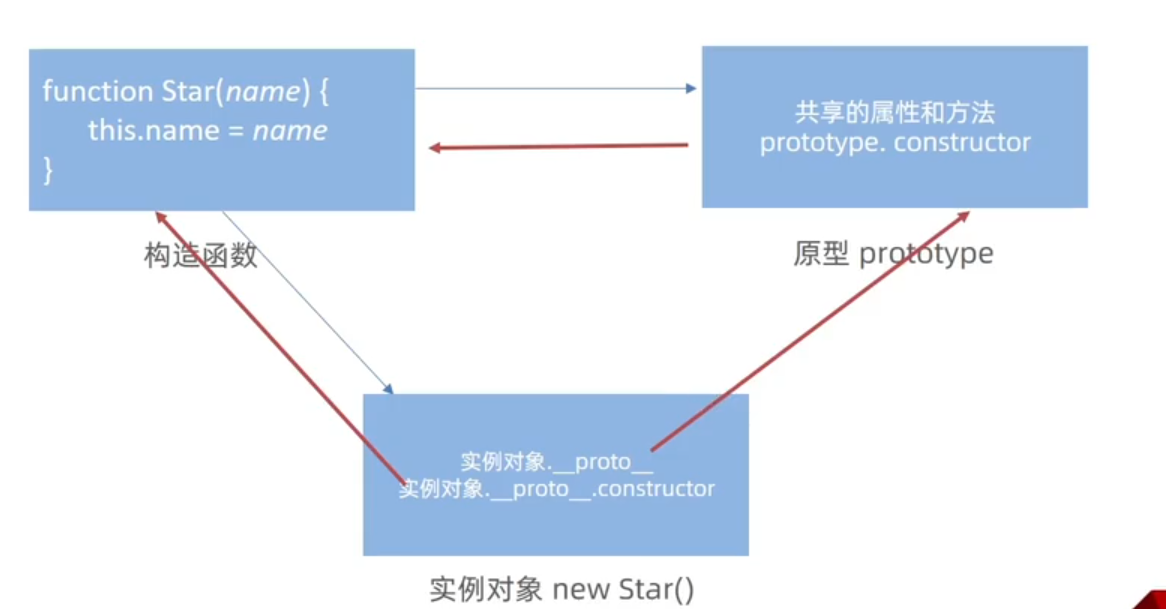
__proto__是JS非标准属性[[prototype]]和__proto__意义相同- 用来表明当前实例对象指向哪个原型对象
prototype __proto__对象原型里面也有一个constructor属性,指向创建该实例对象的构造函数
Student.prototype = {//还有让constructor重新指回原型对象的构造函数constructor: Student,sing: function () {console.log('I am singing')},dance: function () {console.log('I am dancing')}}var s = new Student('Tom', 12);console.log(s)//对象原型__proto__指向构造函数的原型对象prototypeconsole.log(s.__proto__===Student.prototype)//true
//console.log(s.__proto__.constructor==Student)//trueconsole.log(Student.prototype.constructor === Student)//True

5. 原型继承
核心代码:子类的原型=new 父类()
const Persons={eyes:2,head:1}function Women(){}//Women通过原型来继承PersonWomen.prototype=Persons;console.log(Women.prototype)//让原型对象上的constructor指回构造函数Women.prototype.constructor=Women;const red=new Women();console.log(red)console.log(red.__proto__)

上面的写法问题是Women和Men都共用一个prototype,要给Women的prototype上添加方法或属性时,Men也会同时拥有,但有时只想给Women添加,这时就需要用到构造函数,因为现在的需求是:结构相同,对象不同
function Persons() {this.eyes = 2;this.age = 13;}function Women() {}//直接使用new Person()创建一个新的对象,和Men的互不干扰Women.prototype = new Persons();//让原型和对象上的constructor指回构造函数Women.prototype.constructor = Women;Women.prototype.baby=function(){console.log('I am a baby')}const red = new Women();function Men() {}Men.prototype = new Persons();//让原型和对象上的constructor指回构造函数Men.prototype.constructor = Women;const green = new Men();
6. 原型链
- 只要是对象都有
__proto__,指向构造函数的原型对象prototype - 构造函数的原型对象也是一个对象,也有
__proto__,指向的是Object的原型对象prototype - 只要是原型对象,就有
constructor,指回构造函数
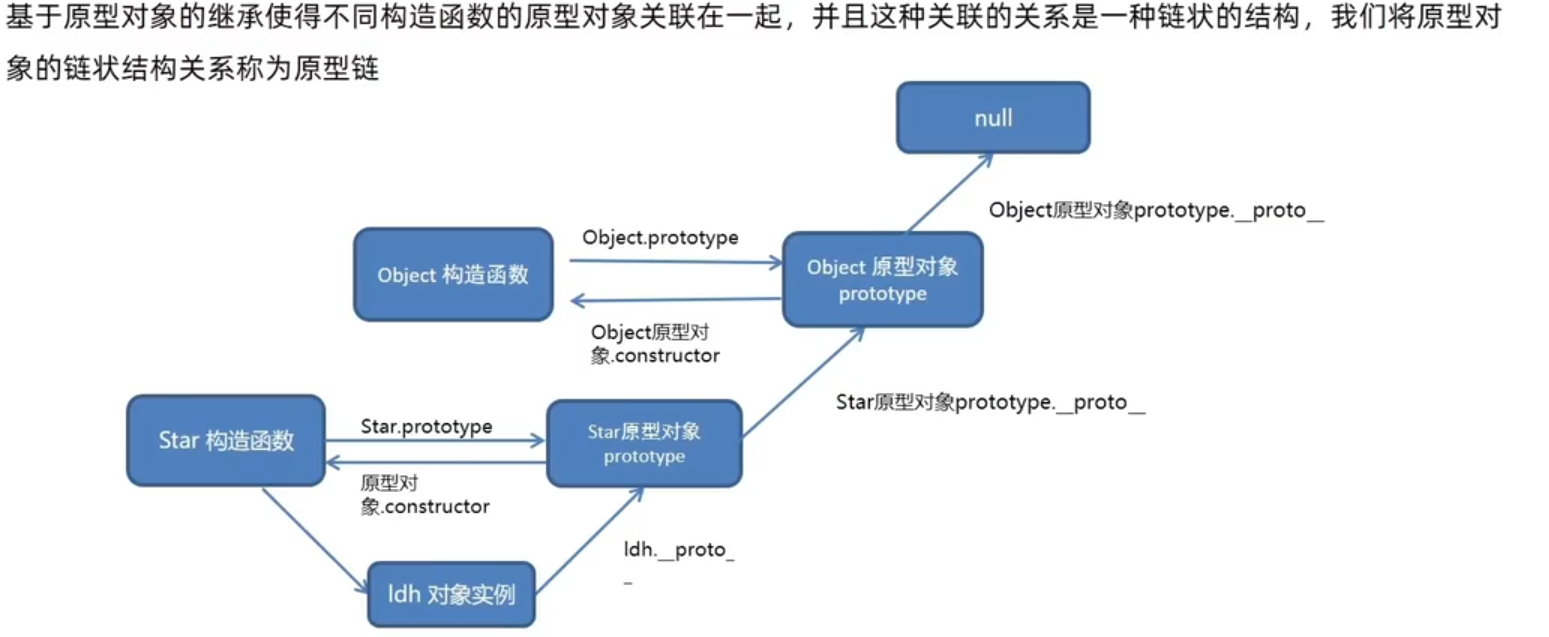
原型链- 查找规则:
- 当访问一个对象的属性或方法时,首先查找这个对象自身有没有
- 如果没有就查找他的原型(也就是__proto__指向的prototype原型对象)
- 如果还没有就查找原型对象的原型(Object的原型对象)
- 以此类推一直找到Object(null)为止
- __proto__对象原型的意义就在于为对象成员查找机制提供一个方向,或者说一条路线
- 可以使用instanceof运算符用于检测构造函数的prototype属性是否出现在某个实例对象的原型链身上
console.log(green instanceof Men)//trueconsole.log(green instanceof Persons)//trueconsole.log(green instanceof Object)//true
7. 构造函数应用
<body><button class="delete">删除</button><button class="login">登录</button><script>function Modal(title = '', message = '') {// 构造函数中创建属性要使用thisthis.modalBox = document.createElement('div')this.modalBox.className = 'modal'this.modalBox.innerHTML = `<div class="header">${title}</div><i>x</i><div class="body">${message}</div>`console.log(this.modalBox)}new Modal('温馨提示', '您没有权限进行删除操作')new Modal('友情提示', '您还未登录')//给构造函数原型挂载open方法Modal.prototype.open = function () {//判断页面中是否有盒子//有就移除const box = document.querySelector('.modal')box&&box.remove()document.body.append(this.modalBox)//盒子显示出来,就可以绑定关闭事件了//这个地方要使用箭头函数,因为this指向的是实例对象,如果用普通函数,this指的就是i标签,不是我们所期望的this.modalBox.querySelector('i').onclick = () => {this.close()}}//挂载close方法Modal.prototype.close = function () {this.modalBox.remove()}//点击删除按钮document.querySelector('.delete').addEventListener('click', function () {const del = new Modal('温馨提示', '您没有权限进行删除操作')del.open()})//点击登录按钮document.querySelector('.login').addEventListener('click', function () {const log = new Modal('友情提示', '您还未登录')log.open()})</script>
</body>

学习总结
这周主要复习了JS高级相关的知识,但是还没复习完,下周把JS高级和ES6再复习复习
