vue3知识点-ref和reactive以及toRefs与toRef
【尚硅谷Vue2.0+Vue3.0全套教程丨vuejs从入门到精通】 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Zy4y1K7SH/?p=29&share_source=copy_web&vd_source=63c6218111021d177660d3bec318e593
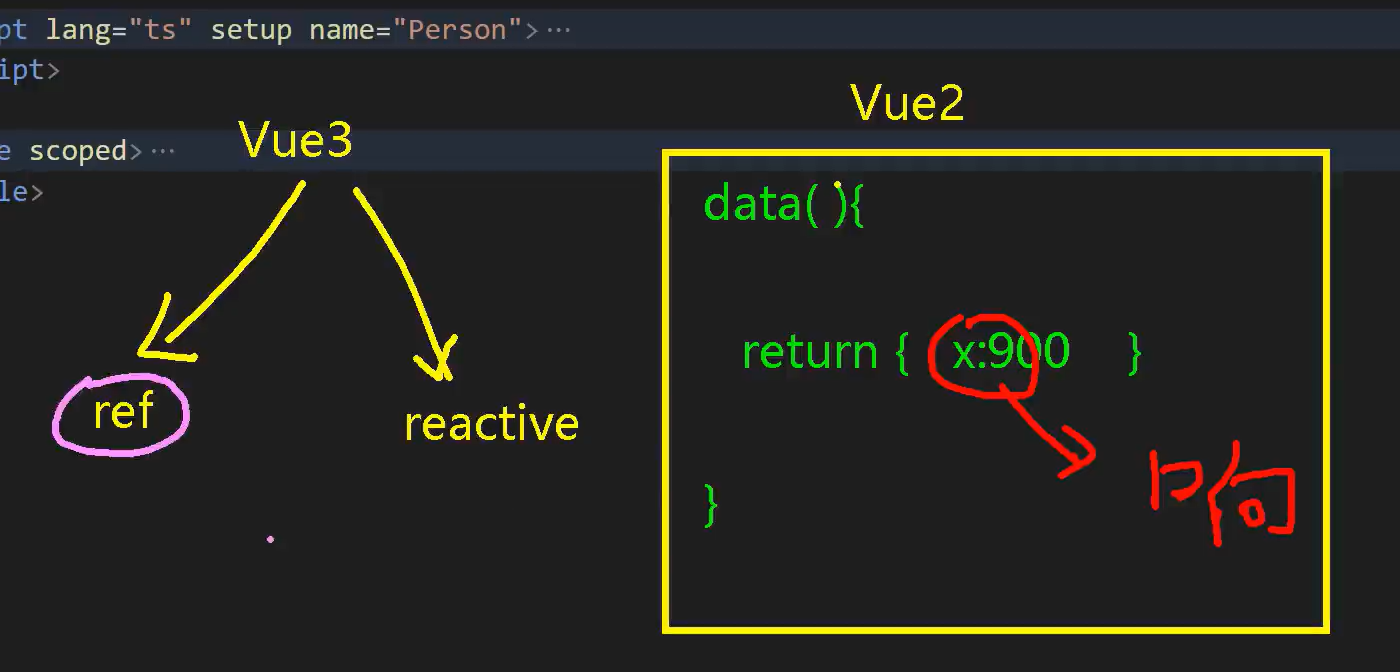
引入:响应式数据写法对比vue2
Vue2:使用data数据,直接就是响应式的
Vue3:使用ref和reactive才能使数据是响应式的
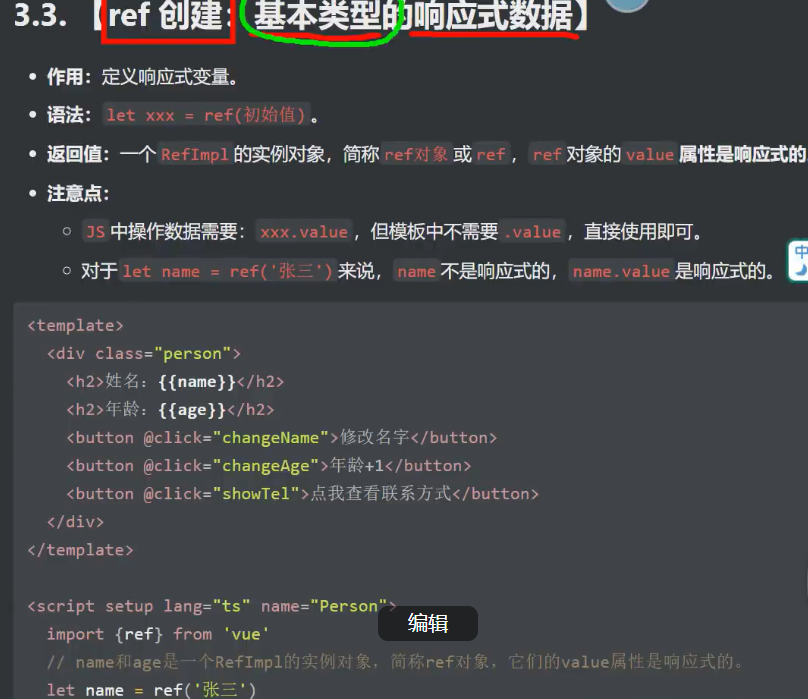
1.ref创建_基本类型的响应式数据
1.1引入ref
import {ref} from 'vue'
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
let name = ref('xst')
let age = ref(18)
let tel = '5201314'
function showTel() {
alert(tel)
}
function changename() {
name.value = 'cuz'
console.log(name.value)
}
function changeage() {
age.value += 1
console.log(age.value)
}
</script>
2.reactive创建_对象类型的响应式数据
<template>
<div class="person">
<h2>
一辆车品牌是{{ car.brand}},价格是{{ car.price }}
<button @click="zengjia">zengjia</button>
</h2>
</div>
</template>
<!-- 专门用于指定组件名的script标签 -->
<script lang="ts">
export default {
name: 'Person' // 明确指定组件名称
}
</script>
<!-- 组合式API逻辑 -->
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {reactive} from 'vue';
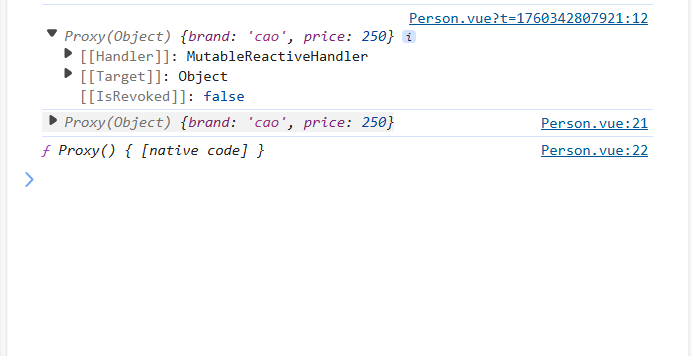
let car=reactive({brand:'cao',price:250})
console.log(car);
function zengjia()
{
car.price+=10
}
</script>
经过reactive包裹变成一个proxy函数
2.1数组对象
<template>
<div class="person">
<h2>
一辆车品牌是{{ car.brand}},价格是{{ car.price }}
<button @click="zengjia">zengjia</button>
</h2>
<h2>游戏列表
<br>
<ul>
<li v-for="g in games" :key="g.id">
{{ g.name }}
</li>
</ul>
<button @click="gai">
修改游戏列表
</button>
</h2>
</div>
</template>
<!-- 专门用于指定组件名的script标签 -->
<script lang="ts">
export default {
name: 'Person' // 明确指定组件名称
}
</script>
<!-- 组合式API逻辑 -->
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {reactive} from 'vue';
let car=reactive({brand:'cao',price:250})
console.log(car);
let games =reactive([
{id:1,name:'和平精英'
}
])
function gai()
{
games[0].name='地铁跑路'
}
function zengjia()
{
car.price+=10
}
</script>
2.2嵌套对象(深层次数据类型)
<template>
<div class="person">
<hr>
<h2>
ceshi{{ obj.a.b.c }}
</h2>
<button @click="xiugaiceshi">修改测试对象
</button>
</div>
</template>
<!-- 专门用于指定组件名的script标签 -->
<script lang="ts">
export default {
name: 'Person' // 明确指定组件名称
}
</script>
<!-- 组合式API逻辑 -->
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {reactive} from 'vue';
let obj=
reactive({
a:{
b:{
c:666
}
}
})
function xiugaiceshi()
{
obj.a.b.c=999
}
</script>
3.ref创建_对象类型的响应式数据

用ref创建,使用value值即可
<template>
<div class="person">
<h2>
一辆车品牌是{{ car.brand}},价格是{{ car.price }}
<button @click="zengjia">zengjia</button>
</h2>
<h2>游戏列表</h2>
<br>
<ul>
<li v-for="g in games" :key="g.id">
{{ g.name }}
</li>
</ul>
<button @click="gai">
修改游戏列表
</button>
</div>
</template>
<!-- 专门用于指定组件名的script标签 -->
<script lang="ts">
export default {
name: 'Person' // 明确指定组件名称
}
</script>
<!-- 组合式API逻辑 -->
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {ref} from 'vue';
let car=ref({brand:'cao',price:250})
console.log(car);
let games =ref([
{id:1,name:'和平精英'
}
])
function gai()
{
games.value[0].name='地铁跑路'
}
function zengjia()
{
car.value.price+=10
}
</script>
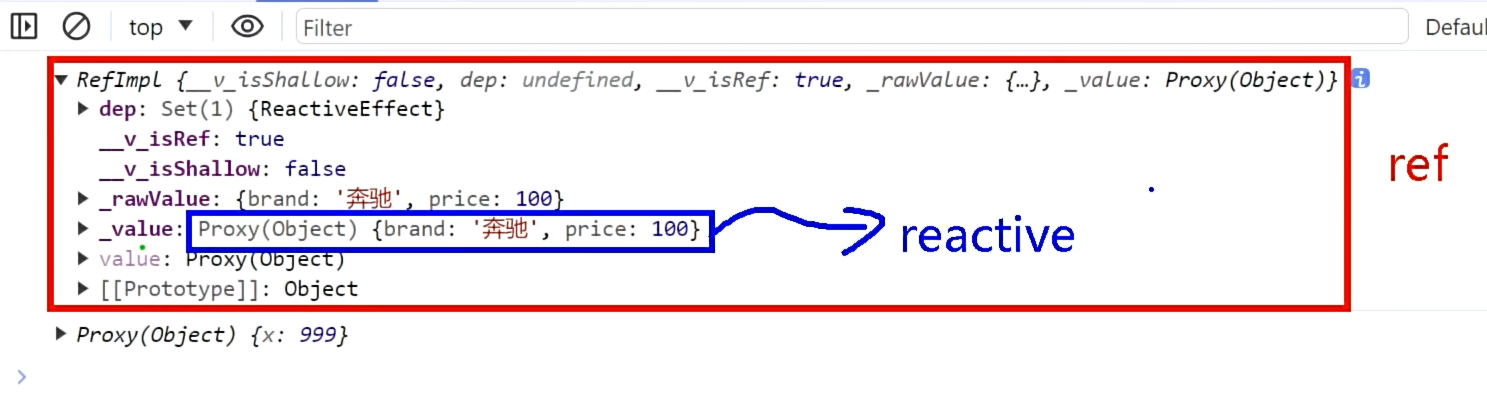
ref虽然可处理对象类型,但实际上,当ref遇到对象类型的时候,仍然底层是用reactive处理的。
4.对比ref和reactive
4.1添加自动补全value功能
4.2reactive重新定义一个新对象
![]()
import {reactive} from 'vue';
let car=reactive({brand:'xiayu',price:250})
console.log(car);
// function qiche()
// {
// car={brand:'biexiale',price:1}
// }无法是响应式的数据
function qiche()
{
Object.assign(car,{brand:'biexiale',price:1})
}
4.3ref和reactive的使用原则

5.toRefs与toRef

5.1补充:解构赋值:
5.1.1数组的解构赋值
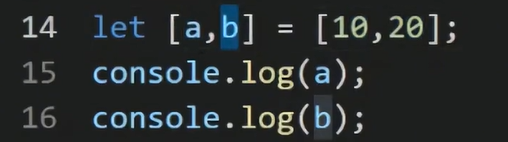
便于实现交换
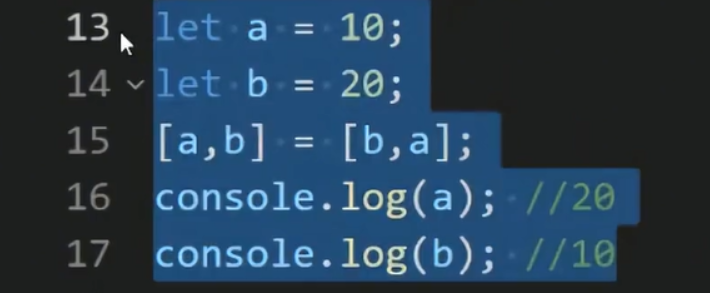
5.1.2对象的解构赋值
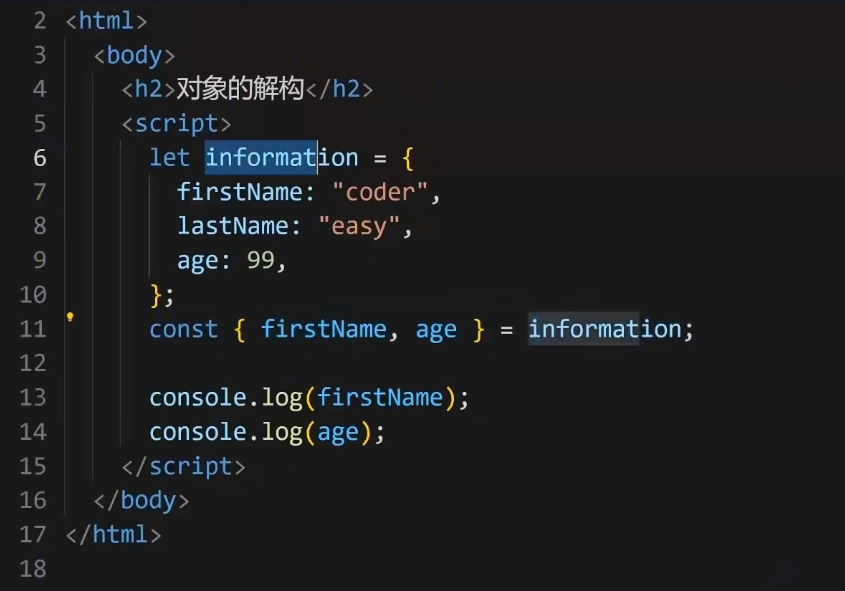
5.1.2.1注意:当有再次赋值时,若由原值则使用原值
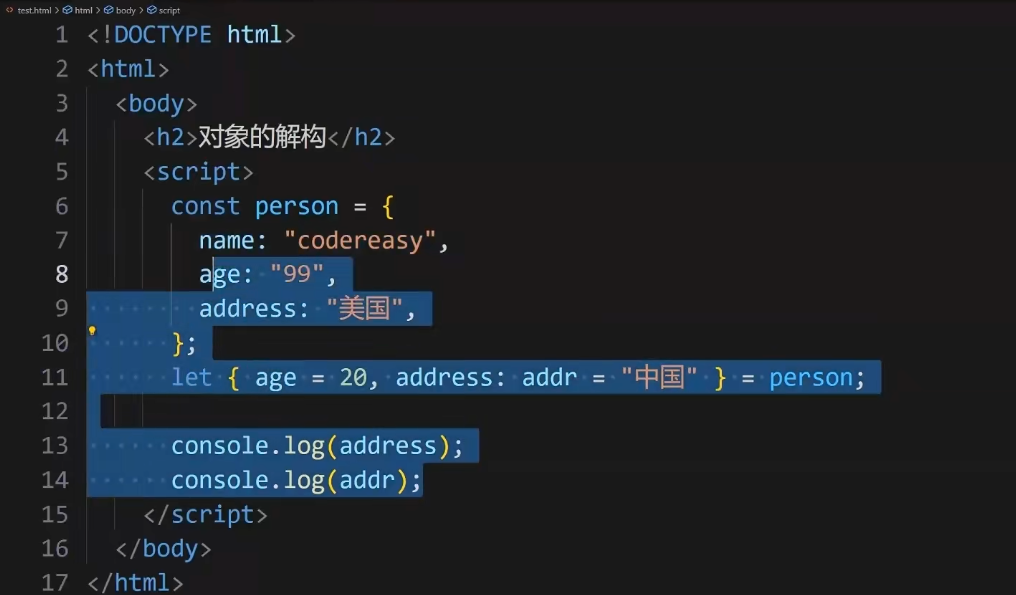
输出为:99,美国。
5.2对比区别

