pq|二维前缀和
二维前缀和
lc304
class NumMatrix {
vector<vector<int>> sum;
public:
NumMatrix(vector<vector<int>> &matrix) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
sum.resize(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
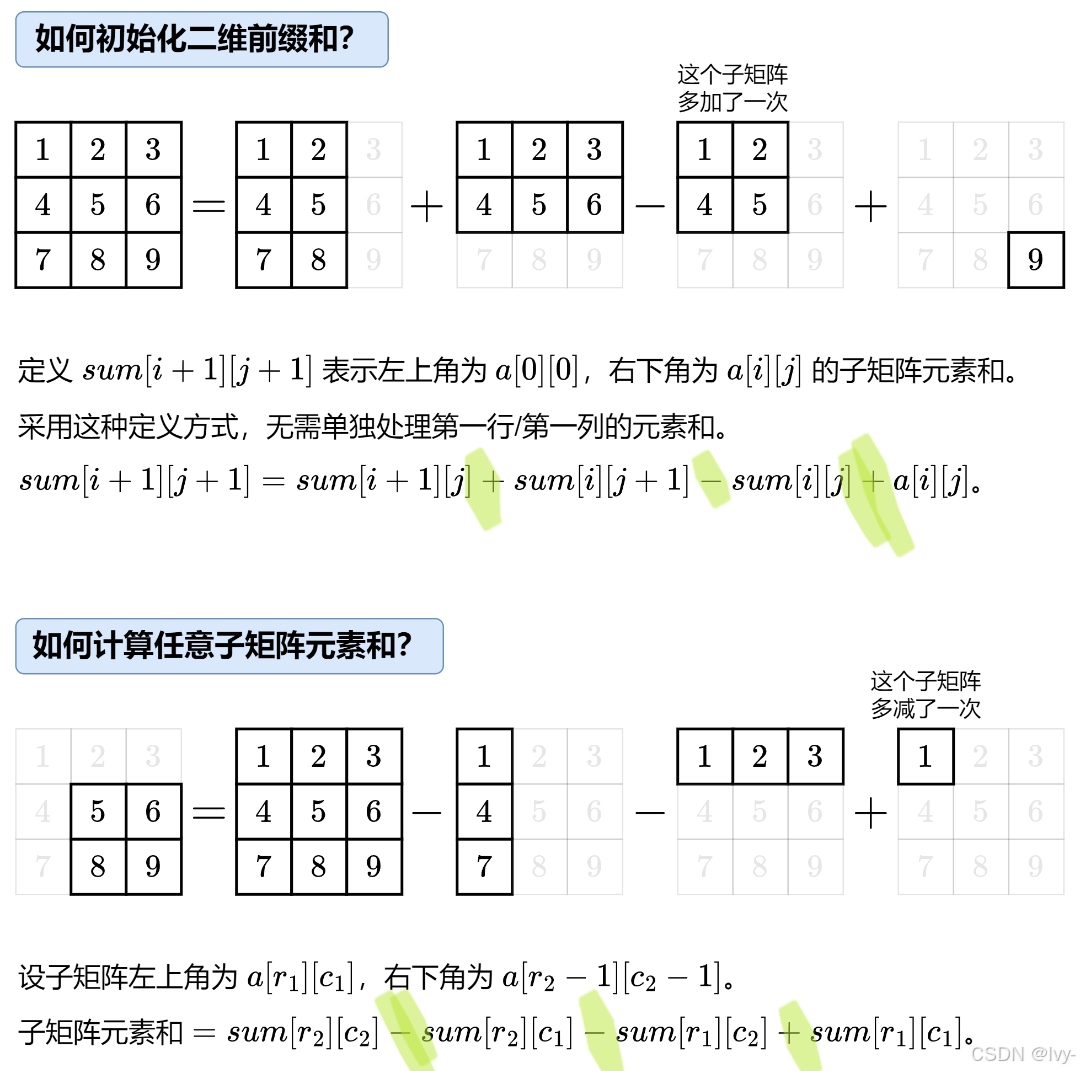
sum[i + 1][j + 1] = sum[i + 1][j] + sum[i][j + 1] - sum[i][j] + matrix[i][j]; //+-+
}
}
}
// 返回左上角在 (r1,c1) 右下角在 (r2,c2) 的子矩阵元素和
int sumRegion(int r1, int c1, int r2, int c2) {
return sum[r2 + 1][c2 + 1] - sum[r2 + 1][c1] - sum[r1][c2 + 1] + sum[r1][c1];//--+
}
};
lc1738
二维异或和
neat
只要满足交换律并且重复计算 那么二维矩阵不管是什么处理 都可以用二维前缀和加法的思想
这里XOR是一样的
还可利用 a ^ a ^ a = a,进行一维优化

class Solution {
public:
int kthLargestValue(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int k) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
vector<int> a;
vector<vector<int>> s(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
s[i + 1][j + 1] = s[i + 1][j] ^ s[i][j + 1] ^ s[i][j] ^ matrix[i][j];
}
//添加每行
a.insert(a.end(), s[i + 1].begin() + 1, s[i + 1].end());
}
ranges::nth_element(a, a.end() - k);
return a[a.size() - k];
}
};
第k大--快速选择算法
要理解最后两行如何获取第 k 大的元素,结合快速选择算法(由 ranges::nth_element 实现)
1. 快速选择算法的作用
ranges::nth_element 是 C++20 引入的算法,基于快速选择思想:
- 它会对容器(这里是 vector<int> a )进行部分排序,使得指定位置的元素最终处于“正确排序后”的位置。
- 具体来说, ranges::nth_element(a, a.end() - k) 会将 a 中第 (a.size() - k) 个位置的元素,调整为“若整个数组排序后,该位置应有的值”。此时:
- 该位置左边的所有元素都小于等于它,
- 该位置右边的所有元素都大于等于它
2. 结合“第 k 大”的逻辑
数组的“第 k 大”元素,等价于排序后数组中从后往前数的第 k 个元素。
- 假设数组长度为 len ,排序后最后一个元素是第 1 大,倒数第二个是第 2 大,……,倒数第 k 个就是第 k 大。
- 因此,“第 k 大的位置”对应数组的索引为 len - k (数组从 0 开始计数)。
3. 代码中两行的联动
- 第一步: ranges::nth_element(a, a.end() - k) 将 a 中索引为 a.size() - k 的元素,调整为“排序后该位置应有的值”(即第 k 大的元素)。
- 第二步: return a[a.size() - k]; 直接返回该位置的元素,即为矩阵所有子矩阵异或和中的第 k 大值。
简单来说, nth_element 通过部分排序,直接定位到“第 k 大”的位置,无需对整个数组完全排序(时间复杂度为 O(N) ,远优于完全排序的 O(N \log N) ),效率更高
lc767
pq
pq每次选出现次数最多的字符来排
若当前字符能放就放
不能放就选次多的放,以此重构字符串,保证相邻字符不同,若无法做到则返回空。
class Solution {
public:
string reorganizeString(string s) {
int n = s.size();
unordered_map<char, int> hash;
// 统计每个字符的出现次数
for (auto c : s) {
hash[c]++;
if (hash[c] > (n + 1) / 2) {
return "";
}
}
// 优先队列(最大堆),按字符出现次数从大到小排列
priority_queue<pair<int, char>> pq;
for (auto& [c, cnt] : hash) {
pq.push({cnt, c});
}
string res;
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto [cnt1, c1] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
// 如果结果字符串为空,或者当前字符与结果字符串最后一个字符不同
if (res.empty() || c1 != res.back()) {
res += c1;
if (--cnt1 > 0) {
pq.push({cnt1, c1});
}
} else {
// 如果当前字符不能放,取次多的字符
if (pq.empty())
return "";
auto [cnt2, c2] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
res += c2;
if (--cnt2 > 0)
pq.push({cnt2, c2});
pq.push({cnt1, c1});//放回
}
}
return res;
}
};
lc640
求解一元一次方程
拆解等号左右两边的字符串,分别计算出x的系数和常数项
再移项计算x的值
同时处理“无穷解”和“无解”的情况

class Solution {
public:
pair<int, int> calcnt(string str){
int a = 0, b = 0;
if(str[0] != '+' && str[0] != '-') str = '+' + str; //前导补齐符号,方便统一处理
int c = 1; //当前的符号是正(1)或负(0)
int n = str.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){
if(str[i] == '+'){
c = 1;
continue;
}else if(str[i] == '-'){
c = 0;
continue;
}else if(str[i] == 'x'){
if(c == 1) a ++;
else a --;
continue;
}else{
int j = i;
int t = 0;
while(j < n && isdigit(str[j])){
t = t * 10 + (str[j] - '0');
j ++;
}
if(c == 0) t = -t;
if(str[j] == 'x'){ //混合数字和x的情况, 例如"+2x"
a += t;
i = j;
}else{
b += t;
i = j - 1;
}
}
}
return {a, b};
}
string solveEquation(string equation) {
int x = equation.find('=');
string ls = equation.substr(0, x), rs = equation.substr(x + 1);
auto lres = calcnt(ls), rres = calcnt(rs);
int a = lres.first - rres.first, b = rres.second - lres.second;
if(!a){
if(!b) return "Infinite solutions";
else return "No solution";
}
return "x=" + to_string(b / a);
}
};
这个地方的计算处理可以多看几遍🤔

lc632
pq维护各列表当前元素
不断更新区间左右端点
找到包含所有列表至少一个元素的最小区间

class Solution {
public:
vector<int> smallestRange(vector<vector<int>>& nums)
{
priority_queue<tuple<int, int, int>, vector<tuple<int, int, int>>, greater<>> pq;
int r = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
pq.emplace(nums[i][0], i, 0); // 把每个列表的第一个元素入堆
r = max(r, nums[i][0]);
}
int ans_l = get<0>(pq.top()); // 第一个合法区间的左端点
int ans_r = r; // 第一个合法区间的右端点
while (true) {
auto [_, i, j] = pq.top();
if (j + 1 == nums[i].size()) { // 堆顶列表没有下一个元素
break;
}
pq.pop();
int x = nums[i][j + 1]; // 堆顶列表的下一个元素
pq.emplace(x, i, j + 1); // 入堆
r = max(r, x); // 更新合法区间的右端点
int l = get<0>(pq.top()); // 当前合法区间的左端点
if (r - l < ans_r - ans_l) {
ans_l = l;
ans_r = r;
}
}
return {ans_l, ans_r};
}
};
lc1654
确定bound后bfs memo

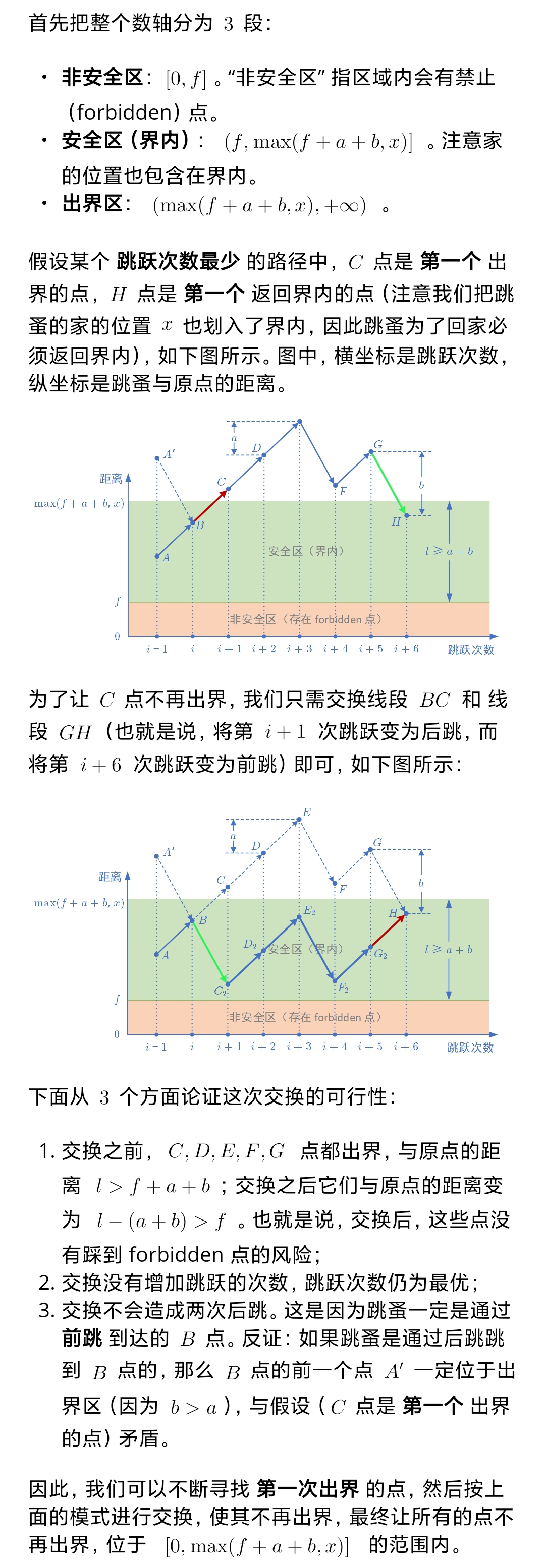
把数轴分成非安全区、安全区、出界区三段
假设存在最少跳跃次数的路径里有第一个出界的点 C 和第一个返回界内的点 H ,通过交换相关跳跃线段(把第 i + 1 次后跳、第 i + 6 次前跳交换),能让原来出界的点不再出界,还不增加跳跃次数、不违反连续后跳规则
这样就能把所有点限制在 [0, max(f + a + b, x)] 范围内,保证找最少跳跃次数时不用考虑出界情况

class Solution {
public:
int minimumJumps(vector<int>& forbidden, int a, int b, int x) {
// 最远距离 bound = max(F + a + b, x + b)
int F = *max_element(forbidden.begin(), forbidden.end()), bound = max(F + a + b, x + b);
int ban[bound + 1];
memset(ban, 0, sizeof(ban));
for(int f : forbidden) {
ban[f] = 1;
}
int dist[bound + 1][2]; // dist[i][0] - 上一次前跳, dist[i][1] - 上一次后跳
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof(dist));
dist[0][0] = 0;
queue<pair<int,int>> q({{0, 0}});
while(q.size()) {
auto [i, pre] = q.front(); q.pop();
if(i == x)
return dist[i][pre];
if(pre == 0 && i-b >= 0 && !ban[i-b] && dist[i][pre] + 1 < dist[i-b][1]) {
dist[i-b][1] = dist[i][pre] + 1;
q.emplace(i-b, 1);
}
if(i+a <= bound && !ban[i+a] && dist[i][pre] + 1 < dist[i+a][0]) {
dist[i+a][0] = dist[i][pre] + 1;
q.emplace(i+a, 0);
}
}
return -1;
}
};
lc653
class Solution
{
unordered_set<int> hash;
int k;
bool f=false;
public:
bool findTarget(TreeNode* root, int k) {
this->k=k;
dfs(root);
return f;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* node)
{
if(!node) return;
int t=k-node->val;
if(hash.count(t))
{
f=true;
return;
}
else
hash.insert(node->val);
dfs(node->left);
dfs(node->right);
}
};
优化
减少成员变量、提前终止遍历、规范代码风格三个维度改进,可读性和效率更优:
class Solution {
public:
bool findTarget(TreeNode* root, int k) {
unordered_set<int> valSet;
// 用引用传递集合,避免拷贝;返回bool实现提前终止
return dfs(root, k, valSet);
}
private:
// 私有辅助函数,封装遍历逻辑,返回值标识是否已找到目标
bool dfs(TreeNode* node, int k, unordered_set<int>& valSet) {
if (!node) return false;
if (valSet.count(k - node->val)) return true;
valSet.insert(node->val);
return dfs(node->left, k, valSet) || dfs(node->right, k, valSet);
}
};
核心优化点
1. 移除冗余成员变量:将 hash 、 k 、 f 改为函数内/参数传递,避免类成员状态管理,代码更简洁。
2. 实现提前终止:
- 辅助函数返回 bool ,找到目标值时直接返回 true ,不再继续遍历后续节点。
- 利用 || 短路特性,左右子树只要有一个找到结果,就停止递归。
3. 规范访问控制:辅助函数 dfs 设为 private ,符合类的封装原则,对外隐藏实现细节。
