手写MyBatis第104弹:SqlSession从工厂构建到执行器选择的深度剖析
MyBatis SqlSession创建全链路解析:从工厂构建到执行器选择的深度剖析
「MyBatis SqlSession诞生记:SqlSessionFactoryBuilder构建流程+Executor选择策略+事务管理初始化全揭秘」
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder:MyBatis框架的启动引擎
在MyBatis的整体架构中,
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder扮演着框架启动器的关键角色。它不仅仅是配置文件的解析器,更是整个MyBatis运行时环境的构建者。理解其工作机理,是掌握MyBatis框架运行机制的重要基础。
目录
MyBatis SqlSession创建全链路解析:从工厂构建到执行器选择的深度剖析
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder:MyBatis框架的启动引擎
build()方法的完整执行链路
构建过程的层次化分析
错误处理与上下文管理
DefaultSqlSessionFactory:SqlSession的制造工厂
openSession方法族的多维度支持
openSessionFromDataSource:核心创建逻辑深度解析
事务管理器的初始化时机与策略
事务工厂的选择机制
事务实例的创建过程分析
连接获取与事务属性设置
Executor类型的选择策略与执行机制
Executor体系的架构设计
各种Executor的性能特性对比
SimpleExecutor:标准执行器
ReuseExecutor:语句重用执行器
BatchExecutor:批量处理执行器
CachingExecutor:缓存装饰器模式应用
插件机制在SqlSession创建中的增强作用
拦截器链的构建与执行
典型插件的执行时机分析
性能优化与实践建议
Executor选择的性能影响
事务配置的最佳实践
连接池参数调优
总结与展望
🥂(❁´◡`❁)您的点赞👍➕评论📝➕收藏⭐是作者创作的最大动力🤞
💖📕🎉🔥 支持我:点赞👍+收藏⭐️+留言📝欢迎留言讨论
🔥🔥🔥(源码 + 调试运行 + 问题答疑)
🔥🔥🔥 有兴趣可以联系我。文末有免费源码
免费获取源码。
更多内容敬请期待。如有需要可以联系作者免费送
更多源码定制,项目修改,项目二开可以联系作者
点击可以进行搜索(每人免费送一套代码):千套源码目录(点我)2025元旦源码免费送(点我)
我们常常在当下感到时间慢,觉得未来遥远,但一旦回头看,时间已经悄然流逝。对于未来,尽管如此,也应该保持一种从容的态度,相信未来仍有许多可能性等待着我们。
build()方法的完整执行链路
构建过程的层次化分析
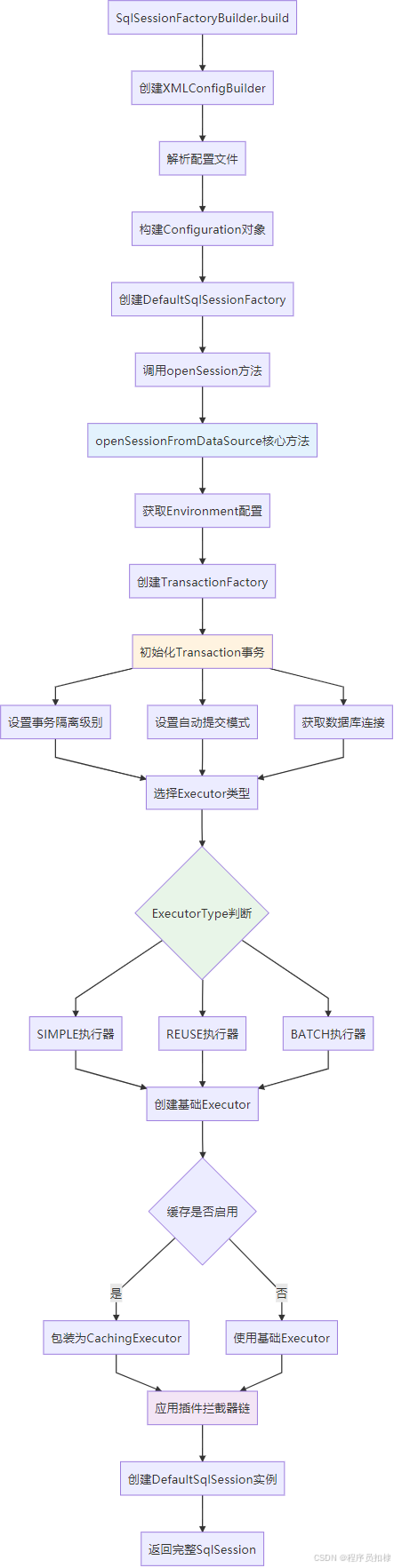
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build()方法采用了典型的建造者模式,将复杂的构建过程封装在简洁的API之后:
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {// 核心构建方法 - 承载多种重载版本的统一入口public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {try {// 阶段1:配置解析器初始化XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);// 阶段2:配置对象构建Configuration config = parser.parse();// 阶段3:SqlSessionFactory实例化return build(config);} catch (Exception e) {// 异常处理与资源清理throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);} finally {ErrorContext.instance().reset();closeInputStream(inputStream);}}}错误处理与上下文管理
MyBatis在构建过程中采用了精细的错误处理机制:
// ErrorContext采用ThreadLocal实现线程安全的错误上下文管理public class ErrorContext {private static final ThreadLocal<ErrorContext> LOCAL = new ThreadLocal<>();private String resource;private String activity;private String object;private String message;private String sql;private Throwable cause;public static ErrorContext instance() {ErrorContext context = LOCAL.get();if (context == null) {context = new ErrorContext();LOCAL.set(context);}return context;}}这种设计确保了在多线程环境下,每个线程都能拥有独立的错误上下文,便于问题定位和诊断。
DefaultSqlSessionFactory:SqlSession的制造工厂
openSession方法族的多维度支持
DefaultSqlSessionFactory通过方法重载提供了灵活的SqlSession创建选项,满足不同场景的需求:
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {private final Configuration configuration;// 基础版本 - 使用默认配置@Overridepublic SqlSession openSession() {return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);}// 自动提交控制版本@Overridepublic SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit) {return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, autoCommit);}// 事务隔离级别指定版本@Overridepublic SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level) {return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), level, false);}// 执行器类型指定版本@Overridepublic SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType) {return openSessionFromDataSource(execType, null, false);}// 连接参数指定版本@Overridepublic SqlSession openSession(Connection conn) {return openSessionFromConnection(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), conn);}}openSessionFromDataSource:核心创建逻辑深度解析
这是SqlSession创建过程中最核心的方法,包含了事务初始化、执行器选择等关键决策:
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level,boolean autoCommit) {Transaction tx = null;try {// 步骤1:环境配置获取final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();if (environment == null) {throw new ConfigurationException("Environment is required.");}// 步骤2:事务工厂实例化final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);// 步骤3:事务对象创建(关键时机点)tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);// 步骤4:执行器创建与装饰final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);// 步骤5:SqlSession实例化return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);} catch (Exception e) {// 异常处理:关闭已创建的事务closeTransaction(tx);throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);}}事务管理器的初始化时机与策略
事务工厂的选择机制
事务管理器的初始化发生在SqlSession创建流程的早期阶段,这体现了MyBatis对数据一致性的重视:
private TransactionFactory getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(Environment environment) {// 环境未配置时的默认策略if (environment == null || environment.getTransactionFactory() == null) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Using default transaction factory: ManagedTransactionFactory");}return new ManagedTransactionFactory();}// 返回配置的事务工厂if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Using configured transaction factory: " + environment.getTransactionFactory().getClass().getSimpleName());}return environment.getTransactionFactory();}事务实例的创建过程分析
不同的事务工厂创建不同类型的事务管理器:
// JDBC事务工厂实现public class JdbcTransactionFactory implements TransactionFactory {@Overridepublic Transaction newTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level,boolean autoCommit) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Creating new JDBC transaction with autoCommit: " + autoCommit);}return new JdbcTransaction(ds, level, autoCommit);}}// 托管事务工厂实现public class ManagedTransactionFactory implements TransactionFactory {@Overridepublic Transaction newTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level,boolean autoCommit) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Creating new Managed transaction");}return new ManagedTransaction(ds, level, autoCommit);}}连接获取与事务属性设置
事务管理器在初始化时会立即获取数据库连接并设置事务属性:
public class JdbcTransaction implements Transaction {protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");}// 获取数据库连接connection = dataSource.getConnection();// 设置事务隔离级别(如果指定)if (level != null) {int currentLevel = connection.getTransactionIsolation();if (currentLevel != level.getLevel()) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Changing transaction isolation level from " + currentLevel + " to " + level.getLevel());}connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());}}// 设置自动提交模式setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommit);}private void setDesiredAutoCommit(boolean desiredAutoCommit) {boolean currentAutoCommit = connection.getAutoCommit();if (currentAutoCommit != desiredAutoCommit) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Changing autocommit from " + currentAutoCommit + " to " + desiredAutoCommit);}connection.setAutoCommit(desiredAutoCommit);}}}Executor类型的选择策略与执行机制
Executor体系的架构设计
MyBatis设计了灵活的Executor体系,通过配置化的方式支持不同的执行策略:
public class Configuration {// 执行器创建的核心方法public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {// 执行器类型推断逻辑executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;Executor executor;// 基于类型的执行器实例化if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Creating executor of type: " + executorType);}switch (executorType) {case BATCH:executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);break;case REUSE:executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);break;default:executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);}// 二级缓存装饰(如果启用)if (cacheEnabled) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Enabling cache for executor");}executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);}// 插件机制增强executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);return executor;}}各种Executor的性能特性对比
SimpleExecutor:标准执行器
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {@Overridepublic <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {Statement stmt = null;try {Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);// 每次执行都创建新的PreparedStatementstmt = prepareStatement(handler);return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);} finally {// 执行完成后立即关闭StatementcloseStatement(stmt);}}
}适用场景:通用查询场景,内存敏感环境
ReuseExecutor:语句重用执行器
public class ReuseExecutor extends BaseExecutor {// 重用相同SQL的PreparedStatementprivate final Map<String, PreparedStatement> statementMap = new HashMap<>();@Overridepublic <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter,RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);String sql = boundSql.getSql();PreparedStatement stmt;// 检查是否已存在相同SQL的PreparedStatementif (hasStatementFor(sql)) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Reusing prepared statement for SQL: " + sql);}stmt = getStatement(sql);} else {// 创建新的PreparedStatement并缓存stmt = prepareNewStatement(handler, sql);}handler.parameterize(stmt);return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);}
}适用场景:相同SQL频繁执行的OLTP系统
BatchExecutor:批量处理执行器
public class BatchExecutor extends BaseExecutor {private final List<Statement> statementList = new ArrayList<>();private final List<BatchResult> batchResultList = new ArrayList<>();private String currentSql;private MappedStatement currentStatement;@Overridepublic int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {// 批量操作逻辑if (isSameBatch(ms, parameter)) {// 添加到当前批次addToCurrentBatch(ms, parameter);return BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE;} else {// 执行当前批次并开始新批次executeBatch();startNewBatch(ms, parameter);return BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE;}}@Overridepublic void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {// 提交时执行所有批量操作executeBatch();super.commit(required);}
}适用场景:大数据量批量插入、更新操作
CachingExecutor:缓存装饰器模式应用
通过装饰器模式为执行器添加二级缓存功能,体现了开闭原则的优雅应用:
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {private final Executor delegate;private final TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();@Overridepublic <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject,RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler,CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {// 检查是否启用缓存Cache cache = ms.getCache();if (cache == null) {return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);}// 缓存刷新检查flushCacheIfRequired(ms);// 缓存查询逻辑if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);if (list == null) {// 缓存未命中,委托给底层执行器查询list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);// 将结果放入缓存tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);} else {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Cache hit for key: " + key);}}return list;}return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);}
}插件机制在SqlSession创建中的增强作用
拦截器链的构建与执行
MyBatis通过责任链模式实现插件机制,在SqlSession创建过程中对Executor进行增强:
public class InterceptorChain {private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();public Object pluginAll(Object target) {// 按顺序应用所有拦截器for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Applying interceptor: " + interceptor.getClass().getSimpleName());}target = interceptor.plugin(target);}return target;}
}典型插件的执行时机分析
以分页插件为例,观察其在SqlSession创建过程中的介入时机:
@Intercepts({@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
public class PageInterceptor implements Interceptor {@Overridepublic Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {// 在Executor.query方法执行前后进行拦截Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) args[0];Object parameter = args[1];RowBounds rowBounds = (RowBounds) args[2];// 分页逻辑处理if (shouldPage(rowBounds)) {return handlePagedQuery(invocation, ms, parameter, rowBounds);}// 继续执行原始逻辑return invocation.proceed();}
}性能优化与实践建议
Executor选择的性能影响
根据实际业务场景选择合适的Executor类型:
-
SIMPLE执行器:
-
优点:内存占用小,无状态
-
缺点:频繁创建/销毁PreparedStatement
-
适用:查询多样性高的场景
-
-
REUSE执行器:
-
优点:减少PreparedStatement创建开销
-
缺点:内存占用较高,需要维护Statement缓存
-
适用:SQL模板化程度高的OLTP系统
-
-
BATCH执行器:
-
优点:批量操作性能极佳
-
缺点:编程模型复杂,内存占用大
-
适用:数据导入、批量更新场景
-
事务配置的最佳实践
<!-- 生产环境推荐配置 -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"><property name="autoCommit" value="false"/>
</transactionManager><!-- 开发环境便捷配置 -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"><property name="autoCommit" value="true"/>
</transactionManager>连接池参数调优
<dataSource type="POOLED"><!-- 根据并发量调整连接数 --><property name="poolMaximumActiveConnections" value="50"/><property name="poolMaximumIdleConnections" value="10"/><property name="poolMaximumCheckoutTime" value="20000"/><!-- 根据网络状况调整超时时间 --><property name="poolTimeToWait" value="20000"/><!-- 连接有效性检查 --><property name="poolPingEnabled" value="true"/><property name="poolPingQuery" value="SELECT 1"/><property name="poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor" value="3600000"/></dataSource>总结与展望
SqlSession的创建过程是MyBatis框架初始化的核心环节,它完美体现了框架在设计上的诸多考量:
-
灵活性设计:通过多种openSession重载方法支持不同使用场景
-
性能优化:提供多种Executor实现满足不同性能需求
-
扩展性支持:通过插件机制允许功能增强
-
资源管理:完善的事务和连接生命周期管理
深入理解这一过程,不仅有助于我们更好地使用MyBatis,更能从中学习到优秀框架的设计思想和实现技巧,为我们的技术成长提供宝贵的参考。
🥂(❁´◡`❁)您的点赞👍➕评论📝➕收藏⭐是作者创作的最大动力🤞
💖📕🎉🔥 支持我:点赞👍+收藏⭐️+留言📝欢迎留言讨论
🔥🔥🔥(源码 + 调试运行 + 问题答疑)
🔥🔥🔥 有兴趣可以联系我。文末有免费源码
💖学习知识需费心,
📕整理归纳更费神。
🎉源码免费人人喜,
🔥码农福利等你领!💖常来我家多看看,
📕网址:扣棣编程,
🎉感谢支持常陪伴,
🔥点赞关注别忘记!💖山高路远坑又深,
📕大军纵横任驰奔,
🎉谁敢横刀立马行?
🔥唯有点赞+关注成!
往期文章推荐:
基于Springboot + vue实现的学生宿舍信息管理系统
免费获取宠物商城源码--SpringBoot+Vue宠物商城网站系统
【2025小年源码免费送】
