打工人日报#20251011
打工人日报#20251011
知识点
FIFO IP 核
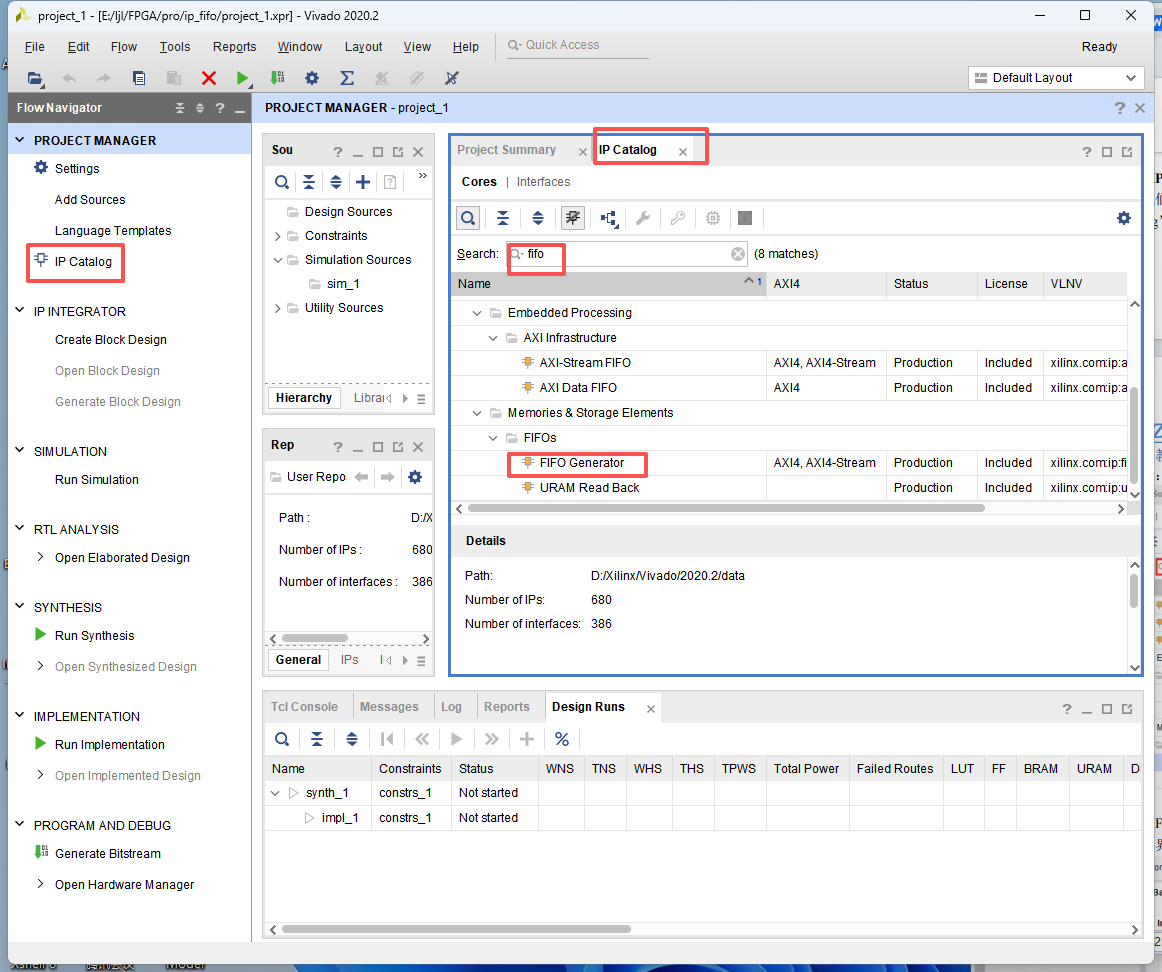
在弹出的“IP Catalog”窗口的搜索栏中输入“fifo”关键字后,我们找到“FIFO Generator”
ip_fifo.v
module ip_fifo(
input sys_clk , // 系统时钟信号
input sys_rst_n // 系统复位信号
);//wire define
wire clk_50m ; // 50M 时钟
wire clk_100m ; // 100M 时钟
wire locked ; // 时钟锁定信号wire rst_n ; // 复位,低有效wire wr_rst_busy ; // 写复位忙信号wire rd_rst_busy ; // 读复位忙信号wire fifo_wr_en ; // FIFO 写使能信号wire fifo_rd_en ; // FIFO 读使能信号wire [7:0] fifo_wr_data ; // 写入到 FIFO 的数据wire [7:0] fifo_rd_data ; // 从 FIFO 读出的数据wire almost_full ; // FIFO 将满信号wire almost_empty ; // FIFO 将空信号wire full ; // FIFO 满信号wire empty ; // FIFO 空信号wire [7:0] wr_data_count ; // FIFO 写时钟域的数据计数wire [7:0] rd_data_count ; // FIFO 读时钟域的数据计数//*****************************************************//** main code//*****************************************************//通过系统复位信号和时钟锁定信号来产生一个新的复位信号assign rst_n = sys_rst_n & locked;//例化 PLL IP 核clk_wiz_0 clk_wiz_0 (// Clock out ports.clk_out1(clk_50m ), // output clk_out1.clk_out2(clk_100m), // output clk_out2// Status and control signals.locked (locked ), // output locked// Clock in ports.clk_in1 (sys_clk ) // input clk_in1); //例化 FIFO IP 核fifo_generator_0 fifo_generator_0 (.rst (~rst_n ), // input wire rst.wr_clk (clk_50m ), // input wire wr_clk.rd_clk (clk_100m ), // input wire rd_clk.wr_en (fifo_wr_en ), // input wire wr_en.rd_en (fifo_rd_en ), // input wire rd_en.din (fifo_wr_data ), // input wire [7 : 0] din.dout (fifo_rd_data ), // output wire [7 : 0] dout.almost_full (almost_full ), // output wire almost_full.almost_empty (almost_empty ), // output wire almost_empty.full (full ), // output wire full.empty (empty ), // output wire empty.wr_data_count (wr_data_count), // output wire [7 : 0] wr_data_count.rd_data_count (rd_data_count), // output wire [7 : 0] rd_data_count.wr_rst_busy (wr_rst_busy ), // output wire wr_rst_busy.rd_rst_busy (rd_rst_busy ) // output wire rd_rst_busy);//例化写 FIFO 模块fifo_wr u_fifo_wr (.wr_clk (clk_50m ), // 写时钟.rst_n (rst_n ), // 复位信号.wr_rst_busy (wr_rst_busy ), // 写复位忙信号.fifo_wr_en (fifo_wr_en ), // fifo 写请求.fifo_wr_data (fifo_wr_data), // 写入 FIFO 的数据.empty (empty ), // fifo 空信号.almost_full (almost_full ) // fifo 将满信号);//例化读 FIFO 模块fifo_rd u_fifo_rd (.rd_clk (clk_100m ), // 读时钟.rst_n (rst_n ), // 复位信号.rd_rst_busy (rd_rst_busy ), // 读复位忙信号.fifo_rd_en (fifo_rd_en ), // fifo 读请求.fifo_rd_data (fifo_rd_data), // 从 FIFO 输出的数据.almost_empty (almost_empty), // fifo 将空信号.full (full ) // fifo 满信号);endmodulefifo_wr.v
module fifo_wr(
//mudule clock
input wr_clk , // 时钟信号
input rst_n , // 复位信号
//FIFO interface
input wr_rst_busy , // 写复位忙信号
input empty , // FIFO 空信号
input almost_full , // FIFO 将满信号
output reg fifo_wr_en , // FIFO 写使能output reg [7:0] fifo_wr_data // 写入 FIFO 的数据);//reg definereg empty_d0;reg empty_d1;//*****************************************************//** main code//*****************************************************//因为 empty 信号是属于 FIFO 读时钟域的//所以对 empty 打两拍同步到写时钟域下always @(posedge wr_clk or negedge rst_n) beginif(!rst_n) beginempty_d0 <= 1'b0;empty_d1 <= 1'b0;endelse beginempty_d0 <= empty;empty_d1 <= empty_d0;endend//对 fifo_wr_en 赋值,当 FIFO 为空时开始写入,写满后停止写always @(posedge wr_clk or negedge rst_n) beginif(!rst_n)fifo_wr_en <= 1'b0;else if(!wr_rst_busy) beginif(empty_d1)fifo_wr_en <= 1'b1;else if(almost_full)fifo_wr_en <= 1'b0; endelsefifo_wr_en <= 1'b0;end //对 fifo_wr_data 赋值,0~254always @(posedge wr_clk or negedge rst_n) beginif(!rst_n)fifo_wr_data <= 8'b0;else if(fifo_wr_en && fifo_wr_data < 8'd254)fifo_wr_data <= fifo_wr_data + 8'b1;elsefifo_wr_data <= 8'b0;endendmodule
fifo_rd.v
module fifo_rd(
//system clock
input rd_clk , //时钟信号
input rst_n , //复位信号
//FIFO interface
input rd_rst_busy , //读复位忙信号
input [7:0] fifo_rd_data, //从 FIFO 读出的数据
input full , //FIFO 满信号
input almost_empty, //FIFO 将空信号output reg fifo_rd_en //FIFO 读使能);//reg definereg full_d0;reg full_d1;//*****************************************************//** main code//*****************************************************//因为 full 信号是属于 FIFO 写时钟域的//所以对 full 打两拍同步到读时钟域下always @(posedge rd_clk or negedge rst_n) beginif(!rst_n) beginfull_d0 <= 1'b0;full_d1 <= 1'b0;endelse beginfull_d0 <= full;full_d1 <= full_d0;endend //对 fifo_rd_en 进行赋值,FIFO 写满之后开始读,读空之后停止读always @(posedge rd_clk or negedge rst_n) beginif(!rst_n)fifo_rd_en <= 1'b0;else if(!rd_rst_busy) beginif(full_d1)fifo_rd_en <= 1'b1;else if(almost_empty)fifo_rd_en <= 1'b0;endelsefifo_rd_en <= 1'b0;endendmodule
tb_ip_fifo.v
`timescale 1ns / 1ps //仿真单位/仿真精度module tb_ip_fifo();//parameter define
parameter CLK_PERIOD = 20; //时钟周期 20ns//reg define
reg sys_clk;reg sys_rst_n;//信号初始化initial beginsys_clk = 1'b0;sys_rst_n = 1'b0;#200sys_rst_n = 1'b1;//模拟按下复位#10000 ;sys_rst_n = 0;#160 ;sys_rst_n = 1;end//产生时钟always #(CLK_PERIOD/2) sys_clk = ~sys_clk;ip_fifo u_ip_fifo (.sys_clk (sys_clk ),.sys_rst_n (sys_rst_n));endmodule
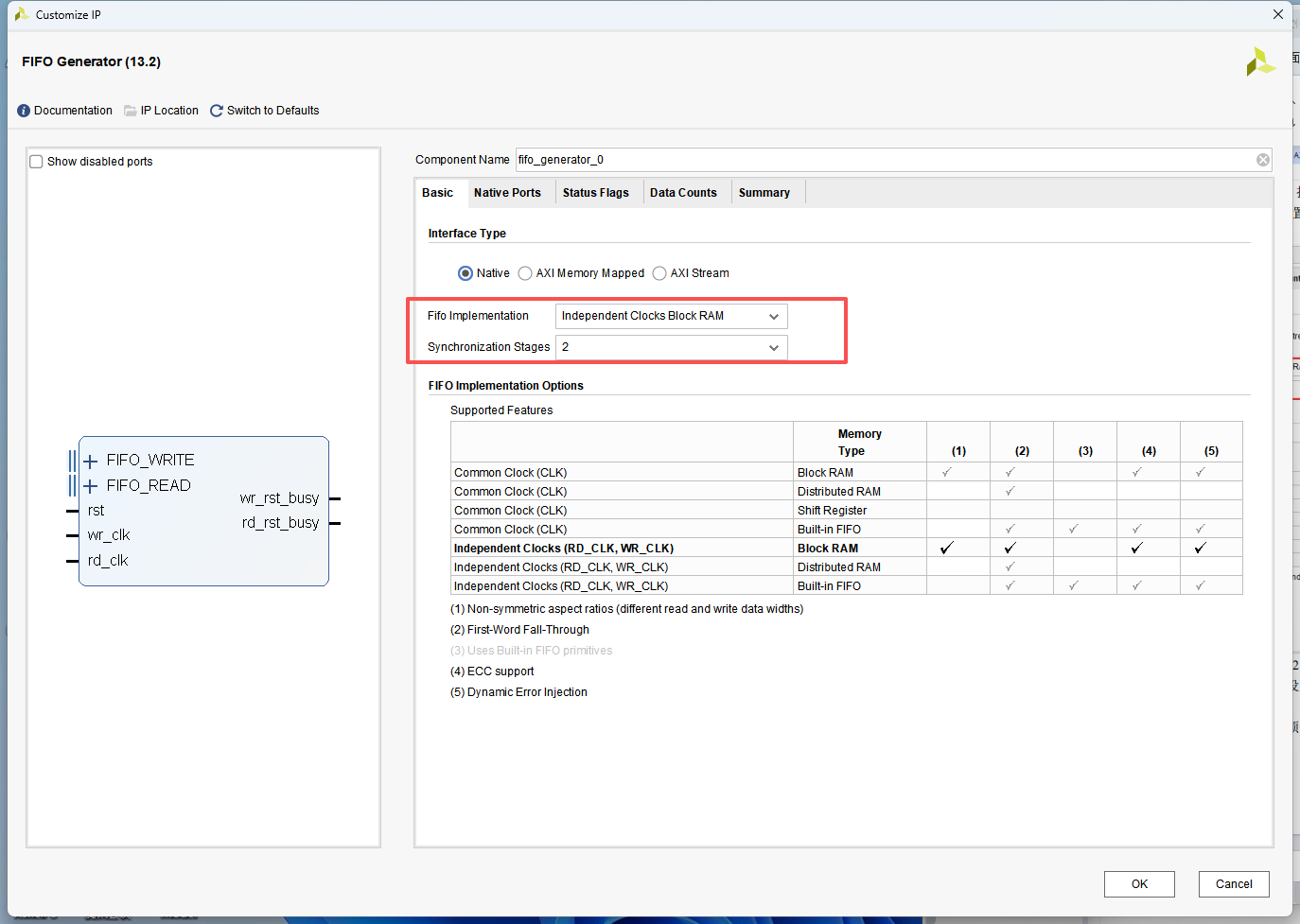
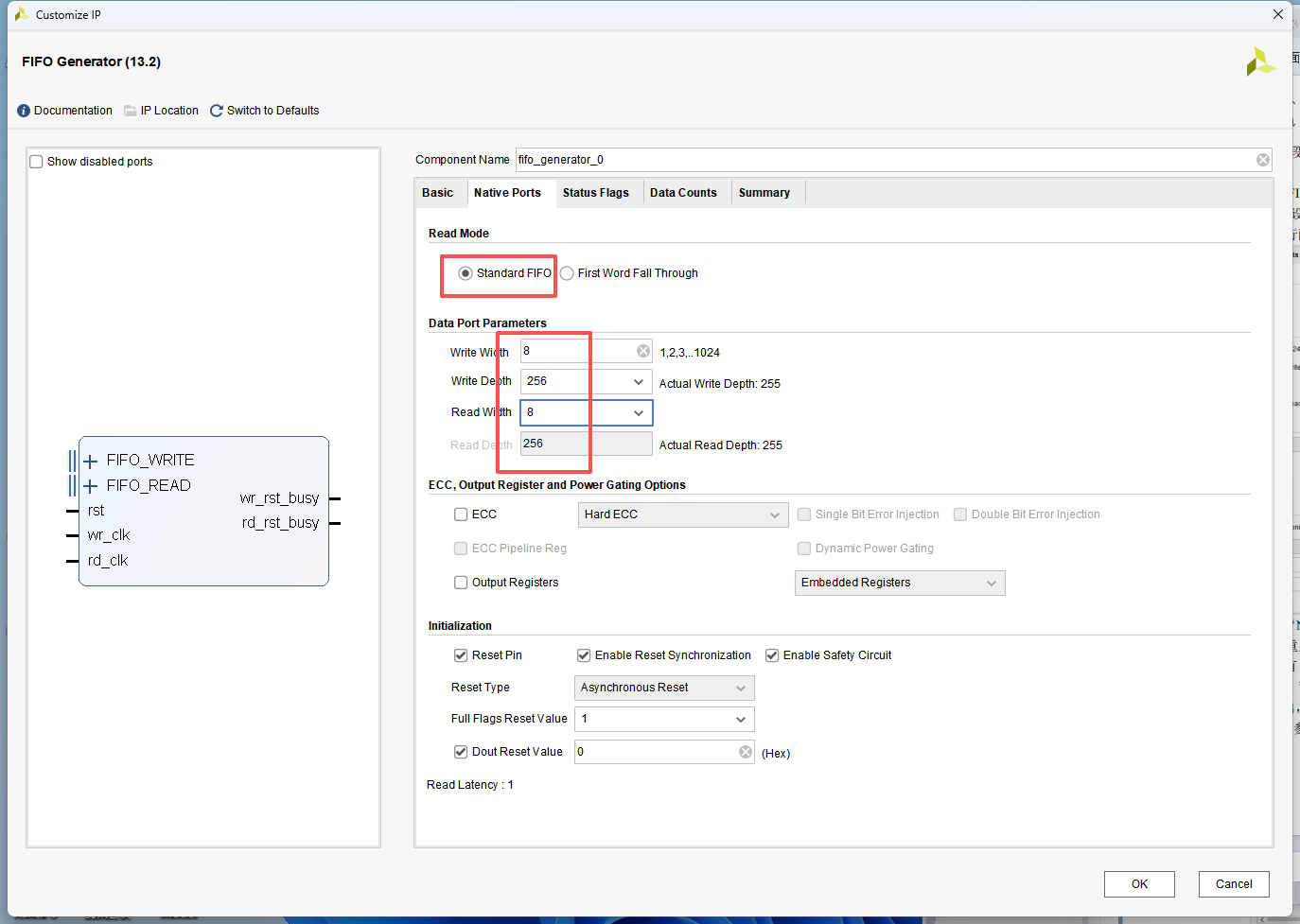
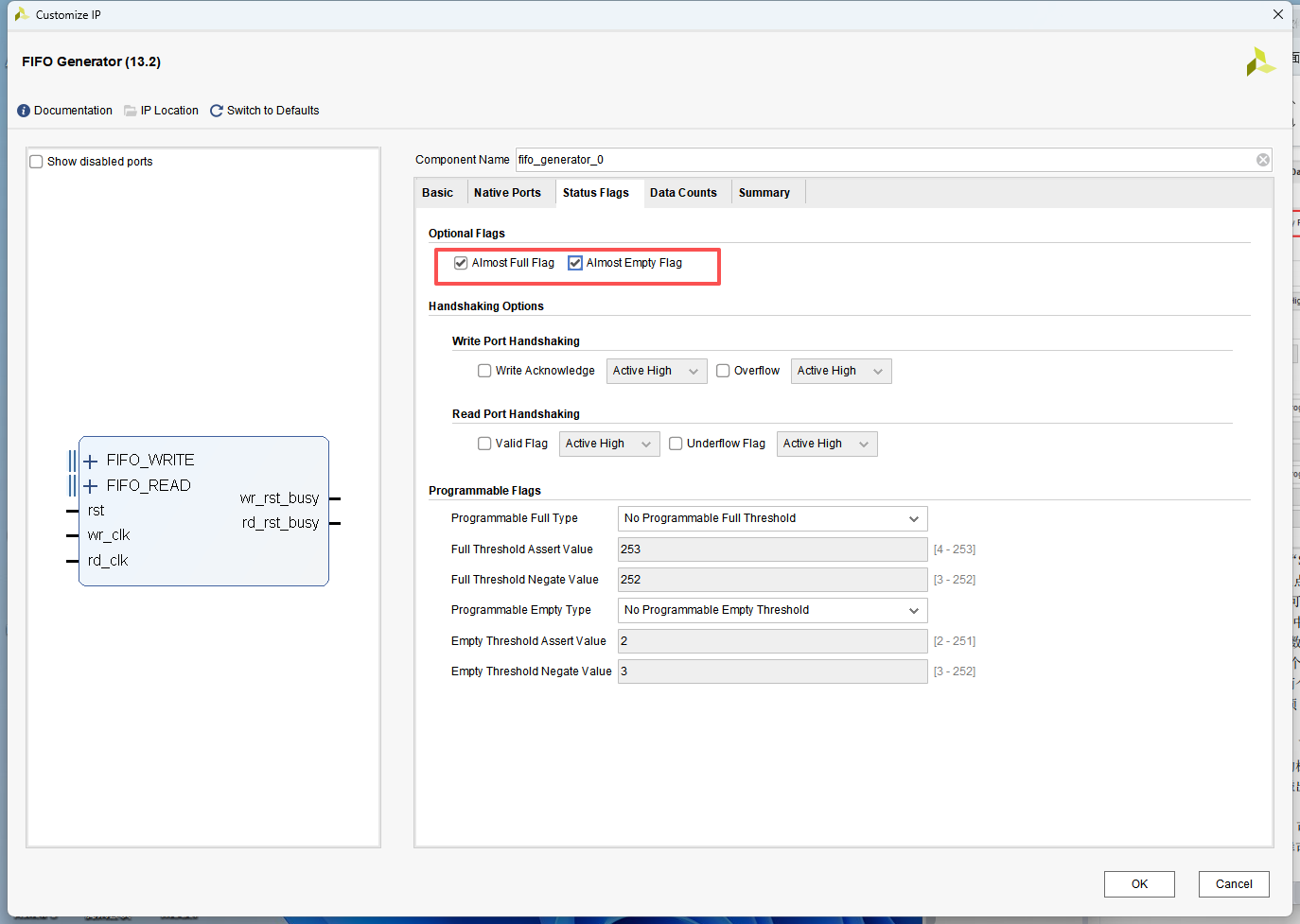
IP 配置
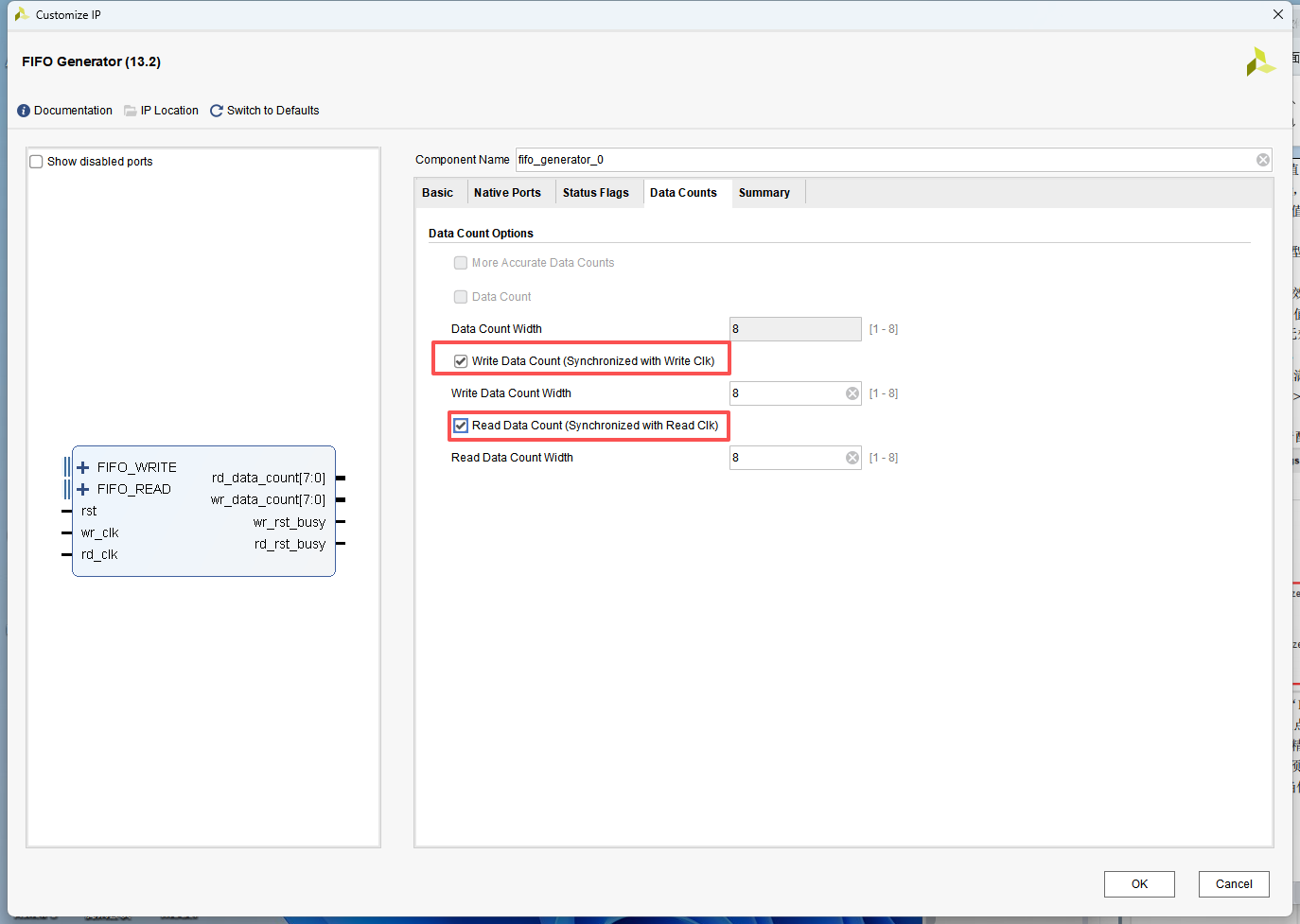
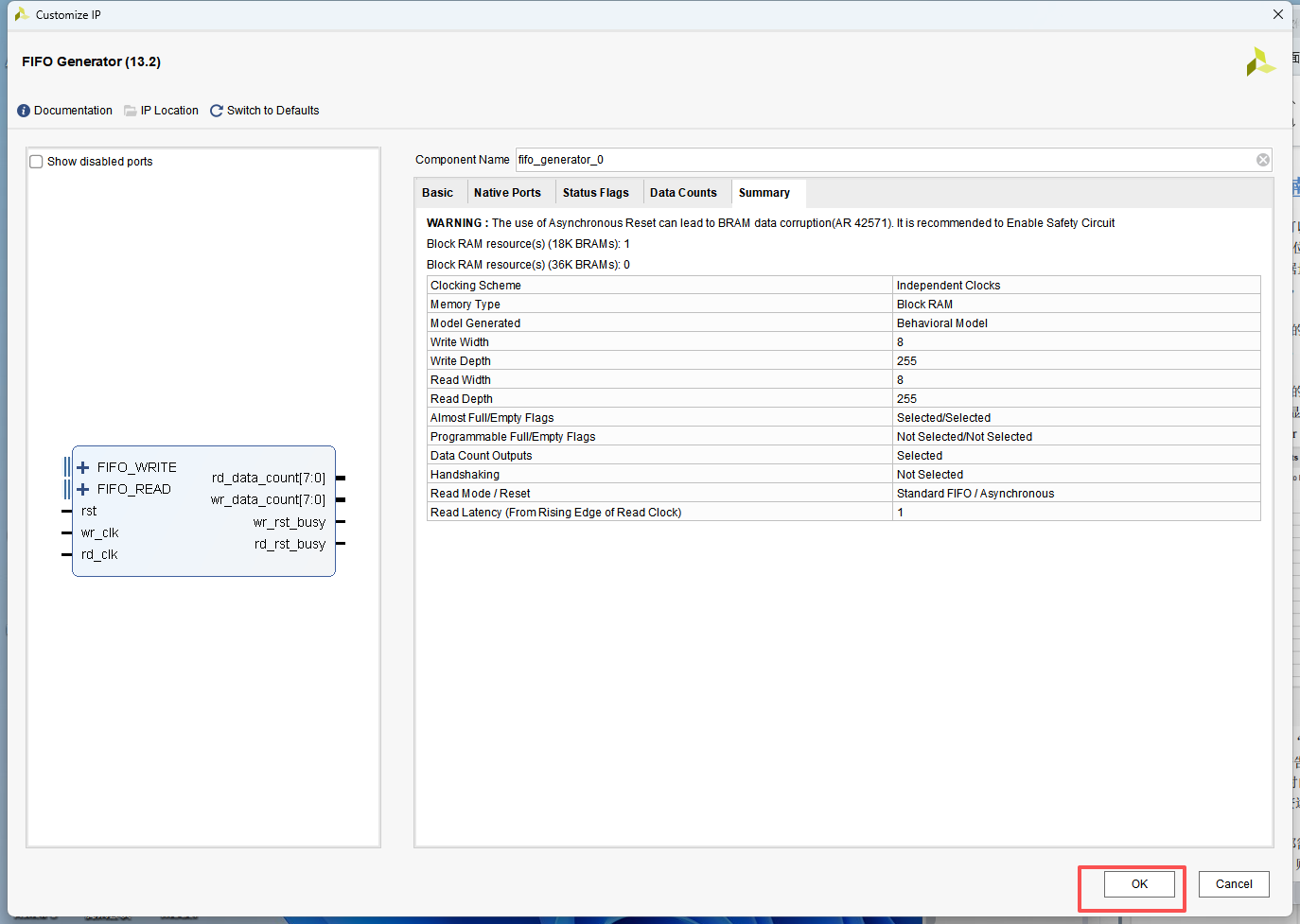
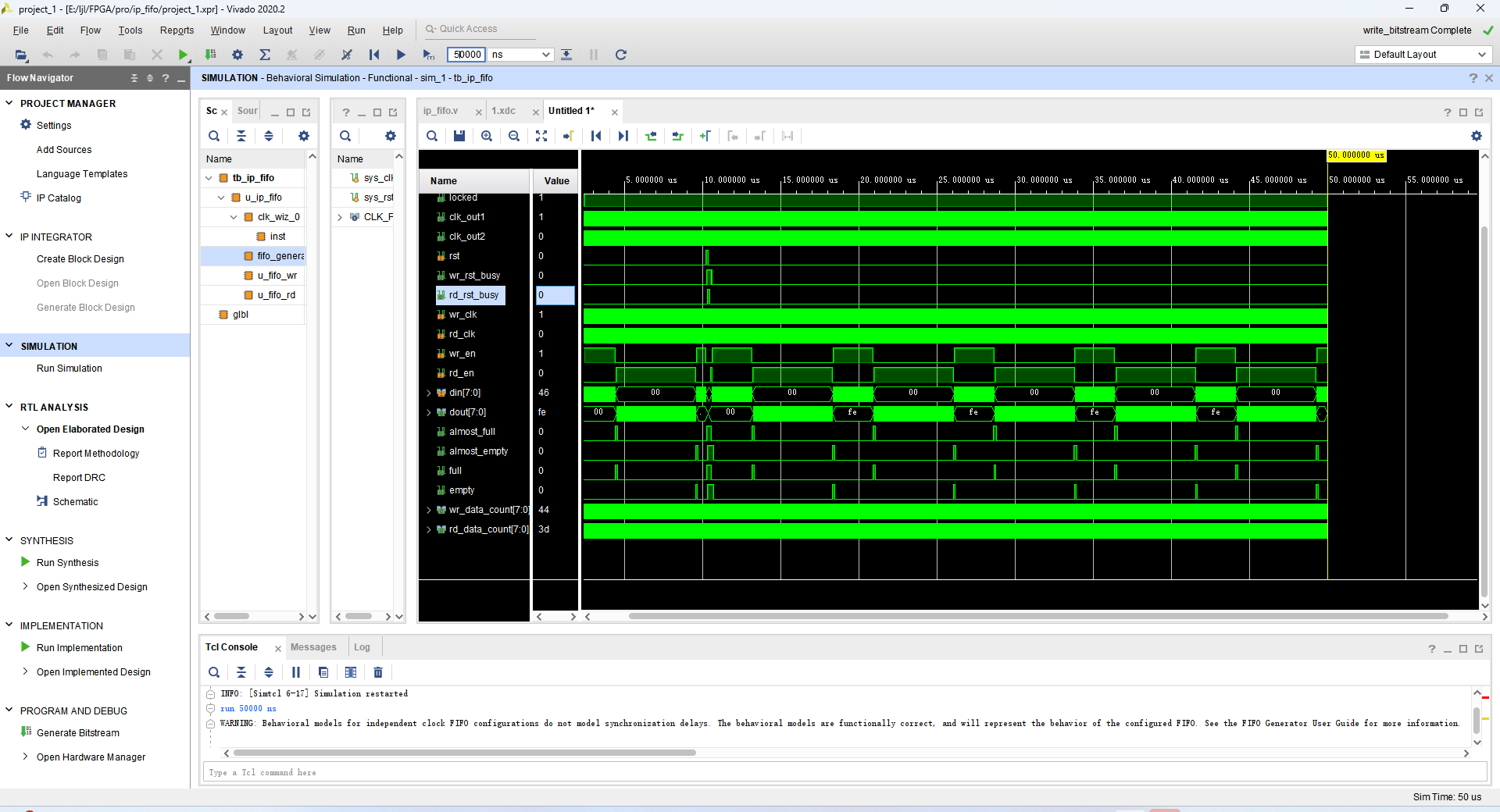
写使能拉高后开始向 FIFO 中写入数据,当写完倒数第二个数时,写使能为高,当写完最后一个数时,写使能为高被拉低
可以发现 FIFO 写时钟域的数
据计数器(wr_data_count)在写操作前并不是以 1 为步进递减的,这是 FIFO 的读写速率不同导致的;而且
wr_data_count 也并没有递减到 0,这是因为读时钟域与写时钟域下的信号存在数个时钟周期的同步延迟,
而我们通过检测空信号的方式在其延迟更新前就开启了写使能,所以我们没有看到 wr_data_count 更新到 0
的过程。
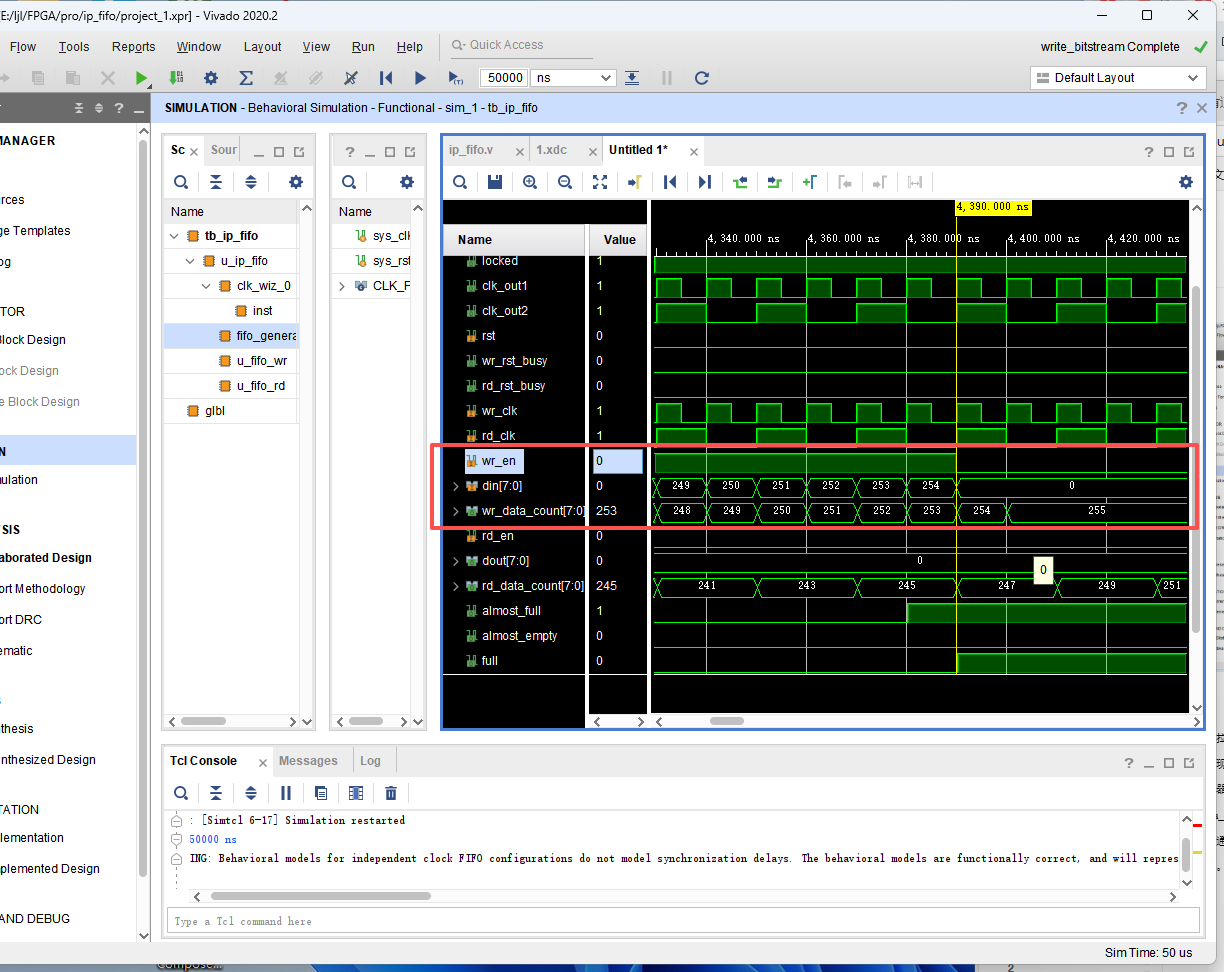
读使能拉高后开始从 FIFO 中读出数据,当读完倒数第二个数时,将空信号被
拉高,当读完最后一个数时,空信号拉高,读使能被拉低。
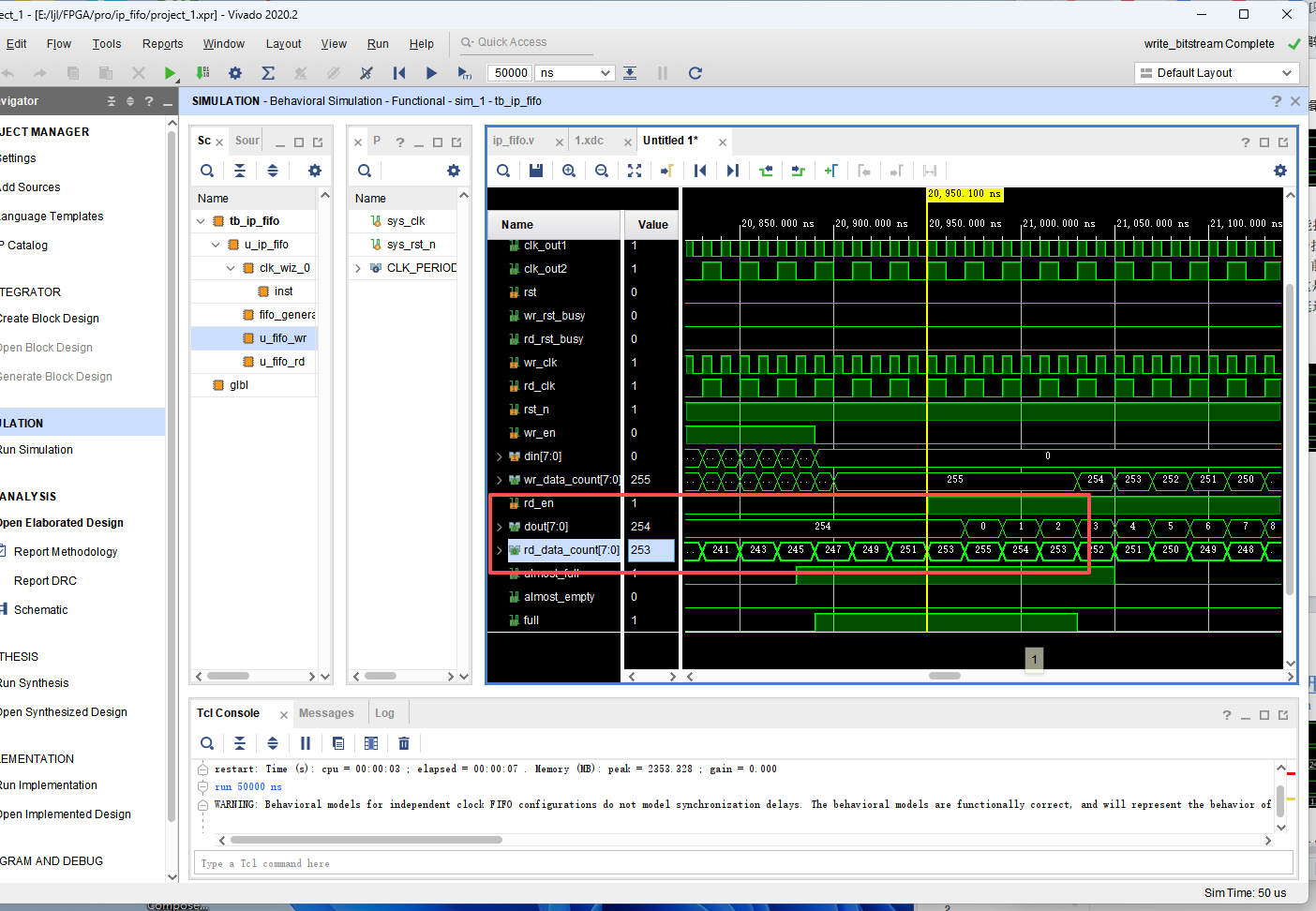
当读完倒数第二个数时,将空信号被
拉高,当读完最后一个数时,空信号拉高,读使能被拉低。
ila
//写时钟域下 ila
ila_0 u_ila_wr (.clk (clk_50m ), // input wire clk.probe0 (fifo_wr_en ), // input wire [0:0] probe0 .probe1 (fifo_wr_data ), // input wire [7:0] probe1 .probe2 (almost_full ), // input wire [0:0] probe2 .probe3 (full ), // input wire [0:0] probe3
.probe4 (wr_data_count) // input wire [7:0] probe4
);
//读时钟域下 ila
ila_1 u_ila_rd (.clk (clk_100m ), // input wire clk.probe0 (fifo_rd_en ), // input wire [0:0] probe0 .probe1 (fifo_rd_data ), // input wire [7:0] probe1 .probe2 (almost_empty ), // input wire [0:0] probe2 .probe3 (empty ), // input wire [0:0] probe3 .probe4 (rd_data_count) // input wire [7:0] probe4
);
阅读
《杀死一只知更鸟》
第十四章

