mysql大表批量查询中IN vs JOIN vs CTE 性能实验
实验
背景
一张1000w的表tb_sku 。
本次实验旨在比较三种批量查询方式在不同 IDsPerQuery (id数量)规模下的执行性能,以评估最优查询策略。
三种方法分别是:
- IN 查询
- 临时表 + JOIN 查询
- CTE (Common Table Expression) 查询
这几种方式具体来说:
1️⃣ IN 查询
SELECT * FROM tb_sku WHERE id IN (%s);
特点:
- 简单直接;
- SQL语句长度与
ids数量线性增长;
2️⃣ 临时表 + JOIN 查询
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE temp_ids (id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY);
INSERT INTO temp_ids VALUES (...);
SELECT s.* FROM tb_sku s JOIN temp_ids t ON s.id = t.id;
DROP TEMPORARY TABLE temp_ids;
特点:
- 适合大批量;
- 减少 SQL 语句解析负担;
- 临时表在服务器端高效 JOIN。
3️⃣ CTE 查询
WITH args AS (SELECT 1 AS id UNION ALLSELECT 2 UNION ALLSELECT 3 ...
)
SELECT * FROM tb_sku JOIN args USING (id);
特点:
- 无需创建临时表;
- 服务端可直接在内存中执行;
- 在中小批量下性能最佳;
- 但大批量时会因栈空间限制导致报错:
❌ Error 1436 (HY000): Thread stack overrun
Use ‘mysqld --thread_stack=#’ to specify a bigger stack.
实验结果
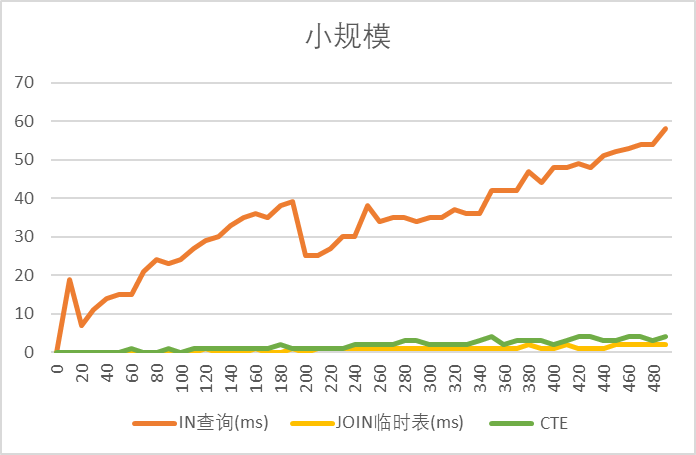
1️⃣ 小规模(≤ 1000)
| IDsPerQuery | IN查询(ms) | JOIN(ms) | CTE(ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 860 | 99 | 4 | 6 |
| 900 | 100 | 4 | 6 |
| 950 | 109 | 3 | 7 |
| 1000 | 116 | 5 | 7 |
CTE ≈ JOIN ≪ IN
→ CTE 性能最佳,JOIN 接近,IN 明显慢。
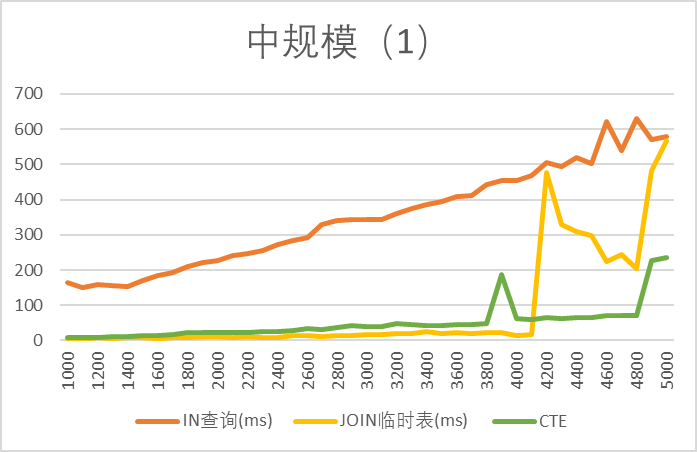
2️⃣ 中规模(1k ~ 10k)
| IDsPerQuery | IN查询(ms) | JOIN(ms) | CTE(ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 163 | 4 | 8 |
| 1100 | 149 | 3 | 8 |
| 2300 | 254 | 7 | 25 |
| 2400 | 273 | 9 | 25 |
| 2500 | 283 | 14 | 28 |
| 3300 | 374 | 20 | 46 |
| 3400 | 385 | 24 | 42 |
| 3500 | 394 | 19 | 43 |
| 4600 | 621 | 223 | 72 |
| 4700 | 540 | 244 | 70 |
| 4900 | 571 | 483 | 228 |
| 5000 | 578 | 569 | 234 |
| 6800 | 764 | 671 | 463 |
| 7000 | 775 | 687 | 601 |
| 10000 | 1148 | 1070 | x |
结论:
- 1k ~ 10k 区间:不爆栈时CTE 最优,其次JOIN 最优,随后逐渐和IN相同
- 临时表存在不稳定的情况(4k时忽高忽低)
- IN 查询性能随 id 数量增长逐渐下降
- CTE 在 5~7k 以上报错,不可用(爆栈)
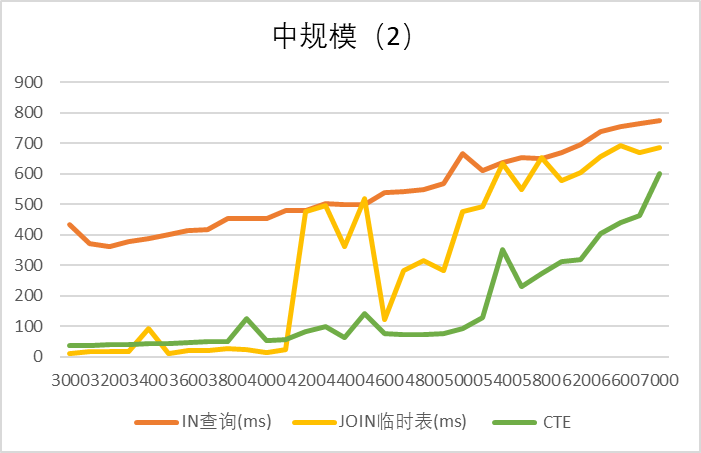
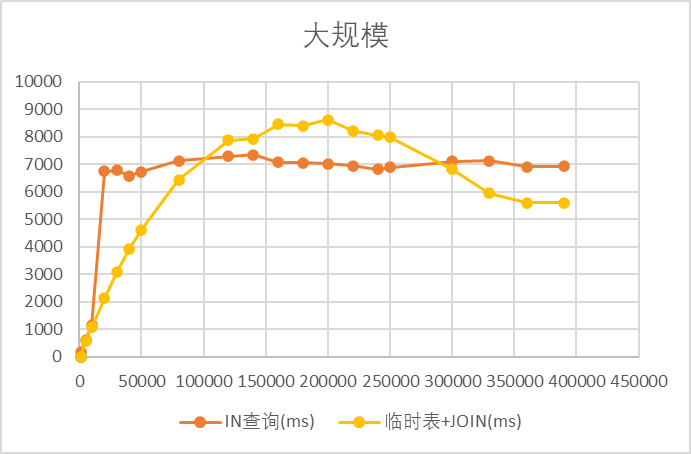
3️⃣ 超大规模(≥ 1w)
| IDsPerQuery | IN查询(ms) | JOIN(ms) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 163 | 3 |
| 5000 | 611 | 579 |
| 10000 | 1148 | 1070 |
| 140000 | 7352 | 7931 |
| 200000 | 7027 | 8626 |
| 300000 | 7108 | 6812 |
| 360000 | 6901 | 5595 |
| 390000 | 6929 | 5605 |
结论:
- 10w 以下:JOIN 性能优;
- 10w 以上:IN 性能略优;
- 30w 以上:JOIN 再次超过 IN;
- 说明 JOIN 优势在极大批量下又显现。
综合结论
| 数据规模 | 推荐方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| ≤ 5000 | ✅ CTE | 内存中执行,无临时表开销,性能极佳 |
| 5000 ~ 100000 | ✅ JOIN 临时表 | 避免 SQL 过长,提高可维护性 |
| > 100000 | ✅ IN / JOIN(视SQL优化器) | 具体取决于数据库优化策略 |
| 并发场景 | 并发 CTE | CTE 最优方案,在多线程并发时效果显著 |
故:
🔹 小批量:CTE = JOIN > IN
🔹 中批量:CTE = JOIN > IN
🔹 超大批量:JOIN ≈ IN
🔹 并发时:CTE 优势最明显(尤其在栈内执行时)
附录
实验代码:
package bigtableimport ("database/sql""fmt""strings""testing""time"
)// --- 工具函数 ---func countDup(nums []int) (int, []int) {freq := make(map[int]int)for _, v := range nums {freq[v]++}var duplicates []intfor num, cnt := range freq {if cnt > 1 {duplicates = append(duplicates, num)}}return len(duplicates), duplicates
}func distinct(nums []int) []int {m := make(map[int]struct{})for _, num := range nums {m[num] = struct{}{}}res := make([]int, 0, len(m))for k := range m {res = append(res, k)}return res
}// --- SQL 批量查询方法 ---// 1️⃣ IN 查询
func queryWithIN(db *sql.DB, ids []int) (int, time.Duration, error) {if len(ids) == 0 {return 0, 0, nil}inParams := make([]string, len(ids))for i, id := range ids {inParams[i] = fmt.Sprintf("%d", id)}query := fmt.Sprintf(`SELECT id,name FROM tb_sku WHERE id IN (%s)`, strings.Join(inParams, ","))start := time.Now()rows, err := db.Query(query)if err != nil {return 0, 0, err}defer rows.Close()var count intfor rows.Next() {var id intvar name stringif err := rows.Scan(&id, &name); err != nil {return count, time.Since(start), err}count++}return count, time.Since(start), nil
}// 2️⃣ 临时表 + JOIN 查询
func queryWithTempTable(db *sql.DB, ids []int, batchSize int) (int, time.Duration, error) {if len(ids) == 0 {return 0, 0, nil}// 删除旧临时表_, _ = db.Exec(`DROP TEMPORARY TABLE IF EXISTS tmp_ids`)// 创建临时表_, err := db.Exec(`CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tmp_ids (id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY)`)if err != nil {return 0, 0, err}// 批量插入for i := 0; i < len(ids); i += batchSize {end := i + batchSizeif end > len(ids) {end = len(ids)}batch := ids[i:end]placeholders := make([]string, len(batch))args := make([]interface{}, len(batch))for j, id := range batch {placeholders[j] = "(?)"args[j] = id}query := fmt.Sprintf("INSERT INTO tmp_ids (id) VALUES %s", strings.Join(placeholders, ","))_, err := db.Exec(query, args...)if err != nil {return 0, 0, err}}// JOIN 查询start := time.Now()rows, err := db.Query(`SELECT s.id, s.name FROM tb_sku s JOIN tmp_ids t ON s.id = t.id`)if err != nil {return 0, 0, err}defer rows.Close()var count intfor rows.Next() {var id intvar name stringif err := rows.Scan(&id, &name); err != nil {return count, time.Since(start), err}count++}return count, time.Since(start), nil
}// 3️⃣ CTE(WITH … AS … UNION ALL)查询
func queryWithCTE(db *sql.DB, ids []int) (int, time.Duration, error) {if len(ids) == 0 {return 0, 0, nil}// 构造 CTEquery := "WITH args AS ("for i, id := range ids {if i > 0 {query += " UNION ALL "}query += fmt.Sprintf("SELECT %d AS id", id)}query += fmt.Sprintf(") SELECT s.id, s.name FROM tb_sku s JOIN args USING (id)")start := time.Now()rows, err := db.Query(query)if err != nil {return 0, 0, err}defer rows.Close()var count intfor rows.Next() {var id intvar name stringif err := rows.Scan(&id, &name); err != nil {return count, time.Since(start), err}count++}return count, time.Since(start), nil
}// --- 测试函数 ---func TestBatchQueriesPerfMultiSize(t *testing.T) {db := openDB()defer db.Close()maxID := 10000000// idsPerQuery 维度,可以测试不同批量idSizes := []int{}for i := 1000; i <= 5000; i += 100 {idSizes = append(idSizes, i)}//for i := 1000; i <= 5000; i += 100 {// idSizes = append(idSizes, i)//}//for i := 3000; i <= 5000; i += 100 {// idSizes = append(idSizes, i)//}//for i := 0; i <= 1000; i += 10 {// idSizes = append(idSizes, i)//}//idSizes := []int{1000, 5000}//idSizes := []int{1000, 5000, 10000, 20000, 30000, 40000, 50000}//idSizes := []int{80000, 120000}//idSizes := []int{140000, 160000}//idSizes := []int{180000, 200000}//idSizes := []int{220000, 240000}//idSizes := []int{250000, 300000}//idSizes := []int{330000, 360000, 390000}batchSize := 1000// 用于记录随 idSizes 变化的耗时inTimes := make([]float64, len(idSizes))tmpTableTimes := make([]float64, len(idSizes))cteTimes := make([]float64, len(idSizes)) // 新增 CTE 方法耗时type result struct {Method stringIDsPerQuery intCount intElapsed time.DurationErr error}var results []resultfmt.Println("IDsPerQuery\tIN查询(ms)\tJOIN临时表(ms) \t CTE")for i, idsPerQuery := range idSizes {rawIDs := randomIDs(idsPerQuery, maxID)ids := distinct(rawIDs)// --- IN 查询 ---countIn, durationIn, err := queryWithIN(db, ids)results = append(results, result{Method: "IN 查询",IDsPerQuery: idsPerQuery,Count: countIn,Elapsed: durationIn,Err: err,})inTimes[i] = float64(durationIn.Milliseconds())// --- 临时表 + JOIN 查询 ---countTmp, durationTmp, err := queryWithTempTable(db, ids, batchSize)results = append(results, result{Method: "JOIN临",IDsPerQuery: idsPerQuery,Count: countTmp,Elapsed: durationTmp,Err: err,})tmpTableTimes[i] = float64(durationTmp.Milliseconds())// CTE 查询_, durationCTE, err := queryWithCTE(db, ids)if err != nil {t.Errorf("CTE 查询失败: %v", err)continue}cteTimes[i] = float64(durationCTE.Milliseconds())//fmt.Printf("%d\t\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\n", idsPerQuery, inTimes[i], tmpTableTimes[i])fmt.Printf("%d\t\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\n", idsPerQuery, inTimes[i], tmpTableTimes[i], cteTimes[i])}t.Logf("idSizes: %v", idSizes)t.Logf("IN 查询耗时: %v", inTimes)t.Logf("临时表+JOIN耗时: %v", tmpTableTimes)// 打印表格化结果//fmt.Println("批量查询性能对比 (不同 IDsPerQuery):")//fmt.Println("IDsPerQuery\t方法\t\t命中行数\t耗时(ms)\t状态")//for _, r := range results {// status := "OK"// if r.Err != nil {// status = fmt.Sprintf("错误: %v", r.Err)// }// fmt.Printf("%d\t\t%s\t%d\t\t%.2f\t%s\n",// r.IDsPerQuery,// r.Method,// r.Count,// float64(r.Elapsed.Milliseconds()),// status,// )//}
}绘图工具:Excel
