线性表——数组描述
目录
一、源代码
myExceptions.h
linearList.h
changeLength1D.h
arrayList.h
构造函数:
复制构造函数:
方法checkIndex:
方法get:
方法indexOf:
方法erase:
方法insert:
方法output:
arrayListWithIterator.h
vectorList.h
二、部分习题
3.
5.
6.
7.
8.9.10.
11,12
13,14
16,17,18
22.
23.
24.
25.
28.
29.
30.
一、源代码
myExceptions.h
// exception classes for various error types#ifndef myExceptions_
#define myExceptions_
#include <string>
#include<iostream>using namespace std;// illegal parameter value
class illegalParameterValue
{public:illegalParameterValue(string theMessage = "Illegal parameter value"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}private:string message;
};// illegal input data
class illegalInputData
{public:illegalInputData(string theMessage = "Illegal data input"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}private:string message;
};// illegal index
class illegalIndex
{public:illegalIndex(string theMessage = "Illegal index"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}private:string message;
};// matrix index out of bounds
class matrixIndexOutOfBounds
{public:matrixIndexOutOfBounds(string theMessage = "Matrix index out of bounds"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}private:string message;
};// matrix size mismatch
class matrixSizeMismatch
{public:matrixSizeMismatch(string theMessage = "The size of the two matrics doesn't match"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}private:string message;
};// stack is empty
class stackEmpty
{public:stackEmpty(string theMessage = "Invalid operation on empty stack"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}private:string message;
};// queue is empty
class queueEmpty
{public:queueEmpty(string theMessage = "Invalid operation on empty queue"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}private:string message;
};// hash table is full
class hashTableFull
{public:hashTableFull(string theMessage = "The hash table is full"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}private:string message;
};// edge weight undefined
class undefinedEdgeWeight
{public:undefinedEdgeWeight(string theMessage = "No edge weights defined"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}private:string message;
};// method undefined
class undefinedMethod
{public:undefinedMethod(string theMessage = "This method is undefined"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}private:string message;
};
#endif
linearList.h
// abstract class linearList
// abstract data type specification for linear list data structure
// all methods are pure virtual functions#ifndef linearList_
#define linearList_
#include <iostream>using namespace std;template<class T>
class linearList
{public:virtual ~linearList() {};virtual bool empty() const = 0;// 判断是否为空virtual int size() const = 0;// 返回元素个数virtual T& get(int theIndex) const = 0;// 返回该索引的元素virtual int indexOf(const T& theElement) const = 0;// 返回该元素的索引virtual void erase(int theIndex) = 0;// 清除该索引元素virtual void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement) = 0;// 在该索引插入元素virtual void output(ostream& out) const = 0;// 输出
};
#endifchangeLength1D.h
// change the length of an array#ifndef changeLength1D_
#define changeLength1D_#include "myExceptions.h"using namespace std;template<class T>
void changeLength1D(T*& a, int oldLength, int newLength)
{if (newLength < 0)throw illegalParameterValue("new length must be >= 0");T* temp = new T[newLength]; // new arrayint number = min(oldLength, newLength); // number to copycopy(a, a + number, temp);delete [] a; // deallocate old memorya = temp;
}#endif将数组大小改变:先创建临时数组,容量为新容量。
然后取新长度和旧长度的较小者,将原数组的前number复制到新数组。
清楚原数组。
改变原指针指向。
arrayList.h
// array implementation of a linear list
// derives from abstract class linearList just to make sure
// all methods of the ADT are implemented
// USES STL ALGORITHMS TO SIMPLIFY CODE#ifndef arrayList_
#define arrayList_#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include "linearList.h"
#include "myExceptions.h"
#include "changeLength1D.h"using namespace std;template<class T>
class arrayList : public linearList<T>
{public:// constructor, copy constructor and destructorarrayList(int initialCapacity = 10);arrayList(const arrayList<T>&);~arrayList() {delete [] element;}// ADT methodsbool empty() const {return listSize == 0;}int size() const {return listSize;}T& get(int theIndex) const;int indexOf(const T& theElement) const;void erase(int theIndex);void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement);void output(ostream& out) const;// additional methodint capacity() const {return arrayLength;}protected:void checkIndex(int theIndex) const;// throw illegalIndex if theIndex invalidT* element; // 1D array to hold list elementsint arrayLength; // capacity of the 1D arrayint listSize; // number of elements in list
};template<class T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(int initialCapacity)
{// Constructor.if (initialCapacity < 1){ostringstream s;s << "Initial capacity = " << initialCapacity << " Must be > 0";throw illegalParameterValue(s.str());}arrayLength = initialCapacity;element = new T[arrayLength];listSize = 0;
}template<class T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(const arrayList<T>& theList)
{// Copy constructor.arrayLength = theList.arrayLength;listSize = theList.listSize;element = new T[arrayLength];copy(theList.element, theList.element + listSize, element);
}template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::checkIndex(int theIndex) const
{// Verify that theIndex is between 0 and listSize - 1.if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex >= listSize){ostringstream s;s << "index = " << theIndex << " size = " << listSize;throw illegalIndex(s.str());}}template<class T>
T& arrayList<T>::get(int theIndex) const
{// Return element whose index is theIndex.// Throw illegalIndex exception if no such element.checkIndex(theIndex);return element[theIndex];
}template<class T>
int arrayList<T>::indexOf(const T& theElement) const
{// Return index of first occurrence of theElement.// Return -1 if theElement not in list.// search for theElementint theIndex = (int) (find(element, element + listSize, theElement)- element);// check if theElement was foundif (theIndex == listSize)// not foundreturn -1;else return theIndex;}template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::erase(int theIndex)
{// Delete the element whose index is theIndex.// Throw illegalIndex exception if no such element.checkIndex(theIndex);// valid index, shift elements with higher indexcopy(element + theIndex + 1, element + listSize,element + theIndex);element[--listSize].~T(); // invoke destructor
}template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement)
{// Insert theElement so that its index is theIndex.if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex > listSize){// invalid indexostringstream s;s << "index = " << theIndex << " size = " << listSize;throw illegalIndex(s.str());}// valid index, make sure we have spaceif (listSize == arrayLength){// no space, double capacitychangeLength1D(element, arrayLength, 2 * arrayLength);arrayLength *= 2;}// shift elements right one positioncopy_backward(element + theIndex, element + listSize,element + listSize + 1);element[theIndex] = theElement;listSize++;
}template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::output(ostream& out) const
{// Put the list into the stream out.copy(element, element + listSize, ostream_iterator<T>(cout, " "));
}// overload <<
template <class T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const arrayList<T>& x){x.output(out); return out;}#endif元素为:
T* element; 数组element
int arrayLength; 数组容量arrayLeng
int listSize; 元素个数
构造函数:
template<class T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(int initialCapacity)
{// Constructor.if (initialCapacity < 1){ostringstream s;s << "Initial capacity = " << initialCapacity << " Must be > 0";throw illegalParameterValue(s.str());}arrayLength = initialCapacity;element = new T[arrayLength];listSize = 0;
}初始化数组长度element,创建动态数组,元素个数listSize初始为0。
复制构造函数:
template<class T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(const arrayList<T>& theList)
{// Copy constructor.arrayLength = theList.arrayLength;listSize = theList.listSize;element = new T[arrayLength];copy(theList.element, theList.element + listSize, element);
}分别初始化arrayLength和listSize,创建动态数组,将原数组元素复制到新数组。
方法checkIndex:
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::checkIndex(int theIndex) const
{// Verify that theIndex is between 0 and listSize - 1.if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex >= listSize){ostringstream s;s << "index = " << theIndex << " size = " << listSize;throw illegalIndex(s.str());}}确定索引合法。
方法get:
template<class T>
T& arrayList<T>::get(int theIndex) const
{// Return element whose index is theIndex.// Throw illegalIndex exception if no such element.checkIndex(theIndex);return element[theIndex];
}检查索引,返回元素。
方法indexOf:
template<class T>
int arrayList<T>::indexOf(const T& theElement) const
{// Return index of first occurrence of theElement.// Return -1 if theElement not in list.// search for theElementint theIndex = (int) (find(element, element + listSize, theElement)- element);// check if theElement was foundif (theIndex == listSize)// not foundreturn -1;else return theIndex;}方法erase:
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::erase(int theIndex)
{// Delete the element whose index is theIndex.// Throw illegalIndex exception if no such element.checkIndex(theIndex);// valid index, shift elements with higher indexcopy(element + theIndex + 1, element + listSize,element + theIndex);element[--listSize].~T(); // invoke destructor
}检查索引,将后一位到最后元素都向前移一位。
方法insert:
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement)
{// Insert theElement so that its index is theIndex.if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex > listSize){// invalid indexostringstream s;s << "index = " << theIndex << " size = " << listSize;throw illegalIndex(s.str());}// valid index, make sure we have spaceif (listSize == arrayLength){// no space, double capacitychangeLength1D(element, arrayLength, 2 * arrayLength);arrayLength *= 2;}// shift elements right one positioncopy_backward(element + theIndex, element + listSize,element + listSize + 1);element[theIndex] = theElement;listSize++;
}若容量已满,扩容二倍,将该元素至末尾元素向后移一位,然后插入。
方法output:
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::output(ostream& out) const
{// Put the list into the stream out.copy(element, element + listSize, ostream_iterator<T>(cout, " "));
}// overload <<
template <class T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const arrayList<T>& x){x.output(out); return out;}arrayListWithIterator.h
// array implementation of a linear list
// derives from abstract class linearList just to make sure
// all methods of the ADT are implemented
// USES STL ALGORITHMS TO SIMPLIFY CODE
// iterator class for arrayList included#ifndef arrayList_
#define arrayList_#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iterator>
#include "linearList.h"
#include "myExceptions.h"
#include "changeLength1D.h"using namespace std;template<class T>
class arrayList : public linearList<T>
{public:// constructor, copy constructor and destructorarrayList(int initialCapacity = 10);arrayList(const arrayList<T>&);~arrayList() {delete [] element;}// ADT methodsbool empty() const {return listSize == 0;}int size() const {return listSize;}T& get(int theIndex) const;int indexOf(const T& theElement) const;void erase(int theIndex);void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement);void output(ostream& out) const;// additional methodint capacity() const {return arrayLength;}// iterators to start and end of listclass iterator;iterator begin() {return iterator(element);}iterator end() {return iterator(element + listSize);}// iterator for arrayListclass iterator {public:// typedefs required by C++ for a bidirectional iteratortypedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;typedef T value_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;typedef T* pointer;typedef T& reference;// constructoriterator(T* thePosition = 0) {position = thePosition;}// dereferencing operatorsT& operator*() const {return *position;}T* operator->() const {return &*position;}// incrementiterator& operator++() // preincrement{++position; return *this;}iterator operator++(int) // postincrement{iterator old = *this;++position;return old;}// decrementiterator& operator--() // predecrement{--position; return *this;}iterator operator--(int) // postdecrement{iterator old = *this;--position;return old;}// equality testingbool operator!=(const iterator right) const{return position != right.position;}bool operator==(const iterator right) const{return position == right.position;}protected:T* position;}; // end of iterator classprotected: // additional members of arrayListvoid checkIndex(int theIndex) const;// throw illegalIndex if theIndex invalidT* element; // 1D array to hold list elementsint arrayLength; // capacity of the 1D arrayint listSize; // number of elements in list
};template<class T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(int initialCapacity)
{// Constructor.if (initialCapacity < 1){ostringstream s;s << "Initial capacity = " << initialCapacity << " Must be > 0";throw illegalParameterValue(s.str());}arrayLength = initialCapacity;element = new T[arrayLength];listSize = 0;
}template<class T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(const arrayList<T>& theList)
{// Copy constructor.arrayLength = theList.arrayLength;listSize = theList.listSize;element = new T[arrayLength];copy(theList.element, theList.element + listSize, element);
}template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::checkIndex(int theIndex) const
{// Verify that theIndex is between 0 and listSize - 1.if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex >= listSize){ostringstream s;s << "index = " << theIndex << " size = " << listSize;throw illegalIndex(s.str());}}template<class T>
T& arrayList<T>::get(int theIndex) const
{// Return element whose index is theIndex.// Throw illegalIndex exception if no such element.checkIndex(theIndex);return element[theIndex];
}template<class T>
int arrayList<T>::indexOf(const T& theElement) const
{// Return index of first occurrence of theElement.// Return -1 if theElement not in list.// search for theElementint theIndex = (int) (find(element, element + listSize, theElement)- element);// check if theElement was foundif (theIndex == listSize)// not foundreturn -1;else return theIndex;}template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::erase(int theIndex)
{// Delete the element whose index is theIndex.// Throw illegalIndex exception if no such element.checkIndex(theIndex);// valid index, shift elements with higher indexcopy(element + theIndex + 1, element + listSize,element + theIndex);element[--listSize].~T(); // invoke destructor
}template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement)
{// Insert theElement so that its index is theIndex.if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex > listSize){// invalid indexostringstream s;s << "index = " << theIndex << " size = " << listSize;throw illegalIndex(s.str());}// valid index, make sure we have spaceif (listSize == arrayLength){// no space, double capacitychangeLength1D(element, arrayLength, 2 * arrayLength);arrayLength *= 2;}// shift elements right one positioncopy_backward(element + theIndex, element + listSize,element + listSize + 1);element[theIndex] = theElement;listSize++;
}template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::output(ostream& out) const
{// Put the list into the stream out.copy(element, element + listSize, ostream_iterator<T>(cout, " "));
}// overload <<
template <class T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const arrayList<T>& x){x.output(out); return out;}#endifvectorList.h
// vector implementation of a linear list
// derives from abstract class linearList just to make sure
// all methods of the ADT are implemented
// USES STL ALGORITHMS TO SIMPLIFY CODE
// iterator class for vectorList included#ifndef vectorList_
#define vectorList_#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iterator>
#include "linearList.h"
#include "myExceptions.h"using namespace std;template<class T>
class vectorList : public linearList<T>
{public:// constructor, copy constructor and destructorvectorList(int initialCapacity = 10);vectorList(const vectorList<T>&);~vectorList() {delete element;}// ADT methodsbool empty() const {return element->empty();}int size() const {return (int) element->size();}T& get(int theIndex) const;int indexOf(const T& theElement) const;void erase(int theIndex);void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement);void output(ostream& out) const;// additional methodint capacity() const {return (int) element->capacity();}// iterators to start and end of listtypedef typename vector<T>::iterator iterator;iterator begin() {return element->begin();}iterator end() {return element->end();}protected: // additional members of vectorListvoid checkIndex(int theIndex) const;vector<T>* element; // vector to hold list elements
};template<class T>
vectorList<T>::vectorList(int initialCapacity)
{// Constructor.if (initialCapacity < 1){ostringstream s;s << "Initial capacity = " << initialCapacity << " Must be > 0";throw illegalParameterValue(s.str());}element = new vector<T>;// create an empty vector with capacity 0element->reserve(initialCapacity);// increase vector capacity from 0 to initialCapacity
}template<class T>
vectorList<T>::vectorList(const vectorList<T>& theList)
{// Copy constructor.element = new vector<T>(*theList.element);
}template<class T>
void vectorList<T>::checkIndex(int theIndex) const
{// Verify that theIndex is between 0 and size() - 1.if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex >= size()){ostringstream s;s << "index = " << theIndex << " size = " << size();throw illegalIndex(s.str());}}template<class T>
T& vectorList<T>::get(int theIndex) const
{// Return element whose index is theIndex.// Throw illegalIndex exception if no such element.checkIndex(theIndex);return (*element)[theIndex];
}template<class T>
int vectorList<T>::indexOf(const T& theElement) const
{// Return index of first occurrence of theElement.// Return -1 if theElement not in list.// search for theElementint theIndex = (int) (find(element->begin(), element->end(),theElement)- element->begin());// check if theElement was foundif (theIndex == size())// not foundreturn -1;else return theIndex;}template<class T>
void vectorList<T>::erase(int theIndex)
{// Delete the element whose index is theIndex.// Throw illegalIndex exception if no such element.checkIndex(theIndex);element->erase(begin() + theIndex);
}template<class T>
void vectorList<T>::insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement)
{// Insert theElement so that its index is theIndex.if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex > size()){// invalid indexostringstream s;s << "index = " << theIndex << " size = " << size();throw illegalIndex(s.str());}element->insert(element->begin() + theIndex, theElement);// may throw an uncaught exception if insufficient// memory to resize vector
}template<class T>
void vectorList<T>::output(ostream& out) const
{// Put the list into the stream out.copy(element->begin(), element->end(), ostream_iterator<T>(cout, " "));
}// overload <<
template <class T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const vectorList<T>& x){x.output(out); return out;}#endif二、部分习题
3.

template<class T>
void changeLength2D(T**& a, int oldRows, int copyRows,int copyColumns, int newRows, int newColumns)
{// 调整二维数组a的大小,该数组原有oldRows行// 调整后数组的维度为 newRows行 x newColumns列// 复制原数组左上角 copyRows行 x copyColumns列 的子数组到新数组中// 确保新数组的维度足够容纳要复制的内容if (copyRows > newRows || copyColumns > newColumns)throw illegalParameterValue("新数组维度太小,无法容纳复制内容");T** temp = new T*[newRows]; // 为新数组的行指针分配内存// 为新数组的每一行分配列元素的内存for (int i = 0; i < newRows; i++)temp[i] = new T[newColumns];// 从旧数组复制数据到新数组,并释放旧数组中已复制行的内存for (int i = 0; i < copyRows; i++){// 复制当前行中前copyColumns个元素到新数组对应行copy(a[i], a[i] + copyColumns, temp[i]);delete [] a[i]; // 释放旧数组中当前行的内存}// 释放旧数组中未被复制的剩余行的内存for (int i = copyRows; i < oldRows; i++)delete [] a[i];delete [] a; // 释放旧数组的行指针数组a = temp; // 将原数组指针指向新创建的数组
}5.
template<class T>
class arrayListWithTrimToSize : public arrayList<T>
{public:// constructor and destructorarrayListWithTrimToSize(int initialCapacity = 10): arrayList<T> (initialCapacity) {}void trimToSize();
};template<class T>
void arrayListWithTrimToSize<T>::trimToSize()
{// Make array length equal to max{listSize, 1}if (arrayLength == listSize)return;if (listSize == 0){// replace with array of length 1delete [] element;element = new T[1];arrayLength = 1;return;}// need to change array length and copy eleements into new arraychangeLength1D(element, listSize, listSize);arrayLength = listSize;
}6.

template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::setSize(int newSize) {// 检查新大小是否合法(非负)if (newSize < 0) {ostringstream s;s << "newSize = " << newSize << " 必须为非负数";throw illegalParameterValue(s.str());}if (newSize < listSize) {// 情况1:新大小 < 当前元素个数 → 删除多余元素(从newSize到listSize-1的位置)for (int i = newSize; i < listSize; ++i) {element[i].~T(); // 调用元素的析构函数(释放资源)}listSize = newSize; // 更新元素个数} else if (newSize > arrayLength) {// 情况2:新大小 > 数组容量 → 扩容数组(保证后续插入不越界,虽然不新增元素)changeLength1D(element, arrayLength, newSize);arrayLength = newSize; // 更新数组容量}// 情况3:newSize == listSize 或 newSize在[listSize, arrayLength]之间 → 无需操作
}7.
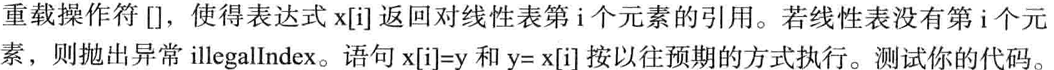
template<class T>
class arrayListWithOverloadIndex : public arrayList<T>
{public:// constructor and destructorarrayListWithOverloadIndex(int initialCapacity = 10): arrayList<T> (initialCapacity) {}T& operator[](int);
};template<class T>
T& arrayListWithOverloadIndex<T>::operator[](int theIndex)
{// Return a reference to position theIndex of the list.checkIndex(theIndex);return element[theIndex];
} operator[] 返回的是 T&(元素的引用),引用可以作为 “左值” 参与赋值操作。例如执行 x[i] = y 时,operator[] 先通过索引检查,然后返回线性表中第 i 个元素的引用,赋值操作会直接修改该元素的值;而 y = x[i] 则是通过引用读取元素值。
8.9.10.
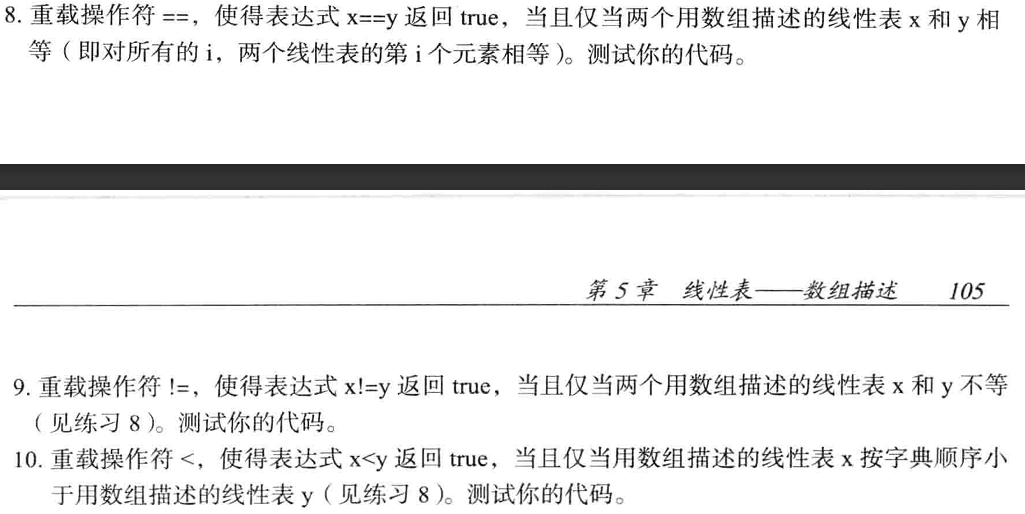
//friend声明友元friend bool operator==(const arrayList<T>& x, const arrayList<T>& y);friend bool operator!=(const arrayList<T>& x, const arrayList<T>& y);friend bool operator<(const arrayList<T>& x, const arrayList<T>& y);//实现==
template<class T>
bool operator==(const arrayList<T>& x, const arrayList<T>& y) {if (x.listSize != y.listSize) return false; // 大小不同,直接不等for (int i = 0; i < x.listSize; ++i) {if (x.element[i] != y.element[i]) return false; // 有一个元素不同则不等}return true; // 所有元素都相等
}
//实现!=,调用==
template<class T>
bool operator!=(const arrayList<T>& x, const arrayList<T>& y) {return !(x == y); // 复用 == 的结果,取反
}
// 实现 <(字典序比较)
template<class T>
bool operator<(const arrayList<T>& x, const arrayList<T>& y) {int minLen = min(x.listSize, y.listSize);for (int i = 0; i < minLen; ++i) {if (x.element[i] < y.element[i]) return true; // x的元素更小,x整体更小if (x.element[i] > y.element[i]) return false; // x的元素更大,x整体更大// 相等则继续比较下一个元素}// 前面元素都相等,**长度更短的线性表字典序更小**return x.listSize < y.listSize;
}字典序(lexicographical order)的逻辑,和查字典时 “单词的排序规则”是一致的,核心是“逐位比较,先出现更小元素的序列整体更小;若所有对应位都相等,则更短的序列更小”。
11,12

插入:先考虑扩增然后插入
删除:先考虑是否为空后删除
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::push_back(const T& theElement) {// 容量已满时,扩容为原来的2倍if (listSize == arrayLength) {changeLength1D(element, arrayLength, 2 * arrayLength);arrayLength *= 2;}// 直接在右端插入元素element[listSize] = theElement;listSize++;
}template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::pop_back() {if (listSize == 0) {throw illegalIndex("pop_back on empty list"); // 空表删除抛异常}listSize--; // 元素个数减1element[listSize].~T(); // 调用右端元素的析构函数
}13,14

13.分别交换指针element,listsize,arraylength即可。
//swap
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::swap(arrayList<T>& theList)
{T *temp=element;element=theList.element;theList.element=temp;int temp1=arrayLength;arrayLength=theList.arrayLength;theList.arrayLength=temp1;int temp2=listSize;listSize=theList.listSize;theList.listSize=temp2;
}//reserve
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::reserve(int theCapacity) {if (theCapacity < 0) { // 容量不能为负ostringstream s;s << "容量 " << theCapacity << " 必须为非负数";throw illegalParameterValue(s.str());}// 只有当前容量小于指定容量时,才扩容if (arrayLength < theCapacity) {changeLength1D(element, arrayLength, theCapacity);arrayLength = theCapacity;}
}16,17,18

16.依次调用该元素的析构函数即可
17.先检查索引范围合法性,再将范围右侧的元素 “左移” 覆盖要删除的范围,最后减少 listSize 并析构被删除的元素。
18.从线性表末尾向前遍历,找到第一个匹配的元素即返回其索引;若遍历完都没找到,返回 -1。
//clear
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::clear() {for (int i = 0; i < listSize; ++i) {element[i].~T(); // 调用元素析构函数(释放资源)}listSize = 0; // 元素个数置为 0
}//removeRange
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {// 检查索引合法性:范围需有效且不越界if (fromIndex < 0 || toIndex > listSize || fromIndex >= toIndex) {ostringstream s;s << "无效范围: from=" << fromIndex << ", to=" << toIndex << ", size=" << listSize;throw illegalIndex(s.str());}int numRemove = toIndex - fromIndex; // 要删除的元素个数// 移动右侧元素覆盖删除范围for (int i = toIndex; i < listSize; ++i) {element[i - numRemove] = element[i];element[i].~T(); // 原位置元素析构}listSize -= numRemove; // 更新元素个数
}//lastIndexOf
template<class T>
int arrayList<T>::lastIndexOf(const T& theElement) const {// 从后往前遍历for (int i = listSize - 1; i >= 0; --i) {if (element[i] == theElement) {return i; // 找到,返回当前索引}}return -1; // 未找到
}22.

template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::reverse() {int left = 0, right = listSize - 1;while (left < right) {// 交换左右指针处的元素T temp = element[left];element[left] = element[right];element[right] = temp;left++; // 左指针右移right--; // 右指针左移}
}template<class T>
void reverseArrayListNonMember(arrayList<T>& list) {int n = list.size();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {T lastElem = list.get(n - 1 - i); // 取原数组倒数第 i+1 个元素list.erase(n - 1 - i); // 删除该元素list.insert(i, lastElem); // 插入到索引 i 的位置}
}23.

template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::leftShift(int i) {// 检查i的合法性:非负且不超过当前元素个数if (i < 0 || i > listSize) {ostringstream s;s << "leftShift: 无效的i = " << i << "(当前元素个数为" << listSize << ")";throw illegalIndex(s.str());}if (i == 0) return; // i为0,无需移动// 移动元素:将 [i, listSize-1] 区间的元素左移i位for (int j = 0; j < listSize - i; ++j) {element[j] = element[j + i]; // 覆盖前i个元素element[j + i].~T(); // 析构被覆盖位置的原元素(若为类对象,释放资源)}listSize -= i; // 元素个数减少i个
}24.

以线性表 x = [0,1,2,3,4] 循环左移 2 位(结果 [2,3,4,0,1])为例,步骤如下:
- 第一步:逆转子数组的前
i个元素 →[0,1]逆转为[1,0],数组变为[1,0,2,3,4]。 - 第二步:逆转子数组的后
n-i个元素(n为总长度)→[2,3,4]逆转为[4,3,2],数组变为[1,0,4,3,2]。 - 第三步:逆转整个数组 →
[1,0,4,3,2]逆转为[2,3,4,0,1],完成循环移动。
// 辅助方法:逆转[from, to]范围的元素
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::reverseRange(int from, int to) {while (from < to) {T temp = element[from];element[from] = element[to];element[to] = temp;from++;to--;}
}template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::circularShift(int i) {int n = listSize;if (n == 0) return; // 空表直接返回i = i % n; // 处理i超过表长的情况(取模,保证i在有效范围)if (i == 0) return; // 移动0位,无需操作// 三次逆转换reverseRange(0, i - 1); // 1. 逆转前i个元素reverseRange(i, n - 1); // 2. 逆转后n-i个元素reverseRange(0, n - 1); // 3. 逆转整个数组
}25.

template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::half() {if (listSize <= 1) {listSize = 0; // 空表或仅1个元素,直接清空return;}int newSize = 0;for (int i = 0; i < listSize; ++i) {if (i % 2 == 0) { // 保留偶数索引的元素element[newSize] = element[i]; // 搬运到新的紧凑位置element[i].~T(); // 析构原位置元素(释放资源)newSize++;} else {element[i].~T(); // 析构要删除的元素}}listSize = newSize; // 更新最终元素个数
}或:
template<class T>
class arrayListWithHalf : public arrayList<T>
{public:// constructor and destructorarrayListWithHalf(int initialCapacity = 10): arrayList<T> (initialCapacity) {}void half();
};template<class T>
void arrayListWithHalf<T>::half()
{// Remove all odd indexed elements.// move even indexed elements to new spotsfor (int i = 2; i < listSize; i += 2)element[i/2] = element[i];// destroy uneeded elementsint newSize = (listSize + 1) / 2;for (int i = newSize; i < listSize; i++)element[i].~T(); listSize = newSize;
}非成员函数:
template<class T>
void halfNonMember(arrayList<T>& list) {int n = list.size();if (n <= 1) {for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) list.erase(0); // 清空所有元素return;}// 从后往前遍历,删除奇数索引for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {if (i % 2 != 0) list.erase(i);}
}28.

创建新线性表,用双指针交替遍历两个输入表,先交替取元素,再将剩余元素追加。
template<class T>
class arrayList : public linearList<T>
{
public:// 其他成员(构造、插入等)...// 合并a和b,返回新线性表static arrayList<T> meld(const arrayList<T>& a, const arrayList<T>& b) {arrayList<T> result;// 预先扩容,避免多次扩容(优化)result.changeLength1D(0, a.listSize + b.listSize);int i = 0, j = 0; // 遍历a、b的指针int k = 0; // 新表的当前索引// 阶段1:交替取a和b的元素while (i < a.listSize && j < b.listSize) {result.element[k++] = a.element[i++];result.element[k++] = b.element[j++];}// 阶段2:a有剩余,全部追加while (i < a.listSize) {result.element[k++] = a.element[i++];}// 阶段3:b有剩余,全部追加while (j < b.listSize) {result.element[k++] = b.element[j++];}result.listSize = k; // 设置新表的元素总数return result;}
};29.

利用双指针法遍历两个非递减有序表 a 和 b,依次比较元素大小,将较小元素放入结果表(调用对象 *this);若其中一个表遍历完毕,直接追加另一个表的剩余元素。
template<class T>
class arrayList : public linearList<T>
{
public:// 其他成员(构造、插入、扩容等)...// 归并两个有序表a和b,结果存入*thisvoid merge(const arrayList<T>& a, const arrayList<T>& b) {int totalSize = a.listSize + b.listSize; // 合并后总长度// 扩容当前对象,确保能容纳所有元素if (arrayLength < totalSize) {changeLength1D(element, arrayLength, totalSize);}int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0; // i遍历a,j遍历b,k填充*this// 双指针比较,取较小元素while (i < a.listSize && j < b.listSize) {if (a.element[i] <= b.element[j]) {element[k++] = a.element[i++];} else {element[k++] = b.element[j++];}}// 追加a的剩余元素while (i < a.listSize) {element[k++] = a.element[i++];}// 追加b的剩余元素while (j < b.listSize) {element[k++] = b.element[j++];}listSize = totalSize; // 更新元素总数}
};30.

template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::split(arrayList<T>& a, arrayList<T>& b) {a.listSize = 0; // 确保a初始为空b.listSize = 0; // 确保b初始为空for (int i = 0; i < listSize; ++i) {if (i % 2 == 0) {a.insert(a.listSize, element[i]); // 偶数索引元素插入a} else {b.insert(b.listSize, element[i]); // 奇数索引元素插入b}}
}